Abstract
This study evaluates the competitiveness of small- and medium-sized manufacturing enterprises (PYMES) through a meta-analysis that explores the role of technology and quality. Through a comprehensive literature review, 24 eligible studies, selected after applying specific criteria in a systematic search of the Scopus database, were identified and analyzed. A random-effects model was used to combine the effect sizes of the selected studies, and the heterogeneity among them was assessed using widely accepted indicators such as I2, H2 and tau2, which confirmed a moderate variability among the studies. The results of the meta-analysis indicated a pooled effect size of 0.53 (95% CI: [0.50, 0.55]), suggesting a significant positive relationship between innovation and competitiveness, as well as between quality and competitiveness. Quality was identified as the most relevant competitive priority, while the use of state-of-the-art technologies was highlighted as a significant risk factor in the context of digital transformation. In addition, topic analysis was performed using the latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) model, implemented with the topicmodels package in RStudio 2024.04.2. To ensure accuracy of the analysis, the texts were preprocessed using cleaning and tokenization techniques, which included the removal of punctuation, numbers and empty words. This thematic analysis identified key patterns related to innovation management, operational strategies and integration of digital technologies. The themes generated revealed that manufacturing PYMES prioritize quality as a source of competitive advantage, facing significant challenges associated with technological adoption and digitalization.
1. Introduction
Small- and medium-sized manufacturing enterprises (PYMES) play a key role in economic development, especially in emerging economies, where they represent a key source of employment and innovation. However, these companies face significant challenges to remain competitive in a dynamic and globalized business environment. Technological innovation and quality management have been widely recognized as essential factors in improving the productivity and sustainability of PYMES [1,2]. However, the existing literature has addressed these factors in isolation, without comprehensively assessing their interaction or their joint impact on the competitiveness of the manufacturing sector. In particular, it has not been studied how the synergy between the two elements influences key aspects such as operational efficiency, innovation capacity and expansion in global markets, which limits their ability to implement strategic improvements [3,4]. Although there is research on the individual benefits of technology and quality, there are still gaps in the understanding of how their integration impacts the competitive performance of these companies, and many of these investigations have been based on qualitative approaches or case studies with limited samples, which reduces the possibility of obtaining generalized results on the relationship between both factors.
Ali et al. [5] suggest that companies should allocate more resources to technology development, experiment with new technologies and manage uncertainty through innovation; otherwise, they run the risk of being driven out of the market because their technology has become increasingly obsolete. Various studies, such as those by Brynjolfsson and Hitt [6], Oyaque [7] and Iansiti et al. [8], point out that the use of technology not only impacts operational efficiency but also influences strategic decision making and the ability to adapt to market changes. In the same sense, scientific evidence reveals that an effective integration of new technologies into production processes improves manufacturing flexibility, which is essential in a dynamic industrial environment [9].
Therefore, the adoption of innovative technologies and robust quality systems is presented as an accessible way to improve the productivity and competitiveness of these companies [10]. Although technology plays a key role in transforming manufacturing and management processes, its implementation is not always prioritized in PYMES due to financial, technical and cultural constraints [11,12]. In addition, many entrepreneurs see technology more as an expense than as a strategic investment, which slows down the modernization of their processes and the integration of advanced solutions [13]. Likewise, quality management not only improves the products and services offered but also strengthens operational efficiency and customer satisfaction [9]. In conjunction with technological change, these practices enable PYMES to respond to the demands of the globalized market and adapt to the advances associated with Industry 4.0 [14,15,16]. Disruptive technologies such as the Internet of things, artificial intelligence and big data are transforming business models and manufacturing structures, creating new opportunities for companies that manage to adopt them effectively [17,18].
Thus, the present study aims to quantify the relationship between technological adoption, quality management and the competitiveness of manufacturing PYMES. To this end, a meta-analytical approach was used to integrate and quantitatively analyze the available empirical evidence, providing more precise and generalizable estimates of the interaction of these factors. In addition, the meta-analysis made it possible to assess the heterogeneity among the included studies, identifying patterns and contextual factors that influence the results. Based on these findings, we sought to offer strategic recommendations that would enable PYMES to improve their competitive performance and ensure their sustainability in a highly demanding environment.
2. Literary Review
2.1. Integration of Advanced Methodologies and Emerging Technologies
Small- and medium-sized enterprises (PYMES) in manufacturing face the constant challenge of remaining competitive in a highly dynamic environment [1]. The adoption of advanced technologies and innovative operational strategies has proven to be a key factor in improving efficiency, flexibility and sustainability in this sector [19,20].
