Abstract
The magnetic properties of nanocrystalline MxFe3−xO4 ferrites with M=Fe, Co, and Zn were investigated. The data support a core–shell model, where the core is ferrimagnetically ordered, and the shell shows a spin glass type behavior. The reduced magnetizations of spin glass components follow an mg = (1 – b/H−1/2) field dependence. The b values are strongly correlated with the intensities of exchange interactions. The field dependences of the magnetoresistances of Fe3O4 and ZnxFe3−xO4 nanoparticles pellets, experimentally determined, are well described if instead of the core reduced magnetization, commonly used, that of the shell is taken into account. For similar compositions of the nanoparticles, identical b values are obtained both from magnetization isotherms and magnetoresistances studies. The half-metallic behavior of spinel Fe3O4 based nanoparticles is discussed comparatively with those of double perovskites.
1. Introduction
Ferrite nanoparticles with a spinel-type structure have garnered a great deal of attention due to their basic properties and applications in various fields such as medicine [1], adsorption potential to abate heavy metals and dyes from aqueous solutions [2], catalytic properties [3], magnetoresistive devices [4], etc. The Fe3O4 based nanoparticles with spinel-type structure can be described as core–shell systems, where the structure and magnetic properties of the shell are different from that of the core [5].
The bulk magnetite (Fe3+)A[Fe3+Fe2+]B, at ambient temperature, has a cubic inverse spinel-type structure. In this lattice, the O2− anions form an fcc type lattice, the Fe3+ ions being located in tetrahedral interstices (A) and the Fe3+ and Fe2+ in the octahedral interstices (B). The nature of spinel structures, such as normal, inverse, or mixed in substitutional ferrites Fe3−xMxO4 with M=Co or Zn, relies on lattice occupancy by these ions. The Zn2+ ions are mainly located in tetrahedral sites [6,7]. The cobalt ferrites exist as partially inverse spinel structures in which both A and B sites contain a fraction of Co2+ ions, the largest being located at B sites [5,8].
Upon cooling, bulk Fe3O4 displays a sharp Verwey transition at the temperature TV = 122 K, characterized by a structural transition from a cubic to monoclinic lattice together with an abrupt drop in the electrical conductivity, associated with a “freezing out” of the electron hopping between the Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in B sublattice, which is the primary conduction mechanism at temperatures T > TV [9].
The surface structure of magnetite differs from that of bulk material. A large number of studies were performed in order to analyze the Fe3O4 surfaces. There are two possible truncations [10]. At the Fe3O4 (111) surface, three distinct terminations are observed, exposing either a close-packed oxygen plane, FeA, or FeB atoms [11]. The stable Fe3O4 (111) termination might have oxygen [12,13] or contain a fraction of iron and oxygen monolayers exposed over a closely packed oxygen layer [14,15]. In the case of Fe3O4 (100), surface terminations with ordered oxygen vacancies or Fe adatoms were proposed [16]. The surface structures are dependent on the sample’s preparation conditions, and thus multiple terminations can exist concurrently [13]. The oxygen termination has been shown to be inert toward adsorbate, whereas cation terminations introduce reactivity [17,18].
Magnetite is ferrimagnetically ordered with magnetic moments of FeA and FeB sites antiparallel oriented. In bulk Fe3O4, there are four easy magnetization [111] axes above the Verwey temperature TV. For Fe3O4 [111] surfaces, one of the axes is perpendicular to the [111] surface, and the other three make an angle of with respect to the surface’s normal direction [19].
The surface structures in nanocrystalline ferrites influence their magnetic properties because of symmetry breaking. The magnetic properties of bulk samples are little influenced by surface effects, the surface volume being only a very small fraction of the sample. In nanocrystalline samples, the surface volume represents a large fraction of that of the nanoparticles. The reduction of saturation magnetization as compared to bulk values is a common experimental observation in magnetite nanoparticles [20]. In early models, this behavior was attributed to the presence of a dead magnetic layer at the surface [21]. A random canting of the surface spins caused by competing antiferromagnetic interactions between sublattices was proposed [22] and experimentally observed in maghemites [23,24,25]. A spin glass type behavior was also shown in the whole volume of nanoparticles [26,27]. A model of a magnetically ordered core surrounded by a surface layer of canted spins has been also proposed [28,29]. The reduction of TC of nanoparticles with respect to the bulk one was also attributed to symmetry breaking of the surface and consequently to a lower density of magnetic bonds [30]. The noncollinear spin structure, which originated from the pinning of the surface spins and coated surfactant at the interface of iron oxide results in the reduction of magnetic moments in nanoparticles [31].
Surfactant organic molecules, such as oleic acid, can restore the magnetism in Fe3O4 nanoparticle surfaces [32]. Of the four Fe ions at the surface unit cell, two bond to the organic acid, whereas the other two remain unbonded. The Fe ions bonded to the organic acid oxygens have six O nearest neighbors as in the bulk, while the remaining iron ions are similar to the bare surface. The overall effect is that capped surface magnetization density is intermediate between that of bulk and the magnetic layer surface of the bare nanoparticle. The formation of the half-metallic surface state for pyridine/H/Fe3O4 nanoparticles can also be understood on the basis of the interface chemical bonding formed by the coordination of the nitrogen end of pyridine to the surface of Fe atoms [33].
