Abstract
The treatment of landfill leachate, due to its great polluting load, is a very difficult task. In particular, the abatement of high ammonium concentrations represents one of the main issues. Among the available techniques, struvite precipitation is an effective method for the removal and recovery of NH4+ load. However, due to the lack of phosphorus and magnesium amounts, the struvite formation results in an expensive process in the leachate treatment. To overcome this issue, in the present work, we developed a simple and suitable method for ammonium removal by the multiple recycling of struvite decomposition residues. In this regard, a procedure for acid dissolution of struvite, produced by using industrial grade reagents, was initially defined. The effect of pH, temperature, and acid type was investigated. The experimental results proved the effectiveness of both hydrochloric and acetic acid, which allow a high and selective release of ammonium at T = 50 °C and pH = 5.5. The multiple reuse of decomposition products, combined with the supplementation of a small quantity of phosphorus and magnesium at molar ratios of n(N):n(Mg):n(P) = 1:0.05:0.05, guarantees stable NH4+ abatement of about 82%. The proposed process allows a cost saving of around to 74% and can be easily applied in industrial treatment plants.
1. Introduction
The leachates generated as result of water infiltration and decomposition of organic matter in landfills of urban wastes are wastewaters with one of the highest polluting potentials [1,2,3,4,5]. Their uncontrolled disposal can produce severe deterioration of quality of soil and water bodies [4]. The characteristics of these wastewaters depend mainly on the type of landfill site and the kind and degradation degree of wastes. Methanogenic leachates (produced in mature landfills) show particularly high content of ammonium nitrogen and low biodegradable compounds, as well as a great amount of dissolved salts [3]. These characteristics make the treatment of methanogenic leachates, in conventional biological plants [6,7], hardly applicable. In recent years, different physicochemical techniques have been proposed for the treatment of these wastewaters. Specifically, for the removal of low biodegradable compounds, advanced oxidation processes represent a suitable option [8,9,10,11,12,13]. However, the development of effective and economic methods for the abatement of the high nitrogen loads of wastewaters still represents a big issue [14,15]. In this regard, the precipitation of ammonium as struvite is a promising approach, due to its high process efficiency and the ease of management [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27]. Struvite crystals are composed of Mg+2, NH4+, and PO43− in equimolar amounts (MgNH4PO4∙6H2O) [16,17]. The formation of magnesium ammonium phosphate occurs when the concentration of its elements exceeds the solubility product under basic conditions [28]. Despite its high efficiency, struvite precipitation for ammonia removal from landfill leachate is generally a costly treatment. Indeed, due to the lack of Mg2+ and PO43− ions with respect to the ammonium concentrations, great quantities of chemicals must be provided. With the aim to reduce the overall treatment cost, various alternative magnesium sources—such as the byproducts of magnesium oxide [29,30], magnesite mineral [31], and seawater [32]—were efficiently exploited in the treatment of highly concentrated wastewaters. However, the phosphate reagents, being scarce and very expensive, generally represent a large part of the overall outlay. Nevertheless, few researches have paid attention to this aspect [4]. In recent years, the authors have proposed the bone meal of meat waste as an unconventional phosphorus reagent [33,34,35]. The use of this byproduct—in combination with seawater bittern, a residue of marine salt manufacturing—results in an effective and low-expense method for the ammonia removal and recovery from high-strength wastewaters [33,34]. Furthermore, the struvite produced through this method is characterized by a remarkable fertilizer potential [35]. Despite these positive aspects, the supply of unconventional reagents may be difficult and could make the process barely applicable in industrial treatment plants. Moreover, the disposal of struvite could present a problem if its exploitation as fertilizer were not possible. To overcome this issue, the recycling of struvite decomposition products can represent a valid solution to reduce the operation costs. In fact, struvite decomposition causes the release of ammonium, and the resulting residues can be exploited as P and Mg sources for the cyclical treatment of wastewaters. Several decomposition methods, including struvite pyrogenation and acidolysis, have been recently proposed [14,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44]. The pyrogenation in alkali solutions has widely proved its effectiveness for ammonium release. However, in this process, temperatures higher than 90 °C are generally required [36]. Moreover, the possible dispersion of ammonia gas in the atmosphere could hinder the process application in field conditions [14]. Struvite decomposition in an acidic environment can be efficiently performed at lower operating temperature and avoids the release of ammonia gas. In fact, the ammonium ions are dissolved in an acid solution, which could be potentially reused as a fertilizer source [14]. This approach is similar to that of stripping processes, which require the absorption of stripped ammonia into strong acids [8]. Anyhow, many aspects of struvite acid decomposition in the treatment of real wastewaters must be further investigated, such as the type of acid usable for struvite dissolution and the procedure for the use of residues in industrial processes. In this regard, in the present study, several experiments were carried out to optimize the procedures for acid dissolution of struvite produced from landfill leachate and for recycling of decomposition residues. For these purposes, (I) the struvite was obtained from a methanogenic landfill leachate once the treatment was optimized using industrial-grade reagents; (II) the conditions for struvite acid decomposition, using inorganic and organic acids, were investigated; (III) three different methods for reusing residues , applicable for field treatments, were tested; and (IV) an economic analysis of the proposed process was conducted.
2. Description of Experiments
2.1. Materials
The experiments were performed on samples of leachate generated in a landfill of urban solid wastes sited near Cosenza (Southern Italy). The samples were stored at 4 °C in containers of 15 L; the main chemical parameters are reported in Table 1. During the tests, reagents of industrial grade were used and no procedures for their purification were adopted.

Table 1.
Characteristics of landfill leachate.
