Abstract
Blind perceptual quality measurement of stereoscopic 3D (S3D) images has become an important and challenging issue in the research field of S3D imaging. In this paper, a blind S3D image quality measurement (IQM) method that does not depend on examples of distorted S3D images and corresponding subjective scores is proposed. As the main contribution of this work, we replace human subjective scores with a quality codebook of binocular rivalry responses (BRRs); this allows blind S3D-IQM methods to be learned without evaluation performance loss. Our results, using the publicly accessible LIVE S3D dataset, confirm that our method is highly robust and efficient.
1. Introduction
In recent years, stereoscopic 3D (S3D) technologies have attracted considerable research interest. S3D measurement can be classified into S3D content measurement (e.g., visual discomfort, quality of experience, or unnatural experience) and S3D image quality measurement (IQM) (e.g., the measurement of compression distortions or transmission impairments for S3D images). However, research on S3D content measurement is still limited. In recent decades, blind S3D-IQM has been attracting attention in the research field of S3D imaging [1,2,3]. State-of-the-art blind S3D-IQM methods learn to measure S3D quality via regression from the subjective scores of training samples. For instance, in [4], Akhter et al. introduced a blind S3D-IQM method that extracts both 2D and S3D quality-aware features from an S3D image and a depth/disparity map. Next, a regression model is adapted to obtain a final quality value from the above-mentioned features. Similar studies were also conducted in [5]; Chen et al. proposed a blind S3D-IQM method based on a “cyclopean” view and disparity map. Zhou et al. introduced blind S3D-IQM based on the self-similarity of binocular features [6]. Other relevant existing studies can be found in [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. These methods require human-scored S3D images for training; however, obtaining subjective scores through subjective evaluation is often expensive, cumbersome, and time-consuming, which limits their usability in practice. Thus, a significant problem is triggered: can we learn to measure S3D image quality blindly without relying on human-scored S3D images?
Quality measurement of 2D images has been extensively studied, and several excellent methods have been proposed [15,16,17,18]. For example, in [16], Xue et al. presented a quality-aware clustering metric, which can learn centroids to act as a quality-aware codebook for measuring distorted image quality. Inspired by [16], we propose a blind S3D-IQM method that learns a quality codebook of binocular rivalry responses (BRRs). The main contributions of this work are three-fold.
First, in the offline training phase, we learn a quality codebook from the BRRs of the original and distorted S3D images; this codebook will be used to replace human subjective scores to learn blind S3D-IQM methods.
Second, a BRR-weighted local binary pattern (LBP) histogram scheme is used to extract quality-predictive features; this scheme is effective for describing degradation patterns.
Third, in the online testing phase, a distance-based weighting scheme is used for perceptual quality pooling. Experimental results obtained using the publicly accessible LIVE S3D dataset indicate that the proposed method performs competitively and provides quality prediction performance and generalization ability.
2. Proposed Method
The block diagram for our blind S3D-IQM method is depicted in Figure 1. During the offline training phase, similarity scores and a weighted LBP histogram are generated from training S3D images; subsequently, a quality codebook is constructed. During the online testing phase, by implementing feature extraction for test S3D images, blind perceptual quality pooling can be easily achieved by a distance-based weighting scheme. Our method is described in detail as follows.
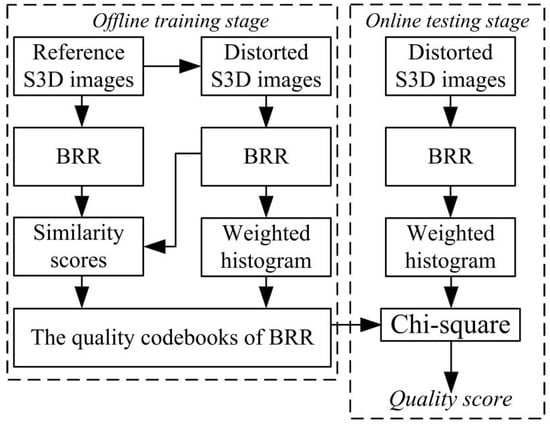
Figure 1.
Block diagram for our blind S3D-IQM.
