Autoimmune Thyroid Disease and Pregnancy: The Interaction Between Genetics, Epigenetics and Environmental Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Forms of Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases
2.1. Autoimmune Hyperthyroidism
2.2. Autoimmune Hypothyroidism
3. Pregnancy and Autoimmune Thyroid Disease
3.1. Autoimmune Hyperthyroidism in Pregnancy

3.2. Autoimmune Hypothyroidism in Pregnancy
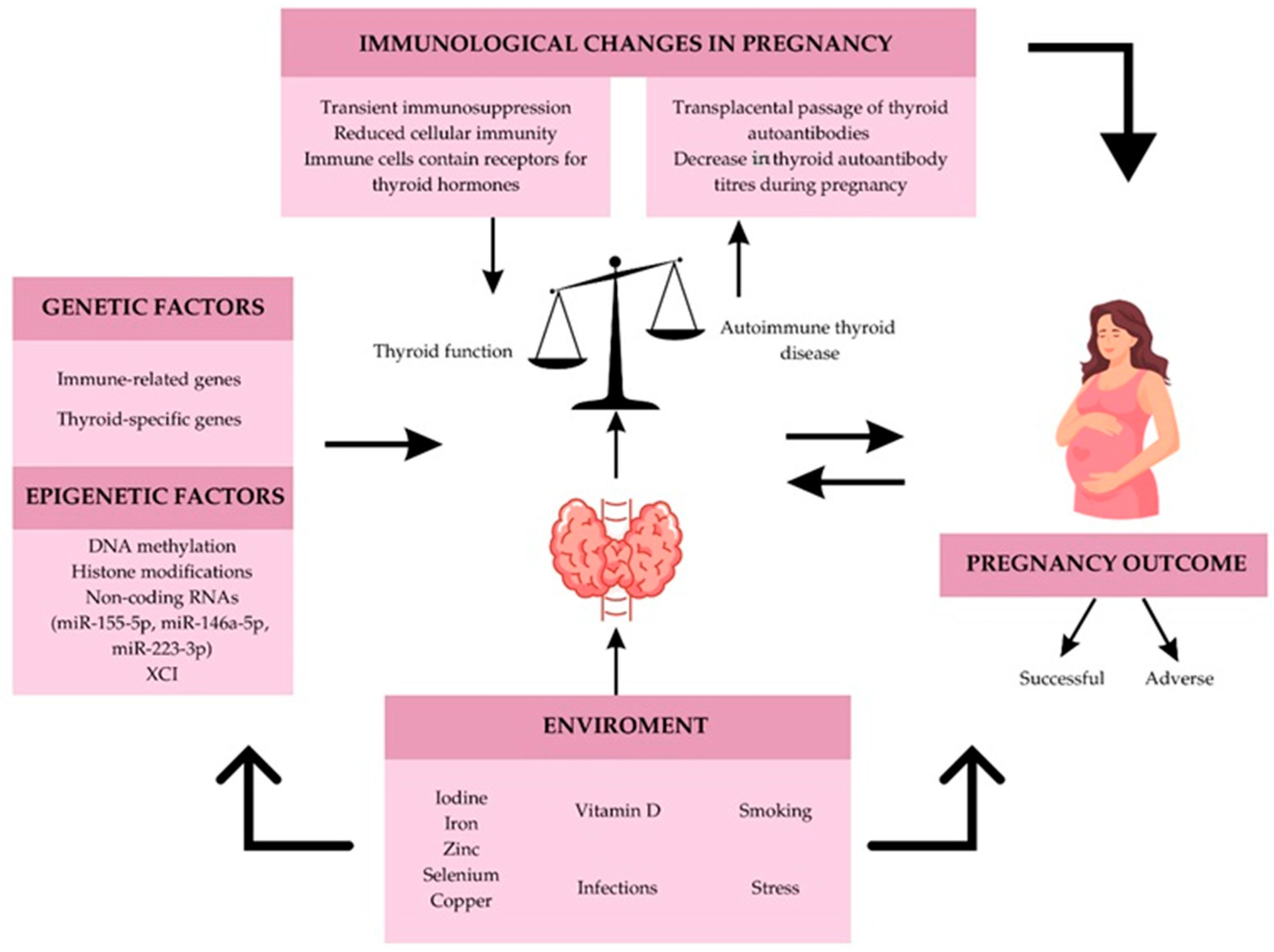
4. Genetic Factors and Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases
4.1. Immune-Related Genes
4.2. Thyroid-Specific Genes
4.3. Epigenetics Factors in Autoimmune Thyroid Disease
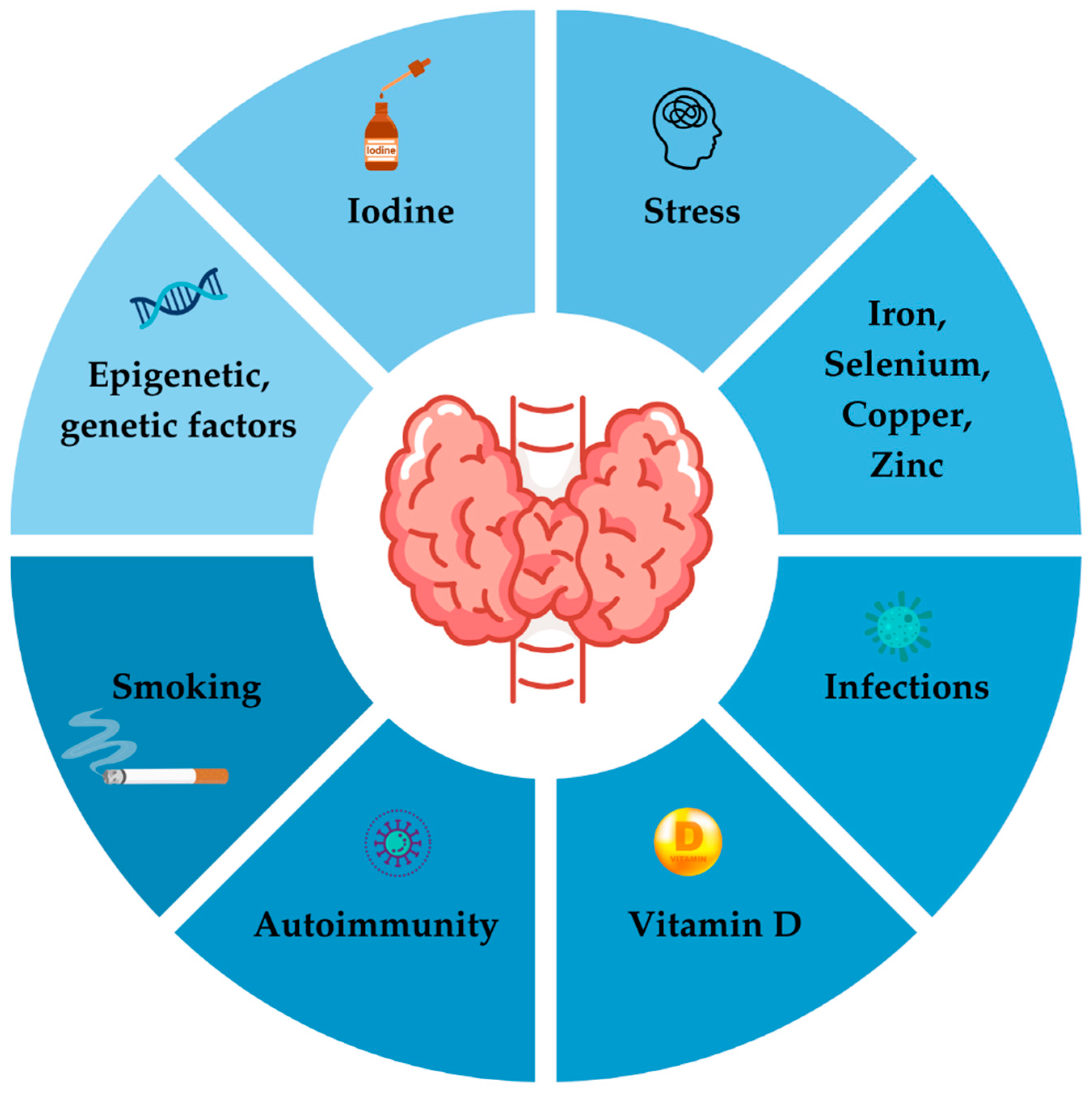
4.4. Environmental Factors
4.4.1. Iodine Intake and Autoimmune Thyroid Disease
4.4.2. Iodine Disbalance During Pregnancy with Autoimmune Thyroid Disease
4.4.3. Selenium and Autoimmune Thyroid Disease: A Scientific Overview
4.4.4. Selenium and Autoimmune Thyroiditis in Pregnancy
4.4.5. Autoimmune Thyroid Disease, Pregnancy and Iron—Causal Connections and Implications
4.4.6. Vitamin D and Thyroid Dysfunction
4.4.7. Smoking and Autoimmune Thyroid Disease
4.4.8. Smoking and Thyroid Function During Pregnancy
4.4.9. Infections and Autoimmune Thyroid Disease
4.4.10. Stress and Autoimmune Thyroid Disease
4.4.11. Stress and Thyroid Function During Pregnancy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bogusławska, J.; Godlewska, M.; Gajda, E.; Piekiełko-Witkowska, A. Cellular and molecular basis of thyroid autoimmunity. Eur. Thyroid J. 2022, 11, e210024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Hernández, R.; Sánchez de la Blanca, N.; Sacristán-Gómez, P.; Serrano-Somavilla, A.; Muñoz De Nova, J.L.; Sánchez Cabo, F.; Heyn, H.; Sampedro-Núñez, M.; Marazuela, M. Unraveling the molecular architecture of autoimmune thyroid diseases at spatial resolution. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaya, J.M.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Rojas-Villarraga, A.; Levy, R.A.; Cervera, R. (Eds.) Autoimmunity: From Bench to Bedside; El Rosario University Press: Bogota, Colombia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Caturegli, P.; De Remigis, A.; Rose, N.R. Hashimoto thyroiditis: Clinical and diagnostic criteria. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csaba, G. Hormones in the immune system and their possible role. A critical review. Acta. Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2014, 61, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomer, Y. Mechanisms of autoimmune thyroid diseases: From genetics to epigenetics. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2014, 9, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostami, R.; Nourooz-Zadeh, S.; Mohammadi, A.; Khalkhali, H.R.; Ferns, G.; Nourooz-Zadeh, J. Serum Selenium Status and Its Interrelationship with Serum Biomarkers of Thyroid Function and Antioxidant Defense in Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, G.; Zhu, Y.; Fang, L. Correlation Between Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis-Related Thyroid Hormone Levels and 25-Hydroxyvitamin D. Front. Endocrinol 2020, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cyna, W.; Wojciechowska, A.; Szybiak-Skora, W.; Lacka, K. The Impact of Environmental Factors on the Development of Autoimmune Thyroiditis—Review. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Xiao, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Z. Gut Microbiota Changes and Its Potential Relations with Thyroid Disorders: From Composition to Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2024, 17, 3719–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Wong, C.H. Bugging inflammation: Role of the gut microbiota. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2016, 5, e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.M.; Yeh, H.J.; Lin, T.M.; Chang, Y.S.; Hsu, H.C.; Shen, Y.C.; Kuo, T.T.