Abstract
Klebsiella pneumoniae is an increasingly important hospital pathogen. Classical K. pneumoniae (cKp) and hypervirulent K. pneumoniae (hvKp) are two distinct evolutionary genetic lines. The recently ongoing evolution of K. pneumoniae resulted in the generation of hybrid hvKP-MDR strains. K. pneumoniae distinct isolates (n = 70) belonged to 20 sequence types with the prevalence of ST395 (27.1%), ST23 (18.6%), ST147 (15.7%), and ST86 (7.1%), and 17 capsular types with the predominance of K2 (31.4%), K57 (18.6%), K64 (10.0%), K1 (5.7%) were isolated from patients of the Moscow neurosurgery ICU in 2014–2019. The rate of multi-drug resistant (MDR) and carbapenem-resistant phenotypes were 84.3% and 45.7%, respectively. Whole-genome sequencing of five selected strains belonging to cKp (ST395K47 and ST147K64), hvKp (ST86K2), and hvKp-MDR (ST23K1 and ST23K57) revealed blaSHV, blaTEM, blaCTX, blaOXA-48, and blaNDM beta-lactamase genes; acr, oqx, kpn, kde, and kex efflux genes; and K. pneumoniae virulence genes. Selective pressure of 100 mg/L ampicillin or 10 mg/L ceftriaxone induced changes of expression levels for named genes in the strains belonging to cKp, hvKp, and hybrid hvKp-MDR. Obtained results seem to be important for epidemiologists and clinicians for enhancing knowledge about hospital pathogens.
1. Introduction
Klebsiella pneumoniae is an increasingly important hospital pathogen causing a wide range of infections including urinary tract infections, pneumonia, bacteremia, and liver abscesses. In severe clinical cases, it can also lead to multiple organ failure, or even death [1]. Two different evolutionary genetic lines, classical K. pneumoniae (cKp) and hypervirulent K. pneumoniae (hvKp), were described and are both global pathogens [2]. Most multidrug-resistant (MDR) K. pneumoniae strains belong to particular clones (ST11, ST395, ST147, etc.) producing beta-lactamases in combination with other functional classes of resistance determinants [3]. Hypervirulent K. pneumoniae were attributed to sequence types ST23, ST86, ST65, etc., and capsular types K1, K2, K57, K20, etc. [4]. Virulence determinants of hvKp include siderophore systems for iron acquisition, increased capsule production, and the colibactin toxin commonly located on virulence plasmids [5].
Recent studies have shown the ongoing evolution of K. pneumoniae resulting in the generation of hybrid hvKp-MDR strains. Mechanisms for the emergence of such strains can be a result of acquiring hypervirulent plasmids by cKp [6], acquiring MDR plasmids by hvKp [7], and acquiring hybrid virulence-MDR plasmids [8]. However, the relative expression of resistance and virulence genes in bacteria of cKp, hvKp, and hybrid hvKp-MDR evolutionary branches is poorly studied.
This study aimed to determine the genetic lines of K. pneumoniae strains collected in Moscow neurosurgery ICU in 2014–2019, to identify resistance and virulence genes in their cells, and to estimate relative expression levels of such genes in selected strains belonging to epidemiology significant genetic lines cKp (ST395K47 and ST147K64), hvKp (ST86K2), and hybrid hvKp-MDR (ST23K1 and ST23K57).
2. Results
2.1. Bacterial Isolates and Clinical Data
K. pneumoniae caused about 28% among the agents of nosocomial infections in neurosurgery ICU during the period from January 2014 to May 2019. The incidence rates of K. pneumoniae infections were 8.0 per 100 patient infections of the central nervous system, 4.3/100 of bloodstream infections, 26.3/100 of respiratory infections, and 25.3/100 of urinary tract infections [9,10]. A total of 545 K. pneumoniae clinical isolates were collected from 283 patients in this period, including those isolated from the respiratory system (n = 271), urine (n = 166), the nervous system (n = 41), blood (n = 36), surgical wounds (n = 27), and other (n = 4).
2.2. K. pneumoniae Sequence Types and Capsular Types
Seventy non-duplicate isolates selected from the collection of 545 isolates were characterized by sequence types and capsular types. These isolates were collected from the respiratory system (n = 34), urine (n = 19), the nervous system (n = 8), blood (n = 6), and surgical wounds (n = 3). As a result, 20 sequence types were identified, the majority of them were ST395, ST23, ST147, and ST86, and a total of 17 capsular types were identified. Predominant K-types were K2, K57, K64, and K1 (Figure 1).
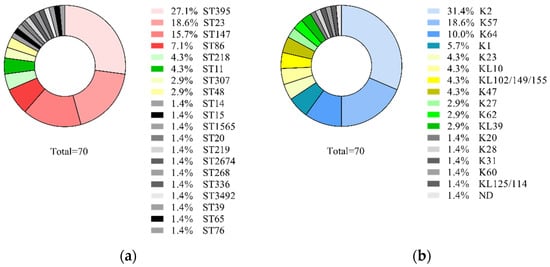
Figure 1.
Prevalence of K. pneumoniae genetic lines among 70 isolates collected in Neuro-ICU in 2014–2019: (a) sequence types; (b) capsular types.
2.3. Susceptibility to Antimicrobials and Resistance Genes
It was shown that major K. pneumoniae isolates were resistant to ampicillin (100.0%), ampicillin-sulbactam (90.0%), cefuroxime (86.8%), cefoxitin (68.8%), ceftriaxone (77.8%), ceftazidime (72.8%), cefoperazone-sulbactam (82.7%), cefepime (69.2%), ertapenem (48.1%), tetracycline (80.7%), ciprofloxacin (81.2%), chloramphenicol (77.0%), gentamicin (67.1%), tobramycin (83.0%), trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (69.2%), and nitrofurantoin (82.2%). Fewer resistant isolates were found for imipenem (33.8%), tigecycline (37.2%), and amikacin (31.8%) (Figure 2).
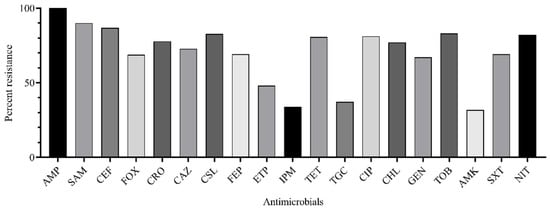
Figure 2.
Rate of K. pneumoniae isolates (n = 70) resistant to antimicrobials: AMP, ampicillin; SAM, ampicillin-sulbactam; CXM, cefuroxime; FOX, cefoxitin; CRO, ceftriaxone; CAZ, ceftazidime; CSL, cefepime; FEP, cefepime; ETP, ertapenem; IPM, imipenem; TET, tetracycline; TGC, tigecycline; CIP, ciprofloxacin; CHL, chloramphenicol; GEN, gentamicin; TOB, tobramycin; AMK, amikacin; SXT, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole; NIT, nitrofurantoin.