In nanocrystalline Fe3O4, the spin canting effect can be induced by: (1) the symmetry breaking by the broken exchange bonds at the surface layer; (2) competition between the ferromagnetic interactions inside the magnetic sublattices and antiferromagnetic between them; (3) the cations distribution in tetrahedral and octahedral sites; (4) the surface anisotropy which depends on the iron site occupation.
In this paper, we analyze the magnetic behavior of some nanocrystalline iron-based ferrites by extending our previous studies [5,7,34]. The presence of spin-glass behavior superposed on essentially ferrimagnetic-type ordering was shown and analyzed in correlation with the exchange interactions between the two sublattices. The field dependences of the magnetoresistances are well described when using instead of core reduced magnetization that of nanoparticles shell, of spin-glass type, highlighting their importance in magnetotransport properties. These properties of spinelic ferrites are analyzed comparatively with those of double perovskites.
2. Materials and Methods
The nanocrystalline ferrites from series Fe3O4, CoFe2O4, and ZnxFe3−xO4 were prepared using a typical hydrothermal method, as already described [5,7,34]. The morphology of the nanoparticles has been investigated by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) using Hitachi HD2700 equipment. The compositions of the nanoparticles were determined by the EDS method and by chemical analyses. The elemental analyses by the ICP-OES method yielded, for ZnxFe3−xO4 nanoparticles, values of x = 0.12(3) and 0.18(3), respectively, in rather good agreement with EDS measurements. The crystal structure and mean crystallite sizes were determined by XRD measurements, performed at ambient temperature with a Bruker DS Advance diffractometer. The mean crystallite sizes were estimated by Rietveld refinement of the XRD patterns using FullProf Suite software. The investigated nanocrystalline ferrites crystallize in a cubic type spinel structure with lattice parameters given in Table 1. No other phases were present in their XRD patterns. The nanocrystallite sizes were determined by the analysis of their histograms as given in Figure 1 for Fe3O4 and Zn0.12Fe2.88O4 samples. The mean nanocrystalline sizes are in closer agreement with those estimated from X-ray measurements. The data for CoFe2O4 nanoparticles were already reported [5]. The determined lattice parameters and mean nanograins sizes are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Lattice parameters and nanocrystallite sizes.
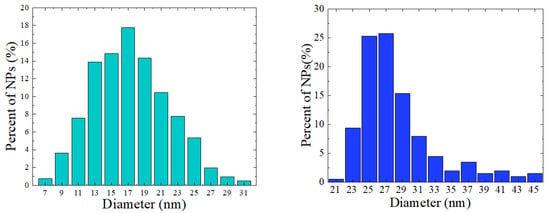
Figure 1.
The size distributions for: Fe3O4 (left) and Zn0.12Fe2.88O4 (right) nanoparticles.
Magnetic measurements were made at T = 4.2 K and 300 K in external fields up to 12 T using a vibrating sample magnetometer from Cryogenic Limited (London). In order to obtain accurate values of the magnetizations, at T = 4.2 K, attention has been given to stabilizing the external field.
3. Results
The magnetization isotherms at T = 4.2 K for selected Fe3O4 and Fe3−xMxO4 with M=Co and Zn nanoparticles are given in Figure 2 (inset). Their saturation magnetizations are somewhat lower than those of the bulk samples having the same compositions [35,36]. This trend was attributed to the small particle size effect, where noncollinear spin arrangements occur primarily at or near the surface. Close related data were obtained in the Fe3−xZnxO4 nanoparticles system [7,37,38,39].
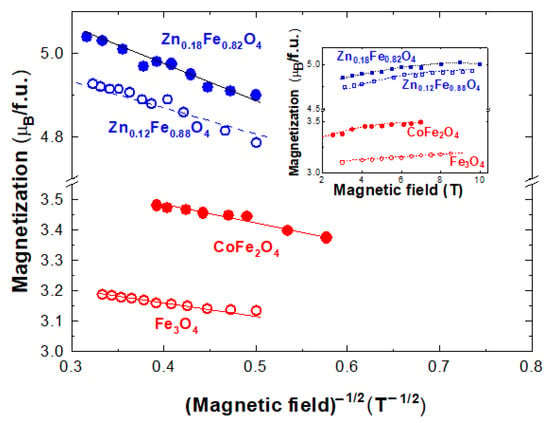
Figure 2.
Field dependences of magnetizations at T = 4.2 K in Fe3O4, CoFe2O4 and ZnxFe3−xO4 with x = 0.12 and 0.18 ferrites. In the inset are the respective magnetization curves.