2.2. Struvite Production
The tests were carried out both to identify the dosages of phosphorus and magnesium reagents and the modality of reactant addition to maximize the ammonium abatement. MgCl2∙6H2O solution (50 g/50 mL) and phosphoric acid (75% w/v) were used as magnesium and phosphorus sources. In a first set of experiments, n(Mg):n(N) and n(P):n(N), molar ratios between 1 and 1.5, were tested. In these tests, the solutions of Mg and P were added to leachate samples until the established values of n(Mg):n(N) and n(P):n(N) molar ratios were reached. Afterwards, the mixture pH was set to 9, identified as the most favorable for struvite precipitation [3,31], by means of instantaneous additions of NaOH (40% w/v). The tests were carried out on leachate volumes of 200 mL and mixed at 300 rpm for 15 min by means of magnetic stirrers. In a second set of experiments, the solutions of magnesium, phosphorus, and NaOH were contextually dosed. Specifically, the chemicals were gradually fed to leachate so as to maintain the pH constantly around to 9. These tests were conducted on leachate volumes of 1.5 L by testing n(Mg):n(N) and n(P):n(N) ratios of 1.1, 1.2, and 1.3. For this purpose, beakers of 3 L, equipped with mechanical stirrers, were used. The reaction mixtures were continuously mixed (300 rpm) for an additional 15 min after addition of the reactants was completed.
All the experiments were conducted at room temperature (20 ± 2 °C) and pressure. After the reaction time, the mixtures were left to settle for about 30 min to promote the struvite sedimentation. The liquid phase was then sampled for analytic determinations. The precipitate, produced applying the more favorable conditions identified, was recovered and directly used for decomposition tests.
2.3. Struvite Decomposition
In order to define the optimal procedure for struvite decomposition, the effects of temperature, pH, and acid type were investigated. In particular, the experiments were carried out at 20 °C and 50 °C, at pH of 3.5 and 5.5, and using both inorganic and organic acids. Specifically, H2SO4 (95%), HCl (32%), HNO3 (60%), and CH3COOH (80%) were applied as solubilizing agents.
The wet precipitate recovered from the treatment of landfill leachate was directly used for decomposition tests; no washing phases or drying steps were adopted for its purification. In each test, 25 g of wet solid was put into a 100 mL beaker containing 20 mL of deionized water. The temperature of mixture was adjusted by means of a heating plate and then the pH value was set by the addition of acid reactants. The mixture was magnetically mixed at 400 rpm for 2 h. At the end of the treatment, after a settling time of 1 h, the liquid phase was taken to be subjected to the determination of both ammonium and phosphorus content as reported in the literature [14]. Once the optimal decomposition conditions were defined, the settled solids were recovered and used, without purification, for recycling tests.
2.4. Reuse of Struvite Decomposition Residues
A first set of experiments was carried out with the aim of identifying the quantity of struvite decomposition residues required to efficiently remove the ammonium load. In this regard, wet decomposition products of 7.5%, 8.5%, 10%, 20%, 30% (w/v) were tested for the treatment of 200 mL of raw landfill leachate. The tests were performed using beakers of 400 mL equipped with magnetic stirrers. In each test, the struvite residues were mixed with leachate before the pH was set to about 9 using NaOH. A reaction time of 2 h was adopted. The process performance was investigated by analyzing the supernatant withdrawn after a settling phase of 1 h.
For multiple recycling of decomposition residues, the following sequential batch operating mode was adopted, using the same equipment just abovementioned: (1) struvite was produced from the treatment of raw leachate according to the optimal conditions identified by means of the experiments described in Section 2.1; (2) the supernatant was withdrawn; (3) an appropriate amount of settled solid was directly decomposed in the reactor through the identified optimal procedure; (4) after a settling step, the liquid phase was taken; (5) the raw landfill leachate was fed into the beaker containing the decomposed solids; (6) the pH was set to 9 and a reaction phase was conducted by stirring the mixture (300 rpm) for 2 h; steps 2–6 were repeated several times. In order to identify the more favorable conditions for phase 6 , three treatment methods were tested. For two of these, the treatment cycles for ammonia removal were conducted by exclusively exploiting the struvite decomposition products, without any supply of Mg and P reactants. For the first method, the process pH was set by means of NaOH, but for the second method air insufflation (flowrate of 10 L/min) was used. In the third method, MgCl2∙6H2O and H3PO4 were supplied at a molar ratio of n(N):n(Mg):n(P) 1:0.05:0.05 (5% of magnesium and phosphorus molar amounts required for struvite production from raw leachate); the pH was set by means of chemical addition (NaOH, 40% w/v). The supernatant formed at the end of each cycle was collected for chemical characterization.
2.5. Analytical Methods
The liquid samples were filtered through a 0.45 μm filter before analytical determinations. The temperature, conductivity, and pH were estimated by means of a multiparametric probe; COD (chemical oxygen demand) and alkalinity by means of titration techniques; BOD5 (biochemical oxygen demand) by respirometric procedure; ammonium nitrogen and reactive phosphorus through UV spectrophotometric methods; and atomic adsorption spectrophotometry (GBC Scientific Equipment, Braeside (Victora), Australia ) was used for determination of magnesium, calcium, and potassium [45]. The total (TS) and volatile (VS) suspended solids were measured by drying the sample, respectively, at 105 °C and 550 °C. The solid compound produced during the various processes was washed using deionized water, filtered at 0.45 μm, and dried at room temperature before characterization by means of X-ray diffraction (GNR Analytical Instruments, Agrate Conturbia (Novara), Italy) and chemical analysis. The analysis of the elements was performed after an acid digestion of dried sample, which was conducted according to the procedure described in a previous work [35].
Each measurement was conducted five times and the mean value was calculated; the relative standard deviation was always lower than 5%
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Struvite Production
The leachate used in this study showed a characteristic composition of wastewaters produced in landfills in a methanogenic phase (Table 1). Indeed, a basic pH of around 8.15 and a high alkalinity, close to 13 gCaCO3/L, were detected. Moreover, the value of conductivity, almost 23 mS/cm, denotes a great quantity of dissolved salts. The low BOD5/COD ratio indicates a low content of degradable compounds. The N-NH4+ amount was higher than 2.6 g(N)/L and, with respect to this value, the concentrations of magnesium and phosphorus were negligible, as highlighted by the n(M):n(Mg):n(P) molar ratios. This clearly makes the use of great amounts of reactants necessary to allow struvite production.
