Abstract
The daggertooth pike conger, Muraenesox cinereus, is an important demersal fish species in East Asia but the catch amount has declined in recent years. Spawning areas of M. cinereus have not yet been determined; identifying these have serious implications for resource management. Ichthyoplankton surveys are an effective method of distinguishing fish spawning areas and periods. Fish eggs were sampled from the waters adjacent to South Korea in August 2020 and 2022 using a Multiple Opening/Closing Net and Environmental Sensing System or a bongo net. In 2021, M. cinereus eggs were not collected. Three unidentified eggs (2.0–2.2 mm in diameter) were collected from the southeastern sea of Jeju Island at a seawater depth of 20–30 m and temperature of 20–22 °C. Muraenesox cinereus preleptocephali were gathered at 10–20 m depths from Jeju Island’s southernmost and eastern sea areas. The eggs and preleptocephali were identified as M. cinereus by their mitochondrial DNA 16S rRNA sequences. This is a new finding of eggs and leptocephalus of Muraenesox cinereus off Jeju Island, South Korea, which increases our understanding of the recruitment process of M. cinereus to facilitate resource management and species conservation.
1. Introduction
The daggertooth pike conger (Muraenesox cinereus), in the Muraenesocidae family, of the order, Anguilliformes, is widely distributed throughout South Korea, Japan, the Yellow Sea, East China Sea, and Indo-Western Pacific Ocean [1,2]. These fish live in soft sand at a water depth of less than 100 m and feed mainly on small benthic fish and crustaceans [3,4,5]. Muraenesox cinereus is an important commercial species mainly caught in trawl and longline fisheries in South Korea, Japan, and China [6]. Various studies have been conducted on M. cinereus age and growth [7,8,9], maturation and spawning [10], feeding [3,11], distribution and migration [12], reproductive ecology [13,14], resource amount, and management planning [15,16]. Through the collection of mature mothers, spawning areas of M. cinereus have been suggested in the seas around Jeju Island, Seto Island of Japan, and the coast of Zhejiang Province, China [10,13,17]. However, no studies have accurately identified M. cinereus spawning areas in natural conditions according to the presence of fish eggs and preleptocephali, that is, the stage immediately after hatching.
Similarly, identifying the spawning areas of two other commercial Anguilliformes species, Anguilla japonica and Conger myriaster, was a long-standing problem in marine science. However, following the collection of fish eggs and preleptocephali from the 1990s to the present, researchers discovered that these species spawn in the Mariana Trench in the Philippines [18,19,20]. In addition, spawning areas for C. myriaster have only been identified on the Kyushu-Palau Ridge and in the Mariana Trench based on the appearance of preleptocephali; eggs in the natural state have not yet been collected [20]. Umezawa et al. [21] conducted on egg development during the artificial breeding of Japanese M. cinereus. Further, Ji et al. [6] conducted an morphological characteristics and age analysis of the otoliths of M. cinereus leptocephali collected offshore of Jeju Island, which suggested that the spawning areas of M. cinereus may be located in the East China Sea, instead of coastal areas. A subsequent study of eggs recorded the presence of M. cinereus in the East China Sea close to northern Taiwan in summer [22]. However, no records currently exist of M. cinereus eggs in the waters adjacent to South Korea and Japan. Morphology-based identification methods used to estimate the spawning areas and life stages of fish include examining the gonads of mature fish and examining eggs and larvae fish [23]. For the latter, egg and larval samples are collected using an ichthyoplankton net at sea, followed by sorting and identification processes [24]. Previous studies based on these morphological identification methods have resulted in many cases of misidentification; however, the development of molecular identification technology has made it possible to accurately identify various eggs and juveniles [25]. The accurate identification of fish eggs using DNA analysis has enabled the discovery of spawning areas for different fish species [26,27]. In the current study, we aimed to identify the spawning areas of M. cinereus in the waters adjacent to South Korea. We identified M. cinereus eggs in their natural state for the first time off of the southeast coast of Jeju Island during a summertime (August) monitoring survey. The detailed morphological characteristics, distribution depths, and marine environment of M. cinereus eggs and leptocephali are reported. Additionally, for the first time, the vertical distribution of M. cinereus preleptocephali and leptocephali have been reported.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
Ichthyoplankton samples were collected from the sea offshore of the Jeju Island in 2020 and 2022 using Tamgu 22 (1458 tons) and Tamgu 23 (1670 tons) fishery resource research vessels operated by the National Institute of Fisheries Science (NIFS) (Figure 1). The Multiple Opening/Closing Net and Environmental Sensing System (MOCNESS) was used to collect samples at 22 sampling stations, whereas bongo nets were used to collect samples from 81 sampling stations (Figure 1). Tamgu 22 and 23 operated simultaneously, and 14 days were required with a 24 h investigation per day. Samples were collected by nets for 5 min in each of the seven water layers (surface to 10 m, 10–20 m, 20–30 m, 30–40 m, 40–60 m, 60–80 m, 80–110 m) using a MOCNESS device (net area 1 m2, mesh 330 µm). Oblique collection was performed from the bottom to the surface using a Bongo net (net area 80 cm, mesh 330 µm).