The field dependences of magnetization for a spin glass system are determined by the anisotropy as well as on the exchange field, Hex, acting on magnetic ions, as also evidenced in amorphous systems [40]. When the anisotropy is weak (ferromagnet with wondering axes), the approach to saturation when the external field, H, is smaller than the exchange field, Hex, can be described by a 1/H−1/2 law, while for H > Hex follows a 1/H2 trend as for systems having high anisotropy. Consequently, both the anisotropy and exchange fields in the investigated systems were estimated in order to correlate with model prediction.
The estimated anisotropy constants are rather low in the order of (1–4)104 J/m3. The exchange fields, Hex in the studied systems were estimated from the exchange interaction parameters JAB between the two sublattices, in the mean-field approximation:
where S is the spin value, zi the number of magnetic nearest neighbors, g the spectroscopic splitting factor, and µB the Bohr magneton.
The exchange interactions JAB, between the two magnetic sublattices determined by neutron diffraction are JAB = −2.02 meV for Fe3O4 and −1.95 meV for CoFe2O4 [41]. The exchange interactions between iron ions in tetrahedral and octahedral sites, respectively, in ZnxFe3−xO4 were estimated starting from magnetic measurements [7,41,42] Values JAB = 1.64 meV for x = 0.18 and 1.76 meV when x = 0.12 were obtained.
The ZnxFe3−xO4 system has very interesting magnetic properties. The ferrimagnetic phase coexists with antiferromagnetic and spin disordered regions [43]. The above behavior can be correlated with the presence of iron ions having different local environments, where the number of non-magnetic Zn ions predominates. Consequently, the exchange interactions between iron ions are rather low, and the spin disorder disappears even in the presence of a low magnetic field. When iron is substituted by a small fraction of Zn ions, as in the ZnxFe3−xO4 series with x ≤ 0.18, the exchange interactions both inside and between magnetic sublattices are rather strong and the samples remain ferrimagnetically ordered. The magnetic coupling between octahedral and tetrahedral sublattices decreases only by ≅19% when x = 0.18 as compared to that in pure Fe3O4.
The location of Zn ions in the ZnxFe8-xO4 nanoparticles systems was determined from magnetic measurements, the extrapolated moment at T = 4.2 K, and H→∞, respectively. In this state, the iron magnetic moments are oriented along the same axis in the framework of ferrimagnetic ordering. The highest magnetization for x < 0.3 is obtained when Zn2+ ions are distributed in tetrahedral sites. The expected magnetic moments for this location are 4.72 µB/f.u. when x = 0.12 and 5.08 µB/f.u. for x = 0.18, respectively. The experimentally determined saturation moments are ≅5% higher than the above values suggesting that Zn ions occupy the tetrahedral sites. The observed differences can be correlated with the sample’s compositions situated within the low limit of experimental errors.
Taking into account the distributions of constituent ions in tetrahedral and octahedral sites [5,7,34], the exchange fields, Hex, acting on octahedral and tetrahedral sites, were estimated in the mean-field approximation, according to relation (1). In the spinel structure, as Fe3O4, each tetrahedral Fe3+ ion is surrounded by 12 octahedral ions, while an octahedral Fe3+ has 6 tetrahedral nearest neighbors. According to the distributions of ions in [Co2+0.838Fe3+1.162](Co2+0.162 Fe3+0.838)O4, a tetrahedral Fe3+ ion, has as neighbors 4 Fe and 2 Co octahedral ions and an octahedral Fe3+ has 7 Co and 5 Fe tetrahedral ions, respectively [4]. In [Fe3+1.12 Fe2+0.88](Fe3+0.88Zn2+0.12)O4 in tetrahedral sites are located in mean 5 Fe3+ and 1 Zn2+ ions. On this basis, the exchange fields acting on iron in octahedral and tetrahedral sites were estimated. As for example in CoFe2O4, these values were estimated at Hex(oct) = 110 T and Hex(tetra) = 55 T, respectively. Somewhat smaller values of 90 T and 38 T were obtained in Zn0.12Fe2.88O4 ferrite. Although these values characterize the bulk samples, they give a rather good approximation in the case of nanocrystalline systems. The exchange field acting on magnetic ions in octahedral sites is higher than in tetrahedral ones, and both are higher than the external field used for measurements. Consequently, a field dependence of H−1/2 is suggested. In addition, at the nanograin surface, different spin canting for octahedral and tetrahedral ions is expected, in addition to the effect of broken bonds.
The magnetic properties of these nanoparticles can be described as a superposition of a spin glass contribution on mainly ferrimagnetic type ordering. Spin glasses are a highly complex magnetic state intrinsically linked to spin frustration and structural disorder. For external fields greater than 3–4 T, when the core particle magnetization is saturated, the magnetization isotherms follow a field dependence described by the relation:
as predicted by the model [40] in Figure 1. The determined b parameters, at T = 4.2 K, describe the approach to saturation behavior of the spin-glass component. These values increase in the sequence b = 0.108 T−1/2 for magnetite, 0.127 T−1/2, for cobalt ferrite, while for ZnxFe3−xO4, b = 0.155 T−1/2 for x = 0.12 and 0.174 T−1/2 when x = 0.18. The b values, determined at higher temperatures, are a little smaller than those obtained at T = 4.2 K, a behavior attributed to thermal effects. A linear dependence of b parameters on the JAB values is shown in Figure 3. These data suggest that the approach to saturation of spin glass components (parallel alignment of the spins) is more difficult as the exchange interactions between the two sublattices increase. It is to be noted that in CoFe2O4 nanoparticles, there is a change of spin-glass behavior in fields higher than 8–9 T, correlated with the presence of magnetic Co ions [5]. The extrapolation of magnetization at T = 4.2 K according to 1/H−1/2 law, to infinite fields is expected to characterize the situation when the moments at both core and shell are oriented along the same axis and are ferrimagnetically ordered.