With the aim of identifying the most favorable dosages of magnesium and phosphorous reactants, a set of tests was carried out by testing n(Mg):n(N) and n(P):n(N) ratios between 1 and 1.5. In these tests, all the reagents were instantly dosed. In particular, the pH of mixture was corrected after the initial addition of Mg and P solutions. This operating modality was selected on the basis of our previous works, which demonstrated that the initial setting of pH, followed by the dosages of magnesium and phosphorus, is not suitable for struvite precipitation [34]. Indeed, the acid characteristics of P and Mg reagents, if they were fed after the base addition, produce an instantaneous reduction of pH, which hinders the struvite crystallization. The results of the tests conducted in this study, instead, showed satisfactory process performances with the adopted procedure. In particular, ammonium removals of about 72% were obtained using n(P):n(N) = 1 and adjusting the n(Mg):n(N) ratio between 1 and 1.2 (Figure 1). By holding the phosphorus dosage constant and increasing the magnesium molar amount, the efficiency slightly increased to 78%. The increase of the phosphorus dose to 1.2, for a given n(Mg):n(N) ratio, produced an almost proportional increase in ammonium abatement. This growth was contextually accentuated by the increase of magnesium dosage up to a value of 1.2, reaching maximum abatements close to 95% (Figure 1). The necessity to dose higher amounts of Mg and P reagents, with respect to the stoichiometric ratio (n(N):n(Mg):n(P) = 1:1:1), is imputable to the precipitation, besides to struvite particles, of further salts composed of magnesium and phosphorus, such as magnesium and calcium phosphates [22]. The formation of these products removes some of the Mg2+ and PO43− available for struvite crystallization, therefore, an overdose of reagents is necessary. In further researches, the benefit of overdosing magnesium and phosphorus was verified [18,19,32]. Clearly, the optimal dosages reported in the literature are related to many factors, such as the characteristics of treated wastewaters, the exploited reactants, and the applied process conditions. In the present study, as abovementioned, the highest ammonium abatements were reached with n(N):n(Mg):n(P) = 1:1.2:1.2.
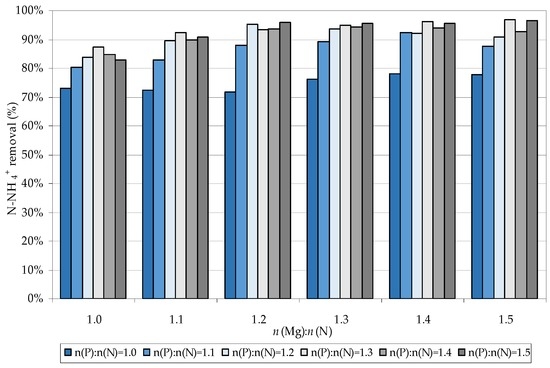
Figure 1.
Ammonium removal during the tests conducted by using industrial grade reagents.
In addition to NH4+ abatement, the phosphorus recovery was monitored since this element is undesirable in treated wastewaters. The recovery performance was always close to 100% for the tests conducted with stoichiometric ratios n(P):n(N) = 1, while it generally decreased with the increase of P addition (Figure 2). These reductions were much more pronounced for the lower magnesium additions (Figure 2). Indeed, as expected, the recovery efficiency is worse when the phosphorus dosage greatly exceeds that of magnesium.
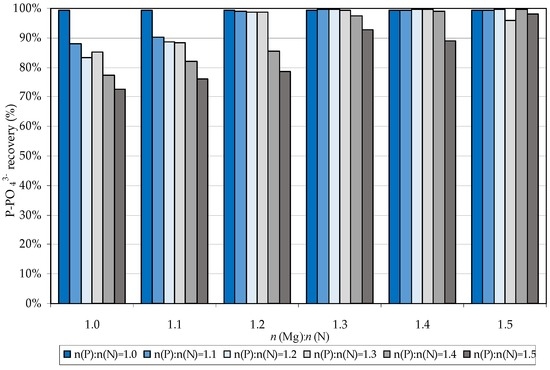
Figure 2.
Phosphorus recovery during the tests conducted by using industrial grade reagents.
Anyhow, the actual recovered mass of added phosphorus was, for each tested dosage, higher than that of ammonium removed. This confirmed the coprecipitation, with struvite, of other types of insoluble compounds containing phosphorus [22,23]. The production of these compounds, obviously, is lower for the operating conditions for which the maximum ammonium was removed. Nevertheless, the discussed results confirmed that struvite precipitation can be efficiently performed by using industrial-grade reagents.
However, in order to define a more favorable procedure for the application in real treatment plants, other tests were carried out. Indeed, the great volumes of reagents (of the order of cubic meters) required in industrial processes must be dosed slowly to avoid a great formation of foams, which result from rapid pH changes. In this regard, the next experiments were performed by providing the simultaneous dosage of both Mg and P reagents with NaOH. This operating modality makes the process management easier and impedes the foam generation, by maintaining the pH at around 9. The tests were conducted on leachate volumes of 1.5 L, applying flow rates for the dosage of P, Mg, and NaOH solutions of about 5 mL/min, 15 mL/min, 10 mL/min, respectively.
On the basis of the results discussed above, n(N):n(Mg):n(P) of 1:1.1:1.1, 1:1.2:1.2, and 1:1.3:1.3 were tested. The detected results showed process performances in line with those reached in previous tests. In fact, an ammonium abatements near 92% (Figure 3) and a complete phosphorus recovery (Figure 4) were reached with n(Mg):n(N) and n(P):n(N) ratios equal to 1.2. The high efficiencies indicate that the struvite formation occurs gradually as the chemicals are fed, and prove the applicability of the tested technique. The X-ray diffractogram of collected solid (Figure 5), produced by applying this dosage modality, proved the formation of struvite crystals. Indeed, the position and intensity of main peaks correspond to those of struvite standard. Anyhow, the n(N):n(Mg):n(P) molar ratios were of about 1:1.18:1.17, that, if compared with the stoichiometric values of pure struvite (1:1:1), confirm the formation of further insoluble amorphous salts of phosphorus and magnesium [22,23]. The wet precipitate, characterized by solid of 22% (humidity of 78%), was exploited in the struvite decomposition tests.