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, S.H.; Chang, C.C. Association of interferon-based therapy with risk of autoimmune diseases in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection: A population-based Taiwanese cohort study. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 992819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Wu, S.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y.; Peng, J. Thyroid dysfunction is associated with the loss of hepatitis B surface antigen in patients with chronic hepatitis B undergoing treatment with a-interferon. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 3000605211025139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajjan, R.A.; Weetman, A.P. The Pathogenesis of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: Further Developments in our Understanding. Horm. Metab. Res. 2015, 47, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiersinga, W.M. Clinical relevance of environmental factors in the pathogenesis of autoimmune thyroid disease. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 31, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.M.; Fallahi, P.; Antonelli, A.; Benvenga, S. Environmental Issues in Thyroid Diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stathatos, N.; Daniels, G.H. Autoimmune thyroid disease. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2012, 24, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, C.M.; Daniels, G.H. Chronic autoimmune thyroiditis. N. Engl. J Med. 1996, 335, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menconi, F.; Oppenheim, Y.L.; Tomer, Y. Graves disease. In Diagnostic Criteria in Autoimmune Diseases; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 231–235. [Google Scholar]
- Brent, G.A. Clinical practice. Graves’ disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2594–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, B.; Bhusal, K. Graves Disease; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, Y.S.; Hookham, J.C.; Allahabadia, A.; Balasubramanian, S.P. Epidemiology, management and outcomes of Graves’ disease-real life data. Endocrine 2017, 56, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.S. Hyperthyroidism. Lancet 2003, 362, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kravchenko, V.; Zakharchenko, T. Thyroid hormones and minerals in immunocorrection of disorders in autoimmune thyroid diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1225494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, H. Zur Kenntniss der lymphoatosen Veranderung der Schilddrüse (Struma lymphomatoa). Langenbecks. Arch. Klin. Chirurg. 1912, 97, 219–248. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Ye, X.P.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, C.F.; Li, R.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, R.J.; Li, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; et al. Lymphocyte infiltration and thyrocyte destruction are driven by stromal and immune cell components in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witebsky, E.; Rose, N.R.; Terplan, K.; Paine, J.R.; Egan, R.W. Chronic thyroiditis and autoimmunization. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1957, 164, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralli, M.; Angeletti, D.; Fiore, M.; D’Aguanno, V.; Lambiase, A.; Artico, M.; de Vincentiis, M.; Greco, A. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: An update on pathogenic mechanisms, diagnostic protocols, therapeutic strategies, and potential malignant transformation. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, J.S.; Amaya-Amaya, J.; Anaya, J.M. Thyroid disease and autoimmune diseases. In Autoimmunity: From Bench to Bedside; Anaya, J.M., Shoenfeld, Y., Rojas-Villarraga, A., Eds.; El Rosario University Press: Bogota, Colombia, 2013; Chapter 30. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459466/ (accessed on 3 October 2024).