(1) Training dataset preparation: We select 12 reference S3D images collected from Mobile S3DTV and MPEG (please refer to Figure 2) [19]. From each reference S3D image, we then generate distorted S3D images using four types of distortions, including JPEG2000 (JP2K), Gaussian blur (Gblur), white noise (WN), and JPEG. For each distortion, five quality levels are generated by controlling different parameters.

Figure 2.
Left views of the training S3D images in this paper.
(2) Quality measurement of the training S3D images: Neuroscience has made rapid progress in comprehending the human visual mechanism and how S3D visual signals are transmitted to the human brain. BRR is a well-researched visual mechanism of competition in the visual cortex [20]. BRR is a human visual response whereby the binocular visual mechanism alternates between contradictory monocular images viewed by both eyes. Some findings in [20] showed that BRR can be strongly regulated by low-level sensory features, and a classic linear mathematical model is provided. Motivated by the above, 2D-Gabor is used for both views to simulate the rivalries. Consequently, BRR, which can be denoted by Rbin(x,y,σ), is defined as
where d denotes a disparity value estimated using an S3D matching algorithm [21] (Reference [22] reports that similar performance is attained when using either the ground truth or the estimated disparity). Subscripts “l” and “r” are the left and right views, respectively. Ml(x,y,σ) and Mr(x,y,σ) are the monocular responses of both views, which can be obtained using a difference of Gaussian (DoG) filter
where σ denotes the scales parameter and k is used to control the scales of the DoG. r denotes the l2 norm. In this study, scales σ of the DoG are set to 0, 1, 1.6, 2.56, and 4.096 (the same values as the filter used in [2]), with k = 1.6. Wl and Wr denote the weights for imitating the BRR. They are represented as Wl(x,y) = Gl(x,y)/(Gl(x,y) + Gr(x + d,y)) and Wr(x + d,y) = Gr(x + d,y)/(Gl(x,y) + Gr(x + d,y)), respectively, where Gl(x,y) and Gr(x,y) denote the respective 2D-Gabor responses of both views. The 2D Gabor filter can be defined as:
where σx and σy denote the standard deviations along the x and y axes, ζx and ζy, and θ denotes spatial frequencies and orients the filter. The design of the 2D-Gabor filter was based on the research conducted by Su et al. [23].
The similarity score between the BRRs of the original S3D image and distorted S3D images is defined as:
where T is a small positive constant. In this study, we set T = 0.085 in our experiments. Ω indicates the whole spatial domain, denotes the l2 norm, and represents the inner product. Subscript “n” is the index of the n-th training distorted S3D images. Subscripts “o” and “d” are the original and distorted S3D images, respectively.
(3) Quality-predictive features extraction: Based on Marr’s theory [24], local structural features based on the visual cortex (area V1) are related to image quality. LBPs are basic feature extractors that are commonly used to represent an image’s structural and textural information [25]. First, we compute the rotation invariant uniform LBP map, , for BRR by comparing BRR intensity against its eight neighbors (in consideration of computational complexity, R and P were set to 1 and 8, respectively). To effectively capture textural and structural features, the BRR-weighted LBP histogram is applied to extract quality-predictive features of BRR, which are defined as
where .
(4) BRR quality codebook: Thus far, we have gained a set of human-scored S3D images for training. All the quality scores (denoted by {Sn}) and all the feature vectors (denoted by ) of the distorted S3D images for training constitute a BRR quality codebook to reflect different quality levels of visual signals and associated quality-predictive features.
(5) Blind perceptual quality pooling: After obtaining a BRR quality codebook, we use the codes to predict the quality score of a test S3D image, relying on the hypothesis that S3D images with similar quality-aware features should share similar visual qualities. First, let represent the quality-aware features of the n-th test S3D image. We define the distance Hm,n between and as the product of the chi-square distance between each pair of quality-predictive features.
