Changes in Diffuse Tensor Imaging and Therapeutic Effect of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Traumatic Brain Injury with Central Pain
Abstract
1. Introduction
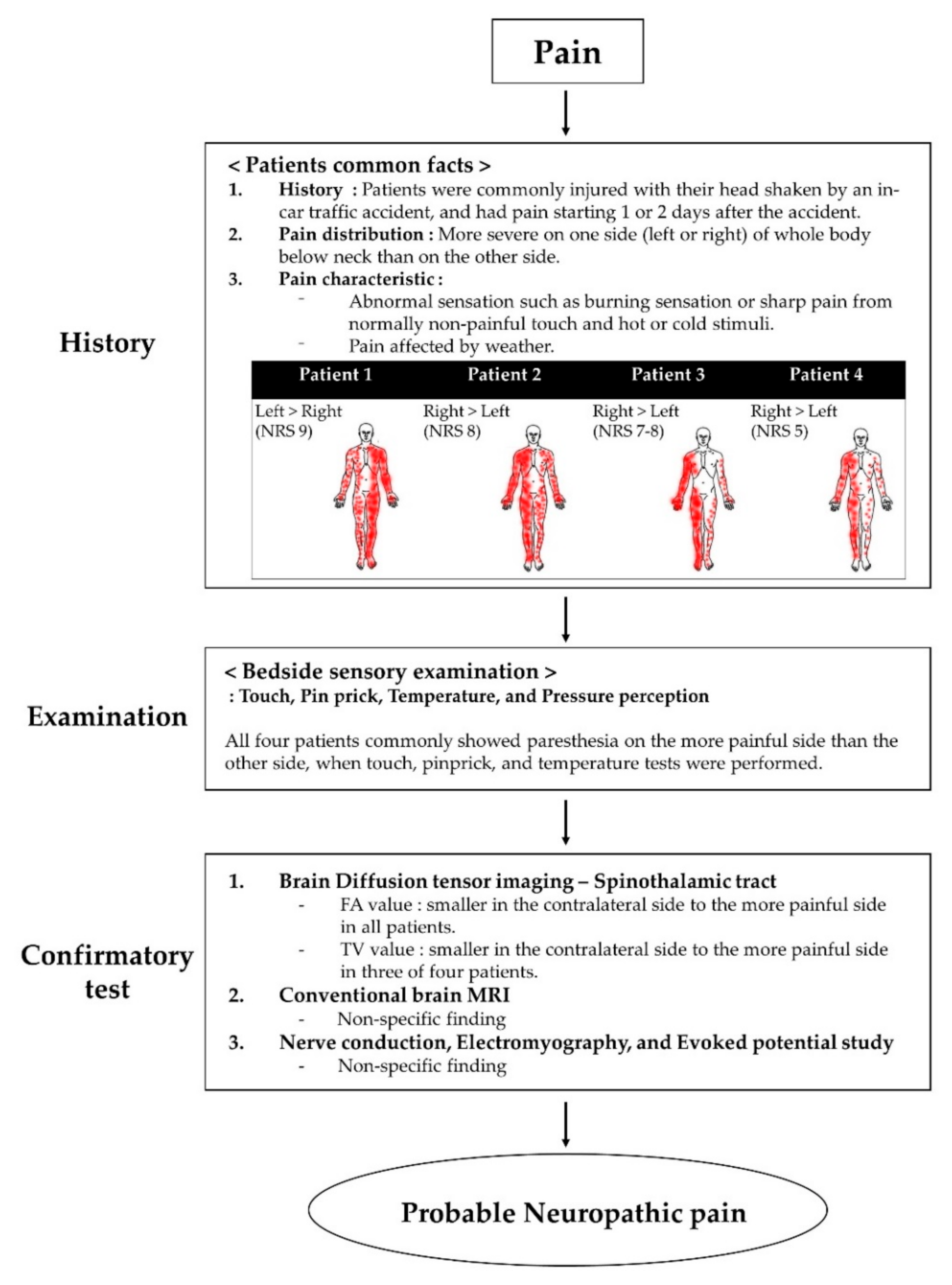
2. Materials and Methods
Case Report
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nampiaparampil, D.E. Prevalence of chronic pain after traumatic brain injury: A systematic review. JAMA 2008, 300, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, K.B.; Goldberg, M.; Bell, K.R. Traumatic brain injury and pain. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. 2006, 17, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofek, H.; Defrin, R. The characteristics of chronic central pain after traumatic brain injury. Pain 2007, 131, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devulder, J.; Crombez, E.; Mortier, E. Central pain: An overview. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2002, 102, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Lefaucheur, J.; Drouot, X.; Menard-Lefaucheur, I.; Keravel, Y.; Nguyen, J. Motor cortex rTMS restores defective intracortical inhibition in chronic neuropathic pain. Neurology 2006, 67, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowsher, D. Central pain: Clinical and physiological characteristics. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1996, 61, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attal, N.; Cruccu, G.; Haanpää, M.; Hansson, P.; Jensen, T.S.; Nurmikko, T.; Sampaio, C.; Sindrup, S.; Wiffen, P. EFNS guidelines on pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Neurol. 2006, 13, 1153–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S. Pharmacological management of central post-stroke pain: A practical guide. CNS Drugs 2014, 28, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefaucheur, J.-P.; Aleman, A.; Baeken, C.; Benninger, D.H.; Brunelin, J.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Filipović, S.R.; Grefkes, C.; Hasan, A.; Hummel, F.C.; et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS): An update (2014–2018). Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 474–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platz, T. Therapeutic RTMS in Neurology: Principles, Evidence, and Practice Recommendation, 1st ed.; Springer: Greifswald, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Cho, Y.W.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, S.H. The relation between injury of the spinothalamocortical tract and central pain in chronic patients with mild traumatic brain injury. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2015, 30, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.H.; Bai, D.S.; Jeong, J.Y.; Choi, B.Y.; Chang, C.H.; Kim, S.-H.; Ahn, S.H.; Jang, S.H. Injury of the spino-thalamo-cortical pathway is necessary for central post-stroke pain. Eur. Neurol. 2010, 64, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, B.C.; Lee, S.W.; Choi, E.S.; Sung, J.H.; Hong, J.T. Motor cortex stimulation for central pain following a traumatic brain injury. Pain 2006, 123, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.; Donohue, M.; Xu, R.; Lee, R.; Lefaucheur, J.