- Ragusa, F.; Fallahi, P.; Elia, G.; Gonnella, D.; Paparo, S.R.; Giusti, C.; Churilov, L.P.; Ferrari, S.M.; Antonelli, A. Hashimotos’ thyroiditis: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinic and therapy. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 33, 101367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Zou, D.; Cai, H.; Liu, Y. Ultrasonography in the diagnosis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Front. Biosci. 2016, 21, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljarad, M.; Alhalabi, N.; Hamad, A.; Nmr, N.; Abbas, F.; Alkhatib, A.; Alhalabi, M.; Al-Hammami, H.; Ibrahim, N. Prevalence of Thyroid Autoimmune Antibodies in Women Seeking Fertility Care in Damascus, Syria. Cureus 2019, 11, e5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondi, B.; Cappola, A.R.; Cooper, D.S. Subclinical hypothyroidism: A review. JAMA 2019, 322, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selmer, C.; Olesen, J.B.; Hansen, M.L.; von Kappelgaard, L.M.; Madsen, J.C.; Hansen, P.R.; Pedersen, O.D.; Faber, J.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Gislason, G.H. Subclinical and overt thyroid dysfunction and risk of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular events: A large population study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 2372–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klubo-Gwiezdzinska, J.; Wartofsky, L. Hashimoto thyroiditis: An evidence-based guide to etiology, diagnosis and treatment. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2022, 132, 16222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Quintero, B.; Yazbeck, C.; Sweeney, L.B. Thyroiditis: Evaluation and Treatment. Am. Fam. Physician 2021, 104, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Botta, A.; Rizzo, F.; Antonielli, T.; Ciliberti, A.; Garufi, E.; Lanzone, A.; Garufi, C.; De Carolis, S. The Detrimental Effect of Thyroiditis on Pregnancy Outcome of Patients Affected by Autoimmune Diseases: An Open Question. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 827735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Couture, C.; Girard, S. Innate and Adaptive Immune Systems in Physiological and Pathological Pregnancy. Biology 2023, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareva, I. Immune Suppression in Pregnancy and Cancer: Parallels and Insights. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croce, L.; Di Dalmazi, G.; Orsolini, F.; Virili, C.; Brigante, G.; Gianetti, E.; Moleti, M.; Napolitano, G.; Tonacchera, M.; Rotondi, M. Graves’ Disease and the Post-partum Period: An Intriguing Relationship. Front. Endocrin. 2019, 10, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moleti, M.; Di Mauro, M.; Sturniolo, G.; Russo, M.; Vermiglio, F. Hyperthyroidism in the pregnant woman: Maternal and fetal aspects. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2019, 16, 100190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, H.; Amin, P.; Lazarus, J.H. Hyperthyroidism and pregnancy. BMJ 2008, 336, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, D.S.; Laurberg, P. Hyperthyroidism in pregnancy. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2013, 1, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, A.W.; Lau, K.S.; Kohn, L.D. Epitope mapping of tsh receptor-blocking antibodies in Graves’ disease that appear during pregnancy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 3647–8653. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kung, A.W.; Jones, B.M. A change from stimulatory to blocking antibody activity in Graves’ disease during pregnancy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueta, Y.; Fukui, H.; Murakami, H.; Yamanouchi, Y.; Yamamoto, R.; Murao, A.; Santou, Y.; Taniguchi, S.; Mitani, Y.; Shigemasa, C. Development of primary hypothyroidism with the appearance of blocking-type antibody to thyrotropin receptor in Graves’ disease in late pregnancy. Thyroid 1999, 9, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargallo Fernández, M. Hyperthyroidism and pregnancy. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2013, 60, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negro, R.; Stagnaro-Green, A. Clinical aspects of hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, and thyroid screening in pregnancy. Endocr. Pract. 2014, 20, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Mestman, J.H. Graves’ hyperthyroidism in pregnancy. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2019, 26, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorah, K.; Alderson, T.L. Hyperthyroidism in Pregnancy; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024; p. 32644629. [Google Scholar]
- Illouz, F.; Luton, D.; Polak, M.; Besançon, A.; Bournaud, C. Graves’ disease and pregnancy. Ann. Endocrinol. 2018, 79, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurberg, P.; Andersen, S.L. Endocrinology in pregnancy: Pregnancy and the incidence, diagnosing and therapy of Graves’ disease. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 175, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groot, L.; Abalovich, M.; Alexander, E.K.; Amino, N.; Barbour, L.; Cobin, R.H.; Eastman, C.J.; Lazarus, J.H.; Luton, D.; Mandel, S.J.; et al. Management of thyroid dysfunction during pregnancy and postpartum: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 2543–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.R.; Lachica, R.; Lee, R.H.; Montoro, M.; Mestman, J. Diagnosis and Management of Hyperthyroidism in Pregnancy: A Review. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2016, 71, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobaly, K.; Mandel, S.J. Hyperthyroidism and Pregnancy. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 48, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Bischoff, L.A. Management of Hyperthyroidism during the Preconception Phase, Pregnancy, and the Postpartum Period. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2016, 34, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, I.R.; Martins, J.R.; Jerónimo, M.; Caetano, J.S.; Cardoso, R.; Dinis, I.; Mirante, A. Neonates Born to Mothers with Graves’ Disease: 15 Year Experience of a Pediatric Endocrinology Department. Acta Med. Port. 2020, 33, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyrżak, B.; Rumińska, M.; Witkowska-Sędek, E.; Kucharska, A. Follow-Up of Thyroid Function in Children with Neonatal Hyperthyroidism. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 877119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, E.K.; Pearce, E.N.; Brent, G.A.; Brown, R.S.; Chen, H.; Dosiou, C.; Grobman, W.A.; Laurberg, P.; Lazarus, J.H.; Mandel, S.J.; et al. Guidelines of the American Thyroid Association for the Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Disease During Pregnancy and the Postpartum. Thyroid 2017, 27, 315–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahaly, G.J.; Bartalena, L.; Hegedüs, L.; Leenhardt, L.; Poppe, K.; Pearce, S.H. European Thyroid Association Guideline for the Management of Graves’ Hyperthyroidism. Eur. Thyroid J. 2018, 7, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, J.S.; Cunningham, F.G. Thyrotoxicosis and heart failure that complicate pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 190, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Pearce, E.N. Hyperthyroidism: A Review. JAMA 2023, 17, 1472–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moleti, M.; Sturniolo, G.; Di Mauro, M.; Russo, M.; Vermiglio, F. Autoimmune thyroid diseases and pregnancy. Ann. Thyroid 2018, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, R.; Crowther, C.A.; Middleton, P. Interventions for hyperthyroidism pre-pregnancy and during pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 19, CD008633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarantaki, A.; Tsiorou, K.; Gourount, K. The impact of Hashimoto’s disease on female fertility: A systematic review. Int. J. Reprod. Contracept. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 11, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Z.; Pan, X.; Leung, W.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Sima, Y.; Gober, H.J.; et al. The Clinical Value and Variation of Antithyroid Antibodies during Pregnancy. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 8871951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkoszka, N.; Gibula-Tarlowska, E.; Kotlinska, J.; Bielenica, A.; Gawel, K.; Kedzierska, E. Selenium Intake and Postnatal Depression—A brief overview. Nutrients 2024, 18, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oken, E.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Amarasiriwardena, C.; Jayawardene, I.; Bellinger, D.C.; Hibbeln, J.R.; Wright, R.O.; Gillman, M.W. Maternal prenatal fish consumption and cognition in mid childhood: Mercury, fatty acids, and selenium. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2016, 57, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipowicz, D.; Majewska, K.; Kalantarova, A.; Szczepanek-Parulska, E.; Ruchała, M. The rationale for selenium supplementation in patients with autoimmune thyroiditis, according to the current state of knowledge. Endokrynol. Pol. 2021, 72, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gać, P.; Czerwińska, K.; Macek, P.; Jaremkow, A.; Mazur, G.; Pawlas, K.; Poreba, R. The importance of selenium and zinc deficiency in cardiovascular disorders. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 82, 103553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuria, A.; Tian, H.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Aaseth, J.O.; Zang, J.; Cao, Y. Selenium status in the body and cardiovascular disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Food. Sci. Nutr. 2020, 61, 3616–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastola, M.M.; Locatis, C.; Maisiak, R.; Fontelo, P. Selenium, copper, zinc and hypertension: An analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2011–2016). BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinceti, M.; Chawla, R.; Filippini, T.; Dutt, C.; Cilloni, S.; Loomba, R.; Bargellini, A.; Orsini, N.; Dhillon, K.S.; Whelton, P. Blood pressure levels and hypertension prevalence in a high selenium environment: Results from a cross-sectional study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 29, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korevaar, T.I.M.; Medici, M.; Visser, T.J.; Peeters, R.P. Thyroid disease in pregnancy: New insights in diagnosis and clinical management. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarus, J.; Brown, R.S.; Daumerie, C.; Hubalewska-Dydejczyk, A.; Negro, R.; Vaidya, B. European thyroid association guidelines for the management of subclinical hypothyroidism in pregnancy and in children. Eur. Thyroids J. 2014, 3, 76–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korevaar, T.I.M.; Derakhshan, A.; Taylor, P.N.; Meima, M.; Chen, L.; Bliddal, S.; Carty, D.M.; Meems, M.; Vaidya, B.; Shields, B.; et al. Association of thyroid function test abnormalities and thyroid autoimmunity with preterm birth: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2019, 322, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Chu, R.; Pan, S.; Lai, X.; Ran, J.; Li, X. Impact of subclinical TPOAb-negative maternal hypothyroidism in early pregnancy on adverse pregnancy outcomes. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 12, 20420188211054690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magri, F.; Bellingeri, C.; De Maggio, I.; Croce, L.; Coperchini, F.; Rotondi, M.; Chiovato, L.; Spinillo, A.; Beneventi, F. First trimester serum TSH in the range of 4–10 mIU/L is associated with obstetric complications in thyroid peroxidase antibody-negative women. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2023, 46, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppe, K.G. Levothyroxine in Pregnancy. In 70 Years of Levothyroxine; Kahaly, G.J., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 47–60. [Google Scholar]
- Solha, S.T.G.; Mattar, R.; Teixeira, P.F.D.S.; Chiamolera, M.I.; Maganha, C.A.; Zaconeta, A.C.M.; Souza, R.T. Screening, diagnosis and management of hypothyroidism in pregnancy. Rev. Bras. Ginecol. Obstet. 2022, 44, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Stefan-Lifshitz, M.; Li, C.W.; Tomer, Y. Genetics and epigenetics of autoimmune thyroid diseases: Translational implications. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 37, 101661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas Uricoechea, H. Molecular Mechanisms in Autoimmune Thyroid Disease. Cells 2023, 12, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, E.M.; Tomer, Y. The CD40, CTLA-4, thyroglobulin, TSH receptor, and PTPN22 gene quintet and its contribution to thyroid autoimmunity: Back to the future. J. Autoimmun. 2007, 28, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogović Crnčić, T.; Girotto, N.; Ilić Tomaš, M.; Krištović, I.; Klobučar, S.; Batičić, L.; Ćurko-Cofek, B.; Sotošek, V. Innate Immunity in Autoimmune Thyroid Disease during Pregnancy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mei, Y.; He, B.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Hu, R.; Li, L.; Ding, Z. General and Specific Genetic Polymorphism of Cytokines-Related Gene in AITD. Mediators. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 3916395. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, E.M.; Huber, A.; Tomer, Y. The HLA gene complex in thyroid autoimmunity: From epidemiology to etiology. J. Autoimmun. 2008, 30, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, R.A.; McIntosh, R.S.; Marelli-Berg, F.; Lombardi, G.; Lechler, R.; Weetman, A.P. Detection of CD40 on human thyroid follicular cells: Analysis of expression and function. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysliwiec, J.; Oklota, M.; Nikolajuk, A.; Waligorski, D.; Gorska, M. Serum CD40/CD40L system in Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis related to soluble Fas, FasL and humoral markers of autoimmune response. Immunol. Investig. 2007, 36, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzieri, A.; Montanucci, P.; Basta, G.; Calafiore, R. The role behind the scenes of Tregs and Th17s in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: Toward a pivotal role of FOXP3 and BACH2. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1098243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, R.N.; Chowdhary, K.; Leon, J.; Mathis, D.; Benoist, C. FoxP3 associates with enhancer-promoter loops to regulate Treg-specific gene expression. Sci. Immunol. 2022, 7, eabj9836. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mizuma, T.; Watanabe, M.; Inoue, N.; Arakawa, Y.; Tomari, S.; Hidaka, Y.; Iwatani, Y. Association of the polymorphisms in the gene encoding thyroglobulin with the development and prognosis of autoimmune thyroid disease. Autoimmunity 2017, 50, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomari, S.; Watanabe, M.; Inoue, N.; Mizuma, T.; Yamanaka, C.; Hidaka, Y.; Iwatani, Y. The polymorphisms in the thyroid peroxidase gene were associated with the development of autoimmune thyroid disease and the serum levels of anti-thyroid peroxidase antibody. Endocr. J. 2017, 64, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Shao, X.; Song, R.; Xu, D.; Zhang, J.A. The Emerging Role of Epigenetics in Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, L.D.; Le, T.; Fan, G. DNA methylation and its basic function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafontaine, N.; Wilson, S.G.; Walsh, J.P. DNA Methylation in Autoimmune Thyroid Disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Jia, J.; Du, T.; Zhang, N.; Tang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Fang, D. Overview of Histone Modification. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1283, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Haga, E.; Inoue, N.; Iwatani, Y.; Arakawa, Y.; Morita, E.; Hashimoto, H.; Noguchi, Y.; Hidaka, Y.; Watanabe, M. Intraindividual variation in histone acetylation and its impact on autoimmune thyroid diseases. Endocr. J. 2023, 70, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.; Baltimore, D. MicroRNAs as regulatory elements in immune system logic. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, R.; Noel, D.; Pers, Y.M.; Apparailly, F.; Jorgensen, C. Deregulation and therapeutic potential of microRNAs in arthritic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seddiki, N.; Brezar, V.; Ruffin, N.; Levy, Y.; Swaminathan, S. Role of miR-155 in the regulation of lymphocyte im-mune function and disease. Immunology 2014, 142, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.Q.; Papp, G.; Szodoray, P.; Zeher, M. The role of microRNAs in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Munoz, A.; Martinez-Hernandez, R.; Ramos-Levi, A.M.; Serrano-Somavilla, A.; Gonzalez-Amaro, R.; Sanchez-Madrid, F.; de la Fuente, H.; Marazuela, M. Circulating microvesicles regulate Treg and Th17 differentiation in human autoimmune thyroid disorders. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, e1531–e1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhang, R.; Lin, Z.; Lu, T.; Bai, X.; Li, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Q. Integrative analysis of mRNA and miRNA array data reveals the suppression of retinoic acid pathway in regulatory T cells of Graves’ disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, e2620–e2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernecker, C.; Lenz, L.; Ostapczuk, M.S.; Schinner, S.; Willenberg, H.; Ehlers, M.; Vordenbäumen, S.; Feldkamp, J.; Schott, M. MicroRNAs miR-146a1, miR-155_2, and miR-200a1 are regulated in autoimmune thyroid diseases. Thyroid 2012, 22, 1294–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishido, N.; Inoue, N.; Watanabe, M.; Hidaka, Y.; Iwatani, Y. The relationship between skewed X chromosome inactivation and the prognosis of Graves’ and Hashimoto’s diseases. Thyroid 2015, 25, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wu, C.; Wang, Z.; Wu, C.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, X.; Hu, Y.P.; Shi, Z.; Song, Q.; Cui, X.; et al. Iodine nutrition status and thyroid autoimmunity during pregnancy: A cross-sectional study of 4635 pregnant women. Nutr. J. 2022, 21, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shang, F.; Liu, C.; Zhai, X. The correlation between iodine and metabolism: A review. Front. Nutr. 2024, 19, 1346452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farebrother, J.; Zimmermann, M.B.; Andersson, M. Excess iodine intake: Sources, assessment, and effects on thyroid function. Ann. N. Y. Acad Sci. 2019, 1446, 44–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Kawashima, A.; Ishido, Y.; Yoshihara, A.; Oda, K.; Hiroi, N.; Ito, T.; Ishii, N.; Suzuki, K. Iodine excess as an environmental risk factor for autoimmune thyroid disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 12895–12912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teti, C.; Panciroli, M.; Nazzari, E.; Pesce, G.; Mariotti, S.; Olivieri, A.; Bagnasco, M. Iodoprophylaxis and thyroid autoimmunity: An update. Immunol. Res. 2021, 69, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, L.; Lian, X.; Liu, C.; Shan, Z.; Shi, B.; Shi, L.; Tong, N.; Weng, J.; Zhao, J.; et al. Urinary iodine concentration is inversely associated with thyroglobulin antibodies. Endocr. Pract. 2019, 25, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrick, K.A.; Perrine, C.G.; Aoki, Y.; Caldwell, K.L. Iodine status and consumption of key iodine sources in the U.S. population with special attention to reproductive age women. Nutrients 2018, 10, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dineva, M.; Rayman, M.P.; Levie, D.; Guxens, M.; Peeters, R.P.; Vioque, J.; González, L.; Espada, M.; Ibarluzea, J.; Sunyer, J.; et al. Similarities and differences of dietary and other determinants of iodine status in pregnant women from three European birth cohorts. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsatsoulis, A. The role of iodine versus selenium in the rising trend of autoimmune thyroiditis in iodine-sufficient countries. Endocrinol. Metab. Int. 2018, 6, 412–414. [Google Scholar]
- Wémeau, J.L.; Klein, M.; Sadoul, J.L.; Briet, C.; Vélayoudom-Céphise, F.L. Graves’ disease: Introduction, epidemiology, endogenous and environmental pathogenic factors. Ann. Endocrinol. 2018, 79, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burek, C.L.; Talor, M.V. Environmental triggers of autoimmune thyroiditis. J. Autoimmun. 2009, 33, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carayanniotis, G. Molecular parameters linking thymoglobulin iodination with autoimmune thyroiditis. Hormones 2011, 10, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duntas, L.H. The catalytic role of iodine excess in loss of homeostasis in autoimmune thyroiditis. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2018, 25, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, M.; Knudsen, N.; Carlé, A.; Andersen, S.; Jørgensen, T.; Perrild, H.; Ovesen, L.; Rasmussen, L.B.; Thuesen, B.H.; Pedersen, I.B. Increased incidence rate of hypothyroidism after iodine fortification in Denmark: A 20-year prospective population-based study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, A.; Stokes, B.; Otaha, L.P.; Owens, D.; Burgess, J.R. Temporal trends in thyroid- stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroid peroxidase antibody (ATPO) testing across two phases of iodine fortification in Tasmania (1995–2013). Clin. Endocrinol. 2017, 87, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khattak, R.M.; Ittermann, T.; Nauck, M.; Below, H.; Völzke, H. Monitoring the prevalence of thyroid disorders in the adult population of Northeast Germany. Popul. Health Metr. 2016, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, D.; Yang, W.; Shi, X.; Li, Y.; Ba, J.; Chen, B.; Du, J.; He, L.; Lai, X.; Li, Y.; et al. An inverse relationship between iodine intake and thyroid antibodies: A national cross-sectional survey in mainland China. Thyroid 2020, 30, 1656–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Vieja, A.; Santisteban, P. Role of iodide metabolism in physiology and cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moleti, M.; Trimarchi, F.; Vermiglio, F. Thyroid physiology in pregnancy. Endocr. Pract. 2014, 20, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, M.B. Iodine deficiency in pregnancy and the effects of maternaliodine supplementation on the offspring: A review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toloza, F.J.K.; Motahari, H.; Maraka, S. Consequences of Severe Iodine Deficiency in Pregnancy: Evidence in Humans. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, E.N.; Lazarus, J.H.; Moreno-Reyes, R.; Zimmermann, M.B. Consequences of iodine deficiency and excess in pregnant women: An overview of current knowns and unknowns. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zheng, H.; Li, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Z. Associations of maternal iodine status and thyroid function with adverse pregnancy outcomesin Henan Province of China. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 47, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, J.L.; Ali, M.; Buck Louis, G.M.; Kannan, K.; Weck, J.; Wan, Y.; Maisog, J.; Giannakou, A.; Sundaram, R. Pregnancy loss and iodine status: The LIFE prospective cohort study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.M.; Braverman, L.E. Consequences of excess iodine. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, P.; Su, X.; Zou, S.; Song, J.; Liu, S. A comparison of iodine status in children and pregnant women after a policy change in the iodized salt standard in Shanghai, China. Biol. Trac Elem. Res. 2018, 185, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, P.; Su, X.; Zou, S.; Song, J.; Liu, S. A Comparative Study of Iodized Salt Programs: Shanghai and Switzerland. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 187, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, S.; Eastman, C.J.; Gallego, G. The impact of mandatory iodine fortification and supplementation on pregnant and lactating women in Australia. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 28, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Southern, A.P.; Anastasopoulou, C.; Jwayyed, S. Iodine Toxicity; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024; p. 32644629. [Google Scholar]