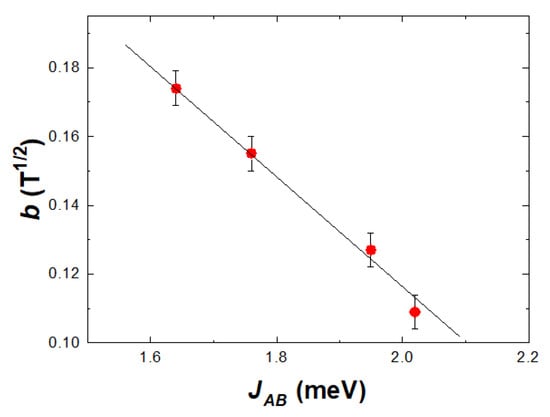
Figure 3.
The b parameter as a function of exchange interactions between magnetic sublattices.
Assuming core–shell sphere type nanoparticles, the relative volume corresponding to a shell having the width of one lattice parameter is dependent on the nanograins diameter, being 15% for the Zn0.12Fe2.88O4 and 27–31% for Fe3O4, CoFe2O4, and Zn0.18Fe2.82O4 nanoparticles. The spin-glass contribution to the magnetization was estimated as the difference between magnetizations obtained by extrapolation of H−1/2 dependence at infinite field and saturation magnetizations by using the classical approach to saturation law. These are between 7% and 9% of the total magnetizations. This suggests that not all the magnetic ions from one atomic unit cell are involved in the spin-glass type magnetism. This is in agreement with the result of Fe3O4 interface studies, where only a fraction of magnetic ions from the unit cell have surface terminations and breaking bonds [14,15] and thus spin-glass type magnetism.
The bulk spin-resolved band structure of Fe3O4 predicts that the majority spin population is insulating in character and the minority carriers possess a metallic character, with states derived predominantly from the Fe3d bands of octahedral sublattice, present at the Fermi level [44,45]. Due to their half-metallic properties and high Curie temperature, these ferrites are of interest for spintronic applications [33,46]. Magnetite was assumed to be a candidate for building sensors based on the intergrain tunneling magnetoresistance (ITMR) at ambient temperature. As already discussed, the Fe3O4 core–shell nanoparticles have a core material with high spin polarization and a shell that has a spin glass oxygen termination, which can act as an insulator.
There are a large number of studies concerning the analysis of the magnetoresistances (MR) of the Fe3O4 nanoparticles pressed into pellets on the external field, temperature, grain sizes, or their shape [47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54]. Magnetoelectronic devices composed of ordered three-dimensional arrays of magnetite nanoparticles on the SiO2 isolation layer [51] as well as of the SiO2 coated Fe3O4 nanospheres were investigated [55,56]. The magnetoresistances of Fe3O4-CoFe2O4 core–shell nanoparticles [57] were also studied.
The magnetoresistances in Fe3O4 were investigated above the Verwey temperature. The MR was shown to be of tunneling type [4,50,52,54,58]. The field dependences of the magnetoresistance Δρ/ρ were also analyzed [55,59] starting from the relation [60]:
where P is the polarization and m is the reduced bulk (core) magnetization.
The above relation does not describe well the field dependence of magnetoresistances. The Ziese model [60] was used in order to analyze the spin polarization in Fe3O4 nanorods [53]. A difference in the saturation fields of sample magnetization and magnetoresistance was also shown [51].
The ITMR in polycrystalline magnetic materials is determined by the magnetic state in the vicinity of the grain boundary (GB) [50,61,62,63]. Thus, in relation (3), the reduced bulk magnetization m(H) must be replaced by that at the grain boundary mg(H), as given by the relation (1). The study of Fe3O4 nanograins magnetoresistance in high external fields also evidenced a contribution due to spin disorder, which is linear in the field [61]. Taking the above into account, the relation (3) used to analyze in order to analyze the experimental data has the form [62,63]:
By fitting experimental data, (for fields higher than 0.1 T (where MR were estimated with accuracy) [33,38,46,50,51,54,58], with the relation (4), the P, b, and c values were obtained, see Table 1. The curves thus obtained describe the experimental results nicely as can be seen, for example, in Figure 4 in the case of ZnxFe3−xO4 nanoparticle pellets with x = 0 and x = 0.2. The b parameters are near the same as those determined from magnetic measurements according to relation (1). This fact stresses that really surface magnetization is involved in the ITMR process. The magnetoresistance in Fe3O4 pellets was shown to be rather low, behavior attributed to the damaged surface [46]. The negative polarization of the Fermi edge region (−30% to −40%) suggests that surface imperfections reduce the overall polarization by approximately 60% in Fe3O4 (001) thin films [64].
