Abstract
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a rare neuromuscular disease, with an estimated incidence of about 1 in 10,000 live births. To date, three orphan drugs have been approved for the treatment of SMA: nusinersen, onasemnogene abeparvovec, and risdiplam. The aim of this narrative review was to provide an overview of the pre- and post-marketing evidence on the pharmacological treatments approved for the treatment of SMA by identifying preclinical and clinical studies registered in clinicaltrials.gov and in the EU PAS register from their inception until the 4 January 2023. The preclinical evidence on the drugs approved for SMA allowed a significant acceleration in the experimental phase of these drugs. However, since these drugs had been authorized through accelerated programs, the conduction of post-marketing studies was requested as a condition of their marketing approval to better understand their risk–benefit profiles in real-world settings. As of the 4 January 2023, a total of 69 post-marketing studies concerning the three orphan drugs approved for SMA were identified in clinicaltrials.gov (N = 65; 94.2%) and in the EU PAS register (N = 4; 5.8%). Currently, ongoing studies are primarily aimed at providing evidence concerning the risk–benefit profile of the three drugs in specific populations that were not included in the pivotal trials and to investigate the long-term safety and clinical benefits of these drugs. Real-world data sources collecting information regarding the natural history of the disease and post-marketing surveillance of the available therapies are increasingly becoming essential for generating real-world evidence on this rare disease and its orphan drugs.
1. Introduction
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a rare, autosomal-recessive neuromuscular disease, with an estimated incidence of about 1 in 10,000 live births [1].
SMA is caused by biallelic mutations in the SMN1 gene, encoding for the survival motor neuron (SMN) protein, that plays a key role in the proper functioning and survival of motor neurons. Insufficient levels of the SMN protein cause the progressive degeneration of motor neurons in the brainstem and spinal cord, leading to muscle weakness, motor difficulties, and atrophy of limbs, trunk, and respiratory muscles [2]. The impairment of the latter, in particular, is responsible for respiratory failure, which is the main cause of death in patients with SMA [3]. To date, genetic blood testing to identify depletions and mutations in the SMN gene is the first diagnostic step for patients with suspected SMA and represents the diagnostic reference standard [4].
SMA is classified into different phenotypes (i.e., SMA type 0, type 1, type 2, type 3, and type 4) based on the age of onset as well as the severity of the clinical conditions, which is inversely related to the amount of SMN protein available at the motor neuron level [1]. The phenotype–genotype correlation of the disease depends, in part, on the number of copies of a second gene, called SMN2, which is a paralogue of SMN1. In 90% of SMN2 transcriptions, the SMN2 transcript undergoes splicing of exon 7, thus yielding an unstable SMN∆7 protein, while, in the remaining 10%, a normal and functional SMN protein is produced, contributing to the survival of the spinal motor neurons and influencing the severity of the clinical manifestations [5].
To date, three orphan drugs have been approved for the treatment of SMA: nusinersen, an antisense oligonucleotide, onasemnogene abeparvovec, a gene therapy, and risdiplam, a SMN2 pre-mRNA splicing small-drug modifier. Considering the seriousness of the disease and the urgent need for effective treatments, these drugs have been authorized through accelerated assessment procedures that reduce the timeframe for the European Medicines Agency (EMA) Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) to review a marketing-authorization application from 210 to 150 days [6].
SMA is a clear example of how it is possible to implement strategies shared among different stakeholders (e.g., research centers, industries, and regulators) to build a solid path, based on robust preclinical, translational, and clinical evidence (in both pre- and post-marketing settings), aimed at supporting regulatory processes and ultimately providing patients with effective treatment strategies. This is particularly important for advanced therapies like onasemnogene abeparvovec, which have completely different pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles than conventional therapies.
The aim of this narrative review is to provide an overview of the pre- and post-marketing evidence on the pharmacological treatments approved for the treatment of SMA by identifying preclinical as well as clinical studies (both experimental and observational). With this aim, PubMed Central and Embase were searched using index terms (i.e., MeSH terms and emtree terms) related to SMA and its pharmacological therapies. Furthermore, relevant studies were also identified by searching two large repositories such as clinicaltrials.gov and the EU PAS register.
2. Pre-Marketing Evidence on SMA Pharmacological Therapies
2.1. Preclinical Studies
The deeper knowledge of the molecular mechanisms underlying SMA’s onset and progression has represented a significant milestone for the development of specific therapeutic strategies (Figure 1).
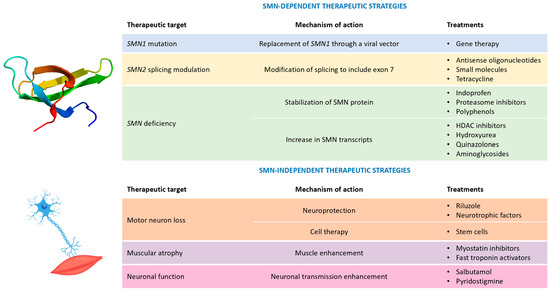
Figure 1.
