Abstract
Background: The association between Body Mass Index (BMI) and clinical outcomes following sepsis continues to be debated. We aimed to investigate the relationship between BMI and in-hospital clinical course and mortality in patients hospitalized with bacteremic sepsis using real-world data. Methods: A sampled cohort of patients hospitalized with bacteremic sepsis between October 2015 and December 2016 was identified in the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) database. In-hospital mortality and length of stay were defined as the relevant outcomes. Patients were divided into 6 BMI (kg/m2) subgroups; (1) underweight ≤ 19, (2) normal-weight 20–25, (3) over-weight 26–30, (4) obese I 31–35, (5) obese II 36–39, and (6) obese stage III ≥ 40. A multivariable logistic regression model was used to find predictors of mortality, and a linear regression model was used to find predictors of an extended length of stay (LOS). Results: An estimated total of 90,760 hospitalizations for bacteremic sepsis across the U.S. were analyzed. The data showed a reverse-J-shaped relationship between BMI and study population outcomes, with the underweight patients (BMI ≤ 19 kg/m2) suffering from higher mortality and longer LOS as did the normal-weight patients (BMI 20–25 kg/m2) when compared to the higher BMI groups. The seemingly protective effect of a higher BMI diminished in the highest BMI group (BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2). In the multivariable regression model, BMI subgroups of ≤19 kg/m2 and ≥40 kg/m2 were found to be independent predictors of mortality. Conclusions: A reverse-J-shaped relationship between BMI and mortality was documented, confirming the “obesity paradox” in the real-world setting in patients hospitalized for sepsis and bacteremia.
1. Introduction
Body mass index (BMI) is a commonly utilized index for characterizing weight status in clinical and research settings despite it not differentiating between adipose and muscular tissue []. Six BMI groups are currently defined by the World Health Organization (WHO); under-weight (BMI ≤ 18.5 kg/m2); normal-weight (BMI 18.5–24.9 kg/m2); over-weight (BMI 25–29.9 kg/m2); obese class I (BMI 30–34.9 kg/m2); obese class II (BMI 35–39.9 kg/m2); obese stage III (BMI ≥ 40 Kg/m2) [,]. Higher BMI was associated with an increased risk of overall mortality as well as many case-specific causes of death in a large study of the general population in the UK []. Higher BMI during adolescence has been associated with adult mortality from infectious diseases []. While these studies appraise the lifetime risk of mortality, they do not predict survival during acute events.
Multiple studies have investigated the effect of different BMI-grouped cohorts on short and long-term mortality rates in patients hospitalized with bacteremia, sepsis, and septic shock []. While some studies suggested that obesity independently portends negative outcomes [,], others showed that the higher-BMI groups might have a more favorable course [,]. The phenomenon of obesity having a protective effect from negative outcomes has been referred to as the ‘obesity paradox’. The existence of a true paradox and the theories explaining its occurrence have been highly debated.
In this study, we aimed to find predictors of negative outcomes in patients with bacteremic sepsis during the initial hospitalization and analyze the outcomes between the different BMI subgroups.
2. Materials and Methods
The data were drawn from the National Inpatient Sample (NIS), the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP), and Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) []. The NIS database only includes de-identified data; therefore, this study was considered exempt from institutional review by the Human Research Committee.
The NIS is the largest database of all-payer hospitalizations in the United States (U.S.) and represents an approximate 20% stratified sample of all inpatients admitted to U.S. hospitals []. This includes information at the hospital level, such as hospital region, teaching status, bed size, and cost of hospitalization, and other data at the patient level, including demographic characteristics, primary and secondary diagnoses and procedures, comorbidities, and length of stay (LOS). National estimates can be calculated using the patient-level and hospital-level sampling weights that are provided by the HCUP.
Using data from the NIS, we created a database of relevant patients hospitalized between the years 2015 and 2016 for use in several studies examining outcomes in several disease states and BMI groups [,,,]. The data was extracted and analyzed with similar methods in all studies. The International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) was used from the last quarter of 2015 and thereafter for reporting diagnoses and procedures in the NIS database during the study period. For each index hospitalization, the database provides a principal discharge diagnosis and a maximum of 14 or 24 additional diagnoses, in addition to a maximum of 15 procedures. We restricted our cohort to the period during which data was coded with ICD-10 codes because the ICD-10 system includes individual codes for BMI values and ranges.
