Abstract
Being one of the most common dermatological inflammatory disorders, psoriasis is a frequent subject of research. It is considered to be a T cell-dependent immune disease whose pathogenesis is influenced by cytokines, such as IL-10, IL-17A, IL-17RA, IL-23A and IL-23R. The present study examines whether the expression of selected genes is correlated with the clinical course of psoriasis, assessed by the PASI, BSA and DLQI scales. Skin biopsies and blood from 60 patients with psoriasis and 24 healthy controls were obtained for RNA isolation. These were subjected to RT-PCR for IL-10, IL-17A, IL-17RA, IL-23A and IL-23R genes. The results were presented as an RQ value. IL-17A and IL-23R expression levels were higher in psoriatic skin compared to controls, while IL-10 expression was lower. A positive correlation was also found between RQ for IL-23A and PASI index. Psoriatic skin is characterised by elevated expression of IL-17A and IL-23R and decreased expression of IL-10. This indicates that the selected cytokines may be one of the factors involved in the pathogenesis and pathomechanism of psoriasis, but more studies need to be made before we can elucidate the exact reason for the unbalance in cytokine expression levels.
1. Introduction
Psoriasis vulgaris is a chronic, recurrent dermatosis causing erythematosus and scaly skin plaques [1,2,3,4,5,6]. It is regarded as the most common T cell-mediated inflammatory disease in humans, with a mean prevalence in Caucasian populations of 2–3% [7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. Men and women are equally often affected [14,15]. It is an immunologically mediated disease, but genetic and epigenetic factors also play an important role in its development [16,17,18,19,20,21]; however, these may be modulated by initiating environmental factors, such as infections, medications, injuries, stress or alcohol abuse [19,20,22,23,24,25,26]. Psoriasis often coexists with other autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune thyroid diseases, inflammatory bowel diseases, celiac disease and vitiligo [27,28,29,30,31].
However, until now, the exact etiopathogenesis of psoriasis vulgaris and the mechanisms leading to its development remain unclear. Despite this, recent studies suggest that immunological mechanisms associated with Th1 and Th17 lymphocytes play a dominant role in the development of psoriatic lesions, with the activation of the interleukin (IL)-12/Th1/interferon (IFN)-γ and IL-23/Th17/IL-17 pathways being critical. The stimulation of Th1 lymphocytes to secrete pro-inflammatory molecules, such as tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α, IFN-γ, IL-2 and IL-3 leads to the induction and maintenance of skin inflammation and an increase in the number of keratinocytes in the epidermis. In turn, Th17 lymphocytes activated by IL-23 begin to secrete effector cytokines, such as IL-17, TNF-α, IL-22 or IL-6. These cytokines lead to the inflow of neutrophils and other inflammatory cells to the skin and epidermis, excessive proliferation of keratinocytes and parakeratosis [28,32,33,34,35,36,37,38].
IL-10 is also believed to play a role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis by inhibiting the formation of antigen-induced Th1 lymphocytes, as well as the production of cytokines, particularly IFN-γ and IL-2, and the secretion of TNF, IL-1α, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, granulocyte colony-stimulating-factor (G-CSF) and granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating-factor (GM-CSF) by macrophages and monocytes. In addition, IL-10 enhances the adaptive abilities of regulatory T cells. Together, these immunological processes result in the manifestation of clinical symptoms in the form of a dermal-epidermal papule covered with silvery-white scales [39,40].
The aim of the study is to determine the role of selected genes viz. IL-10, IL-17A, IL-17RA (interleukin 17A receptor), IL-23A (interleukin 23 subunit α) and IL-23R (interleukin 23 receptor) in the development of psoriasis. The study determined their expression (RQ—relative quantification) in regulatory T cells in blood and skin biopsies taken from patients with psoriasis, and correlated them with samples from healthy volunteers. All genetic parameters were compared with selected clinical indicators of the activity and severity of the disease process in patients: the PASI (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index), BSA (Body Surface Area) and DLQI (Dermatology Life Quality Index) ratios.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Features of Patients and Skin Samples
The research covered a group of 60 adults suffering from plaque psoriasis, 18 women (30%) and 42 men (70%), aged from 23 to 83 years (mean age 51.22 ± 15.95 years). The patients were treated in the Department of Dermatology and Venereology and/or in the Diagnostic and Treatment Centre of Skin Diseases between March 2016 and February 2020. After obtaining written consent from the patients, a 4 mm diameter sample was taken from the area of the skin lesion by punch-biopsy, and 10 mL of venous whole blood was collected into EDTA anticoagulant.
The control group was matched for gender and age. It comprised 24 healthy people (11 women and 13 men), aged from 29 to 79 years (mean age 51.42 ± 16.34 years), without family history of the presence of psoriasis. Skin biopsies were taken by a surgeon. Exclusion criteria from participation in the study included pregnancy, lactation and the use of drugs that excessively prolong bleeding time.
2.2. Isolation of T-regulatory Lymphocytes (CD4/CD25) from Whole Blood
From venous whole blood collected from all patients, T-regulatory (T-reg) lymphocytes were isolated. The principle of isolation of CD4/CD25 cells from blood is based on the protocol of two-step selection of T-regulatory lymphocytes (T-reg), according to Sugiyama H. et al., 2005 [41] (with minor modifications and the use of kits StemCell Technologies, Vancouver, BC, Kanada). Firstly, CD4+ cells were obtained by negative selection using the RosetteSep®Humane CD4+ T Cell Enrichment Cocktail kit (StemCell Technologies), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Following this, CD25+ T lymphocytes were positively selected from enriched CD4+ cells using the EasySep® Human CD25 Positive Selection Cocktail kit (StemCell Technologies) and magnetic beads EasySep® Magnetic Nanoparticles (StemCell Technologies). The positively-selected cells were resuspended in 1 × PBS and used for RNA isolation.
2.3. Homogenisation of Skin Biopsies
Skin samples immediately after excision were placed in fixRNA buffer (Eurx, Gdańsk, Poland) and stored at 2–8 °C until use. After the fixRNA buffer was removed, the samples were divided into smaller parts, 600 μL of lysis buffer was added and the mixture was homogenised using a pellet pestle homogeniser (Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany). Total RNA was isolated from skin homogenates.
2.4. RNA Isolation, Qualitative and Quantitative RNA Evaluation
Isolation of total RNA from T-regulatory cells and skin homogenates was performed using the mirVana™ miRNA Isolation Kit (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA), which provides efficient isolation of small RNA-containing total RNA. This kit is compatible with virtually all cell and tissue types, and has been used previously to isolate RNA from body fluids and tissues [42,43,44]. Isolation of total RNA was carried out following the manufacturer’s recommendations. Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of the isolated RNA was performed spectrophotometrically by measuring the absorbance with the Eppendorf BioPhotometerTM Plus apparatus (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany), at 260/280 nm wavelengths. The prepared RNA was divided into portions and frozen at −80 °C for real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) analysis.
2.5. Evaluation of Gene Expression
The evaluation of gene expression was performed analogously to the previously described procedure [44]. The reverse transcription (RT) reaction was performed using the High-Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA, USA) in a volume of 20 μL. The reaction mixture contained 10 × RT buffer, 25 × dNTP Mix (100 mM), 10 × RT Random Primers, MultiScribe™ Reverse Transcriptase, RNase Inhibitor and nuclease-free water. Each sample included 100 ng of total RNA in the reaction mixture. A negative control was included using water instead of RNA. The following RT reaction conditions were used: 10 min at 25 °C, 120 min at 37 °C, 5 min at 85 °C and cooling at 4 °C.