Possible therapeutic strategies for spinal muscular atrophy. Legend: HDAC = histone deacetylase; and SMN = survival motor neuron.
In this frame, animal testing provided a crucial help: several SMA animal models (Caenorhabditis elegans, zebrafish, and Drosophila) were indeed developed in the past. Nonetheless, only the setting up of a murine model able to accurately reproduce the human disease phenotype represented the actual cornerstone for preclinical studies [7]. Firstly, it must be considered that mice have only one SMN gene encoding for the SMN protein, instead of two as in humans. Moreover, homozygous mutations in the SMN gene induce early embryonic death in mice, whereas heterozygous SMN mice (SMN±) display a normal phenotype [8]. To overcome these issues, a novel transgenic murine model was developed, introducing the human SMN2 gene in the SMN-null mice. This strategy made the murine disease phenotype more similar to the human one, also considering that SMN2 manipulation allows for the introduction of specific patients’ mutations. This was also paralleled by the adoption of reliable and highly reproducible experimental protocols. The Translational Research in Europe for the Assessment and Treatment of Neuromuscular Diseases (TREAT-NMD) network [9] played a key role in this approach through the provision of internationally validated, standard operating procedures, useful to optimize protocols and accelerate the research process [10]. The timeline of the most important preclinical studies in the SMA field is summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Timeline of preclinical studies of orphan drugs approved for spinal muscular atrophy treatment.
2.1.1. Nusinersen
Nusinersen was the first SMA orphan drug approved in 2016 by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and, in 2017, by the EMA. Nusinersen belongs to the class of antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) and is able to target a specific splicing silencer site (ISS-N1, intronic splice silencing) located within the SMN2 intron 7. As previously mentioned, small differences in the SMN2 gene sequence led to alternative splicing processes, inducing the skipping of exon 7 in the SMN2 transcript and the subsequent synthesis of a truncated, non-functional protein (SMNΔ7). Nusinersen prevents the binding of specific splicing repressors, hnRNPA1 and hnRNPA2, to ISS-N1, allowing the integration of exon 7 into the final transcript and the synthesis of a full-length SMN protein. Since 2006, systematic screenings have been conducted to find the most effective ASO. Several ASOs were tested in murine models and in patient-derived fibroblasts, shifting along the ISS-N1, one base at a time. Once the strongest sequence had been identified, the specific ASO was administered in SMA mice to evaluate the effects of the compound on in vivo and ex vivo disease readouts. These treatments markedly increased the SMN protein levels and ameliorated the disease phenotype, extending the median lifespan (severely reduced in the SMA mice) by 25-fold and leading to the significant recovery of motor functions (including α-motor neuron count, mean area of muscle fibers, heart weight, thickness of the interventricular septum, left ventricular wall, and integrity of neuromuscular junctions), which were all relevant effects from a clinical perspective [14]. Moreover, the pharmacokinetic analysis performed on murine models and non-human primates highlighted a good bioavailability of the compound at the central nervous system level if administered by intrathecal infusion. These promising data provided a solid base for the following successful clinical trials, ending with nusinersen’s approval for SMA treatment in children and adults. The main drawback of nusinersen use is represented by its inability to cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB) and the subsequent need for recurrent lumbar punctures for intrathecal administration. This considerably reduces therapeutic compliance, particularly for patients with severe scoliosis.
2.1.2. Onasemnogene Abeparvovec
The replacement of the SMN1 defective gene is an alternative therapeutic approach that has been recently explored. Onasemnogene abeparvovec was approved in 2020 as the first, and currently unique, gene therapy for SMA, and it was indicated for SMA patients aged <2 years with bi-allelic mutations in the SMN1 gene and three or fewer copies of the SMN2 gene or infantile-onset SMA. The small dimension of the SMN1 gene facilitated its delivery via a recombinant self-complementary adeno-associated viral vector serotype 9 (scAAV9). Preclinical studies in mice and non-human primates demonstrated the ability of the drug to cross the BBB after intravenous injection. Furthermore, this gene therapy significantly improved lifespan (median of 282 days for treated mice vs. 17.5 days for untreated SMAΔ7 mice) and ameliorated motor functions, particularly in early-treated animals [19,20]. Toxicology studies confirmed the safety and good tolerability of the treatment after intravenous injection, opening for the translatability of the drug in humans using this specific route of administration. In addition, it must be underlined that preclinical studies were performed on juvenile animals: the very encouraging obtained results supported again the importance of early administration. In fact, intravenous injection in mice within 24 h of birth showed greater efficacy compared to a later administration (within 5 or 10 days of birth), thus further reinforcing the relevance of neonatal screenings for early treatment.