We identified patients 18 years of age or older with a final diagnosis based on ICD-10 indicating bacteremic sepsis: 78.81, R65.20, R65.21, A40, A40.0, A40.01, A40.02, A40.3, A40.8, A40.9, A41.X (1–5), A41.50, A41.51, A41.52, A41.53, A41.58, A42.7, A22.7, B37.7, A26.7, A28.2, A54.86, B00.7, A32.7, A24.1, A39.2-A39.4, A20.7, A21.7, A48.3–as “I10_Dx1. The following codes represent the six BMI subgroups we have created for our study: Z68.1, BMI ≤ 19 kg/m2, under-weight group; Z68.20–25, BMI 20–25 kg/m2, normal-weight group; Z68.26–30, BMI 26–30 kg/m2, over-weight group; Z68.31–35, BMI 31–35 kg/m2, obese I group; Z68.36–39 kg/m2, BMI 36–39, obese II group; Z68.4, BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2, obese stage III group.
The following patient demographics were collected from the database: age, sex, and race. Prior comorbidities were identified by measures from the AHRQ. For calculating Deyo-Charlson Comorbidity Index (Deyo-CCI), additional comorbidities were identified from the database using ICD-10 cm codes. Deyo-CCI is a modification of the Charlson Comorbidity Index, containing 17 comorbid conditions of differential weights, with a total score ranging from 0 to 33 (detailed information on Deyo-CCI is provided in Appendix A Table A1). Higher Deyo-CCI scores indicate a greater burden of comorbid diseases and are associated with mortality 1 year after admission []. The index has been used extensively in studies from administrative databases, with proven validity in predicting short- and long-term outcomes [,]. Our primary outcome in this study was in-hospital mortality. Length of stay in the hospital was measured as a secondary outcome.
The chi-square (χ2) and Wilcoxon rank sum tests were used to compare categorical variables and continuous variables, respectively. The NIS provides discharge sample weights that are calculated within each sampling level as the ratio of discharges in the universe to discharges in the sample [].
We generated a weighted logistic regression model to identify independent predictors of in-hospital mortality. Candidate variables included patient-level characteristics, Deyo-CCI, and hospital-level factors. We included all candidate variables that were associated with our primary and secondary outcomes in our final multivariable regression model. A linear regression model was used to identify predictors of LOS.
For all analyses, we used SAS® software version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Study Cohort
A total sample of 18,152 hospitalizations for bacteremic sepsis across the U.S. during 2015 (last quarter) and 2016 were included in the analysis. After implementing the weighting method, these represented an estimated total of 90,760 hospitalizations for bacteremic sepsis during the index hospitalization. The majority of patients (57.0%) were female, and the mean age of the cohort was 64 ± 34.1 years. In this study, patients from all defined BMI categories were well represented.
3.2. Patient Characteristics
Demographic and clinical characteristics are shown in detail in Table 1. Female predominance and increased rates of comorbidities such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic renal disease, atrial fibrillation/flutter, and higher Deyo-CCI scores were observed in both under-weight (BMI ≤ 19 kg/m2) and obese stage III groups (BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Frequency distribution of demographic characteristics and outcomes of patients with bacteremic sepsis by BMI group.
3.3. Length of Stay and Mortality Per BMI Groups
A reverse-J relationship was found between the BMI and the study outcomes. Underweight patients (BMI ≤ 19 kg/m2) had higher mortality and longer LOS, as did the normal-weight patients (BMI 20–25 kg/m2) when compared to the higher BMI groups (Figure 1). The seemingly protective effect of a higher BMI diminished in the highest BMI group (BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2). The overall mortality rate during the study period was 7.7%, with a noticeably higher rate in under-weight (13.7%) and normal-weight (10.7%) patient population groups (p < 0.001) (Table 1). The overall mean LOS was 9.00 ± 0.07 days. Longer LOS was documented in the under-weight (10.74 ± 0.21 days), normal weight (9.99 ± 0.19 days), and over-weight subgroup (9.08 ± 0.19 days) (p < 0.001) (Table 1).