where N is the total number of training S3D images. Let represent the chi-square distances of 10 of the nearest quality-predictive features, which are calculated using the n-th test set and the selected training set. A distance-based weighting method is then utilized to measure the perceptual visual quality of the test set. The normalized weight for the 10 similarity scores of the selected training set, which is denoted by , can be represented as
By distributing larger weights to the similarity values of the selected neighboring training S3D images, the final quality value of the n-th test S3D image is calculated as
3. Results
In the experiment, the effectiveness of our method was verified using the LIVE S3D [5] dataset, which includes 365 symmetrically distorted S3D images (in the future, we plan to understand how asymmetrical distortion affects perceptual quality (for the case of blur artifacts, the perceptual quality of asymmetric blurred S3D images is mainly dominated by the view that contains more information. For the case of JPEG artifacts, the binocular perceptual quality has a tendency towards the lower quality view) and extension of the proposed method to facilitate asymmetrical distortion S3D-IQM). In order to facilitate the experiment (refer to [16]), we utilized only four distortion types: JP2K, WN, JPEG, and Gblur. The images in the dataset were assigned difference mean opinion scores (DMOS), which represent subjective judgments.
In order to compare the proposed method against existing S3D-IQM methods, two widely used performance criteria were calculated by applying the DMOS and the predicted quality scores. The first was a Pearson’s linear correlation coefficient (PLCC), which was computed to evaluate the prediction accuracy. The second was a Spearman’s rank order correlation coefficient (SROCC), which measured the prediction monotonicity. For an ideal IQM method, values close to 1 were needed for SROCC and PLCC.
To demonstrate the robustness and effectiveness of the proposed method, we compared it with several existing representative IQM methods, including three 2D-IQM methods—SSIM (full reference, FR) [26], IL_NIQE (blind, not depending on DMOSs) [15], and Xue’s method (blind, not depending on DMOSs) [16]—and seven S3D-IQM methods—Lin’s method (FR) [2], Akhter’s method (blind, depending on DMOSs) [4], Chen’s method (blind, depending on DMOSs) [5], Yue’s method (blind, depending on DMOSs) [9], Zhou’s method (blind, depending on DMOSs) [12], Shao’s method (blind, not depending on DMOSs) [13], and Zhou’s method (blind, not depending on DMOSs) [14]. All IQM methods are based on the grayscales of S3D images. The SROCC and PLCC results are listed in Table 1; the criterion that provides the best evaluation performance is emphasized in boldface (all the blind methods that do not depend on DMOSs). As shown in Table 1, compared with other methods, it is evident that our method correlates well with the DMOSs, owing to its sufficient application of human visual perception. It thereby delivers a performance that is superior to most blind and FR methods, including SSIM and IL_NIQE, and the methods proposed by Xue, Lin, Shao, and Zhou. Thus, our method is an accurate, effective, and consistent S3D-IQM method, even though it does not use human-scored S3D images.

Table 1.
Overall performance evaluation of nine methods.
Another experiment was conducted to further investigate the evaluation ability of the IQM methods for specific distortion types. In this experiment, we tested the performance of the state-of-the-art methods on individual distortion types. The SROCC and PLCC results are listed in Table 2. For each individual distortion type, the top two results are emphasized in boldface (all blind methods that do not depend on DMOS). As shown in Table 2, our method placed among the top methods most often. Although some methods may provide good performance for some distortion types, the proposed method performs better than, or on par with, the best method for each individual distortion type.

Table 2.
Performance of nine methods for each individual distortion type.
Next, we discuss the influence of disparity estimation performance on the proposed method. The performance of the proposed method using ground truth, SAD [27], and Klaus [21] are listed in Table 3. Table 3 shows that a similar performance is attained when using either the ground truth or the estimated disparity.

Table 3.
The performance of the proposed method using different stereo methods.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, we proposed a new blind S3D-IQM method that does not depend on DMOS during learning. The main contribution of this study is that we constructed a quality-aware codebook to obtain blind IQM using a perceptual pooling strategy. Experimental results show that the proposed method can produce assessments that are statistically much more consistent with DMOS.
Further work will mainly focus on: (1) other binocular visual perception (e.g., binocular fusion, binocular suppression) can be considered for improving the performance of the proposed method, (2) the effect of disparity information needs to be further addressed and, besides disparity, many other factors, such as monocular depth cues, visual comfort, visual direction, etc., should be considered in modeling S3D-IQM without relying on human-scored S3D images.