2.1.3. Risdiplam
The success of nusinersen considerably boosted research for further therapies, in particular for those administered through a less invasive route. Innovative drug design techniques in combination with high-throughput screening methods permitted the identification of novel, small molecules that shared nusinersen’s mechanism of action, promoting the inclusion of exon 7. The first molecule of interest was an orally administered coumarin derivative, subsequently modified to overcome potential in vitro mutagenicity issues and the phototoxicity typically associated with this drug class. Further compound optimization ameliorated the selectivity and affinity to the target, allowing a reduction of the dose required to achieve the therapeutic goals while limiting the side effects. Finally, after these implementations, the pyrido-pyrimidinone derivative risdiplam was synthesized and successively approved by the FDA and EMA as the first oral drug for SMA treatment in 2020 and 2021, respectively [21]. Preclinical studies performed in mice and non-human primates confirmed the drug’s efficacy in restoring proper SMN protein levels and demonstrated a strong correlation between plasma and tissue concentration, overcoming the bioavailability issues of nusinersen [22]. In fact, several preclinical studies demonstrated that the SMN protein carries out a wide variety of actions at multiple levels and in different tissues, explaining the non-motor symptoms related to the pathology. Pharmacokinetic analyses documented the excellent distribution of risdiplam in several tissues, paving the way for an innovative therapy which combined an easier method of administration with the possibility to treat also peripheral symptoms. Real-world studies will help evaluate whether this systemic distribution could determine off-target effects, affecting the risk–benefit ratio of risdiplam.
2.2. Pivotal Clinical Trials
The characteristics of the pivotal clinical trials supporting the marketing approval of the three pharmacological therapies for the treatment of SMA are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Pivotal clinical trials leading to the marketing authorization of nusinersen, onasemnogene abeparvovec, and risdiplam.
The efficacy of nusinersen was proved in the ENDEAR study, a 13-month double-blind phase 3 clinical trial, which enrolled 121 patients diagnosed with infantile-onset SMA before 6 months of age and who were under 7 months of age at the time of receiving the first dose [23]. The patients were randomized, in a 2:1 ratio, to receive an intrathecal injection of nusinersen (treatment group) or a sham procedure (control group). The primary endpoints included the achievement of a motor milestone response defined according to the Hammersmith Infant Neurological Examination and the event-free survival (i.e., time to death or requiring permanent assisted ventilation). The results of the per protocol analysis showed that 51% of the patients in the treatment group and no patients in the control group achieved a motor milestone response and that the likelihood of event-free survival was higher in the treatment group than in the control group (hazard ratio for death or the use of permanent assisted ventilation, 0.53; p = 0.005). However, the ENDEAR trial was terminated early due to the results of the interim analysis and to the ethical consideration for the patients in the control group, and this led to the loss of data and a short time period for the assessment of the safety and the efficacy of nusinersen.
Concerning onasemnogene abeparvovec, its efficacy was demonstrated in the STR1VE-US study, an open-label phase 3 clinical trial including 22 symptomatic patients diagnosed with SMA type 1 who were younger than 6 months [24]. The enrolled patients were followed-up until the age of 18 months. The co-primary efficacy endpoints were independent sitting for ≥30 s at the study visit at 18 months of age and event-free (i.e., time to death or requiring permanent ventilation) survival at 14 months of age. Such endpoints were compared to 23 untreated infants aged ≤6 months with SMA type 1 from the Pediatric Neuromuscular Clinical Research (PNCR) dataset, a historical cohort of untreated infants with SMA type 1 [27]. The first co-primary endpoint was met by 13 (59%) of the 22 patients in the treatment group vs. 0 patients in the PNCR cohort, while the second was achieved by 20 (91%) patients in the treatment group vs. 6 (26%) in the PNCR cohort. The main limitations of the STR1VE-US trial were the lack of a randomized comparison to a control group, potentially leading to an overestimation of the treatment effect, the lack of masking for both intervention and outcome evaluation, the strict inclusion criteria, and the short follow-up period.
The marketing approval of risdiplam was based on two pivotal clinical trials: the FIREFISH trial in infantile-onset SMA [26] and the SUNFISH trial in late-onset SMA [25]. The FIREFISH study was an open-label, single-arm study including 41 infants aged between 1 and 7 months, with genetically confirmed Type 1 SMA. The primary endpoint was the ability to sit without support for at least 5 s after 12 months of treatment, a milestone that is never achieved in untreated patients affected by Type 1 SMA. After 12 months of treatment, 12 patients (29%) met this endpoint [26]. The internal validity of the FIREFISH trial was affected by the single-arm design, precluding a precise estimation of the magnitude of the benefit.
The SUNFISH study was a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial in patients aged between 2 and 25 years with confirmed type 2 or type 3 SMA. Patients were randomized, in a 2:1 ratio, to receive daily oral risdiplam (treatment group, N = 120) or daily oral placebo (control group, N = 60), and they were followed-up for 12 months. The primary endpoint was the change from the baseline in the 32-item Motor Function Measure (MFM32)’s total score at month 12. After one year, the least squares mean change from the baseline was 1.36 (95% confidence interval 0.61 to 2.11) in the risdiplam group and −0.19 (−1.22 to 0.84) in the placebo group, with a treatment difference of 1.55 (0.30 to 2.81, p = 0.016) in favor of risdiplam. However, the improvement in motor function was mainly detected in the younger patients (i.e., children aged between 2 and 5 years) rather than in the adolescent and adult patients, thus leaving unanswered questions for risdiplam use in adults with SMA when considering efficacy and long-term expectations [28].