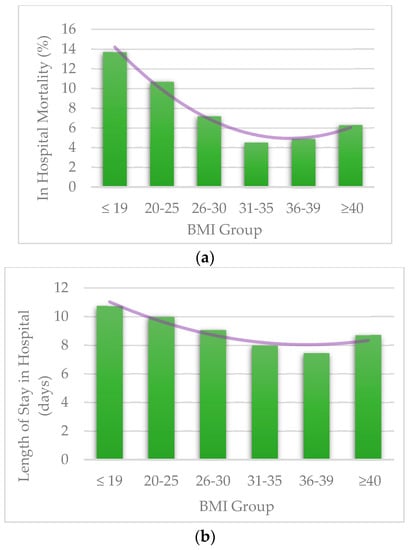
Figure 1.
(a) Mortality per BMI groups; (b) Length of Stay per BMI groups. BMI = Body Mass Index.
3.4. Predictors of In-Hospital Mortality
Univariate and multivariate analysis identified male gender, older age, increasing Deyo-CCI score, chronic renal failure, atrial fibrillation/flutter, and congestive heart failure as predictors of in-hospital mortality (p < 0.001) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Predictors of In-Hospital mortality for bacteremic sepsis (univariate).
A reverse-J relationship between BMI and mortality was seen in the multivariable analysis. BMI ≤ 19 kg/m2 predicted in-hospital mortality after adjusting for potential confounders, with the highest risk of mortality occurring in underweight patients. (OR 1.35; [95% CI 1.25–1.47], p < 0.001). Excluding the underweight group, all other BMI ranges were associated with lower odds of mortality as compared to the index range of BMI 20–25 kg/m2 (p < 0.001) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Predictors of In-Hospital mortality for bacteremic sepsis (multivariate).
3.5. Predictors of Length of Stay in Hospital
A reverse-J relationship between BMI and the secondary outcome of LOS was seen in univariable and multivariable analyses (Appendix A Table A2 and Table A3). In the multivariate analysis, we found that demographic characteristics such as age above 60, male gender, Deyo-CCI score of 2 or higher, atrial fibrillation/flutter, renal failure, and congestive heart failure were all associated with longer LOS (p < 0.001) (Appendix A Table A2).
In multivariable analysis after adjusting for potential confounders, BMI < 19 kg/m2 was associated with a longer LOS in the underweight patients compared to obese stage III patients (Mean LOS 9.73; [95% CI 9.34,10.12], p < 0.001 vs. Mean LOS 7.34; [95% CI 7.05,7.63], p < 0.001, respectively). Excluding the underweight group, all other BMI ranges were associated with shorter LOS as compared to the index range of BMI 20–25 kg/m2 (p < 0.001) (Appendix A Table A3).
4. Discussion
In this paper, using real-world data from a large U.S. database, we aim to better describe the controversial ‘obesity paradox’ for inpatients with a diagnosis of bacteremic sepsis. To the best of our knowledge, this is the largest study analyzing the relationship between BMI and mortality in patients hospitalized for bacteremic sepsis, including a weighted total of 90,760 hospitalizations. After adjusting for confounders, the underweight group (BMI ≤ 19 kg/m2) predicted in-hospital mortality and prolonged LOS with significantly better outcomes in the obese subgroups. Interestingly, the protective effect of a higher BMI diminished in the highest BMI group (BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2) in comparison to the normal weight group as well as the obese I and obese II groups yet remained a protective factor.
