Abstract
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that has detrimental effects on patient’s health-related quality of life (HRQoL). Owing to its immense heterogeneity of symptoms and its complexity regarding comorbidity burden, management of SLE necessitates interdisciplinary care, with the goal being the best possible HRQoL and long-term outcomes. Current definitions of remission, low disease activity, and response to treatment do not incorporate self-reported patient evaluation, while it has been argued that the physician’s global assessment should capture the patient’s perspective. However, even the judgment of a very well-trained physician might not replace a patient-reported outcome measure (PROM), not only owing to the multidimensionality of self-perceived health experience but also since this notion would constitute a direct contradiction to the definition of PROMs. The proper use of PROMs is not only an important conceptual issue but also an opportunity to build bridges in the partnership between patients and physicians. These points of consideration adhere to the overall framework that there will seldom be one single best marker that helps interpret the activity, severity, and impact of SLE at the same time. For optimal outcomes, we not only stress the importance of the use of PROMs but also emphasize the urgency of adoption of the conception of forming alliances with patients and facilitating patient participation in surveillance and management processes. Nevertheless, this should not be misinterpreted as a transfer of responsibility from healthcare professionals to patients but rather a step towards shared decision-making.
1. Introduction
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that has detrimental effects on a patient’s health-related quality of life (HRQoL) [1]. It is widely known that SLE is a rheumatic condition that is challenging to diagnose and treat, mainly owing to its immense heterogeneity of clinical symptoms and complexity with regard to comorbidity burden, often necessitating interdisciplinary care, with the goal being the best possible quality of life and long-term outcomes [2,3]. With the premise that preventing is better than restoring, early diagnosis and treatment initiation is imperative [4], a need of particular urgency given that up to 10% of SLE patients develop life-threatening conditions or complications, such as end-stage kidney disease [5,6]. Patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) receive increasing attention within the lupus research community, especially PROMs addressing HRQoL [7]. Even though this signifies a shift of the current paradigm towards increasing patient participation in their care, more distance has to be bridged before PROMs are an integral part of the evaluation in clinical practice.
2. PROMs in the Treat-to-Target Context
Remission of systemic symptoms and organ manifestations was identified by the treat-to-target for SLE initiative (T2T/SLE) as one of the most important targets in the management of patients with SLE [8]. Several definitions of remission were used in clinical trials and observational studies of SLE [9]. The Definitions Of Remission In SLE (DORIS) is an international task force consisting of expert rheumatologists, nephrologists, dermatologists, clinical immunologists, and patient representatives, who jointly proposed a set of remission definitions in response to the T2T/SLE research agenda [10]. Later, the group decided on one prevailing remission definition that incorporated a physician-reported global assessment (PhGA), the SLE Disease Activity Index 2000 (SLEDAI-2K) [11] after suppression of the serological descriptors (anti-double-stranded (ds)DNA and complement levels), the current daily glucocorticoid dose, and restrictions regarding medication allowance. Practically, however, some patients’ individual situations make it hard for them to achieve this stringent target. In such cases, one should aim for low disease activity (LDA). Again, several definitions of LDA have been proposed in the literature, with the Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS) [12] being the most commonly used.
In addition, several recent clinical trials of SLE have used composite indices to define response to treatment, e.g., the SLEDAI Responder Index (SRI) [13] or the British Isles Lupus Assessment Group (BILAG)-based Combined Lupus Assessment (BICLA) [14]. Notably, none of the proposed definitions of remission, LDA, or response to treatment incorporate self-reported patient evaluation, which may constitute a pitfall of the definitions. Indeed, the DORIS task force discussed the issue of the non-inclusion of a PROM and partwise argued that the PhGA should incorporate the patient’s perspective by paying careful attention to the patient’s symptoms and experience [15]. However, even the judgment of a very well-trained physician might not replace a PROM, not only owing to the multidimensionality of patient-perceived health experience (Figure 1), but also since this notion would constitute a direct contradiction to the definition of a PROM; patient-reported outcomes are directly recorded by patients, without interpretation by their clinicians, and are additional markers in the assessment of treatment impact [16,17]. In the definition of remission in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), the patient’s global assessment (PtGA) was chosen as one of the four Boolean criteria because of its ability to show a large sensitivity to change and its discriminatory validity between active drug and placebo in clinical trials [15]. However, it is not easy to address the question of whether PtGA is an ideal PROM to complement the current definition of remission. In fact, a debate has been ongoing for a decade with regard to the appropriateness of PtGA to be included in the remission definition in RA, at least with the currently used cut-offs, since substantial proportions of patients score their disease activity higher than their rheumatologists [18,19,20]. Due to the lack of evidence-based alternatives to PtGA, a summary report of an Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT) interest group recently stated that currently, no better tools for representing the patients’ perspective are available, thus the definition should be kept as is [21]. It is, however, worth noting that the differences in heterogeneity and complexity between SLE and RA are also reflected in discrepant longitudinal patterns of self-reported health experience [22] and direct comparisons or extrapolations of psychometric properties of PROMs between the two diseases may be misleading.
