Abstract
To date, SARS-CoV-2 infectious disease, named COVID-19 by the World Health Organization (WHO) in February 2020, has caused millions of infections and hundreds of thousands of deaths. Despite the scientific community efforts, there are currently no approved therapies for treating this coronavirus infection. The process of new drug development is expensive and time-consuming, so that drug repurposing may be the ideal solution to fight the pandemic. In this paper, we selected the proteins encoded by SARS-CoV-2 and using homology modeling we identified the high-quality model of proteins. A structure-based pharmacophore modeling study was performed to identify the pharmacophore features for each target. The pharmacophore models were then used to perform a virtual screening against the DrugBank library (investigational, approved and experimental drugs). Potential inhibitors were identified for each target using XP docking and induced fit docking. MM-GBSA was also performed to better prioritize potential inhibitors. This study will provide new important comprehension of the crucial binding hot spots usable for further studies on COVID-19. Our results can be used to guide supervised virtual screening of large commercially available libraries.
Keywords:
COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; computational chemistry; structure-based; pharmacophore; docking; MM-GBSA 1. Introduction
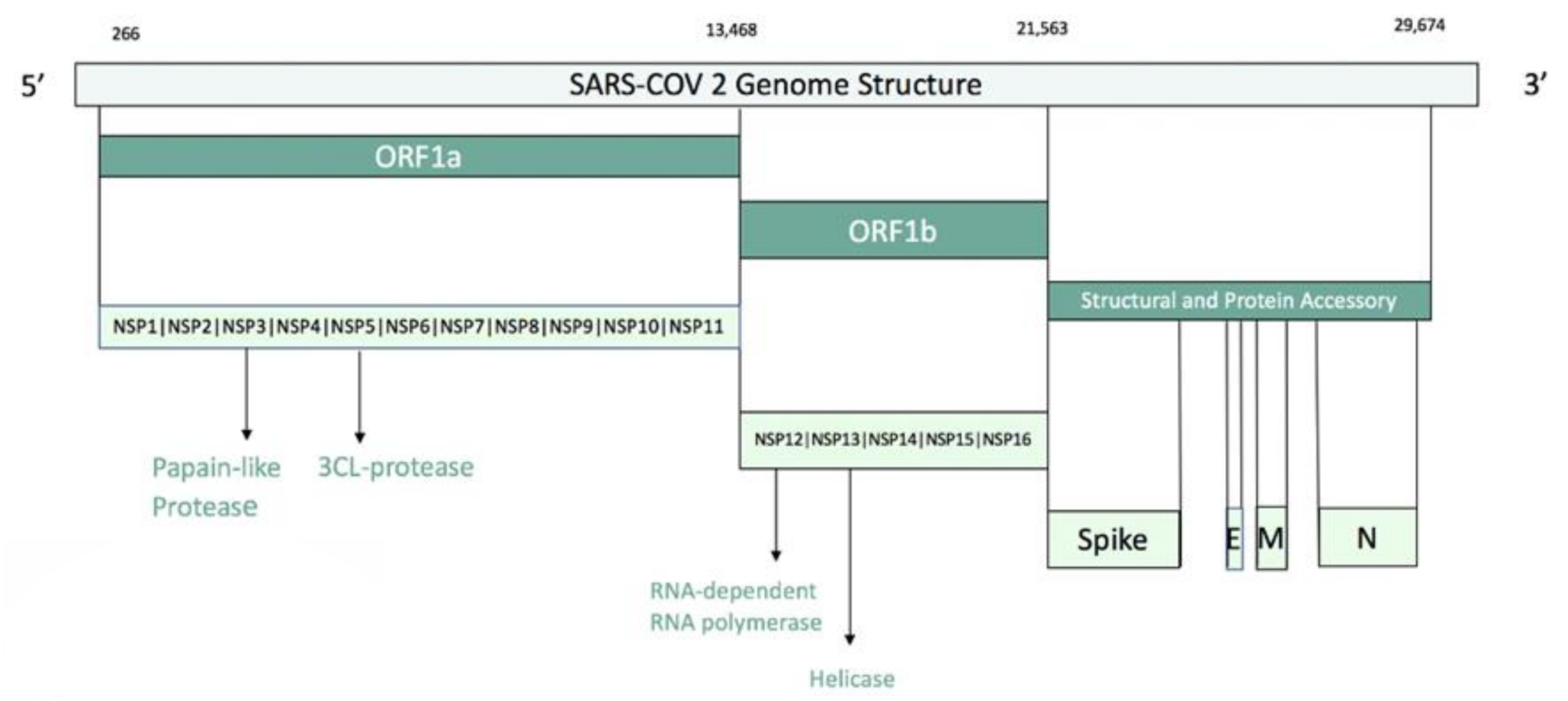
Coronaviruses (CoVs) are one of the major pathogens that primarily targets the human respiratory system which caused previous outbreaks such as the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-CoV and the Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)-CoV. The novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 has become a pandemic threat (COVID-19) to public health. It is a respiratory diseasecausing fever, fatigue, dry cough, muscle aches, shortness of breath and some instances lead to pneumonia [1]. The SARS-CoV-2 genome comprises 29,903 nucleotides, with 10 Open Reading Frames (ORFs). The 3′ terminal regions encode structural viral proteins: whereas the 5′ terminal ORF1ab encodes two viral replicasepolyproteins pp1a and pp1b. The proteolytic cleavage of pp1a and pp1b produces 16 nonstructural proteins (nsp1 to nsp16). Among these, there are nsp3, the papain-like protease (PLpro) and nsp5, the 3-chymotrypsin-like protease (3CLpro, also known as the main proteaseMpro). The viral polyprotein processing is essential for maturation and infectivity of the virus (Figure 1) [2]. Because of the crucial roles, these two proteases are important targets for antiviral drug design. Moreover, the virus encoded for other proteins that could be potential targets of antiviral drugs. The mature proteins of SARS-CoV-2 are: host translation inhibitor nsp1 (nsp1); nonstructural protein 2 (nsp2); papain-like proteinase (PLpro); nonstructural protein 4 (nsp4); 3C-like proteinase (3CLpro), nonstructural protein 6 (nsp6), nonstructural protein 7 (nsp7), nonstructural protein 8 (nsp8), nonstructural protein 9 (nsp9), nonstructural protein 10 (nsp10), RNA-directed RNA polymerase (Pol/RdRp), helicase (Hel), guanine-N7 methyltransferase (ExoN/nsp14), uridylate-specific endoribonuclease (NendoU/nsp15), 2’-O-ribose methyltransferase (nsp16), Spike glycoprotein (S glycoprotein), protein 3a, Envelope small membrane protein (E protein), Membrane protein (M protein), nonstructural protein 6 (nsp6), protein 7a, nonstructural protein 7b (nsp7b), nonstructural protein 8 (nsp8), nucleoprotein (NC), ORF10 protein. These proteins can form hetero-oligomeric complexes such as: nsp7/nsp8 hetero-oligomeric complex; nsp7/nsp8/Pol hetero-oligomeric complex; nsp10/nsp14 hetero-oligomeric complex; nsp10/nsp16 hetero-oligomeric complex; Spike glycoprotein/hACE2 hetero-oligomeric complex.Anti-coronavirus therapies can be split into two main approaches: the first approach is to act on the human immune system or human cells level, and the other approach is to focus on coronavirus itself [3]. In exploring novel therapies for COVID-19, researchers are using computational approaches to aid in the discovery of potential candidates [4]. In particular, in silico drug repurposing, also named drug repositioning, is a strategy used to identify novel uses for existing approved and investigational drugs. This strategy offers numerous advantages over traditional drug development pipelinesthat suffer risks failure in preclinical or early stage clinical trials due to safety and/or toxicological issues. On the contrary, the drug repurposing strategy reduces this risk by using drugs that have demonstrated safety records from previous trials. The real advantage of drug repurposing is that preclinical and early stage clinical trials do not need to be repeated. This determines cost reductions compared to traditional drug development [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. The number of in silico studies on drug repositioning against SARS-CoV2 is growing rapidly in these last months. A major part of these studies is focused on the repurposing of approved and investigational drugs against the 3CLpro or Mpro by using both ligand-based approaches and structure-based approaches. Structure-based approaches are related to different docking analysis [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29]. In another work, Battisti and coworkers used two different approaches related to docking and pharmacophore combined with molecular dynamics to perform virtual screening of a large database of compounds on 10 different SARS-CoV-2 proteins [30]. To our knowledge, Touret and coworkers performed, to date, the only in vitro screening of an FDA approved chemical library which revealed potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 replication [21]. Nevertheless, the identification of potential inhibitors is still challenging for all the researchers involved in the field. In this study, a computational analysis of the proteins encoded by the SARS-CoV-2 genes was performed. Such an analysis was used as a starting point for a druggability assessment and a computational drug repurposing work-frame. First, high-quality protein structures were built employing homology modeling or exploiting existing experimental structures. Starting from the models, a computational assessment was done to find out a druggable binding pocket for those proteins of which catalytic site is not known in the literature. The best druggable sites found in the previous analysis, together with the catalytic sites reported in the literature, were then used to build structure-based pharmacophore models. In the end, these models were used to screen the DrugBank library (approved and investigational drugs) [31] as a first screening approach.