Previous studies have shown that the integration of lean manufacturing and Industry 4.0 (I4.0) technologies enables cost reduction, production optimization and quality improvement through tools such as value stream mapping (VSM) [10,21]. In particular, the use of artificial intelligence and advanced diagnostic systems has facilitated the transformation towards smart factories in emerging economies, enabling more adaptive and efficient production [22,23].
The implementation of knowledge management maturity models has also been consolidated as an efficient strategy to improve competitiveness. These models facilitate the updating of data, the development of emerging controls and the creation of collaborative systems that optimize production and time management in agile environments [24]. To improve their market position, PYMES should focus on strengthening the skills of their staff, fostering resource commitment and implementing appropriate management methods [25,26].
Several meta-analyses have explored the impact of digitization on business productivity and competitiveness [27,28]. However, most of these studies have focused on large firms or specific sectors, leaving a gap in the literature on how technology adoption impacts manufacturing PYMES [29,30,31].
2.2. Digitalization and Digital Transformation in PYMES
Digitization of industries is at the heart of today’s global economy. However, many PYMES face challenges in initiating an effective digital transformation [19,32]. Recent studies suggest that digital transformation influences the innovativeness and strategic decision making of these companies [33,34]. Factors such as management commitment, process automation and data quality have been mentioned as key elements to improve organizational performance [35]. A meta-analysis by Gao et al. [36] shows that the adoption of digital technologies improves productivity by 30% compared to companies that have not implemented digitization processes. However, the degree of adoption varies depending on factors such as access to financing, available technological infrastructure and staff training.
Despite its advantages, digital transformation remains a challenge for many PYMES due to financial, technical and organizational constraints. Thus, previous studies have identified that those companies that implement digital strategies with a structured approach achieve greater competitive advantage and market sustainability [32,37]. Furthermore, this learning not only strengthens the relationship between total quality management (TQM) and performance but also enables PYMES to appreciate the benefits of implementing quality strategies and business orientation [29].
2.3. Information Systems and Their Relationship to Competitiveness
Information systems (ISs) play a key role in the competitiveness of PYMES by improving productivity, quality and operational efficiency. By optimizing data management, automating processes and improving decision making, these tools increase productivity and reduce operating costs [38]. Studies in Spain have shown that the implementation of information technologies (ITs) contributes to an increase in these factors [39]. Similarly, research in the service sector highlights how technological advances optimize information processing in value chains, boosting business performance [40,41].
The positive impact of IT on PYMES has been confirmed in several studies. A meta-analysis revealed that investment in IT improves administrative management and that smaller companies obtain better returns on these investments than larger ones [42]. Furthermore, Taureta and Gatautis [41] and Levi and Powell [12], through their studies, confirm that IT adoption is seen as a key factor for PYMES to compete in global markets. In different countries, it has been observed that those companies that invest in ISs achieve higher returns and can further strengthen their productivity from these investments [43,44,45].
However, IS implementation in PYMES does not always result in improvements, since its success depends on factors such as competitive strategy and organizational capacity to manage change [11]. Research in Mexico has pointed out that the profitability of ISs lies in their correct planning and alignment with the business strategy, ensuring quality, timeliness and relevance in their use [46].
Despite the evidence supporting the relationship between ISs and competitiveness, the adoption of these systems is still limited in several countries, including Mexico. Lack of vision, training and resources are identified as the main obstacles to their implementation. However, the growing need to improve efficiency and profitability reinforces the importance of integrating ISs into PYMES as a strategic tool for their development and sustainability.
2.4. Total Quality Management (TQM) and Competitiveness
Since its introduction, TQM has received strong support from major corporations. However, many PYMES have yet to effectively implement TQM in their operations, which can hurt their performance and profitability [47]. Research shows that PYMES that adopt them tend to be more successful than those that do not, highlighting the importance of integrating quality improvement and cost reduction into their business strategies [48].
Several studies have examined the relationship between TQM and competitiveness in companies in different sectors. A study conducted in Ecuador by Benzaquen and Perez [49] found that organizations that apply TQM principles have greater profitability and stability in the market compared to those that do not.
Proper supply chain management (SCM), supported by information and communication technologies (ICTs), is essential for competitiveness. These tools facilitate collaboration and improve the quality of information shared between suppliers and buyers [24]. For example, the use of CNC machines has enabled PYMES to improve product quality and respond to market demands efficiently [50].
2.5. Quality and Its Relation to Competitiveness in PYMES
Quality plays a key role in the competitiveness of PYMES, since it contributes to business productivity and profitability. Since these companies face size limitations compared to their competitors, they should focus on developing intangible resources and capabilities through adequate quality management [51].