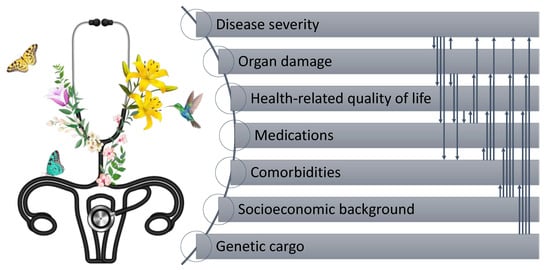
Figure 1.
Illustration of the multilateral impact across disease facets and health-related quality of life in people living with systemic lupus erythematosus.
The issue of imperfect agreement in the perception of disease severity between patients and physicians was also addressed in the field of SLE. While LDA is coupled with an overall favorable HRQoL experience, at least when assessed with the LLDAS [23], results from other investigations are conflicting. One study used a Systemic Lupus Activity Questionnaire (SLAQ) score < 6 as the cut-off for LDA as perceived by the patients and found that only one-quarter of patients who were classified as being in LLDAS fulfilled the definition of SLAQ score < 6 [24]. In the same study, Medical Outcomes Survey Short Form 36 (SF-36) component summary scores and Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy Fatigue scale (FACIT-F) scores were higher among patients in LLDAS who reported SLAQ scores < 6 than among patients in LLDAS who reported SLAQ scores ≥ 6 [24]. This not only underscores that the physician’s perspective does not entirely represent the patient’s perception of HRQoL, but also highlights that LLDAS alone may not be a sufficient target in the management of people with SLE. The inclusion of HRQoL measures in treatment evaluation processes was supported by the T2T statements and received additional weight through findings indicating that poor HRQoL is associated with increased mortality [8,25]. To this end, it is important to clarify that this discussion is not intended to devalue the PhGA or the rheumatologists’ ability to perform adequate clinical judgment; in fact, PhGA scores have shown good correlates with mental health, overall disease activity, and flares [26].
3. The Matter of Not Only Optimal Choice but Also Optimal Use of PROMs
The OMERACT IV consensus conference [27] propounded disease activity, HRQoL, medication side-effects, and organ damage as the four core outcomes for SLE clinical trials in that priority order. In light of accumulating evidence of the discordance in perceptions of disease activity between physicians and patients with SLE [28], PROMs are increasingly used in SLE clinical trials [7]. The SF-36 [29] and FACIT-F [30] were reviewed for their psychometric properties with regard to the extent to which they comply with the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) guidance [31] and were suggested as secondary endpoints to support the labeling of novel therapies for SLE [32]. Changes in scores in various SF-36 domains and FACIT-F have shown an ability to discriminate between verum drug (belimumab) and placebo in the BLISS-52 and BLISS-76 clinical trials [33]. In the same analysis, changes in EQ-5D utility index scores [34] did not exhibit discriminative ability. However, in light of satisfactory psychometric properties of EQ-5D for SLE patients, particularly in terms of validity and reliability [35], a recent study investigated the discriminative ability and known-group validity of EQ-5D full health state (FHS), i.e., a utility index score of 1, and found a remarkably robust ability of EQ-5D FHS to discriminate between drug and placebo, and between responders and non-responders in the BLISS-52 and BLISS-76 clinical trials [36]. This not only illustrates the need for determining optimal PROMs in SLE but also supports the notion that optimal use of the currently available ones may be even more important. For example, the differential ability of PROMs to capture changes in the different SLE disease patterns, i.e., persistently quiescent, persistently relapsing-remitting, and persistently active disease [37], comprises one of the many questions framing the future research agenda.