Author Contributions
S.H. conceived and designed the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the paper. W.Z. supervised the work, helped with designing the conceptual framework, and edited the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61,502,429) and the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. LY18F020012).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jiang, Q.; Shao, F.; Lin, W.; Jiang, G. Learning a referenceless stereopair quality engine with deep nonnegativity constrained sparse autoencoder. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 76, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Wu, J.L. Quality assessment of stereoscopic 3D image compression by binocular integration behaviors. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 1527–1542. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Lin, W.; Fang, Y. BSD: Blind image quality assessment based on structural degradation. Neurocomputing 2017, 236, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, R.; Baltes, J.; Sazzed, Z.; Horita, Y. No-reference stereoscopic image quality assessment. In Stereoscopic Displays and Applications XXI; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2010; Volume 7524, p. 75240T. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.-J.; Cormack, L.K.; Bovik, A.C. No-Reference quality assessment of natural stereopairs. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 3379–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Pan, T.; Yu, L.; Qiu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, T. Blind 3D image quality assessment based on self-similarity of binocular features. Neurocomputing 2017, 224, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; He, M.; Yu, M.; Shao, F.; Peng, Z. Perceptual stereoscopic image quality assessment method with tensor decomposition and manifold learning. IET Image Process. 2018, 12, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, W.; Li, W. Blind stereoscopic video quality assessment: From depth perception to overall experience. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, G.; Hou, C.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, Y. Blind stereoscopic 3D image quality assessment via analysis of naturalness, structure, and binocular asymmetry. Signal Process. 2018, 150, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jiang, B.; Wang, Y.; Lu, W.; Meng, Q. Sparse representation based stereoscopic image quality assessment accounting for perceptual cognitive process. Inf. Sci. 2018, 430, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, B.; Huang, H. No-reference stereopair quality assessment based on singular value decomposition. Neurocomputing 2018, 275, 1823–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Chen, Z.; Li, W. Dual-Stream Interactive Networks for No-Reference Stereoscopic Image Quality Assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 3946–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, F.; Lin, W.; Wang, S.; Jiang, G.; Yu, M.; Dai, Q. Learning receptive fields and quality lookups for blind quality assessment of stereoscopic images. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2016, 46, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Yu, L.; Qiu, W.; Luo, T.; Wang, Z.; Wu, M.W. Utilizing binocular vision to facilitate completely blind 3D image quality measurement. Signal Process. 2016, 129, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Bovik, A.C. A feature-enriched completely blind image quality evaluator. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 2579–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X. Learning without human scores for blind image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 995–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Yu, L.; Qiu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, M. Local gradient patterns (LGP): An effective local statistical features extraction scheme for no-reference image quality assessment. Inf. Sci. 2017, 397, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Qiu, W.; Wu, M.-W.; Luo, T. Local and global feature learning for blind quality evaluation of screen content and natural scene images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 2086–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobile 3DTV Content Delivery Optimization over DVB-H System. Available online: http://sp.cs.tut.fi/mobile3dtv/stereo-video/ (accessed on 16 March 2011).
- Levelt, W.J. The alternation process in binocular rivalry. Br. J. Psychol. 1966, 57, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, A.; Sormann, M.; Karner, K. Segment-based stereo matching using belief propagation and a self-adapting dissimilarity measure. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR’06), Hong Kong, China, 20–24 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.J.; Su, C.C.; Kwon, D.K.; Cormack, L.K.; Bovik, A.C. Full-reference quality assessment of stereopairs accounting for rivalry. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2013, 28, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.-C.; Bovik, A.C.; Cormack, L.K. Natural scene statistics of color and range. In Proceedings of the 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 11–14 September 2011; pp. 257–260. [Google Scholar]
- Marr, D.; Hildreth, E. Theory of edge detection. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1980, 207, 187–217. [Google Scholar]
- Ojala, T.; Pietikinen, M.; Menp, T. Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 24, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharstein, D.; Szeliski, R. A taxonomy and evaluation of dense two-frame stereo correspondence algorithms. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2002, 47, 7–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).