Abstract
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are small peptides and play important roles in host innate immune response against microbial invasion. Aquatic animals secrete different kinds of antimicrobial peptides which have antimicrobial activity towards microorganisms. NK-lysins, mature peptides produced by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells, are comprised of 74–78 amino acid residues, demonstrating broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and parasites. In this study, three distinct NK-lysin mature peptide (mNKLs), transcripts (76 amino acid residues) cloned from the channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) head kidney were ligated into plasmid vector pET-32a(+) to express the mNKLs fusion protein. The fusion protein was successfully expressed in E. coli Rosetta (DE3) under optimized conditions. After purification by affinity column chromatography, the fusion protein was successfully cleaved by enterokinase and released the peptide mNKLs. Tricine-SDS-PAGE results showed that mNKLs (approximately 8.6 kDa) were successfully expressed. The purified peptide mNKLs exhibited antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and E. coli.
1. Introduction
Antimicrobial peptides are essential effector molecules that provide the host immune response against pathogen challenge. To date, antimicrobial peptides have been shown to have activities against infection from a wide range of microorganisms including bacteria, fungi, viruses and other pathogens [1,2,3,4,5,6]. G. Boman discovered the first antimicrobial peptide from Hyalophora cecropia in 1972, namely cecropins [7]. Nearly 1500 antimicrobial peptides were gradually identified from life entities including bacteria, fungi, plants, insects, fish, amphibians, birds and mammals [8,9,10,11,12,13]. Fish, as an indispensable organism in water, also possess numerous AMPs (antimicrobial peptides). Since then, over 100 fish AMPs have been isolated, artificially synthesized or expressed by genetic engineering [14], including cathelicidin, chrysophsin, hepcidin, hipposin, misgurin, moronecidin, liver expressed antimicrobial peptide 2 (LEAP-2), oncorhyncin, parasin, pardaxin, piscidin, pleurocidin, NK-lysin [14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. According to different structural features, fish antimicrobial peptides can be broadly classified into four classes. These four classes are “traditional” classes that have had comprehensive studies through recent years. In addition to the previously known four classes, the fifth class of antimicrobial polypeptides has been identified [21] and it includes NK-lysin [22], HDL [23], misgurin [24] and myxidin [25].
NK-lysin was first identified from porcine natural killer cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes based on its antibacterial activity [26]. Compared with the first four classical antimicrobial peptides, NK-lysin is much larger with 74–78 amino acid residues than the former AMPs [27]. It possesses six half-cystine residues in three intrachain disulphide bonds [28]. A study shows that porcine NK-lysin has strong antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli and Bacillus megaterium, and it also exerts activity towards an NK-sensitive tumor cell line of murine animals [26]. However, the porcine NK-lysin has no lytic activity against erythrocytes [26,28]. Artificially synthesized Japanese flounder NK-lysin has been found to have activity against various Gram-negative bacteria [29]. Until now, various animals’ NK-lysin gene sequences have been identified including mammalian species such as cow [30], pig [26] and horse [31]; birds such as chicken [32]; and aquatic animals such as channel catfish [33], zebrafish [34] and Cynoglossus semilaevis [35]. Three distinct NK-lysin transcripts have been identified in channel catfish, respectively NK-lysin 1, NK-lysin 2, NK-lysin 3 [36]. They are highly expressed in gill, head kidney, spleen and trunk kidney, but are incapable of being expressed in all tissues, and all three genes have different expression profiles [36,37]. Previously, it was found that the expressions of NK-lysin 1, NK-lysin 2 and NK-lysin 3 were all up-regulated from the second or third day to the seventh day or even longer after being infected by Edwardsiella ictaluri [36,38]. Therefore, NK-lysin is an important component of the immune response of channel catfish and possesses the potential of against pathogen challenge.
With the development of biotechnology, the genetic recombinant technique has become a more effective way to produce drug proteins and polypeptides than traditional isolation or artificial synthesis methods. Many AMPs have been expressed in heterologous hosts, especially with the Escherichia coli expression system [39]. The E. coli system is widely accepted for the use of heterologous protein production [40]. It is a high-yield and reliable system because the E. coli can survive in a wide range of environmental conditions and the system can be easily controlled. However, AMPs have high toxicity towards host strains so that different molecular chaperones are used in order to reduce toxicity and inclusion bodies to improve fusion protein expression [41]. Molecular chaperones are then removed by enterokinase digestion to obtain a similar structure of native peptides. In the present study, we cloned NK-lysin mature peptides (mNKLs) and ligated them into the pET-32a(+) plasmid vector to express mNKLs mature peptides in E. coli Rosetta (DE3) cells. The expressed fusion protein was cleaved by enterokinase to obtained recombinant mNKLs. Further, we analyzed the antibacterial activity of the synthesized peptides against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Extraction of RNA, Reverse-Transcription (RT)-PCR and Sequence Analysis
Total RNA was extracted from healthy channel catfish (approximately 100 g) head kidney using RNAiso Plus (Takara, Dalian, China) following manufacturer’s instructions. Extracted RNA was stored in −80 °C freezer before using as template for reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The first chain complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA) was synthesized from the isolated RNA using the PrimeScript 1st strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Takara, Dalian, China) and served as template to amplify channel catfish NK-lysin cDNA by PCR. The forward primer and reverse primer were designed with the reference to the database nucleotide sequence (GenBank ID: AY934592, DQ153189, DQ153187). The mNKLs were predicted by SMART and Qun Wang et al. [22]. The PCR was conducted as follows; an initial denaturation step at 95 °C for 5 min, 30 cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, 56 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 10 min. Subsequently, cDNA fragment which encodes the mNKL were amplified including BamHI and HindIII sites (underlined) and enterokinase cleavage site (bold and italic) by using forward and reverse primers (Table 1). The amplified product was eluted from gel electrophoresis and cloned into pMD19-T vector (Takara, Dalian, China), subsequently transform into E. coli strain DH5α (Tiangen, Berjing, China) as a host.