The frequency of the multi-drug resistant (MDR) phenotype was 84.3%, with the carbapenem-resistant phenotype consitituting 45.7%. K. pneumoniae isolates carried beta-lactamase genes blaSHV (100.0%), blaCTX-M (74.2%), blaTEM (51.4%), blaOXA-48 (40.0%), blaNDM (11.4%), class 1 (37.6%) and 2 (2.1%) integrons, and porin protein gene ompK36 (91.5%). Both blaOXA-48 and blaNDM carbapenemase genes were detected in four (5.7%) isolates. Beta-lactamase genes blaKPC, blaVIM, and blaIMP were not detected (Table S1).
2.4. K. pneumoniae Virulence Genes
Eight virulence genes were detected in 70 K. pneumoniae isolates: rmpA (34.2%), aer (21.4%), kfu (17.1%), uge (85.7%), wabG (100.0%), fimH (97.1%), allS (94.3%), and allR (5.7%). Twelve virulence gene combinations were identified. The most prevalent combination was uge+wabG+fimH+allS (51.4% isolates), followed by rmpA+aer+uge+wabG+fimH+allS (11.4%), uge+wabG+kfu+fimH+allS (7.1%), rmpA+wabG+fimH+allS (5.7%), and rmpA+aer+ +uge+wabG+kfu+fimH+allR (5.7%). The rarest combinations were wabG+fimH+allS (4.3%), rmpA+uge+wabG+fimH+allS (4.3%), uge+wabG+allS (2.8%), rmpA+aer+wabG+fimH+allS (2.8%), rmpA+wabG+kfu+fimH+allS (1.4%), rmpA+aer+uge+wabG+kfu+fimH+allS (1.4%), and rmpA+wabG+kfu+fimH+allS (1.4%) (Table S2).
2.5. Hypermucoviscousity Phenotype
Phenotype of hypermucoviscousity was detected for 11 of 70 isolates (15.7%) collected from the respiratory system (n = 9) and urine (n = 2), belonging to genetic lines ST23K1 (n = 4), ST86K2 (n = 3), ST23K57 (n = 2), ST65K2 (n = 1), and ST218K57 (n = 1). Isolates of ST23K1 carried rmpA+aer+uge+wabG+kfu+fimH+allR; isolates of ST86K2 and ST218K57 harbored rmpA+aer+uge+wabG+fimH+allS; isolates of ST23K57 carried two combinations, rmpA+uge+wabG+fimH+allS and rmpA+wabG+kfu+fimH+allS; and isolates of ST65K2 carried rmpA+aer+uge+wabG+kfu+fimH+allS virulence gene combinations. All 11 hypermucoviscous isolates carried rmpA, wabG, and fimH genes. Major isolates of hypermucoviscousity-positive isolates were MDR (n = 6), resistant to 3–7 antimicrobial functional groups (beta-lactams, aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, phenicols, fluoroquinolones, sulfonamides, nitrofurans). Among them, two isolates were CR. The remaining isolates were resistant to ampicillin only. As a result, there was no revealed correlation between the hypermucoviscousity phenotype and genetic line or the antimicrobial phenotype or virulence gene profiles (Tables S1 and S2).
2.6. Whole-Genome Sequencing
Five clinical isolates belonging to epidemically significant K. pneumoniae genetic lines, cKp (ST395K47 and ST147K64), hvKp (ST86K2), and hvKp-MDR (ST23K1 and ST23K57), were analyzed by whole-genome sequence and quantitative analyses of antimicrobial resistance and virulence gene expression. One of these strains (B2523/18) was resistant to AMP and carried only one beta-lactamase gene of the blaSHV type. In contrast, the other four strains that belonged to the MDR category were resistant to 10–18 antimicrobials. The latter strains carried beta-lactamase genes of blaSHV, blaTEM, blaCTX-M, blaOXA-48, and blaNDM types and the resistance determinants for other antimicrobial groups in the genomes: aminoglycosides, fosfomycin, streptogramins, phenicols, quinolones, sulfonamide, tetracyclines, sulfonamides, macrolides, and rifamycins, as well as genes coding 4–5 efflux pumps and 1–4 genes of heavy metal resistance. The following genetic determinants of K. pneumoniae virulence were identified in the genomes: peg-344 (n = 3), rmpA (n = 3), rmpA2 (n = 1), iroB (n = 2), iroN (n = 2), iroD (n = 2), uge (n = 5), wabG (n = 5), kfu (n =1 ), fimH (n = 5), allR (n = 1), irp (n = 4), iuc (n = 3), entB (n = 3), iut (n = 4), mrk (n = 5), ybt (n = 4), fyu (n =4 ), treC (n = 5), celB (n = 5), and ureA (n = 5) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Characteristics of K. pneumoniae strains used for whole-genome sequence analysis.
2.7. Relative mRNA Levels of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Genes in K. pneumoniae Cells
The expression levels of the resistance genes in all K. pneumoniae strains during growth without selective pressure of antimicrobials were different: the chromosomal beta-lactamase genes blaSHV were transcribed significantly lower compared with those of the reference gene rpoD. In contrast, other beta-lactamase genes (blaTEM, blaCTX-M, blaOXA-48, and blaNDM), as well as porin gene ompK36 were transcribed at higher levels compared with the reference gene, with the exception of blaTEM in the hvKp-MDR strain of ST23K1 which exhibited lower expression. The efflux pump genes and the virulence genes were expressed mostly at the same or lower levels compared with the rpoD gene, with the exception of two virulence genes: treC in the strains of ST395K47, ST147K64, ST23K1, and ST23K57; and celB in the strain of ST86K2 (Figure 3).
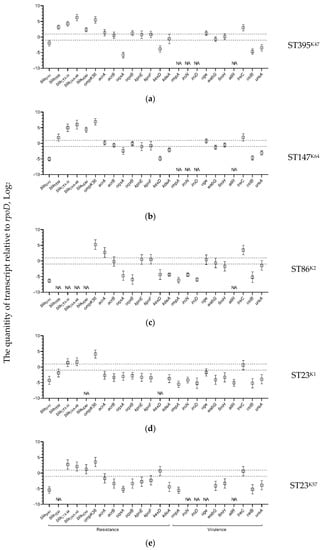
Figure 3.
Expression levels of K. pneumoniae antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes detected in the strains: (a) B-185/19; (b) B-16K/19; (c) B-2523/18; (d) B-2580/14; and (e) B-1261/19 detected by qPCR compared with rpoD gene as a reference. Expression levels for three replicates along with the standard error of the mean are shown on the plots; the area of no significant differences with the expression of the reference gene (from minus 1 to 1) are circumscribed by dotted lines; NA, not acceptable.