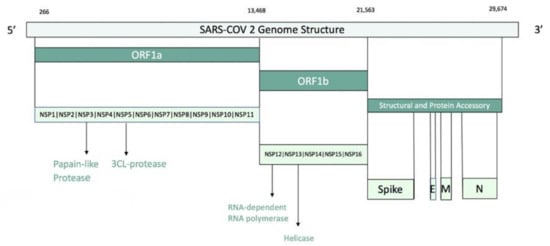
Figure 1.
SARS-COV2 genome structure.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Library Preparation
A total of 8752 experimental, investigational and approved molecules were downloaded from the DrugBank database (www.drugbank.ca). First, the database molecules were prepared using Schrödinger LigPrep v. 2018-4. The force field adopted was OPLS3e and Epik [32] was selected as an ionization tool at pH 7.0 ± 2.0. Tautomers generation was flagged and the maximum number of conformers generated was set at 32. The database obtained was prepared as a Pharmacophore Screening database, in *.lbd format, through Idbgen (extension present in the LigandScout 4.3 [17] package), which allowed obtaining the best conformation of the ligand (at low energy) between the 200 the application can calculate. The tautomers were considered as separate molecules and those molecules that were duplicated or whose conformation calculation had failed were eliminated.
2.2. Homology Modeling and Protein Preparation
The full SARS-CoV-2 proteome based on the NCBI reference sequence NC_045512, which is identical to GenBank entry MN908947 and annotations from UniProt, was modeled in the SWISS-MODEL [33] workspace (swissmodel.expasy.org/workspace). Only for 10 proteins, it was possible to obtain high-quality models and experimental structures that were considered for further analysis. Investigated proteins are 3C-like protease (3CLpro), papain-like protease (PLpro), guanine-N7 methyltransferase (nsp14), uridylate-specific endoribonuclease (NendoU/nsp15), nsp4, nsp7/nsp8 supercomplex, nsp9, nsp7/nsp8/nsp12 hetero-oligomeric complex, helicase (Hel), 2’-O-ribose methyltransferase (nsp16).For each structure, templates with the highest identity available at the time of this study (25 March 2020) were selected and respective models were generated.
For 3C-like protease (3CLpro) the crystal structure of the COVID-19 main protease (PDB ID: 6LU7) was available. The structure of papain-like protease (PLpro) of SARS virus (PDB ID: 3E9S) was used as a template of the human coronavirus papain-like model (82.86% sequence identity). This one was the best available experimental structure at the time of the study (25 March 2020). On 27 May 2020, the crystal structure of PLpro of SARS-CoV-2 was released (PDB ID: 6WZU). We performed the overlapping of our model and the experimental structure. The RMSD value of 3.99 Åshows that the two structures are identical unless few residues in the C-terminal (See Supplementary Information). For guanine-N7 methyltransferase (nsp14) we used as template the SARS-related coronavirus (PDB ID: 5C8S) that shows 95.07% of sequence identity. For uridylate-specific endoribonuclease (NendoU/nsp15), we used the experimental structure as reported in the Protein Data Bank [34] (PDB ID: 6W01). The crystal structure of nsp4 from mouse hepatitis virus A59 (PDB ID: 3VCB) was used as a template of SARS-CoV-2 nsp4 (61.36% sequence identity). The crystal structure of SARS-CoV super complex of nonstructural proteins (PDB ID: 2AHM) was chosen as a template of nsp7/nsp8 supercomplex (97.86% sequence identity). For nsp9 the template of nsp9 from SARS-coronavirus (PDB ID: 1UW7) was used. It shares a sequence identity of 97.35%. The X-ray structure of SARS coronavirus nsp7/8/12 (PDB ID: 6NUR) was selected as a template of nsp7/nsp8/nsp12 hetero-oligomeric complex (96.70% sequence identity). The crystal structure of SARS-coronavirus helicase (PDB ID: 6JYT) was used as template for SARS-CoV-2 helicase (Hel). It shows a high sequence identity (99.83%). On 29 July 2020, the experimental structure of SARS-CoV-2 helicase (PDB ID: 6ZSL) was released. The overlapping of our model and the experimental structure shows a RMSD value of 4.17 Å. This means a quite identical structure unless some loops (See Supplementary Information). The crystal structure of nsp16/nsp10 SARS coronavirus complex (PDB ID: 2XYQ) was chosen as a template of the model of 2’-O-ribose methyltransferase (nsp16) with 93.45% sequence identity. The models obtained and the PDBs were refined using the protein preparation wizard tool of Maestro Suite Software [35]. This tool allowed the protein structure optimization, including missing loops, side chains and hydrogens, optimization of the protonation state in a pH range 7.0 ± 2.0 and analysis of atomic clashes. For PDBs containing co-crystallized ligands, Epik [32] was used to predict ionization and tautomeric state of ligand, while PROPKA was used to check for the protonation state of ionizable protein groups. Protein was refined using restrained minimization with OPLS3e as force field.
2.3. Pharmacophore Modeling
Pharmacophore model generation was performed using LigandScout 4.3. The structures were imported into LigandScout. 3C-like proteinase, PLpro, nsp14, nsp15, nsp16–nsp10 are protein–ligand complexes, while, nsp4, nsp9, nsp10–nsp14, helicase, nsp7–nsp8 supercomplex, nsp12are targets without ligand-bound. For protein–ligand complexes, a structure-based pharmacophore model was generated [31]. When the model showed more features, to improve the performance of virtual screening, we considered the features for the binding, in other cases the features were omitted until hits were found. The calculate pockets tool has been used to find the binding pockets for the structures without ligand-bound. A grid was calculated over the entire protein structure and grid points were evaluated according to their buriedness and their number of neighboring grid points. Isocontour surfaces were generated. Then, a model was created by selecting the nature and number of six features according to the features showed in the protein–ligand complexes utilizing “Create Apo Site Grids”. Next, the pharmacophore model was generated for each one. The obtained pharmacophore models were used as a query to screen the DrugBank library. For apo protein, such an approach allow to evaluate if a putative binding site is suitable for ligand binding.
Pharmacophore screening was preferred to be used prior to docking for two reasons. First, it exploits a rapid screening techniques that is crucial in the first stage of virtual screening cascade. Indeed, this is very common to use it as a first step in virtual screening campaign on large databases [36]. Second, the structure-based pharmacophore uses a static conformation of protein side chains, while the docking funnel here used was set to have a gradually increasing precision with a final step of IFD that allow user to simulate side-chains-induced fit based on the ligand.
2.4. Docking
The hits identified by the virtual screening were submitted to a docking study using Glide [37] in standard precision (SP) with the OPLS3e [38] force field. The crystal structures were optimized using protein preparation wizard in Maestro [35] adding bond orders and hydrogen atoms to the crystal structure using the OPLS3e force field. Next prime [39] was used to fix missing residues or atoms in the protein and to remove co-crystallized water molecules. The protonation state, pH 7.2±0.2 of the protein and the ligand were evaluated using Epik 3.1[32]. The hydrogen bonds were optimized through by reorientation of hydroxyl bonds, thiol groups and amide groups. In the end, the systems were minimized with the value of convergence of the RMSD of 0.3 Å [40,41]. For protein–ligand complexes, the grid boxes were built considering the ligands as a centroid. In contrast, for apoproteins, the amino acid residues, previously identified by LigandScout as crucial, were considered for centering the docking grid. The docking study was performed using the Glide docking tool, in extra precision (XP) using no constraints. Van der Waals radii were set at 0.8 and the partial cutoff was 0.15 and flexible ligand sampling. Bias sampling torsion penalization for amides with nonplanar conformation and Epik state penalties were added to the docking score.
2.5. Induced-Fit Docking and MM-GBSA
The induced-fit protocol (IFD)—developed by Schrödinger [24]—is a method for modeling the conformational changes induced by ligand binding. This protocol models induced-fit docking of one ormore ligands using the following steps as also reported in [42]. The protocol starts with an Initial docking of each ligand using a softened potential (van der Waals radii scaling). Then, a side-chain prediction within a given distance of any ligand pose (5 Å) is performed. Subsequently, a minimization of the same set of residues and the ligandfor each protein/ligand complex pose is performed. After this stage, any receptorstructurein each pose reflect an induced fit to the ligand structureand conformation. Finally, the ligand is rigorously docked, using XP Glide, into the induced-fit receptor structure.