Relative gene expression was assessed by real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) using a 7900HT Fast Real-Time PCR System device (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA, USA). A total reaction volume of 20 μL contained: cDNA (1–100 ng), KAPA PROBE FAST qPCR Master Mix (2X) ABI Prism™ (Kapa Biosystems Ltd., London, UK), RNAse-free water and 20 × TaqMan® Gene Expression Assay for the following genes: IL-10 (Hs00961622_m1), IL-17A (Hs00174383_m1), IL-17RA (Hs01056316_m1), IL-23A (Hs00372324_m1), IL-23R (Hs00332759_m1) and GAPDH (Hs99999905_m1) selected as the reference gene in the qPCR reaction. The relative expression level of the studied genes was evaluated by the delta-delta CT method (TaqMan Relative Quantification Assay software, Applied Biosystems) and presented as the RQ value relative to the GAPDH reference gene. The calibrator for which RQ = 1 was RNA isolated from biological material from a healthy patient, without skin lesions. RQ > 1 indicates higher expression of the gene in test samples than in the calibrator sample, and RQ < 1 indicates less expression.
2.6. Dermatological Scales
The severity of skin lesions was assessed using the PASI (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index), BSA (Body Surface Area) and DLQI (Dermatology Life Quality Index) scale.
PASI is the best known and most frequently recommended measurement scale for assessing the extent and severity of psoriasis. It determines the percentage of skin affected by psoriatic lesions in four main body areas: head, trunk, upper and lower extremities. Then, within each location, three parameters are assessed, viz. erythema, infiltration and desquamation, on a scale from 0 (no change) to 4 (very strong intensity). The test yields a single score in the range from 0 to 72 points, with a higher PASI score indicating a greater degree of psoriatic severity and extension [45,46,47,48,49]. A PASI result below 10 points indicates mild psoriasis, and one of 10 or above that the patient has a moderate or severe form of the disease.
The BSA tool is used to determine the percentage (from 0 to 100%) of the area of the skin covered by psoriatic lesions. When calculating this scale, the Wallace rule of nines [45] is followed, in which the surface of the head represents 9% of the surface of the body, each of the upper limbs is also 9%, the front and back torso each 18% (36% in total), each lower limb 18%, and the crotch area 1%. In addition, the surface of the patient’s hand constitutes 1% of the body. Values less than 10% indicate mild psoriasis, and values greater than or equal to 10% indicate moderate to severe psoriasis. Unfortunately, unlike PASI, the BSA index does not assess morphological features of lesions, such as infiltration, erythema and scale, which means that it should not be the only ratio used in assessment.
DLQI is an easy-to-use and concise questionnaire consisting of ten questions designed for a subjective assessment of the impact of psoriasis on the patient’s quality of life in the previous week. Each question concerns the impact of this dermatological disease on a particular area of life and is rated on a scale from 0 to 3. The total number of points ranges from 0 points, indicating that psoriasis has no effect on quality of life, to 30 indicating a very strong negative impact on daily life [45,50]. The questionnaire is completed by the patient, without the help of a doctor.
The patients were divided into groups based on the questionnaire results, i.e., PASI ≤ 10 and >10, BSA ≤ 20 and >20, DLQI ≤ 10 and >10, and the relative expression of the tested cytokine genes was recorded for each of them.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
The results (RQ value) are shown as medians. Statistical analysis was performed using Statistica 13.1 software (StatSoft, Cracow, Poland). The Mann–Whitney U test was used to assess the statistical dependence between the study groups. Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient was used to measure the direction and strength of the relationship for individual variables. The level of correlation was fixed in the following categories: very strong (rho ≥ 0.80), moderate (rho = 0.60–0.79), fair (rho = 0.30–0.59) and poor (rho ≤ 0.29). Statistical significance was assumed for p-values < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. IL-10, IL-17A, IL-17RA, IL-23A and IL-23R Gene Expression in Psoriatic Patients vs. Healthy Volunteers
The relative expression level of genes IL-10, IL-17A, IL-17RA, IL-23A and IL-23R was determined in the material derived from skin sections and from T-regulators lymphocytes (CD4/CD25). The median RQ values for the studied genes and the number of samples with decreased/increased expression compared to housekeeping gene values are presented in Table 1 and Table 2.

Table 1.
Gene expression levels (RQ values) in skin assessed by the ΔΔCT method and percentage of samples with expression levels above and below calibrator values in the psoriatic and control groups.

Table 2.
Gene expression levels (RQ values) in lymphocytes assessed by the ΔΔCT method and percentage of samples with expression levels above and below calibrator values in the psoriatic and control groups.
For IL-10, the median gene expression (RQ value) in skin was 0.078 in psoriatic patients and 0.0312 for healthy volunteers; however, in lymphocytes, it was below detection levels for both groups. In case of IL-17A, the median RQ in skin was 119.636 in the psoriasis group and 2.217 in the control group, but below detection levels for both groups in lymphocytes. For IL-17RA, the RQ values were 0.253 in psoriatic skin, 1.014 in healthy skin, 11.529 in lymphocytes from the psoriatic group and 15.458 in lymphocytes from healthy controls. For IL-23A, median expression was 0.231 in psoriatic skin and 0.130 for control skin, 2.893 for psoriatic lymphocytes and 6.573 for control lymphocytes. For IL-23R, median RQ was 46.695 in psoriatic skin and 7.018 control skin; however, the values were below detection levels in both groups of lymphocytes.
The qPCR results (RQ values) were obtained for all psoriatic skin and control samples (healthy skin). IL-17A and IL-23R expression was upregulated in both groups compared to the calibrator. In addition, IL-17RA expression was decreased in psoriatic skin and elevated in the control group, while IL-10 and IL-23A expression was downregulated in both groups. Statistically significant differences in relative expression level of IL-17A and IL-23R were observed between the psoriatic skin and the control group (p = 0.0000001 and p = 0.000007, respectively; Mann–Whitney U test), with higher expression observed in the psoriatic patient group (see Figure 1). Significantly lower IL-10 and IL-17RA expression was found in psoriatic skin than in controls (p = 0.000005 and p = 0.0000001, respectively; Mann–Whitney U test) (Figure 2).
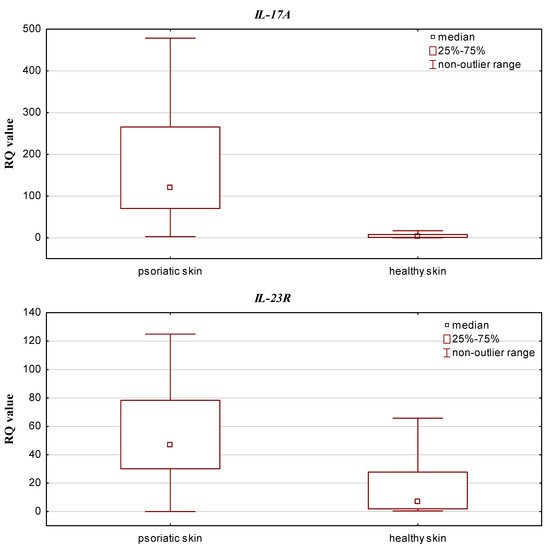
Figure 1.
Box-and-whisker plots presenting higher expression levels (median RQ values) in psoriatic skin vs. healthy skin (controls) for IL-17A and IL-23R.
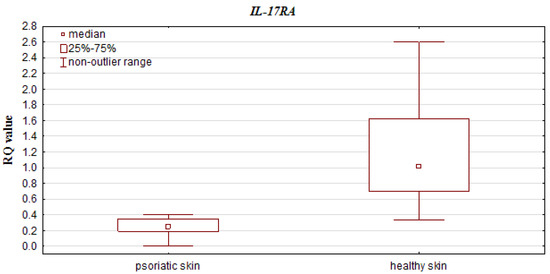
Figure 2.
Box-and-whisker plots, presenting lower expression levels (median RQ values) in psoriatic skin vs. healthy skin (controls) for IL-10 and IL-17RA.
Regarding the biological material derived from T-reg lymphocytes (CD4/CD25), the RQ values of IL-10, IL-17A and IL-23R were below detection levels. The RQ values of IL-23A and IL-17RA in T-reg lymphocytes (CD4/CD25) were upregulated relative to the housekeeping gene in the psoriatic and control group. In addition, participants diagnosed with psoriasis demonstrated lower RQ values for IL-23A and IL-17RA; however, the obtained results were not statistically significant (p = 0.439585 and p = 0.254683, respectively; Mann–Whitney U test).