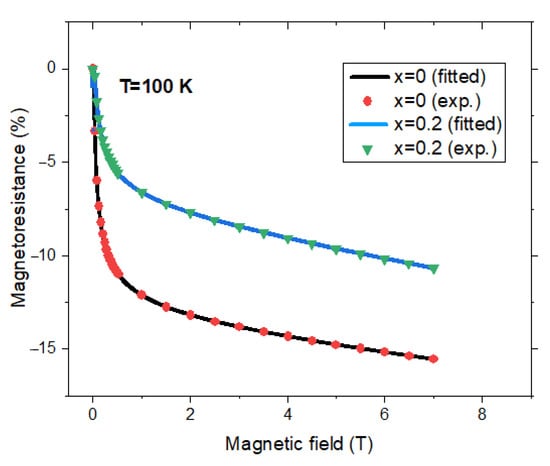
Figure 4.
Field dependences of magnetoresistances for ZnxFe3−xO4 nanocrystalline pellets with x = 0 and 0.2. Experimental data [38] and fitted curves according to relation (4) with parameters listed in Table 2.
The c parameters are of the order of 10−3 T−1 and very close to those determined in double perovskites [61,62]-Table 2. The polarization of the nanocrystalline pellets increases with decreasing temperature.

Table 2.
Data obtained from magnetoresistance measurements.
Higher tunneling magnetoresistance has been generally observed in the surface-functionalized Fe3O4 [33,46,51,52,58]. The tunneling magnetoresistances increase as the surface is restored, as shown in oleic-acid coated [33,52,65,66], polystyrene coated [58], and pyridine coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles [67]. As in the case of bare ferrites, the magnetoresistances are well described by the relation (4) with the parameters P, b, and c, listed in Table 2. The determined polarization is higher than in bare nanocrystalline pellets. The b parameters describing the field dependences of the surface magnetizations are the same as those determined in bare nanoparticles or obtained from magnetic measurements. The c parameter, taking into account the spin disorder inside the grains, is generally higher than in the case of non-functionalized samples and depends on the applied pressure for obtaining pellets. The polarization also depends on measuring temperature. The spin polarization, P, determined in Fe3O4 based nanoparticles above the Vervey temperature, is somewhat lower than in double perovskites.
The coating material at the nanograin surface contributes additionally to the linear field dependence of magnetoresistivity. Probably, it is the result of the interface chemical bonding formed by the coordination of some elements (nitrogen, oxygen) of coating materials with the Fe ions at the surface, as already mentioned. Table 2 also gives the results of the analysis of magnetoresistance in some half-metallic double perovskites. The previous studies on both ball-milled Fe3O4 [50] as well as microcrystalline Sr-based double perovskites having dimensions around 1 µm [59,62,63] show that the field dependence of magnetization in describing ITMR must be that characteristic in the region close to grain boundary and not the bulk magnetization.
The spin-glass state, due to surface effects in double perovskites having weak anisotropy, is well described by 1/H−1/2 law [61,62]. Values b = 0.13 for Sr2FeMoO6 and b = 0.16 for Sr2FeMo0.7W0.3O6 were determined. The behavior of Fe3O4 magnetoresistances-based nanoparticle pellets is similar to that of double perovskites.
4. Conclusions
The magnetic properties of Fe3O4 - based nanoparticles are well described in a core–shell model, where the core is ferrimagnetically ordered, and the shell shows a spin glass type behavior. The spin-glass state is due to a fraction of magnetic ions located in the shell having one lattice parameter width and connected with the symmetry breaking of the surface structure. The reduced magnetization of the spin-glass component follows a field dependence mg = (1 − b/H−1/2), where the b parameters decrease linearly as the exchange interactions between the two sublattices increase.
The field dependences of Fe3O4-based nanoparticles magnetoresistances, experimentally determined, are well described if instead of the reduced magnetization of core, commonly used, that of the shell, of spin glass type is considered. Identical trends for the approach to saturation of reduced magnetizations as described by the b parameter are shown, both starting from magnetic measurements and magnetoresistances studies. Thus, for Fe3O4 nanoparticles, a value b ≅ 0.108 T−1/2 was obtained from magnetic measurements, while for magnetoresistances of the corresponding pellets, these are in the range b = (0.10–0.12)T−1/2. In case of Zn0.18Fe2.82O4 nanoparticles, the determined b = 0.174 T−1/2 from magnetization isotherm at T = 4 K is nearly the same as obtained from the analysis of field dependence of magnetoresistances in Zn0.2Fe2.80O4 nanoparticles pellets.