2.8. Fold Change of Expression Levels of K. pneumoniae Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Genes under AMP and CRO Selective Pressure
We analyzed gene expression patterns of antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes of K. pneumoniae strains belonging to different genetic lines in the presence of 100 mg/L AMP. The MDR strain of ST395K47 demonstrated upregulation of the fimH (4.6-fold) gene, and downregulation of the blaTEM (5.5-fold), acrA (2.4-fold), acrB (2.8-fold), oqxB (4.8-fold), kpnE (3.5-fold), kpnF (2.0-fold), and kdeA (3.0-fold) genes. Another MDR strain of ST147K64 was characterized by the upregulation of the blaTEM (2.2-fold), kpnE (3.2-fold), kdeA (2.7-fold), fimH (2.3-fold), and ureA (14.0-fold) genes, and downregulation of the blaOXA-48 (5.3-fold) gene. The hvKp strain of ST86K2 demonstrated upregulation of only one gene, iroN (4.1-fold), and downregulation of 13 genes: blaSHV (2.6-fold), acrA (9.0-fold), acrB (10.0-fold), oqxB (10.1-fold), kpnE (9.9-fold), kpnF (5.0-fold), kexD (4.9-fold), kdeA (4.8-fold), iroD (4.0-fold), uge (3.2-fold), wabG (6.2-fold), treC (4.8-fold), and ureA (5.3-fold). The hybrid hvKp-MDR strain of ST23K1 showed upregulation of the acrB (3.4-fold), oqxA (2.1-fold), oqxB (2.1-fold), wabG (6.2-fold), fimH (3.2-fold), celB (8.0-fold), and ureA (8.9-fold) genes. The second hvKp-MDR strain of ST23K57 expressed upregulation of the blaTEM (4.1-fold), blaCTX-M (5.3-fold), ompK36 (2.9-fold), acrB (2.3-fold), oqxA (2.9-fold), oqxB (4.6-fold), kpnE (2.3-fold), kpnF (2.0-fold), kexD (3.2-fold), kdeA (11.7-fold), uge (3.4-fold), wabG (14.5-fold), fimH (2.9-fold), celB (3.7-fold), and ureA (3.1-fold) genes (Figure 4).
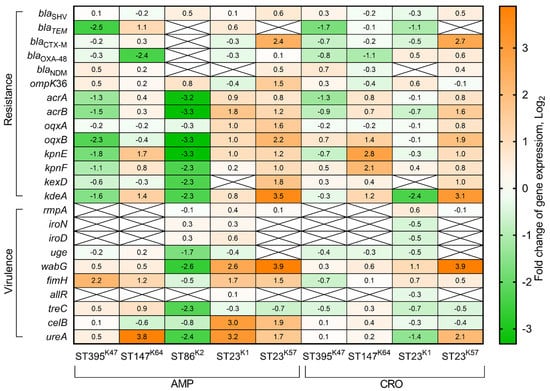
Figure 4.
Heatmap of changes in gene expression levels of K. pneumoniae resistance and virulence genes under ampicillin (100 mg/L) and ceftriaxone (10 mg/L) selective pressure during 90 min in LB medium in comparison with expression levels of these genes in LB medium without antibiotics. Values of each cell represent log2 of gene expression fold changes (fold changes ≥1 or ≤−1 are significant).
Additionally, we estimated fold changes of expression levels for the above listed genes in response to 10 mg/L CRO conditions. The MDR strain of ST395K47 demonstrated downregulation of the blaTEM (3.3-fold) and acrA (2.4-fold) genes. The MDR strain of ST147K64 was characterized by upregulation of the oqxB (2.7-fold), kpnE (7.0-fold), kpnF (4.4-fold), kdeA (2.3-fold) genes, and downregulation of the blaOXA-48 (2.1-fold) gene. The hybrid hvKp-MDR strain of ST23K1 showed upregulation of the fimH (2.1-fold) gene, and downregulation of the blaTEM (2.1-fold), kdeA (5.1-fold), and ureA (2.7-fold) genes. The second hybrid hvKp-MDR strain of ST23K57 expressed upregulation of the blaSHV (2.3-fold), blaTEM (2.4-fold), blaCTX-M (6.3-fold), acrB (3.0-fold), oqxB (3.8-fold), kpnE (2.1-fold), kdeA (8.6-fold), wabG (14.8-fold), and ureA (4.2-fold) genes, and no genes were downregulated (Figure 4).
3. Discussion
K. pneumoniae was one of the major nosocomial pathogens in a Moscow neurosurgery ICU during the period from January 2014 to May 2019, causing about 28% infections including those of the central nervous system, bloodstream, respiratory tract, and urinary tract. This rate was similar to those in the Multispecialty Hospital, Riga, Latvia in 2017–2020 (16–20%) [11], and significantly lower than those reported from 15 China centers in 2012–2016 (52.4%) [12].
Non-duplicate 70 K. pneumoniae isolates collected from 62 patients were attributed to specific genetic lines, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance genotypes. Single isolates were collected from 54 patients and two isolates from eight patients. Double isolates were studied from one patient in a case of their differences in ST (Patients 19, 32, 36, 46, and 48), K-type (Patient 35), and antimicrobial resistance genes profiles (Patients 4 and 39) (Table S1). Two isolates collected from the trachea and urine of the Patient 4 attributed to ST147K64 carried (blaTEM+blaSHV+blaCTX-M+blaOXA-48+blaNDM) and (blaSHV+blaOXA-48) beta-lactamase genes, respectively. Two isolates obtained from the trachea of Patient 39 belonged to ST23K57 (blaTEM+blaSHV+blaCTX-M) and (blaSHV+blaCTX-M+blaOXA-48) beta-lactamase genes, respectively. Different antimicrobial resistance gene profiles of K. pneumoniae named isolates possibly indicate the evolution events in the patient’s body as described previously [13].
Twenty STs and 17 K-types were identified. The most prevalent sequence types were ST395 (27.1%), ST23 (18.6%), ST147 (15.7%), and ST86 (7.1%). The remaining 16 STs were each represented at ≤ 4.3%. The dominant STs were described previously as K. pneumoniae genetic lines common for classical K. pneumoniae (cKp) (ST395 and ST147) and hypervirulent K. pneumoniae (hvKp) (ST23 and ST86). ST395 was reported as prevalent for cKp-MDR strains in studies from Poland, France, Italy, and Russia [14,15,16,17]. ST147 has been estimated as Hight-Risk-Clone of cKp distributed worldwide, causing serious infections and associated with polyresistance [18]. K. pneumoniae of ST23 and ST86 were described previously as hvKp causing bacteremia, sepsis, and liver abscess in India, France, Taiwan, and Russia [19,20,21,22]. The prevalent K-types in our study were K2 (31.4%), K57 (18.6%), K64 (10.0%), and K1 (5.7%); the remaining of the 12 K-types were each present at a frequency of ≤ 4.3%. Among them, K1, K2, and K57 were identified in many studies as specific capsular types for hvKp [23]. K. pneumoniae isolates of K64 commonly were recognized as cKp, but recently some isolates of K64 were described as hybrid hvKp-MDR due to acquiring the hvKp virulence plasmids [24]. Moreover, many reports have been published in the last decade concerning hvKp-MDR hybrids generated on the base of cKp ST11K20/K64, ST395K2, as well as hvKp ST23K1 and ST86K2 [25,26,27,28,29]. Major (84.3%) K. pneumoniae isolates in our study were MDR with resistance to carbapenems for 45.7% isolates. Such high MDR rates were reported from China and Iran [30,31]. The prevalence of beta-lactamase genes blaCTX-M in our study was 74.2%, carbapenemase genes blaOXA-48 and blaNDM at 40.0% and 11.4%, respectively, similar to the prevalence of these genes published previously [31]. Hypermucoviscous isolates identified in this study (n = 11) were attributed to ST23K1, ST86K2, ST23K57, ST65K2, and ST218K57 genetic lines. All of them carried the rmpA gene coding the major virulence-associated factor in hvKP isolates [32], although not all rmpA-positive isolates in this study were hypermucoviscousity-positive, which is in agreement with a previously published report [22]. Hypermucoviscous isolates were characterized in our previous study as hypervirulent in the mouse model [22]. The rate of MDR K. pneumoniae among hypermucoviscousity-positive isolates in this study was 6/11, which is consistent with the modern trend for the appearance of hybrid hvKp-MDR genetic lines [8,33,34].