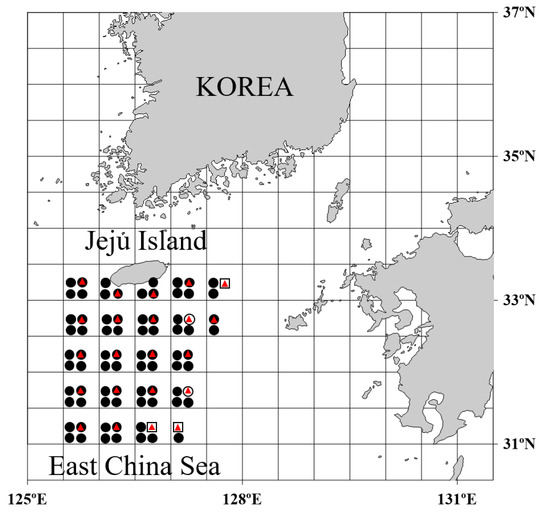
Figure 1.
Location of sampling stations of Muraenesox cinereus eggs and preleptocephali in waters adjacent to Jeju Island in August 2020 and 2022. White dots indicate stations where M. cinereus eggs were collected. White squares indicate stations where M. cinereus preleptocephali and leptocephali were collected. Black dots show sampling stations using the bongo net. Red triangles show sampling stations using Multiple Opening/Closing Net and Environmental Sensing System (MOCNESS).
For species composition analysis on the collected ichthyoplankton sample, M. cinereus fish eggs and preleptocephali were separated. Three individual M. cinereus eggs (2.0–2.2 mm) were collected from the MOCNESS and bongo net at the southernmost end of Jeju Island in August, and eight individuals (11.5–34.4 mm total length; TL) of M. cinereus preleptocephali and leptocephali were collected from MOCNESS at the southernmost end or the eastern sea of Jeju Island in July (Table 1). Muraenesox cinereus preleptocephali (11.5–13.5 mm TL) were collected at 10–20 m depths from the eastern sea area of Jeju Island (Table 1). The flow meter attached to the MOCNESS was used to quantitatively analyze water filtered by the net. The number of individuals that appeared was converted to the number of individuals per unit volume (ind./1000 m3).

Table 1.
List of Muraenesox cinereus eggs and leptocephali collected from offshore of Jeju Island.
To evaluate the marine environment of the study area, the temperature and salinity of each water layer were measured using a conductivity meter, temperature, and depth sensor (SBE 9plus; Sea-Bird Scientific, Bellevue, WA, USA). The collected samples were fixed on-site in 70% ethanol and then registered and stored in the Ichthyoplankton Laboratory of the Fisheries Resources Research Center, NIFS.
2.2. Morphological Identification and Eggs Type Divide
The observation of the morphology and measurement of fish eggs and larvae were conducted using a stereomicroscope (SZX-16; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). Fish eggs were classified into types by egg diameter, embryo development, and perivitelline space for measurement. At least five fish eggs per type for each station were subjected to molecular identification. Leptocephali were identified according to Tabeta and Mochioka [28] and Ji et al. (2011) [6]. Development of leptocephali was divided into two stages (preleptocephalus and leptocephalus), based on the criteria of Kurogi et al. [20].
2.3. Genomic DNA Extraction, Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), and Sequencing
Fish eggs fixed in ethanol were pierced with a needle, right eyeball of eight leptocephali were extracted using forceps, and DNA extraction was performed using the GeneAll Exgene™ Clinic SV DNA extraction kit (GeneAll, Seoul, Korea). To amplify the 16s rRNA genes of mitochondrial DNA, 16Sar (5′-CGC CTG TTT ATC AAA AAC AT-3′) and 16Sbr (5′-CCG GTC TGA ACT CAG ATC ATG T-3′) primers were used [29]. After adding 4 μL of genomic DNA to AccuPower® PCR Premix, tertiary distilled water was added to reach a volume of 20 μL. Subsequently, the PCR method was performed using the Thermal cycler (C1000™; Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) as follows: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 3 min; 37 cycles of PCR reaction (denaturation at 94 °C for 3 s, annealing at 52 °C for 30 s, extension at 72 °C for 1 min); final extension at 72 °C for 5 min.