Table 1.
Primers and their sequences used in this study.
2.2. Expression and Purification of mNKLs
After pMD19-T cloning and direct sequencing, the recombinant plasmids were digested with restriction enzymes BamHI and HindIII. The digested mNKL fragments were inserted into pET-32a(+), which fuses the construct in tandem to the sequence of thioredoxin, generating pET32-mNKL 1, pET32-Mnkl 2, pET32-mNKL 3. The confirmed recombinant expression constructs were first transformed into E. coli BL21 (DE3) (Tiangen, Berjing, China) cells but the expression was unsuccessful in all cases. E. coli Rosetta (DE3) (Tiangen, Berjing, China) cells can enhance the expression of eukaryotic proteins which contains E. coli rare codons. Rare codon was analyzedby Rare Codon Calculator (RaCC), a rare Arg codon (CGA) was observed on the 47th codon of NK-lysin 1 and NK-lysin 2, a rare Arg codon (AGA) was observed on the 38th codon of NK-lysin 3 (data not shown). The confirmed recombinant expression constructs were transformed into E. coli Rosetta (DE3) cells. After optimization of expression condition, higher level expression was induced by isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) to express protein at a final concentration of 0.1 mM for 4 h at 37 °C and harvested by centrifugation at 8000× g, 4 °C, for 10 min. After centrifugation, the pellets were resuspended in Ni-Native-0 buffer (50 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl, pH 8.0). The resuspended bacterial cells were lysed by sonication and the extracted supernatant that may contain soluble proteins were clarified by centrifugation at 12,000 rpm at 4 °C for 20 min, then the supernatants with Ni-Native-0 buffer were added into the equilibrated Ni-NTA-Sefinose column (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China). Ni-Native-250 buffer (50 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl, 250 mM Imidazole, pH 8.0) was used to wash the resin absorbed Histidine-tagged fusion protein. The extracted proteins were analyzed by Tricine-SDS (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfonate)-PAGE (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China), stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 and imaged by a Molecular Imager Gel Doc XR+ imaging system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). The purified products were concentrated then visualized by Tricine-SDS-PAGE (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China). Final concentrations of purified mNKLs were measured by the micro-BCA protein assay reagent according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China).
2.3. Enterokinase Cleavage of mNKLs
The fusion proteins cleaved by Recombinant Bovine Enterokinase Light Chain-His (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China) were performed as follows; One unit:50 μg fusion proteins in 25 mM Tris-HCl, 50 mM NaCl and 2 mM CaCl2 at 25 °C for 16 h. After incubation, NK-lysin proteins were collected and added separately into Ni-NTA-Sefinose Column (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China). Unbinding proteins were collected and analyzed by Tricine-SDS-PAGE. The collected unbinding proteins were concentrated then analyzed by Tricine-SDS-PAGE and final concentrations were measured by the micro-BCA protein assay reagent (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China).
2.4. Antibacterial Activity Assays
Two bacteria were selected to examine the antibacterial activity of recombinant mNKLs: E. coli (strain DH5α) and Staphylococcus aureus (strain ATCC 25923). Bacteria were grown at 37 °C in 10 mL Luria-Bertani medium until mid-logarithmic phase. Incubated bacteria were diluted to 108 cfu/mL then 100 μL of each strain was poured into solidified Luria-Bertani agar medium plates. Ten minutes later, Solidified Luria-Bertani agar medium plates were punched with small wells (diameter 5 mm) and recombinant mNKLs (5 μg of each well) were added into wells [42], incubated overnight at 37 °C. In each Luria-Bertani agar medium plate, 10 μg of ampicillin was added as positive controls and same volume of sterile ddH2O was used as negative controls.
3. Results
3.1. Cloning and Construction of Recombinant Expression Vector
The channel catfish mNKLs (type 1, 2, 3) proteins consisting of 76 amino acids were aligned, with a predicted molecular weight of 8.6 kDa (Figure 1). In order to obtain a similar structure of native peptides, one enterokinase cleavage site (DDDDK) and a termination codon (TGA) were added in the N-terminal and C-terminal of the mNKLs, respectively. The segments containing mNK-lysin genes were amplified by PCR and ligated into the pMD19-T plasmid vector. The positive recombinant plasmids were confirmed by restriction enzyme digestion and sequencing. The pMD19-T-mNKLs were digested with restriction enzymes and then cloned into the pET-32a(+) plasmid vector, which was also confirmed via restriction digest and sequencing (Figure 2).