Five K. pneumoniae strains belonging to prevalent STs and K-types (cKp, ST395K47, and ST147K64; hvKp, ST86K2; and hybrid hvKp-MDR, ST23K1, and ST23K57) were selected for further comparative study of whole-genome sequences, antimicrobial resistance phenotypes, hypermucoviscosity, and altered expression levels of virulence and resistance genes in response to beta-lactams effect (AMP and CRO). It was shown that K. pneumoniae isolates belonging to ST86K2, ST23K1, and ST23K57 demonstrated hypermucoviscosity phenotype in contrast with isolates of ST395K47 and ST147K64, which confirmed the virulent phenotype of three isolates. All K. pneumoniae isolates carried blaSHV genes, including extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) variant blaSHV-12, broad-spectrum variants blaSHV-28 and blaSHV-33, and narrow-spectrum variants blaSHV-67 and blaSHV-190. These alleles of blaSHV genes were previously described in Portugal, Turkey, China, Russia, and Spain [22,35,36]. Three K. pneumoniae isolates (ST395K47, ST147K64, and ST23K1) carried the blaTEM-1B, blaCTX-M-15, and blaOXA-1 genes. It was reported that these genes were horizontally transferred by the IncFIA-FIB-FII and IncHI2 plasmids [37,38]. One isolate (ST23K57) carried the blaCTX-M-55 and blaOXA-1 genes; such gene combination was reported previously from China [39]. It should be noted that MDR isolates of ST395K47 and ST147K64 additionally carried two carbapenemase genes, i.e., blaOXA-48 and blaNDM-1. Previously, it was reported that K. pneumoniae clinical isolates of ST395 and ST147 harbored blaNDM-5 and blaOXA-181/232 in Nepal and that ST11 harbored blaNDM-1 and blaOXA-48 in Greece [33,40]. Of greatest interest are K. pneumoniae isolates belonging to the hvKp evolutionary branch, which acquired the resistance genes and became a hybrid hvKp-MDR. In our study, a hvKp-MDR isolate of ST23K1 carried simultaneously blaCTX-M-15 and blaOXA-48 genes, similar to a recently published study [34]. Moreover, another hvKp-MDR isolate of ST23K57 carried not only the blaCTX-M-55 and blaOXA-48 genes but additionally the blaNDM-1 gene. This is the first report describing K. pneumoniae of ST23K57 genetic-line-acquired cefalosporinase gene blaCTX-M-55, and two carbapenemase genes blaOXA-48 and blaNDM-1, which is particularly alarming. The incidence of high-risk clone ST383 carrying blaCTX-M-14b gene and two carbapenemase genes blaNDM-1 and blaOXA-48 combining both resistance and virulence elements was recently published [8] as well as the incidence of ST147-carrying blaCTX-M-15, blaNDM, and blaOXA-181 genes [41]. Additionally, we detected the efflux pump genes (acrA, acrB, oqxA, oqxB, kpnE, kpnF, kdeA, and kexD) because of their clinical significance for K. pneumoniae beta-lactam resistance presented recently [41]. In our study, one strain of ST23K1 carried four efflux pump genes: acr and oqx of RND-type systems, kde of MATE-type, and kpn of SMF-type. The rest of the four strains carried five efflux pumps: acr, oqx, kde, kpn, and additionally the kex gene of the RND-type efflux system. The same efflux pump genes were detected recently in K. pneumoniae clinical isolates, which exhibited co-resistance to beta-lactams and aminoglycosides, glycopeptides, fluoroquinolones, and tetracyclines in India [41]. Interestingly, the efflux pumps were associated with bacterial virulence, namely biofilm formation [42].
It is known that multiple biomarkers have been shown to predict hvKp isolates: peg-344, iroB, iucA, plasmid-encoded rmpA, and rmpA2 and quantitative siderophore production (entB and ybtS) [43]. In this study, these genes were detected only in the genomes of hvKp isolates of ST86K2, ST23K1, and ST23K57. In contrast, K. pneumoniae virulence genes (uge, wabG, fimH, mrk, treC, cellB, and ureA), common for both hvKp and cKp, were detected in all five isolates. This is in agreement with recently published data [44]. Two strains of ST23K1 and ST23K57 are characterized as hybrid hvKp-MDR. Thus, the data obtained in this study indicate the ongoing formation of hybrid K. pneumoniae on the base of the ST23 genetic line, which was already defined in the last decade [7,22,35,45].
We estimated the basal expression levels of K. pneumoniae resistance and virulence genes at non-selective conditions in vitro and the fold change of expression levels in presence of AMP and CRO. It was shown that ESBL gene blaSHV-12 expressed ~4-fold higher in the MDR strain of ST395K47 than blaSHV-type genes coding broad-spectrum and narrow-spectrum beta-lactamases in the remaining K. pneumoniae strains. This is in agreement with previously reported data that ESBL variants of the blaSHV-12 gene expressed higher than non-ESBL variants [46]. These genes did not change their expression after 90 min growing at 100 mg/L AMP or 10 mg/L CRO.