After completion of the PCR, the PCR product was injected into 1.5% agarose gel, then electrophoresed for 25 min at 100 voltages in a submarine electrophoresis system (Mupid-2plus; Takara Bio Inc., Shiga, Japan) to determine. The final output was confirmed on a gel documentation system (Nippon genetics, Tokyo, Japan). Then, the PCR products were purified using ExoSAP-IT (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, USA), and the ABI BigDye Terminator Cycle Sequencing Ready Reaction Kit v 3.1 was used with an ABI 3730XL DNA Analyzer (Applied Biosystems Inc., Foster City, CA, USA) to obtain the nucleotide sequence by cycle sequencing under the following conditions: 35 cycles of PCR reaction (denaturation at 94 °C for 10 s, annealing at 56 °C for 10 s, extension at 60 °C for 3 min). The nucleotide sequence was aligned using the ClustalW program [30] (BioEdit version 7 [31]). The genetic distance between nucleotide sequences was calculated using the Kimura-2-parameter model [32] (Mega X [32]). The neighbor-joining tree was constructed using the Kimura-2-parameter model [33], with the confidence value assessed using 1000 bootstrap replications. Species identification was performed by comparing the genetic information registered in the National Center for Biotechnology Information.
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Identification Morphological Characteristics of M. cinereus Eggs and Preletocephalus
Details of the collected M. cinereus eggs and preleptocephali are presented in Table 1. After analyzing the sequence of 568 base pairs of mitochondrial DNA 16S rRNA, three eggs and eight preleptocephali collected from the southern sea and the southernmost part of Jeju Island were identified as M. cinereus, by having a 100% match with the nucleotide sequence of adult M. cinereus. Muraenesox cinereus eggs and preleptocephali were identical to those of Muraenesox bagio at a genetic distance of 95.3% (Table 2).

Table 2.
Genetic distance among Muraenesox cinereus eggs, preleptocephalus, and six other Anguilliformes species.
The neighbor-joining tree showed that M. cinereus eggs and preleptocephali were clustered perfectly with adult M. cinereus (Figure 2) and the next nearest neighbor was M. bagio.
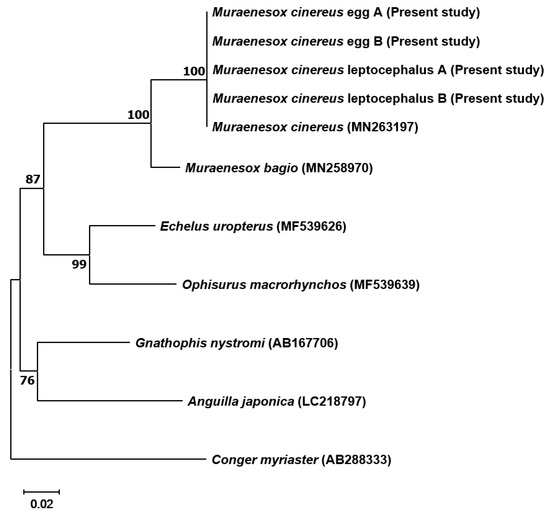
Figure 2.
Neighbor-joining tree based on mtDNA 16S rRNA sequences, showing the relationships between two M. cinereus eggs and two preleptocephali from this study and six Anguilliformes species. The neighbor-joining tree was constructed using the Kimura 2-parameter distance model, with 1000 bootstrap replications. The scale bar indicates a genetic distance of 0.02.
The M. cinereus eggs analyzed in this study were colorless, transparent, spherical, and segregated paternal eggs with a diameter of 2.0–2.2 mm (Figure 3, Table 1). The collected M. cinereus eggs were in an early stage of embryogenesis before the pigmentation of vesicles on the eyeball. The size of the perivitelline space was narrow for the species, yolk was yellow and the embryo was elongated around the yolk in a round shape (Figure 3).
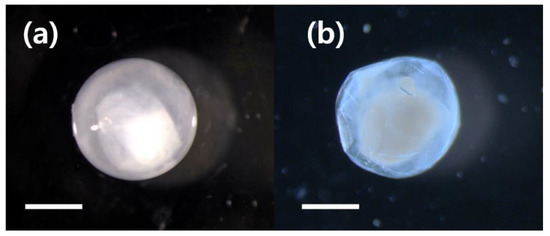
Figure 3.
Photograph of an eggs of M. cinereus collected from waters adjacent to Jeju Island. (a) egg diameter = 2.1 mm, (b) egg diameter = 2.0 mm. Scale bar = 1.0 mm.
