Abstract
Pediatric acute myeloid leukemia (AML) represents 15%–20% of all pediatric acute leukemias. Survival rates have increased over the past few decades to ~70%, due to improved supportive care, optimized risk stratification and intensified chemotherapy. In most children, AML presents as a de novo entity, but in a minority, it is a secondary malignancy. The diagnostic classification of pediatric AML includes a combination of morphology, cytochemistry, immunophenotyping and molecular genetics. Outcome is mainly dependent on the initial response to treatment and molecular and cytogenetic aberrations. Treatment consists of a combination of intensive anthracycline- and cytarabine-containing chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation in selected genetic high-risk cases or slow responders. In general, ~30% of all pediatric AML patients will suffer from relapse, whereas 5%–10% of the patients will die due to disease complications or the side-effects of the treatment. Targeted therapy may enhance anti-leukemic efficacy and minimize treatment-related morbidity and mortality, but requires detailed knowledge of the genetic abnormalities and aberrant pathways involved in leukemogenesis. These efforts towards future personalized therapy in a rare disease, such as pediatric AML, require intensive international collaboration in order to enhance the survival rates of pediatric AML, while aiming to reduce long-term toxicity.
1. Clinical Introduction
1.1. Epidemiology of AML
In children, the most frequently occurring hematological malignancies include acute leukemias, of which 80% are classified as acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and 15%–20% as acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The incidence of AML in infants is 1.5 per 100,000 individuals per year, the incidence decreases to 0.9 per 100,000 individuals aged 1–4 and 0.4 per 100,000 individuals aged 5–9 years, after which it gradually increases into adulthood, up to an incidence of 16.2 per 100,000 individuals aged over 65 years [1]. The underlying cause of AML is unknown, and childhood AML generally occurs de novo. In adult and elderly patients, AML is often preceded by myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), but in children, the occurrence of AML preceded by clonal evolution of preleukemic myeloproliferative diseases, such as MDS or juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML), is rare. Germline affected individuals, such as those with Fanconi anemia or Bloom syndrome, have an increased risk for developing AML as a secondary malignancy [2,3]. Recently, germ-line mutations in several genes, such as TP53, RUNX1, GATA2 and CEBPA, have been found in families with an unexplained high risk of AML, suggesting a familial predisposition to develop AML [4,5,6,7,8].
Children with Down syndrome classically present with a unique megakaryoblastic subtype of AML, classically following a transient myeloproliferative disorder in the neonatal period, which is characterized by somatic mutations in the GATA1 gene. The leukemic cells of patients with Down syndrome are usually highly sensitive to chemotherapy with an exceptional high survival rate, and therefore it is possible to treat these patients with adjusted treatment protocols [9]. In addition, AML may occur following previous radiotherapy or chemotherapy containing alkylating agents or epipodophyllotoxins, as secondary neoplasm. These are typically characterized by either MLL-rearrangements or by monosomy 7 [10,11].
1.2. Diagnostic Approach and Classification
AML is a heterogeneous disease with respect to morphology, immunophenotyping, cooperating underlying germline and somatic genetic abnormalities, as well as clinical behavior. The standard diagnostic process of AML is based on a combination of morphology, cytochemistry, immunophenotyping, cytogenetic and molecular characterization of the leukemic blasts derived from the bone marrow or peripheral blood [12]. Each AML patient can be risk-classified into a clinically relevant subgroup. The previously used morphology-based French-American-British (FAB) classification is nowadays replaced by the World Health Organization (WHO) classification, which also takes karyotype and molecular aberrations into account (Table 1) [13,14]. Cytochemistry and immunophenotyping is generally used to distinguish AML from ALL, which further classifies pediatric AML according to the cell lineage of origin and differentiation stage at which the differentiation arrest occurs. Especially for the diagnosis of FAB-types, M0 and M7 immunophenotyping is indispensable [12,15]. The majority of chromosomal abnormalities is detected by conventional karyotyping and complemented with FISH or reverse transcriptase PCR to detect relevant (cryptic) translocations, fusion genes or loss of chromosome material [16]. In young children under two years of age, it is important to search for specific pediatric AML translocations that are not yet acknowledged in the WHO classification as separate entities, such as t(7;12)(q36;p13), also known as HLXB9-MNX1, t(11;12)(p15;p13)/NUP98-KDM5A and t(1;22)(p13;q13)/RBM15-MKL1 [12,17,18,19].

Table 1.
The WHO classification of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and related neoplasms [14].
| WHO Classification of AML and Related Neoplasms | |
|---|---|
| Acute myeloid leukemia with recurrent genetic abnormalities | AML with t(8;21)(q22;q22); RUNX1-RUNX1T1 |
| AML with inv(16)(p13.1q22) or t(16;16)(p13.1;q22); CBFB-MYH11 | |
| Acute promyelocytic leukemia with t(15;17)(q22;q12); PML-RARA | |
| AML with 11q23 (MLL) abnormalities | |
| AML with t(6;9)(p23;q34); DEK-NUP214 | |
| AML with inv(3)(q21q26.2) or t(3;3)(q21;q26.2); RPN1-EVI1 | |
| t(1;22)(p13;q13); RBM15-MKL1 | |
| Provisional entity: AML with mutated NPM1 | |
| Provisional entity: AML with mutated CEBPA | |
| Acute myeloid leukemia with myelodysplasia-related changes | |
| Therapy-related myeloid neoplasms | |
| Acute myeloid leukemia, not otherwise specified | AML with minimal differentiation |
| AML without maturation | |
| AML with maturation | |
| Acute myelomonocytic leukemia | |
| Acute monoblastic/monocytic leukemia | |
| Acute erythroid leukemia | |
| Pure erythroid leukemia | |
| Erythroleukemia, erythroid/myeloid | |
| Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia | |
| Acute basophilic leukemia | |
| Acute panmyelosis with myelofibrosis | |
| Myeloid sarcoma | |
| Myeloid proliferations related to Down syndrome | Transient abnormal myelopoiesis |
| Myeloid leukemia associated with Down syndrome | |
| Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm | |
1.3. Treatment and Outcome
The clinical outcome of pediatric AML has improved significantly over the past few decades, with current long-term survival rates of ~70% (Table 2) [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. This improvement is due to intensification of chemotherapeutic regimens, better risk-group stratification, better salvage at relapse and improved supportive care. Risk-group stratification is usually based on (cyto)genetic abnormalities present in the leukemic blasts in combination with early response to treatment, either specified as complete remission (CR) rate after one or two courses or applying minimal-residual disease measurements, which in AML is mainly based on flow-cytometry [31]. The chemotherapeutic regimens consist of 4–5 cycles of intensive chemotherapy, typically including cytarabine combined with an anthracycline. In younger adult patients, studies suggest that there is a benefit for outcome using high-dose cytarabine in induction, but from previous trials, a similar effect in pediatric AML patients could not be confirmed [26,32]. In randomized controlled trials, the anthracyclines, daunorubicin and mitoxantrone, resulted in similar overall survival, but mitoxantrone-based treatment eventually resulted in a lower relapse rate [33]. When comparing idarubicin and liposomal daunorubicin, survival was similar, whereas liposomal daunorubicin was more effective in RUNX1/RUNX1T1 translocated cases and caused less treatment-related mortality [34].
The added value of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (SCT) in newly-diagnosed pediatric AML is under discussion, as in general, the occurrence of procedure-related deaths needs to be counterbalanced by the reduction in relapse risk. The procedure-related deaths are dependent on the intensity of the prior induction chemotherapy. SCT in first CR is therefore currently only recommended for a selected subset of high risk cases in most European protocols. SCT plays a more prominent role in most North-American treatment protocols [35,36]. Recent studies show an increase in survival after SCT now that stricter risk stratification is improving. Currently, several trials include minimal residual disease (MRD) levels after Courses 1 or 2 in risk stratification for SCT [37,38,39,40]. Of note is that the excess in mortality and the burden of disease long after myeloablative therapy are not taken into account in the reported survival.
Despite intensive treatment, ~30% of the pediatric patients relapse, and outcome is poor, reflected by the ~30%–40% of patients surviving in the largest and most recent series reported to date [41,42]. Nevertheless, the high frequency of treatment-related deaths (5%–10%), both in treatment protocols for newly-diagnosed, as well as for relapsed disease, and the occurrence of long-term side effects, such as anthracycline-induced cardiomyopathy, illustrate that further intensification of chemotherapy seems no longer feasible [43]. Therefore, knowledge on the molecular and genetic background is of utmost relevance in order to detect novel, leukemia and patient-specific treatment targets.
1.4. Relevant Molecular and Genetic Aberrations in Pediatric AML
AML is thought to arise from at least two classes of cooperating genetic events [44]. Type I abnormalities result in increased, uncontrolled proliferation and/or survival of the leukemic cell and are often activating mutations of genes involved in signal transduction pathways, such as FLT3, KIT, N-RAS, K-RAS and PTPN11. Type II abnormalities impair differentiation and mainly result from genetic aberrations in hematopoietic transcription factors, due to, for instance, the AML-characteristic translocations t(8;21)(q22;q22)/AML1-ETO and 11q23/MLL rearrangements or from mutations in genes, such as NPM1 and CEBPA [7,45,46,47,48]. The most common cytogenetic abnormalities (Type II) in children are t(8;21)(q22;q22), inv(16)(p13.1q22) (together referred to as core binding factor (CBF)-AML), t(15;17)(q22;q21) and 11q23/MLL-rearranged abnormalities (Figure 1A) [49,50,51,52]. Together, these account for approximately half of all pediatric AML cases, a much higher frequency than in adults. Some translocations, for example t(1;22)(p13;q13), t(7;12)(q36;p13) and t(11;12)(p15;p13), are specific for children and are rarely or never found in adults [17,18,19,53,54,55,56,57]. Translocations involving hematopoietic transcription factors often lead to dysregulated gene expression, either as a result of the fusion partner itself or the recruitment of different co-factors to the transcription complex. For example, the MLL gene has histone methyltransferase activity and is part of a chromatin modifying complex. More than 60 fusion partners have been identified in AML, but the breakpoint of the MLL gene is highly conserved [58,59]. Fusion proteins lead to a gain of function of the MLL-complex, resulting in inappropriate histone modification and increased expression of MEIS1 and, specifically, HOXA genes, maintaining a stem-cell phenotype. In addition, the presence of DOT1L, which is recruited into the MLL-complex, is required for the leukemogenic activity of several MLL rearrangements and may be a target for treatment [60,61].