Multiple studies have investigated the effect of different BMI-grouped cohorts on short and long-term mortality rates in patients hospitalized with bacteremia, sepsis, and septic shock []. While some studies suggested that obesity independently portends negative outcomes [,], others showed that the higher-BMI groups might have a more favorable course [,]. This phenomenon has been referred to as the ‘obesity paradox’. One proposed explanation for this paradox is that patients with higher BMI have a blunted inflammatory cytokine response, possibly due to adipose tissue modulation of the immune response or a chronic inflammatory state []. Another theory proposes that the nutritional reserves of obese and overweight patients protect them from the adverse effects of catabolic processes during critical states, such as sepsis. One study suggests that initiating early enteral nutrition during critical disease confers near similar protection as in the higher BMI groups []. Another possible reason for the survival differences could be weight-based variations in medication and fluid dosing in these critically ill patients, as current sepsis guidelines recommend dosing according to weight, which can impact outcomes for BMI outliers [].
While these may explain the protective effects of higher BMI, it seems that the underweight have increased mortality and morbidity. A growing body of research attributes these negative outcomes to the deleterious effects of sarcopenia and skeletal muscle wasting []. This has been studied in hospitalized patients, usually based on US or CT imaging of muscle mass in multiple populations as well as in sepsis, and clearly trends towards negative outcomes in muscle-depleted patients [,]. Several studies indicate that these measures may better predict outcomes when compared to BMI alone in specific populations, e.g., cancer patients [] and elderly patients in ICU settings [], yet it remains to be seen whether these predictors hold up in more heterogenous populations, age groups, and disease states.
Among this study’s strengths are the use of real-world national data from a large heterogenic population with well-represented groups of obese stage III and underweight patients, which were under-represented in previously conducted studies.
In order to fully represent all patient BMI groups, our study specifically included an underweight, a normal weight, and an obese stage III group, contrary to previous studies. Our results showed that underweight patients (BMI ≤ 19 kg/m2) have the highest risk of mortality compared to the other BMI groups, and we believe that this knowledge should be considered in mortality risk scores.
This study population represents the entire nationwide population of patients who were hospitalized with bacteremic sepsis in the US between October 2015 and December 2016, hence eliminating the selection bias in some of the prior studies regarding this population.
To eliminate selection bias, the patient population in this study consisted of a large nationwide cohort of patients hospitalized for bacteremic sepsis in the U.S. during a set time period.
Several limitations should be considered when interpreting this study. First, the NIS database is a retrospective administrative database that contains patient records at the time of discharge, and coding errors may occur. Omitted from the collected data are multiple clinical variables, including vital signs, blood glucose levels, prognostication scores such as the SOFA score, medications, blood tests such as levels of CRP, ESR, and other markers of inflammation, all of which have been independently linked with adverse events, therefore we cannot rule out residual confounding of the associations we observed. Other important data absent from the NIS database includes specific treatment provided in hospitals and geographic variations of these practices. While this study sheds light on the relationship between BMI and sepsis with proven bacteremia, it does not detail the cultured organisms, sepsis severity scoring systems, or infection sources. Furthermore, it is likely that cases of secondary sepsis occurring later during an unrelated hospitalization have been included in the study, and therefore, results do not reflect primary cases of sepsis alone.
Finally, the data collected does not include mortality past 30 days and other outcomes and only reflects the course of the initial hospitalization. The limitations noted above are balanced by the broad real-world data we utilized, which eliminates center-specific bias.
In conclusion, a reverse J-shaped relationship between BMI and mortality was seen in patients hospitalized for bacteremic sepsis in this study. Due to this, it may be warranted to consider BMI as part of the risk assessment for patients admitted with bacteremic sepsis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.R., G.E.-G. and O.A.; methodology, G.R., G.E.-G., and O.A.; formal analysis, G.R. and G.E.-G.; investigation, G.R. and G.E.-G.; resources, G.R. and G.E.-G.; data curation, G.R. and G.E.-G.; writing—original draft preparation, S.L. and G.E.-G.; writing—review and editing, S.L., G.R., Z.A.G., M.K., H.E., H.Z., S.C., O.A, D.P., and G.E.-G.; supervision, O.A.; project administration, O.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The data in the National Inpatient Sample dataset is de-identified; therefore, the Human Research Committee of The Baruch Padeh Medical Center Poriya exempted this study from institutional review.
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived in this nationwide de-identified database by the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP).