3. Post-Marketing Evidence
Post-marketing studies, including both observational studies and clinical trials, play a crucial role in better understanding the clinical benefits and the safety of orphan drugs in real-world settings [29]. This holds particularly true for orphan drugs that are usually marketed through conditional approval and other accelerated programs based on the availability of limited pre-marketing evidence on their benefit–risk profile. As such, the conduction of further clinical trials and even more observational studies to generate post-marketing evidence has been requested as part of the risk-management plans of nusinersen [30], onasemnogene abeparvovec [31], and risdiplam [32], as a condition of their marketing approval (Table 3).

Table 3.
Characteristics of the post-marketing clinical studies concerning marketed orphan drugs that are approved for SMA, as identified in clinicaltrials.gov and the EU PAS register on the 4 January 2023.
Planned, ongoing, and finalized clinical trials, as well as observational studies, concerning the three orphan drugs approved for the treatment of SMA were searched in two study repositories: clinicaltrials.gov and the European post-authorization study (EU PAS) Register from their inception until the 4 January 2023.
Clinicaltrials.gov is a public repository created in 1997 and run by the United States National Library of Medicine at the National Institutes of Health, in which interventional and observational studies receiving US government funding, as well as studies funded by commercial entities and programs providing access to investigational drugs outside of clinical trials (i.e., expanded access), are registered. It was searched for the following keywords: “spinal muscular atrophy” and “nusinersen” or “onasemnogene abeparvovec” or “risdiplam”.
The EU PAS register is a publicly available register of non-interventional post-authorisation studies (PASS) that was launched in 2010. It is established and maintained by the EMA through the European Network of Centres for Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacovigilance (ENCePP), with the aims of increasing transparency, promoting the exchange of information, and ensuring the compliance with the European pharmacovigilance legislation requirements [33]. The current European pharmacovigilance legislation requires the public availability of study protocols and summary of results for PASS to be imposed as an obligation of marketing authorization by competent authorities. This register is also aimed at hosting non-imposed studies, such as those required as per the risk management plan, and all observational studies performed on authorized medicinal products, including effectiveness studies.
For each study, we extracted data on study design (i.e., interventional, observational, expanded-access study), study drug, status, primary purpose, study phase, and patients’ age.
As of the 4 January 2023, a total of 69 studies concerning the three orphan drugs approved for SMA were identified in clinicaltrials.gov (N = 65; 94.2%) and in the EU PAS register (N = 4; 5.8%) (Table 3). Thirty-nine (56.5%) of them were interventional, twenty-seven (39.1%) observational, and three (4.4%) were expanded-access programs. The majority of these studies investigated nusinersen (N = 34; 49.3%), followed by onasemnogene abeparvovec (N = 15; 21.7%), and risdiplam (N = 15; 21.7%); one study concerned both nusinersen and risdiplam, and one study concerned all three drugs. Concerning the status of the studies, forty-four (62.0%) studies were ongoing or planned, nineteen (27.5%) were completed, two (2.9%) were terminated or withdrawn, while, for four studies, the status was not reported (5.8%). As for the funder type, 52 (75.4%) of the 69 studies were funded by pharmaceutical companies, while 17 (24.6%) were funded by universities or research organizations.
The ongoing studies were mainly aimed at providing further evidence concerning the effectiveness of the three drugs on disease progression in specific populations that had not been included in the pivotal trials (e.g., adults, older adults, and pregnant women) and at investigating the long-term safety and clinical benefits of these drugs.
The characteristics of the 69 studies identified in the two repositories are reported in Table 4.

Table 4.
Description of the post-marketing clinical studies of the orphan drugs marketed for SMA treatment as identified in clinicaltrials.gov and in the EU PAS register on the 4 January 2023.
The median size of the enrolled populations in the identified interventional studies was 33 (interquartile range: 24–130.5). Most of these studies (N = 30, 76.9%) were open-label clinical trials and, mostly, single-group trials. Concerning the observational studies, half of them (N = 14; 51.8%) were prospective studies, and the median number of enrolled patients was 50.5 (interquartile range: 26.5–195).
The studies included in the risk-management plan of nusinersen were the following: two open-label extension studies (i.e., the SHINE and the NURTURE trials) investigating the long-term safety, tolerability, and efficacy of repeated doses of nusinersen administered through intrathecal injections in infants with genetically diagnosed and pre-symptomatic SMA; two registry-based observational studies (i.e., the TREAT-NMD network [9] and the Muscular Dystrophy Association United States (MDA US) Neuromuscular Disease Registry [34]); and one natural history study (i.e., the ISMAC study) [35].
