Abstract
Jiatang scroll paintings listed in the Chinese intangible cultural heritage list are an important form of family trees. In this paper, a Jiatang scroll painting drawn in the seventh year of Guangxu (AD 1881) was chosen as a prototype to analyze its components. Samples were taken from different parts of the Jiatang scroll painting to analyze the composition of fibers, pigments, and adhesives. Herein, fiber analyzer, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and Herzberg stain were conducted to identify the type of fiber used. Microstructural and microchemical analyses by means of SEM-EDX and Raman spectroscopy were performed to characterize the pigments present in the painting, while the nature of the adhesive was examined using pyrolysis gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (Py-GC/MS). The results show that the painting fiber is from cotton, while the red, black, and green pigments were identified as cinnabar, carbon black, and emerald green, respectively. Finally, the adhesive is a mixture of animal glue, benzoin gum, and starch. The research results provide a basis for the protection and restoration of this precious cultural heritage in the future.
1. Introduction
As a type of Gaomi New Year’s Eve painting, Jiatang scroll paintings have a unique function and are an important form of family trees. They are also listed in the Chinese intangible cultural heritage list. Jiatang scroll paintings originated in the late Ming Dynasty and, after a series of innovations by craftsmen, reached their peak in the late Ming and early Qing Dynasties. Jiatang scroll paintings reveal the spirit of ancestor worship and inheritance of Chinese people and also provide a historical record of the evolution and development of individual families. The object of this paper (Figure 1) is from Henan Province, China. It was drawn in the seventh year of the Guangxu Emperor (AD 1881) and was part of a family collection. It was hung on the wall of the family when they worshiped their ancestors. Pictures of the ancestors (Figure 1b,f), the names of the ancestors (Figure 1c,d), and decorations (Figure 1a,e) were drawn on the support. Due to the ages of the paintings and the limited preservation conditions by the family, some of the Jiatang scroll paintings have been severely damaged.
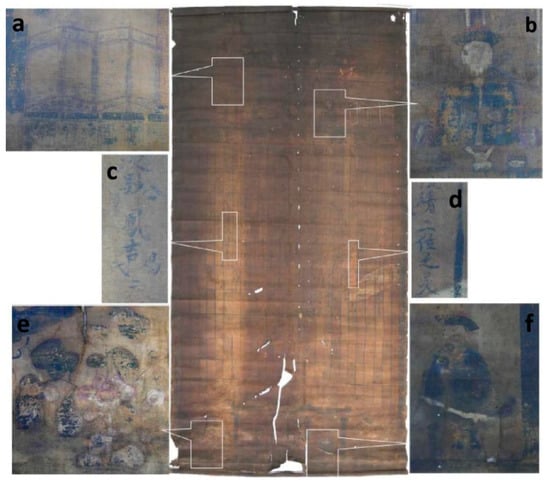
Figure 1.
Pictures of the Jiatang scroll painting. (a) Domestic instrument; (b,f) ancestral portraits; (c,d) ancestor names; (e) flowers.
Materials like cotton, silk, and hemp were usually used as raw materials in the creation of scroll paintings. The paintings are highly desirable due to the uniqueness of the work of art and the features of flexibility, heterogeneity, and draping quality. Unfortunately, ancient textiles including cotton, silk, and hemp have aged and degraded due to uncontrolled temperatures, relative humidity, light, and non-standard storage [1,2]. The fibers of the painting may have reacted with water, carbon dioxide, and sulfur dioxide in the air, which leads to the loss of tensile strength and pliability [3,4]. This information is of great value for the protection and restoration of the works of archaeological textiles. The degradation mechanism and the preservation environment of cotton, silk, and hemp [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14] have aroused the interest of scientists. In addition, these works provide an important reference for understanding the inheritance and development of culture in ancient China.