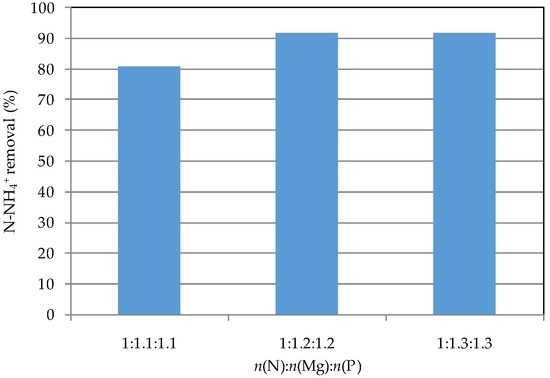
Figure 3.
Ammonium removal during the tests conducted with the simultaneous dosage of reagents.
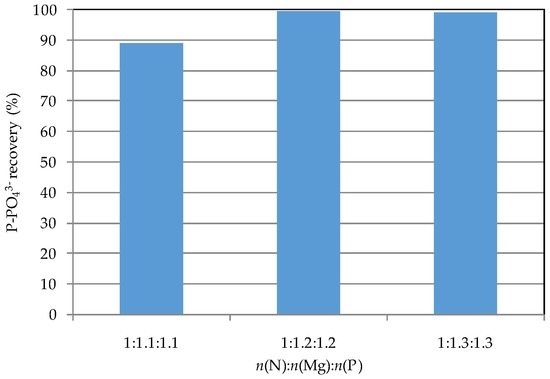
Figure 4.
Phosphorus recovery during the tests conducted with the simultaneous dosage of reagents.
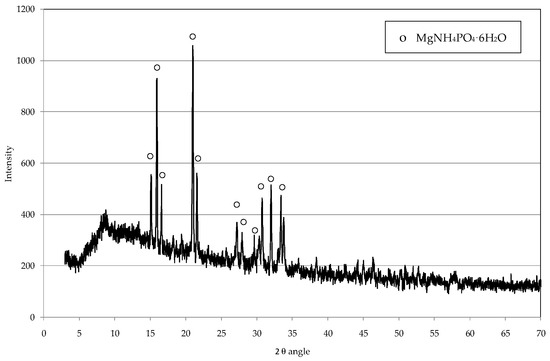
Figure 5.
Diffractogram of solid produced from the leachate treatment using industrial-grade reagents, simultaneously dosed.
3.2. Struvite Decomposition
The decomposition of struvite aims to maximize the dissolution of ammonium and, on the contrary, to minimize the release of phosphorus. In this way, the solid residues could be properly used as reactants for the NH4+ removal in the subsequent treatments of raw leachate. During the tests, the influence of pH, temperature, and acid type on release of ammonium and phosphorus from wet struvite was investigated. The results of conducted experiments showed that, at room temperature, for both the tested values of pH, the amount of dissolved ammonium was around to 0.7 mmol (N)/g (millimoles per gram of decomposed solid) when using hydrochloric and acetic acid as solubilizing agents (Figure 6). Lower releases, between 0.4–0.5 mmol (N)/g, were observed with sulfuric and nitric acid. The effects of reactant used on struvite decomposition were much more pronounced at the temperature of 50 °C. In fact, small rises in dissolved NH4+ amounts were observed by increasing the temperature in the tests with H2SO4 and HNO3 (Figure 6). On the contrary, a notable growth in ammonium release was detected, respect the values observed at 20 °C, by exploiting hydrochloric acid or acetic acid. Moreover, with these reagents, at 50 °C the solubilization performance was positively affected by the pH reduction. In fact, for a process pH of 5.5, the monitored amount of dissolved ammonium was of about 1.5 mmol (N)/g, which increased, at pH 3.5, up to about 1.9 and 2.18 for HCl and CH3COOH, respectively (Figure 6). The use of these two acids was advantageous also in terms of phosphorus release. In fact, in these cases, the lowest amounts of dissolved phosphate were observed (Figure 7). This is clearly a positive aspect because the phosphorus remains as an insoluble form, and the residual solid can be efficiently reused for the treatment of raw leachate. Also the use of nitric acid produced low solubilization of phosphates, while the detected dissolved amounts were much higher in the tests carried out with sulfuric acid. This high phosphorus release denotes a poor applicability of H2SO4 for struvite decomposition.
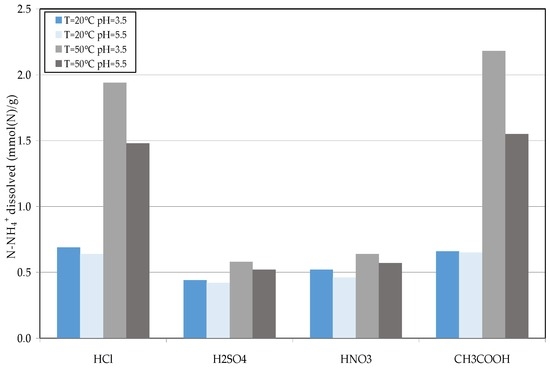
Figure 6.
N-NH4+ release (millimoles per gram of decomposed solids) detected during the struvite decomposition tests.