Developmental counts and measurement of M. cinereus preleptocephali and leptocephali are presented in Table 3. The TL of hatched M. cinereus preleptocephali and leptocephali was 11.5–13.5 and 20.9–34.4 mm, respectively, and their morphological features were as follows: total myomeres 145–153; preanal myomeres, 93–98; transparent and deeply compressed body; relatively large head; highly acute anterior end of snout; well-developed eyes; fang-like teeth on both jaws; two nostrils present in front of eyes; liver tissue located in anterior body; anus located in posterior body; branch-shaped melanophores present along the lateral surfaces of the head to behind the anus and extending to the caudal terminus; and branch-shaped melanophores present in the intestine (Figure 4). The upper jaw of 11.5 mm TL M. cinereus preleptocephalus was more protruded than the lower jaw (Figure 4a), and the length of both upper and lower jaws were identical in leptocephalus of 23.5 mm TL (Figure 4b). The tail fin of leptocephalus with 31.5–34.4 mm TL had begun to develop (Figure 4c). As they grew from 31.5 mm TL and above following hatching, their body depth became smaller and their myomeres became identical to those of an adult fish.

Table 3.
Comparisons of measurements and counts for Muraenesox cineleus preleptocephali and leptocephali.
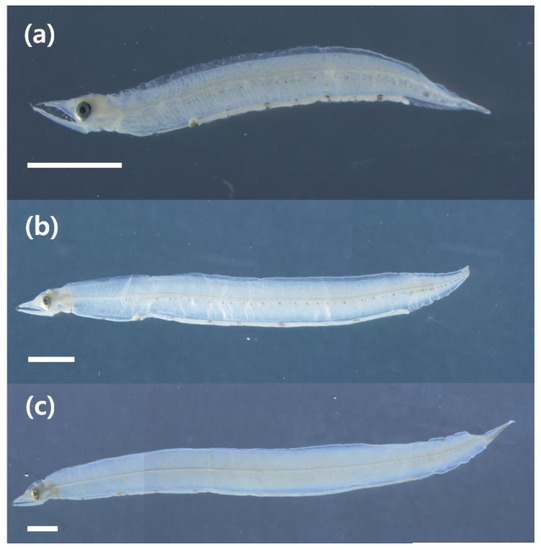
Figure 4.
Photograph of preleptocephalus and leptocephali of M. cinereus collected from waters adjacent to Jeju Island: (a) preleptocephalus, total length (TL) = 11.5 mm, (b) leptocephalus, total length (TL) = 23.5 mm, (c) leptocephalus, total length (TL) = 34.4 mm Scale bars = 2.0 mm.
3.2. Spawning Area Characteristics of Muraenesox cinereus and Collection of Preleptocephalus
During the ichthyoplankton investigation performed in this study in the vast sea area of the southern sea of Jeju Island, M. cinereus fish eggs and preleptocephalus appeared only in Jeju Island’s eastern and southern sea areas (Figure 1). Muraenesox cinereus fish eggs were collected at two sampling stations, covering the scope of latitude of 31°75′–32°75′ and longitude of 127°25′ in August 2020 and 2022, whereas the M. cinereus preleptocephalus and leptocephalus were collected from three sampling stations with the scope of the latitude of 31°25′–33°25′ and longitude of 126°75′–127°75′ in July (Table 1).
The spawning ground where M. cinereus fish eggs were gathered in August was at a water level of 120 m, surface level water temperature of 30 °C, and 100–120 m water temperature of 16 °C. The salinity was 31 Practical Salinity Unit (PSU) at the surface level and 34.5–34.7 PSU at 90–120 m. These spawning areas are affected by the warm Kuroshio Current in August. Muraenesox cinereus eggs were distributed over a depth of 20–30 m, water temperature range of 20–22 °C, and salinity range of 33.4–33.6 PSU (Figure 4). All M. cinereus fish eggs were at 20–30 m depths (19.3 ind./1000 m3), with no eggs gathered at 0–10, 30–40, 40–60, 60–80, 80–110 m depths (Figure 5a). The summer southern area around Jeju Island where M. cinereus fish eggs were collected in this study had a strong thermocline with increasing water depth. The salinity tended to increase as the water depth increased; however, salinocline was not formed at 30–120 m depths. Muraenesox cinereus fish eggs were distributed close to the upper water layer of the thermocline. This is the first study to collect M. cinereus eggs in their natural state from the waters around Jeju Island, which indicates the existence of M. cinereus spawning areas in the waters near South Korea; specifically, in waters 50–100 km off the southeast coast of Jeju Island.