Beta-lactamase genes blaTEM, blaCTX-M, blaOXA-48, and blaNDM and porin gene ompK36 were expressed at higher levels, with the exception of blaTEM in the hvKp-MDR strain of ST23K1. Notably, the expression levels of the beta-lactamase (blaTEM and blaCTX-M) and carbapenemase (blaOXA-48, and blaNDM) genes were higher in cKp-MDR strains than those in hybrid hvKp-MDR strains. Possibly, the reason for this observation is the higher metabolic load in Klebsiella cells producing resistance and virulence factors simultaneously. Growing at AMP conditions for 90 min induced upregulation of blaTEM gene expression in cKp-MDR of ST147K64 (2.1-fold), as well as the blaCTX-M (5.3-fold) and ompK36 (2.8-fold) genes in hvKp-MDR of ST23K57, but downregulation of blaTEM gene expression in cKp-MDR of ST395K47 and the blaOXA-48 gene in cKp-MDR of ST147K64. In contrast, growing at CRO conditions induced upregulation of the blaCTX-M gene in hvKp-MDR of ST23K57 (6.5-fold) and downregulation of the blaTEM gene in cKp-MDR of ST395K47 (3.3-fold), in hvKp-MDR of ST23K1 (2.1-fold), and the blaOXA-48 gene in cKp-MDR of ST147K64 (2.1-fold).
The basal level of efflux pump gene expression was very different for cKp, hvKp, and hybrid hvKp-MDR strains. In cKp-MDR strains, 5–6 efflux genes were expressed on the same level as reference gene ropD, and 2–3 genes were lower than the reference. In the hvKp strain, one efflux gene expression was higher, three genes were expressed at the same level, and four genes were lower than the reference gene. In contrast, major efflux genes in hybrid hvKp-MDR strains were expressed lower than the rpoD gene, and one gene in the strain of ST23K57 was expressed on the same level as the reference. Interestingly, the previously described expression of the arcB efflux gene showed upregulation of this gene in carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae strains compared with non-resistant ones [47]. The relatively high expression level of efflux genes in cKp and hvKp strains indicates the importance of efflux pumps for virulence of both Klebsiella evolutionary branches that are consistent with previous reports [48]. It is known that efflux pumps use different antimicrobials as substrates. Our results suggest that the change in efflux gene expression in certain K. pneumoniae genetic lines may reflect differences in bacterial surface structures in particular K-types: downregulation in the strains of K47 and K2, and upregulation in the strains of K1 and K57 in response to AMP; and upregulation in the strains of K64 and K57 in response to CRO (Figure 4).
It was shown in our study that transcripts of K. pneumoniae virulence genes common for both the cKp and hvKp evolutionary branches (uge, wabG, fimH, and treC) were present at higher levels in the cKp strains of ST395K47, ST147K64, and hvKP ST86K2 than in the hybrid hvKp-MDR strains of ST23K1 and ST23K57. In conditions containing 100 mg/L AMP, these genes were upregulated in cKp and hybrid hvKp-MDR strains (fimH 2.3-4.6-fold) and wabG in hvKp-MDR strains (6.1–14.9-fold), while downregulated in the hvKp strain (uge, wabG, and treC, 3.2-4.9-fold). In conditions with 10 mg/L CRO, only the wabG gene was upregulated in hybrid hvKp-MDR strains (2.3-14.9-fold). The expression levels of the remaining virulence genes common for cKp and hvKp (celB and ureA), as well as common for only hvKp (rmpA, iroN, iroD, and allR), were approximately equal in all studied strains at non-selective conditions. The celB gene expression at AMP medium was upregulated in hvKp-MDR strains (3.7–8.0-fold); the ureA gene expression was upregulated in the cKp strain of ST147K64 (13.9-fold) and hvKp-MDR strains of ST23K1 (9.2-fold) and ST23K57 (3.2-fold). It was detected that CRO induced upregulation of the ureA gene in a hvKp-MDR strain of ST23K57 (4.3-fold) and downregulation of this gene in a hvKp-MDR strain of ST23K1 (2.6-fold). Expression levels of virulence genes common for hvKp strains were not changed under selective pressure generated by AMP or CRO in the growth media (Figure 4).
In summary, expression levels of antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes were characteristic for K. pneumoniae of different certain genetic lines. Selective pressure by sub-inhibitory concentrations of ampicillin or ceftriaxone induced differential upregulation or downregulation of these genes depending on the strain belonging to classical cKp, hypervirulent hvKp, or hybrid hvKp-MDR evolutionary branches. Results obtained in this study may be fruitful for future studies of evolution, the spread of antimicrobial and virulence genetic determinants, and the clinical impact of K. pneumoniae genetic lines.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bioethical Requirements and Patients
K. pneumoniae isolates were collected from the patients of the neuro-intensive care unit (Neuro-ICU) in a specialized Neurosurgical Hospital in Moscow, Russia. Following the requirements of the Russian Federation Bioethical Committee, each patient signed informed voluntary consent to treatment and laboratory examination. The materials used in the study did not contain the personal data of patients.
4.2. Bacterial Isolates, Identification, and Growth Conditions
Seventy K. pneumoniae isolates were collected from the respiratory system, blood, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, and wounds of 62 patients of the neuro-ICU. Bacteria identification was performed using by a Vitek-2 Compact instrument (BioMérieux, Paris, France) and a MALDI-TOF Biotyper (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany). Bacteria were grown at 37 °C with agitation on Luria-Bertani broth (Difco Laboratories, Detroit, MI, USA) and Muller-Hinton broth (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). Bacterial isolates were stored in 20% glycerol at minus 80 °C.
4.3. Susceptibility to Antimicrobials
Minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of ampicillin (AMP), ampicillin-sulbactam (SAM), cefuroxime (CXM), cefoxitin (FOX), ceftriaxone (CRO), ceftazidime (CAZ), cefoperazone-sulbactam (CSL), cefepime (FEP), ertapenem (ETP), imipenem (IPM), tetracycline (TET), tigecycline (TGC), ciprofloxacin (CIP), chloramphenicol (CHL), gentamicin (GEN), tobramycin (TOB), amikacin (AMK), trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (SXT), and nitrofurantoin (NIT) were determined using a Vitek-2 instrument with VITEK-2 using AST n-101 and AST n-102 cards (BioMérieux, Paris, France). The results were interpreted according to the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (http://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints, accessed on 1 November 2021). E. coli strains ATCC 25922 and ATCC 35218 were used for quality control. Strains non-susceptible to ≥1 agent in ≥3 antimicrobial categories were identified as multi-drug resistant (MDR), according to Magiorakos et al., 2012 [49].
4.4. Hypermucoviscousity Testing
The string test was used for the identification of hypermucoviscous K. pneumoniae strains growing on the plates with Luria-Bertani broth (Difco Laboratories, Detroit, MI, USA) overnight at 37 °C [23]. The positive test was assigned if a colony of K. pneumoniae formed viscous strings >5 mm length using a standard bacteriological loop.
4.5. K. pneumoniae Sequence Type and Capsular Type Identification
Sequence types (STs) of K. pneumoniae isolates were determined by the Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) scheme of Pasteur Institute (Paris, France) using the previously published primers [50,51]. The PCR capsular serotyping of the K. pneumoniae isolates was performed using specific primers for the wzy gene associated with K serotypes K1, K2, K20, and K57 [52] and by wzi gene sequencing for identification of capsular types K23, K27, K28, K31, K47, K60, K62, and K64 [53]. Bacterial thermolysates were used as DNA templates for amplification.