4. Can Lupus Patients Take the Driver’s Seat in Their Disease Monitoring?
Several questions regarding the validity of PROMs for people with SLE were clarified over the past decades [38,39]. We outlined their value in the interpretation of trial data for therapies that are potentially beneficial in the management of SLE. It is apparent that treatment cannot be narrowed down to the pharmacological component only, when the goal is remission on the one hand and a state of good or acceptable HRQoL for people living with SLE on the other. Knowing that SLE influences multiple domains of life, the use of generic and disease-specific measures in structured evaluation processes is justified. In this regard, it is worth noting that mainly generic PROMs have been used in randomized clinical trials of SLE, particularly the SF-36, while instruments with the ability to discriminate across clinically distinct groups are found to be more responsive to change, lending support for broader use of disease-specific PROMs [40]. The SLE-specific SLAQ is designed to capture self-reported symptoms that are usually evaluated by the rheumatologist [41] and is based on the Systemic Lupus Activity Measure [42]. While it shows adequate reliability and correlates with SF-36, it is not always congruous with traditional clinical parameters [43]. The Lupus Patient-Reported Outcome tool (LupusPRO) entails several domains of HRQoL and additionally prompts patients to reflect on support, medications, satisfaction, and cognition [44]. The LupusPRO correlates with the SF-36 and shows responsiveness in relation to the physician-reported activity index BILAG [45]. However, a systematic comparison across available PROMs in relation to generic domains of HRQoL and SLE-specific symptoms to determine the best correlates with traditional physician-reported disease features has yet to be conducted.
Assessments and interventions need to be tailored to the individual patient and decided upon together with the patient. In fact, shared decision-making constitutes a primary overarching principle of the T2T/SLE task force recommendations [8]. For some people with SLE, the impact of the disease acts as a negative spiral, in particular with regard to mental health, whereas high pain and global disease burden are coupled with negative future outcomes [46]. Physical or functional domains of HRQoL may still be contracted in considerable proportions of patients irrespective of their overall response to treatment, which has been shown to be more prominent in patients with established organ damage, and furthermore, dependent on ethnicity [47]. PROMs are scored worse in people with lower health literacy, which is not necessarily related to lower income or education, albeit resources of people with lower socioeconomic backgrounds are under stronger constraints [48,49]. It is also important to bear in mind that comorbidities may have an impact on how patients score their HRQoL, e.g., depressive or other disorders causing chronic mental distress may impact on pain, fatigue, or PtGA scores [46,50]. Thus, persistently high scores or persistent discordance between patient’s and physician’s assessments should intrinsically prompt further investigation for potential comorbid conditions as underlying causes and, if needed, the commencement of suitable adjunct therapy. Nevertheless, the considerable variability of PhGA scoring across assessors highlights the need to adopt optimal tools and determine the optimal timing for the assessment, as well as integrate multiple items, including the patient perspective, with the ultimate goal being a holistic apprehension of the disease status [51,52].
The proper use of PROMs is not only an important conceptual issue but also an opportunity to build bridges in the partnership between patients and physicians. These points of consideration adhere to the overall framework that there will seldom be one single best marker that helps us to interpret the activity, severity, and impact of SLE at the same time. By contrast, in clinical practice, there is a battery of tests and assessment instruments that the healthcare team may choose from, based on what is relevant to the respective patient and the respective condition. However, harmonization and integration of different tests in surveillance and overall patient management should be supported by data and strive for optimization, taking environmental, personal, and disease-specific conditions into account.