With the aim to (i) understand the technological and scientific level developed at that time and (ii) optimize future conservation and restoration actions for this kind of object, it is necessary to analyze the painting’s ontology, which includes the identification of its fibers, pigments, and binding materials using modern material analysis and characterization techniques. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Raman and Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, and chromatography have been applied to analyze ancient cultural objects to provide an important reference for formulating effective restoration plans [15,16,17,18,19]. SEM-EDX (Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis) has been used to analyze the micromorphology of a canvas, and it was concluded that the base material of cultural heritage textiles was pure cotton fiber [20]. FTIR and Raman spectroscopy have been applied to identify wool and cotton fibers [21,22]. Mineral pigments have been widely used in ancient paintings, so their analysis has been particularly important in the conservation of historical and cultural heritage. Costa et al. analyzed the materials of Louis-Auguste Moreaux paintings through a series of methods—the elemental composition of each pigment was identified by using SEM-EDS, and the molecular characteristics of the adhesives and pigments were analyzed by applying FTIR spectroscopy [23]. The high molecular weight compound, that is, the adhesive, was characterized by employing pyrolysis gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (Py-GC/MS). Chiavari et al. studied five kinds of adhesive by using the Py-GC/MS method [24]. Hao et al. investigated the film coating on the surface of wooden cultural relics from the Qing Dynasty in China by applying the Py-GC/MS and other methods [25]. Additionally, the application of non-invasive, portable equipment that allows for the investigation of paintings without sampling is a very important method. X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analysis combined with mid- and near-FTIR has been demonstrated to be of great value for the non-invasive characterization of key elements [26,27]. Therefore, a combination of multiple methods can achieve an overall comprehensive analysis that can be used to identify the materials used in ancient paintings.
The object of this study was to explore the production technology and to provide a scientific basis for the better preservation of Jiatang scroll paintings. Samples were taken from the painting edges that have fallen off. FTIR, SEM, and Herzberg stain were employed to analyze the types of fibers. SEM-EDS and Raman spectroscopy were applied to characterize the pigments. Thermal pyrolysis gas chromatography–mass spectrometry was used to identify the binding materials.
2. Experimental Design
2.1. Sample Description
The overall appearance and details of the Jiatang scroll painting are shown in Figure 2. The painting is 180 cm in height, 90 cm in width, and 0.322 μm thick. Samples for analysis were taken from different parts of the painting (Table 1). Fiber and fiber with adhesive samples were taken from the dropped residue, and pigment samples were taken from the dropped pigment particles by dipping cotton swabs in water.

Figure 2.
The sampling locations.

Table 1.
Analysis after sampling from the corresponding position of the painting.
2.2. Analysis of Fiber and Pigment
Sample 1 was taken from the edge of the painting for fiber analysis. It was washed with water and ethanol to remove contaminants on the surface before analysis. Samples 2–4 were stained with cotton swabs for pigment analysis.
FTIR spectroscopy: Non-destructive infrared analysis of Sample 1 was performed using a diamond mid-infrared/far-infrared spectrometer (PE-Frontier, Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA). The spectral range was 400–5000 cm−1, the resolution was 4 cm−1, and the number of scans was 32.
SEM-EDS: Sample 1 was attached to a platform with conductive glue and sprayed with gold for 150 s. Then, it was analyzed by SEM (SU3500, Hitachi High-Tech Company (Tokyo, Japan)). The accelerating voltage was 5 kV. The elements of pigment samples 2, 3, and 4 were determined by the same instrument with an energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS). The voltage was 15 kV.
Herzberg stain: Fiber staining was analyzed according to GB/T 4688-2002. Sample 1 was suspended in water and then dropped onto a glass slide. Then, it was stained with Herzberg stain (zinc chloride–iodine stain) for 2 min and covered with a cover glass. The excess stain was soaked up with filter paper. The stained fiber sample was analyzed with an XWY-VIII fiber analyzer made by Beijing Lunhua Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China).
Raman spectroscopy: A LabRAM HR Evolution series confocal Raman spectrometer produced by the Horiba Group Corporation of Japan was used to analyze Samples 2, 3, and 4. The grating was 1800 reticles per millimeter, and the objective lens was 100×. The acquisition time was 3 s. According to the sensitivity of each pigment to different laser wavelengths, the samples were analyzed following different experimental conditions. Specifically, Sample 2 was analyzed using a laser excitation wavelength of 785 nm with a power of 50 mW, while a laser excitation wavelength of 532 nm with powers of 50 and 10 mW was adopted to examine Samples 3 and 4, respectively.