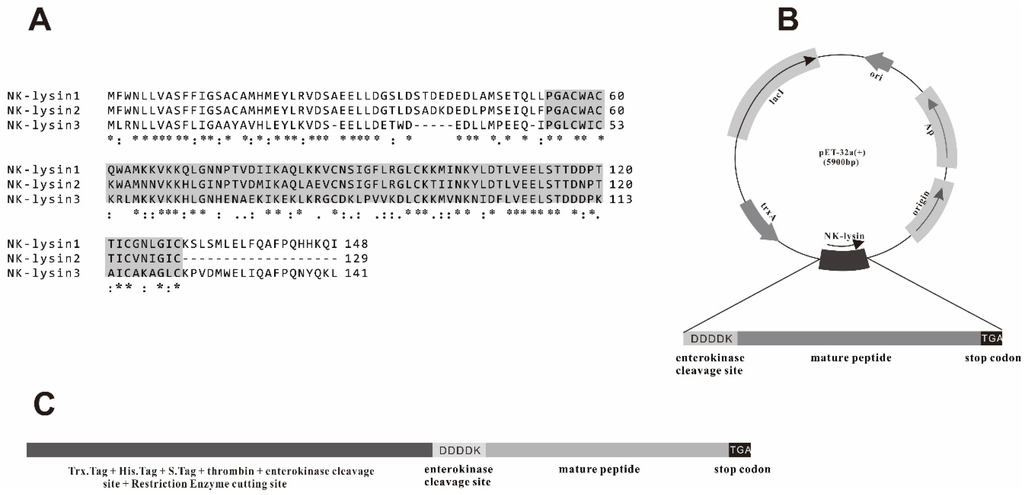
Figure 1.
(A) Alignment of channel catfish NK-lysin amino acid residues. The mature peptides (about 8.6 kDa) were indicated in gray background which were predicted by SMART and the report of Qun Wang et al. (2006) [36]. Regions of identity (*), strong similarity (:) and weak similarity (.) were indicated; (B) The construction of prokaryotic expression vector pET-32a-mNKL. In order to obtain the recombinant mNKLs with similar structure of native NK-lysins, the enterokinase cleavage site (DDDDK) and termination codon (TGA) were added in N-terminal and C-terminal of mNKLs, respectively; (C) Fusion protein produced as translation of pET-32a(+) vector.
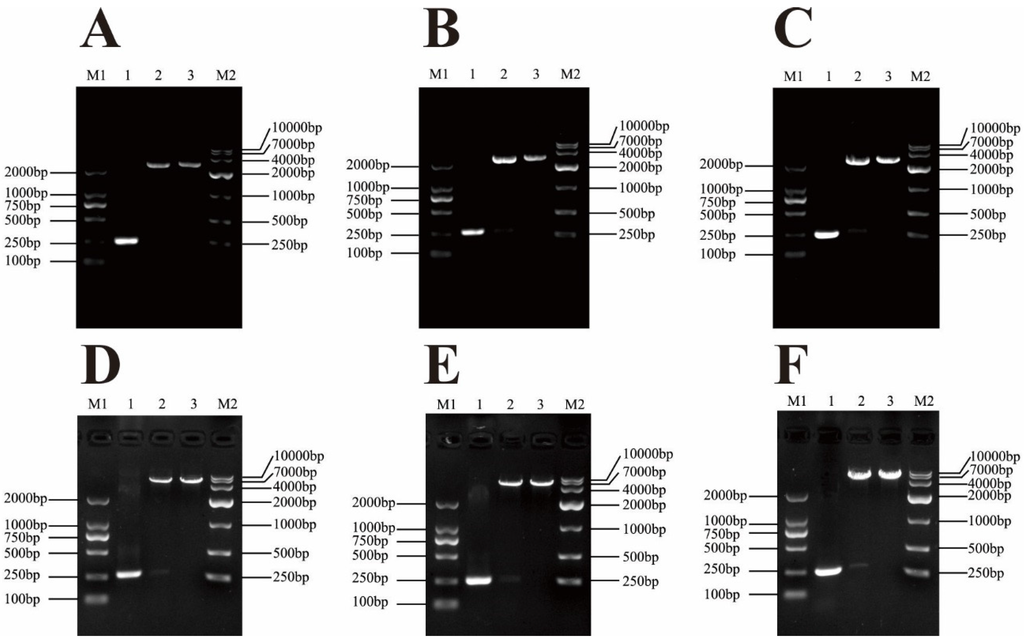
Figure 2.
Identification of the recombinant plasmid pMD19-T-mNKLs and pET-32a-mNKLs by restriction digestion and PCR-based amplification. (A–C) M1, DNA marker of 2000 bp; M2, DNA marker of 10,000 bp; lane 1, PCR amplification product of mNKL 1, mNKL 2 and mNKL 3, respectively (approximately 260 bp); lane 2, pMD19-T-mNKL 1/2/3 were digested by Bam HI and Hind III; lane 3, pMD19-T-mNKL1/2/3 were digested by Bam HI; (D–F) M1, DNA marker of 2000 bp; M2, DNA marker of 10,000 bp; lane 1, PCR amplification product of mNKL 1, mNKL 2 and mNKL 3, respectively (approximately 260 bp); lane 2, pET-32a-mNKL 1/2/3 were digested by Bam HI and Hind III; lane 3, pET-32a-mNKL 1/2/3 were digested by Bam HI.