3.2. RQ Value Genes vs. Clinical Features (PASI, BSA, DLQI) of Psoriatic Patients
In the researched psoriatic group, PASI values ranged from 3.0 to 25.4 (mean 9.58), BSA from 7.5 to 61 (mean 23.83), while DLQI from 0 to 30 (mean 13.13).
The relative expression of IL-10, IL-17A, IL-17RA, IL-23A and IL-23R genes was analysed depending on the classification of psoriatic patients, according to the used scales (PASI, BSA, DLQI). Regarding the biological material derived from skin sections, a positive correlation was found between the RQ value of IL-23A and PASI (rho = 0.278984, p = 0.030881; Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient), and a negative correlation between the RQ value of IL-23R and BSA (rho = −0.265377, p = 0.040436; Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient). No significant correlations were found between the RQ values of the IL-10, IL-17A and IL-17RA genes and PASI, BSA or DLQI scores (p > 0.05; Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient).
Higher RQ values of IL-23A were observed in patients with PASI > 10 than PASI < 10 (0.158 vs. 0.436) (p = 0.010699; Mann–Whitney U test) (see Figure 3). No significant differences were observed for IL-10, IL-17A, IL-17RA and IL-23R gene RQs between patients with high and low PASI scores (p = 0.234864, p = 0.865768, p = 0.247344, p = 0.450768, respectively; Mann–Whitney U test).
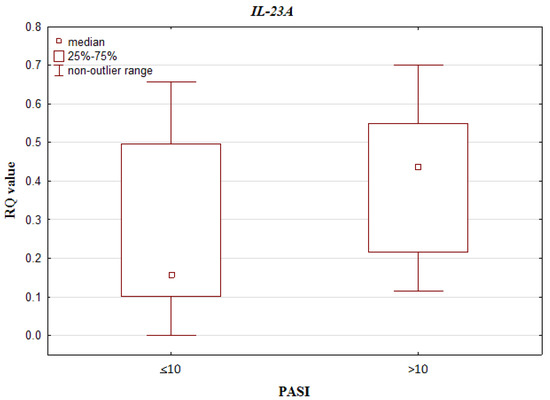
Figure 3.
Box-and-whisker plots, presenting relative expression levels (median RQ values) of IL-23A in psoriatic patients with PASI ≤ 10 vs. PASI > 10.
Regarding BSA, IL-10, IL-17A, IL-17RA, IL-23A and IL-23R demonstrated higher RQ values among patients with BSA ≤ 20 than among those who had BSA > 20 (0.081 vs. 0.076, 168.586 vs. 108.592, 0.260 vs. 0.224, 0.234 vs. 0.231 and 51.366 vs. 36.545; respectively). Of these, only IL-17A demonstrated a statistically significant difference in relation to the BSA scale (p = 0.042520; Mann–Whitney U test). The results are presented in Figure 4. No such statistically significant differences were found for the remainder: IL-10 p = 0.326967, IL-23A p = 0.622077, IL-17RA p = 0.246764 and IL-23R p = 0.115034; Mann–Whitney U test.
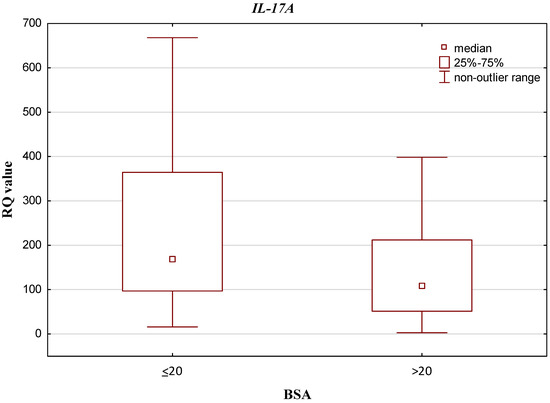
Figure 4.
Box-and-whisker plots, presenting relative expression levels (median RQ values) of IL-17A in psoriatic patients with BSA ≤ 20 vs. BSA > 20.
Regarding DLQI, IL-10, IL-17A and IL-17RA demonstrated higher RQ values in the DLQI ≤ 10 group than the DLQI > 10 group (0.084 vs. 0.066, 148.100 vs. 110.145 and 0.264 vs. 0.234, respectively). In contrast, IL-23A and IL-23R demonstrated lower RQ in DLQI ≤10 than in DLQI > 10 group (0.220 vs. 0.233, 39.046 vs. 53.525, respectively). None of these differences were statistically significant with the p-values being p = 0.414612, p = 0.296663, p = 0.318285, p = 0.987968 and p = 0.39990 for IL-10, IL-17A, IL-17RA, IL-23A and IL-23R, respectively; Mann–Whitney U test.
Regarding the biological material derived from T-reg lymphocytes (CD4/CD25), no significant correlations were found regarding the expression level of IL-10, IL-17A and IL-23R and patient classification (PASI, BSA, DLQI) (p > 0.05, Mann–Whitney U test).
4. Discussion
Psoriasis is a disease with a complex etiopathogenesis characterized by excessive growth and aberrant differentiation of keratinocytes; however, despite much research, it remains not fully understood. It is known, however, that disorders in the immune system play a very important role. The present study examines the expression of the genes IL-10, IL-17A, IL-17RA, IL-23A and IL-23R in the skin and peripheral blood of patients with psoriasis and of healthy people, to identify potential factors regulating the development of psoriatic lesions. Understanding the molecular basis of this mechanism may allow the development of improved forms of tailored therapy.
4.1. IL-10
IL-10 is a homodimeric anti-inflammatory protein, which acts as an immunoregulator which inhibits the synthesis of other cytokines. It is encoded by the IL-10 gene. It is produced mainly by monocytes, stimulated T lymphocytes (especially Th2, but also Treg) and B lymphocytes, macrophages and keratinocytes. IL-10 is believed to inhibit the inflammatory response and regulate cell-mediated immune processes by inhibiting the synthesis of INF-γ by Th1 lymphocytes and IL-1α, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, TNF-α, G-CSF and GM-CSF by monocytes or macrophages. In addition, it can suppress the ability of antigen-presenting cells (mainly monocytes) and stimulate the production of IL-1 receptor antagonists [51,52,53,54,55].
Our findings indicate a relative deficiency in cutaneous IL-10 mRNA expression in both study groups, but that levels were significantly lower in patients with psoriasis. This is consistent with Cheng et al. [56], who report a relative deficiency in IL-10 mRNA expression in psoriatic lesions compared with normal skin tissues. Similar relationships were found in the work of Asadullah et al. [51], who observed a low level of IL-10 expression in the psoriatic skin versus skin with other inflammatory diseases. This is also supported by immunohistochemical results suggesting a low cutaneous IL-10 protein expression in psoriasis [57].
However, conflicting data have also been published—Wolk et al. report elevated expression of IL-10 in biopsies from patients with psoriasis relative to healthy donors [58], but Uyemura et al. [59] and Schlaak et al. [60] weakly or not at all detected IL-10 mRNA. In addition, exogenous supply of IL-10 in treatment has been found to increase intradermal IL-10 mRNA expression [51] and significantly decrease PASI [61]. The clinical effectiveness of IL-10 application has also been confirmed by Reich et al. [62] and McInnes et al. [63].
This suggests that IL-10 may have anti-psoriatic effects and could be an alternative form of therapy for psoriasis. Despite this, a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind 12 week treatment trial of recombinant human IL-10 failed to markedly change baseline PASI score [64]. This is confirmed by the fact that not all laboratory tests analysing the pathological processes underlying the development of the disease result in the subsequent registration of the medical product. The results of laboratory observations have been verified by drug studies on the safety and effectiveness of therapy.
The RQ of IL-10 in CD4/CD25 T-regulatory lymphocytes was below detection for both patients and healthy people, indicating that the gene is not expressed in CD4/CD25. This is also confirmed by the results of researchers from the Berlin Humboldt University [51], which indicate that IL-10 mRNA expression was not elevated in peripheral blood monoclonal cells from psoriatic patients in comparison to controls. In addition, the same group of scientists observed that IL-10 mRNA expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells was higher during conventional anti-psoriatic therapy than before treatment. This may suggest that IL-10 has an anti-psoriatic effect.