IFD was performed using a standard protocol and OPLS3e force field was chosen [38]. Receptor box was centered on the co-crystallized ligands on the crucial residues identified within the binding site. During the initial docking procedure, the van der Waals scaling factor was set at 0.5 for both receptor and ligand. Prime refinement step was set on side chains of residues within 5Å of the ligand. For each ligand docked, a maximum of 20 poses was retained to be then redocked at XP mode. IFD calculation was followed by prime/MM-GBSA for the estimation of ∆Gbinding. The MM-GBSA approach employs molecular mechanics, the generalized Born model and the solvent accessibility method to elicit free energies from structural information circumventing the computational complexity of free-energy simulations wherein the net free energy is treated as a sum of a comprehensive set of individual energy components, each with a physical basis [41,43,44,45]. The conformational entropy change—TΔS—can be computed by normal-mode analysis on docking poses, but many authors have reported that the lack of the evaluation of the entropy is not critical for calculating the MM-GBSA (or MM-PBSA) free energies for similar systems [46,47,48,49]. For these reasons, the entropy term–TΔS was not calculated to reduce computational time. In our study, the VSGB solvation model was chosen using OPLS3e force field with a minimized sampling method.
3. Results and Discussion
Recently, SARS-CoV-2 caused the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) threatening global health security. To date, no approved antiviral drugs or vaccines are available against COVID-19 although several clinical trials are underway. In this framework, computational methods offer an immediate and scientifically sound basis to potentially design highly specific inhibitors against important viral proteins and guide the antiviral drug discovery process [50]. In this work, SARS-CoV-2 encoded proteins were analyzed from PDB structures and homology models were generated by using the most similar PDB crystal structures as templates. For the homology models created, starting from the high similarity between SARS-CoV-2 proteins and some available crystal structures from SARS-CoV, ligand coordinates of the available most similar crystals were exploited for the structure-based pharmacophore creation. Below we report the analyzed proteins and the related pharmacophore maps composition.
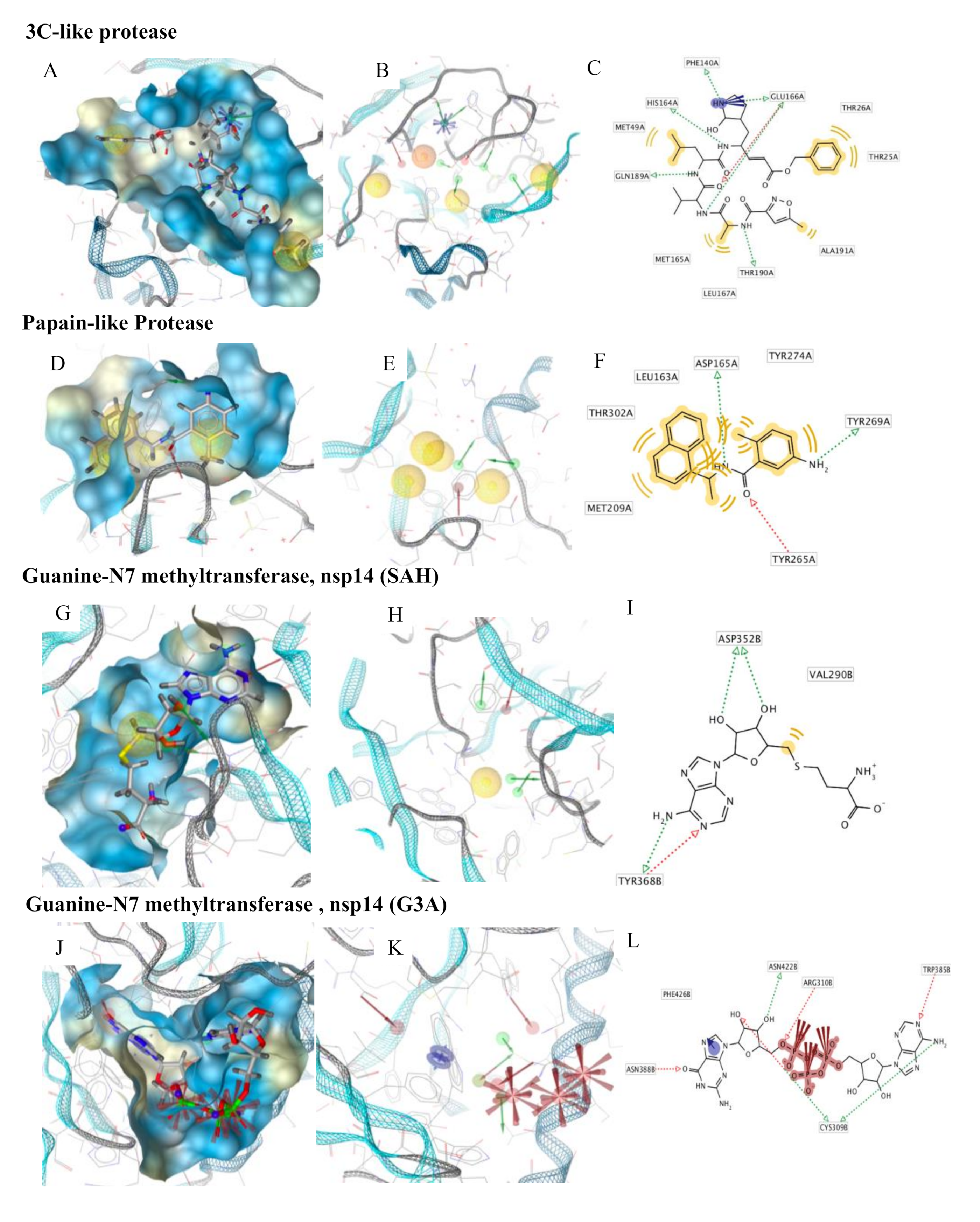
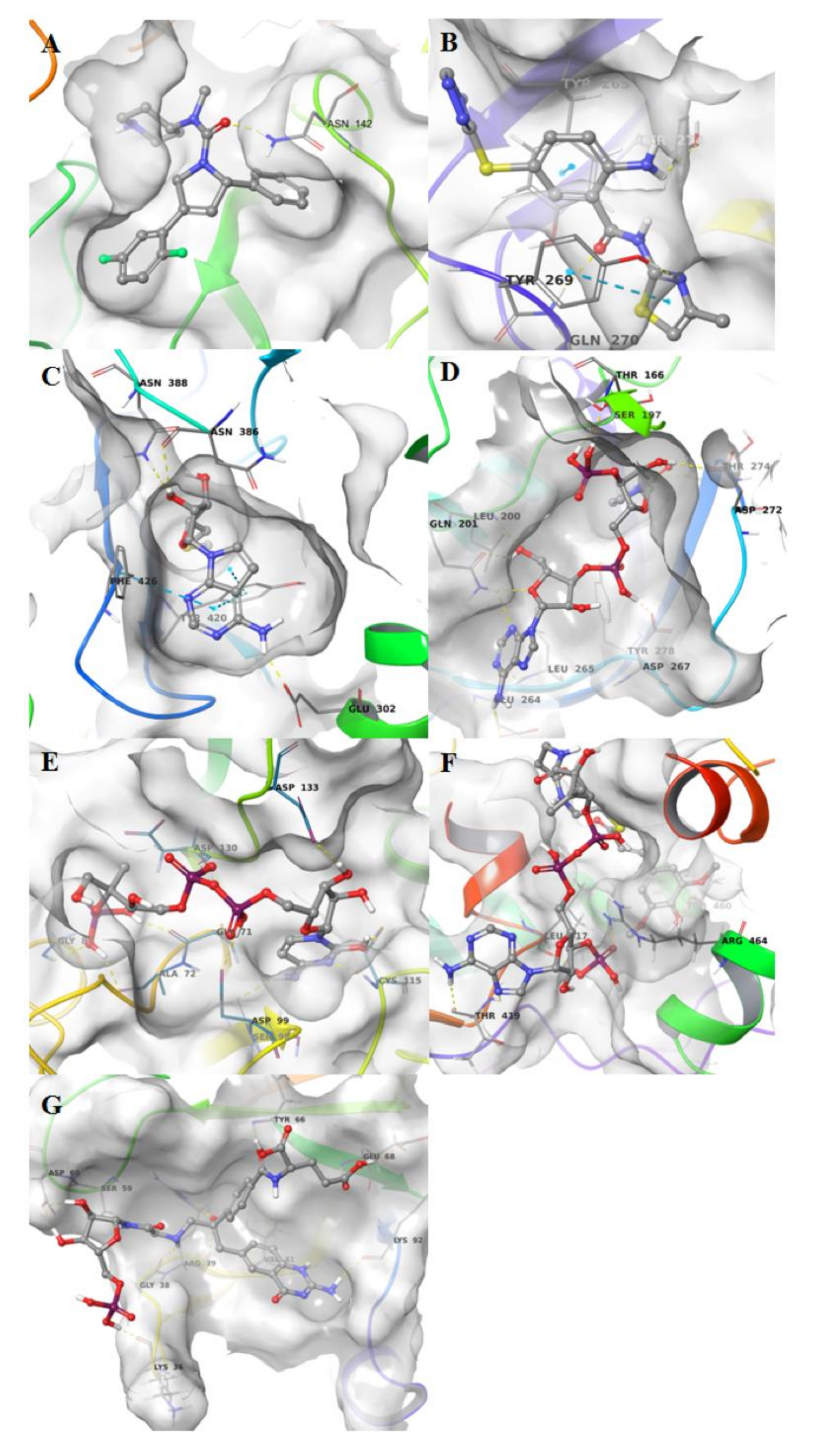
3C-like proteinase (3CLpro), also termed the main protease, cleaves most of the sites in the polyproteins and the products are nonstructural proteins (NSPS), which assemble into the replicase–transcriptase complex (RTC). The binding site of the main protease consists of a conserved catalytic dyad, i.e., Cys145 and His41 with other crucial residues, which is Phe140, Leu141 Asn142, Gly143, Ser144, Cys145, Met165, Glu166, Gln189 and Thr190 [27] (Figure 2A). The pharmacophore model was developed on the co-crystallized ligand (N3) that is present in the PDB ID 6LU7; this ligand was covalently bound to Cys145. We modified N3, by breaking the covalent bond and filling in open valence. The final pharmacophore showed 12 features: 2 H-bond acceptors (HBAs) interacting one with Glu166 and the other with Gly143; 4 H-bond donors (HBDs) which interact, respectively, with Phe140, His164, Glu166, Gln189 and Thr190; 4 hydrophobic features interacting with Thr25, Thr26, Met49 and Ala191; and a negative ionizable area with Glu166 (Figure 2B,C).