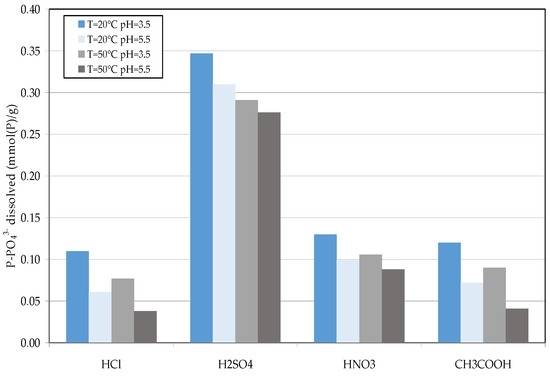
Figure 7.
P-PO43− release (millimoles per gram of decomposed solid) detected during the struvite decomposition tests.
For every reactant tested, the experimental results showed a reduction of phosphorus solubilization in response of pH and temperature increase (Figure 7).
This causes a corresponding increase of molar ratio between the dissolved ammonium and phosphates n(N):n(P), as it can be noticed by the analysis of trends plotted in Figure 8. Clearly, this behavior is much more pronounced when using HCl and CH3COOH. The increase of the n(N):n(P) ratio indicates that the increase of temperature to 50 °C and pH to 5.5 promotes a more selective release of NH4+ with respect to phosphorus. Indeed, despite that the maximum ammonium dissolution occurred at pH 3.5, the corresponding amount of solubilized P limits the n(N):n(P) values. These findings are in agreement with Zhang et al. [14], who observed maximum n(N):n(P) molar ratios similar to those detected in this study. The increase of the n(N):n(P) ratio with the process pH from 3.5 to 5.5 is clearly a positive aspect because it allows reduction of the acid amount required during the decomposition phase. Furthermore, as above mentioned, the detected results showed a great effect of the acid type on struvite decomposition. In particular, a low applicability of sulfuric and nitric acid was found; instead, acetic acid proved to have a high efficiency, comparable with that of HCl. Indeed, the maximum n(N):n(P) values were obtained with hydrochloric and acetic acid at 50 °C and pH = 5.5. Anyhow, as HCl is easily available in industrial treatment plants, this reagent was used to perform the struvite decomposition in the subsequent cyclical tests. The precipitate obtained with the defined operating conditions (50 °C and pH = 5.5) was characterized by a dry solid content of about 20% (humidity of 80%) and the n(N):n(P):n(Mg) ratios were about 1:3.15:3.21.
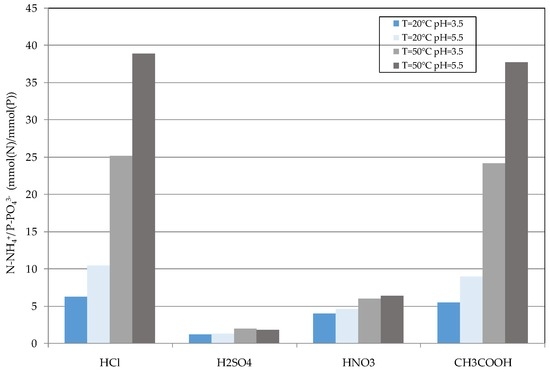
Figure 8.
N:P molar ratio of dissolved ammonium and phosphorus, detected during the struvite decomposition tests.
The X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis showed the appearance of typical peaks of newberyite (MgHPO4∙3H2O) [21] and a substantial intensity reduction of peaks of struvite with respect to those observed on precipitate before the acidolysis (Figure 9). These results confirm that, in proper acid conditions, part of struvite is converted in hydrated magnesium phosphates with the release of ammonium in the acid solution, according to the following reaction:
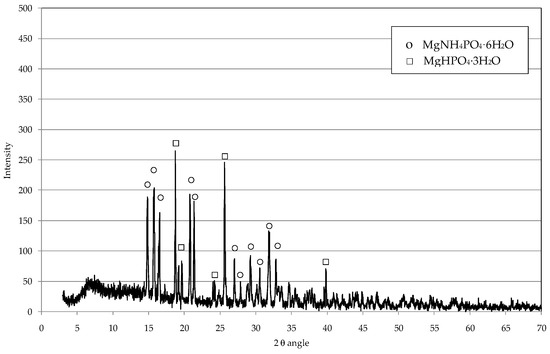
Figure 9.
Diffractogram of struvite residues obtained by using HCl at 50 °C and pH = 5.5.
The volume of residual acid solution was only 8% of the leachate treated to obtain the struvite subjected to the dissolution procedure. Therefore, the volume to be managed after the decomposition step is quite low. Furthermore, this solution could be exploited as a fertilizer source as it is characterized by NH4+ concentrations of up to 18 g(N)/L. In fact, it is mainly composed of ammonium chloride, a compound commonly used as inorganic fertilizer [14]. Obviously, the practical application of residual liquid phase for fertilizers production must be investigated.
3.3. Reuse of Struvite Decomposition Residues
The first tests were conducted to identify the optimal quantity of wet solid, obtained through the defined decomposition procedure, for ammonia removal from raw landfill leachate. In this regard, amounts of 7.5%, 8.5%, 10%, 20%, and 30% (w/v) of wet residues were used to treat 200 mL of leachate at pH = 9. The experimental results showed that NH4+ abatements of about 82% can be obtained by using amounts of struvite residues up to 8.5% (Figure 10). The efficiencies increased up to around 94% with the dosage of 10%, beyond which only further restricted performance increases were observed.
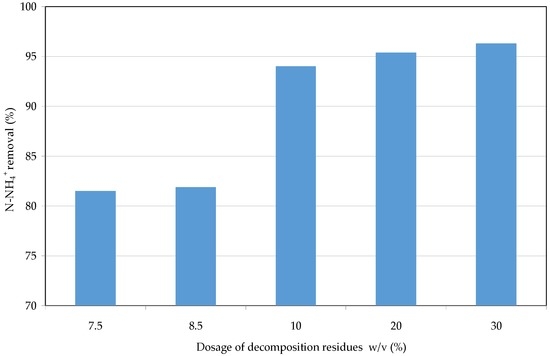
Figure 10.