- Rebagliato, M.; Murcia, M.; Alvarez-Pedrerol, M.; Espada, M.; Fernández-Somoano, A.; Lertxundi, N.; Navarrete-Muñoz, E.M.; Forns, J.; Aranbarri, A.; Llop, S.; et al. Iodine supplementation during pregnancy and infant neuropsychological development. INMA Mother and Child Cohort Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 177, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdue-Smithe, A.C.; Männistö, T.; Bell, G.A.; Mumford, S.L.; Liu, A.; Kannan, K.; Kim, U.J.; Suvanto, E.; Surcel, H.M.; Gissler, M.; et al. The Joint Role of Thyroid Function and Iodine Status on Risk of Preterm Birth and Small for Gestational Age: A Population-Based, Nested Case-Control Study of Finnish Women. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winther, K.H.; Rayman, M.P.; Bonnema, S.J.; Hegedus, L. Selenium in thyroid disorders—Essential knowledge for clinicians. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomburg, L. Selenium Deficiency Due to Diet, Pregnancy, Severe Illness, or COVID-19-A Preventable Trigger for Autoimmune Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minnetti, M.; Sada, V.; Feola, T.; Giannetta, E.; Pozza, C.; Gianfrilli, D.; Isidori, A.M.; Cozzolino, A. Selenium Supplementation in Pregnant Women with Autoimmune Thyroiditis: A Practical Approach. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Ziros, P.G.; Chartoumpekis, D.V.; Psarias, G.; Duntas, L.; Zuo, X.; Li, X.; Ding, Z.; Sykiotis, G.P. Traditional Chinese Medicine for Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: Focus on Selenium and Antioxidant Phytochemicals. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huwiler, V.V.; Maissen-Abgottspon, S.; Stanga, Z.; Mühlebach, S.; Trepp, R.; Bally, L.; Bano, A. Selenium Supplementation in Patients with Hashimoto Thyroiditis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Thyroid 2024, 34, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Liang, S.S.; Ren, J.J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Deng, X.X.; Liu, W.D.; Yan, Y.L.; Song, G.H.; Li, X.X. The Effects of Selenium Supplementation in the Treatment of Autoimmune Thyroiditis: An Overview of Systematic Reviews. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulhai, A.M.; Rotondo, R.; Petraroli, M.; Patianna, V.; Predieri, B.; Iughetti, L.; Esposito, S.; Street, M.E. The Role of Nutrition on Thyroid Function. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jiang, Q.L.; Xu, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Jiang, R.; Jiang, J. Selenium regulates T cell differentiation in experimental autoimmune thyroiditis in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 124, 110993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Feng, W.; Chen, H.; Shi, H.; Jiang, L.; Zheng, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Ge, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Effect of selenium on thyroid autoimmunity and regulatory T cells in patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: A prospective randomized- controlled trial. Clin. Tansl. Sci. 2021, 14, 1390–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.Q.; Qiu, G.Y.; Yang, Z.B.; Tan, Z.X.; Quan, X.Q. Clinical efficacy of selenium supplementation in patients with Hashimoto thyroiditis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicin 2023, 102, e33791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhrle, J. Selenium and the thyroid. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2015, 22, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, A.R.; Dore, G.; Aboud, L.; Makama, M.; Nguyen, P.Y.; Mills, K.; Sanderson, B.; Hastie, R.; Ammerdorffer, A.; Vogel, J.P. The effect of selenium supplementation in pregnant women on maternal, fetal, and newborn outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 2023, 5, 101160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yigit, E.; Sayar, I. Selenium Supplementation and Gestational Diabetes: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Journal of the College of Physicians and Surgeons—Pakistan. JCPSP 2024, 34, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Negro, R.; Greco, G.; Mangieri, T.; Pezzarossa, A.; Dazzi, D.; Hassan, H. The influence of selenium supplementation on postpartum thyroid status in pregnant women with thyroid peroxidase autoantibodies. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2007, 92, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitts, M.W.; Byrns, C.N.; Ogawa-Wong, A.N.; Kremer, P.; Berry, M.J. Selenoproteins in nervous system development and function. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 161, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircan, K.; Chillon, T.S.; Jensen, R.C.; Jensen, T.K.; Sun, Q.; Bonnema, S.J.; Glintborg, D.; Bilenberg, N.; Andersen, M.S.; Schomburg, L. Maternal selenium deficiency during pregnancy in association with autism and ADHD traits in children: The Odense Child Cohort. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 1, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.S.E.; Ji, Y.; Raghavan, R.; Wang, G.; Hong, X.; Pearson, C.; Mirolli, G.; Bind, E.; Steffens, A.; Mukherjee, J.; et al. Maternal prenatal selenium levels and child risk of neurodevelopmental disorders: A prospective birth cohort study. Autism. Res. 2021, 14, 2533–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, M.; Melo, M.; Carrilho, F. Selenium and thyroid disease: From pathophysiology to treatment. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubalewska-Dydejczyk, A.; Duntas, L.; Gilis-Januszewska, A. Pregnancy, thyroid, and the potential use of selenium. Hormones 2020, 19, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, V.; Condorelli, R.A.; Cannarella, R.; Aversa, A.; Calogero, A.E.; La Vignera, S. Relationship between Iron Deficiency and Thyroid Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Wang, X.; Yuan, L.; Guo, L. Iron Deficiency, a Risk Factor of Thyroid Disorders in Reproductive-Age and Pregnant Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 25, 629831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, W.; Elmugabil, A.; Hamdan, H.Z.; Rayis, D.A.; Adam, I. Iron deficiency and thyroid dysfunction among sudanese women in first trimester of pregnancy: A cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2023, 13, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Mao, M.; Guo, T.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Dai, J.; Huang, Y. Iron Status, Thyroid Dysfunction, and Iron Deficiency Anemia: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2024, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, W.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Xu, X.; Wu, H. Association Between Serum Ferritin Levels in Early Pregnancy and Thyroid Function and Pregnancy Outcomes in Chinese Population. Int. J. Womens Health 2023, 11, 1951–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.B.; Burgi, H.; Hurrell, R.F. Iron deficiency predicts poor maternal thyroid status during pregnancy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 3436–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veltri, F.; Decaillet, S.; Kleynen, P.; Grabczan, L.; Belhomme, J.; Rozenberg, S.; Pepersack, T.; Poppe, K. Prevalence of thyroid autoimmunity and dysfunction in women with iron deficiency during early pregnancy: Is it altered? Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 175, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleić, N.; Babić Leko, M.; Gunjača, I.; Zemunik, T. Vitamin D and thyroid function: A mendelian randomization study. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khozam, S.A.; Sumaili, A.M.; Alflan, M.A.; Shawabkeh, R.A.S. Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Autoimmune Thyroid Disorder: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 12, e25869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durá-Travé, T.; Gallinas-Victoriano, F. Autoimmune Thyroiditis and Vitamin, D. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 9, 3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, B.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Cao, Z.; Pang, T.; Wang, Q.; Wei, J. Association between serum vitamin D level and Graves’ disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. J. 2024, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, M.; Pham, H.; Rahman, S.T.; Baxter, C.; Duarte Romero, B.; Armstrong, B.K.; Ebeling, P.R.; English, D.R.; Hartel, G.; van der Pols, J.C.; et al. The Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Hypothyroidism in the Randomized Controlled D-Health Trial. Thyroid 2023, 33, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellastella, G.; Maiorino, M.I.; Petrizzo, M.; De Bellis, A.; Capuano, A.; Esposito, K.; Giugliano, D. Vitamin D and autoimmunity: What happens in autoimmune polyendocrine syndromes? J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2015, 38, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, D.; Baci, D.; Kustrimovic, N.; Lanzo, N.; Patera, B.; Tanda, M.L.; Piantanida, E.; Mortara, L. How Does Vitamin D Affect Immune Cells Crosstalk in Autoimmune Diseases? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 28, 4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, B.; Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; Mathieu, C.; Vallone, C.V.; Mascitelli, L.; Bizzaro, G.; Altieri, V.M.; Tirabassi, G.; Balercia, G.; et al. Does vitamin D play a role in autoimmune endocrine disorders? A proof of concept. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2017, 18, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houen, G. Auto-immuno- deficiency syndromes. Autoimmun. Rev. 2024, 23, 103610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinharay, M.; Dasgupta, A.; Karmakar, A. Association between Vitamin D Receptor Gene Polymorphism (Fok 1), Vitamin D Status and Autoimmune Thyroiditis. Mymensingh Med. J. 2024, 33, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soda, M.; Priante, C.; Pesce, C.; De Maio, G.; Lombardo, M. The Impact of Vitamin D on Immune Function and Its Role in Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: A Narrative Review. Life 2024, 17, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, J.; Yan, Z.; Yu, X.; Huang, H. Higher prevalence of thyroid-specific autoibodies (TPOAb and TgAb) is related to a higher prevalence of fractures in females: Results from NHANES 2007-2010. Osteoporos. Int. 2024, 35, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Kim, M.J.; Yoon, S.G.; Myong, J.P.; Yu, H.W.; Chai, Y.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, K.E. Impact of smoking on thyroid gland: Dose-related effect of urinary cotinine levels on thyroid function and thyroid autoimmunity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 12, 4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, N.; Chen, L.; Lian, X.; Liu, C.; Shan, Z.; Shi, B.; Tong, N.; et al. The association between cigarette smoking and serum thyroid stimulating hormone, thyroid peroxidase antibodies and thyroglobulin antibodies levels in Chinese residents: A cross-sectional study in 10 cities. PLoS ONE 2019, 25, e0225435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadkhodazadeh, H.; Amouzegar, A.; Mehran, L.; Gharibzadeh, S.; Azizi, F.; Tohidi, M. Smoking status and changes in thyroid-stimulating hormone and free thyroxine levels during a decade of follow-up: The Tehran thyroid study. Caspian. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 11, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Vestergaard, P.; Rejnmark, L.; Weeke, J.; Hoeck, H.C.; Nielsen, H.K.; Rungby, J.; Laurberg, P.; Mosekilde, L. Smoking as a risk factor for Graves’ disease, toxic nodular goiter, and autoimmune hypothyroidism. Thyroid 2002, 12, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohidi, M.; Derakhshan, A.; Akbarpour, S.; Amouzegar, A.; Mehran, L.; Baghbani-Oskouei, A.; Azizi, F.; Hadaegh, F. Thyroid Dysfunction States and Incident Cardiovascular Events: The Tehran Thyroid Study. Horm. Metab. Res. 2018, 50, e1. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kunutsor, S.K.; Dey, R.S.; Touw, D.J.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Dullaart, R.P.F. Urine cotinine versus self-reported smoking and the risk of chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2024, 39, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruppen, E.G.; Kootstra-Ros, J.; Kobold, A.M.; Connelly, M.A.; Touw, D.; Bos, J.H.J.; Hak, E.; Links, T.P.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Dullaart, R.P.F. Cigarette smoking is associated with higher thyroid hormone and lower TSH levels: The PREVEND study. Endocrine 2020, 67, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldin, O.P.; Goughenour, B.E.; Gilbert, S.Z.; Landy, H.J.; Soldin, S.J. Thyroid hormone levels associated with active and passive cigarette smoking. Thyroid 2009, 19, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbownik-Lewińska, M.; Stępniak, J.; Iwan, P.; Lewiński, A. Iodine as a potential endocrine disruptor—A role of oxidative stress. Endocrine 2022, 78, 219–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, S.L.; Olsen, J.; Wu, C.S.; Laurberg, P. Smoking reduces the risk of hypothyroidism and increases the risk of hyperthyroidism: Evidence from 450,842 mothers giving birth in Denmark. Clin. Endocrinol. 2014, 80, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, B.; Hill, A.; Bilous, M.; Knight, B.; Hattersley, A.T.; Bilous, R.W.; Bijay, V. Cigarette Smoking during Pregnancy Is Associated with Alterations in Maternal and Fetal Thyroid Function. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, R.; Pinto, R.; Li, E.; Sohrab, M.; Distefano, A.G. Thyroid Eye Disease. Life 2022, 12, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Kong, E.; Choi, J. Associations of urinary cotinineverified active and passive smoking with thyroid function: Analysis of population-based nationally representative data. Thyroid 2018, 28, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehran, L.; Amouzgar, A.; Delshad, H.; Azizi, F. The association of cigarette smoking with serum TSH concentration and thyroperoxidase antibody. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2012, 120, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, N.H.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, H.L.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, S.H.; Lim, S.; Park, Y.J.; Park, D.J.; Jang, H.C.; et al. Interaction between cigarette smoking and iodine intake and their impact on thyroid function. Clin. Endocrinol. 2010, 73, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudzadeh, L.; Abtahi Froushani, S.M.; Ajami, M.; Mahmoudzadeh, M. Effect of Nicotine on Immune System Function. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2023, 13, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, F.; Liang, C.L.; Liu, H.; Zeng, Y.Q.; Hou, S.; Huang, S.; Lai, X.; Dai, Z. Impacts of cigarette smoking on immune responsiveness: Up and down or upside down? Oncotarget 2017, 8, 268–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.J.; Bremner, A.P.; Hadlow, N.C.; Feddema, P.; Leedman, P.J.; O’Leary, P.C.; Walsh, J.P. The log TSH-free T4 relationship in a community-based cohort is nonlinear and is influenced by age, smoking and thyroid peroxidase antibody status. Clin. Endocrinol. 2016, 85, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quelhas, D.; Kompala, C.; Wittenbrink, B.; Han, Z.; Parker, M.; Shapiro, M.; Downs, S.; Kraemer, K.; Fanzo, J.; Morris, S.; et al. The association between active tobacco use during pregnancy and growth outcomes of children under five years of age: A systematic review and metaanalysis. BMC Public Health 2018, 13, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnerbeck, A.; Edstedt Bonamy, A.K.; Wikström, A.K.; Granath, F.; Wickström, R.; Cnattingius, S. Maternal snuff use and smoking and the risk of oral cleft malformations: A population- based cohort study. PLoS ONE 2014, 15, e84715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, M.; Albieri, V.; Kjaer, S.K.; Jensen, A. Maternal smoking in pregnancy and risk for congenital malformations: Results of a Danish register-based cohort study. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2014, 93, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbagh, H.J.; Hassan, M.H.A.; Innes, N.P.T.; Elkodary, H.M.; Little, J.; Mossey, P.A. Passive smoking in the etiology of non-syndromic orofacial clefts: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suter, M.A.; Aagaard, K.M. The impact of tobacco chemicals and nicotine on placental development. Prenat. Diagn. 2020, 40, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Liu, J.; Larsson, S.C. Smoking, alcohol and coffee consumption and pregnancy loss: A Mendelian randomization investigation. Fertil. Steril. 2021, 116, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Probst, C.; Rehm, J.; Popova, S. National, regional, and global prevalence of smoking during pregnancy in the general population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e769–e776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, S.L.; Knøsgaard, L.; Handberg, A.; Vestergaard, P.; Andersen, S. Maternal adiposity, smoking, and thyroid function in early pregnancy. Endocr. Connect. 