Data Availability Statement
The Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Data Use Agreement does not allow us to make the data from the NIS database used for this study available to others. The NIS database is available for purchase by the public, and our detailed and transparent description of methods used for the data analysis allows anyone who wishes to do so to reproduce our results.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Ran Nir-Paz for his insights and constructive feedback.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Deyo comorbidity index.
Table A1.
Deyo comorbidity index.
| ICD-10 CM Codes | Condition | Score |
|---|---|---|
| I21.x, I22.x, I25.2 | Myocardial infarction | 1 |
| I09.9, I11.0, I13.0, I13.2, I25.5, I42.0, I42.5-I42.9, I43.x, I50.x, P29.0 | Congestive heart failure | 1 |
| I70.x, I71.x, I73.1, I73.8, I73.9, I77.1, I79.0, I79.2, K55.1, K55.8, K55.9, Z95.8, Z95.9 | Peripheral vascular disease | 1 |
| G45.x, G46.x, H34.0, I60.x-I69.x | Cerebrovascular disease | 1 |
| F00.x-F03.x, F05.1, G30.x, G31.1 | Dementia | 1 |
| I27.8, I27.9, J40.x-J47.x, J60.x-J67.x, J68.4, J70.1, J70.3 | Chronic pulmonary disease | 1 |
| M05.x, M06.x, M31.5, M32.x-M34.x, M35.1, M35.3, M36.0 | Rheumatologic disease | 1 |
| K25.x-K28.x | Peptic ulcer disease | 1 |
| B18.x, K70.0-K70.3, K70.9, K71.3-K71.5, K71.7, K73.x, K74.x, K76.0, K76.2-K76.4, K76.8, K76.9, Z94.4 | Mild liver disease | 1 |
| E10.0, E10.l, E10.6, E10.8, E10.9, E11.0, E11.1, E11.6, E11.8, E11.9, E12.0, E12.1, E12.6, E12.8, E12.9, E13.0, E13.1, E13.6, E13.8, E13.9, E14.0, E14.1, E14.6, E14.8, E14.9 | Diabetes | 1 |
| E10.2-E10.5, E10.7, E11.2-E11.5, E11.7, E12.2-E12.5, E12.7, E13.2-E13.5, E13.7, E14.2-E14.5, E14.7 | Diabetes with chronic complications | 2 |
| G04.1, G11.4, G80.1, G80.2, G81.x, G82.x, G83.0-G83.4, G83.9 | Hemiplegia or paraplegia | 2 |
| I12.0, I13.1, N03.2-N03.7, N05.2-N05.7, N18.x, N19.x, N25.0, Z49.0-Z49.2, Z94.0, Z99.2 | Renal disease | 2 |
| C00.x-C26.x, C30.x-C34.x, C37.x-C41.x, C43.x, C45.x-C58.x, C60.x-C76.x, C81.x-C85.x, C88.x, C90.x-C97.x | Any malignancy including leukemia and lymphoma | 2 |
| I85.0, I85.9, I86.4, I98.2, K70.4, K71.1, K72.1, K72.9, K76.5, K76.6, K76.7 | Moderate or severe liver disease | 3 |
| C77.x-C80.x | Metastatic solid tumor | 6 |
| B20.x-B22.x, B24.x | Acquired Immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) | 6 |

Table A2.
Predictors of length of stay (days) for indication: bacteremic sepsis (univariate).
Table A2.
Predictors of length of stay (days) for indication: bacteremic sepsis (univariate).