N-NH4+ removal detected by changing the dosage of struvite residues for the treatment of raw leachate.
The above results prove that ammonia removal can be efficiently performed by using struvite decomposition products as source of magnesium and phosphorus. In fact, in basic environment, newberyite reacts with the NH4+ ion to again form MgNH4PO4∙6H2O, according to the following reaction [14]:
This was confirmed by the XRD analysis of solids recovered after the leachate treatment, which showed mainly the peaks characteristic of struvite, while those representative of MgHPO4∙3H2O were much less pronounced (Figure 11). Furthermore, the results of conducted tests showed that for used amounts of decomposition residues lower than 20%, residual phosphorus and magnesium concentrations were in line with those of raw leachate. Beyond this dosage, moderate increases, up to 35 mg(P)/L and 72 mg(Mg)/L, were observed. These increases are attributable to the dissolved phosphorus and magnesium contained in the liquid phase of struvite residues. On the basis of the above results, an amount of 10% was assumed as optimal for the treatment of raw leachate. Therefore, by considering the humidity (80%) of decomposition products, the actual ratio between the dry struvite residues and leachate is about 2% (w/v).
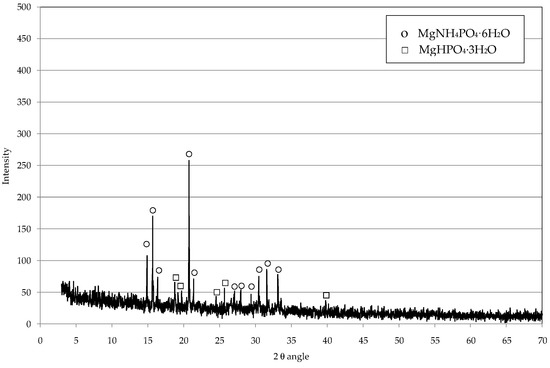
Figure 11.
Diffractogram of precipitate produced by reusing the struvite decomposition residues for the treatment of raw leachate.
The above dose was exploited to begin the multiple recycling tests. In particular, in the first reuse cycle amounts of wet struvite products, corresponding to the identified ratio (10%), were used to treat raw leachate. In the subsequent treatments, the quantity of decomposition residues obtained from the previous cycle was exploited. Specifically, as described in the Experimental section, the tests were conducted according to the sequential batch operating mode. Therefore, each phase of the process was sequentially executed in the reactor. In this way, the settled solids produced in each step were used in wet form without being subject to any further separation or drying treatments. This procedure simplifies the management of the process and could be easily applied in industrial plants.
Three methods for the repeated treatment of raw leachate were tested. In two cases, the cycles were conducted without the supply of any Mg and P reactants and the pH was set, respectively, by means of NaOH and air insufflation. In the third method, MgCl2∙6H2O and H3PO4 were fed at a molar ratio of n(N):n(Mg):n(P) 1:0.05:0.05, and NaOH addition was used for pH adjustment.
The experimental results showed that, during the first reusing cycle, the ammonium removal was around 92% for each operating method tested (Figure 12). Without supplementation of reagents and by setting the pH with NaOH, the process performance resulted in around 86% for the second and third cycle, and then gradually decreased to about 54%. The performance reduction is a consequence of a progressive decrease of the precipitate that was produced from each treatment (Table 2). This reduction caused a corresponding decrease of solid residues obtained during the decomposition steps (Table 2). Consequently, the availability of reactants in the subsequent cycles for leachate treatment progressively diminished. This effect was more marked in the tests with air insufflations (Table 2). Indeed, with this operating modality, the NH4+ abatements decreased more quickly to an efficiency of only about 23% in the 5th cycle. Thus, the detected trends prove that the pH correction through chemical addition is more favorable for the treatment of leachate using struvite decomposition residues. Indeed, in the tests conducted by means of air insufflation, a lower settleability of solids formed was observed in each cycle. This, clearly, makes the phases of recovery and reuse more difficult. The process with the supplementation of proper amounts of magnesium and phosphorus source was much more effective. In fact, by dosing the reactants at molar ratios of only n(N):n(Mg):n(P) = 1:0.05:0.05, the ammonium removal was constantly maintained at approximately 82% (Figure 12).
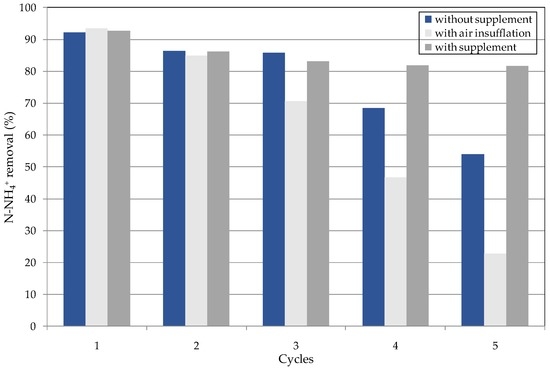
Figure 12.
Ammonium removal during the repeated cycles conducted by using the struvite decomposition residues.

Table 2.
Amounts of produced precipitate, decompositions residues, and solubilized N-NH4+ and P-PO43− detected during the treatment cycles.
Moreover, the residual phosphorus and magnesium amounts, in the treated leachate, were steadily around to 37 mg(P)/L and 69 mg(Mg)/L. The performance stability is attributable to the amount of produced precipitate, that, in the subsequent treatments, did not show substantial reductions (Table 2). Consequently, after each acid dissolution phase, the solubilized NH4+ and PO43− and the amount of decomposition residues remained pretty steady (Table 2). This ensured adequate availability of Mg and P in the sequential treatments of raw leachate. Moreover, the XRD analyses of struvite residues was always in line with those showed in Figure 9, which indicates that the formation of newberyite repeatedly occurred during the sequential decomposition steps. Therefore, the generation of other adverse compounds, such as Mg2P2O7 [44], able to hinder the ammonia removal in leachate treatment, was prevented.