5. Conclusions
As a concluding remark, for optimal outcomes, we not only stress the importance of the use of PROMs but also emphasize the urgency to adopt the concept of forming alliances with each individual patient and facilitating active patient participation in surveillance and management processes as an integral part within the clinical consultations, and continuously during the disease course. The positive impact of this mindset on patients’ lives has been explored more in-depth for people with inflammatory arthritis [53,54]; being a considerably more complex condition, it would be counterintuitive to anticipate holistic pertinence in the management of SLE without active patient involvement in all steps. Nevertheless, this should not be misinterpreted as a transfer of responsibility from healthcare professionals to patients, but should rather be considered a step towards shared decision-making, which in fact should impose responsibility to healthcare to ensure adequate patient education and confidence in patients in understanding the need and the options. Thus, while time becomes more mature for patients with SLE to take the driver’s seat in their disease monitoring and management, healthcare professionals should not release themselves from responsibility but retain the seat of the navigator and inspirer.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.P. and P.S.; investigation, I.P. and P.S.; resources, I.P. and P.S.; writing—original draft preparation, I.P. and P.S.; writing—review and editing, I.P. and P.S.; visualization, I.P. and P.S.; funding acquisition, I.P. and P.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
I.P. is supported by the Swedish Rheumatism Association (R-941095), King Gustaf V’s 80-year Foundation (FAI-2020-0741), Professor Nanna Svartz Foundation (2020-00368), Ulla and Roland Gustafsson Foundation (2021-26), Region Stockholm (FoUI-955483) and Karolinska Institutet. P.S. is supported by the FOREUM research fellowship grant.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Yvonne Enman and Gunilla von Perner, both representatives of the Swedish lupus patient community, for reviewing the manuscript and providing useful patient insights and perspectives. We also thank Sarai Llamas (http://saraillamas.com; Accessed on 11 January 2022) for kindly providing the artistic illustration used to create the figure.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest related to this work.
References
- Jolly, M. How does quality of life of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus compare with that of other common chronic illnesses? J. Rheumatol. 2005, 32, 1706–1708. [Google Scholar]
- Piga, M.; Arnaud, L. The Main Challenges in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Where Do We Stand? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, A.; Gordon, C.; Crow, M.K.; Touma, Z.; Urowitz, M.; Van Vollenhoven, R.; Ruiz-Irastorza, G.; Hughes, G. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 16039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kernder, A.; Richter, J.G.; Fischer-Betz, R.; Winkler-Rohlfing, B.; Brinks, R.; Aringer, M.; Schneider, M.; Chehab, G. Delayed diagnosis adversely affects outcome in systemic lupus erythematosus: Cross sectional analysis of the LuLa cohort. Lupus 2021, 30, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moe, S.R.; Haukeland, H.; Molberg, Ø.; Lerang, K. Long-Term Outcome in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus; Knowledge from Population-Based Cohorts. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, H.-J.; Saxena, R.; Zhao, M.-H.; Parodis, I.; Salmon, J.E.; Mohan, C. Lupus nephritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020, 6, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annapureddy, N.; Devilliers, H.; Jolly, M. Patient-reported outcomes in lupus clinical trials with biologics. Lupus 2016, 25, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Mosca, M.; Bertsias, G.; Isenberg, D.; Kuhn, A.; Lerstrøm, K.; Aringer, M.; Bootsma, H.; Boumpas, D.; Bruce, I.N.; et al. Treat-to-target in systemic lupus erythematosus: Recommendations from an international task force. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steiman, A.J.; Urowitz, M.B.; Ibanez, D.; Papneja, A.; Gladman, D.D. Prolonged clinical remission in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 41, 1808–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vollenhoven, R.; Voskuyl, A.; Bertsias, G.; Aranow, C.; Aringer, M.; Arnaud, L.; Askanase, A.; Balážová, P.; Bonfa, E.; Bootsma, H.; et al. A framework for remission in SLE: Consensus findings from a large international task force on definitions of remission in SLE (DORIS). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 76, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladman, D.D.; Ibañez, D.; Urowitz, M.B. Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 288–291. [Google Scholar]
- Franklyn, K.; Lau, C.S.; Navarra, S.V.; Louthrenoo, W.; Lateef, A.; Hamijoyo, L.; Wahono, C.S.; Chen, S.L.; Jin, O.; Morton, S.; et al. Definition and initial validation of a Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 75, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luijten, K.; Tekstra, J.; Bijlsma, J.; Bijl, M. The Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Responder Index (SRI); A new SLE disease activity assessment. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, D.J.; Kalunian, K.; Petri, M.A.; Strand, V.; Houssiau, F.A.; Pike, M.; Kilgallen, B.; Bongardt, S.; Barry, A.; Kelley, L.; et al. Efficacy and safety of epratuzumab in patients with moderate/severe active systemic lupus erythematosus: Results from EMBLEM, a phase IIb, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 73, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felson, D.; Smolen, J.S.; Wells, G.; Zhang, Y.; van Tuyl, L.; Funovits, J.; Aletaha, D.; Allaart, C.F.; Bathon, J.; Bombardieri, S.; et al. American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Provisional Definition of Remission in Rheumatoid Arthritis for Clinical Trials. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- EULAR. Outcome Measures Library. Available online: http://oml.eular.org/ (accessed on 9 April 2020).