| Predictors | Mean (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| BMI Group | <0.001 | |
| Below 20 | 10.86 (10.53,11.20) | 0.002 |
| 20–25 | 10.09 (9.71,10.46) | N/A |
| 26–30 | 9.00 (8.60,9.40) | <0.001 |
| 31–35 | 7.96 (7.62,8.30) | <0.001 |
| 36–39 | 7.45 (7.06,7.84) | <0.001 |
| 40 and Above | 8.55 (8.34,8.76) | <0.001 |
| Age Group, yrs | <0.001 | |
| 18–44 yrs | 9.56 (9.18,9.94) | N/A |
| 45–59 yrs | 9.44 (9.19,9.70) | 0.623 |
| 60–74 yrs | 8.83 (8.62,9.04) | <0.001 |
| 75 yrs or older | 8.25 (8.00,8.51) | <0.001 |
| Gender | <0.001 | |
| Male | 9.42 (9.22,9.62) | N/A |
| Female | 8.56 (8.39,8.73) | <0.001 |
| Race | <0.001 | |
| Non-white | 9.51 (9.27,9.75) | N/A |
| White | 8.64 (8.48,8.79) | <0.001 |
| Deyo-CCI | <0.001 | |
| 1 | 8.15 (7.84,8.46) | N/A |
| 0 | 7.90 (7.54,8.25) | 0.296 |
| 2 or higher | 9.30 (9.15,9.46) | <0.001 |
| Comorbidities | ||
| Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter | <0.001 | |
| No | 8.65 (8.50,8.79) | N/A |
| Yes | 9.88 (9.61,10.15) | <0.001 |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | 0.052 | |
| No | 9.00 (8.85,9.16) | N/A |
| Yes | 8.72 (8.48,8.96) | 0.052 |
| Congestive heart failure | 0.072 | |
| No | 8.87 (8.73,9.01) | N/A |
| Yes | 9.19 (8.87,9.50) | 0.072 |
| Diabetes Mellitus | <0.001 | |
| No | 9.26 (9.10,9.42) | N/A |
| Yes | 8.31 (8.09,8.53) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | <0.001 | |
| No | 9.62 (9.46,9.79) | N/A |
| Yes | 7.96 (7.76,8.16) | <0.001 |
| Peripheral vascular disorders | 0.016 | |
| No | 8.87 (8.73,9.01) | N/A |
| Yes | 9.41 (8.99,9.83) | 0.016 |
| Prior MI | <0.001 | |
| No | 8.99 (8.86,9.12) | N/A |
| Yes | 7.62 (7.05,8.19) | <0.001 |
| Renal failure | <0.001 | |
| No | 8.71 (8.56,8.86) | N/A |
| Yes | 9.44 (9.20,9.69) | <0.001 |
CI = Confidence Interval; BMI = Body Mass Index; Deyo-CCI = Deyo Comorbidity Index; MI = Myocardial Infarction; N/A = Not Applicable.

Table A3.
Predictors of length of stay for indication: bacteremic sepsis (multivariate).
Table A3.
Predictors of length of stay for indication: bacteremic sepsis (multivariate).
| Predictors | Mean (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| BMI Group | <0.001 | |
| Below 20 | 9.73 (9.34,10.12) | 0.004 |
| 20–25 | 8.98 (8.55,9.41) | N/A |
| 26–30 | 7.91 (7.46,8.36) | <0.001 |
| 31–35 | 6.94 (6.55,7.33) | <0.001 |
| 36–39 | 6.32 (5.88,6.77) | <0.001 |
| 40 and Above | 7.34 (7.05,7.63) | <0.001 |
| Age Group, yrs | <0.001 | |
| 18–44 yrs | 8.56 (8.13,8.99) | N/A |
| 45–59 yrs | 8.38 (8.05,8.71) | 0.458 |
| 60–74 yrs | 7.81 (7.51,8.11) | 0.001 |
| 75 yrs or older | 6.73 (6.40,7.06) | <0.001 |
| Gender | <0.001 | |
| Female | 7.60 (7.34,7.86) | <0.001 |
| Male | 8.14 (7.86,8.43) | N/A |
| Race | 0.076 | |
| Non-white | 8.00 (7.69,8.32) | N/A |
| White | 7.73 (7.50,7.97) | 0.076 |
| Deyo-CCI | <0.001 | |
| 0 | 7.22 (6.82,7.62) | 0.103 |
| 1 | 7.62 (7.27,7.98) | N/A |
| 2 or higher | 8.77 (8.52,9.01) | <0.001 |
| Comorbidities | ||
| Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter | <0.001 | |
| No | 7.64 (7.40,7.88) | N/A |
| Yes | 9.35 (8.98,9.71) | <0.001 |
| Congestive heart failure | 0.033 | |
| No | 7.84 (7.61,8.08) | N/A |