Efficiencies even greater than those detected in the present study have been achieved by Zhang et al. [14] by reusing struvite residues obtained by acid dipping, after a washing and drying phase. These purification treatments clearly accentuate the effectiveness of decomposition products, however, they are very expensive and hardly applicable in field conditions. On the contrary, the proposed method makes the process management easier and reduces the overall costs and, at the same time, ensures satisfactory performances.
3.4. Economic Analysis
To evaluate the economic suitability of the proposed recycling procedure, the expense required for the removal of 1 kg of ammonium was estimated and compared to that of the conventional struvite precipitation process by using industrial-grade reagents. In this regard, the expense for chemicals consumption and for energy utilization during the decomposition phase were considered. Through an analysis of Italian industrial market of chemicals, the price of H3PO4 (75%), MgCl2∙6H2O, HCl (32%), and NaOH (40%) can be assumed to be about 790 €/m3, 420 €/ton, 125 €/m3, and 250 €/m3, respectively, similar to those considered in other works [1]. On the basis of the operating conditions identified (n(N):n(Mg):n(P) = 1:1.2:1.2), phosphoric acid and magnesium chloride amounts of 7.4 L and 18.4 kg must be dosed for struvite precipitation. Furthermore, about 15 L of NaOH (40%) are necessary to set the pH to 9. Therefore, an overall expense of around 17.3 €/kg(Nrem) can be estimated. By applying the proposed recycling process, the phosphorus and magnesium sources can be supplied at molar ratios of only n(N):n(Mg):n(P) = 1:0.05:0.05, to which corresponds amounts of 0.37 L and 0.94 kg, respectively. Moreover, a volume of 5.7 L of NaOH is necessary for pH adjustment and 6.8 L of HCl are consumed during struvite dissolution. Consequently, the cost for chemicals consumption is around 3 €/kg(Nrem). The energy outlay for the mixture heating during the struvite decomposition phase can be assumed to be about 1.5 €/kg(Nrem). Therefore, the total expense is approximately 4.5 €/kg(Nrem). By comparing this value to that for conventional struvite precipitation, around 74% of overall outlay can be avoided by means of the proposed recycling technique. The cost saving achievable with the developed method is even higher with respect to those detectable with other recycling methods [44].
4. Conclusions
In the present work, we defined a suitable procedure for the ammonium removal from landfill leachate by means of multiple recycling of struvite residues, obtained through an acid decomposition phase. The experimental results showed that struvite dissolution is not feasible by using sulfuric acid or nitric acid. In fact, with H2SO4 and HNO3, a maximum n(N):n(P) ratio of only 2 and 6.5 mmol (N):mmol (P) were reached, respectively. On the contrary, high ammonia releases of up to 1.5 mmol (N)/g and NH4+/PO43− molar ratios of around 38 mmol (N)/mmol (P) were obtained with HCl and CH3COOH at 50 °C and pH 5.5. The characterization of residues proved that MgHPO4∙3H2O was the main product of acid decomposition treatment. The liquid phase, due to its high ammonium concentrations, could be exploited as a fertilizer source. The multiple recycling tests showed a progressive reduction of ammonium removal by exclusively exploiting struvite residues as a magnesium and phosphorus source for the treatment of raw leachate. In these tests, after the fifth cycle, the efficiencies were of about 54% and 23% when performing the pH correction with NaOH and air insufflation, respectively. On the other hand, supplementation of P and Mg reagents at a very small molar ratios (n(N):n(Mg):n(P) = 1:0.05:0.05) resulted in a stable NH4+ removal that remained around 82%; this is a consequence of the struvite regeneration during each treatment cycle. The developed method is economically suitable; in fact, with respect to the expense required for the conventional struvite process, a cost saving of about 74% is achievable. Furthermore, the process is even more advantageous because it is easily managed and can be applied with simple equipment. Indeed, each phase is subsequently conducted in the reactor without the need for complex purification treatments or drying phases of recovered solids. Currently, the process is being tested in the industrial treatment plant of ECONET Company, situated at Lamezia Terme in Southern Italy.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by ECONET srl.
Author Contributions
A.S. planned the work, analyzed the results and prepared the manuscript. M.A.S. and C.L. performed the experiments. F.M. contributed to the analysis of the data and revised the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Di Iaconi, C.; Pagano, M.; Ramadori, R.; Lopez, A. Nitrogen recovery from a stabilized municipal landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1732–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabdaşli, I.; Şafak, A.; Tünay, O. Bench-scale evaluation of treatment schemes incorporating struvite precipitation for young landfill leachate. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2386–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Ryu, H.D.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.I. Enhancing struvite precipitation potential for ammonia nitrogen removal in municipal landfill leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, L. Removal of ammonia from landfill leachate by struvite precipitation with the use of low-cost phosphate and magnesium sources. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 145, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Z.; Zhao, Q.L. Recovery of ammonium-nitrogen from landfill leachate as a multi-nutrient fertilizer. Ecol. Eng. 2003, 20, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, A.; de Rosa, S. Experimental formulation of a kinetic model describing the nitrification process in biological aerated filters filled with plastic elements. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, A.; de Rosa, S. An experimental model of COD abatement in MBBR based on biofilm growth dynamic and on substrates’ removal kinetics. Environ. Technol. 2016, 37, 2058–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Lo, W.-H.; Chan, G.Y.S. Physico-chemical treatments for removal of recalcitrant contaminants from landfill leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, B129, 80–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochany, J.; Lipczynska-Kochany, E. Utilization of landfill leachate parameters for pretreatment by Fenton reaction and struvite precipitation—A comparative study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, G.; Perathoner, S.; Centi, G.; de Rosa, S.; Granato, T.; Katovic, A.; Siciliano, A.; Tagarelli, A.; Tripicchio, F. Wet hydrogen peroxide catalytic oxidation of olive oil mill wastewaters using Cu-zeolite and Cu-pillared clay catalysts. Catal. Today 2007, 124, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, S.; Siciliano, A. A catalytic oxidation process of olive oil mill wastewaters using hydrogen peroxide and copper. Desalt. Water Treat. 2010, 23, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, A.; Stillitano, M.A.; de Rosa, S. Increase of the anaerobic biodegradability of olive mill wastewaters through a pre-treatment with hydrogen peroxide in alkaline conditions. Desalt. Water. Treat. 