Although no significant relationships were observed between the level of IL-10 expression and the PASI, BSA or DLQI value in all patients, higher IL-10 expression was observed in the BSA ≤ 20 and DLQI ≤ 10 groups. It has previously been found that therapy with the use of recombinant IL-10 did not significantly decrease PASI value [64], suggesting that cutaneous levels of IL-10 are not indicative of disease severity. In contrast, many studies show a reduction in PASI score after the IL-10 treatment, but no total recovery [51,52,61,62,63,65].
It is possible therefore that IL-10 might have a certain role in the regression of psoriasis and may be considered as a therapeutic approach; however, further investigations are needed to establish its exact anti-psoriatic role.
4.2. IL-17A and IL-17RA
The interleukin 17 family includes six members labelled from A to F [66,67]. Although all are produced by T-helper lymphocytes, particularly IL-17A, in response to stimulation by various compounds, including IL-23 [68,69,70], IL-17A is also produced in small amounts by other cells such as natural killer (NK) cells, neutrophils and mastocytes. Biologically active IL-17A binds to the receptor IL-17RA, resulting in the activation of signalling cascades (including increased production of cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-6, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, IL-1β, G-CSF and GM-CSF), which in turn provoke the induction of chemokines that attract monocytes, neutrophils and dendritic cells to the place of inflammation [71]. Such an imbalance in the level of cytokines and chemokines allows uninhibited proliferation of Th17 lymphocytes and the production of IL-17 in psoriatic lesions; this plays a key role in the pathogenesis of this disease, because IL-17A is a factor leading to the dysfunction of epidermal keratinocytes and promotes their abnormal differentiation [72].
IL-17RA is a ubiquitous glycoprotein associated with the biological membrane structure, and is expressed in many tissues, including epithelial cells in abundance [71]. It is one of five receptors for IL-17 family [73,74]. It interacts with both IL-17A and IL-17F, but a heterodimeric junction consisting of both IL-17RA and also IL-17RC is required to transmit the signal for these interleukins [66,73].
Li et al. [75], Teunissen et al. [76], Zaba et al. [77], Lowes et al. [78] and Haider et al. [79] reported significantly higher expression of IL-17 mRNA in psoriatic lesions than in healthy controls. Chan et al. [80] described the same relationship for IL-17A mRNA expression. This is in line with the results of the present study. Similarly, previous studies have noted greater expression of mRNA encoding IL-17A or IL-17 in lesional than non-lesional biopsies of patients with psoriasis [81,82]. These findings suggest that up-regulated IL-17 expression may be related to the pathogenesis of psoriasis by amplifying the development or sustaining chronic inflammatory responses in the skin. This has been confirmed by the effectiveness of anti-IL-17 biological drugs [83,84,85,86].
Our present results show decreased expression of IL-17RA in psoriatic skin and an increase in healthy individuals. In contrast, Johansen and colleagues [81] reported no difference in the IL-17RA mRNA expression level between lesional and non-lesional psoriatic skin; however, it should be noted that the study group only included nine patients. It may be possible that no significant relationship exists between the mRNA levels of the IL-17R family members and their corresponding ligands [81], or that cellular responses to the IL-17A (and IL-17F) stimulation require expression of the entire IL-17RA and IL-17RC receptor complex, not just IL-17RA alone [66,73,87,88,89].
Our present findings indicate that IL-17 gene expression was below detection levels in CD4/CD25 lymphocytes in both patient and control groups. However, Suárez-Fariñas et al. [82] reported increased expression of IL-17 in the blood of psoriasis patients compared with healthy population. Interestingly, in the present study, IL-17A receptor gene expression was elevated in peripheral blood lymphocytes in both study groups. The presence of IL-17 expression in the skin but not on CD4/CD25 blood cells may indicate local rather than systemic involvement in the inflammation process in psoriasis.
In addition, no significant correlation was found between the level of IL-17A and IL-17RA expression and the PASI, BSA or DLQI value in any patient. However, the group with mild psoriasis (BSA ≤ 20 and DLQI ≤ 10) demonstrated higher levels of expression of IL-17A and IL-17RA. These findings are consistent with those of Hijnen et al. [90], who also reported that level of expression of IL-17, but also IL-22, IFN-ɤ and IL-13, in skin biopsies of patients with psoriasis did not correlate with PASI. This may be explained by the argument that the local cytokine production in single plaque does not reflect the general activity of the disease. Previous studies report a positive correlation between IL-17A and psoriasis severity, but they assessed IL-17A protein level in serum or tissue, not gene expression [91,92,93,94,95]. In support of this hypothesis, recent data indicate that anti-IL-17 agents, such as secukinumab (anti-IL-17A antibody), ixekizumab (anti-IL-17A antibody), brodalumab (anti-IL-17RA antibody) and bimekizumab (anti-IL-17A and -17F antibody) are effective forms of treating moderate to severe psoriasis, which is expressed by reducing PASI and/or BSA score [83,84,85,86,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103].
IL-17A seems to fulfil a key role in the pathway of the pathogenesis of psoriasis, and biological therapies targeting IL-17A and/or IL-17RA yield remarkable effects for inflammatory skin dermatoses like psoriasis.
4.3. IL-23A and IL-23R
IL-23 is a heterodimer cytokine consisting of two subunits. The first, marked as p19 (subunit A, IL-23A), is specific, homologous to the p35 subunit of IL-12, and encoded by the IL-23A gene. The second subunit is p40 (subunit B, IL-12B), common to IL-23 and IL-12, encoded by the IL-12B gene [71]. Activated dendritic cells, macrophages or monocytes and keratinocytes are the main sources of IL-23 [104,105,106,107]. The receptor for IL-23 is a complex consisting of two elements: IL-12Rβ1 (IL-12RB1), which binds to the p40 subunit, and IL-23R, which binds to the p19 subunit [71,108].
IL-23 plays an important role in the proliferation, maturation and differentiation of T cells into Th1, Th17 and Th22 cells, and enables the release of IL-6, IL-17, IL-21, IL-22 and GM-CSF by Th17 cells [71]. Moreover, it strongly induces the secretion of INF-γ from T lymphocytes and the production of acute-phase proteins. The whole process leads to excessive, accelerated proliferation of keratinocytes and inflammation.
In the present study, IL-23A gene expression was decreased in the psoriasis group and the controls. This may be because the expression of p40 subunit, which is shared by IL-23 and IL-12, can be a key factor in the development and maintenance of psoriatic skin lesions: previous studies report elevated level of gene expression of IL-12B in diseased skin [44,109,110]. Different results were presented by Fitch et al. [71], Chan et al. [80], Lee et al. [108] and Chamian et al. [111], who reported an increase in p19 mRNA in psoriatic skin compared with healthy skin, as well as an elevated level of p40 in lesional tissues, but not p35, which suggests IL-23 plays a greater role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis than IL-12. A similar relationship with p40 and p35 levels was found by Cheng et al. [56]. Because the p40 subunit of IL-12 is shared with IL-23, it is possible that p40 overexpression may be incorrectly attributed to IL-12 instead of IL-23. Increased levels of IL-23 expression and IL-12 p40 in tissue of patients with psoriasis was also observed by Tonel et al. [112]; however, they also described an elevated level of IL-12 p35. This is consistent with many previous studies [111,113,114,115,116], in which the level of IL-23 (assessed by either mRNA or protein) decreased together with clinical efficacy after psoriatic treatment. Furthermore, therapy based on anti-p40 monoclonal antibody, which target both IL-12 and IL-23, resulted in clinical improvement in patients with psoriasis [113,117,118,119,120].
In the case of IL-23R, Tonel et al. [112] reported that IL-23 receptor expression was increased in the skin of patients with psoriasis. Similar results were obtained in the present study: while IL-23R expression was elevated in skin biopsies from both the patients and control groups, the increase was markedly higher for the psoriatic group.
While IL-23A expression was detected in T-regs (CD4/CD25) in both the patient and control groups, IL-23R expression was beneath the level of detection. While Kagami et al. [121] reported elevated IL-23R expression in peripheral blood of patients with versus without psoriasis, Tonel et al. [112] reported no such significant difference in various cells.