2021, 10, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbo, M.; Crinier, A.; Vely, F.; Vivier, E. Innate lymphoid cells: Major players in inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Andrés, J.; Novakovic, B.; Li, Y.; Scicluna, B.P.; Gresnigt, M.S.; Arts, R.J.W.; Oosting, M.; Moorlag, S.J.C.F.M.; Groh, L.A.; Zwaag, J.; et al. The Itaconate Pathway Is a Central Regulatory Node Linking Innate Immune Tolerance and Trained Immunity. Cell. Metab. 2019, 29, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorkstrom, N.K.; Ljunggren, H.G.; Michaelsson, J. Emerging insights into natural killer cells in human peripheral tissues. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.A.; Fehniger, T.A.; Caligiuri, M.A. The biology of human natural killer-cell subsets. Trends Immunol. 2001, 22, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.K.; Sunwoo, J.B. Natural Killer Cells and Thyroid Diseases. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 34, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisgalla, A.; Ramien, C.; Streitz, M.; Schlickeiser, S.; Lupu, A.R.; Diemert, A.; Tolosa, E.; Arck, P.C.; Bellmann-Strobl, J.; Siebert, N.; et al. Alterations of NK Cell Phenotype during Pregnancy in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 907994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harinarayan, C.V.; Akhila, H.; Shanthisree, E. Modern India and Dietary Calcium Deficiency-Half a Century Nutrition Data-Retrospect-Introspect and the Road Ahead. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 583654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaivode, I.; Zake, T.; Strele, I.; Upmale-Engela, S.; Gogins, D.; Gersone, G.; Skesters, A.; Dambrova, M.; Konrade, I. Stress-Related Immune Response and Selenium Status in Autoimmune Thyroid Disease Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhabhar, F.S. Effects of stress on immune function: The good, the bad, and the beautiful. Immunol. Res. 2014, 58, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, D.J.; Alfulaij, N.; Berry, M.J. Stress and the Brain: An Emerging Role for Selenium. Front. Neurosci 2021, 15, 666601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vita, R.; Lapa, D.; Trimarchi, F.; Benvenga, S. Stress triggers the onset and the recurrences of hyperthyroidism in patients with Graves’ disease. Endocrine 2015, 48, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effraimidis, G.; Strieder, T.G.; Tijssen, J.G.; Wiersinga, W.M. Natural history of the transition from euthyroidism to overt autoimmune hypo- or hyperthyroidism: A prospective study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 164, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markomanolaki, Z.S.; Tigani, X.; Siamatras, T.; Bacopoulou, F.; Tsartsalis, A.; Artemiadis, A.; Megalooikonomou, V.; Vlachakis, D.; Chrousos, G.P.; Darviri, C. Stress Management in Women with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Mol. Biochem. 2019, 8, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruggeri, R.M.; Vicchio, T.M.; Cristani, M.; Certo, R.; Caccamo, D.; Alibrandi, A.; Giovinazzo, S.; Saija, A.; Campennì, A.; Trimarchi, F.; et al. Oxidative Stress and Advanced Glycation End Products in Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis. Thyroid 2016, 26, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corso, A.; Engel, H.; Müller, F.; Fiacco, S.; Mernone, L.; Gardini, E.; Ehlert, U.; Fischer, S. Early life stress in women with autoimmune thyroid disorders. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puttaswamy, S.H.; Nandibewur, N.P.; Kumar, P.; Venkataiah, V.; Pinjar, M.J. A Cross-Sectional Study of the Relationship Between Perceived Stress and Thyroid Function Among Apparently Normal Women in the Reproductive Age. Cureus 2024, 16, 55567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staneva, A.; Bogossian, F.; Pritchard, M.; Wittkowski, A. The effects of maternal depression, anxiety, and perceived stress during pregnancy on preterm birth: A systematic review. Women Birth 2015, 28, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bergh, B.R.; Dahnke, R.; Mennes, M. Prenatal stress and the developing brain: Risks for neurodevelopmental disorders. Dev. Psychopathol. 2018, 30, 743–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, Y.H.; Barry, J.; Ding, T.; Baio, G.; Muscat, R.; Todd, B.K.; Wang, F.F.; Hardiman, P.J. The association between psychological stress and miscarriage: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Tan, S.; Gluckman, P.D.; Godfrey, K.M.; Saw, S.M.; Teoh, O.H.; Chong, Y.S.; Meaney, M.J.; Kramer, M.S.; Gooley, J.J.; et al. Sleep quality and nocturnal sleep duration in pregnancy and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus. Sleep 2017, 40, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slade, P.; Sheen, K.; Weeks, A.; Wray, S.; De Pascalis, L.; Lunt, K.; Bedwell, C.; Thompson, B.; Hill, J.; Sharp, H. Do stress and anxiety in early pregnancy affect the progress of labor: Evidence from theWirral Child Health and Development Study. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2021, 100, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanni, K.R.; Eeva, E.; Noora, S.M.; Laura, K.S.; Linnea, K.; Hasse, K. The influence of maternal psychological distress on the mode of birth and duration of labor: Findings from the FinnBrain Birth Cohort Study. Arch. Womens Ment. Health 2022, 25, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dai, F.; Razali, N.S.; Tagore, S.; Chern, B.S.; Tan, K.H. Poor sleep is associated with higher blood pressure and uterine artery pulsatility index in pregnancy: A prospective cohort study. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2021, 128, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anifantaki, F.; Pervanidou, P.; Lambrinoudaki, I.; Panoulis, K.; Vlahos, N.; Eleftheriades, M. Maternal Prenatal Stress, Thyroid Function and Neurodevelopment of the Offspring: A Mini Review of the Literature. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 692446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, C.M.; Entringer, S.; Buss, C. Translating basic research knowledge on the biological embedding of early-life stress into novel approaches for the developmental programming of lifelong health. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 105, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benker, G.; Raida, M.; Olbricht, T.; Wagner, R.; Reinhardt, W.; Reinwein, D. TSH secretion in Cushing’s syndrome: Relation to glucocorticoid excess, diabetes, goitre, and the ‘sick euthyroid syndrome. Clin. Endocrinol. 1990, 33, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, A.; Sousa, N. Maternal hormonal milieu influence on fetal brain development. Brain Behav. 2018, 8, e00920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bogović Crnčić, T.; Ćurko-Cofek, B.; Batičić, L.; Girotto, N.; Tomaš, M.I.; Kršek, A.; Krištofić, I.; Štimac, T.; Perić, I.; Sotošek, V.; et al. Autoimmune Thyroid Disease and Pregnancy: The Interaction Between Genetics, Epigenetics and Environmental Factors. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010190
Bogović Crnčić T, Ćurko-Cofek B, Batičić L, Girotto N, Tomaš MI, Kršek A, Krištofić I, Štimac T, Perić I, Sotošek V, et al. Autoimmune Thyroid Disease and Pregnancy: The Interaction Between Genetics, Epigenetics and Environmental Factors. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(1):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010190
Chicago/Turabian StyleBogović Crnčić, Tatjana, Božena Ćurko-Cofek, Lara Batičić, Neva Girotto, Maja Ilić Tomaš, Antea Kršek, Ines Krištofić, Tea Štimac, Ivona Perić, Vlatka Sotošek, and et al. 2025. "Autoimmune Thyroid Disease and Pregnancy: The Interaction Between Genetics, Epigenetics and Environmental Factors" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 1: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010190
APA StyleBogović Crnčić, T., Ćurko-Cofek, B., Batičić, L., Girotto, N., Tomaš, M. I., Kršek, A., Krištofić, I., Štimac, T., Perić, I., Sotošek, V., & Klobučar, S. (2025). Autoimmune Thyroid Disease and Pregnancy: The Interaction Between Genetics, Epigenetics and Environmental Factors. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(1), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010190