3.2. Expression and Affinity Column Purification of Fusion mNKLs
The recombinant expression constructs (pET32-mNKLs) were transformed successfully into E. coli Rosetta (DE3) cells and expressed the Trx-His-mNKLs (approximately 24.6 kDa) (Figure 3). Tricine-SDS-PAGE analysis results showed that the fusion mNKLs were mainly expressed in the supernatant in soluble form. The recombinant mNKLs were purified successfully by affinity column chromatography in the native condition (Figure 3). The yield of recombinant mNKLs was about 6.7 mg/L for each protein; then the purified recombinant mNKLs were enriched to a concentration at 1.1 mg/mL for mNKL1, 1.4 mg/mL for mNKL2, 1.7 mg/mL for mNKL3.
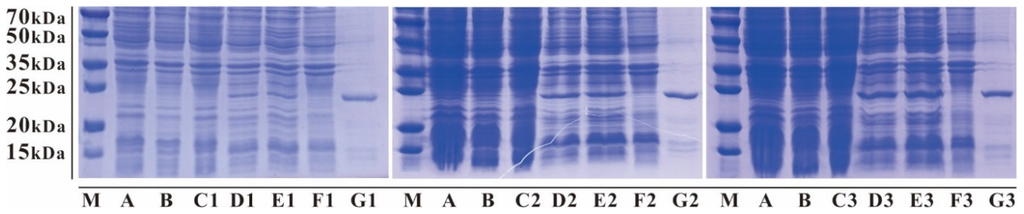
Figure 3.
SDS-PAGE analysis of the recombinant mNKLs. Recombinant vectors pET32-mNKLs and pET-32a(+) were transformed into E. coli Rosetta (DE3) and induced by 0.1 mM IPTG for 4 h at 37 °C. Induced bacterial cells including pET32-mNKLs were disrupted by ultrasonication, and the supernatant and precipitation were separated by centrifugation. The recombinant mNKLs was purified by affinity column chromatography. All the samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, and the protein was stained with Coomassie Blue R250 in the gel. M, molecular mass marker in kDa; Lane A–B, the E. coli Rosetta (DE3) including pET-32a(+) were not induced and induced, respectively; lane C, the E. coli Rosetta (DE3) including pET32-mNKLs were not induced; lane D, the full bacteria lysates of E. coli Rosetta (DE3) including pET32-mNKLs were induced; lane E–F, the supernatant and precipitation of the E. coli Rosetta (DE3) including pET32-mNKLs were induced; lane G, purified mNKLs. 1, 2 and 3 represented mNKL 1, mNKL 2 and mNKL 3, respectively.
3.3. Cleavage and Purification of mNKLs
The fusion proteins were cleaved by Recombinant Bovine Enterokinase Light Chain-His (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China) at an enterokinase cleavage site (DDDDK) and the 24.6 kDa Trx-His-mNKLs proteins were separated into His-tagged Trx (approximately 16.0 kDa) and mNKL (approximately 8.6 kDa) (Figure 4). However, there still are some unseparated Trx-His-mNKLs proteins in the cleaved products (Figure 4). Then the affinity column chromatography was used to purify the mNKL peptides in native condition and the unbinding proteins of three mNKLs transcripts were collected and concentrated (Figure 4).
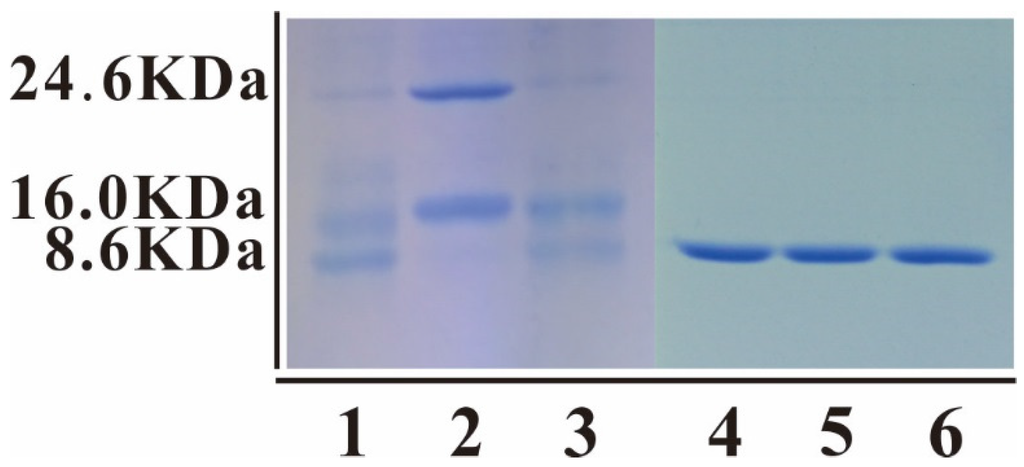
Figure 4.