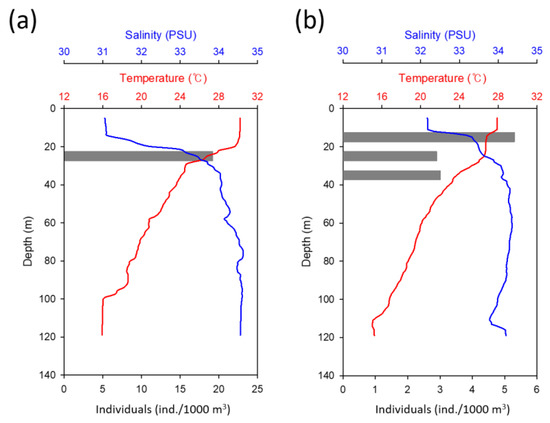
Figure 5.
Water depth, salinity, and temperature distribution of M. cinereus eggs and preleptocephali collected in this study. (a) M. cinereus eggs, (b) M. cinereus preleptocephali and leptocephali.
Muraenesox cinereus preleptocephali and leptocephali were collected in July, and their vertical distribution was concentrated at 10–40 m depths. A total of 5.4 ind./1000 m3 of M. cinereus leptocephali were collected at 10–20 m depths, 3.1–3.2 ind./1000 m3 at 20–30 m and 30–40 m depths, and none were collected at surface layer–10 m, 40–60 m, 60–80 m, and 80–110 m depths (Figure 5b). The water temperature and salinity of their main distribution water depth was 21–27 °C and 33.3–34.2 PSU, respectively. Muraenesox cinereus preleptocephali were collected at 10–20 m depths. In our surveys, M. cinereus preleptocephali and leptocephali were abundant and widely distributed during July (Figure 1). Leptocephali with 11.5–13.5 mm TL were collected from the eastern sea areas of Jeju Island, whereas those with 22.1–34.2 mm TL were collected from the southernmost sea area of Jeju Island (Figure 1).
4. Discussion
In this study, M. cinereus eggs and preleptocephali from the southern sea area of Jeju Island (where mature M. cinereus females had appeared in the past) were collected to accurately investigate the spawning ground. The eggs analyzed were colorless, transparent, spherical, and segregated paternal eggs with a 2.0–2.2 mm diameter (Figure 3). A previous study on egg development during the artificial breeding of Japanese M. cinereus reported that the egg diameter ranges from 1.8 to 2.1 mm, which is slightly smaller than the size of M. cinereus in the wild [21]. Comparing the size of M. cinereus eggs with those of the Anguilliformes species, the former were larger than those of artificial breeding C. myriaster (0.86–1.06 mm), but smaller than those of Ophichthidae (2.20–3.83 mm) [34]. Under artificial breeding conditions, M. cinereus eggs hatch in 36 h at a water temperature of 25 °C [21]. The water temperature of the sea area where the M. cinereus eggs were collected was 23 °C, and the eggs were estimated to have been fertilized within approximately 30 h before collection. Previous studies on the spawning characteristics of M. cinereus based on the collection of mature fish suggested the existence of spawning areas in the waters surrounding Jeju Island, the continental coast of Zhejiang Province in China, and the coast of Seto Island in Japan [10,13,17]. However, spawning areas cannot be accurately estimated from the distribution of mature fish alone. In the case of sedentary fish species that do not migrate to spawn, it is possible to investigate spawning grounds by collecting the distribution of mature fish during the main spawning season, as well as by collecting fish eggs and yolk sac larvae. However, in the case of migratory fish species, it is only possible to accurately estimate spawning areas by collecting eggs or yolk sac larvae, because they migrate to a suitable environment for spawning according to factors such as water temperature, salinity, prey, etc. [19,20].
In mature, female A. japonica and C. myriaster, which migrate long distances for spawning, naturally-spawned fish eggs are rarely found, even after conducting intensive investigation into the estimated sea areas of spawning grounds [18]. Despite searching for young hatchlings and eggs in the sea, the spawning grounds of A. japonica remained a mystery for 100 years and were only recently discovered to be in the western sea area of Mariana Trench through the collection of naturally spawned eggs [18,19]. Collected preleptocephali of C. myriaster allowed its significant spawning ground to be estimated to be in the western sea area of Mariana Trench, with another spawning ground likely formed in Japan’s southernmost end of Ryukyu Island [20]. However, C. myriaster eggs have yet to be collected in nature. The southern sea area of Jeju Island (the study area in this research) is dense in fishery resources as it is a nursery ground and spawning ground for fish that migrate along the Tsushima Warm Current from the East China Sea Kuroshio Current [35,36].