| Yes | 8.24 (7.83,8.66) | 0.033 |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | 0.008 | |
| No | 7.93 (7.69,8.18) | N/A |
| Yes | 7.52 (7.18,7.87) | 0.008 |
| Diabetes Mellitus | <0.001 | |
| No | 8.07 (7.83,8.32) | N/A |
| Yes | 7.12 (6.78,7.45) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | <0.001 | |
| No | 8.45 (8.18,8.72) | N/A |
| Yes | 7.18 (6.90,7.46) | <0.001 |
| Prior MI | <0.001 | |
| No | 7.90 (7.67,8.14) | N/A |
| Yes | 6.56 (5.93,7.18) | <0.001 |
| Peripheral vascular disorders | 0.154 | |
| No | 7.85 (7.61,8.09) | N/A |
| Yes | 8.18 (7.69,8.67) | 0.154 |
| Renal failure | <0.001 | |
| No | 7.78 (7.54,8.02) | N/A |
| Yes | 8.43 (8.06,8.79) | <0.001 |
CI = Confidence Interval; BMI = Body Mass Index; Deyo-CCI = Deyo Comorbidity Index; MI = Myocardial Infarction; N/A = Not applicable.
References
- Khanna, R.; Wachsberg, K.; Marouni, A.; Feinglass, J.; Williams, M.V.; Wayne, D.B. The Association between Night or Weekend Admission and Hospitalization-Relevant Patient Outcomes. J. Hosp. Med. 2011, 6, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.S.; Ning, H.; Wilkins, J.T.; Allen, N.; Carnethon, M.; Berry, J.D.; Sweis, R.N.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M. Association of Body Mass Index With Lifetime Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Compression of Morbidity. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO/Europe. Nutrition—Body Mass Index—BMI. Available online: https://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/disease-prevention/nutrition/a-healthy-lifestyle/body-mass-index-bmi (accessed on 22 April 2022).
- Twig, G.; Geva, N.; Levine, H.; Derazne, E.; Goldberger, N.; Haklai, Z.; Leiba, A.; Kark, J.D. Body Mass Index and Infectious Disease Mortality in Midlife in a Cohort of 2.3 Million Adolescents. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 42, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, V.; Bavishi, C.; Jean, R. Impact of Obesity on Sepsis Mortality: A Systematic Review. J. Crit. Care 2015, 30, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttunen, R.; Laine, J.; Lumio, J.; Vuento, R.; Syrjänen, J. Obesity and Smoking Are Factors Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Bacteraemia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper, D.J.; Demirkale, C.Y.; Sun, J.; Rhee, C.; Fram, D.; Eichacker, P.; Klompas, M.; Suffredini, A.F.; Kadri, S.S. Does Obesity Protect Against Death in Sepsis? A Retrospective Cohort Study of 55,038 Adult Patients. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabi, Y.M.; Dara, S.I.; Tamim, H.M.; Rishu, A.H.; Bouchama, A.; Khedr, M.K.; Feinstein, D.; Parrillo, J.E.; Wood, K.E.; Keenan, S.P.; et al. Clinical Characteristics, Sepsis Interventions and Outcomes in the Obese Patients with Septic Shock: An International Multicenter Cohort Study. Crit Care 2013, 17, R72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prescott, H.C.; Chang, V.W.; O’Brien, J.M.; Langa, K.M.; Iwashyna, T.J. Obesity and One-Year Outcomes in Older Americans with Severe Sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HCUP-US NIS Overview. Available online: https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/nisoverview.jsp (accessed on 22 April 2022).