-P.; Khedr, E.M.; Saitoh, Y.; André-Obadia, N.; Rollnik, J.; Wallace, M.; et al. rTMS for suppressing neuropathic pain: A meta-analysis. J. Pain 2009, 10, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawker, G.A.; Mian, S.; Kendzerska, T.; French, M. Measures of adult pain: Visual analog scale for pain (vas pain), numeric rating scale for pain (nrs pain), mcgill pain questionnaire (mpq), short-form mcgill pain questionnaire (sf-mpq), chronic pain grade scale (cpgs), short form-36 bodily pain scale (sf-36 bps), and measure of intermittent and constant osteoarthritis pain (icoap). Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, S240–S252. [Google Scholar]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Haroutounian, S.; Kamerman, P.; Baron, R.; Bennett, D.L.; Bouhassira, D.; Cruccu, G.; Freeman, R.; Hansson, P.; Nurmikko, T.; et al. Neuropathic pain: An updated grading system for research and clinical practice. Pain 2016, 157, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.H.; Son, S.M.; Jang, S.H. Identification of spinothalamic tract and its related thalamocortical fibers in human brain. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 468, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, Y.; Pasternak, O. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)-based white matter mapping in brain research: A review. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2008, 34, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.H.; Lee, J.; Yeo, S.S. Central post-stroke pain due to injury of the spinothalamic tract in patients with cerebral infarction: A diffusion tensor tractography imaging study. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, S.; Crain, B.J.; Chacko, V.P.; Van Zijl, P.C. Three-dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 45, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.H.; Chang, C.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, C.S.; Seo, J.P.; Yeo, S.S. Functional role of the corticoreticular pathway in chronic stroke patients. Stroke 2013, 44, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, E.; Agosta, F.; Rocca, M.A.; Caputo, D.; Filippi, M. Voxel-based analysis derived from fractional anisotropy images of white matter volume changes with aging. NeuroImage 2008, 41, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmgren, H.; Leijon, G.; Boivie, J.; Johansson, I.; Ilievska, L. Central post-stroke pain—Somatosensory evoked potentials in relation to location of the lesion and sensory signs. Pain 1990, 40, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treede, R.-D.; Jensen, T.S.; Campbell, J.N.; Cruccu, G.; Dostrovsky, J.O.; Griffin, J.W.; Hansson, P.; Hughes, R.; Nurmikko, T.; Serra, J. Neuropathic pain: Redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology 2008, 70, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefaucheur, J.; Drouo, T.X.; Menard-Lefaucheur, I.; Keravel, Y.; Nguyen, J. Motor cortex rTMS in chronic neuropathic pain: Pain relief is associated with thermal sensory perception improvement. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2008, 79, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.; Summers, J.; Pridmore, S. Changes to somatosensory detection and pain thresholds following high frequency repetitive TMS of the motor cortex in individuals suffering from chronic pain. Pain 2006, 123, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, R.; Dickenson, A. Spinal and supraspinal contributions to central sensitization in peripheral neuropathy. Neurosignals 2005, 14, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klit, H.; Finnerup, N.B.; Jensen, T.S. Central post-stroke pain: Clinical characteristics, pathophysiology, and management. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, H.; Holmes, G. Sensory disturbances from cerebral lesions. Brain 1911, 34, 102–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.H.; Lee, H.D. Central pain due to spinothalamic tract injury caused by indirect head trauma following a pratfall. Brain Inj. 2016, 30, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefaucheur, J.-P.; Jarry, G.; Drouot, X.; Ménard-Lefaucheur, I.; Keravel, Y.; Nguyen, J.-P. Motor cortex rTMS reduces acute pain provoked by laser stimulation in patients with chronic neuropathic pain. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2010, 121, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bihan, D.; Poupon, C.; Clark, C.A.; Pappata, S.; Molko, N.; Chabriat, H. Diffusion tensor imaging: Concepts and applications. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2001, 13, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 39 | 40 | 43 | 45 |
| Sex | Female | Male | Female | Female |
| Time of pain onset | 1 day | 1 day | 2 days | 1 day |
| Vector | In-car accident—vehicle rotated due to side collision | |||
| Before rTMS | After rTMS | |
|---|---|---|
| Patient 1 | 9 | 4 |
| Patient 2 | 8 | 5 |
| Patient 3 | 7–8 | 4 |
| Patient 4 | 5 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, D.-H.; Kim, G.-W. Changes in Diffuse Tensor Imaging and Therapeutic Effect of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Traumatic Brain Injury with Central Pain. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120929
Kang D-H, Kim G-W. Changes in Diffuse Tensor Imaging and Therapeutic Effect of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Traumatic Brain Injury with Central Pain. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(12):929. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120929
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Dong-Ha, and Gi-Wook Kim. 2020. "Changes in Diffuse Tensor Imaging and Therapeutic Effect of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Traumatic Brain Injury with Central Pain" Brain Sciences 10, no. 12: 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120929
APA StyleKang, D.-H., & Kim, G.-W. (2020). Changes in Diffuse Tensor Imaging and Therapeutic Effect of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Traumatic Brain Injury with Central Pain. Brain Sciences, 10(12), 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120929