This was the first study to collect M. cinereus eggs in their natural state from the waters around Jeju Island, which indicated the existence of M. cinereus spawning areas in the waters near South Korea; specifically, in waters 50–100 km off the southeast coast of Jeju Island. This agreed with previous research that predicted the formation of a spawning ground near the sea areas of Jeju Island through the collection of mature M. cinereus females [10]. Therefore, we report that one of the principal spawning grounds of M. cinereus in East Asia is in the sea of Jeju Island in the East China Sea, in the route of the Kuroshio and Tsushima Warm Currents with high water temperatures. A spawning area was the east southern sea area of Jeju Island; however, no fish eggs or preleptocephali were collected here. This was attributed to the spawning ground of M. cinereus being impacted by the northward moving ocean current.
A previous study recorded the widespread presence of M. cinereus eggs in the East China Sea to the north of Taiwan during summer [22]. Muraenesox cinereus are also distributed in the waters of East Asian countries such as South Korea, China, and Japan; thus, their spawning areas are also presumed to include various sea areas [10,13,17]. This study was the first to reveal the marine environment and fish egg distribution water depth of a spawning ground of M. cinereus (Figure 4a). The water depth (20–30 m) where M. cinereus fish eggs were collected had a water temperature of 20–22 °C and salinity of 33–34 PSU. In comparison, the eggs of another Anguilliformes species (A. japonica) were collected at water depths of 150–180 m, the water temperature of 20–25 °C, and salinity of 34.4–35.5 PSU. While the water depth was different, the water temperature and salinity were similar to the spawning environment of M. cinereus [37]. The fish egg water layer distribution is different for each major commercial Anguilliformes species, and water depth was considered to be relevant to the spawning sea area. Moreover, the collection period of M. cinereus eggs in the current study coincided with the spawning season of M. cinereus (June–October) caught in the waters around South Korea and Seto Island, Japan [13,14]. Muraenesox cinereus preleptocephali (11.5–34.2 mm TL) were collected at the eastern and southernmost sea areas of Jeju Island in mid-July. Ji et al. [6] reported the daily ring of preleptocephali (16.6–29.0 mm TL) as 18–30 d and estimated that preleptocephali hatched between the end of June and early July. Thus, the primary spawning season of M. cinereus was estimated to be between June and July. Furthermore, Ji et al. [6] performed age analysis on the leptocephali of M. cinereus (16.6–29.0 mm in total length) and suggested spawning areas near Jeju Island or in the East China Sea. These findings are supported by the results of our study, which identified M. cinereus eggs in the waters around Jeju Island and its southernmost tip during August.
This research was the first to reveal the vertical distribution of M. cinereus leptocephali (Figure 4b). Muraenesox cinereus preleptocephali and leptocephali were distributed in water levels at 10–40 m depths, with a marked increase at 10–20 m, followed by 20–30 m. Muraenesox cinereus leptocephali were distributed at 10–20 m. The distribution depth of M. cinereus preleptocephali and M. cinereus eggs were identical; therefore, both fishes were determined to spawn, hatch, and grow at approximately 20 m depth. Furthermore, A. japonica and C. myriaster preleptocephali have been found to be distributed at 150–200 and 50–150 m depths [19,20]. Research on the vertical distribution of Anguilliformes leptocephali from sea areas near the North Equatorial Current have revealed that Ariosoma, Avocettina, Nemichthys, and Serrivomerdiae leptocephali are dominant at 30–50 m depths, where the surface water layers are mixed, whereas Anguilla, Conger, Derichthys, Chlopsidae, Muraenidae, and Ophichthidae leptocephali are distributed at the top layer of the 70–100 m thermocline [38]. Thus, the vertical distribution of preleptocephali could be distinguished by species, and M. cinereus leptocephali were determined to be distributed in a shallower layer than A. japonica leptocephali and C. myriaster preleptocephali.
Previous studies on near-sea M. cinereus leptocephali distribution are lacking; however, research has been conducted on the species’ distribution in the sea area near Jeju Island in South Korea and M. cinereus leptocephali just before metamorphosis were collected in August from the coral reef at the coast of Ishigaki Island located east of Taiwan [39]. Ji et al. [6] reported that M. cinereus leptocephali before metamorphosis, collected from the south coast of South Korea in August, spawned near the south coast, migrated with the current after hatching, and spent their initial stage undergoing metamorphosis near the coast.
It is postulated that that M. cinereus distributed in the waters around South Korea spawn in the waters around Jeju Island during the primary spawning season, after which the hatched leptocephali grow up and move north with the oceanic current toward the coast. In the future, a more intensive survey of the spawning areas and period of M. cinereus could shed light on the migration or recruitment process of M. cinereus leptocephali with oceanic currents. Furthermore, future studies should be conducted to collect more detailed information on M. cinereus through continuous monitoring of their early life cycles, such as spawning characteristics and growth, which are essential for resource management.