Enterokinase cleavage of fusion mNKLs: 1, 2 and 3 were cleaved trxA-mNKL 1, trxA-mNKL 2 and trxA-mNKL 3, including not cleaved recombinant proteins (approximately 24.6 KDa), His-tagged Trx (approximately 16.0 kDa) and mNKLs (approximately 8.6 kDa); 4, 5 and 6 were purified and concentrated mNKL 1, mNKL 2 and mNKL 3, respectively.
3.4. Antibacterial Activity of the Peptide mNKLs
Antibacterial activity of recombinant mNKLs was assayed against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The chosen bacteria were spread on solidified Luria-Bertani medium and recombinant mNKLs were added into wells. Antibacterial activity of mNKL (5 µg/well) was evidenced by maximum zones of inhibition for Staphylococcus aureus (strain ATCC 25923) and E. coli (strain DH5α) (Figure 5).
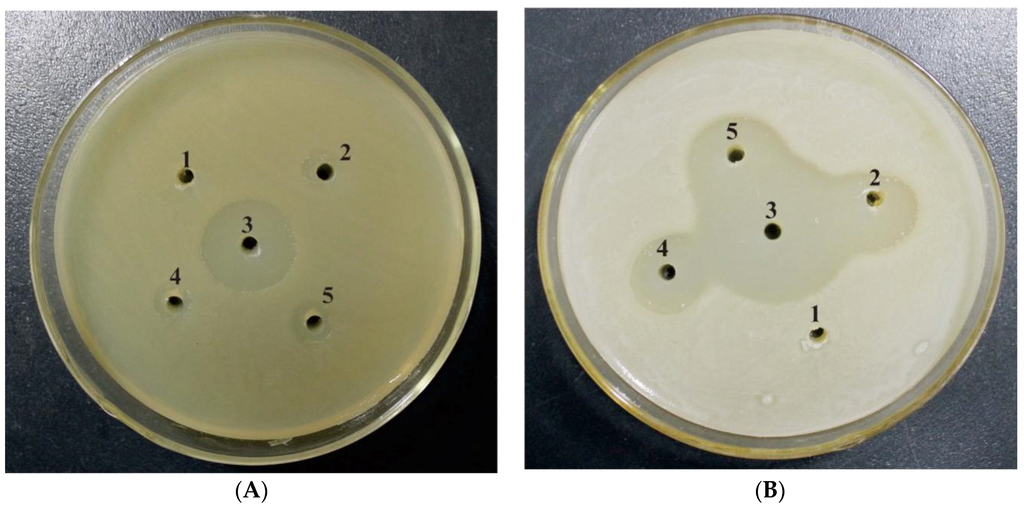
Figure 5.
Antibacterial activity analysis of combinational mNKLs against Staphylococcus aureus (A strain ATCC 25923) and E. coli (B strain DH5α). 1 was sterile ddH2O; 2, 4, 5 were recombinant mNKL1, mNKL2 and mNKL3 (5 μg/well), respectively; 3 was ampicillin (10 μg/well).
4. Discussion
By means of genetic engineering, desired antimicrobial peptide proteins are generated by several systems including eukaryotic systems such as the E. coli expression system [43] and the baculovirus expression vector system [39], and prokaryotic systems such as the yeast expression system [44,45]. E. coli is the least expensive and most efficient expression system for small proteins [40]. Advantages include rapid bacterial growth, quick expression and high product yields [46]. Several antibacterial peptides with biological activities have been expressed successfully by the E. coli expression system. According to the reports, Beta-defensin-4 from human [47,48], bovine LfcinB [36], porcine cecropin P1 [49], sarcotoxin IA from Sarcophaga peregrina larva [50] and adenoregulin from arboreal frog (Phyllomedusa bicolor) [51] were expressed with an E. coli expression system. Among aquatic species, previous reports have revealed that hepcidin from Tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) [52] and channel catfish [42], Piscidin-1 from Striped bass (Morone saxatilis) [53], LEAP-2 from Grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) [54] have been successfully expressed via an E. coli expression system. In our study, three mNKLs were expressed via an E. coli expression system and produced the approximately 24.6 kDa Trx-His-mNKLs. After purification, we finally received the concentration of mNKL 1 at 1.1 mg/mL, mNKL 2 at 1.4 mg/mL and mNKL 3 at 1.7 mg/mL.