The studies included in the risk-management plan of onasemnogene abeparvovec were three phase 3 clinical trials (i.e., the STR1VE-US, the SPR1NT, and the STR1VE-US trials) and three observational studies, including a prospective observational registry (i.e., the RESTORE study) and two long-term follow-up studies (i.e., the START and the AVXS-101-LT-002 studies) aimed at collecting safety data of patients with SMA treated using this drug.
Finally, the risk-management plan of risdiplam included four open-label extension studies (i.e., the FIREFISH, the SUNFISH, the JEWELFISH, and the RAINBOWFISH trials) and two observational studies aimed at collecting data concerning selected pregnancy outcomes and complications in women with SMA receiving risdiplam (Study BN42833) and at estimating the effects of single, oral doses of risdiplam on the QT interval of the electrocardiogram (Study BP42817).
Real-world data (RWD), defined as data relating to a patient’s health status and the delivery of health services that are collected during daily clinical practice, have a considerable potential for the evaluation of the safety and effectiveness of orphan drugs, as well as for providing relevant information concerning the epidemiology and the natural history of rare diseases. Real-world evidence (RWE), i.e., the evidence generated through the analysis of RWDs, therefore, plays a crucial role in better understanding the benefit–risk profile of orphan drugs and in supporting regulatory processes. Indeed, regulatory agencies are increasingly promoting the use of RWD for supporting regulatory processes, especially in the field of rare diseases. In particular, the EMA and the FDA promote the use of RWD for supporting drug approval, especially when the latter is based on limited pre-marketing evidence [36,37].
Disease registries provide very useful data not only for studying the clinical course of diseases and for conducting natural history studies, but also for identifying prognostic factors and for evaluating the clinical outcomes of available therapies [38]. In particular, the ISMAC natural history study is an ongoing prospective cohort study conducted by three national networks in the United States, Italy, and the United Kingdom, aimed at recording information that allows researchers to phenotype SMA patients and at following them over the years [39]. The TREAT-NMD is a registry collecting data from natural history studies conducted in several countries with the aim of gaining more information on the natural history of SMA, thus providing a context to better understand the safety and efficacy of new treatments and support their post-marketing surveillance [9]. Finally, the MDA US Neuromuscular Disease Registry is a prospective longitudinal registry aimed at collecting data on four neuromuscular diseases (i.e., SMA, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies), with the purpose of facilitating translational research to improve standards of care and patients’ clinical outcomes [34].
4. Current Knowledge about the Risk–Benefit Profile of the Drugs Approved for the Treatment of SMA
To date, several studies summarizing mid- and long-term follow-up in SMA patients treated with nusinersen, risdiplam, and onasemnogene abeparvovec have been published. Such studies provide interesting data about the effectiveness and the safety of these innovative therapies. As expected, the largest amount of data concerns nusinersen, since it received the FDA’s approval first. A prospective 3-year registry study (SMArtCARE), published in January 2023, highlighted a stabilization of the disease’s progression in 231 ambulant patients (114 pediatric patients with a median age of 8.6 years and 117 adult patients with a median age of 37 years), in parallel with an improvement in motor function [40]. In total, 31 of the pediatric patients (27.2%) and 31 of the adult patients (26.5%) achieved an improvement of more than 30 m in the 6-minutes WalkTest. On the contrary, among the patients receiving nusinersen, only five adult patients (7.7%) experienced a decline in walking a distance over 30 m, and two pediatric patients (1.8%) lost the ability to walk without assistance [40]. Another observational study published in March 2023 reported the results of a 4-year follow-up in 48 patients aged between 7 days and 12 years who had been treated with nusinersen [41]. The study confirmed the safety and the efficacy of the therapy over time, with evidence of a mild but significant amelioration of disease-related neuromuscular symptoms evaluated through the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Infant Test of Neuromuscular Disorders (CHOP INTEND) and the Hammersmith Infant Neurological Examination (HINE-II). During the 4-year follow-up period, only one patient receiving nusinersen died between the second and the fourth year of follow-up [41].
More recently, Novartis rolled out relevant data regarding a long-term follow-up in patients treated with onasemnogene abeparvovec [42]. A single intravenous infusion administered to symptomatic SMA patients ensured the maintenance of the motor milestones previously achieved, even after 7.5 years. Importantly, preliminary results of the LT-002 study showed that all of the 25 enrolled children, treated during the pre-symptomatic phase, maintained the highest milestone previously achieved during the parent study, according to the Developmental Milestone Checklist, and independent walking. These results underline the importance of early interventions to minimize motor-function loss, according to the accepted “time-is-neuron” view [43].
On February 2023, after two fatal cases of acute liver failure were reported in SMA patients treated with onasemnogene abeparvovec, the EMA Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) disseminated a Direct Healthcare Professional Communication (DHPC) to alert physicians about the risk of hepatotoxicity [44].
Overall, the evidence on the pharmacological therapies for SMA is still limited and should be cautiously interpreted. The majority of the published studies analyzed involved only children and mainly focused on the motor outcomes, while only few of them investigated the effects on the bulbar and respiratory items. As such, several questions regarding the benefit–risk profile of these treatments are still unanswered, especially regarding the long-term effects of these therapies on patients’ survival and quality of life. To date, no studies regarding the mid- or long-term safety and effectiveness on risdiplam have been published, although a recruitment phase for a long-term follow-up study is currently ongoing [45].