2.3. Analysis of the Adhesive
Py-GC/MS: All ancient adhesives are natural organic substances with relatively large molecular weights and complex structures. They are also prone to degradation and low contents, which makes them difficult to analyze. Py-GC/MS has been used to characterize the adhesives of ancient art [28]. Sample 5 was used for adhesive analysis using pyrolysis-gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (Py-GC/MS). It was equipped with a pyrolyzer (EGA/PY-3030D, Frontier Labs, Fukushima, Japan) and combined with a gas chromatograph–mass spectrometer (GCMS-QP2010Ultra, Shimadzu, Japan). The capillary column was DB-5MS UI (5% diphenyl/95% dimethylsiloxane), with a size of 0.18 mm × 0.18 μm × 24 m. The thermal cracking furnace temperature was set to 600 °C, the injector temperature was set to 290 °C, and the split injection mode was adopted. The initial temperature of the column oven was 35 °C, which was increased to 100 °C at a rate of 60 °C/min, then to 250 °C at a rate of 14 °C/min. Finally, the temperature reached 315 °C at a rate of 6 °C/min and then held for 5 min. The mass detector voltage was 70 eV, and the scanning range was m/z 35–500. The GC-MS data were systematically analyzed using the automatic mass spectrometry deconvolution and identification system (AMDIS) developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST, Gaithersburg, MD, USA). The analysis results were input into the RAdICAL system developed by the Getty Conservation Institute (Los Angeles, CA, USA) and J. Paul Getty Museum (Los Angeles, CA, USA) [29]. The classification information of each material was displayed in a dedicated diagnostic chart.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fiber Analysis
The painting fibers were analyzed using FTIR, SEM, and a fiber analyzer to obtain their molecular structure characteristics and micromorphology. The micromorphology of Jiatang painting fibers was observed by SEM (Figure 3). As shown in Figure 3a, the canvas of the painting was woven with plain weave, double-warp, and single-weft fabric. Each string was made up of about 30 threads. The fiber displays cracking and shedding. As shown in Figure 3b, the fibers were in the shape of flat ribbons, which is highly consistent with the features of cotton fibers [30]. In addition, the surface of the fibers was rough, with a few cracks due to abrasion and degradation.
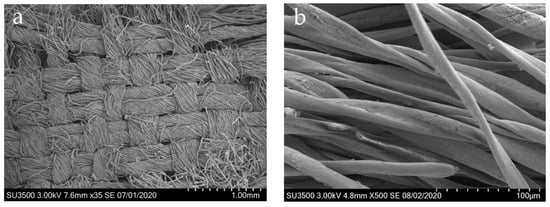
Figure 3.
SEM image of Sample 1. (a) 100×; (b) 1000×.
The FTIR spectrum of painting fibers is shown in Figure 4, and the peak shape and positions are consistent with those of cellulosic fibers. The characteristic infrared absorption frequencies were mainly concentrated in four frequency ranges—1100–1000, 1350–1300, 1450–1400, and 2950–2830 cm−1 [21]. The broad and strong absorption peak at 3200–3450 cm−1 was attributed to the stretching vibration of –OH groups. The absorption band at 2900 cm−1 was assigned to CH stretching vibrations. The peak at 1635 cm−1 corresponded to the vibration of water molecules absorbed in cellulose. The CH bending vibration appeared at 1429 cm−1. The bands at 1158 cm−1 were COC stretching vibrations. The absorption at 1108 cm−1 was the asymmetric vibration of glucose rings. The band at 898 cm−1 was due to the β-glycosidic linkages between glucose units.
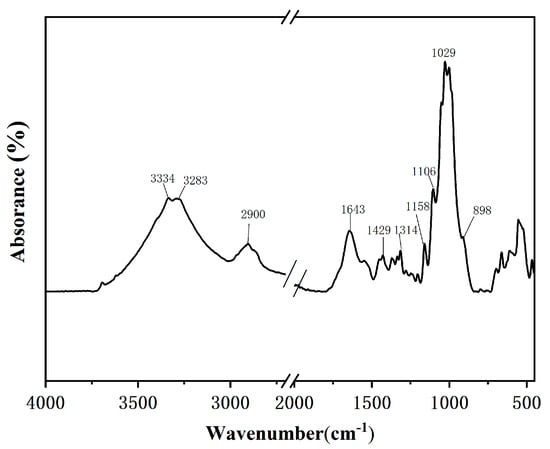
Figure 4.