2014, 55, 1735–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, A.; Stillitano, M.A.; de Rosa, S. Biogas production from wet olive mill wastes pretreated with hydrogen peroxide in alkaline conditions. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yao, C.; Feng, X.; Yang, M. Repeated use of MgNH4PO4·6H2O residues for ammonium removal by acid dipping. Desalination 2004, 170, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, A. Use of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron (NZVI) Particles for Chemical Denitrification under Different Operating Conditions. Metals 2015, 5, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabegovic, L.; Uldal, M.; Werker, A.; Morgan-Sagastume, F. Phosphorus recovery potential from a waste stream with high organic and nutrient contents via struvite precipitation. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saidou, H.; Ben Moussa, S.; Ben Amor, M. Influence of airflow rate and substrate nature on heterogeneous struvite precipitation. Environ. Technol. 2009, 30, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çelen, I.; Türker, M. Recovery of Ammonia as Struvite from Anaerobic Digester Effluents. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Diwani, G.; El Rafie, S.H.; El Ibiari, N.N.; El-Aila, H.I. Recovery of ammonia nitrogen from industrial wastewater treatment as struvite slow releasing fertilizer. Desalination 2007, 214, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Bhuiyan, H.; Mavinic, D.S. Assessing struvite precipitation in a pilot-scale fluidized bed crystallizer. Environ. Technol. 2008, 29, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korchef, A.; Saidou, H.; Ben Amor, M. Phosphate recovery through struvite precipitation by CO2 removal: Effect of magnesium, phosphate and ammonium concentrations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Corre, K.S.; Valsami-Jones, E.; Hobbs, P.; Parsons, S.A. Impact of calcium on struvite crystal size, shape and purity. J. Cryst. Growth 2005, 283, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, L.; Mangin, D.; Ferrer, J.; Seco, A. Struvite formation from the supernatants of an anaerobic digestion pilot plant. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, H.D.; Lim, C.S.; Kang, M.K.; Lee, S.I. Evaluation of struvite obtained from semiconductor wastewater as a fertilizer in cultivating Chinese cabbage. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 221–222, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal, A.; Yilmazel, Y.D.; Demirer, G.N. The determination of fertilizer quality of the formed struvite from effluent of a sewage sludge anaerobic digester. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uludag-Demirer, S.; Demirer, G.N.; Chen, S. Ammonia removal from anaerobically digested dairy manure by struvite precipitation. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 3667–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, S. Improving the prediction of ammonium nitrogen removal through struvite precipitation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 347–360. [Google Scholar]
- Fattah, K.P.; Sabrina, N.; Mavinic, D.S.; Koch, F.A. Reducing operating costs for struvite formation with a carbon dioxide stripper. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimenos, J.M.; Fernández, A.I.; Villalba, G.; Segarra, M.; Urruticoechea, A.; Artazab, B.; Espiella, F. Removal of ammonium and phosphates from wastewater resulting from the process of cochineal extraction using MgO-containing by-product. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, M.; Colmenarejo, M.F.; Barrera, J.; García, G.; García, E.; Bustos, A. Use of a byproduct of magnesium oxide production to precipitate phosphorus and nitrogen as struvite from wastewater treatment liquors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunay, A.; Karadag, D.; Tosun, I.; Ozturk, M. Use of magnesit as a magnesium source for ammonium removal from leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.I.; Weon, S.Y.; Lee, C.W.; Koopman, B. Removal of nitrogen and phosphate from wastewater by addition of bittern. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, A.; Ruggiero, C.; de Rosa, S. A new integrated treatment for the reduction of organic and nitrogen loads in methanogenic landfill leachates. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2013, 91, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, A.; de Rosa, S. Recovery of ammonia in digestates of calf manure through a struvite precipitation process using unconventional reagents. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, A. Assessment of fertilizer potential of the struvite produced from the treatment of methanogenic landfill leachate using low-cost reagents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 5949–5959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Du, W.; Harada, H. Repeated use of MAP decomposition residues for the removal of high ammonium concentration from landfill leachate. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 2233–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Xu, C.; Zhang, W. Removal of nutrients from piggery wastewater using struvite precipitation and pyrogenation technology. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2523–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, L. Recovery and removal of ammonia–nitrogen and phosphate from swine wastewater by internal recycling of struvite chlorination product. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 172, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.H.; Kumar, S.; Kwag, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.D.; Ra, C.S. Recycle of electrolytically dissolved struvite as an alternative to enhance phosphate and nitrogen recovery from swine wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 195, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.-H.; Qiu, G.-L.; Yuan, P.; Cui, X.-Y.; Peng, J.-F.; Zeng, P.; Duan, L.; Xiang, L.-C.; Qian, F. Nutrients removal and recovery from anaerobically digested swine wastewater by struvite crystallization without chemical additions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Ding, L.; Ren, H.; Xiong, X. Ammonium nitrogen removal from coking wastewater by chemical precipitation recycle technology. Water Res. 2009, 43, 5209–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Türker, M.; Cęlen, I. Removal of ammonia as struvite from anaerobic digester effluents and recycling of magnesium and phosphate. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1529–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.; Geng, J.; Ren, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, K. Struvite pyrolysate recycling combined with dry pyrolysis for ammonium removal from wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 132, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Xiao, D.; Liu, J.; Hou, L.; Ding, L. Recovery and removal of nutrients from swine wastewater by using a novel integrated reactor for struvite decomposition and recycling. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Public Health Association, Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association; Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).