- Steiner, C.; Elixhauser, A.; Schnaier, J. The Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project: An Overview DATABASE. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP)-a Family of Databases Including the State Inpatient Databases (SID), the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS), the Kids’ Inpatient Database (KID), and the Outpatient Databases State Ambulatory Surgery Data (SASD) and State Emergency Department Data (SEDD). SPECIAL TOPIC. Eff. Clin. Pract. 1988, 5, 143–151. [Google Scholar]
- Rozen, G.; Elbaz-Greener, G.; Marai, I.; Heist, E.K.; Ruskin, J.N.; Carasso, S.; Birati, E.Y.; Amir, O. The Relationship between the Body Mass Index and In-Hospital Mortality in Patients Admitted for Sudden Cardiac Death in the United States. Clin. Cardiol. 2021, 44, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz-Greener, G.; Rozen, G.; Carasso, S.; Kusniec, F.; Marai, I.; Sud, M.; Strauss, B.; Smart, F.W.; Planer, D.; Amir, O. The Relationship between Body Mass Index and In-Hospital Mortality in the Contemporary Era of an Acute Myocardial Infarction Management. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2021, 17, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozen, G.; Elbaz-Greener, G.; Margolis, G.; Marai, I.; Heist, E.K.; Ruskin, J.N.; Carasso, S.; Roguin, A.; Birati, E.Y.; Amir, O. The Obesity Paradox in Real-World Nation-Wide Cohort of Patients Admitted for a Stroke in the U.S. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbaz-Greener, G.; Rozen, G.; Carasso, S.; Kusniec, F.; Yarkoni, M.; Marai, I.; Strauss, B.; Wijeysundera, H.C.; Smart, F.W.; Erez, E.; et al. The Relationship Between Body Mass Index and In-Hospital Mortality in Patients Following Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Surgery. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 754934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyo, R.A.; Cherkin, D.C.; Ciol, M.A. Adapting a Clinical Comorbidity Index for Use with ICD-9-CM Administrative Databases. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1992, 45, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.T.; Ng, Y.Y.; Wu, S.C. Comparison of Different Comorbidity Measures for Use with Administrative Data in Predicting Short- and Long-Term Mortality. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2010, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovanovic, D.; Seifert, B.; Urban, P.; Eberli, F.R.; Rickli, H.; Bertel, O.; Puhan, M.A.; Erne, P. Validity of Charlson Comorbidity Index in Patients Hospitalised with Acute Coronary Syndrome. Insights from the Nationwide AMIS Plus Registry 2002–2012. Heart 2014, 100, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HCUP Methods Series Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS) Redesign Final Report Report # 2014-04. Available online: https://hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/methods/2014-04.pdf (accessed on 11 January 2022).
- Wacharasint, P.; Boyd, J.H.; Russell, J.A.; Walley, K.R. One Size Does Not Fit All in Severe Infection: Obesity Alters Outcome, Susceptibility, Treatment, and Inflammatory Response. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.; Zhou, J.; Liu, X.; Hassan, E.; Badawi, O. The Obesity Paradox Is Not Observed in Critically III Patients on Early Enteral Nutrition. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, M.A.; Kuttab, H.I.; Lykins, V.J.D.; Wroblewski, K.; Hughes, M.D.; Keast, E.P.; Kopec, J.A.; Rourke, E.M.; Purakal, J. The Effect of Body Mass Index and Weight-Adjusted Fluid Dosing on Mortality in Sepsis. J. Intensive Care Med. 2022, 37, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, S.J.; Braunschweig, C.A. Prevalence of Sarcopenia and Associated Outcomes in the Clinical Setting. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2016, 31, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.R.; Ahn, J.Y.; Jeong, S.J.; Ku, N.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Yeom, J.S.; Song, Y.G. The Impact of Sarcopenia on Short-Term and Long-Term Mortality in Patients with Septic Shock. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 2054–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, L.; Birdsell, L.; MacDonald, N.; Reiman, T.; Clandinin, M.T.; McCargar, L.J.; Murphy, R.; Ghosh, S.; Sawyer, M.B.; Baracos, V.E. Cancer Cachexia in the Age of Obesity: Skeletal Muscle Depletion Is a Powerful Prognostic Factor, Independent of Body Mass Index. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moisey, L.L.; Mourtzakis, M.; Cotton, B.A.; Premji, T.; Heyland, D.K.; Wade, C.E.; Bulger, E.; Kozar, R.A. Skeletal Muscle Predicts Ventilator-Free Days, ICU-Free Days, and Mortality in Elderly ICU Patients. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).