The magnetoresistances of Fe3O4—based nano-particles pellets are similar to those of A2FeMoO6 (A = Sr, Ba) double perovskites having grain sizes of ≅ 1 µm. The spin polarization, P, determined in Fe3O4 based nanoparticles above the Vervey temperature, are somewhat lower than in double perovskites. The crystal sizes and shell surfaces are different, influencing the polarization degree.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.B.; investigation, E.B. and R.T. resources, E.B. and R.T.; formal analysis, R.T. and E.B.; writing—original draft preparation, E.B.; writing—review and editing, E.B. and R.T.; supervision, E.B.; project administration, E.B. and R.T. funding acquisition, E.B. and R.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Romanian National Authority for Scientific Research, CNCSIS-UEFISCDI, through the exploratory research project No. PN-III-P4-ID-PCCF-2016-0112.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Du, H.; Udochukwu, O.; Yao, C.; Yang, F. Transition metal ion-doped ferrites for bioimanging and cancer therapy. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 15, 101264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javalakshmi, R.; Jeyanthi, J.; Aswin Sidhaarth, K.R. Versatile application of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for the removal of heavy metals and dyes from aqueous solution. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 12, 100659. [Google Scholar]
- Miri, A.; Sarani, M.; Najafidoust, A.; Mehrabani, M.; Zadech, F.A.; Varma, R.S. Photocatalytic performance and cytotoxic activity of green-synthesized ferrite nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 2022, 149, 111706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.A.; Ray, S.; Chakraverty, S.; Sarma, D.D.; Anil Kumar, P. Magnetoresistance and Electroresistance Effects in Fe3O4 Nanoparticle System. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2014, 9, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortnic, R.; Szatmari, A.; Souca, G.; Hirian, R.; Dudric, R.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Toma, V.; Tetean, R.; Burzo, E. New Insights into the Magnetic Properties of CoFe2O4@SiO2@Au Magnetoplasmonic Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, G.; Johri, U.C. A Study on Structural and Magnetic Properties of Ni-Substituted Magnetite Nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 577, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souca, G.; Dudric, R.; Iacovita, C.; Moldovan, A.; Frentiu, T.; Stiufiuc, R.; Lucaciu, C.M.; Tetean, R.; Burzo, E. Physical Properties of Zn Doped Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2020, 22, 298–302. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, K.S.; Choudary, G.S.V.R.K.; Rao, K.H.; Sujatha, C. Structural and Magnetic Properties of Ultrafine CoFe2O Nanoparticles. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2015, 10, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwey, E. Electronic Conduction of Magnetite (Fe3O4) and Its Transition Point at Low Temperatures. Nature 1939, 144, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentcheva, R.; Moritz, W.; Rundgren, J.; Frank, S.; Schrupp, D.; Scheffler, M. A Combined DFT/LEED-Approach for Complex Oxide Surface Structure Determination: Fe3O4 (001). Surf. Sci. 2008, 602, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.K.; Jung, J.; Kato, H.S.; Kim, Y.; Kawai, M. Termination and Verwey Transition of the (111) Surface of Magnetite Studied by Scanning Tunneling Microscopy and First-Principles Calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 235429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limot, L.; Kröger, J.; Berndt, R.; Garcia-Lekue, A.; Hofer, W.A. Atom Transfer and Single-Adatom Contacts. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 126102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berdunov, N.; Murphy, S.; Mariotto, G.; Shvets, I.V. Room Temperature Study of a Strain-Induced Electronic Superstructure on a Magnetite (111) Surface. Phys. Rev. B-Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2004, 70, 085404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner Weiss, W.R. Surface Chemistry and Catalysis on Well-Defined Epitaxial Iron-Oxide Layers. Prog. Surf. Sci. 2002, 70, 1–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennie, A.R.; Condon, N.G.; Leibsle, F.M.; Murray, P.W.; Thornton, G.; Vaughan, D.J. Structures of Fe3O4 (111) Surfaces Observed by Scanning Tunneling Microscopy. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 53, 10244–10253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentcheva, R.; Wendler, F.; Meyerheim, H.L.; Moritz, W.; Jedrecy, N.; Scheffler, M. Jahn-Teller Stabilization of a “Polar” Metal Oxide Surface: Fe3O4 (001). Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 126101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, K.T.; Mu, T.; Fitts, J.P.; Adib, K.; Nicholas, l.; Iii, C.; Osgood, R.M.; Batista, E.R.; Friesner, R.A.; Joyce, S.A.; et al. Scanning Tunneling Microscopy and Theoretical Study of Competitive Reactions in the Dissociative Chemisorption of CCl4 on Iron Oxide Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 16753–16760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotny, Z.; Mulakaluri, N.; Edes, Z.; Schmid, M.; Pentcheva, R.; Diebold, U.; Parkinson, G.S. Probing the Surface Phase Diagram of Fe3O4 (001) towards the Fe-Rich Limit: Evidence for Progressive Reduction of the Surface. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 195410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakawa, K.; Kawauchi, T.; Zhang, X.; Katsuyuki Fukutani, F. Non-Collinear Magnetic Structure on the Fe3O4 (111) Surface. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2017, 86, 074601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, X.; Labarta, A. Finite-Size Effects in Fine Particles: Magnetic and Transport Properties. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2002, 35, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkowitz, A.E.; Schuele, W.J.; Flanders, P.J. Influence of Crystallite Size on the Magnetic Properties of Acicular γ-Fe2O3 Particles. J. Appl. Phys. 1968, 39, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D. Noncollinear Spin Arrangement in Ultrafine Ferrimagnetic Crystallites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1971, 27, 1140–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, A.; Watanabe, K.; Kiyama, M.; Shinjo, T.; Bando, Y.; Toshio Takada, T. Surface Magnetic Properties of γ-Fe2O3 by 57Fe Mössbauer Emission Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1981, 50, 2777–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millan, A.; Urtizberea, U.; Silva, N.J.O.; Palacio, F.; Amaral, V.S.; Snoeck, E.; Serin, V. Surface Effects in Maghermitr Nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 312, L5–L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneda, K.; Morrish, A.H. Cation Distributions in Octahedral and Tetrahedral Sites of the Ferrimagnetic Spinel CoFe2O4. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 63, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, F.T.; Foster, M.W.; Margulies, D.T.; Berkowitz, A.E. Spin Canting, Surface Magnetization, and Finite-Size Effects in γ-Fe2O3 Particles. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 47, 7885–7891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.P.; Serna, C.J.; Bødker, F.; Mørup, S. Spin Canting Due to Structural Disorder in Maghemite. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1997, 9, 5461–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, B.; Obradors, X.; Balcells, L.; Rouanet, A.; Monty, C. Low Temperature Surface Spin-Glass Transition in γ-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köseoglu, Y.; Kavas, H. Size and Surface Effects on Magnetic Properties of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazo-Zuluaga, J.; Restrepo, J.; Mejía-López, J. Surface Anisotropy of a Fe3O4 Nanoparticle: A Simulation Approach. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2007, 398, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, R.H.; Berkowitz, A.E.; McNiff, E.J., Jr.; Foner, S. Surface Spin Disorder in NiFe2O4 Nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salafranca, J.; Gazquez, J.; Pérezpérez, N.; Labarta, A.; Pantelides, S.T.; Pennycook, S.J.; Batlle, X.; Varela, M. Surfactant Organic Molecules Restore Magnetism in Metal-Oxide Nanoparticle Surfaces. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yue, F.J.; Wu, D. Enhanced Magnetoresistance in Self-Assembled Monolayer of Oleic Acid Molecules on Nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 12507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudric, R.; Souca, G.; Szatmári, Á.; Szilárd, T.; Nitica, S.; Iacovita, C.; Moldovan, A.I.; Stiufiuc, R.; Tetean, R.; Burzo, E. Magnetite Nanoparticles for Medical Applications. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2218, 030014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhbou, M.; Džubinská, A.; Reiffers, M.; Bessais, L.; Lemziouka, H.; Lassri, M.; Tuyikeze, V.; Fraija, F.; Sajeddine, M.; Lassri, H. Magnetic, Structural and Magnetocaloric Effect Investigations on the Substituted Spinel Mg1−xZnxFe2O4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) Prepared by Sol-Gel Method. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 896, 162836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Han, B.; Hu, X.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X.; Deng, X. Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles and Their Magnetic Properties. Procedia Eng. 2012, 27, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsikau, D.; Pankov, V.; Petrova, E.; Natarov, V.; Filimonov, D.; Pokholok, K. Structural, Magnetic and Hyperfine Characterization of ZnxFe3–XO4 Nanoparticles Prepared by Sol-Gel Approach via Inorganic Precursors. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 114, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.L.; Lv, L.Y.; Zhu, J.M.; Li, S.D.; Liu, X.C.; Zou, W.Q.; Zhang, F.M.; Du, Y.W. Magnetic and Transport Property Studies of Nanocrystalline ZnxFe3–XO4. Solid State Commun. 2006, 137, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alae, M.; Kerroum, A.; Iacovita, C.; Baaziz, W.; Ihiawakrim, D.; Rogez, G.; Benaissa, M.; Lucaciu, C.M.; Ersen, O. Quantitative Analysis of the Specific Absorption Rate Dependence on the Magnetic Field Strength in ZnxFe3–XO4 Nanoparticles. Internat. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7775. [Google Scholar]