FT-IR spectrum of a fiber sample.
When dyeing fibers with dyes, different lignin quantities in the fibers can affect the color of the fibers after dyeing. Lignin-free fibers from rags (hemp, ramie, and cotton) were dyed in wine-red color [31,32]. To further determine the types of fibers in the painting, dyeing analysis was performed. The fibers were dyed with Herzberg stain (zinc chloride–iodine stain) and then observed with an optical microscopic. As shown in Figure 5, the fiber sample from the Jiatang scroll painting dyed with Herzberg stain was wine-red in color. There were no cross striations or nodes, and the fibers were long and twisted. The characteristics of the dyed fibers were compared to the data gallery on the fiber analyzer. Combined with the above analysis, it can be determined that the fibers in the Jiatang scroll painting are cotton fibers.
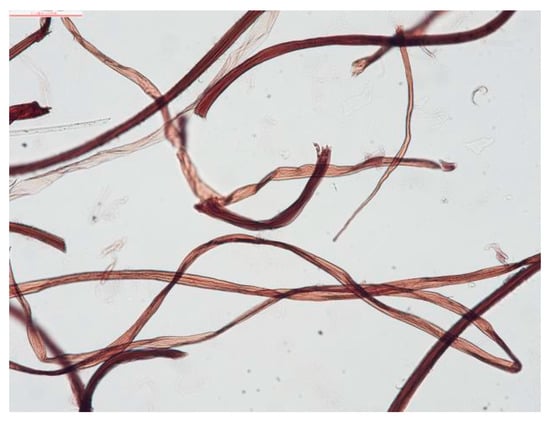

Figure 5.
The optical microscopic picture of dyed fibers.
3.2. Pigment Identification
The colors of the Jiatang scroll painting were mainly red, green, and black. In order to identify the pigments used in the painting, elemental and molecular analyses were performed by means of SEM-EDX and Raman spectroscopy, respectively. The results are shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7 and Table 2.
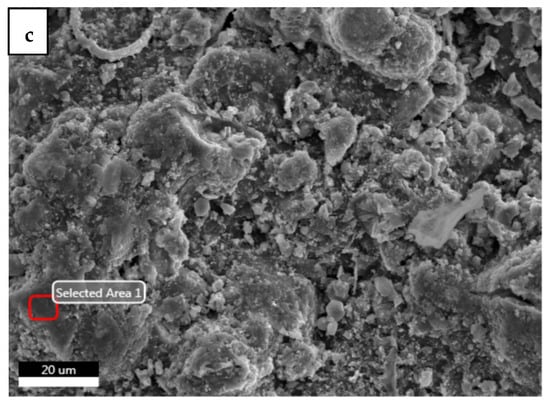


Figure 6.
SEM images in which the areas where EDS analyses were performed are highlighted. (a) Red pigment of Sample 1; (b) black pigment of Sample 2; (c) green pigment of Sample 3.

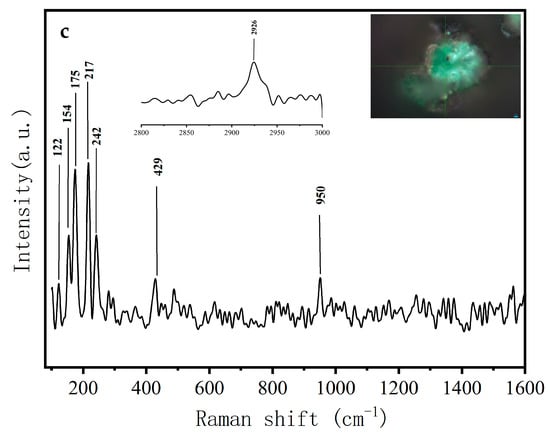
Figure 7.
Raman spectra of the pigments. (a) Red pigment of Sample 2; (b) black pigment of Sample 3; (c) green pigment of Sample 4.

Table 2.
Elemental composition of the pigments.