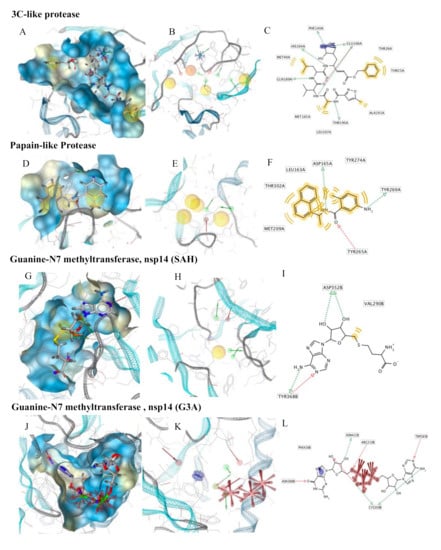
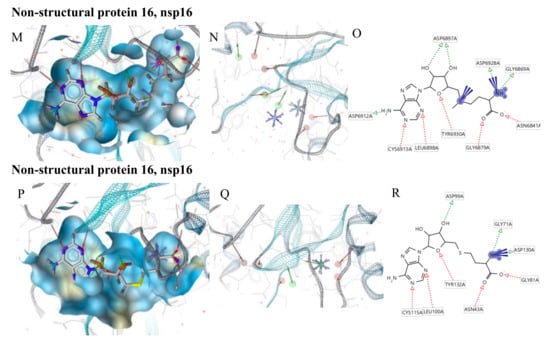
Figure 2.
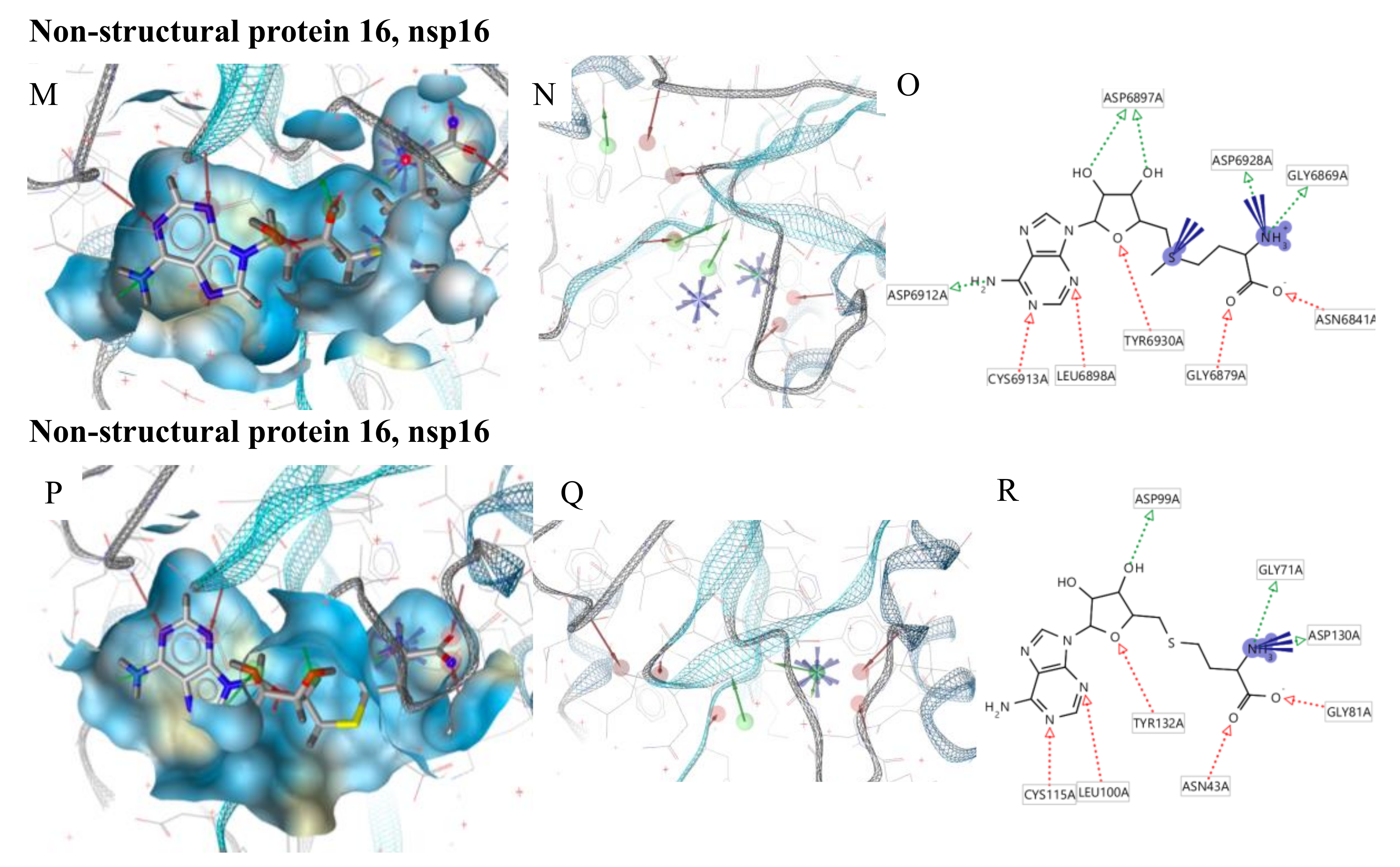
Pharmacophore modeling of ligand–protein complexes. For each structure molecular surface of the active site the co-crystallized ligand (A,D,G,J,M,P), structure-based pharmacophore model (B,E,H,K,N,Q) and ligand interactions (C,F,I,L,O,R) are shown.
Papain-like protease (PLpro) cleaves the nsp1/2, nsp2/3 and nsp3/4 boundaries. It works with 3CLpro to cleave the polyproteins into NSPS [51]. It showed in the active site residues Gly164, Asp165, Arg166, Glu168, Pro248, Pro249, Tyr 265, Gly267, Asn268, Tyr 269, Gln270, Cys271, Gly272, Tyr274 and Thr302 (Figure 2D). The pharmacophore model was developed on the co-crystallized ligand present in the PDB ID 3E9S. The pharmacophore map was composed of 7 features: 1 HBA with Gln270; 2 HBDs, one with Tyr265 and the other with Tyr269; and 4 hydrophobic interactions with Leu163, Met209, Tyr274 and Thr302 (Figure 2E,F).
Guanine-N7 methyltransferase (nsp14) is important for viral replication and transcription. The N-terminal exoribonuclease (ExoN) domain plays a proofreading role in the prevention of lethal mutagenesis and the C-terminal domain functions as a guanine-N7 methyltransferase (N7-MTase) for mRNA capping [52]. The models were developed using as template the PDB ID 5C8S, which shows nsp14 in complex with its activator Nonstructural protein10 (nsp10) and two functional ligands: S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine (SAH) and guanosine-P3-adenosine-5,5′-triphosphate (G3A). One molecule of nsp10 interacts with ExoN of nsp14 to stabilize it and stimulate its activity. SAH and G3A bind the guanine-N7 methyltransferase site. The SAH binding pocket contains residues Trp292, Gly333, Asp352, Phe367 and Tyr368 [29] (Figure 2G). The derived pharmacophore model showed 5 features: 1 HBA with Tyr368, 3 HBDs, two with Asp352 and one with Tyr368 and hydrophobic interaction with Val290 (Figure 2H,I). The binding pocket engaging G3A contains the following residues: Trp292, Arg310, Gly333, Pro335, Lys336, Asn386, Asn388, Tyr420 and Phe426 (Figure 2J). Therefore, the derived pharmacophore model showed 10 features: 4 HBAs which interacted, respectively, with Cys309, Arg310, Trp385, Asn388, 3 HBDs, two with Cys309 and one with Asn422, 3 negative ionizable features at the 3 phosphate groups and an aromatic ring with Phe426 (Figure 2K,L).