Only 20%–25% of pediatric AML cases are cytogenetically normal [48,62]. Of interest in these cases, specific Type II mutations and translocations are identified in ~70% of the cases, such as NPM1 mutations, biallelic CEBPA mutations, as well as the cryptic translocations, NUP98/NSD1, all invisible with conventional karyotyping and, hence, requiring additional molecular diagnostics (Figure 1B) [17,46,57,63].
The combination of the Type I and Type II mutations does not seem to be completely random; specific combinations seem more prevalent, such as the Ras pathway mutations, which are often found in combination with MLL-rearrangements, KIT mutations, which are mainly found in CBF-AML, and FLT3-itd, which is often seen in combination with PML/RARA and NUP98/NSD1 (Figure 1) [48,57].
Mutations in epigenetic regulators, such as EZH2, ASXL1 and DNMT3A, add another level of complexity and contribute to both the maturation arrest and proliferative capacity, which are needed to develop AML (Figure 2) [63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71]. These mutations are rare in pediatric AML, but specific Type II subgroups present with an altered methylation (hypo- or hyper-methylation), which may indicate that these children could benefit from treatment with demethylating agents or histone modification inhibitors, as recently described for infants suffering from ALL [72].
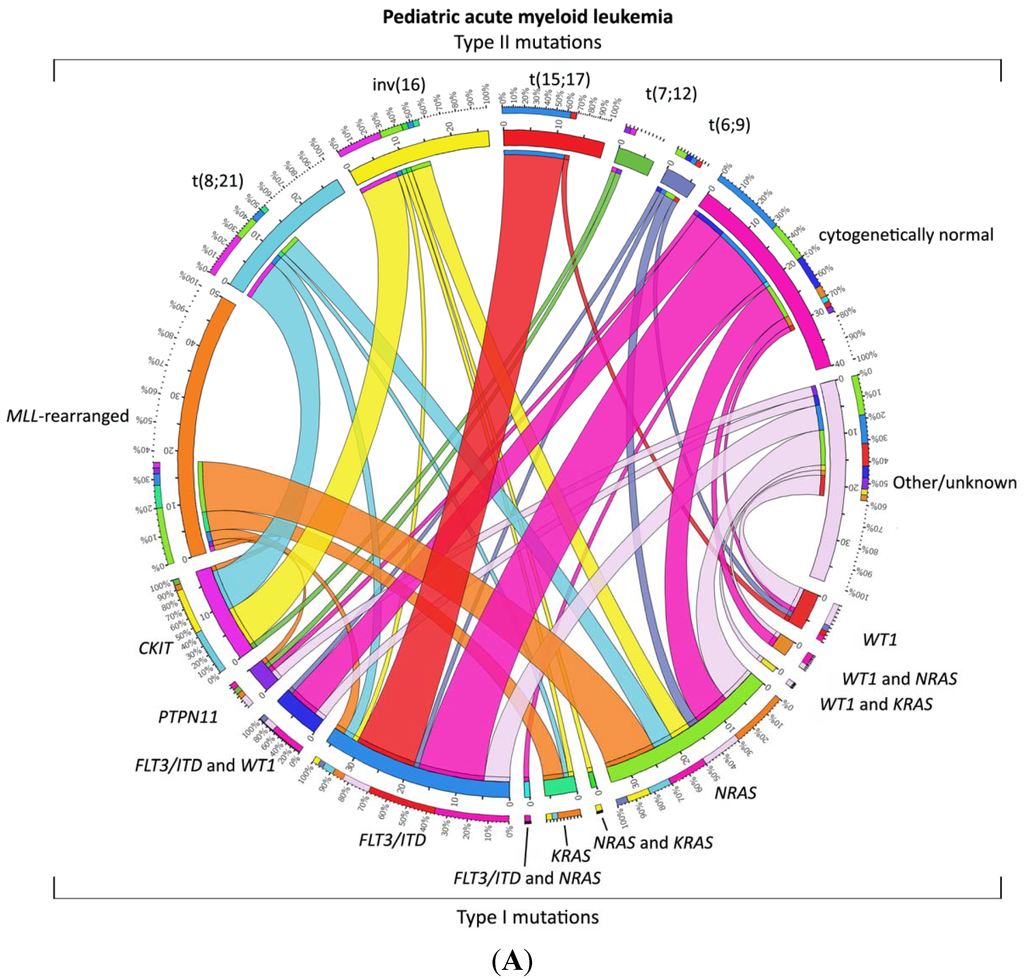
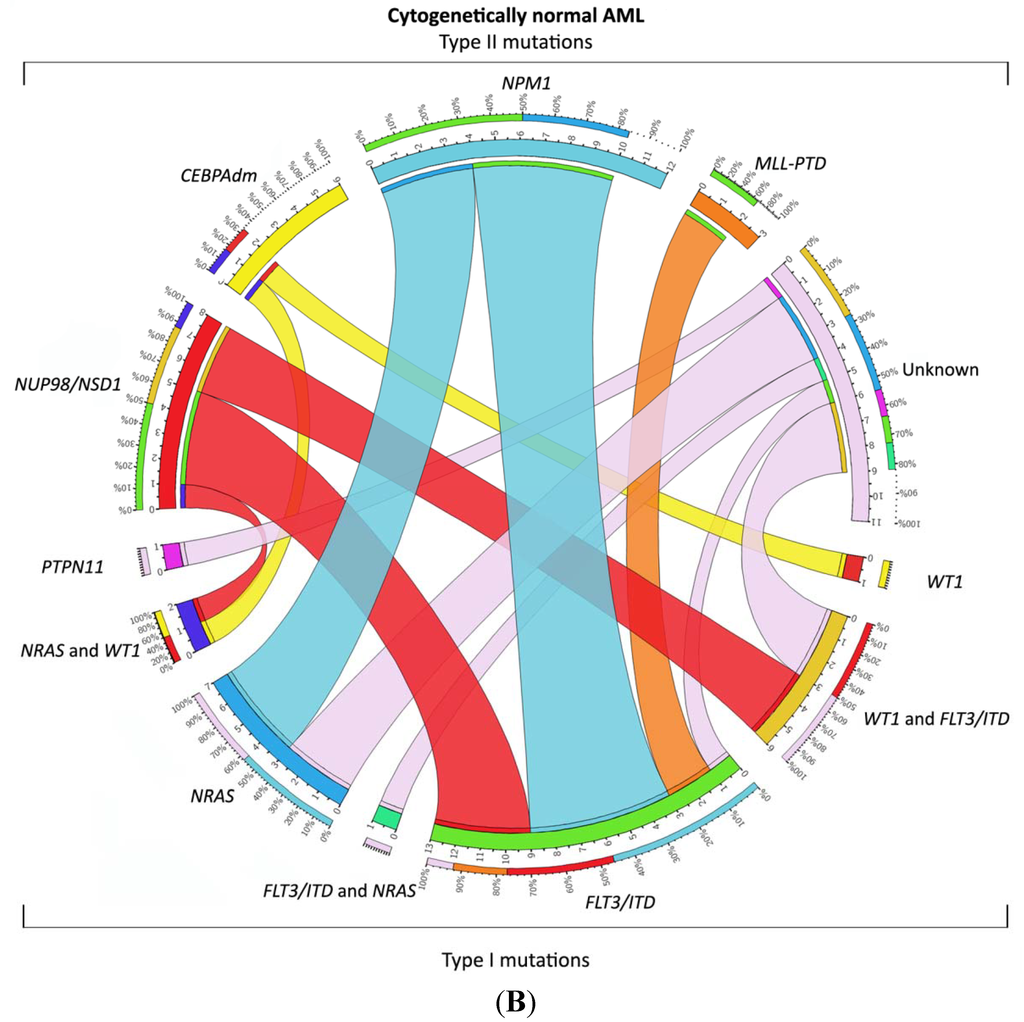
Figure 1.
Distribution of Type I/II abnormalities in pediatric AML. (A) Cooperating Type I and Type II mutations in pediatric AML. The circos plot [73] depicts the frequency of the Type II mutations and co-occurrence of Type I mutations in patients with de novo pediatric AML. The length of the arch corresponds to the frequency of the Type II mutation and the width of the ribbon with the percentage of patients with a specific Type I mutation or a combination of Type I mutations. FLT3/ITD denotes FLT3 internal tandem duplication; (B) Cooperating Type I and Type II mutations in cytogenetically normal AML. The circos plot [73] depicts the frequency of the Type II mutations and co-occurrence of Type I mutations in patients with de novo pediatric cytogenetically normal AML. The length of the arch corresponds to the frequency of the Type II mutation, and the width of the ribbon with the percentage of patients with a specific Type I mutation or a combination of Type I mutations. FLT3/ITD denotes FLT3 internal tandem duplication.