5. Conclusions
This is a new finding of eggs and leptocephalus of M. cinereus in nature during August 2020 and 2022, as part of an analysis of eggs and larvae for major fishery resources in the waters adjacent to South Korea. The collected eggs appeared in the early stage of embryonic development at a depth of 20–30 m and temperature of 20–22 °C. The eggs were identified as M. cinereus using the mitochondrial DNA 16s rRNA region. Muraenesox cinereus leptocephali and preleptocephali were distributed between depths of 10–40 m and 10–20 m, respectively, with the depth distribution of leptocephali concurring with that of the fish eggs in the spawning ground. Muraenesox cinereus spawns in the southernmost end of Jeju Island and East China Sea between July and August, and the hatched preleptocephali migrate northward with the current for their initial stage of life. Muraenesox cinereus is an important commercial species in South Korea, Japan, and China, but the catch amount has been rapidly decreasing in recent years, requiring significant efforts for resource management. Our understanding of the recruitment process of M. cinereus and help facilitate resource management and species conservation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.-S.J.; methodology, H.-S.J. and J.-K.K.; software, H.-S.J.; validation, H.-S.J. and J.-K.K.; investigation, H.-S.J. and H.-J.Y.; data curation, H.-S.J.; writing—original draft preparation, H.-S.J.; writing—review and editing, H.-S.J. and J.-K.K.; visualization, H.-S.J.; supervision, S.-J.L.; project administration, S.K.; funding acquisition, S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Institute of Fisheries Science (NIFS, R2023001).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The sequence data that support the findings of this study are deposited in NCBI/GenBank (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, accessed on 3 January 2023) under accession numbers MN263197, MN258970, MF539626, MF539639, AB167706, LC218797, AB288333.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the many researchers and crew of the Tamgu 22, 23 fishery resource research vessels (NIFS) for the survey.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Russel, B.C.; Houston, W. Offshore fishes of the Arafura Sea. Beagle 1989, 6, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschmeyer’s Catalog of Fishes. Available online: http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/fishcatmain.asp (accessed on 13 December 2022).
- An, Y.S.; Park, J.M.; Kim, H.J.; Haeck, G.W. Feeding habitat of daggertooth pike conger Muraenesox cinereus in the coastal water off Goseong, Korea. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 45, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. Fishbase. Available online: http://www.fishbase.org (accessed on 2 January 2023).
- NIFS (National Institute of Fisheries Science). Ecology and Fishing Ground of Fisheries Resources in the Korean Waters; Ye-Moon-Publishing: Busan, Korea, 2021; pp. 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, H.S.; Kim, J.K.; Oh, T.Y.; Choi, K.H.; Choi, J.H.; Seo, Y.I.; Lee, D.W. Larval distribution pattern of Muraenesox cinereus (Anguilliformes: Muraenesocidae) leptocephali in waters adjacent to Korea. Ocean Sci. J. 2015, 50, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Kang, Y.J.; Park, C.S. A study on the stock management of sharp-toothed eel, Muraenesox cinereus (FORSKAL) in Korean waters II. Age and growth. J. Korean Soc. Fish. Res. 1998, 1, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Watari, S.; Murata, M.; Hinoshita, Y.; Mishiro, K.; Oda, S.; Ishitani, M. Re-examination of age and growth of daggertooth pike conger Muraenesox cinereus in the western Seto Inland Sea. Jpn. Fish. Sci. 2013, 79, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kor, E.H.; Kwon, D.H.; Kim, Y.H. Age and growth of daggertooth pike conger Muraenesox cinereus in the South Sea of Korea. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 52, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, H.K.; Seo, Y.I.; Oh, T.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, S.G.; Choi, M.S. Reproductive ecology of the sharp toothed eel in the southern Korean waters. Korean Soc. Fish. Technol. 2012, 48, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wu, C. Feeding habit of conger pike Muraenesox cinereus in Zhejiang coastal waters. J. Zhejiang Ocean Univ. 1992, 2, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki, T.; Ueta, Y.; Hamano, T. Distribution and migration of daggertooth pike-conger Muraenesox cinereus in the eastern Seto Inland Sea, Japan estimated by mark and recapture experiments. Nippon. Suisan Gakkaishi 2012, 78, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Mototani, T.; Murayama, F.; Sakamoto, T. Basic reproductive biology of daggertooth pike conger, Muraenesox cinereus: A possible model for oogenesis in Anguilliformes. Zool. Lett. 2015, 1, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kor, E.H.; Kwon, D.H.; Jang, C.S. Basic reproductive biology of Muraenesox cinereus in Korean waters. J. Korean Soc. Fish. Technol. 2018, 54, 353–359. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.D.; Xu, H.X. Biomass estimates of Muraenesox cinereus are calculated by LCA in the East China Sea. J. Zhejiang Ocean Univ. 2007, 4, 399–403. [Google Scholar]