Nonstructural protein 16 (nsp16) also termed 2’-O-methyltransferase is activated only by the binding of nsp10. We considered the structure of the nsp16–nsp10 complex from SARS-COV-2 with 1.80 Å of resolution (PDB ID: 6W4H). This complex shows S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) in the binding site. It forms hydrogen bonds with Asp6928, Tyr6930, Asp6897 and Cys6913 (Figure 2P). The derived pharmacophore model on the co-crystallized ligand showed 9 features: 4 HBAs with Gly248 and Thr341, 1 HBD with His250 and 2 negative ionizable areas with Gly248 and Lys290 (Figure 2Q,R).
Moreover, we used the nsp16–nsp10 SARS coronavirus complex (PDB ID: 2XYQ), which shows S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine (SAH) in the binding site. SAH forms hydrogen bonds with Lys46, Asp130, Lys170 e Glu203 (Figure 2S). The derived pharmacophore model showed 9 features: 4 HBAs with Asn43, Leu100, Tyr132, Cys115, 4 HBDs with Gly71 and Asp99, 2 negative ionizable areas with Asp130 (Figure 2T,U).
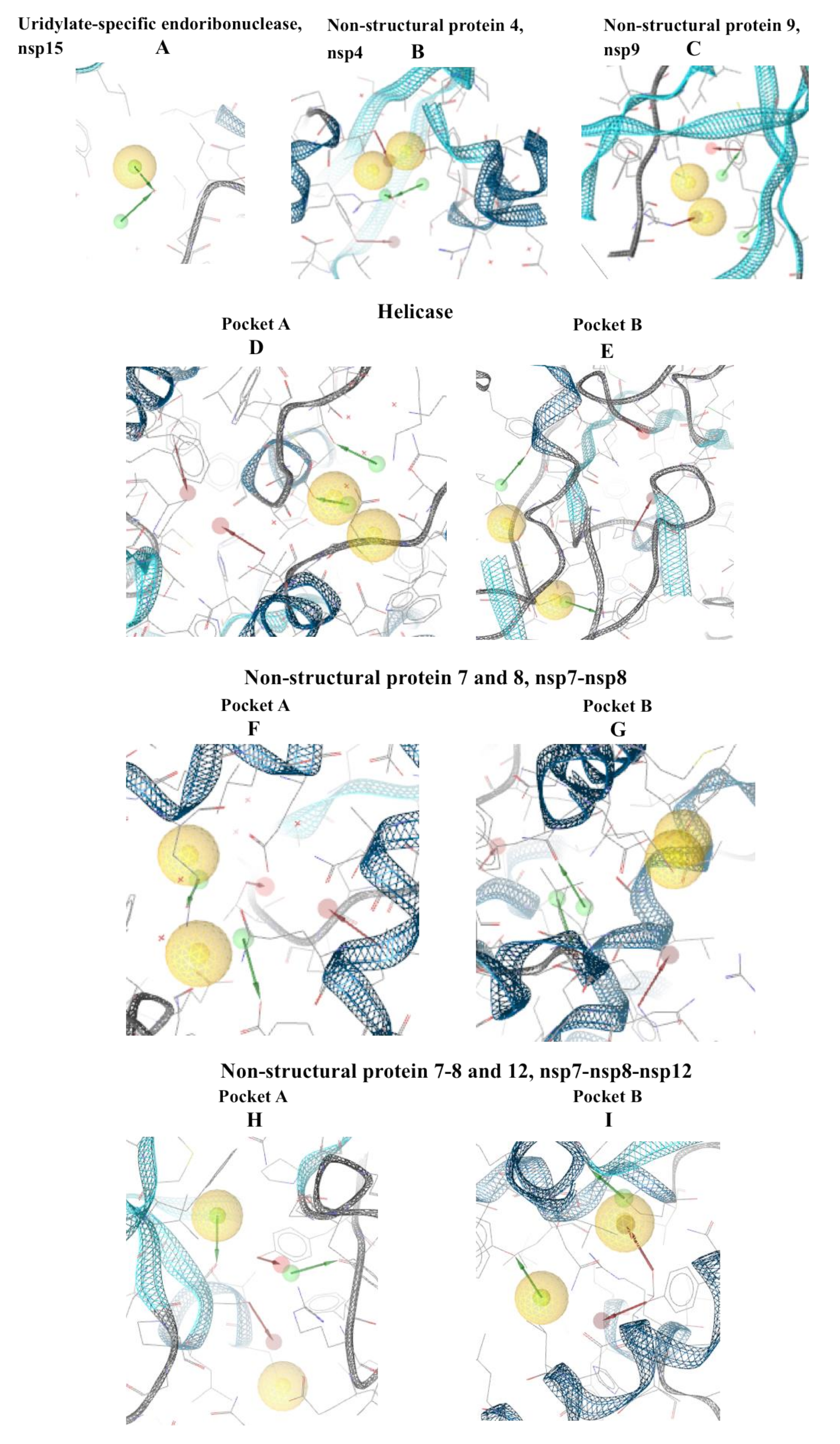
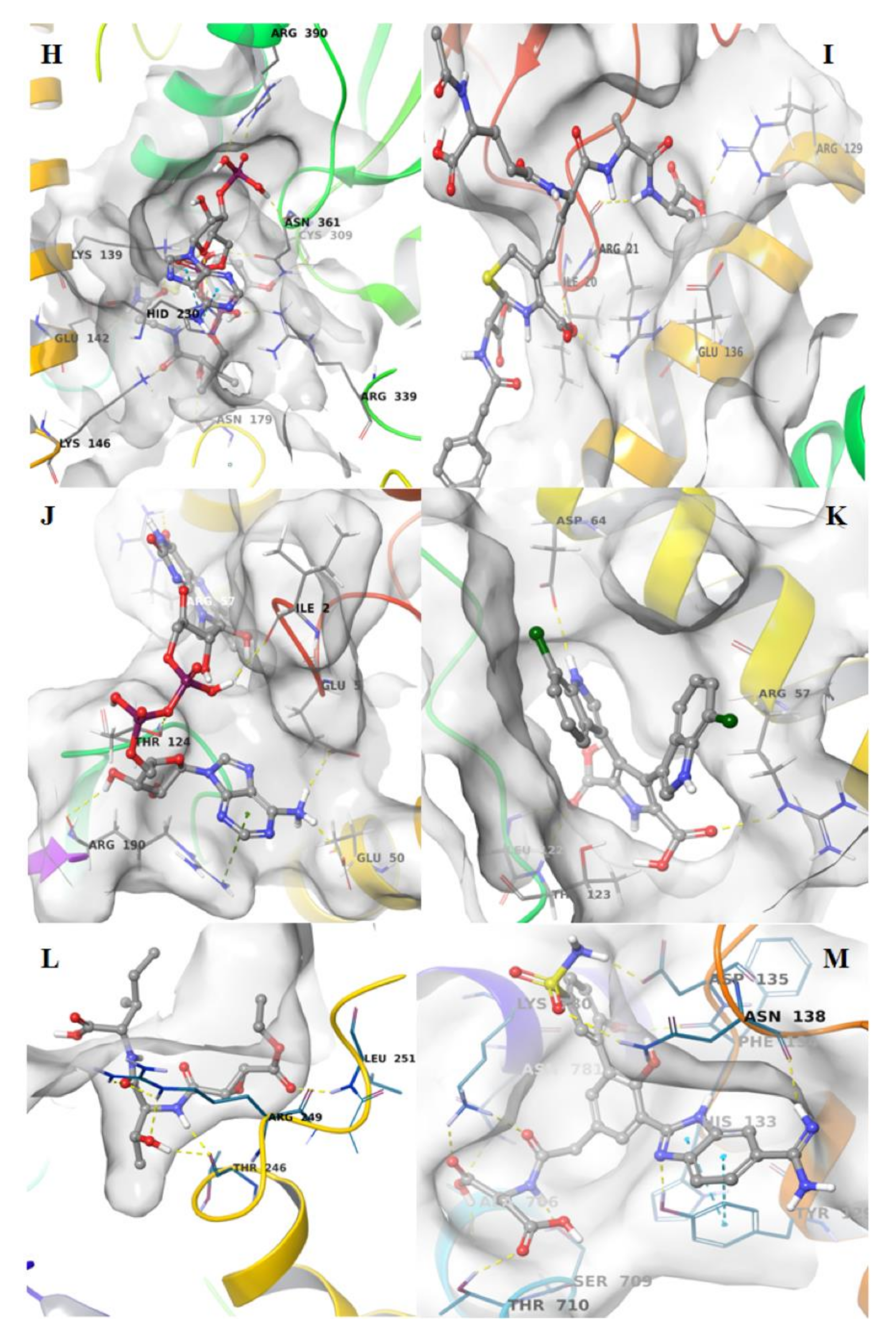
The other pharmacophore models were developed exploring the apoprotein surfaces as follows: uridylate-specific endoribonuclease (NendoU/nsp15) forms a hexameric endoribonuclease, that preferentially cleaves 3’ of uridines. It is one of the RNA-processing enzymes encoded by the coronavirus [52]. Exploring the apoprotein surface, a potential active site was found, and a pharmacophore model was generated (Figure 3A). It contained the following residues: Thr166, Arg198, Asp267 and Ser273. The pharmacophore model showed 3 features: 2 HBDs and one hydrophobic feature.