Table 2.
Survival of pediatric AML.
| Study Group | Study and Inclusion Time (Calendar Years of Inclusion) | Patients (n) | Patients Treated with SCT (n) | EFS (%) | OS (%) | Relapse (%) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BFM-SG | AML-BFM 2004 (2004–2010) | 521 | NA | 5 years 55 ± 2 | 5 years 74 ± 2 | 29 | Creutzig et al., 2013 [34] |
| JACLS | AML99 (2003–2006) | 146 | 22 (15%) | 5 years 66.7 ± 4.0 | 5 years 77.7 ± 8.0 | 30.2 | Imamura et al., 2012 [74] |
| AML99 (2000–2002) | 240 | Allo-SCT 41 (17%) Auto-SCT 5 (2%) | 5 years 61.6 ± 6.5 | 5 years 75.6 ± 5.3 | 32.2 | Tsukimoto et al., 2009 [27] | |
| AIEOP | AML2002/01 (2002–2011) | 482 | Allo-SCT 141 (29%) Auto-SCT 102 (21%) | 8 years 55.0 ± 2.6 | 8 years 67.7 ± 2.4 | 24 | Pession et al., 2013 [30] |
| COG | AAML03P1 (2003–2005) | 340 | 73 (21%) | 3 years 53 ± 6 | 3 years 66 ± 5 | 33 ± 6 | Cooper et al., 2012 [75] |
| NOPHO | NOPHO AML 2004 (2004–2009) | 151 | 22 (15%) | 3 years 57 ± 5 | 3 years 69 ± 5 | 30 | Abrahamsson et al., 2011 [20] |
| MRC | MRC AML12 (1995–2002) | 564 | 64 (11%) | 10 years 54 | 10 years 63 | 32 | Gibson et al., 2011 [33] |
| SJCRH | AML02 (2002–2008) | 216 | 59 (25%) | 3 years 63 | 3 years 71 | 21 | Rubnitz et al., 2010 [26] |
| PPLLSG | PPLLSG AML-98 (1998–2002) | 104 | Allo-SCT 14 (13%) Auto-SCT 8 (8%) | 5 years 47 ± 5 | 5 years 50 ± 5 | 24 | Dluzniewska et al., 2005 [76] |
Abbreviations: n, indicates number; SCT, stem cell transplantation; EFS, event-free survival; OS, overall survival; BFM-SG, Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster-Study-Group (Germany); AML, acute myeloid leukemia; JACLS, Japan Association of Childhood Leukemia Study; Allo, allogeneic; Auto, autologous; AIEOP, Italian association of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology (Associazione Italiana Ematologia Oncologia Pediatrica); COG, Childhood Oncology Group (United States of America); NOPHO, Nordic Society of Pediatric Haematology and Oncology; MRC, Medical Research Council (United Kingdom); SJCRH, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital (United States of America); PPLLSG, Polish Pediatric Leukemia/Lymphoma Study Group.
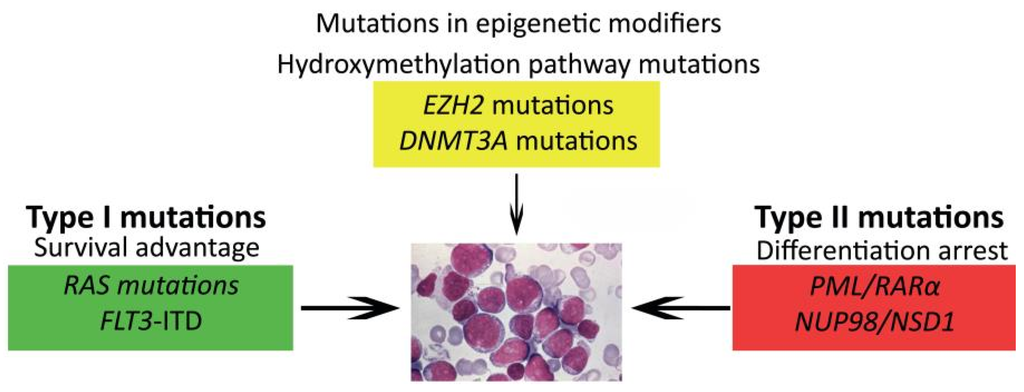
Figure 2.
Model of cooperating genetic events in AML. Different types of genetic and epigenetic events collaborate in leukemogenesis.
1.5. Prognostic Factors and Risk Group Stratification
Most important prognostic factors for the survival of pediatric AML are the initial response to treatment and the underlying genetic and molecular aberrations [12,77,78]. CBF-AML is a favorable prognostic subgroup [48,52,79]. Outcome in MLL-rearranged AML is variable and depends on the translocation partner. For example, the MLL-translocation t(1;11)(q21;q23) is associated with a very favorable outcome in pediatric AML. In contrast, poor survival rates were reported in pediatric AML with translocations t(6;11)(q27;q23) and t(10;11)(p12;q23) [80,81]. The acute megakaryoblastic leukemias (AMKL, FABM7) in non-Down syndrome patients represent a subgroup with poor outcome, with the exception of AMKL harboring t(1;22)(p13;q13), which seems to confer a favorable prognostic group, in contrast to Down syndrome, where AMKL confers a favorable outcome [9,17]. Monosomy 7 is a well-known poor-prognostic factor and confers a worse outcome [52,82]. Deletion of 7q is described as an intermediate risk in the prognosis in adults, in contrast to the outcome of pediatric AML with a 7q deletion in children. In those pediatric patients, the outcome seems to be dependent on other cytogenetic abnormalities in the leukemic cell [52,82]. The described poor prognostic abnormalities in adult AML of chromosomes 3q and 5q and the monosomal karyotypes are rare in children [30,83,84,85]. Overexpression of EVI1 caused by 3q26 abnormalities predicts an adverse outcome in adult AML, but EVI1 overexpression is not an independent prognostic factor in pediatric AML [86,87]. The Type I mutations of WT1 and FLT3-itd predict a poor outcome, the latter dependent on the allele ratio, and these mutations are described as events in clonal evolution towards relapse [88].
A special subtype of pediatric AML is the cytogenetically normal (CN) AML group, where clinical outcome is highly dependent on the presence of single-gene mutations or cryptic translocations. Of special interest are NPM1 and bi-allelic CEBPA mutations, conferring a favorable prognosis, while the cryptic translocation NUP98/NSD1 confers a poor prognosis, due to a poor response to treatment and a high risk for relapse, independent of the poor prognostic Type I FLT3-itd abnormality [46,57,89].
2. Future Strategies
2.1. Genomic Approaches to Unravel the Biology of Pediatric AML
In order to provide more insight into the heterogeneity and biology of AML, genome-wide approaches have been recently employed, although the success rate is variable. Array-based comparative genomic hybridization (array-CGH) and single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) arrays identified several regions with loss of heterozygosity and recurrent copy number variations (CNVs), albeit with low frequency in AML [90]. These CNVs included aberrations in WT1, NF1 and TET2, the latter being more common in adults than in children [47,65,67,91].
Gene expression profiling could predict the cytogenetic subtypes of AML with high accuracy, although its value for diagnostic purposes remains limited, since most aberrations can be identified with conventional karyotyping [92,93,94,95]. Nevertheless, novel genes involved in the pathogenesis of pediatric AML subtypes were identified using this method, such as BRE and IGSF4 [96,97].
In addition to discovering novel gene mutations, next generation sequencing has also proven to be a powerful tool in the study of the clonal evolution of both adult and pediatric AML [98,99]. By comparing the mutational spectrum of diagnosis-relapse pairs, it was shown that the founding clone gained novel mutations and evolved into the relapse clone. Moreover, minor subclones present at diagnosis can survive chemotherapy, gain mutations and present as dominant clones at relapse, illustrating their leukemia-driving capacity. Therapeutic targeting of novel identified mutations to prevent relapse may provide an improved outcome for selected patients [100,101].
Epigenetic profiling was able to distinguish cytogenetic subtypes of adult AML [102]. Differences in promoter hypermethylation of selected genes between pediatric and adult AML warrant the profiling of DNA methylation in pediatric AML [103]. These studies may point out subsets of patients eligible for treatment with demethylating agents or histone modification inhibitors, as was shown for pediatric ALL [72].
Differences in microRNA expression levels can classify several types of cancer [104]. Profiling studies in adult AML have shown that variations in microRNA expression patterns are associated with subtypes of AML and that specific microRNAs target genes of interest for the biology of AML [105,106,107]. In pediatric AML, microRNA expression patterns vary among subtypes of AML, as well, although some differences in the expression patterns of specific microRNAs were observed between children and adults [108].
2.2. Towards Optimized Therapy
The translation from molecular aberrations towards targeted therapy might be the solution to improve outcome in the next few decades. Since further intensification of current chemotherapy treatment seems not feasible in pediatric AML, due to high morbidity and mortality rates, new therapeutic approaches that are more tumor-specific and cause less severe side effects are urgently needed. Some new compounds directed at specific molecular targets have already been investigated in early clinical trials in pediatric AML.
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors directed at inhibiting the constitutive activation of the FLT3 gene are among the best studied drugs in this respect in pediatric AML and include trials using PKC412, CEP701, AC220 and sorafenib [109,110,111]. Recent data suggest a potentially generic mechanism of drug resistance when combining these inhibitors with chemotherapy due to FLT3 ligand upregulation, which questions their use in this fashion, although novel, more potent inhibitors may overcome this [112,113]. In the AAML1031 study of the Childhood Oncology Group (COG), patients with a FLT3 gene mutation are treated with sorafenib in addition to standard intensive chemotherapy [114]. However, there are no convincing randomized studies to date showing an increase in overall survival in FLT3 mutated patients with such therapeutic regimens.