4.6. Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Genes
Beta-lactamase genes blaSHV, blaCTX-M, blaTEM, blaOXA-48, blaKPC, blaVIM, blaIMP, and blaNDM, class 1 and 2 integrons, and porin protein gene ompK36, as well as 8 genes associated with K. pneumoniae virulence, rmpA (hypermucoid phenotype regulator), aer (aerobactin), kfu (ferric absorption system), uge (uridine diphosphate-galacturonate-4-epimerase), wabG (glucosyltransferase), fimH (fimbria type I), allS and allR (allantoin regulon), were detected by PCR using specific primers as was described previously [10].
4.7. Real-Time PCR Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Genes
Oligonucleotides for RT-PCR (Table 2) were designed using Vector NTI Advance 11.0 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and purchased from Evrogen (Moscow, Russia). Secondary structures were controlled with Gene Runner 6.5.52 (http://www.generunner.net/, accessed on 1 November 2021) and in silico analysis by insilico.ehu.eus [54] was performed to check primer specificity. K. pneumoniae virulence genetic determinants (rmpA, iroN, iroD, mrkD, uge, wabG, fimH, treC, celB, ureA, and allR) and antibacterial resistance genes (blaTEM, blaSHV, blaCTX-M, blaOXA-48, blaNDM, blaKPC, blaVIM, ompK36) were detected by RT-PCR using qPCRmix-HS SYBR (Evrogen, Moscow, Russia) and the CFX96 Real-Time PCR system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA) with the following program: 95° for the 20s, 61° for 20s, 72° for 30 s, repeat 40 times. Bacterial thermolysates were used as DNA templates.

Table 2.
Oligonucleotide primers for RT-PCR were used in this study for the detection of K. pneumoniae antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes.
4.8. Whole-Genome Sequencing
WGS was carried out on the Illumina MiSeq platform using Nextera DNA Library Preparation Kit (Illumina, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and MiSeq Reagent Kits v3 (Illumina, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The obtained single reads were collected into contigs using the SPAdes 3.9.0 software (Petersburg State University, St-Petersburg, Russia). De novo assembled genomes were annotated in the GenBank database (https://github.com/ncbi/pgap, accessed on 1 November 2021). Antimicrobial resistance genes, STs, plasmids, and restriction-modification systems were identified using the web resource of the Center for Genomic Epidemiology (http://www.genomicepidemiology.org/, accessed on 1 November 2021). Virulence genes, capsular type, genes conferring resistance to heavy metals, and efflux pumps were identified by the Institut Pasteur, Paris, France, BIGS database web-resource of (https://bigsdb.pasteur.fr/, accessed on 1 November 2021).
4.9. K. pneumoniae Growing in Antimicrobial Conditions and RNA Isolation
Overnight bacterial culture was diluted 1/50 in Luria-Bertani broth (Difco Laboratories, Detroit, MI, USA) containing/not containing antimicrobials (100 mg/L AMP or 10 mg/L CRO) and incubated at 37 °C with agitation for 90 min. Each experiment was represented by three independent repeats. All following steps for RNA isolation were performed at 4 °C to limit RNase activity. Total RNA was isolated by phenol-chloroform extraction using kit RNA-extran (Sintol, Moscow, Russia), following manufacturer protocol. After isolation, RNA was treated with TURBO DNase (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) to remove traces of genomic DNA.
4.10. cDNA Synthesis and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
One µg of isolated total RNA was used for cDNA synthesis with RevertAid RT Reverse Transcription Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). qPCR was performed using qPCRmix-HS SYBR (Evrogen, Moscow, Russia) and the CFX96 Real-Time PCR system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA) with the following program: 40 cycles of 20 s at 95 °C for denaturation, 20 s at 61 °C for annealing, 30 s at 72 °C for extension and SYBR Green detection. The melting curve analysis in the temperature range from 60 °C to 94 °C, with a fluorescence estimation step of 0.2 °C, was performed to confirm the specificity of the reaction. Relative quantification of the target gene expression was normalized with reference genes proC, recA, and rpoD expression. Three technical replicates per each of the three biological samples were used for statistical validity. The relative transcript levels of antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method [56]. A heat map of changes in gene expression levels relative to reference genes was designed using GraphPad Prism version 8.0.1 for Windows (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA, www.graphpad.com accessed on 1 November 2021). Gene expression levels of each gene at present of AMP and CRO were compared to those in conditions without antimicrobials.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/antibiotics11010007/s1, Table S1: Clinical characteristics, susceptibility to antibacterials, and antimicrobial resistance gene profiles of K. pneumoniae clinical isolates collected from 62 patients of Moscow Neuro-ICU, Table S2: K. pneumoniae virulence gene profiles of the clinical isolates collected from 62 patients of Moscow Neuro-ICU.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.K.F., O.N.E.; methodology, I.A.A., A.D.F., M.V.F.; software, N.K.F., A.A.K.; validation, T.S.N., M.V.F.; formal analysis, O.N.E., N.K.F.; investigation, I.A.A., E.I.A., T.S.N., G.N.F., A.D.F.; resources, E.I.A., G.N.F.; data curation, I.A.D.; writing—original draft preparation, N.K.F., M.V.F.; writing—review and editing, N.K.F.; visualization, A.D.F., E.I.A.; supervision, N.K.F., O.N.E.; project administration, I.A.D., O.N.E.; funding acquisition, N.K.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation, grant number 075-15-2019-1671 (agreement dated 31 October 2019).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of The Burdenko National Medical Research Center of Neurosurgery Review Board (protocol code #11/2018, 1 November 2018).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available in the GenBank database at accession numbers [PUXF00000000.1, JAGRZF000000000.1, JAGVVS000000000.1, JAGVVR000000000.1, JAGVVQ000000000.1].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bengoechea, J.A.; Sa Pessoa, J. Klebsiella Pneumoniae Infection Biology: Living to Counteract Host Defences. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 43, 123–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialek-Davenet, S.; Criscuolo, A.; Ailloud, F.; Passet, V.; Jones, L.; Delannoy-Vieillard, A.S.; Garin, B.; le Hello, S.; Arlet, G.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.H.; et al. Genomic Definition of Hypervirulent and Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Clonal Groups. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraniak, A.; Izdebski, R.; Fiett, J.; Sadowy, E.; Adler, A.; Kazma, M.; Salomon, J.; Lawrence, C.; Rossini, A.; Salvia, A.; et al. Comparative Population Analysis of Klebsiella Pneumoniae Strains with Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases Colonizing Patients in Rehabilitation Centers in Four Countries. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1992–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struve, C.; Roe, C.C.; Stegger, M.; Stahlhut, S.G.; Hansen, D.S.; Engelthaler, D.M.; Andersen, P.S.; Driebe, E.M.; Keim, P.; Krogfelt, K.A. Mapping the Evolution of Hypervirulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae. mBio 2015, 6, e00630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choby, J.E.; Howard-Anderson, J.; Weiss, D.S. Hypervirulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae—Clinical and Molecular Perspectives. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 287, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Yang, X.; Xu, Q.; Ye, L.; Chen, K.; Zheng, Z.; Dong, N.; Sun, Q.; Shu, L.; Gu, D.; et al. Clinical Evolution of ST11 Carbapenem Resistant and Hypervirulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.T.; Su, W.Q. Whole Genome Sequencing of NDM-1-Producing Serotype K1 St23 Hypervirulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae in China. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turton, J.; Davies, F.; Turton, J.; Perry, C.; Payne, Z.; Pike, R. Hybrid Resistance and Virulence Plasmids in “High-Risk” Clones of Klebsiella Pneumoniae, Including Those Carrying Blandm-5. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ershova, K.; Savin, I.; Kurdyumova, N.; Wong, D.; Danilov, G.; Shifrin, M.; Alexandrova, I.; Sokolova, E.; Fursova, N.; Zelman, V.; et al. Implementing an Infection Control and Prevention Program Decreases the Incidence of Healthcare-Associated Infections and Antibiotic Resistance in a Russian Neuro-ICU. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fursova, N.K.; Astashkin, E.I.; Ershova, O.N.; Aleksandrova, I.A.; Savin, I.A.; Novikova, T.S.; Fedyukina, G.N.; Kislichkina, A.A.; Fursov, M.V.; Kuzina, E.S.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Causing Severe Infections in the Neuro-Icu. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Jansone, I.; Obidenova, T.; Sīmanis, R.; Meisters, J.; Straupmane, D.; Reinis, A. Epidemiological Characterization of Clinical Fungal Isolates from Pauls Stradinš Clinical University Hospital, Latvia: A 4-Year Surveillance Report. Life 2021, 11, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, K.H.; Chen, W.; Yu, Y.; Feng, S.F. Epidemiology and Risk Factors for Nosocomial Infection in the Respiratory Intensive Care Unit of a Teaching Hospital in China: A Prospective Surveillance during 2013 and 2015. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fursova, N.K.; Astashkin, E.I.; Knyazeva, A.I.; Kartsev, N.N.; Leonova, E.S.; Ershova, O.N.; Alexandrova, I.A.; Kurdyumova, N.V.; Sazikina, S.Y.; Volozhantsev, N.V.; et al. The spread of bla OXA-48 and bla OXA-244 carbapenemase genes among Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis and Enterobacter spp. isolated in Moscow, Russia. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2015, 14, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izdebski, R.; Baraniak, A.; Zabicka, D.; Machulska, M.; Urbanowicz, P.; Fiett, J.; Literacka, E.; Bojarska, K.; Kozińska, A.; Zieniuk, B.; et al. Enterobacteriaceae Producing OXA-48-like Carbapenemases in Poland, 2013-January 2017. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muggeo, A.; Guillard, T.; Klein, F.; Reffuveille, F.; François, C.; Babosan, A.; Bajolet, O.; Bertrand, X.; de Champs, C. Spread of Klebsiella Pneumoniae ST395 Non-Susceptible to Carbapenems and Resistant to Fluoroquinolones in North-Eastern France. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 13, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maida, C.M.; Bonura, C.; Geraci, D.M.; Graziano, G.; Carattoli, A.; Rizzo, A.; Torregrossa, M.V.; Vecchio, D.; Giuffrè, M. Outbreak of ST395 KPC-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit in Palermo, Italy. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2018, 39, 496–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fursova, N.K.; Astashkin, E.I.; Gabrielyan, N.I.; Novikova, T.S.; Fedyukina, G.N.; Kubanova, M.K.; Esenova, N.M.; Sharapchenko, S.O.; Volozhantsev, N.V. Emergence of Five Genetic Lines ST395NDM-1, ST13OXA-48, ST3346OXA-48, ST39CTX-M-14, and Novel ST3551OXA-48of Multidrug-Resistant Clinical Klebsiella Pneumoniae in Russia. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 26, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peirano, G.; Chen, L.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; Pitout, J.D.D. Emerging Antimicrobial-Resistant High-Risk Klebsiella Pneumoniae Clones ST307 and ST147. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e01148-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, C.; Jacob, J.J.; Vasudevan, K.; Biswas, R.; Manesh, A.; Sethuvel, D.P.M.; Varughese, S.; Biswas, I.; Veeraraghavan, B. Emergence of Multidrug Resistant Hypervirulent ST23 Klebsiella Pneumoniae: Multidrug Resistant Plasmid Acquisition Drives Evolution. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 575289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, S.A.; Pascale, L.M.; Million, M.; Briantais, A.; Durand, J.M.; Hadjadj, L.; Rolain, J.M. Whole Genome Sequencing to Decipher the Virulence Phenotype of Hypervirulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae Responsible for Liver Abscess, Marseille, France. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.H.; Huang, Y.T.; Chang, C.Y.; Hsu, H.S.; Hsueh, P.R. Capsular Serotypes and Multilocus Sequence Types of Bacteremic Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolates Associated with Different Types of Infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lev, A.I.; Astashkin, E.I.; Kislichkina, A.A.; Solovieva, E.V.; Kombarova, T.I.; Korobova, O.V.; Ershova, O.N.; Alexandrova, I.A.; Malikov, V.E.; Bogun, A.G.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Klebsiella Pneumoniae Strains Isolated in 2012–2016 That Differ by Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Virulence Genes Profiles. Pathog. Glob. Health 2018, 112, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, A.S.; Bajwa, R.P.S.; Russo, T.A. Hypervirulent (Hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella Pneumoniae: A New and Dangerous Breed. Virulence 2013, 4, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jin, L.; Ouyang, P.; Wang, Q.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Gao, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, H. Evolution of Hypervirulence in Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae in China: A Multicentre, Molecular Epidemiological Analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.L.; Lam, M.M.C.; Holt, K.E. Population Genomics of Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Dong, N.; Chen, K.; Yang, X.; Ye, L.; Chan, E.W.C.; Zhang, R.; Chen, S. A Hybrid Plasmid Formed by Recombination of a Virulence Plasmid and a Resistance Plasmid in Klebsiella Pneumoniae. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 23, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, C.; Chang, Y.F.; Chen, W.; Nian, S.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, F.; et al. Bla NDM-5 Carried by a Hypervirulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae with Sequence Type 29. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad Ali Tabrizi, A.; Badmasti, F.; Shahcheraghi, F.; Azizi, O. Outbreak of Hypervirulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae Harbouring BlaVIM-2 among Mechanically-Ventilated Drug-Poisoning Patients with High Mortality Rate in Iran. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 15, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazareva, I.; Ageevets, V.; Sopova, J.; Lebedeva, M.; Starkova, P.; Likholetova, D.; Lebedeva, M.; Gostev, V.; Moiseenko, V.; Egorenkov, V.; et al. The Emergence of Hypervirulent BlaNDM-1-Positive Klebsiella Pneumoniae Sequence Type 395 in an Oncology Hospital. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 85, 104527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.H.; Song, X.Y.; Ma, X.B.; Zhang, S.Y.; Zhang, J.Q. Molecular Characterization of Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolates. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, M.; Ahanjan, M.; Goli, H.R.; Haghshenas, M.R.; Gholami, M. High Frequency of Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) Klebsiella Pneumoniae Harboring Several β-Lactamase and Integron Genes Collected from Several Hospitals in the North of Iran. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2021, 20, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.W.; Zheng, J.X.; Bai, B.; Xu, G.J.; Lin, F.J.; Chen, Z.; Sun, X.; Qu, D.; Yu, Z.J.; Deng, Q.W. Characteristics of Hypervirulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae: Does Low Expression of RmpA Contribute to the Absence of Hypervirulence? Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protonotariou, E.; Meletis, G.; Chatzopoulou, F.; Malousi, A.; Chatzidimitriou, D.; Skoura, L. Emergence of Klebsiella Pneumoniae ST11 Co-Producing NDM-1 and OXA-48 Carbapenemases in Greece. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 19, 81–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, M.; López-Urrutia, L.; Abad, D.; Serna, M.D.F.; Ocampo-Sosa, A.A.; Eiros, J.M. First Report of an Extensively Drug-Resistant ST23 Klebsiella Pneumoniae of Capsular Serotype K1 Co-Producing CTX-M-15, OXA-48 and ArmA in Spain. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, I.; Carvalho, J.A.; Martínez-álvarez, S.; Sadi, M.; Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Rabbi, F.; de Lurdes Nunes Enes Dapkevicius, M.; Igrejas, G.; Torres, C.; et al. Characterization of Esbl-Producing Escherichia Coli and Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolated from Clinical Samples in a Northern Portuguese Hospital: Predominance of Ctx-m-15 and High Genetic Diversity. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, J.; Ladona, M.G.; Segura, C.; Coira, A.; Reig, R.; Ampurdanés, C. SHV-1 β-Lactamase Is Mainly a Chromosomally Encoded Species-Specific Enzyme in Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 2856–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awosile, B.B.; Agbaje, M. Genetic Environments of Plasmid-Mediated BlaCTXM-15 Beta-Lactamase Gene in Enterobacteriaceae from Africa. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barguigua, A.; el Otmani, F.; Talmi, M.; Reguig, A.; Jamali, L.; Zerouali, K.; Timinouni, M. Prevalence and Genotypic Analysis of Plasmid-Mediated β-Lactamases among Urinary Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolates in Moroccan Community. J. Antibiot. 2013, 66, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Qin, J.; Mi, Z. A Klebsiella pneumoniaesputum culture isolate from China carrying blaOXA-1, blaCTX-M-55 and aac(69)-Ib-cr. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 1588–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sherchan, J.B.; Tada, T.; Shrestha, S.; Uchida, H.; Hishinuma, T.; Morioka, S.; Shahi, R.K.; Bhandari, S.; Twi, R.T.; Kirikae, T.; et al. Emergence of Clinical Isolates of Highly Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Co-Harboring BlaNDM-5 and BlaOXA-181 or -232 in Nepal. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 92, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, N.; Jangra, M.; Tambat, R.; Nandanwar, H. Alliance of Efflux Pumps with β-Lactamases in Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolates. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaie, A.; Ranjbar, R. Antibiotic Resistance, Virulence-Associated Genes Analysis and Molecular Typing of Klebsiella Pneumoniae Strains Recovered from Clinical Samples. AMB Express 2021, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Olson, R.; Fang, C.T.; Stoesser, N.; Miller, M.; MacDonald, U.; Hutson, A.; Barker, J.H.; la Hoz, R.M.; Johnson, J.R.; et al. Identification of Biomarkers for Differentiation of Hypervirulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae from Classical K. Pneumoniae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00776-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, T.A.; MacDonald, U.; Hassan, S.; Camanzo, E.; LeBreton, F.; Corey, B.; McGann, P. An Assessment of Siderophore Production, Mucoviscosity, and Mouse Infection Models for Defining the Virulence Spectrum of Hypervirulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae. mSphere 2021, 6, e00045-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaidullina, E.; Shelenkov, A.; Yanushevich, Y.; Mikhaylova, Y.; Shagin, D.; Alexandrova, I.; Ershova, O.; Akimkin, V.; Kozlov, R.; Edelstein, M. Antimicrobial Resistance and Genomic Characterization of OXA-48-and CTX-M-15-Co-Producing Hypervirulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae St23 Recovered from Nosocomial Outbreak. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, F.; Qarasnji, B.K.; Abdullah Tawgozy, F.H.; Amin, B.K. Molecular Study of SHV-11 and SHV-12 Genes among Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolated from UTI Patients in Erbil City. Zanco J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2016, 28, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, A.; Dhara, L.; Tripathi, A. Contribution of AcrB Upregulation & OmpC/Ompk36 Loss over the Presence of BlaNDM towards Carbapenem Resistance Development among Pathogenic Escherichia Coli & Klebsiella Spp. Indian J. Med. Res. 2019, 149, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennequin, C.; Robin, F. Correlation between Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence in Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Bacteria: An International Expert Proposal for Interim Standard Definitions for Acquired Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diancourt, L.; Passet, V.; Verhoef, J.; Grimont, P.A.D.; Brisse, S. Multilocus Sequence Typing of Klebsiella Pneumoniae Nosocomial Isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4178–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisse, S.; Fevre, C.; Passet, V.; Issenhuth-Jeanjean, S.; Tournebize, R.; Diancourt, L.; Grimont, P. Virulent Clones of Klebsiella Pneumoniae: Identification and Evolutionary Scenario Based on Genomic and Phenotypic Characterization. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.T.; Lai, S.Y.; Yi, W.C.; Hsueh, P.R.; Liu, K.L.; Chang, S.C. Klebsiella Pneumoniae Genotype K1: An Emerging Pathogen That Causes Septic Ocular or Central Nervous System Complications from Pyogenic Liver Abscess. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisse, S.; Passet, V.; Haugaard, A.B.; Babosan, A.; Kassis-Chikhani, N.; Struve, C.; Decre, D. Wzi Gene Sequencing, a Rapid Method for Determination of Capsulartype for Klebsiella Strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 4073–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikandi, J.; Millán, R.S.; Rementeria, A.; Garaizar, J. In Silico Analysis of Complete Bacterial Genomes: PCR, AFLP-PCR and Endonuclease Restriction. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 798–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, A.É.I.; Stuchi, L.P.; Siqueira, N.M.G.; Henrique, J.B.; Vicentini, R.; Ribeiro, M.L.; Darrieux, M.; Ferraz, L.F.C. Selection and Validation of Reference Genes for Gene Expression Studies in Klebsiella Pneumoniae Using Reverse Transcription Quantitative Real-Time PCR. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).