Our present findings indicate a positive correlation between PASI and IL-23A expression, i.e., the higher IL-23 gene expression was observed in the higher PASI (>10) group. In addition, the IL-23A expression was significantly higher in patients with moderate to severe disease (with PASI > 10) than those with the mild (PASI ≤ 10) form of psoriasis. These results are reflected in many reports of treatment with biological drugs that affect IL-23: ustekinumab and briakinumab (monoclonal antibodies against the IL-12/IL-23p40 subunit), guselkumab (fully human, monoclonal IL-23 antagonist targeting the unique p19 subunit of IL-23), tildrakizumab and risankizumab (humanized monoclonal antibodies inhibiting selectively the p19 subunit of IL-23) were found to significantly reduce PASI and BSA score [113,117,118,119,120,122]. However, in the present study, IL-23 and IL-23R gene expression was elevated in the BSA ≤ 20 group, but the differences failed to reach statistical significance. Moreover, a decrease in IL-23R expression was observed as the BSA increased; this may be due to the fact that the BSA scale assesses only the extent of psoriasis, but not its severity, as it does not take into account the morphological features (infiltration, scale and erythema) of lesions [45,46,47,49].
Therefore, IL-23 antagonists appear to have a therapeutic effect on psoriasis, and this selective blockade of IL-23 subunit may have greater efficacy than the blockade of the p40 subunit, common to IL-12 and IL-23. This may be because IL-12 is a crucial cytokine involved in promotion of Th1 lymphocyte differentiation. Nevertheless, further studies comparing the roles of IL-12 or IL-23 in the pathogenesis of psoriasis should be conducted.
5. Conclusions
The exact course of the pathogenetic cascade in psoriasis is still not fully understood. Nevertheless, it is generally accepted that immune system cell mediators are important factors in the development and maintenance of psoriatic lesions. Our findings, i.e., the increased level of IL-17A and IL-23R expression, the decreased IL-10 expression in the skin of psoriasis patients and the positive correlation between IL-23A and PASI index, suggest that IL-17, IL-23 and IL-10 may be important factors in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and could be valuable therapeutic targets. Only weak associations, if any, were observed between IL-17A, IL-17RA and IL-10 expression and severity of psoriatic lesions, represented by PASI and BSA; this may result from the fact that these indicators include an assessment of the extent of the disease—a parameter that is also influenced by factors other than gene expression level. However, further studies are needed to demonstrate specific involvement of selected cytokines in the pathogenesis of psoriasis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and funding acquisition: A.W. and E.B.-L. Data curation and formal analysis: M.M.-S. Investigation, methodology, visualisation, validation and writing—original draft: M.K. and M.M.-S. Project administration, writing—review and editing: A.W. and M.K. Resources: M.K., M.M.-S. and P.Z. Supervision: A.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was supported by grant from Medical University of Lodz, Poland, grant number: 503/1-152-01/503-11-001-19-00.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the principles of Good Clinical Practice (GCP) and the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. The protocol of this study has been approved by the Bioethics Committee of the Medical University of Lodz (resolution no. RNN/15/16/KE of 9 January 2016).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest concerning this study.
References
- Christophers, E.; Mrowietz, U. Psoriasis. In Dermatology, 3rd ed.; Burgdorf, W.H.C., Plewig, G., Wolff, H.H., Landthaler, M., Eds.; Czelej: Lublin, Poland, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 526–546. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, C.E.M.; Armstrong, A.W.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Barker, J.N.W.N. Psoriasis. Lancet 2021, 397, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Read, C. Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment of Psoriasis: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Meglio, P.; Villanova, F.; O Nestle, F. Psoriasis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a015354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.B.; Jerome, D.; Yeung, J. Diagnosis and management of psoriasis. Can. Fam. Physician 2017, 63, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luba, K.M.; Stulberg, D. Chronic Plaque Psoriasis. Am. Fam. Physician 2006, 73, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valdimarsson, H.; Baker, B.S.; Jónsdóttir, I.; Fry, L. Psoriasis: A disease of abnormal keratinocyte proliferation induced by T lymphocytes. Immunol. Today 1986, 7, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdimarsson, H.; Baker, B.S.; Jónsdóttir, I.; Powles, A.; Fry, L. Psoriasis: A T-cell-mediated autoimmune disease induced by streptococcal superantigens? Immunol. Today 1995, 16, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdimarsson, H.; Sigmundsdóttir, H.; Jónsdóttir, I. Is psoriasis induced by streptococcal superantigens and maintained by M-protein-specific T cells that cross-react with keratin? Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1997, 107, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, P.R.; de Andrade Lima, E.V.; de Andrade Lima, M.M.; de Melo Rego, M.J.; Marques, C.D.; da Rocha Pitta, I.; Duarte, A.L.; da Rocha Pitta, M.G. Clinical and cytokine profile evaluation in Northeast Brazilian psoriasis plaque-type patients. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2016, 27, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, R.; Symmons, D.P.; Griffiths, C.E.; Ashcroft, D.M. Identification and Management of Psoriasis and Associated ComorbidiTy (IMPACT) Project Team. Global epidemiology of psoriasis: A systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gelfand, J.M.; Stern, R.S.; Nijsten, T.; Feldman, S.R.; Thomas, J.; Kist, J.; Rolstad, T.; Margolis, D.J. The prevalence of psoriasis in African Americans: Results from a population—Based study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 52, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebwohl, M.G.; Bachelez, H.; Barker, J.; Girolomoni, G.; Kavanaugh, A.; Langley, R.G.; Paul, C.F.; Puig, L.; Reich, K.; van der Kerkhof, P.C.M. Patient perspectives in the management of psoriasis: Results from the population-based Multinational Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Survey. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 70, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrandiz, C.; Bordas, X.; Garcia-Patos, V.; Puig, S.; Pujol, R.; Smandia, A. Prevelence of psoriasis in Spain (Epiderma Project: Phase I). J. Eur Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2001, 15, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfand, J.M.; Weinstein, R.; Porter, S.B.; Neimann, A.L.; Berlin, J.A.; Margolis, D.J. Prevalence and treatment of psoriasis in the United Kingdom: A population-based study. Arch. Dermatol. 2005, 141, 1537–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.; Ray, A.; Senapati, S.; Chatterjee, R. Genetic and epigenetic basis of psoriasis pathogenesis. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 64, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopytalska, K.; Ciechanowicz, P.; Wiszniewski, K.; Szymańska, E.; Walecka, I. The Role of Epigenetic Factors in Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, R.A.; Abji, F.; Gladman, D.D. Epigenetics of psoriatic disease: A systematic review and critical appraisal. J. Autoimmun. 2017, 78, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roszkiewicz, M.; Dopytalska, K.; Szymańska, E.; Jakimiuk, A.; Walecka, I. Environmental risk factors and epigenetic alternations in psoriasis. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2020, 27, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, D.; Gottlieb, A. Evaluation and management of psoriasis: An internist’s guide. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 93, 1291–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trowbridge, R.M.; Pittelkow, M.R. Epigenetics in the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of psoriasis vulgaris. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2014, 13, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Luo, S.; Huang, Y.; Lu, Q. Critical role of environmental factors in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. J. Dermatol. 2017, 44, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alesa, D.I.; Alshamrani, H.M.; Alzahrani, Y.A.; Alamssi, D.N.; Alzahrani, N.S.; Almohammadi, M.E. The role of gut microbiome in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and the therapeutic effects of probiotics. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2019, 8, 3496–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, K.; Kishimoto, M.; Sugai, J.; Komine, M.; Ohtsuki, M. Risk factors for the Development of Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dika, E.; Bardazzi, F.; Balestri, R.; Maibach, H.I. Environmental Factors and Psoriasis. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 2007, 35, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naldi, L. Psoriasis and smoking: Links and risks. Psoriasis 2016, 6, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, L.N.; Armstrong, A.W. Psoriasis and autoimmune disorders: A review of the literature. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 67, 1076–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furue, K.; Ito, T.; Tsuji, G.; Kadono, T.; Nakahara, T.; Furue, M. Autoimmunity and autoimmune co-morbidities in psoriasis. Immunology 2018, 154, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vashist, S.; Mahajan, V.K.; Mehta, K.S.; Chauhan, P.S.; Yadav, R.S.; Sharma, S.B.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, A.; Chowdhary, B.; Kumar, P. Association of Psoriasis with Autoimmune Disorders: Results of a Pilot Study. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2020, 11, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.J.; Nguyen, T.U.; Poon, K.-Y.T.; Herrinton, L.J. The association of psoriasis with autoimmune diseases. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 67, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiguradze, T.; Bruins, F.M.; Guido, N.; Bhattacharya, T.; Rademaker, A.; Florek, A.G.; Posligua, A.; Amin, S.; Laumann, A.E.; West, D.P.; et al. Evidence for the association of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis with psoriasis: A cross-sectional retrospective study. Int. J. Dermatol. 2017, 56, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Owczarczyk-Saczonek, A.; Placek, W. Psoriasis as an autoimmune disease. Dermatol. Rev. 2014, 101, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georgescu, S.R.; Tampa, M.; Caruntu, C.; Sarbu, M.I.; Mitran, C.I.; Mitran, M.I.; Matei, C.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M. Advances in Understanding the Immunological Pathways in Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fallen, R.S.; Mitra, A.; Morrisey, L.; Lima, H. Psoriasis as a chess board—An update of psoriasis pathophysiology. In Psoriasis—Types, Causes and Medication; Lima, H., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013; pp. 57–90. [Google Scholar]
- Kunz, M.; Ibrahim, S.M. Cytokines and Cytokine Profiles in Human Autoimmune Diseases and Animal Models of Autoimmunity. Mediat. Inflamm. 2009, 2009, 979258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdaca, G.; Colombo, B.M.; Puppo, F. The role of Th17 lymphocytes in the autoimmune and chronić inflammatory diseases. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2011, 6, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiricozzi, A.; Romanelli, P.; Volpe, E.; Borsellino, G.; Romanelli, M. Scanning the Immunopathogenesis of Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vičić, M.; Kaštelan, M.; Brajac, I.; Sotošek, V.; Massari, L.P. Current Concepts of Psoriasis Immunopathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadullah, K.; Sterry, W.; Volk, H.D. Interleukin-10 and Psoriasis. In Madame Curie Bioscience Database [Internet]; Landes Bioscience: Austin, TX, USA, 2000–2013. [Google Scholar]
- Trifunović, J.; Miller, L.; Debeljak, Ž.; Horvat, V. Pathologic patterns of interleukin 10 expression—A review. Biochem Med. 2015, 25, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, H.; Gyulai, R.; Toichi, E.; Garaczi, E.; Shimada, S.; Stevens, S.R.; McCormick, T.S.; Cooper, K.D. Dysfunctional Blood and Target Tissue CD4+CD25high Regulatory T Cells in Psoriasis: Mechanism Underlying Unrestrained Pathogenic Effector T Cell Proliferation. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piotrowski, W.J.; Kiszałkiewicz, J.; Pastuszak-Lewandoska, D.; Górski, P.; Antczak, A.; Migdalska-Sęk, M.; Górski, W.; Czarnecka, K.H.; Domańska, D.; Nawrot, E.; et al. Expression of HIF-1A/VEGF/ING-4 Axis in Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 866, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuss, M.; Migdalska-Sęk, M.; Brzeziańska-Lasota, E.; Michalska-Kasiczak, M.; Bazela, P.; Sewerynek, E. Assessment of Wnt pathway selected gene expression levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of postmenopausal patients with low bone mass. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2021, 21, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutwin, M.; Migdalska-Sęk, M.; Brzeziańska-Lasota, E.; Zelga, P.; Woźniacka, A. Analysis of molecular markers as IL-12, IL-22 and IFN-γ in correlation with a clinical course in patients with psoriasis. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2020, 33, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bożek, A.; Reich, A. How to reliably evaluate the severity of psoriasis? Forum Dermatol. 2016, 2, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Spuls, P.I.; Lecluse, L.L.; Poulsen, M.L.; Bos, J.D.; Stern, R.S.; Nijsten, T. How good are clinical severity and outcome measures for psoriasis?: Quantitative evaluation in a systemic review. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paul, C.; Gourraud, P.A.; Bronsard, V.; Prey, S.; Puzenat, E.; Aractingi, S.; Aubin, F.; Bagot, M.; Cribier, B.; Joly, P.; et al. Evidence-based recommendations to assess psoriasis severity: Systematic literature review and expert opinion of a panel of dermatologists. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2010, 24, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langley, R.G.; Ellis, C.N. Evaluating psoriasis with Psoriasis Area and Severity Index, Psoriasis Global Assessment, and Lattice System Physician’s Global Assessment. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2004, 51, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, A.; Adamski, Z.; Chodorowska, G.; Kaszuba, A.; Krasowska, D.; Lesiak, A.; Maj, J.; Narbutt, J.; Osmola-Mańkowska, A.J.; Owczarczyk-Saczonek, A.; et al. Psoriasis. Diagnostic and therapeutic recommendations of the Polish Dermatological Society. Part 1. Dermatol. Rev. 2020, 107, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlay, A.Y.; Khan, G.K. Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI)—A simple practical measure for routine clinical use. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 1994, 19, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadullah, K.; Sterry, W.; Stephanek, K.; Jasulaitis, D.; Leupold, M.; Audring, H.; Volk, H.D.; Döcke, W.D. IL-10 is a key cytokine in psoriasis. Proof of principle by IL-10 therapy: A new therapeutic approach. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadullah, K.; Döcke, W.D.; Sabat, R.V.; Volk, H.D.; Sterry, W. The treatment of psoriasis with IL-10: Rationale and review of the first clinical trials. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2000, 9, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, A.; Aste-Amezaga, M.; Valiante, N.M.; Ma, X.; Kubin, M.; Trinchieri, G. Interleukin 10 (IL-10) Inhibits Human Lymphocyte Interferon ă-Production by Suppressing Natural Killer Cell Stimulatory Factor/IL-12 Synthesis in Accessory Cells. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 178, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Waal Malefyt, R.; Abrams, J.; Bennett, B.; Figdor, C.G.; de Vries, J.E. Interleukin 10 (IL-10) Inhibits Cytokine Synthesis by Human Monocytes: An Autoregulatory Role of IL-10 Produced by Monocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1991, 174, 1209–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jenkins, J.K.; Malyak, M.; Arend, W.P. The effects of interleukin-10 on interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and interleukin-1 beta production in human monocytes and neutrophils. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1994, 13, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Tu, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, D. A study on the expression of interleukin (IL)-10 and IL-12 P35, P40 mRNA in the psoriatic lesions. J. Tongji Med. Univ. 2001, 21, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickoloff, B.J.; Fivenson, D.P.; Kunkel, S.L.; Strieter, R.M.; Turka, L.A. Keratinocyte Interleukin-10 Expression is Upregulated in Tape-Stripped Skin, Poison Ivy Dermatitis, and Sezary Syndrome, but not in Psoriatic Plaques. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1994, 73, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolk, K.; Witte, E.; Reineke, U.; Witte, K.; Friedrich, M.; Sterry, W.; Asadullah, K.; Volk, H.D.; Sabat, R. Is there an interaction between interleukin-10 and interleukin-22? Genes Immun. 2005, 6, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uyemura, K.; Yamamura, M.; Fivenson, D.F.; Modlin, R.L.; Nickoloff, B.J. The Cytokine Network in Lesional and Lesion-Free Psoriatic Skin is Characterized by a T-Helper Type 1 Cell-Mediated Response. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1993, 101, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlaak, J.F.; Buslau, M.; Jochum, W.; Hermann, E.; Girndt, M.; Gallati, H.; Meyer zum Büschenfelde, K.H.; Fleischer, B. T Cells Involved in Psoriasis Vulgaris Belong to the Th1 Subset. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1994, 102, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asadullah, K.; Döcke, W.D.; Ebeling, M.; Friedrich, M.; Belbe, G.; Audring, H.; Volk, H.D.; Sterry, W. Interleukin 10 treatment of psoriasis: Clinical results of phase 2 trial. Arch. Dermatol. 1999, 135, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, K.; Brück, M.; Gräfe, A.; Vente, C.; Naumann, C.; Garbe, C. Treatment of psoriasis with interleukin-10. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1998, 111, 1235–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, I.B.; Illei, G.G.; Danning, C.L.; Yarboro, C.H.; Crane, M.; Kuroiwa, T.; Schlimgen, R.; Lee, E.; Foster, B.; Flemming, D.; et al. IL-10 Improves Skin Disease and Modulates Endothelial Activation and Leukocyte Effector Function in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 4075–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimball, A.B.; Kawamura, T.; Tejura, K.; Boss, C.; Hancox, A.R.; Vogel, J.C.; Steinberg, S.M.; Turner, M.L.; Blauvelt, A. Clinical and immunologic assessment of patients with psoriasis in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial using recombinant human interleukin 10. Arch. Dermatol. 2002, 138, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reich, K.; Garbe, C.; Blaschke, V.; Maurer, C.; Middel, P.; Westphal, G.; Lippert, U.; Neumann, C. Response of Psoriasis to Interleukin-10 is Associated with Suppression of Cutaneous Type 1 Inflammation, Downregulation of the Epidermal Interleukin-8/CXCR2 Pathway and Normalization of Keratinocyte Maturation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 116, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shabgah, A.G.; Fattahi, E.; Shahneh, F.Z. Interleukin-17 in human inflammatory diseases. Postepy Dermatol. Alergol. 2014, 31, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, C. Th17 cells in development: An updated view of their molecular identity and genetic programming. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, L.E.; Hatton, R.D.; Managan, P.R.; Turner, H.; Murphy, T.L.; Murphy, K.M.; Weaver, C.T. Interleukin 17–producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, N.J.; Boniface, K.; Chan, J.R.; McKenzie, B.S.; Blumenschein, W.M.; Mattson, J.D.; Basham, B.; Smith, K.; Chen, T.; Morel, F.; et al. Development, cytokine profile and function of human interleukin 17–producing helper T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Tato, C.M.; Muul, L.; Laurence, A.; O’Shea, J.J. Distinct Regulation of Interleukin-17 in Human T Helper Lymphocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 2936–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitch, E.; Harper, E.; Skorcheva, I.; Kurtz, S.E.; Blauvelt, A. Pathophysiology of Psoriasis: Recent Advances on IL-23 and Th17 Cytokines. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2007, 9, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutowska-Owsiak, D.; Schaupp, A.L.; Salimi, M.; Selvakumar, T.A.; McPerson, T.; Taylor, S.; Ogg, G.S. IL-17 downregulates filaggrin and affects keratinocyte expression of genes associated with cellular adhesion. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaffen, S.L. Structure and signalling in the IL-17 receptor superfamily. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhao, X.; Lu, H.; Wang, W.; Yang, X.O.; Shi, Y.; Wang, X.; Lai, Y.; Dong, C. Interleukin-17 receptor D constitutes an alternative receptor for interleukin-17A important in psoriasis-like skin inflammation. Sci. Immunol. 2019, 4, 9657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, D.; Tan, Z. The Expression of Interleukin-17, Interferon-gamma, and Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-3 Alpha mRNA in Patients with Psoriasis Vulgaris. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 2004, 24, 294–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, M.B.M.; Koomen, C.W.; de Waal Malefyt, R.; Wierenga, E.A.; Bos, J.D. Interleukin-17 and Interferon-γ Synergize in the Enhancement of Proinflammatory Cytokine Production by Human Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1998, 111, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaba, L.C.; Cardinale, I.; Gilleaudeau, P.; Sullivan-Whalen, M.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Novitskaya, I.; Khatcherian, A.; Bluth, M.J.; Lowes, M.A.; et al. Amelioration of epidemal hyperplasia by TNF inhibition is associated with reduced Th17 responses. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 3183–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowes, M.A.; Kikuchi, T.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Cardinale, I.; Zaba, L.C.; Haider, A.S.; Bowman, E.P.; Krueger, J.G. Psoriasis Vulgaris Lesions Contain Discrete Populations of Th1 and Th17 T cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1207–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.S.; Lowes, M.A.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Zaba, L.C.; Cardinale, I.; Khatcherian, A.; Novitskaya, I.; Wittkowski, K.M.; Krueger, J.G. Identification of cellular pathways of type 1, Th17 T cells, and TNF—And inducible nitric oxide synthase-producing dendritic cells in autoimmune inflammation through pharmacogenomic study of cyclosporine A in psoriasis. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 1913–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, J.R.; Blumenschein, W.; Murphy, E.; Diveu, C.; Wiekowski, M.; Abbondanzo, S.; Lucian, L.; Geissler, R.; Brodie, S.; Kimball, A.B.; et al. IL-23 stimulates epidermal hyperplasia via TNF and IL-20R2-dependent mechanisms with implications for psoriasis pathogenesis. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2577–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, C.; Usher, P.A.; Kjellerup, R.B.; Lundsgaard, D.; Iversen, L.; Kragballe, K. Characterization of the interleukin-17 isoforms and receptors in lesional psoriatic skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 160, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Li, K.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Hayden, K.; Brodmerkel, C.; Krueger, J.G. Expanding the psoriasis disease profile: Interrogation of the skin and serum of patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 2552–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almutairi, N.; Eassa, B.I. Comparing the efficacy and safety of IL-17 inhibitors for treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis: A randomized double blind pilot study with a review of literature. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2021, 38, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piros, É.A.; Szabó, Á.; Rencz, F.; Brodszky, V.; Wikonkál, N.; Miheller, P.; Horváth, M.; Holló, P. Anti-Interleukin-17 Therapy of Severe Psoriatic Patients Results in an Improvement of Serum Lipid and Inflammatory Parameters’ Levels, but Has No Effect On Body Composition Parameters. Life 2021, 11, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariae, C.; Gordon, K.; Kimball, A.B.; Lebwohl, M.; Blauvelt, A.; Leonardi, C.; Braun, D.; McKean-Matthews, M.; Burge, R.; Cameron, G. Efficacy and Safety of Ixekizumab Over 4 Years of Open-Label Treatment in a Phase 2 Study in Chronic Plaque Psoriasis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 79, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canavan, T.N.; Elmets, C.A.; Cantrell, W.L.; Evans, J.M.; Elewski, B.E. Anti-IL-17 Medications Used in the Treatment of Plaque Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: A Comprehensive Review. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2016, 17, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutet, M.A.; Nerviani, A.; Afflitto, G.G.; Pitzalis, C. Role of the IL-23/IL-17 Axis in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: The Clinical Importance of Its Divergence in Skin and Joints. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toy, D.; Kugler, D.; Wolfson, M.; Bos, T.V.; Gurgel, J.; Derry, J.; Tocker, J.; Peschon, J. Cutting Edge: Interleukin 17 Signals through a Heteromeric Receptor Complex. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuestner, R.E.; Taft, D.W.; Haran, A.; Brandt, C.S.; Brender, T.; Lum, K.; Harder, B.; Okada, S.; Ostrander, C.D.; Kreindler, J.L.; et al. Identification of the IL-17 receptor related molecule IL-17RC as the receptor for IL-17F. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 5462–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijnen, D.; Knol, E.F.; Gent, Y.Y.Y.Y.; Giovannone, B.; Beijn, S.J.; Kupper, T.S.; Bruijnzeel-Koomen, C.A.F.M.; Clark, R.A. CD8(+) T Cells in the Lesional Skin of Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis Patients Are an Important Source of IFN-ɤ, IL-13, IL-17, and IL-22. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michalak-Stoma, A.; Bartosińska, J.; Kowal, M.; Juszkiewicz-Borowiec, M.; Gerkowicz, A.; Chodorowska, G. Serum Levels of Selected Th17 and Th22 Cytokines in Psoriatic Patients. Dis. Markers 2013, 35, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalak-Stoma, A.; Bartosińska, J.; Kowal, M.; Raczkiewicz, D.; Krasowska, D.; Chodorowska, G. IL-17A in the psoriatic patients’ serum and plaque scales as potential marker of the diseases severity and obesity. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 7420823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, Y.B.; Hwang, Y.J.; Hahn, H.J.; Jung, J.W.; Jung, H.J.; Lee, Y.W.; Ahn, K.J.; Youn, J.I. A comparison of serum inflammatory cytokines according to a phenotype in patients with psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 167, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Tsuji, H.; Hashimoto, Y.; Ishida-Yamamoto, A.; Iizuka, H. Serum cytokines and growth factor levels in Japanese patients with psoriasis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 35, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arican, O.; Aral, M.; Sasmaz, S.; Ciragil, P. Serum levels of TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-17, and IL-18 in patients with active psoriasis and correlatio.on with disease severity. Mediat. Inflamm. 2005, 2005, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Langley, R.G.; Elewski, B.E.; Lebwohl, M.; Reich, K.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Papp, K.; Puig, L.; Nakagawa, H.; Spelman, L.; Sigurgeirsson, B.; et al. Secukinumab in plaque psoriasis—Results of two phase 3 trials. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bissonnette, R.; Luger, T.; Thaçi, D.; Toth, D.; Lacombe, A.; Xia, S.; Mazur, R.; Patekar, M.; Charef, P.; Milutinovic, M.; et al. Secukinumab demonstrates high sustained efficacy and a favourable safety profile in patients with modarete-to-severe psoriasis through 5 years of treatment (SCULPTURE Extension Study). J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leonardi, C.; Maari, C.; Philipp, S.; Goldblum, O.; Zhang, L.; Burkhardt, N.; Ball, S.; Mallbris, L.; Gonzales, P.; Fernández-Peñas, P.; et al. Maintenance of skin clearance with ixekizumab treatment of psoriasis: Three-year results from the UNCOVER-3 study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 79, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blauvelt, A.; Gooderham, M.; Iversen, L.; Ball, S.; Zhang, L.; Agada, N.O.; Reich, K. Efficacy and safety of ixekizumab for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: Results through 108 weeks of a randomized, controlled phase 3 clinical trial (UNCOVER-3). J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papp, K.; Menter, A.; Leonardi, C.; Soung, J.; Weiss, S.; Pillai, R.; Jacobson, A. Long-term efficacy and safety of brodalumab in psoriasis through 120 weeks and after withdrawal and retreatment: Subgroup analysis of a randomized phase III trial (AMAGINE-1). Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papp, K.A.; Reich, K.; Paul, C.; Blauvelt, A.; Baran, W.; Bolduc, C.; Toth, D.; Langley, R.G.; Cather, J.; Gottlieb, A.B.; et al. A prospective phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of brodalumab in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 175, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauvelt, A.; Papp, K.A.; Merola, J.F.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Cross, N.; Madden, C.; Wang, M.; Cioffi, C.; Griffiths, C.E.M. Bimekizumab for patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: 60-week results from BE ABLE 2, a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, phase 2b extension study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, K.A.; Merola, J.F.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Cross, N.; Peterson, L.; Cioffi, C.; Blauvelt, A. Dual neutralization of both interleukin 17A and interleukin 17F with bimekizumab in patients with psoriasis: Results from BE ABLE 1, a 12-week randomized, double-blinde.e.ed, placebo-controlled phase 2b trial. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 79, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piskin, G.; Sylva-Steenland, R.M.R.; Bos, J.D.; Teunissen, M.B.M. In Vitro and In Situ Expression of IL-23 by Keratinocytes in Healthy Skin and Psoriasis Lesions: Enhanced Expression in Psoriatic Skin. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 1908–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppmann, B.; Lesley, R.; Blom, B.; Timans, J.C.; Xu, Y.; Hunte, B.; Vega, F.; Yu, N.; Wang, J.; Singh, K.; et al. Novel p19 Protein Engages IL-12p40 to Form a Cytokine, IL-23, with Biological Activities Similar as Well as Distinct from IL-12. Immunity 2000, 13, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.G.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, M.G. The Origin of Skin Dendritic Cell Network and Its Role in Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKenzie, B.S.; Kastelein, R.A.; Cua, D.J. Understanding the IL-23–IL-17 Immune Pathway. Trends Immunol. 2006, 27, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Trepicchio, W.L.; Oestreicher, J.L.; Pittman, D.; Wang, F.; Chamian, F.; Dhodapkar, M.; Krueger, J.G. Increased Expression of Interleukin 23 p19 and p40 in Lesional Skin of Patients with Psoriasis Vulgaris. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yawalkar, N.; Karlen, S.; Hunger, R.; Brand, C.U.; Braathen, L.R. Expression of interleukin-12 is increased in psoriatic skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1998, 111, 1053–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, O.G.; Moustafa, W.; Essmat, S.; Abdel-Halim, M.; El-Komy, M. The role of interleukin-12 in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Clin. Biochem. 2006, 39, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamian, F.; Lowes, M.A.; Lin, S.L.; Lee, E.; Kikuchi, T.; Gilleaudeau, P.; Sullivan-Whalen, M.; Cardinale, I.; Khatcherian, A.; Novitskaya, I.; et al. Alefacept reduces infiltrating T cells, activated dendritic cells, and inflammatory genes in psoriasis vulgaris. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2075–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tonel, G.; Conrad, C.; Laggner, U.; Di Meglio, P.; Grys, K.; McClanahan, T.K.; Blumenschein, W.M.; Qin, J.Z.; Xin, H.; Oldham, E.; et al. Cutting Edge: A Critical Functional Role for IL-23 in Psoriasis. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 5688–5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toichi, E.; Torres, G.; McCormick, T.S.; Chang, T.; Mascelli, M.A.; Kauffman, C.L.; Aria, N.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Everitt, D.E.; Frederick, B.; et al. An Anti-IL-12p40 Antibody Down-Regulates Type 1 Cytokines, Chemokines, and IL-12/IL-23 in Psoriasis. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 4917–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piskin, G.; Tursen, U.; Sylva-Steenland, R.M.R.; Bos, J.D.; Teunissen, M.B.M. Clinical improvement in chronic plaque-type psoriasis lesions after narrow-band UVB therapy is accompanied by the decrease in the expression of IFN-γ inducers—IL-12, IL-18 and IL-23. Exp. Dermatol. 2004, 13, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, A.B.; Chamian, F.; Masud, S.; Cardinale, I.; Abello, M.V.; Lowes, M.A.; Chen, F.; Magliocco, M.; Krueger, J.G. TNF Inhibition Rapidly Down-Regulates Multiple Proinflammatory Pathways in Psoriasis Plaques. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 2721–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pithadia, D.J.; Reynolds, K.A.; Lee, E.B.; Liao, W.; Wu, J.J. Tildrakizumab in the treatment of psoriasis: Latest evidence and place in therapy. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2019, 10, 2040622319865658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krulig, E.; Gordon, K.B. Ustekinumab: An evidence-based review of its effectiveness in the treatment of psoriasis. Core Evid. 2010, 5, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leonardi, C.L.; Kimball, A.B.; Papp, K.A.; Yeilding, N.; Guzzo, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Dooley, L.T.; Gordon, K.B.; PHOENIX 1 Study Investigators. Efficacy and safety of ustekinumab, a human interleukin-12/23 monoclonal antibody, in patients with psoriasis: 76-week results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (PHOENIX 1). Lancet 2008, 371, 1665–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, L. The role of IL-23 in tretment of psoriasis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 13, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Chen, S.; Qian, H.; Huang, W. Interleukin-23: As a drug target for autoimmune inflammatory diseases. Immunology 2012, 135, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagami, S.; Rizzo, H.L.; Lee, J.J.; Koguchi, Y.; Blauvelt, A. Circulating Th17, Th22, and Th1 cells are increased in psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fotiadou, C.; Lazaridou, E.; Sotiriou, E.; Ioannides, D. Targeting IL-23 in psoriasis: Current perspectives. Psoriasis 2018, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).