Other potential targets in AML include KIT and RAS gene mutations. Patients with KIT mutations include the imatinib-resistant patients with the D816V/Y mutation, who are sensitive to dasatinib [48,115]. A phase I study of dasatinib has been completed in children [116]. There is an ongoing trial in adults using dasatinib together with chemotherapy in CBF-AML [117]. No trials have been reported using small molecule RAS-pathway inhibitors, e.g., MEK-inhibitors, after studies using farnesyl transferase inhibitors failed to show a benefit in older patients with AML [118]. To inhibit signal transduction pathways, such as the Ras-pathway, which is notorious for escaping behavior, which makes the leukemic cell survives despite intensive chemotherapy, combinations of inhibitors may be more promising, and this approach is currently being further explored in synthetic lethality screens, which combines different inhibitors in order to find a lethal combination for the leukemic cells, for different types of cancer [119,120].
In MLL-rearranged AML, efforts are directed at developing targeted therapy, for instance by inhibiting DOT1L, which is part of the MLL-complex, with current clinical trials ongoing [60]. Interestingly, these DOT1L inhibitors also seem valuable in the treatment of t(6;11)(q27;q23)-positive cells, which lack DOT1L in the formed complex, indicating that this drug is able to target aberrant H3K79 methylation [121].
Gemtuzumab ozogamicin is a conjugated monoclonal antibody against CD33 and linked to a cytostatic agent, calicheamicin, an anti-tumor antibiotic. AML cells often express CD33 and are therefore targeted by this drug. The first phase III studies did not show an improvement in disease-free and overall survival in pediatric AML patients, but it was favorable in patients with refractory or relapsed disease and was effective at reducing MRD levels before SCT [75,122,123,124,125].
Clofarabine is a purine nucleoside antimetabolite, registered for relapsed or refractory pediatric ALL. Early trials in pediatric AML did not show convincing efficacy, probably due to the intensive pre-treatment in these cases [126]. However, in refractory or relapsed pediatric AML patients, the combination of clofarabine and cytarabine resulted in 48% responders, with a three-year overall survival of 46% [127]. In ongoing studies, fludarabine, used in the “FLAG”-therapy, consisting of fludarabine, cytarabine and G-CSF, is replaced by clofarabine, as well as clofarabine combined with cyclophosphamide and etoposide [128]. Another phase II study showed a beneficial outcome for patients treated with the combination of clofarabine, topotecan, vinorelbine and thiotepa in pediatric patients with refractory or relapsed AML [129].
In xenograft models, treatment of AML with a combination of decitabine, a hypomethylating agent, and cytarabine was more effective at reducing tumor burden in comparison to cytarabine alone [130]. Low-dose decitabine was administered to high-risk relapsed or refractory AML patients, and 3/8 patients responded to this therapy [131]. Azacitidine, another hypomethylating agent, and decitabine show comparable treatment efficacy, but azacitidine may result in less adverse events [132].
International collaboration, which has been pursued over the last few decades on the levels of the International Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster Study Group (IBFM-SG), Innovative Therapies for Children with Cancer (ITCC), European Network for Cancer Research in Children and Adolescents (ENCCA), Therapeutic Advances in Childhood Leukemia (TACL) and Childhood Oncology Group (COG), has been proven successful in clinical and biological studies and will speed up efforts to enhance therapeutic options and the availability of novel agents for individual pediatric AML patients [12,17,28,80,81,82].
3. Conclusions
Current survival of pediatric AML is ~70%, and a therapeutic plateau has been reached with current chemotherapy. Further intensification of treatment is not feasible because of toxicity. The heterogeneity of AML is illustrated by the various prognostically relevant non-randomly associated molecular and cytogenetic aberrations that were discovered in recent years. However, many cooperating events in leukemogenesis still remain unknown. The application of new techniques, especially next generation sequencing, will contribute to our understanding of the genetic landscape of AML and enable the development of more targeted and personalized therapy in the near future. To achieve such goals for such a rare disease as pediatric AML, international collaboration is crucial.
Acknowledgments
Jasmijn D. E. de Rooij was funded by Kinder Oncologisch Centrum Rotterdam (KOCR).
Author Contributions
Jasmijn D. E. de Rooij, C. Michel Zwaan and Marry M. van den Heuvel-Eibrink designed the study. Jasmijn D. E. de Rooij performed the literature search. C. Michel Zwaan and Marry M. van den Heuvel-Eibrink supervised and reviewed the study. Jasmijn D. E. de Rooij wrote the manuscript. C. Michel Zwaan and Marry M. van den Heuvel-Eibrink critically reviewed the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Howlader, N.N.A.; Krapcho, M.; Garshell, J.; Miller, D.; Altekruse, S.F.; Kosary, C.L.; Yu, M.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovich, Z.; Mariotto, A.; et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2011; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Seif, A.E. Pediatric leukemia predisposition syndromes: Clues to understanding leukemogenesis. Cancer Genet. 2011, 204, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonnies, H.; Huber, S.; Kuhl, J.S.; Gerlach, A.; Ebell, W.; Neitzel, H. Clonal chromosomal aberrations in bone marrow cells of Fanconi anemia patients: Gains of the chromosomal segment 3q26q29 as an adverse risk factor. Blood 2003, 101, 3872–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, C.N.; Chong, C.E.; Carmichael, C.L.; Wilkins, E.J.; Brautigan, P.J.; Li, X.C.; Babic, M.; Lin, M.; Carmagnac, A.; Lee, Y.K.; et al. Heritable GATA2 mutations associated with familial myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, D.C.; Schuettpelz, L.G.; Shen, D.; Wang, J.; Walter, M.J.; Kulkarni, S.; Payton, J.E.; Ivanovich, J.; Goodfellow, P.J.; Le Beau, M.; et al. Identification of a novel TP53 cancer susceptibility mutation through whole-genome sequencing of a patient with therapy-related AML. JAMA 2011, 305, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, C.; Barnett, M.; Fitzgibbon, J. Familial myelodysplasia and acute myeloid leukaemia—A review. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 140, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.L.; Cavenagh, J.D.; Lister, T.A.; Fitzgibbon, J. Mutation of CEBPA in familial acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2403–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.J.; Sullivan, M.G.; Legare, R.D.; Hutchings, S.; Tan, X.; Kufrin, D.; Ratajczak, J.; Resende, I.C.; Haworth, C.; Hock, R.; et al. Haploinsufficiency of CBFA2 causes familial thrombocytopenia with propensity to develop acute myelogenous leukaemia. Nat. Genet. 1999, 23, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwaan, M.C.; Reinhardt, D.; Hitzler, J.; Vyas, P. Acute leukemias in children with Down syndrome. Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 2008, 55, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandler, E.S.; Friedman, D.J.; Mustafa, M.M.; Winick, N.J.; Bowman, W.P.; Buchanan, G.R. Treatment of children with epipodophyllotoxin-induced secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer 1997, 79, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, B.; Vora, A.; Huberty, J.; Hawkins, R.A.; Matthay, K.K. Secondary myelodysplastic syndrome and leukemia following 131I-metaiodobenzylguanidine therapy for relapsed neuroblastoma. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2003, 25, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creutzig, U.; van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.; Gibson, B.; Dworzak, M.N.; Adachi, S.; de Bont, E.; Harbott, J.; Hasle, H.; Johnston, D.; Kinoshita, A.; et al. Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in children and adolescents: Recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood 2012, 120, 3187–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.M.; Catovsky, D.; Daniel, M.T.; Flandrin, G.; Galton, D.A.; Gralnick, H.R.; Sultan, C. Proposals for the classification of the acute leukaemias. French-American-British (FAB) co-operative group. Br. J. Haematol. 1976, 33, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardiman, J.W.; Thiele, J.; Arber, D.A.; Brunning, R.D.; Borowitz, M.J.; Porwit, A.; Harris, N.L.; Le Beau, M.M.; Hellstrom-Lindberg, E.; Tefferi, A.; et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: Rationale and important changes. Blood 2009, 114, 937–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.M.; Catovsky, D.; Daniel, M.T.; Flandrin, G.; Galton, D.A.; Gralnick, H.R.; Sultan, C. Criteria for the diagnosis of acute leukemia of megakaryocyte lineage (M7). A report of the French-American-British Cooperative Group. Ann. Intern. Med. 1985, 103, 460–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrozek, K.; Heinonen, K.; Bloomfield, C.D. Clinical importance of cytogenetics in acute myeloid leukaemia. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2001, 14, 19–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rooij, J.D.; Hollink, I.H.; Arentsen-Peters, S.T.; van Galen, J.F.; Berna Beverloo, H.; Baruchel, A.; Trka, J.; Reinhardt, D.; Sonneveld, E.; Zimmermann, M.; et al. NUP98/JARID1A is a novel recurrent abnormality in pediatric acute megakaryoblastic leukemia with a distinct HOX gene expression pattern. Leukemia 2013, 27, 2280–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercher, T.; Busson-Le Coniat, M.; Nguyen Khac, F.; Ballerini, P.; Mauchauffe, M.; Bui, H.; Pellegrino, B.; Radford, I.; Valensi, F.; Mugneret, F.; et al. Recurrence of OTT-MAL fusion in t(1;22) of infant AML-M7. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2002, 33, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Bergh, A.R.; van Drunen, E.; van Wering, E.R.; van Zutven, L.J.; Hainmann, I.; Lonnerholm, G.; Meijerink, J.P.; Pieters, R.; Beverloo, H.B. High incidence of t(7;12)(q36;p13) in infant AML but not in infant ALL, with a dismal outcome and ectopic expression of HLXB9. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2006, 45, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahamsson, J.; Forestier, E.; Heldrup, J.; Jahnukainen, K.; Jonsson, O.G.; Lausen, B.; Palle, J.; Zeller, B.; Hasle, H. Response-guided induction therapy in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia with excellent remission rate. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creutzig, U.Z.M.; Dworzak, M.; Bourquin, J.P.; Neuhoff, C.; Sander, A.; Stary, J.; Reinhardt, D. Study AML-BFM 2004: Improved Survival In Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukemia without Increased Toxicity. 2010. Available online: https://ash.confex.com/ash/2010/webprogram/Paper31036.html (accessed on 15 December 2014).