In the next years, real-world studies will play a key role in providing evidence on the long-term safety as well as the disease’s stabilization in both pediatric and adult patients treated with the three treatments currently approved for the treatment of SMA. Furthermore, real-world experiences will be useful to guide patients and caregivers in the choice of the most suitable therapeutic option or, eventually, for changing therapy if a lack of efficacy is observed.
Despite the considerable advances in scientific research concerning the pharmacological treatments of SMA, some issues related to each of the three approved drugs remain, and caution is needed when interpreting study results, especially for adult patients. As for nusinersen, in addition to the above-mentioned administration issues, the lack of efficacy in controlling peripheral symptoms should also be considered. In fact, the SMN protein is also located in extra central nervous system organs (such as muscle, heart, pancreas, afferent nerves, bones, and gastroenteric system) and low levels of SMN induce a wide variety of non-motor symptoms (i.e., impaired skeletal muscle development, cardiomyopathy, altered liver function, severe diarrhea, and lower bone density) [46,47]. Regarding onasemnogene abeparvovec, the long-term effects of gene therapy are not known yet, and the therapeutic effect produced by this drug is not as valid in patients with late-onset SMA. Finally, as for risdiplam, the systemic effect followed by its administration could produce delayed side effects caused by a large-scale synthesis of the SMN protein.
5. Conclusions
Preclinical and translational studies are currently being carried out to discover and test potentially new therapies for the treatment of SMA, including the use of innovative platforms such as organoids. Furthermore, several interventional, as well as observational, studies focusing on the three available orphan drugs approved for SMA treatment are currently ongoing, with the aim of generating post-marketing evidence to better understand their risk–benefit profile.
Researchers are also putting great efforts in enhancing therapeutic strategies with innovative or repositioned drugs that can influence neuronal death processes or peripheral consequences due to the lack of the SMN protein. In this regard, translational research acquires an increasingly important role in accelerating drug development, and real-world data sources such as disease registers, collecting information regarding the natural history of the disease and post-marketing surveillance of the available therapies, are increasingly becoming essential tools to generate real-world evidence on rare disease with the dual aim of refining preclinical research and supporting the regulatory processes of orphan drugs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.T. and A.D.L.; writing—original draft preparation, S.C., B.B. and G.V.; writing—review and editing, S.C., B.B. and G.V.; and supervision, G.T. and A.D.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
G.T. has served, over the last 3 years, on advisory boards/seminars funded by Sanofi, Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Abbvie, Novo Nordisk, Gilead, and Amgen; he is also a scientific coordinator of the academic spin-off “INSPIRE srl”, which has received funding from several pharmaceutical companies for conducting observational studies. None of these listed activities are related to the topic of the article. The other authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or a financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the article, apart from those disclosed.
References
- Schorling, D.C.; Pechmann, A.; Kirschner, J. Advances in Treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy—New Phenotypes, New Challenges, New Implications for Care. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2020, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, S.; Bürglen, L.; Reboullet, S.; Clermont, O.; Burlet, P.; Viollet, L.; Benichou, B.; Cruaud, C.; Millasseau, P.; Zeviani, M.; et al. Identification and characterization of a spinal muscular atrophy-determining gene. Cell 1995, 80, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, S.J.; Kissel, J.T. Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Neurol. Clin. 2015, 33, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, W.D.; Flanigan, K.M. A Practical Approach to Molecular Diagnostic Testing in Neuromuscular Diseases. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 23, 589–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorson, C.L.; Androphy, E.J. An exonic enhancer is required for inclusion of an essential exon in the SMA-determining gene SMN. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. Accelerated Assessment. 2018. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory/marketing-authorisation/accelerated-assessment (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- Edens, B.M.; Ajroud-Driss, S.; Ma, L.; Ma, Y.C. Molecular mechanisms and animal models of spinal muscular atrophy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebee, T.W.; Dominguez, C.E.; Chandler, D.S. Mouse models of SMA: Tools for disease characterization and therapeutic development. Hum. Genet. 