Previous studies have shown that AMPs have high toxicity towards host strains. Therefore, different molecular chaperones are used in order to reduce toxicity and inclusion bodies to improve fusion protein expression [27]. The pET-32a(+) plasmid vector includes the Trx.Tag™ thioredoxin protein which is widely used as a fusion molecular chaperone for protein expression in E. coli [42]. The thioredoxin can dramatically increase the solubility of heterologous proteins synthesized in the E. coli cytoplasm and reduce the toxicity towards host strains, and the thioredoxin fusion proteins usually accumulate to a high level [55,50]. However, the thioredoxin fusion proteins will impress the activity of recombined AMPs. Enterokinase can specially recognize the amino acid sequence DDDDK and digest the peptide bond after the lysine residue. This is particularly important to get mature short peptides in the E. coli expression system such as mNKLs that are only 76 residues and account for only 34.9% of the fusion protein. In order to get a higher level of expression and soluble protein, different induction temperatures (25 °C, 30 °C and 37 °C), IPTG concentrations (0.1 mM to 1.0 mM) and induction times (1 h to 24 h) were optimized for recombinant mNKLs expression. In addition, a higher level of expression of fusion soluble Trx-His-mNKLs (approximately 24.6 kDa) was induced by 0.1 mM IPTG for 4 h at 37 °C. Subsequently, the mNKLs (approximately 8.6 kDa) were cleaved with Recombinant Bovine Enterokinase Light Chain-His and the enterokinase, Trx-His tag and unseparated Trx-His-mNKLs proteins were removed by the Ni-NTA-Sefinose column. However, the production of cleaved mNKLs was very low (approximately 0.1 mg/mL).
In recent years, an increasing number of antimicrobial peptides have been identified and extensive research has been conducted for the analysis of their structures and antimicrobial activity. Although some have also been reported to have potent activities against other microorganisms such as fungi, protozoa, and parasites [1,2,4,56], antibacterial activity is still the primary function of antimicrobial peptides. Although studies on the antibacterial mechanism of AMPs have been conducted widely, the precise mechanism of action is not fully understood. Regardless of their precise mode of action, AMPs consistently demonstrate antibacterial activity by interacting with bacterial cell membranes [57]. Similar to other members of the SAPLIP family, NK-lysins posses the general ability to interact with lipids [21]. This property gives rise to the function of its antibacterial activity. Several research results have shown that NK-lysins possess wide antibacterial activities against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. A report showed that porcine NK-lysin has high activity against Escherichia coli and Bacillus megaterium and moderate activity against Acinetobacter calcoaceticus and Streptococcus pyogeneis [26]. Human granulysin, a T cell product, exhibits antimicrobial activity towards Escherichia coli and M. tuberculosis [2]. Bovine NK-lysins have shown extensive antibacterial activity, especially against E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus [1,30]. However, there are only few reports on the antibacterial activity of NK-lysins from aquatic species. Only the Japanese flounder NK-lysin proteins have been identified to have antibacterial activity against various Gram-negative bacteria [29]. In the current study, although three distinct mNKLs all consisted of 76 amino acids, they showed diversity in amino acid sequences. We independently tested the antibacterial activities of the three mNKLs and determined that all three mNKLs have antibacterial activity against both Gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Gram-negative bacteria E. coli, but it is limited against S. aureus. For eukaryotic proteins in prokaryotic expression systems, the formation of disulphides is one of the crucial caveats associated with the protein correctly folding which will influence production activity. So it is necessary to know whether the disulphides have been completely correctly formed or the difference between antibacterial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria is existed in future study.
5. Conclusions
The studies reported here demonstrate conclusively that the protocol developed could be used for the production of channel catfish peptide mNKLs (type 1, 2, 3) with antibacterial activity and a broader antimicrobial spectrum. Further studies on the antimicrobial mechanism of NK-lysin and its activities against other microorganisms should be conducted in the future.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from the Youth Innovation Program of the Sichuan Science and Technology Department, P. R China (No. 2014-103), and the Sichuan Province Science and Technology support plan of the Sichuan Science and Technology Department, P. R China (2014JY0143).
Author Contributions
Shurui Cai, Jun Wang, Kaiyu Wang and Defang Chen conceived and designed the experiments; Shurui Cai and Jun Wang carried out the experiments, analyzed the data and drafted the paper; Tao Liu, Yukun Zeng and Xingli Wang participated in the protein expression and purification assay; Xiaowei Dong and Dongmei Wu assisted in cleaving the fusion protein and the antibacterial assay; Shurui Cai, Jun Wang and Kaiyu Wang revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ernst, W.A.; Thoma-Uszynski, S.; Teitelbaum, R.; Ko, C.; Hanson, D.A.; Clayberger, C.; Krensky, A.M.; Leippe, M.; Bloom, B.R.; Ganz, T.; et al. Granulysin, a T cell product, kills bacteria by altering membrane permeability. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 7102–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gansert, J.L.; Kieβler, V.; Engele, M.; Wittke, F.; Röllinghoff, M.; Krensky, A.M.; Porcelli, S.A.; Modlin, R.L.; Stenger, S. Human NKT cells express granulysin and exhibit antimycobacterial activity. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 3154–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcphee, J.B.; Hancock, R.E. Function and therapeutic potential of host defence peptides. J. Pept. Sci. 2005, 11, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenger, S.; Hanson, D.A.; Teitelbaum, R.; Dewan, P.; Niazi, K.R.; Froelich, C.J.; Ganz, T.; Thoma-Uszynski, S.; Melián, A.N.; Bogdan, C. An antimicrobial activity of cytolytic T cells mediated by granulysin. Science 1998, 282, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanetti, M.; Gennaro, R.; Skerlavaj, B.; Tomasinsig, L.; Circo, R. Cathelicidin peptides as candidates for a novel class of antimicrobials. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2002, 8, 779–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zasloff, M. Inducing endogenous antimicrobial peptides to battle infections. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8913–8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boman, H.G.; Nilsson, I.; Rasmuson, B. Inducible antibacterial defence system in drosophila. Nature 1972, 237, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guaní-Guerra, E.; Santos-Mendoza, T.; Lugo-Reyes, S.O.; Terán, L.M. Antimicrobial peptides: General overview and clinical implications in human health and disease. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 135, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.-S.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Bang, H.-S.; Yun, E.-Y.; Kim, S.-R.; Suh, H.-J.; Kang, B.-R.; Nam, S.-H.; Jeon, J.-P. Isolation and characterization of a defensin-like peptide (Coprisin) from the dung beetle, Copris tripartitus. Int. J. Pept. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Boman, A.; Sun, C.; Andersson, M.; Jörnvall, H.; Mutt, V.; Boman, H.G. Antibacterial peptides from pig intestine: Isolation of a mammalian cecropin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 9159–9162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rollins-Smith, L.A. The role of amphibian antimicrobial peptides in protection of amphibians from pathogens linked to global amphibian declines. BBA Biomembr. 2009, 1788, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pukala, T.L.; Bowie, J.H.; Maselli, V.M.; Musgrave, I.F.; Tyler, M.J. Host-defence peptides from the glandular secretions of amphibians: Structure and activity. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 368–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrocal-Lobo, M.; Molina, A.; Rodríguez-Palenzuela, P.; García-Olmedo, F.; Rivas, L. Leishmania donovani: Thionins, plant antimicrobial peptides with leishmanicidal activity. Exp. Parasitol. 2009, 122, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valero, Y.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.A.; Cuesta, A. Biological role of fish antimicrobial peptides. In Antimicrobial Peptides: Properties, Functions and Role in Immune Response; Nova Science Publisher: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 31–60. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, A.M.; Weis, P.; Diamond, G. Isolation and characterization of pleurocidin, an antimicrobial peptide in the skin secretions of winter flounder. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 12008–12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauth, X.; Shike, H.; Burns, J.C.; Westerman, M.E.; Ostland, V.E.; Carlberg, J.M.; Van Olst, J.C.; Nizet, V.; Taylor, S.W.; Shimizu, C. Discovery and characterization of two isoforms of moronecidin, a novel antimicrobial peptide from hybrid striped bass. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 5030–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajanbabu, V.; Chen, J.-Y. Applications of antimicrobial peptides from fish and perspectives for the future. Peptides 2011, 32, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-A.; Zou, J.; Chang, C.-I.; Secombes, C.J. Discovery and characterization of two types of liver-expressed antimicrobial peptide 2 (LEAP-2) genes in rainbow trout. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2004, 101, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanetti, M. Cathelicidins, multifunctional peptides of the innate immunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 75, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppenheim, J.; Biragyn, A.; Kwak, L.; Yang, D. Roles of antimicrobial peptides such as defensins in innate and adaptive immunity. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, ii17–ii21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruhn, H.; Riekens, B.; Berninghausen, O.; Leippe, M. Amoebapores and NK-lysin, members of a class of structurally distinct antimicrobial and cytolytic peptides from protozoa and mammals: A comparative functional analysis. Biochem. J. 2003, 375, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, P.; Liu, Z. NK-lysin of channel catfish: Gene triplication, sequence variation, and expression analysis. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 1676–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concha, M.I.; Smith, V.J.; Castro, K.; Bastias, A.; Romero, A.; Amthauer, R.J. Apolipoproteins A-I and A-II are potentially important effectors of innate immunity in the teleost fish Cyprinus carpio. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 2984–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, S.; Ross, N.W.; MacKinnon, S.L. Myxinidin, a novel antimicrobial peptide from the epidermal mucus of hagfish, Myxine glutinosa L. Mar. Biotechnol. 2009, 11, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.B.; Lee, J.H.; Park, I.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, S.C. A novel antimicrobial peptide from the loach, Misgurnus anguillicaudatus. FEBS Lett. 1997, 411, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Gunne, H.; Agerberth, B.; Boman, A.; Bergman, T.; Olsson, B.; Dagerlind, Å.; Wigzell, H.; Boman, H.; Gudmundsson, G. NK-lysin, structure and function of a novel effector molecule of porcine T and NK cells. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1996, 54, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liepinsh, E.; Andersson, M.; Ruysschaert, J.-M.; Otting, G. Saposin fold revealed by the NMR structure of NK-lysin. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1997, 4, 793–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.; Gunne, H.; Agerberth, B.; Boman, A.; Bergman, T.; Sillard, R.; Jörnvall, H.; Mutt, V.; Olsson, B.; Wigzell, H. NK-lysin, a novel effector peptide of cytotoxic T and NK cells. Structure and CDNA cloning of the porcine form, induction by interleukin 2, antibacterial and antitumour activity. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hirono, I.; Kondo, H.; Koyama, T.; Arma, N.R.; Hwang, J.Y.; Nozaki, R.; Midorikawa, N.; Aoki, T. Characterization of Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) NK-lysin, an antimicrobial peptide. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 22, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endsley, J.J.; Furrer, J.L.; Endsley, M.A.; McIntosh, M.A.; Maue, A.C.; Waters, W.R.; Lee, D.R.; Estes, D.M. Characterization of bovine homologues of granulysin and NK-lysin. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 2607–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, E.G.; Sang, Y.; Rush, B.; Zhang, G.; Blecha, F. Molecular cloning and characterization of equine NK-lysin. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2005, 105, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.O.; Jang, H.-J.; Han, J.Y.; Womack, J.E. Chicken NK-lysin is an alpha-helical cationic peptide that exerts its antibacterial activity through damage of bacterial cell membranes. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Bao, B.; Wang, Y.; Peatman, E.; Liu, Z. Characterization of a NK-lysin antimicrobial peptide gene from channel catfish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006, 20, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereiro, P.; Varela, M.; Díaz-Rosales, P.; Romero, A.; Dios, S.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B. Zebrafish NK-lysins: First insights about their cellular and functional diversification. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 51, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Long, H.; Sun, L. A NK-lysin from Cynoglossus semilaevis enhances antimicrobial defense against bacterial and viral pathogens. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 40, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.-J.; Wang, J.-H.; Shan, A.-S.; Teng, D.; Yang, Y.-L.; Yao, Y.; Yang, G.-P.; Shao, Y.-C.; Liu, S.; Zhang, F. Fusion expression of bovine lactoferricin in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2006, 47, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocabas, A.M.; Li, P.; Cao, D.; Karsi, A.; He, C.; Patterson, A.; Ju, Z.; Dunham, R.A.; Liu, Z. Expression profile of the channel catfish spleen: Analysis of genes involved in immune functions. Mar. Biotechnol. 2002, 4, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pridgeon, J.W.; Mu, X.; Klesius, P.H. Expression profiles of seven channel catfish antimicrobial peptides in response to Edwardsiella ictaluri infection. J. Fish Dis. 2012, 35, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demain, A.L.; Vaishnav, P. Production of recombinant proteins by microbes and higher organisms. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terpe, K. Overview of bacterial expression systems for heterologous protein production: From molecular and biochemical fundamentals to commercial systems. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 72, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, B.; Sumner, I.; Goodenough, P. Isolation, renaturation, and formation of disulfide bonds of eukaryotic proteins expressed in Escherichia coli as inclusion bodies. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1993, 41, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Zhao, D.-M.; Wen, Y. Expression, purification and antibacterial activity of the channel catfish hepcidin mature peptide. Protein Expr. Purif. 2014, 94, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y. Carrier proteins for fusion expression of antimicrobial peptides in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2009, 54, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidner, M.; Taupp, M.; Hallam, S.J. Expression of recombinant proteins in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. J. Vis. Exp. 2010, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, F.; Xu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Gu, D. Expression of recombinant hybrid peptide cecropinA(1–8)–magainin2(1–12) in Pichia pastoris: Purification and characterization. Protein Expr. Purif. 2006, 50, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neidhardt, F.C.; Curtiss, R. Escherichia coli and Salmonella: Cellular and Molecular Biology; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Huang, L.; Peng, L.; Wang, F.; Cen, P. High-level production of bioactive human beta-defensin-4 in Escherichia coli by soluble fusion expression. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 72, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Ai, H.-X.; Song, R.; Liang, Z.-N.; Li, J.-F.; Zhang, S.-Q. Expression and purification of moricin CM4 and human β-defensins 4 in Escherichia coli using a new technology. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 165, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Q.; Ye, J.; Mo, J.; Zhang, H.-Z. Fusion expression of cecropin P1 in Escherichia coli and its antimicrobial activity analysis. Food Drug 2011, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Skosyrev, V.S.; Kulesskiy, E.A.; Yakhnin, A.V.; Temirov, Y.V.; Vinokurov, L.M. Expression of the recombinant antibacterial peptide sarcotoxin IA in Escherichia coli cells. Protein Expr. Purif. 2003, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Y.; Luo, Q.; Wei, D. Expression and purification of antimicrobial peptide adenoregulin with C-amidated terminus in escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2005, 40, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Tao, Y. Hepcidin from tilapia, oreochromis niloticus: Its fusion expression in Escherichia coli and antimicrobial activity. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Agric. Sci.) 2012, 30, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, W.J.; Hwang, D.K.; Park, E.J.; Kim, Y.M.; Chae, Y.K. Recombinant expression, isotope labeling, refolding, and purification of an antimicrobial peptide, piscidin. Protein Expr. Purif. 2007, 51, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Li, J.-L.; Yue, G.-H.; Fu, J.-J.; Zhou, Z.-F. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of the liver-expressed antimicrobial peptide 2 (LEAP-2) gene in grass carp. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2010, 133, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavallie, E.R.; Diblasio, E.A.; Kovacic, S.; Grant, K.L.; Schendel, P.F.; Mccoy, J.M. A thioredoxin gene fusion expression system that circumvents inclusion body formation in the E. coli cytoplasm. Biotechnology 1993, 11, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, T.; Bruhn, H.; Gaworski, I.; Fleischer, B.; Leippe, M. NK-lysin and its shortened analog NK-2 exhibit potent activities against Trypanosoma cruzi. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, R.E.; Rozek, A. Role of membranes in the activities of antimicrobial cationic peptides. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 206, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).