- Entz-Werle, N.; Suciu, S.; van der Werff ten Bosch, J.; Vilmer, E.; Bertrand, Y.; Benoit, Y.; Margueritte, G.; Plouvier, E.; Boutard, P.; Vandecruys, E.; et al. Results of 58,872 and 58,921 trials in acute myeloblastic leukemia and relative value of chemotherapy vs. allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in first complete remission: The EORTC Children Leukemia Group report. Leukemia 2005, 19, 2072–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, B.E.; Wheatley, K.; Hann, I.M.; Stevens, R.F.; Webb, D.; Hills, R.K.; de Graaf, S.S.; Harrison, C.J. Treatment strategy and long-term results in paediatric patients treated in consecutive UK AML trials. Leukemia 2005, 19, 2130–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perel, Y.; Auvrignon, A.; Leblanc, T.; Michel, G.; Reguerre, Y.; Vannier, J.P.; Dalle, J.H.; Gandemer, V.; Schmitt, C.; Mechinaud, F.; et al. Treatment of childhood acute myeloblastic leukemia: Dose intensification improves outcome and maintenance therapy is of no benefit—Multicenter studies of the French LAME (Leucemie Aigue Myeloblastique Enfant) Cooperative Group. Leukemia 2005, 19, 2082–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pession, A.; Rondelli, R.; Basso, G.; Rizzari, C.; Testi, A.M.; Fagioli, F.; de Stefano, P.; Locatelli, F.; AML Strategy & Study Committee of the Associazione Italiana di Ematologia e Oncologia Pediatrica (AIEOP). Treatment and long-term results in children with acute myeloid leukaemia treated according to the AIEOP AML protocols. Leukemia 2005, 19, 2043–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubnitz, J.E.; Inaba, H.; Dahl, G.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Bowman, W.P.; Taub, J.; Pounds, S.; Razzouk, B.I.; Lacayo, N.J.; Cao, X.; et al. Minimal residual disease-directed therapy for childhood acute myeloid leukaemia: Results of the AML02 multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukimoto, I.; Tawa, A.; Horibe, K.; Tabuchi, K.; Kigasawa, H.; Tsuchida, M.; Yabe, H.; Nakayama, H.; Kudo, K.; Kobayashi, R.; et al. Risk-stratified therapy and the intensive use of cytarabine improves the outcome in childhood acute myeloid leukemia: The AML99 trial from the Japanese Childhood AML Cooperative Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4007–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creutzig, U.; Zimmermann, M.; Dworzak, M.N.; Ritter, J.; Schellong, G.; Reinhardt, D. Development of a curative treatment within the AML-BFM studies. Klin. Padiatr. 2013, 225 (Suppl. S1), 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Horibe, K.; Saito, A.M.; Takimoto, T.; Tsuchida, M.; Manabe, A.; Shima, M.; Ohara, A.; Mizutani, S. Incidence and survival rates of hematological malignancies in Japanese children and adolescents (2006–2010): Based on registry data from the Japanese Society of Pediatric Hematology. Int. J. Hematol. 2013, 98, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pession, A.; Masetti, R.; Rizzari, C.; Putti, M.C.; Casale, F.; Fagioli, F.; Luciani, M.; Lo Nigro, L.; Menna, G.; Micalizzi, C.; et al. Results of the AIEOP AML 2002/01 multicenter prospective trial for the treatment of children with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2013, 122, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Velden, V.H.; van der Sluijs-Geling, A.; Gibson, B.E.; te Marvelde, J.G.; Hoogeveen, P.G.; Hop, W.C.; Wheatley, K.; Bierings, M.B.; Schuurhuis, G.J.; de Graaf, S.S.; et al. Clinical significance of flowcytometric minimal residual disease detection in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients treated according to the DCOG ANLL97/MRC AML12 protocol. Leukemia 2010, 24, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becton, D.; Dahl, G.V.; Ravindranath, Y.; Chang, M.N.; Behm, F.G.; Raimondi, S.C.; Head, D.R.; Stine, K.C.; Lacayo, N.J.; Sikic, B.I.; et al. Randomized use of cyclosporin A (CsA) to modulate P-glycoprotein in children with AML in remission: Pediatric Oncology Group Study 9421. Blood 2006, 107, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, B.E.; Webb, D.K.; Howman, A.J.; de Graaf, S.S.; Harrison, C.J.; Wheatley, K.; United Kingdom Childhood Leukaemia Working Group; the Dutch Childhood Oncology Group. Results of a randomized trial in children with Acute Myeloid Leukaemia: Medical research council AML12 trial. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 155, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creutzig, U.; Zimmermann, M.; Bourquin, J.P.; Dworzak, M.N.; Fleischhack, G.; Graf, N.; Klingebiel, T.; Kremens, B.; Lehrnbecher, T.; von Neuhoff, C.; et al. Randomized trial comparing liposomal daunorubicin with idarubicin as induction for pediatric acute myeloid leukemia: Results from Study AML-BFM 2004. Blood 2013, 122, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niewerth, D.; Creutzig, U.; Bierings, M.B.; Kaspers, G.J. A review on allogeneic stem cell transplantation for newly diagnosed pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2010, 116, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhardt, D.K.B.; Zimmermann, M.; Vormoor, J.; Dworzak, M.; Peters, C.; Creutzig, U.; Klingebiel, T. No Improvement of Overall-Survival in Children with High-Risk Acute Myeloid Leukemia by Stem Cell Transplantation in 1st Complete Remission. 2006. Available online: http://abstractshematologylibraryorg/cgi/content/short/108/11/320 (accessed on 15 December 2014).
- Passweg, J.R.; Baldomero, H.; Peters, C.; Gaspar, H.B.; Cesaro, S.; Dreger, P.; Duarte, R.F.; Falkenburg, J.H.; Farge-Bancel, D.; Gennery, A.; et al. Hematopoietic SCT in Europe: Data and trends in 2012 with special consideration of pediatric transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2014, 49, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos-Oreiro, M.; Perez-Corral, A.; Martinez-Laperche, C.; Bento, L.; Pascual, C.; Kwon, M.; Balsalobre, P.; Munoz, C.; Buces, E.; Serrano, D.; et al. Prognostic impact of minimal residual disease analysis by flow cytometry in patients with acute myeloid leukemia before and after allogeneic hemopoietic stem cell transplantation. Eur. J. Haematol. 2014, 93, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anthias, C.; Dignan, F.L.; Morilla, R.; Morilla, A.; Ethell, M.E.; Potter, M.N.; Shaw, B.E. Pre-transplant MRD predicts outcome following reduced-intensity and myeloablative allogeneic hemopoietic SCT in AML. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2014, 49, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasle, H. A critical review of which children with acute myeloid leukaemia need stem cell procedures. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 166, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sander, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Dworzak, M.; Fleischhack, G.; von Neuhoff, C.; Reinhardt, D.; Kaspers, G.J.; Creutzig, U. Consequent and intensified relapse therapy improved survival in pediatric AML: Results of relapse treatment in 379 patients of three consecutive AML-BFM trials. Leukemia 2010, 24, 1422–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaspers, G.J.; Zimmermann, M.; Reinhardt, D.; Gibson, B.E.; Tamminga, R.Y.; Aleinikova, O.; Armendariz, H.; Dworzak, M.; Ha, S.Y.; Hasle, H.; et al. Improved outcome in pediatric relapsed acute myeloid leukemia: Results of a randomized trial on liposomal daunorubicin by the International BFM Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slats, A.M.; Egeler, R.M.; van der Does-van den Berg, A.; Korbijn, C.; Hahlen, K.; Kamps, W.A.; Veerman, A.J.; Zwaan, C.M. Causes of death—Other than progressive leukemia—In childhood acute lymphoblastic (ALL) and myeloid leukemia (AML): The Dutch Childhood Oncology Group experience. Leukemia 2005, 19, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kelly, L.M.; Gilliland, D.G. Genetics of myeloid leukemias. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2002, 3, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.; Sternberg, A.; Hall, G.; Thomas, A.; Smith, O.; O’Marcaigh, A.; Wynn, R.; Stevens, R.; Addison, M.; King, D.; et al. Natural history of GATA1 mutations in Down syndrome. Blood 2004, 103, 2480–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollink, I.H.; van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.; Arentsen-Peters, S.T.; Zimmermann, M.; Peeters, J.K.; Valk, P.J.; Balgobind, B.V.; Sonneveld, E.; Kaspers, G.J.; de Bont, E.S.; et al. Characterization of CEBPA mutations and promoter hypermethylation in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2011, 96, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollink, I.H.; van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.; Zimmermann, M.; Balgobind, B.V.; Arentsen-Peters, S.T.; Alders, M.; Willasch, A.; Kaspers, G.J.; Trka, J.; Baruchel, A.; et al. Clinical relevance of Wilms tumor 1 gene mutations in childhood acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2009, 113, 5951–5960. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balgobind, B.V.; Hollink, I.H.; Arentsen-Peters, S.T.; Zimmermann, M.; Harbott, J.; Beverloo, H.B.; von Bergh, A.R.; Cloos, J.; Kaspers, G.J.; de Haas, V.; et al. Integrative analysis of type-I and type-II aberrations underscores the genetic heterogeneity of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2011, 96, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betts, D.R.; Ammann, R.A.; Hirt, A.; Hengartner, H.; Beck-Popovic, M.; Kuhne, T.; Nobile, L.; Caflisch, U.; Wacker, P.; Niggli, F.K. The prognostic significance of cytogenetic aberrations in childhood acute myeloid leukaemia. A study of the Swiss Paediatric Oncology Group (SPOG). Eur. J. Haematol. 2007, 78, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimwade, D. The clinical significance of cytogenetic abnormalities in acute myeloid leukaemia. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2001, 14, 497–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, C.J.; Hills, R.K.; Moorman, A.V.; Grimwade, D.J.; Hann, I.; Webb, D.K.; Wheatley, K.; de Graaf, S.S.; van den Berg, E.; Burnett, A.K.; et al. Cytogenetics of childhood acute myeloid leukemia: United Kingdom Medical Research Council Treatment trials AML 10 and 12. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2674–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Neuhoff, C.; Reinhardt, D.; Sander, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Bradtke, J.; Betts, D.R.; Zemanova, Z.; Stary, J.; Bourquin, J.P.; Haas, O.A.; et al. Prognostic impact of specific chromosomal aberrations in a large group of pediatric patients with acute myeloid leukemia treated uniformly according to trial AML-BFM 98. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2682–2689. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Kim, M.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Han, K.; Lee, J.; Chung, N.G.; Cho, B.; Kim, H.K. Three-way complex translocations in infant acute myeloid leukemia with t(7;12)(q36;p13): The incidence and correlation of a HLXB9 overexpression. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2009, 191, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, H.M.; Oseth, L.; Nguyen, P.; O’Leary, M.; Conklin, K.F.; Hirsch, B. Cytogenetic and molecular heterogeneity of 7q36/12p13 rearrangements in childhood AML. Leukemia 2002, 16, 2408–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slater, R.M.; von Drunen, E.; Kroes, W.G.; Weghuis, D.O.; van den Berg, E.; Smit, E.M.; van der Does-van den Berg, A.; van Wering, E.; Hahlen, K.; Carroll, A.J.; et al. t(7;12)(q36;p13) and t(7;12)(q32;p13)—Translocations involving ETV6 in children 18 months of age or younger with myeloid disorders. Leukemia 2001, 15, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, L.; Lisboa, S.; Vieira, J.; Cerveira, N.; Santos, J.; Pinheiro, M.; Correia, C.; Bizarro, S.; Almeida, M.; Teixeira, M.R. Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia with a four-way variant translocation originating the RBM15-MKL1 fusion gene. Blood Cancer 2011, 56, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollink, I.H.; van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.; Arentsen-Peters, S.T.; Pratcorona, M.; Abbas, S.; Kuipers, J.E.; van Galen, J.F.; Beverloo, H.B.; Sonneveld, E.; Kaspers, G.J.; et al. NUP98/NSD1 characterizes a novel poor prognostic group in acute myeloid leukemia with a distinct HOX gene expression pattern. Blood 2011, 118, 3645–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, C.; Kowarz, E.; Hofmann, J.; Renneville, A.; Zuna, J.; Trka, J.; Ben Abdelali, R.; Macintyre, E.; De Braekeleer, E.; De Braekeleer, M.; et al. New insights to the MLL recombinome of acute leukemias. Leukemia 2009, 23, 1490–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, C.; Hofmann, J.; Burmeister, T.; Groger, D.; Park, T.S.; Emerenciano, M.; Pombo de Oliveira, M.; Renneville, A.; Villarese, P.; Macintyre, E.; et al. The MLL recombinome of acute leukemias in 2013. Leukemia 2013, 27, 2165–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernt, K.M.; Zhu, N.; Sinha, A.U.; Vempati, S.; Faber, J.; Krivtsov, A.V.; Feng, Z.; Punt, N.; Daigle, A.; Bullinger, L.; et al. MLL-rearranged leukemia is dependent on aberrant H3K79 methylation by DOT1L. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marschalek, R. Mechanisms of leukemogenesis by MLL fusion proteins. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 152, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcucci, G.; Haferlach, T.; Dohner, H. Molecular genetics of adult acute myeloid leukemia: Prognostic and therapeutic implications. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, T.J.; Ding, L.; Walter, M.J.; McLellan, M.D.; Lamprecht, T.; Larson, D.E.; Kandoth, C.; Payton, J.E.; Baty, J.; Welch, J.; et al. DNMT3A mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2424–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, M.E.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Lu, C.; Ward, P.S.; Patel, J.; Shih, A.; Li, Y.; Bhagwat, N.; Vasanthakumar, A.; Fernandez, H.F.; et al. Leukemic IDH1 and IDH2 mutations result in a hypermethylation phenotype, disrupt TET2 function, and impair hematopoietic differentiation. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delhommeau, F.; Dupont, S.; Della Valle, V.; James, C.; Trannoy, S.; Masse, A.; Kosmider, O.; Le Couedic, J.P.; Robert, F.; Alberdi, A.; et al. Mutation in TET2 in myeloid cancers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2289–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollink, I.H.; Feng, Q.; Danen-van Oorschot, A.A.; Arentsen-Peters, S.T.; Verboon, L.J.; Zhang, P.; de Haas, V.; Reinhardt, D.; Creutzig, U.; Trka, J.; et al. Low frequency of DNMT3A mutations in pediatric AML, and the identification of the OCI-AML3 cell line as an in vitro model. Leukemia 2012, 26, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langemeijer, S.M.; Jansen, J.H.; Hooijer, J.; van Hoogen, P.; Stevens-Linders, E.; Massop, M.; Waanders, E.; van Reijmersdal, S.V.; Stevens-Kroef, M.J.; Zwaan, C.M.; et al. TET2 mutations in childhood leukemia. Leukemia 2011, 25, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, P.A.; Alonzo, T.A.; Kopecky, K.J.; Miller, K.L.; Kuhn, J.; Zeng, R.; Gerbing, R.B.; Raimondi, S.C.; Hirsch, B.A.; Oehler, V.; et al. Molecular alterations of the IDH1 gene in AML: A Children’s Oncology Group and Southwest Oncology Group study. Leukemia 2010, 24, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.J.; Xu, J.; Gu, Z.H.; Pan, C.M.; Lu, G.; Shen, Y.; Shi, J.Y.; Zhu, Y.M.; Tang, L.; Zhang, X.W.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies somatic mutations of DNA methyltransferase gene DNMT3A in acute monocytic leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valerio, D.G.; Katsman-Kuipers, J.E.; Jansen, J.H.; Verboon, L.J.; de Haas, V.; Stary, J.; Baruchel, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Pieters, R.; Reinhardt, D.; et al. Mapping epigenetic regulator gene mutations in cytogenetically normal pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2014, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardis, E.R.; Ding, L.; Dooling, D.J.; Larson, D.E.; McLellan, M.D.; Chen, K.; Koboldt, D.C.; Fulton, R.S.; Delehaunty, K.D.; McGrath, S.D.; et al. Recurring mutations found by sequencing an acute myeloid leukemia genome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumpel, D.J.; Schneider, P.; van Roon, E.H.; Boer, J.M.; de Lorenzo, P.; Valsecchi, M.G.; de Menezes, R.X.; Pieters, R.; Stam, R.W. Specific promoter methylation identifies different subgroups of MLL-rearranged infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia, influences clinical outcome, and provides therapeutic options. Blood 2009, 114, 5490–5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, T.; Iwamoto, S.; Kanai, R.; Shimada, A.; Terui, K.; Osugi, Y.; Kobayashi, R.; Tawa, A.; Kosaka, Y.; Kato, K.; et al. Outcome in 146 patients with paediatric acute myeloid leukaemia treated according to the AML99 protocol in the period 2003–06 from the Japan Association of Childhood Leukaemia Study. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 159, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, T.M.; Franklin, J.; Gerbing, R.B.; Alonzo, T.A.; Hurwitz, C.; Raimondi, S.C.; Hirsch, B.; Smith, F.O.; Mathew, P.; Arceci, R.J.; et al. AAML03P1, a pilot study of the safety of gemtuzumab ozogamicin in combination with chemotherapy for newly diagnosed childhood acute myeloid leukemia: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Cancer 2012, 118, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dluzniewska, A.; Balwierz, W.; Armata, J.; Balcerska, A.; Chybicka, A.; Kowalczyk, J.; Matysiak, M.; Ochocka, M.; Radwanska, U.; Rokicka-Milewska, R.; et al. Twenty years of Polish experience with three consecutive protocols for treatment of childhood acute myelogenous leukemia. Leukemia 2005, 19, 2117–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachas, C.; Schuurhuis, G.J.; Reinhardt, D.; Creutzig, U.; Kwidama, Z.J.; Zwaan, C.M.; van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.; de Bont, E.S.; Elitzur, S.; Rizzari, C.; et al. Clinical relevance of molecular aberrations in paediatric acute myeloid leukaemia at first relapse. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 166, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creutzig, U.; Zimmermann, M.; Dworzak, M.N.; Gibson, B.; Tamminga, R.; Abrahamsson, J.; Ha, S.Y.; Hasle, H.; Maschan, A.; Bertrand, Y.; et al. The prognostic significance of early treatment response in pediatric relapsed acute myeloid leukemia: Results of the international study Relapsed AML 2001/01. Haematologica 2014, 99, 1472–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubnitz, J.E.; Raimondi, S.C.; Halbert, A.R.; Tong, X.; Srivastava, D.K.; Razzouk, B.I.; Pui, C.H.; Downing, J.R.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Behm, F.G. Characteristics and outcome of t(8;21)-positive childhood acute myeloid leukemia: A single institution’s experience. Leukemia 2002, 16, 2072–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balgobind, B.V.; Raimondi, S.C.; Harbott, J.; Zimmermann, M.; Alonzo, T.A.; Auvrignon, A.; Beverloo, H.B.; Chang, M.; Creutzig, U.; Dworzak, M.N.; et al. Novel prognostic subgroups in childhood 11q23/MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia: Results of an international retrospective study. Blood 2009, 114, 2489–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coenen, E.A.; Raimondi, S.C.; Harbott, J.; Zimmermann, M.; Alonzo, T.A.; Auvrignon, A.; Beverloo, H.B.; Chang, M.; Creutzig, U.; Dworzak, M.N.; et al. Prognostic significance of additional cytogenetic aberrations in 733 de novo pediatric 11q23/MLL-rearranged AML patients: Results of an international study. Blood 2011, 117, 7102–7111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasle, H.; Alonzo, T.A.; Auvrignon, A.; Behar, C.; Chang, M.; Creutzig, U.; Fischer, A.; Forestier, E.; Fynn, A.; Haas, O.A.; et al. Monosomy 7 and deletion 7q in children and adolescents with acute myeloid leukemia: An international retrospective study. Blood 2007, 109, 4641–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, D.L.; Alonzo, T.A.; Gerbing, R.B.; Hirsch, B.; Heerema, N.A.; Ravindranath, Y.; Woods, W.G.; Lange, B.J.; Gamis, A.S.; Raimondi, S.C. Outcome of pediatric patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and -5/5q- abnormalities from five pediatric AML treatment protocols: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 2073–2078. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kelly, M.J.; Horan, J.T.; Alonzo, T.A.; Eapen, M.; Gerbing, R.B.; He, W.; Lange, B.J.; Parsons, S.K.; Woods, W.G. Comparable survival for pediatric acute myeloid leukemia with poor-risk cytogenetics following chemotherapy, matched related donor, or unrelated donor transplantation. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2014, 61, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manola, K.N.; Panitsas, F.; Polychronopoulou, S.; Daraki, A.; Karakosta, M.; Stavropoulou, C.; Avgerinou, G.; Hatzipantelis, E.; Pantelias, G.; Sambani, C.; et al. Cytogenetic abnormalities and monosomal karyotypes in children and adolescents with acute myeloid leukemia: Correlations with clinical characteristics and outcome. Cancer Genet. 2013, 206, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balgobind, B.V.; Lugthart, S.; Hollink, I.H.; Arentsen-Peters, S.T.; van Wering, E.R.; de Graaf, S.S.; Reinhardt, D.; Creutzig, U.; Kaspers, G.J.; de Bont, E.S.; et al. EVI1 overexpression in distinct subtypes of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2010, 24, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groschel, S.; Lugthart, S.; Schlenk, R.F.; Valk, P.J.; Eiwen, K.; Goudswaard, C.; van Putten, W.J.; Kayser, S.; Verdonck, L.F.; Lubbert, M.; et al. High EVI1 expression predicts outcome in younger adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia and is associated with distinct cytogenetic abnormalities. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2101–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachas, C.; Schuurhuis, G.J.; Hollink, I.H.; Kwidama, Z.J.; Goemans, B.F.; Zwaan, C.M.; van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.; de Bont, E.S.; Reinhardt, D.; Creutzig, U.; et al. High-frequency type I/II mutational shifts between diagnosis and relapse are associated with outcome in pediatric AML: Implications for personalized medicine. Blood 2010, 116, 2752–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollink, I.H.; Zwaan, C.M.; Zimmermann, M.; Arentsen-Peters, T.C.; Pieters, R.; Cloos, J.; Kaspers, G.J.; de Graaf, S.S.; Harbott, J.; Creutzig, U.; et al. Favorable prognostic impact of NPM1 gene mutations in childhood acute myeloid leukemia, with emphasis on cytogenetically normal AML. Leukemia 2009, 23, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavan, M.; Lillington, D.M.; Skoulakis, S.; Debernardi, S.; Chaplin, T.; Foot, N.J.; Lister, T.A.; Young, B.D. Genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphism analysis reveals frequent partial uniparental disomy due to somatic recombination in acute myeloid leukemias. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balgobind, B.V.; van Vlierberghe, P.; van den Ouweland, A.M.; Beverloo, H.B.; Terlouw-Kromosoeto, J.N.; van Wering, E.R.; Reinhardt, D.; Horstmann, M.; Kaspers, G.J.; Pieters, R.; et al. Leukemia-associated NF1 inactivation in patients with pediatric T-ALL and AML lacking evidence for neurofibromatosis. Blood 2008, 111, 4322–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balgobind, B.V.; Van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.; De Menezes, R.X.; Reinhardt, D.; Hollink, I.H.; Arentsen-Peters, S.T.; van Wering, E.R.; Kaspers, G.J.; Cloos, J.; de Bont, E.S.; et al. Evaluation of gene expression signatures predictive of cytogenetic and molecular subtypes of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2011, 96, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, M.E.; Mahfouz, R.; Onciu, M.; Liu, H.C.; Zhou, X.; Song, G.; Shurtleff, S.A.; Pounds, S.; Cheng, C.; Ma, J.; et al. Gene expression profiling of pediatric acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood 2004, 104, 3679–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valk, P.J.; Verhaak, R.G.; Beijen, M.A.; Barjesteh van Waalwijk van Doorn-Khosrovani, S.; Erpelinck, C.A.; Boer, J.M.; Beverloo, H.B.; Moorhouse, M.J.; van der Spek, P.J.; Lowenberg, B.; et al. Prognostically useful gene-expression profiles in acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1617–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wouters, B.J.; Jorda, M.A.; Keeshan, K.; Louwers, I.; Erpelinck-Verschueren, C.A.; Tielemans, D.; Langerak, A.W.; He, Y.; Yashiro-Ohtani, Y.; Zhang, P.; et al. Distinct gene expression profiles of acute myeloid/T-lymphoid leukemia with silenced CEBPA and mutations in NOTCH1. Blood 2007, 110, 3706–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balgobind, B.V.; Zwaan, C.M.; Reinhardt, D.; Arentsen-Peters, T.J.; Hollink, I.H.; de Haas, V.; Kaspers, G.J.; de Bont, E.S.; Baruchel, A.; Stary, J.; et al. High BRE expression in pediatric MLL-rearranged AML is associated with favorable outcome. Leukemia 2010, 24, 2048–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuipers, J.E.; Coenen, E.A.; Balgobind, B.V.; Stary, J.; Baruchel, A.; de Haas, V.; de Bont, E.S.; Reinhardt, D.; Kaspers, G.J.; Cloos, J.; et al. High IGSF4 expression in pediatric M5 acute myeloid leukemia with t(9;11)(p22;q23). Blood 2011, 117, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Ley, T.J.; Larson, D.E.; Miller, C.A.; Koboldt, D.C.; Welch, J.S.; Ritchey, J.K.; Young, M.A.; Lamprecht, T.; McLellan, M.D.; et al. Clonal evolution in relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia revealed by whole-genome sequencing. Nature 2012, 481, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meshinchi, S.R.R.; Trevino, L.R.; Hampton, O.A.; Alonzo, T.A.; Farrar, J.E.; Guidry Auvil, J.M.; Davidsen, T.M.; Gesuwan, P.; Muzny, D.M.; Gamis, A.S.; et al. Identification of Novel Somatic Mutations, Regions of Recurrent Loss of Heterozygosity (LOH) and Significant Clonal Evolution From Diagnosis to Relapse in Childhood AML Determined by Exome Capture Sequencing-an NCI/COG Target AML Study. 2012. Available online: https://ash.confex.com/ash/2012/webprogram/Paper51517.html (accessed on 15 December 2014).
- Kohlmann, A.M.G.; Hofmann, W.-K.; Kronnie, G.; Chiaretti, C.; Preudhomme, C.; Tagliafico, E.; Hernandez, J.; Gabriel, C.; Lion, T.; Vandenberghe, P.; et al. The Interlaboratory Robustness of Next-Generation Sequencing (IRON) Study Phase II: Deep-Sequencing Analyses of Hematological Malignancies Performed by an International Network Involving 26 Laboratories. 2012. Available online: https://ash.confex.com/ash/2012/webprogram/Paper49866.html (accessed on 15 December 2014).
- Kohlmann, A.W.S.; Schoeck, U.; Grossmann, V.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, C.; Schnittger, S.; Haferlach, T. First Results of a 31-Gene Panel Targeted to Investigate Myeloid Malignancies by Next-Generation Amplicon Deep-Sequencing. 2012. Available online: https://ash.confex.com/ash/2012/webprogram/Paper48970.html (accessed on 15 December 2014).