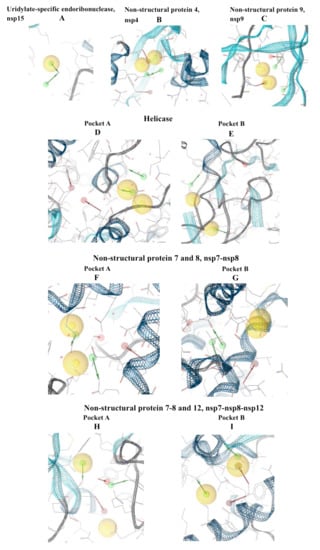
Figure 3.
Pharmacophore modeling of the apoproteins. The first step was to find putative active sites, then the pharmacophore models were built in the identified pockets. Four of the structures had two active sites. (A) Uridylate-specific endoribonuclease, nsp15; (B) nsp4; (C) nsp9; (D) Helicase pocket A; (E) Helicase pocket B; (F) nsp7-nsp8 pocket A; (G) nsp7-nsp8 pocket B; (H) nsp7-8-12 pocket A; (I) nsp7-8-12 pocket B.
Nonstructural protein 4 (nsp4) is localized at the endoplasmic reticulum membrane when expressed alone, but this protein can be recruited into the replication complex in infected cells [52]. After scanning the protein surface, a potential binding pocket was identified containing residues Leu417, Thr460 and Arg464. The derived pharmacophore model showed 6 features: 2 HBAs, 2 HBDs and a hydrophobic feature (Figure 3B).
Nonstructural protein 9 (nsp9), encoded by ORF1a, does not present a designated function, but is most likely involved with viral RNA synthesis. The crystal structure suggests that the protein is dimeric, whereas nsp9 binds RNA and interacts with nsp8 [53]. The potential identified binding site contains the following residues: Gly38, Arg39, Ser59 and Thr64. The derived pharmacophore model showed 6 features: 2 HBAs, 2 HBDs and one hydrophobic feature (Figure 3C).
Helicase (hel) catalyzes the unwinding of duplex oligonucleotides into single strands in an NTP-dependent manner. The structure of SARS-CoV-2 nsp13 adopted a triangular pyramid shape comprising five domains. Among these, there are two “RecA-like” domains, 1A (261–441 a.a.) and 2A (442–596 a.a.) and 1B domain (150–260 a.a.) forming the triangular base, while N-terminal zinc-binding domain (ZBD) (1–99 a.a.) and stalk domain (100–149 a.a.), which connects ZBD and 1B domain, are arranged at the apex of the pyramid [27]. Exploring the apoprotein surface, two putative binding sites were found, pocket A and pocket B. Pocket A contained residues from the stalk domain (Lys139, Lys146), 1B domain (Asn179) and 1A domain (Cys309, Arg339) and domain 1B (Thr228-Thr231) important for helicase activity. Pocket B contained residue from the N-terminal zinc-binding domain, ZBD domain, (Ile20, Arg21, Arg22) and stalk domain (Arg129). The pharmacophore models obtained for each pocket have the same 6 features: 2 HBAs, 2 HBDs and two hydrophobic features.
Nonstructural protein 7 and 8 (nsp7–nsp8) supercomplex are essential cofactors for Nsp12 polymerase [33]. Two putative active sites were found: pocket A and pocket B. Pocket A between chains C, G and H, pocket B between chainG–H of nsp8. The pocket A showed as residues: Glu50 of chain C; Thr124 and Arg190 of chain G; Glu5, Arg57, of chain H. The pocket B of chains G–H of nsp8 showed the residues: Arg57 and Asp64 of chain G; Leu122 and Thr123 of chain H. The pharmacophore model showed 6 features each: 2 HBAs, 2 HBDs and two hydrophobic features (Figure 3F,G).
Nonstructural protein 12 bound to nsp7-8 co-factors (nsp7–nsp8–nsp12) hetero-oligomeric complex is an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. It is bound to its essential co-factors nsp7 and nsp8 greatly stimulates the replication and transcription activities of the polymerase. The nsp12 contains a polymerase domain (a.a. 398–919) that assumes a structure resembling a cupped “right hand”. The polymerase domain consists of a finger domain (a.a. 398–581, 628–687), a palm domain (a.a. 582–627, 688–815) and a thumb domain (a.a. 816–919). CoV nsp12 also contains a nidovirus-unique N-terminal extension (a.a. 1–397) [27]. The putative active sites, pocket A and pocket B were found into conserved motif regions (A–G) possessed of all polymerases [33]. Pocket A contained residues of N-terminal extension Thr246 and Arg249; pocket B contained residues of N-terminal extension Tyr129, His133, Asn138 and motif D (Ala706–Asp711), The pharmacophore model showed 6 features: 2 HBAs, 2 HBDs and two hydrophobic features (Figure 3H,I).
The identified pharmacophore models were used to perform a virtual screening against the DrugBankdatabase of experimental, investigational and approved drugs considering as a first filter.
The hits found were submitted to docking studies to evaluate the poses and interactions at the putative active site. First, XP docking was performed and subsequently, the highest-ranked hits were submitted to induced fit docking analysis and MM-GBSA calculation to further filter. For just one protein (nsp16), no hits were identified in the DrugBank database. At the end of the computational exploration, we have identified a total of 34 hits for all the explored targets. Among these compounds, 26 are experimental drugs, 5 investigational drugs and 3 approved drugs. The summary results were reported in the Supporting Information. In the main text, we will discuss the molecular recognition analysis for the best binder hits for each target. The rest of the identified hits, docking scores, ∆Gbinding, and protein–ligand interactions is reported in a table in Supplementary Information as well as 2D ligand interaction diagrams of the best binders.
The best docked hit molecule for 3CL-protease is the experimental drug DB082309, a phenyl pyrroline derivative (∆G = −72.56 kcal/mol). This compound is characterized by an H-bond between the carbonyl oxygen with Asn142, but the principal contribution to the binding is given by the ∆GvdW = −52.56 kcal/mol and the ∆Glipo = −23.65 due to the 2 aromatic rings (phenyl and O-difluorophenyl) of the molecules which are located in two hydrophobic pockets (Leu140, Phe141, Leu167, Pro168) and the piperazine moiety interacting with His41 and Met49 (Figure 4A).
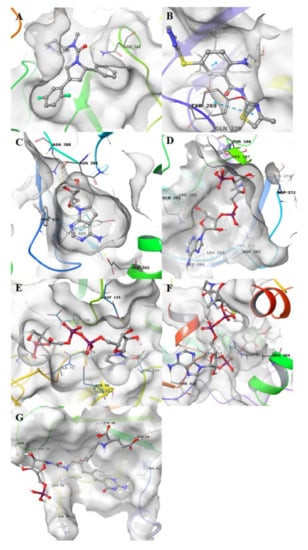
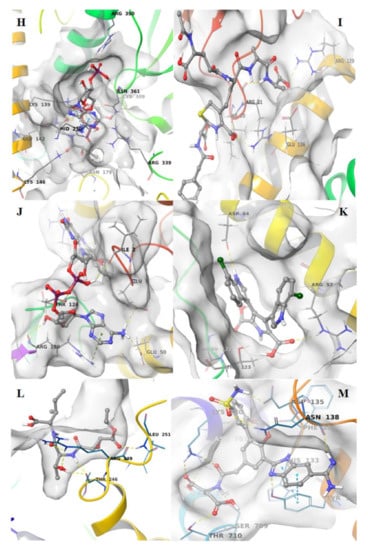
Figure 4.
(A) DB08239 binding pose in 3C-like protease; (B) DB07358 binding pose in papain-like protease; (C) DB02933 binding pose in guanine-N7-methyltransferase (nsp14); (D) DB01792 binding pose in NendoU/nsp15; (E) DB01859 binding pose in nsp16; (F) synapoylCoenzyme A binding pose in nsp4; (G) DB02794 binding pose in nsp9.(H) DB04579 binding pose in helicase, pocket A; (I) PCI-27483 binding pose in helicase, pocket B; (J) flavin-N7 protonated-adenine dinucleotide binding pose in nsp7-8, pocket A; (K) DB06955 binding pocket in nsp7-8, pocket B; (L) DB04579 binding pose in nsp7-8–12, pocket A; (M) PCI-27483 in nsp7-8–12, pocket B.
The most promising drug candidate for papain-like protease is the experimental drug DB07358 (∆G= −50.662 kcal/mol), a benzamide derivative. In our study, the experimental drug DB07358 forms three H-bonds with Tyr269, Gln270 and Tyr274. Moreover, the binding is characterized by a strong pi-stacking of the thiazol moiety with the phenyl ring of Tyr269 and phenylamino moiety with the phenyl ring of Tyr274 (∆Glipo = −19.47 kcal/mol, ∆GvdW = −38.50 kcal/mol) (Figure 4B).