- Tejada, J.; Martinez, B.; Labarta, A.; Chudnovsky, E.M. Correlated Spin Glass Generated by Structural Disorder in the Amorphous Dy6Fe74B20 Alloy. Phys. Rev. B 1991, 44, 7698–7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, C.M.; Srinivasan, G.; Nanadikar, N.G. Exchange Constants in Spinel Ferrites. Phys. Rev. B 1979, 19, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, Y. Exchange Interaction and Cubic Crystal Field Splitting Parameter of Fe3+ in Spinel Structure. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1960, 15, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobos, M.A.; Hernando, A.; Marco, J.F.; Puente-Orench, I.; Jimenez, J.A.; Llorente, I.; Garcia-Escorial, A.; de la Presa, P. Unveiling the hidden entropy in ZnFe2O4. Materials 2022, 15, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Satpathy, S. Electron States, Magnetism, and the Verwey Transition in Magnetite. Phys. Rev. B 1991, 44, 13319–13331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentcheva, R.; Pickett, W.E. Electronic Phenomena at Complex Oxide Interfaces: Insights from First Principles. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2010, 22, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.; Barick, B.; Mohapatra, J.; Sharma, H.; Meena, S.S.; Aslam, M. Large Tunneling Magnetoresistance in Octahedral Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 55007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, H.-W.; Wang, C.-S.; Wang, Y.-J.; Zhan, W.-S.; Li, F.-Y.; Jin, C.-Q.; Meng, F.-B.; Li, Y.-X. Magnetoresistance and Magnetic Properties of Fe3O4 Nanoparticle Compacts. Chin. Phys. 2002, 11, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Ban, D.; Liu, E.; Li, X.; Peng, H.; Yao, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Zhai, H. Effect of Substrate Temperature on Antiphase Boundaries and Spin Polarization of Thin Fe3O4 Film on Si (100). Thin Solid Film. 2020, 693, 137698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.Y.; Kuo, P.C.; Yao, Y.D.; Wu, T.H.; Chen, S.C.; Sun, A.C.; Huang, C.H.; Chen, J.W. Magnetoresistance and Microstructure of the Sintered Ferrite of the Mixture of Fe3O4 and Co-Ferrite Powder. Phys. Stat. Sol. 2004, 1, 3410–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrate, D.; De Teresa, J.M.; Algarabel, P.A.; Fernández-Pacheco, R.; Galibert, J.; Ibarra, M.R. Grain-boundary magnetoresistance up to 42 T in cold-pressed Fe3O4 nanopowders. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 084317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Black, C.T.; Sandstrom, R.L.; Rice, P.M.; Murray, C.B.; Sun, S. Magnetotransport of Magnetite Nanoparticle Arrays. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 020402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohiki, S.; Kinoshita, T.; Nara, K.; Akiyama-Hasegawa, K.; Mitome, M. Large, Negative Magnetoresistance in an Oleic Acid-Coated Fe3O4 Nanocrystal Self-Assembled Film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mitra, A.; Mohapatra, J.; Sharma, H.; Meena, S.S.; Aslam, M. Controlled Synthesis and Enhanced Tunnelling Magnetoresistance in Oriented Fe3O4 Nanorod Assemblies. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 085002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhao, L.; Klavins, P. Extrinsic Magnetoresistance in Magnetite Nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 7951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shi, J.; Tian, D.; Deng, H.; Li, Y.; Song, P.; Chen, C. Fabrication and enhanced magnetoresistance of SiO2-coated Fe3O4 nanosphere compact. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 213106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, K.M.; Sethupathi, K.; Rao, M.S.R. Extrinsic Magnetoresistance in Magnetite Nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 7951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.A.; Ray, S.; Chakraverty, S.; Sarma, D. Engineered spin-valve type magnetoresistance in Fe3O4-CoFe2O4 core-shell nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 102406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yu, M.; Batzill, M.; He, J.; Diebold, U.; Tang, J. Enhanced Tunneling Magnetoresistance and High-Spin Polarization at Room Temperature in a Polystyrene-Coated Fe3O4 Granular System. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 134412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, J.; Maekawa, S. Theory of Tunneling Magnetoresistance in Granular Magnetic Films. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 53, R11927–R11929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziese, M. Spin Hopping in a Discontinuous La0.7Ca0.3MnO3 Film. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrate, D.; De Teresa, J.M.; Algarabel, P.A.; Ibarra, M.R.; Galibert, J. Intergrain Magnetoresistance up to 50 T in the Half-Metallic (Ba0.8Sr0.2)2FeMoO6 Double Perovskite: Spin-Glass Behavior of the Grain Boundary. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 104409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burzo, E.; Balasz, I.; Valeanu, M.; Pop, I.G. The Effects of Thermal Treatment on the Physical Properties of Sr2FeMo1−xMxO6 Perovskite with M = W, Ta and x ≤ 0.3. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burzo, E. Magnetic and Transport Properties of Double Perovskites. Stud. UBB Chem. 2021, LXVI, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, S.A.; Waddill, G.D.; Kim, S.; Ivan, K.; Schuller, S.A.; Chambers, J.G.T. Spin-Resolved Photoelectron Spectroscopy of Fe3O4. Surf. Sci. 2002, 513, L451–L457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddar, P.; Fried, T.; Markovich, G. First-Order Metal-Insulator Transition and Spin-Polarized Tunneling in Fe3O4 Nanocrystals. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 172405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taub, N.; Tsukernik, A.; Markovich, G. Inter-Particle Spin-Polarized Tunneling in Arrays of Magnetite Nanocrystals. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 1933–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurahashi, M.; Sun, X. Observation of a Half-Metallic Interface State for Pyridine-Adsorbed H/Fe3O4 (100). J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 8489–8494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).