- Figueroa, M.E.; Lugthart, S.; Li, Y.; Erpelinck-Verschueren, C.; Deng, X.; Christos, P.J.; Schifano, E.; Booth, J.; van Putten, W.; Skrabanek, L.; et al. DNA methylation signatures identify biologically distinct subtypes in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhl-Christensen, C.; Ommen, H.B.; Aggerholm, A.; Lausen, B.; Kjeldsen, E.; Hasle, H.; Hokland, P. Genetic and epigenetic similarities and differences between childhood and adult AML. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2012, 58, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongen-Lavrencic, M.; Sun, S.M.; Dijkstra, M.K.; Valk, P.J.; Lowenberg, B. MicroRNA expression profiling in relation to the genetic heterogeneity of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2008, 111, 5078–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzon, R.; Volinia, S.; Liu, C.G.; Fernandez-Cymering, C.; Palumbo, T.; Pichiorri, F.; Fabbri, M.; Coombes, K.; Alder, H.; Nakamura, T.; et al. MicroRNA signatures associated with cytogenetics and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2008, 111, 3183–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debernardi, S.; Skoulakis, S.; Molloy, G.; Chaplin, T.; Dixon-McIver, A.; Young, B.D. MicroRNA miR-181a correlates with morphological sub-class of acute myeloid leukaemia and the expression of its target genes in global genome-wide analysis. Leukemia 2007, 21, 912–916. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Danen-van Oorschot, A.A.; Kuipers, J.E.; Arentsen-Peters, S.; Schotte, D.; de Haas, V.; Trka, J.; Baruchel, A.; Reinhardt, D.; Pieters, R.; Zwaan, C.M.; et al. Differentially expressed miRNAs in cytogenetic and molecular subtypes of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2012, 58, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrinkar, P.P.; Gunawardane, R.N.; Cramer, M.D.; Gardner, M.F.; Brigham, D.; Belli, B.; Karaman, M.W.; Pratz, K.W.; Pallares, G.; Chao, Q.; et al. AC220 is a uniquely potent and selective inhibitor of FLT3 for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Blood 2009, 114, 2984–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaba, H.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Coustan-Smith, E.; Li, L.; Furmanski, B.D.; Mascara, G.P.; Heym, K.M.; Christensen, R.; Onciu, M.; Shurtleff, S.A.; et al. Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the multikinase inhibitor sorafenib in combination with clofarabine and cytarabine in pediatric relapsed/refractory leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3293–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, T.C.; Cooper, T. Sorafenib as treatment for relapsed or refractory pediatric acute myelogenous leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2012, 59, 756–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levis, M.; Ravandi, F.; Wang, E.S.; Baer, M.R.; Perl, A.; Coutre, S.; Erba, H.; Stuart, R.K.; Baccarani, M.; Cripe, L.D.; et al. Results from a randomized trial of salvage chemotherapy followed by lestaurtinib for patients with FLT3 mutant AML in first relapse. Blood 2011, 117, 3294–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.C.; Wang, Q.; Chin, C.S.; Salerno, S.; Damon, L.E.; Levis, M.J.; Perl, A.E.; Travers, K.J.; Wang, S.; Hunt, J.P.; et al. Validation of ITD mutations in FLT3 as a therapeutic target in human acute myeloid leukaemia. Nature 2012, 485, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The world’s chilhood cancer experts. Available online: http://www.childrensoncologygroup.org/index.php/aaml1031 (accessed on 15 December 2014).
- Goemans, B.F.; Zwaan, C.M.; Miller, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Harlow, A.; Meshinchi, S.; Loonen, A.H.; Hahlen, K.; Reinhardt, D.; Creutzig, U.; et al. Mutations in KIT and RAS are frequent events in pediatric core-binding factor acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2005, 19, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwaan, C.M.; Rizzari, C.; Mechinaud, F.; Lancaster, D.L.; Lehrnbecher, T.; van der Velden, V.H.; Beverloo, B.B.; den Boer, M.L.; Pieters, R.; Reinhardt, D.; et al. Dasatinib in children and adolescents with relapsed or refractory leukemia: Results of the CA180–018 phase I dose-escalation study of the Innovative Therapies for Children with Cancer Consortium. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 2460–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcucci, G.G.S.; Zhao, J.; Carrol, A.J.; Bucci, D.; Vij, R.; Blum, W.; Pardee, T.; Wetzler, M.; Stock, W.; Bloomfield, C.D.; et al. Adding The KIT Inhibitor Dasatinib (DAS) To Standard Induction and Consolidation Therapy For Newly Diagnosed Patients (pts) With Core Binding Factor (CBF) Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): Initial Results Of The CALGB 10801 (Alliance) Study. 2013. Available online: https://ash.confex.com/ash/2013/webprogram/Paper63516.html (accessed on 15 December 2014).
- Burnett, A.K.; Russell, N.H.; Culligan, D.; Cavanagh, J.; Kell, J.; Wheatley, K.; Virchis, A.; Hills, R.K.; Milligan, D.; Institute AMLWGotUNCR. The addition of the farnesyl transferase inhibitor, tipifarnib, to low dose cytarabine does not improve outcome for older patients with AML. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 158, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamba, S.; Russo, M.; Sun, C.; Lazzari, L.; Cancelliere, C.; Grernrum, W.; Lieftink, C.; Bernards, R.; di Nicolantonio, F.; Bardelli, A. RAF Suppression Synergizes with MEK Inhibition in KRAS Mutant Cancer Cells. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 1475–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Hobor, S.; Bertotti, A.; Zecchin, D.; Huang, S.; Galimi, F.; Cottino, F.; Prahallad, A.; Grernrum, W.; Tzani, A.; et al. Intrinsic resistance to MEK inhibition in KRAS mutant lung and colon cancer through transcriptional induction of ERBB3. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, A.J.; Chen, L.; Fazio, M.; Sinha, A.U.; Bernt, K.M.; Banka, D.; Dias, S.; Chang, J.; Olhava, E.J.; Daigle, S.R.; et al. Leukemic transformation by the MLL-AF6 fusion oncogene requires the H3K79 methyltransferase Dot1l. Blood 2013, 121, 2533–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hear, C.; Inaba, H.; Pounds, S.; Shi, L.; Dahl, G.; Bowman, W.P.; Taub, J.W.; Pui, C.H.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Coustan-Smith, E.; et al. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin can reduce minimal residual disease in patients with childhood acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer 2013, 119, 4036–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersdorf, S.H.; Kopecky, K.J.; Slovak, M.; Willman, C.; Nevill, T.; Brandwein, J.; Larson, R.A.; Erba, H.P.; Stiff, P.J.; Stuart, R.K.; et al. A phase 3 study of gemtuzumab ozogamicin during induction and postconsolidation therapy in younger patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2013, 121, 4854–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwaan, C.M.; Reinhardt, D.; Zimmerman, M.; Hasle, H.; Stary, J.; Stark, B.; Dworzak, M.; Creutzig, U.; Kaspers, G.J.; International BFMSGoPAML. Salvage treatment for children with refractory first or second relapse of acute myeloid leukaemia with gemtuzumab ozogamicin: Results of a phase II study. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 148, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasle, H.; Abrahamsson, J.; Forestier, E.; Ha, S.Y.; Heldrup, J.; Jahnukainen, K.; Jonsson, O.G.; Lausen, B.; Palle, J.; Zeller, B.; et al. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin as postconsolidation therapy does not prevent relapse in children with AML: Results from NOPHO-AML 2004. Blood 2012, 120, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeha, S.; Razzouk, B.; Rytting, M.; Rheingold, S.; Albano, E.; Kadota, R.; Luchtman-Jones, L.; Bomgaars, L.; Gaynon, P.; Goldman, S.; et al. Phase II study of clofarabine in pediatric patients with refractory or relapsed acute myeloid leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4392–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, T.M.; Alonzo, T.A.; Gerbing, R.B.; Perentesis, J.P.; Whitlock, J.A.; Taub, J.W.; Horton, T.M.; Gamis, A.S.; Meshinchi, S.; Loken, M.R.; et al. AAML0523: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group on the efficacy of clofarabine in combination with cytarabine in pediatric patients with recurrent acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer 2014, 120, 2482–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijiya, N.; Thomson, B.; Isakoff, M.S.; Silverman, L.B.; Steinherz, P.G.; Borowitz, M.J.; Kadota, R.; Cooper, T.; Shen, V.; Dahl, G.; et al. Phase 2 trial of clofarabine in combination with etoposide and cyclophosphamide in pediatric patients with refractory or relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2011, 118, 6043–6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, N.; Kobos, R.; Renaud, T.; Steinherz, L.J.; Steinherz, P.G. Phase II trial of clofarabine with topotecan, vinorelbine, and thiotepa in pediatric patients with relapsed or refractory acute leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2014, 61, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, S.M.; Perry, T.; Woodman, C.B.; Kearns, P. Sequential treatment with cytarabine and decitabine has an increased anti-leukemia effect compared to cytarabine alone in xenograft models of childhood acute myeloid leukemia. PLoS One 2014, 9, e87475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, C.L.; Davies, S.M.; McMasters, R.; Absalon, M.; O’Brien, M.; Mo, J.; Broun, R.; Moscow, J.A.; Smolarek, T.; Garzon, R.; et al. Low dose decitabine in very high risk relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukaemia in children and young adults. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 161, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.G.; Kim, I.; Yoon, S.S.; Park, S.; Cheong, J.W.; Min, Y.H.; Lee, J.O.; Bang, S.M.; Yi, H.G.; Kim, C.S.; et al. Comparative analysis between azacitidine and decitabine for the treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 161, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).