2012, 131, 1277–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treatment of Neuromuscular Diseases Network. Translational Research in Europe—Assessment & Treatment of Neuromuscular Diseases (TREAT-NMD) Alliance Registries. Available online: https://treat-nmd.org/ (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- Van Putten, M.; Aartsma-Rus, A.; Grounds, M.D.; Kornegay, J.N.; Mayhew, A.; Gillingwater, T.H.; Takeda, S.I.; Rüegg, M.A.; De Luca, A.; Nagaraju, K.; et al. Update on Standard Operating Procedures in Preclinical Research for DMD and SMA Report of TREAT-NMD Alliance Workshop, Schiphol Airport, 26 April 2015, The Netherlands. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2018, 5, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Singh, N.N.; Androphy, E.J.; Singh, R.N. Splicing of a critical exon of human Survival Motor Neuron is regulated by a unique silencer element located in the last intron. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Vickers, T.A.; Okunola, H.L.; Bennett, C.F.; Krainer, A.R. Antisense masking of an hnRNP A1/A2 intronic splicing silencer corrects SMN2 splicing in transgenic mice. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 82, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passini, M.A.; Bu, J.; Richards, A.M.; Kinnecom, C.; Sardi, S.P.; Stanek, L.M.; Hua, Y.; Rigo, F.; Matson, J.; Hung, G.; et al. Antisense oligonucleotides delivered to the mouse CNS ameliorate symptoms of severe spinal muscular atrophy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 72ra18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Y.; Sahashi, K.; Rigo, F.; Hung, G.; Horev, G.; Bennett, C.F.; Krainer, A.R. Peripheral SMN restoration is essential for long-term rescue of a severe spinal muscular atrophy mouse model. Nature 2011, 478, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foust, K.D.; Nurre, E.; Montgomery, C.L.; Hernandez, A.; Chan, C.M.; Kaspar, B.K. Intravascular AAV9 preferentially targets neonatal neurons and adult astrocytes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, E.; Marais, T.; Chatauret, N.; Benkhelifa-Ziyyat, S.; Duque, S.; Ravassard, P.; Carcenac, R.; Astord, S.; de Moura, A.P.; Voit, T.; et al. Intravenous scAAV9 delivery of a codon-optimized SMN1 sequence rescues SMA mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naryshkin, N.A.; Weetall, M.; Dakka, A.; Narasimhan, J.; Zhao, X.; Feng, Z.; Ling, K.K.; Karp, G.M.; Qi, H.; Woll, M.G.; et al. Motor neuron disease. SMN2 splicing modifiers improve motor function and longevity in mice with spinal muscular atrophy. Science 2014, 345, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratni, H.; Karp, G.M.; Weetall, M.; Naryshkin, N.A.; Paushkin, S.V.; Chen, K.S.; McCarthy, K.D.; Qi, H.; Turpoff, A.; Woll, M.G.; et al. Specific Correction of Alternative Survival Motor Neuron 2 Splicing by Small Molecules: Discovery of a Potential Novel Medicine to Treat Spinal Muscular Atrophy. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 6086–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, J.W.; Mendell, J.R.; Mercuri, E.; Finkel, R.S.; Strauss, K.A.; Kleyn, A.; Tauscher-Wisniewski, S.; Tukov, F.F.; Reyna, S.P.; Chand, D.H. Clinical Trial and Postmarketing Safety of Onasemnogene Abeparvovec Therapy. Drug Saf. 2021, 44, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.; Ferraiuolo, L.; Schmelzer, L.; Braun, L.; McGovern, V.; Likhite, S.; Michels, O.; Govoni, A.; Fitzgerald, J.; Morales, P.; et al. Improving single injection CSF delivery of AAV9-mediated gene therapy for SMA: A dose-response study in mice and nonhuman primates. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2015, 23, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratni, H.; Scalco, R.S.; Stephan, A.H. Risdiplam, the First Approved Small Molecule Splicing Modifier Drug as a Blueprint for Future Transformative Medicines. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 874–877. [Google Scholar]
- Poirier, A.; Weetall, M.; Heinig, K.; Bucheli, F.; Schoenlein, K.; Alsenz, J.; Bassett, S.; Ullah, M.; Senn, C.; Ratni, H.; et al. Risdiplam distributes and increases SMN protein in both the central nervous system and peripheral organs. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2018, 6, e00447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, R.S.; Mercuri, E.; Darras, B.T.; Connolly, A.M.; Kuntz, N.L.; Kirschner, J.; Chiriboga, C.A.; Saito, K.; Servais, L.; Tizzano, E.; et al. Nusinersen versus Sham Control in Infantile-Onset Spinal Muscular Atrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, J.W.; Finkel, R.S.; Chiriboga, C.A.; Connolly, A.M.; Crawford, T.O.; Darras, B.T.; Iannaccone, S.T.; Kuntz, N.L.; Peña, L.D.; Shieh, P.B.; et al. Onasemnogene abeparvovec gene therapy for symptomatic infantile-onset spinal muscular atrophy in patients with two copies of SMN2 (STR1VE): An open-label, single-arm, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercuri, E.; Deconinck, N.; Mazzone, E.S.; Nascimento, A.; Oskoui, M.; Saito, K.; Vuillerot, C.; Baranello, G.; Boespflug-Tanguy, O.; Goemans, N.; et al. Safety and efficacy of once-daily risdiplam in type 2 and non-ambulant type 3 spinal muscular atrophy (SUNFISH part 2): A phase 3, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darras, B.T.; Masson, R.; Mazurkiewicz-Bełdzińska, M.; Rose, K.; Xiong, H.; Zanoteli, E.; Baranello, G.; Bruno, C.; Vlodavets, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. Risdiplam-Treated Infants with Type 1 Spinal Muscular Atrophy versus Historical Controls. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkel, R.S.; McDermott, M.P.; Kaufmann, P.; Darras, B.T.; Chung, W.K.; Sproule, D.M.; Kang, P.B.; Foley, A.R.; Yang, M.L.; Martens, W.B.; et al. Observational study of spinal muscular atrophy type I and implications for clinical trials. Neurology 2014, 83, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, V.A. Risdiplam: New opportunities but more to be done. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 23–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisafulli, S.; Sultana, J.; Ingrasciotta, Y.; Addis, A.; Cananzi, P.; Cavagna, L.; Conter, V.; D’Angelo, G.; Ferrajolo, C.; Mantovani, L.; et al. Role of healthcare databases and registries for surveillance of orphan drugs in the real-world setting: The Italian case study. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2019, 18, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Summary of the Risk Management Plan for Spinraza (Nusinersen). 2019. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/rmp-summary/spinraza-epar-risk-management-plan-summary_en.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- European Medicines Agency. Summary of the Risk Management Plan for Zolgensma (Onasemnogene Avìbeparvovec). 2023. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/rmp-summary/zolgensma-epar-risk-management-plan-summary_en.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- European Medicines Agency. Summary of the Risk Management Plan for Evrysdi (Risdiplam). 2021. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/rmp-summary/evrysdi-epar-risk-management-plan-summary_en.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- Sultana, J.; Crisafulli, S.; Almas, M.; Antonazzo, I.C.; Baan, E.; Bartolini, C.; Bertuccio, M.P.; Bonifazi, F.; Capuano, A.; Didio, A.; et al. Overview of the European post-authorisation study register post-authorization studies performed in Europe from September 2010 to December 2018. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2022, 31, 689–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscolar Dystrophy Association. United States Neuromuscular Disease Registry. Available online: https://www.mda.org/ (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- International SMA Consortium Spinal Muscular Atrophy Patient Registry (iSMAC SMA Registry). Available online: https://www.nemours.org/pediatric-research/clinicaltrials/neurology-1238325.html (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- European Medicines Agency. Observational Data (Real World Data). 2017. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/observational-data-real-world-data-subgroup-report_en.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- US Food and Drug Administration. Framework for FDA’s Real-World Evidence Program. 2018. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/120060/download (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- Crisafulli, S.; Trifirò, G. The role of real-world evidence for the study of rare diseases epidemiology and the post-marketing evaluation of orphan drugs. Recent. Prog. Med. 2022, 113, 425–429. [Google Scholar]
- Mercuri, E.; Finkel, R.; Scoto, M.; Hall, S.; Eaton, S.; Rashid, A.; Balashkina, J.; Coratti, G.; Pera, M.C.; Samsuddin, S.; et al. Development of an academic disease registry for spinal muscular atrophy. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2019, 29, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechmann, A.; Behrens, M.; Dörnbrack, K.; Tassoni, A.; Wenzel, F.; Stein, S.; Vogt, S.; Zöller, D.; Bernert, G.; Hagenacker, T.; et al. Improvements in Walking Distance during Nusinersen Treatment—A Prospective 3-year SMArtCARE Registry Study. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2023, 10, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pane, M.; Coratti, G.; Sansone, V.A.; Messina, S.; Catteruccia, M.; Bruno, C.; Sframeli, M.; Albamonte, E.; Pedemonte, M.; Brolatti, N.; et al. Type I spinal muscular atrophy patients treated with nusinersen: 4-year follow-up of motor, respiratory and bulbar function. Eur. J. Neurol. 2023, 30, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novartis. Novartis Shares Zolgensma Long-Term Data Demonstrating Sustained Durability up to 7.5 Years Post-Dosing; 100% Achievement of All Assessed Milestones in Children Treated Prior to SMA Symptom Onset. 2023. Available online: https://www.novartis.com/news/media-releases/novartis-shares-zolgensma-long-term-data-demonstrating-sustained-durability-75-years-post-dosing-100-achievement-all-assessed-milestones-children-treated-prior-sma-symptom-onset (accessed on 28 April 2023).
- Govoni, A.; Gagliardi, D.; Comi, G.P.; Corti, S. Time Is Motor Neuron: Therapeutic Window and Its Correlation with Pathogenetic Mechanisms in Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 6307–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. ZOLGENSMA (Onasemnogene Abeparvovec)—Fatal Cases of Acute Liver Failure. 2023. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/dhpc/direct-healthcare-professional-communication-dhpc-zolgensma-onasemnogene-abeparvovec-fatal-cases_en.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2023).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Long-Term Follow-Up Study of Risdiplam in Participants with Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) (WeSMA). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05232929 (accessed on 28 April 2023).
- Nash, L.A.; Burns, J.K.; Chardon, J.W.; Kothary, R.; Parks, R.J. Spinal Muscular Atrophy: More than a Disease of Motor Neurons? Curr. Mol. Med. 2016, 16, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, G.; Gillingwater, T.H. Spinal muscular atrophy: Going beyond the motor neuron. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).