Top-ranked guanine-N7-methyltransferase (nsp14) hit is the experimental drug DB02933 as known as 5’-deoxy-5’-(methylthio)-tubercidin (∆G = −65.07 kcal/mol). This compound was previously identified as an inhibitor of the h–S-methyl-5’-thioadenosine phosphorylase and bacterial methylthioadenosinenucleosidase. The compound 5’-deoxy-5’-(methylthio)-tubercidin showed 3 H-bond interactions with Asn386, Asn388 and Glu302, but the most contribution to the binding energy is due to pyrrole pyrimidine moiety, which establishes strong pi-stacking interaction with Tyr420 and Phe426 (Figure 4C).
Considering the NendoU/nsp15 protein, the most promising compound is the experimental drug DB01792 as known Adenylyl-(3’-5’)-uridine 3’-monophosphate (∆G = −63.169 kcal/mol). The compound showed a high number of H-bond interactions with several different residues (Thr166, Ser197, Glu264, Asp272, Tyr278) (Figure 4D).
The experimental drug DB01859 resulted in the hit related to the nsp16. The compound is also known as 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2-phosphate (∆G = −25.204 kcal/mol). It showed 9 H-bond interactions with Gly71, Ala72, Gly81, Ser98, Asp99, Asp130 and Asp133. Residue Cys115 showed 2 H-bonds (Figure 4E).
The top-ranked compound for nsp4 is the experimental drug sinapoyl-coA (DG = −80.73 kcal/mol). The binding of sinapoyl-CoA in the nsp4 pocket is influenced by a high number of H-bonds with several different residues (Leu417, Thr419, Arg464, Thr460) (Figure 4F).
The experimental drug DB02794 resulted in the best binding hit related to the nsp9. Due to the presence in the scaffold of many oxygen atoms, DB02794 establishes many H-bond interactions involving Lys36, Gly38, Arg39, Ser59, Asp60, Glu68. Other H-bond interactions involve some nitrogen of the experimental drug and the residues Gly38, Ser59 and Lys92. The strong net of H-bond interactions is reflected by a ∆Gcoul = −84.35 kcal/mol, partially compensated by a loss of binding energy due to the solvation contribution ∆G = +68.45 kcal/mol. It is worthy to note that the next top-ranked hits for nsp9 are 3 approved drugs (ioxilan, Pemetrexed, and isoprenaline), which could be of particular interest due to the status “approved”, which would allow to use them in clinical trials (Figure 4G).
For the helicase, the apo binding pocket analysis identified 2 different putative binding sites. The most promising candidate drug-binding pocket A is the experimental drug 4-hydroxybenzoyl-coA (∆G = −91.90 kcal/mol). The interactions that this compound establishes with the pocket A are characterized by several H-bonds, most of which formed by the three phosphate moieties with Lys139, Arg339, Asn361, Arg390. Other H-bond interactions are among the hydroxyl and carbonyl oxygens and Lys139, Glu142, Lys146, Asp179, His230, Cys309, Arg339, Arg390. Moreover, the purine moiety establishes pi-stacking interactions with the imidazole moiety of His230. Regarding the top-ranked compound in pocket B, this is the experimental drug DB02136, a cephalosporin analog, (∆G = −75.81 kcal/mol). This compound interacts with the residues Ile20, Arg21, Arg22, Arg129, Glu136 forming H-Bonds with carbonyl and hydroxyl oxygen atoms, but the binding mode is strengthened by an important contribution of ∆GvdW = −71.94 kcal/mol (Figure 4H,I).
Furthermore, for the supercomplex nsp7–nsp8, two different pockets were found. The most promising candidate for pocket A is the experimental drug flavin-N7 protonated-adenine dinucleotide (∆G = 78.86 kcal/mol). The flavin moiety interacts with the residue Arg57 forming 2 H-bonds. These latter are also formed among the phosphate and Thr190, the ribose moiety and Arg190 and the purine moiety and Ile2, Ile3, Ile4. Moreover, the binding interaction is strengthened by ionic interactions among the NH3+ and the glutamic residues 5 and 50. The residue Arg190 interacts with the purine moiety employing pi-stacking interactions. The top-ranked compound for pocket B is the experimental drug DB06955 (∆G = −58.14 kcal/mol), a pyrrole-indole derivative, interacting with Arg57, Asp64, Leu122 and Thr123 employing H-bond interactions (Figure 4J,K).
Last, but not least, for the hetero-oligomeric complex nsp7–nsp8–nsp12 two different pockets were identified. In pocket A, the most promising compound is the experimental peptide analog DB04579 (∆G = −57.10 kcal/mol) interacting with the residues Thr246, Arg249, Leu251, Ser255 through H-bond interactions. The most promising compound for the pocket B is the investigational drug PCI-27483, a phenyl benzimidazole derivative to date used for the treatment of the pancreatic adenocarcinoma. The binding mode is characterized by several H-bond interactions involving His133, Phe134, Asp135, Asn138, Ala708, Ser709, Thr710, Lys780 and Asn781. The indole moiety is further involved in pi-stacking interactions with Tyr129 (Figure 4L,M).
4. Conclusions
The recently emerged SARS-CoV-2 caused a major outbreak of COVID-19 and instigated a widespread fear and has threatened global health security because there are no approved therapies for treating. In the attempt to try to speed up the search for new inhibitors of the virus replication, in this study, we performed a computational drug repositioning campaign on the DrugBank database of experimental, investigational and approved drugs. The aim of using such a restricted database had the rationale to identify potential lead compounds to quickly test in vitro and in vivo as they passed toxicity tests. We analyzed the proteome of SARS-CoV-2 and using homology modeling we identified the high-quality models of proteins. A structure-based pharmacophore modeling study was performed to identify pharmacophore features for each target. Successively, the pharmacophore models were used to perform a virtual screening against the DrugBank library. After a docking study, we identified a total of 34 hits for all the explored targets (3CL-protease, papain-like protease, guanine-N7-methyltransferase nsp14, nsp16, NendoU/nsp15, nsp4, nsp9, helicase, nsp7–nsp8 supercomplex and nsp7–nsp8–nsp12 hetero-oligomeric complex). Among these compounds, 26 are experimental drugs, fiveinvestigational drugs and three approved drugs. The final selection of the potential inhibitors was made considering the best binding energy for each compound obtained utilizing MM-GBSA calculation. Molecular recognition analysis showed that these compounds interact with the residues found as crucial for each target. These drugs can be further explored against the successful inhibition of COVID-19. Moreover, a set of hot spot residues and pharmacophore features for each target, which makes substantial contributions to the protein–ligand binding are also identified. This achievement can facilitate us to rationally design novel selective inhibitors targeting SARS-CoV-2, not comprised in the DrugBank. The results of this study offer a double important hint for anti-COVID19 drug discovery campaigns. On one side, it shows putative repurposing drugs to be adopted as a single therapy or in combination with other therapies. On the other side, our deep studies attempted to map out the main binding hot spots for the most important SARS-CoV-2 proteins, opening an important route to the design of new molecules to test.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2079-3197/8/3/77/s1. Table S1: Docking scores, ∆Gbinding and protein-ligand interactions of 36 inhibitors; Figure S1: Ligand interaction diagram of the (a) DB08239 binding pose in 3C-like Protease; (b) DB07358 binding pose in Papain-like Protease; (c) DB02933 binding pose in nsp14; Figure S2: Ligand interaction diagram of the (a) DB1792 binding pose in nsp15; (b) DB01859 binding pose in nsp16; Figure S3: Ligand interaction diagram of the (a) Synapoyl Coenzyme A binding pose in nsp4; (b) the DB02794 binding pose in nsp9; Figure S4: Ligand interaction diagram of the (a) DB04579 binding pose in helicase, pocket A; (b) PCI-27483 binding pocket in helicase, pocket B; Figure S5: Ligand interaction diagram of the (a) Flavin-N7 Protonated-Adenine Dinucleotide binding pose in nsp7-8, pocket A; (b) DB06955 binding pocket in nsp7-8, pocket B; Figure S6: Ligand interaction diagram of the (a) DB04579 binding pose in nsp7-8-12, pocket A; (b) PCI-27483 in nsp7-8-12, pocket B.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.T.; methodology, U.P. and M.T.; formal analysis, G.C.; investigation and data curation U.P. and G.C; writing—original draft preparation, M.T. and U.P.; writing—review and editing, M.T., U.P., A.M.A., M.R.G., M.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Regional Assessorship of Productive Activities—Department of Productive Activities, funds: FSC 2014/2020. Project name: Computational Molecular Design e Screening–CheMISt- CUPG77B17000110001, Scientific Research within the “Patto per il sud” of the Sicily Region.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rothan, H.A.; Byrareddy, S.N. The epidemiology and pathogenesis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 109, 102433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.; Chen, L.; Lan, R.; Shen, R.; Li, P. Computational screening of antagonists against the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) coronavirus by molecular docking. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 2, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhong, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Li, M.; Li, X.; et al. Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods. Acta Pharm. Sin. B. 2020, 10, 766–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciliberto, G.; Cardone, L. Boosting the arsenal against COVID-19 through computational drug repurposing. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 26, 946–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpakom, S.; Iorio, F.; Eyers, P.A.; Escott, K.J.; Hopper, S.; Wells, A.; Doig, A.; Guilliams, T.; Latimer, J.; McNamee, C.; et al. Drug repurposing: Progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 18, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauria, A.; Tutone, M.; Almerico, A.M. Virtual lock-and-key approach: The in silico revival of Fischer model by means of molecular descriptors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 4274–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprea, T.I.; Mestres, J. Drug repurposing: Far beyond new targets for old drugs. AAPS J. 2012, 14, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhaelen, Q.; Mamoshina, P.; Aliper, A.M.; Artemov, A.; Lezhnina, K.; Ozerov, I.; Labat, I.; Zhavoronkov, A. Design of efficient computational workflows for in silico drug repurposing. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March-Vila, E.; Pinzi, L.; Sturm, N.; Tinivella, A.; Engkvist, O.; Chen, H.; Rastelli, G. On the integration of in silico drug design methods for drug repurposing. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Fang, H.; Reagan, K.; Xu, X.; Mendrick, D.L.; Slikker, W.; Tong, W. In silico drug repositioning-what we need to know. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprea, T.I.; Bauman, J.E.; Bologa, C.G.; Buranda, T.; Chigaev, A.; Edwards, B.S.; Jarvik, J.W.; Gresham, H.D.; Haynes, M.K.; Hjelle, B.; et al. Drug repurposing from an academic perspective. Drug Discov. Today Ther. Strateg. 2011, 8, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauria, A.; Tutone, M.; Barone, G.; Almerico, A.M. Multivariate analysis in the identification of biological targets for designed molecular structures: The BIOTA protocol. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 75, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsello, S.M.; Bittker, J.A.; Liu, Z.; Gould, J.; McCarren, P.; Hirschman, J.E.; Johnston, S.E.; Vrcic, A.; Wong, B.; Khan, M.; et al. The Drug Repurposing Hub: A next-generation drug library and information resource. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farha, M.A.; Brown, E.D. Drug repurposing for antimicrobial discovery. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleire, L.; Førde-Tislevoll, H.E.; Netland, I.A.; Leiss, L.; Skeie, B.S.; Enger, P.Ø. Drug repurposing in cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 124, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.; Erez, T.; Reynolds, I.J.; Kumar, D.; Ross, J.; Koytiger, G.; Kusko, R.; Zeskind, B.; Risso, S.; Kagan, E.; et al. Drug repurposing from the perspective of pharmaceutical companies. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutone, M.; Perricone, U.; Almerico, A.M. Conf-VLKA: A structure-based revisitation of the Virtual Lock-and-key Approach. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2017, 71, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutone, M.; Almerico, A.M. The In Silico Fischer Lock-and-Key Model: The Combined Use of Molecular Descriptors and Docking Poses for the Repurposing of Old Drugs. Targeting Enzymes for Pharmaceutical Development. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2089, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Li, F.; Ma, R.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Shi, Y.; Pan, Y.; et al. Repurposing Low-Molecular-Weight Drugs Against the Main Protease of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Almes, F.J. Repurposing approved drugs as potential inhibitors of 3CL-protease of SARS-CoV-2: Virtual screening and structure based drug design. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2020, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touret, F.; Gilles, M.; Barral, K.; Nougairède, A.; van Helden, J.; Decroly, E.; de Lamballerie, X.; Coutard, B. In vitro screening of a FDA approved chemical library reveals potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 replication. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyr, Z.A.; Gorshkov, K.; Chen, C.Z.; Zheng, W. Drug discovery strategies for SARS- CoV-2. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2020, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavasotto, C.; Di Filippo, J. In silico Drug Repurposing for COVID-19: Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Proteins through Docking and Consensus Ranking. Mol. Inform. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J. Fast Identification of Possible Drug Treatment of Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19) through Computational Drug Repurposing Study. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 3277–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, W.R.; Gomes, R.A.; S Novaes, A.L.; Goulart Trossini, G.H. Ligand and structure- based virtual screening applied to the SARS-CoV-2 main protease: An in silico repurposing study. Future Med. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hou, Y.; Shen, J.; Huang, Y.; Martin, W.; Cheng, F. Network-based drug repurposing for novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2. Cell. Discov. 2020, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.U.; Froeyen, M. Structural elucidation of SARS-CoV-2 vital proteins: Computational methods reveal potential drug candidates against main protease, Nsp12 polymerase and Nsp13 helicase. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, C. Coronavirus puts drug repurposing on the fast track. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.E.; Jang, G.M.; Bouhaddou, M.; Xu, J.; Obernier, K.; White, K.M.; O’Meara, M.J.; Rezelj, V.V.; Guo, J.Z.; Swaney, D.L.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature 2020, 583, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisti, V.; Wieder, O.; Garon, A.; Seidel, T.; Urban, E.; Langer, T. A Computational Approach to Identify Potential Novel Inhibitors against the Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Mol. Inform. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Knox, C.; Guo, A.C.; Shrivastava, S.; Hassanali, M.; Stothard, P.; Chang, Z.; Woolsey, J. DrugBank: A comprehensive resource for in silico drug discovery and exploration. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2006, 34, D668–D672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger Epik; Schrödinger: München, Germany, 2018.
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.M.; Battistuz, T.; Bhat, T.N. The protein data bank. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 2002, 58, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger Protein Preparation Wizard; Schrödinger: München, Germany, 2018.
- Schaller, D.; Šribar, D.; Noonan, T.; Lihua Deng, L.; Nguyen, T.N.; Pach, S.; Machalz, D.; Bermudez, M.; Wolber, G. Next generation 3D pharmacophore modeling. WIREsComput. Mol. Sci. 2020, 10, e1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Glide; Schrödinger: München, Germany, 2018.
- Sherman, W.; Day, T.; Jacobson, M.P.; Friesner, R.A.; Farid, R. Novel procedure for modeling ligand/receptor induced fit effects. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 534–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger LLC Prime; Version 3; Schrödinger: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- Perricone, U.; Wieder, M.; Seidel, T.; Langer, T.; Padova, A.; Almerico, A.M.; Tutone, M. A molecular dynamics–shared pharmacophore approach to boost early enrichment virtual screening. A case study on PPAR alpha. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 1399–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almerico, A.M.; Tutone, M.; Lauria, A. Receptor-guided 3D-QSAR approach for the discovery of c-kit tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J. Mol. Model. 2012, 18, 2885–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Almerico, A.M.; Tutone, M.; Pantano, L.; Lauria, A. Molecular dynamics studies on Mdm2 complexes: An analysis of the inhibitor influence. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 424, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genheden, S.; Ryde, U. The MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods to estimate ligand-binding affinities. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutone, M.; Pibiri, I.; Lentini, L.; Pace, A.; Almerico, A.M. Deciphering the Nonsense Readthrough Mechanism of Action of Ataluren: An in Silico Compared Study. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutone, M.; Virzì, A.; Almerico, A.M. Reverse screening on indicaxanthin from Opuntia ficus-indica as natural chemoactive and chemopreventive agent. J. Theor. Biol. 2018, 455, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Yu, R. Molecular dynamics and free energy studies on the wild-type and double mutant HIV-1 protease complexed with amprenavir and two amprenavir-related inhibitors: Mechanism for binding and drug resistance. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massova, I.; Kollman, P.A. Combined molecular mechanical and continuum solvent approach (MM-PBSA/GBSA) to predict ligand binding. Perspect. Drug Discov. 2000, 18, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Morin, P.; Wang, W.; Kollman, P.A. Use of MM-PBSA in Reproducing the Binding Free Energies to HIV-1 RT of TIBO Derivatives and Predicting the Binding Mode to HIV-1 RT of Efavirenz by Docking and MM-PBSA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 5221–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Zia, K.; Ashraf, S.; Uddin, R.; Ul-Haq, Z. Identification of chymotrypsin-like protease inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 via integrated computational approach. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, R.; Das, A.; Prashar, V.; Kumar, M. Potential inhibitors against papain-like protease of novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) from FDA approved drugs. Chemrxiv. Org. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, C.; Ginex, T.; Maestro, I.; Nozal, V.; Barrado-Gil, L.; Cuesta-Geijo, M.A.; Urquiza, J.; Ramírez, D.; Alonso, C.; Campillo, N.E.; et al. COVID-19: Drug targets and potential treatments. J. Med. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lou, Z.; Ma, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, Z.; Tong, X.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, Y.; Deng, H.; Bartlam, M.; et al. Crystal Structure of the C-Terminal Cytoplasmic Domain of Non-Structural Protein 4 from Mouse Hepatitis Virus A59. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, G.; Fry, E.; Carter, L.; Sainsbury, S.; Walter, T.; Nettleship, J.; Berrow, N.; Owens, R.; Gilbert, R.; Davidson, A.; et al. The nsp9 Replicase Protein of SARS-Coronavirus, Structure and Functional Insights. Structure 2004, 12, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).