The main elemental contents of the samples are shown in Table 2. The Raman spectra of the pigments are shown in Figure 7. It can be seen in Table 2 that all four samples contained C and O atoms, which were mainly derived from the cellulose fibers. The other main elements in the red pigment were Hg and S (Figure 7a). The characteristic peaks were located at 254, 287, and 344 cm−1, which are consistent with the characteristic Raman absorption peaks of cinnabar reported in the literature [33]. Combined with the EDS spectrum, the red pigment should be cinnabar (HgS), which was widely used in ancient paintings of China. This is a reference for the use of cinnabar in ancient Chinese pigments.
Ancient black pigments were mainly carbon black, iron black, and lead dioxide. The main elements in the black sample were C and O, and no Fe nor Pb were found. The Raman spectrum of the black pigment is shown in (Figure 7b). The characteristic peaks are located at 1371 and 1586 cm−1, which were assigned to carbon black [1,3,4]. Carbon black is easy to prepare and relatively inexpensive and was widely used in ancient times [34].
The main elements in the green pigment were Cu and As. The Raman spectrum of the green pigment is shown in Figure 7c. The characteristic peaks are located at 122, 154, 175, 217, 242, 952, and 2926 cm−1, which were assigned to emerald green (Cu[C2H3O2]2·3Cu[AsO2]2) [35]. Emerald green is a synthetic pigment that has been applied in decorative paintings in China since the Qing Dynasty.
3.3. Analysis of the Adhesive
Following TMAH derivatization, the samples were analyzed by Py-GC/MS. Figure 8 shows the total ion chromatogram of the samples. The main pyrolysis products are displayed in Table 3. 3-Methyl-1H-pyrrole, trimethyl phosphate, methyl 1-methylpyrrole-2-carboxylate, and protein-unverified 8 were the main pyrrolic compounds, which were inferred to be animal glue, which was used as a pigment binder [36]. Benzoic acid, methyl ester, benzaldehyde, 4-methoxy-benzaldehyde, 4-methoxy-, 2-propenoic acid, 3-phenyl-methyl ester, benzaldehyde, and 3,4-dimethoxy- are benzoin derivatives that were assigned to gum benzoin, which is possibly due to the incense burning during the process of ancestor worship [37]. Schellmannose and starch-unverified 5 were markers of starch, which was used as a sizing material. According to the characteristics of the compounds, the main materials in the sample were proteins, benzoin, and starch.
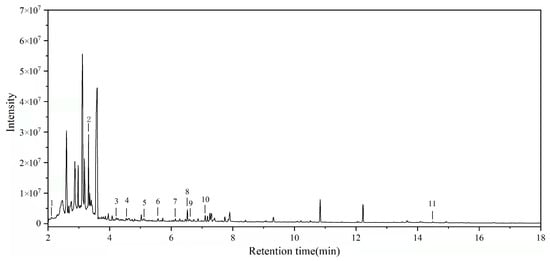
Figure 8.
Py-GC/MS chromatogram of the sample.

Table 3.
The compounds identified by total ion chromatography obtained by Py-GC/MS.
4. Conclusions
A Jiatang scroll painting drawn in the seventh year of Guangxu (AD 1881) was studied. Microscopic studies were performed using fiber analyzer, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and Herzberg stain. It was determined that cotton fibers were used in the weaving of the canvas of the Jiatang scroll painting. The results provide a reference for the subsequent repair of the damaged parts of the Jiatang scroll painting. Cotton fibers can then be used to repair the damaged parts of the fabric. According to the SEM-EDS and Raman spectroscopy analysis, the pigments used in the painting were mainly cinnabar, carbon black, and emerald green, which are all mineral pigments. According to the features of mineral pigments, they are not sensitive to water, which can provide the reference for the chosen cleaning and conservation methods. The adhesives were proved to be animal glue, benzoin gum, and starch, as identified by Py-GC/MS. The animal glue and starch are assigned to the pigment binder and sizing material separately. The benzoin gum is contamination from the incense burning during the process of ancestor worship, so it should be removed. These results lay an important foundation for the subsequent protection and restoration of family scroll paintings drawn in the seventh year of Guangxu. Based on these results, samples can be produced to simulate and verify the restoration process of Jiatang scroll paintings, which is vital to the protection of genealogical relics.