- Weldring, T.; Smith, S.M. Article Commentary: Patient-Reported Outcomes (PROs) and Patient-Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs). Health Serv. Insights 2013, 6, HSI.S11093–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studenic, P.; Radner, H.; Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D. Discrepancies between patients and physicians in their perceptions of rheumatoid arthritis disease activity. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64, 2814–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studenic, P.; Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D. Near misses of ACR/EULAR criteria for remission: Effects of patient global assessment in Boolean and index-based definitions. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1702–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studenic, P.; Felson, D.; De Wit, M.; Alasti, F.; Stamm, T.A.; Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D. Testing different thresholds for patient global assessment in defining remission for rheumatoid arthritis: Are the current ACR/EULAR Boolean criteria optimal? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.; Flurey, C.A.; Proudman, S.; Ferreira, R.J.; Voshaar, M.; Hoogland, W.; Chaplin, H.; Goel, N.; Hetland, M.L.; Hill, C.; et al. Considerations and priorities for incorporating the patient perspective on remission in rheumatoid arthritis: An OMERACT 2020 special interest group report. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 1108–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heijke, R.; Björk, M.; Thyberg, I.; Kastbom, A.; McDonald, L.; Sjöwall, C. Comparing longitudinal patient-reported outcome measures between Swedish patients with recent-onset systemic lupus erythematosus and early rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golder, V.; Kandane-Rathnayake, R.; Hoi, A.Y.-B.; Huq, M.; Louthrenoo, W.; An, Y.; Li, Z.G.; Luo, S.F.; Sockalingam, S.; Lau, C.S.; et al. Association of the lupus low disease activity state (LLDAS) with health-related quality of life in a multinational prospective study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elefante, E.; Tani, C.; Stagnaro, C.; Signorini, V.; Parma, A.; Carli, L.; Zucchi, D.; Ferro, F.; Mosca, M. Articular involvement, steroid treatment and fibromyalgia are the main determinants of patient-physician discordance in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res. 2020, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizoddin, D.R.; Jolly, M.; Arora, S.; Yelin, E.; Katz, P. Patient-Reported Outcomes Predict Mortality in Lupus. Arthritis Rheum. 2018, 71, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Louthrenoo, W.; Kasitanon, N.; Morand, E.; Kandane-Rathnayake, R. Associations between physicians’ global assessment of disease activity and patient-reported outcomes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A longitudinal study. Lupus 2021, 30, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strand, V.; Gladman, D.; Isenberg, D.; Petri, M.; Smolen, J.; Tugwell, P. Endpoints: Consensus recommendations from OMERACT IV. Lupus 2000, 9, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, J.C.; Neville, C.; Fortin, P.R. Discordance between patients and their physicians in the assessment of lupus disease activity: Relevance for clinical trials. Lupus 1999, 8, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ware, J.E., Jr.; Sherbourne, C.D. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med. Care 1992, 30, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yellen, S.B.; Cella, D.F.; Webster, K.; Blendowski, C.; Kaplan, E. Measuring fatigue and other anemia-related symptoms with the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy (FACT) measurement system. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 1997, 13, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services FDA Center for Devices and Radiological Health. Guidance for industry: Patient-reported outcome measures: Use in medical product development to support labeling claims: Draft guidance. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2006, 4, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strand, V.; Simon, L.S.; Meara, A.S.; Touma, Z. Measurement properties of selected patient-reported outcome measures for use in randomised controlled trials in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review. Lupus Sci. Med. 2020, 7, e000373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strand, V.; Levy, R.A.; Cervera, R.; Petri, M.A.; Birch, H.; Freimuth, W.W.; Zhong, Z.J.; Clarke, A.E. Improvements in health-related quality of life with belimumab, a B-lymphocyte stimulator-specific inhibitor, in patients with autoantibody-positive systemic lupus erythematosus from the randomised controlled BLISS trials. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 73, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The EuroQol Group. EuroQol-a new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life. Health Policy 1990, 16, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.; Wilke, C.T.; Pickard, A.S.; Vats, V.; Mikolaitis, R.; Fogg, L.; Block, J.A.; Jolly, M. Psychometric Properties of the EuroQol-5D and Short Form-6D in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindblom, J.; Gomez, A.; Borg, A.; Emamikia, S.; Ladakis, D.; Matilla, J.; Pehr, M.; Cobar, F.; Enman, Y.; Heintz, E.; et al. EQ-5D-3L full health state discriminates between drug and placebo in clinical trials of systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 4703–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Györi, N.; Giannakou, I.; Chatzidionysiou, K.; Magder, L.; Van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Petri, M. Disease activity patterns over time in patients with SLE: Analysis of the Hopkins Lupus Cohort. Lupus Sci. Med. 2017, 4, e000192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, Z. Health-Related Quality of Life Measures in Adult Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 72, 577–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holloway, L.; Humphrey, L.; Heron, L.; Pilling, C.; Kitchen, H.; Højbjerre, L.; Strandberg-Larsen, M.; Hansen, B.B. Patient-reported outcome measures for systemic lupus erythematosus clinical trials: A review of content validity, face validity and psychometric performance. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2014, 12, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izadi, Z.; Gandrup, J.D.F.; Katz, P.P.; Yazdany, J. Patient-reported outcome measures for use in clinical trials of SLE: A review. Lupus Sci. Med. 2018, 5, e000279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlson, E.W.; Daltroy, L.H.; Rivest, C.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Wright, E.A.; Partridge, A.J.; Liang, M.H.; Fortin, P.R. Validation of a systemic lupus activity questionnaire (SLAQ) for population studies. Lupus 2003, 12, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.C.; Koh, H.K.; Chang, D.K.; Kim, M.H.; Park, J.K.; Kim, S.Y. Reliability and validity of systemic lupus activity measure-revised (SLAM-R) for measuring clinical disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2001, 10, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdany, J.; Yelin, E.H.; Panopalis, P.; Trupin, L.; Julian, L.; Katz, P.P. Validation of the systemic lupus erythematosus activity questionnaire in a large observational cohort. Arthritis Care Res. 2007, 59, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azizoddin, D.R.; Weinberg, S.; Gandhi, N.; Arora, S.; Block, J.; Sequeira, W.; Jolly, M. Validation of the LupusPRO version 1.8: An update to a disease-specific patient-reported outcome tool for systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2017, 27, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolly, M.; Pickard, A.S.; Block, J.; Kumar, R.B.; Mikolaitis, R.A.; Wilke, C.T.; Rodby, R.A.; Fogg, L.; Sequeira, W.; Utset, T.O.; et al. Disease-Specific Patient Reported Outcome Tools for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 42, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parperis, K.; Psarelis, S.; Chatzittofis, A.; Michaelides, M.; Nikiforou, D.; Antoniade, E.; Bhattarai, B. Association of clinical characteristics, disease activity and health-related quality of life in SLE patients with major depressive disorder. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 5369–5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, A.; Qiu, V.; Cederlund, A.; Borg, A.; Lindblom, J.; Emamikia, S.; Enman, Y.; Lampa, J.; Parodis, I. Adverse Health-Related Quality of Life Outcome Despite Adequate Clinical Response to Treatment in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Med. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, P.; Dall’Era, M.; Trupin, L.; Rush, S.; Murphy, L.B.; Lanata, C.; Criswell, L.A.; Yazdany, J. Impact of Limited Health Literacy on Patient-Reported Outcomes in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 73, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeQuattro, K.; Yelin, E. Socioeconomic Status, Health Care, and Outcomes in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 46, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, M.; Parodis, I.; Nikiphorou, E. Fatigue in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comparison of Mechanisms, Measures and Management. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chessa, E.; Piga, M.; Floris, A.; Devilliers, H.; Cauli, A.; Arnaud, L. Use of Physician Global Assessment in systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review of its psychometric properties. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 3622–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aranow, C. A pilot study to determine the optimal timing of the Physician Global Assessment (PGA) in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunol. Res. 2015, 63, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikiphorou, E.; Santos, E.J.F.; Marques, A.; Böhm, P.; Bijlsma, J.W.; Daien, C.I.; Esbensen, B.A.; Ferreira, R.J.O.; Fragoulis, G.E.; Holmes, P.; et al. 2021 EULAR recommendations for the implementation of self-management strategies in patients with inflammatory arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rn, I.L.; Bremander, A.; Andersson, M. Patient Empowerment and Associations with Disease Activity and Pain-Related and Lifestyle Factors in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2021, 3, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).