- Watari, S.; Murata, M.; Bada, T.; Oda, S.; Ishitani, M.; Mishiro, K.; Uchida, Y. Fisheries resource management of the daggertooth pike conger, Muraenesox cinereus, using existing limited datasets in western Seo Inland Sea, Japan. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2014, 21, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, U.; Tokimura, M.; Horikawa, H.; Nakabo, T. Fisheries and Fisheries of the East China and Yellow Seas; Tokai University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 2007; pp. 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto, K. Discovery of the spawning area for Japanese eel. Nature 1992, 356, 789–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, K.; Chow, S.; Otake, T.; Kurogi, H.; Mochioka, N.; Miller, M.J.; Aoyama, J.; Kimura, S.; Watanabe, S.; Yoshinaga, T.; et al. Oceanic spawning ecology of freshwater eels in the western North Pacific. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurogi, H.; Mochioka, N.; Okazaki, M.; Takahashi, M.; Miller, M.J.; Tsukamoto, K.; Ambe, D.; Katayama, S.; Chow, S. Discovery of a spawning area of the common Japanese conger Conger myriaster along the Kyushu-Palau ridge in the western north Pacific. Fish. Sci. 2012, 78, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezawa, A.; Otake, T.; Hirokawa, J.; Tsukamoto, K.; Okiyama, M. Development of the eggs and larvae of the pike eel, Muraenesox cinereus. Jpn. J. Ichthyol. 1991, 38, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Chiu, M.Y.; Shih, Y.M.; Chen, I.S.; Lee, M.A.; Shao, K.T. Species composition and assemblages of ichthyoplankton during summer in the East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2016, 126, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIFS (National Institute of Fisheries Science). Fisheries Resources Investigation Techniques; National Institute of Fisheries Science: Busan, Korea, 2021; p. 170. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, H.S.; Yoo, H.J.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, D.N.; Kim, S.T.; Kim, J.N.; Kim, H.J.; Moon, S.Y.; Shin, D.H.; Oh, T.Y.; et al. Fish eggs, Larvae and Juveniles of Korea; Hangeul Graphics: Busan, Korea, 2020; p. 442. [Google Scholar]
- Lira, N.L.; Tonello, S.; Lui, R.L.; Traldi, J.B.; Brandão, H.; Oliveira, C.; Blanco, D.R. Identifying fish eggs and larvae: From classic methodologies to DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 1713–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.H.; Kim, J.K. First report on the occurrence of eggs of the small yellow croaker Larimichthys polyactis from Chilsan-do Island, Jeollanam-do, Korea. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 53, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.I.; Ji, H.S.; Yu, H.J.; Hwang, K.S.; Kim, D.N. Distribution of eggs and larvae in coastal waters of Korea. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2021, 54, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabeta, O.; Mochioka, N. Ophihthidae. In An Atlas of the Early Stage Fishes in Japan; Okiyama, M., Ed.; Tokai Univ Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1998; pp. 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbi, S.R. Nucleic acids II: The polymerase chain reaction. In Molecular Systematics; Hilli, D.M., Moritz, C., Mable, B.K., Eds.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 1996; pp. 205–247. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-frendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, N.; Utoh, T.; Yamada, Y.; Okamura, A.; Zhang, H.; Mikawa, N.; Akazawa, A.; Tanaka, S.; Oka, H. Development of embryos and larvae in the common Japanese conger Conger myriaster. Fish. Sci. 2002, 68, 972–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Go, Y.B.; Kim, B.J. Seasonal variation of species composition and distribution of fish eggs and larvae in the western part of Jeju Island, Korea. Korean J. Ichthyol. 2006, 18, 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.B.; Han, S.H. Distribution of mackerel, Scomber japonicus eggs and larvae in the coast of Jeju Island, Korea in spring. J. Korean Soc. Fish. Technol. 2016, 5, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, J.; Watanabe, S.; Miller, M.J.; Mochioka, N.; Otake, T.; Yoshinaga, T.; Tsukamoto, K. Spawning sites of the Japanese eel in relation to oceanographic structure and the west Mariana ridge. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onda, H.; Miller, J.M.; Takeshige, A.; Miyake, Y.; Kuroki, M.; Aoyama, J.; Kimura, S. Vertical distribution and assemblage structure of leptocephali in the North Equatorial Current region of the western Pacific. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 575, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Shibuno, T.; Tsukamoto, K. Leptocephali collected in light traps near coral reef habitats of Ishigaki Island in the southern Ryukyu Island chain. Coastal Mar. Sci. 2010, 34, 41–54. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).