Author Contributions
F.Z. and H.X. contributions equally. Data curation, Z.J., F.Z., J.W. (Jianwei Wang) and X.C.; formal analysis, Z.J.; funding acquisition, Z.J. and Y.L.; investigation, J.W. (Juanli Wang) and J.L.; project administration, Y.L.; supervision, Y.L.; validation, Z.J.; writing—original draft, Z.J.; writing—review and editing, Z.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 22002080), Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province, China (Grant No. 2021GY-172), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. GK 202103060), and the Science and Technology Project of Xi’an, China (Grant No. 2020KJRC0014).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Yuhu Li for setting up the framework of the entire project. Thanks for the fund support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Olaru, A.; Malutan, T.; Ursescu, C.M.; Geba, M.; Stratulat, L. Structural changes in hemp fibers following temperature, humidity and uv or gamma-ray radiation exposure. Cellul. Chem. Technol. Int. J. Phys. Chem. Technol. Cellul. Lignin. 2016, 50, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Karadag, R. Some non-destructive and micro-analytical methods for the conservation on textiles from cultural heritage. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Cultural Heritage and New Technologies 2014 (CHNT 19, 2014), Vienna, Austria, 3–5 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bresee, R.R. General effects of ageing on textiles. J. Am. Inst. Conserv. 1986, 25, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybulska, M. Archaeological textiles-a need for new methods of analysis and reconstruction. Fibres Text. Eastern Eur. 2007, 15, 64–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilillo, M.; Restivo, A.; Degano, I.; Ribechini, E.; Colombini, M.P. GC/MS investigations of the total lipid fraction of wool: A new approach for modelling the ageing processes induced by iron-gallic dyestuffs on historical and archaeological textiles. Microchem. J. 2015, 118, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowska, I.; Bogdanowicz, A.; Szczęsny, P.; Zielenkiewicz, U.; Laudy, A. Evaluation of bacterial diversity on historical silk velvet textiles from the Museum of King John III’s Palace at Wilanów, Poland. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 131, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavkler, K.; Gunde-Cimerman, N.; Zalar, P.; Demšar, A. FTIR spectroscopy of biodegraded historical textiles. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wanrooij, J.; van Bommel, M.; Quye, A. Characterisation of chemical components for identifying historical Chinese textile dyes by ultra high performance liquid chromatography–photodiode array–electrospray ionisation mass spectrometer. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1479, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelosi, C.; Falletta, G.; Dominicis, B.D.; Baraldi, P. The painted silk panels of palazzo barberini at rome. The scientific investigation and preservation challenge. Proc. Chem. 2013, 8, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serrano, A.; Brokerhof, A.; Ankersmit, B.; van Bommel, M. From the bottom of the sea to the display case: A study into the long-term preservation of archaeological maritime silk textiles in controlled atmosphere. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 45, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.E.; Ziddan, Y.; Shehata, A.B. Identification of natural dyes in rare Coptic textile using HPLC-DAD and mass spectroscopy in museum of Faculty of Arts, Alexandria University, Egypt. Dyes Pigments 2017, 145, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, L.; Henderson, R.L.; Rayner, C.M.; Blackburn, R.S. Mild extraction methods using aqueous glucose solution for the analysis of natural dyes in textile artefacts dyed with Dyer’s madder (Rubia tinctorum L.). J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1487, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulmini, M.; Idone, A.; Diana, E.; Gastaldi, D.; Vaudan, D.; Aceto, M. Identification of dyestuffs in historical textiles: Strong and weak points of a non-invasive approach. Dyes Pigments 2013, 98, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Wertz, J.; Degano, I.; Aceto, M.; Khan, M.I.; Quye, A. Analytical methods for determination of anthraquinone dyes in historical textiles: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1083, 58–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgio, L.; Clark, R.J. Library of FT-Raman spectra of pigments, minerals, pigment media and varnishes, and supplement to existing library of Raman spectra of pigments with visible excitation. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2001, 57, 1491–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizi, L.; Bortolotti, V.; Marmotti, G.; Camaiti, M. Identification of complex structures of paintings on canvas by NMR: Correlation between NMR profile and stratigraphy. Org. Magn. Reson. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Farwell, D.W.; Brooke, C.J. Raman spectroscopic study of a post-medieval wall painting in need of conservation. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 383, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, B. Study of identification results of proteinous binding agents in Chinese painted cultural relics. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 43, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk, N.; Elsayed, Y. Archaeometrical study of a rare embroidered and appliqued leather tapestry from the safavid artworks. Part II: Colored leather. Mediter. Archaeol. Archaeomet. 2020, 20, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavkler, K.; Demšar, A. Examination of cellulose textile fibres in historical objects by micro-Raman spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 78, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kim, H.-J. Separation of underdeveloped from developed cotton fibers by attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yu, L.; Ding, Q.; Wang, R. Textile fiber identification using near-infrared spectroscopy and pattern recognition. Autex Res. J. 2019, 19, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, T.G.; da Silva, B.F.P.; de Mattos, L.P.; Escorteganha, M.R.; Ritcher, F.A.; Correia, M.D.D.M.; Siebert, D.A.; Spudeit, D.A.; Micke, G.A. Analysis of the constituent materials of 19th century paintings attributed to Louis-Auguste Moreaux belonging to the Historical Museum of Santa Catarina–Florianópolis, Brazil. Forensic Chem. 2019, 16, 100177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavari, G.; Galletti, G.C.; Lanterna, G.; Mazzeo, R. The potential of pyrolysis—Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry in the recognition of ancient painting media. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 1993, 24, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Wu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Tong, T.; Li, X.; Yang, C.; Tang, Y.; Shen, X.; Liu, S.; Tong, H. Scientific investigation of the lacquered wooden coffin of Xiang Fei excavated from Eastern Royal Tombs of the Qing Dynasty. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 9806–9814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, F.; Burnstock, A.; Van den Berg, K.J.; Miliani, C.; Brunetti, B.G.; Sgamellotti, A. A non-invasive XRF study supported by multivariate statistical analysis and reflectance FTIR to assess the composition of modern painting materials. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 71, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renda, V.; Nardo, V.M.; Anastasio, G.; Caponetti, E.; Vasi, C.; Saladino, M.; Armetta, F.; Trusso, S.; Ponterio, R. A multivariate statistical approach of X-ray fluorescence characterization of a large collection of reverse glass paintings. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2019, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Teri, G.; Li, J.; Huo, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, Y. Analysis of an ancient architectural painting from the Jiangxue Palace in the Imperial Museum, Beijing, China. Anal. Lett. 2020, 54, 684–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, M.R.; Heginbotham, A.; Van Keulen, H.; Szelewski, M. Beyond the basics: A systematic approach for comprehensive analysis of organic materials in Asian lacquers. Stud. Conserv. 2016, 61, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryszard, M.K.; Maria, M.T. Handbook of Natural Fibres (Second Edition): Volume 1: Types, Properties and Factors Affecting Breeding and Cultivation; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.-L.; Li, T. Technical investigation of 15th and 19th century Chinese paper currencies: Fiber use and pigment identification. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2013, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonsky, M.; Dubinyova, L.; Varga, S.; Vizarova, K.; Sima, J.; Katuscak, S. Cellulose fiber identification through color vectors of stained fibre. Bioresources 2015, 3, 5845–5862. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Rodriguez, J.L.; Robador, M.D.; Centeno, M.A.; Siguenza, B.; Duran, A. Wall paintings studied using Raman spectroscopy: A comparative study between various assays of cross sections and external layers. Spectrochim. Acta Part Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 120, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, K.; Vandenabeele, P.; Moens, L.; Madariaga, J.M. Micro-Raman analysis of coloured lithographs. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 379, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Xia, Y.; Ma, Y.; Lei, Y. Three fabricated pigments (Han purple, indigo and emerald green) in ancient Chinese artifacts studied by Raman microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometry and polarized light microscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2007, 38, 1274–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, G.; Colombini, M.P. GC–MS identification of proteins in wall painting samples: A fast clean-up procedure to remove copper-based pigment interferences. Talanta 2007, 73, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alruways, M.W.; Elrayah, I.E.; Mansi, M.A. Effect of benzoin resin fumes on indoor environmental microbes. Int. J. Med. Res. Health Sci. 2020, 9, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).