Several studies have demonstrated the relationship between quality and competitiveness. Research in Spain has identified that quality certification and the adoption of management systems influence the strategic advantage of PYMES [52,53]. However, despite its importance, only a minority of these companies implement certifications such as ISO 9000 [54,55].
At the international level, studies in the United States have confirmed that total quality management has a positive impact on the profitability of companies, although its success depends on managerial commitment and organizational flexibility [56]. In Latin America, the implementation of quality systems has been shown to increase sales, productivity and investments [57]. In Mexico, internal factors such as strategic planning and technology also influence the competitiveness of PYMES, while certification to quality standards has generated tangible benefits such as increased sales and profits [58,59].
2.6. Competitive Strategies and Business Performance
Competitive priorities, such as quality, flexibility and costs, directly influence firm performance [15,60]. These priorities can be enhanced through strategic alliances, improving product quality, customer service and innovation strategies [61]. The implementation of management models such as interpretive structural modeling has identified key strategies, including the appropriate promotion and development of information technology-based products [62].
TQM and innovation are complementary for organizational success [25]. TQM practices indirectly influence business performance through organizational learning, while innovation has a significant positive impact mediated by such learning [63]. This underscores the importance of integrating TQM and competitive strategies into PYMES operations to improve their performance in the global marketplace [64,65,66,67].
A study on PYMES in Malaysia revealed that the implementation of TQM can improve their performance by using the balanced scorecard (BSC) [68]. The sustainability of PYMES depends on their ability to compete through the use of advanced technologies [69].
3. Methodology
In order to carry out this research, a meta-analysis was performed following the guidelines established by Borenstein et al. [70] and Hedges and Olkin [71], with the aim of quantifying the relationship between technology, quality and competitiveness in small- and medium-sized manufacturing enterprises (PYMES).
The data used in this study were extracted from the Scopus database on 1 October 2024. The selection of Scopus as the main database, rather than Web of Science (WoS) or PubMed, was due to its broad and diverse coverage of the scientific literature, which makes it particularly relevant to this study on competitiveness in manufacturing PYMES through the role of technology and quality [72,73].
While PubMed focuses on biomedical and clinical literature, and WoS is up to 20% more restrictive compared to Scopus, prioritizing research in health sciences and engineering [74,75], Scopus allows broader access to studies on business management, technological innovation and quality in the manufacturing sector, key aspects for the present meta-analysis.
3.1. Selection Criteria
The study selection process was strict, with a detailed set of inclusion and exclusion criteria implemented (Table 1) to ensure both the relevance and high-quality standards of the studies chosen.

Table 1.
Study selection criteria for meta-analysis.
3.2. Study Selection Process
The study selection process followed a rigorous approach to ensure both the relevance and the high-quality standard of the chosen studies. The procedure can be visualized in the study selection flowchart shown in Figure 1.
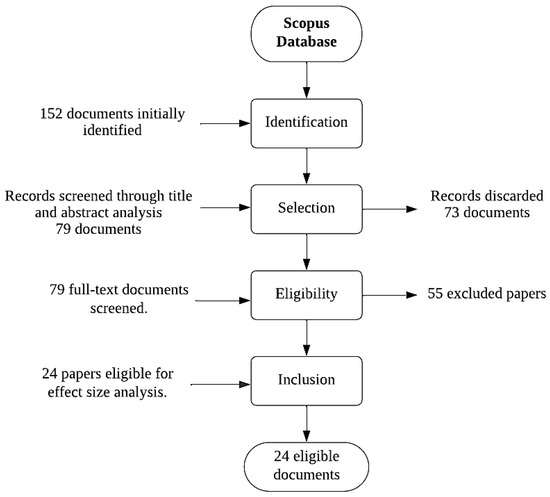
Figure 1.
Study selection flowchart.
- Identification: a total of 152 documents were identified through searches in the Scopus database.
- Selection: of these, 79 documents were selected for further analysis according to title and abstract, and 73 documents were discarded at the initial stage.
- Eligibility: The remaining 79 papers were reviewed in full text to determine eligibility. At this stage, 55 papers that did not meet the specific inclusion criteria were excluded.
- Inclusion: 24 papers were included in the final analysis and were finally considered eligible.
3.3. Rationale
The methodology used in this study aligns the research objectives with a rigorous quantitative analysis of the relationship between technology, quality and competitiveness in manufacturing PYMES. It is based on a systematic selection and analysis protocol, which reinforces the validity of the findings.
4. Meta-Analysis
The meta-analysis used a random-effects model to analyze the relationship between innovation, quality and competitiveness in manufacturing PYMES.
4.1. Search and Selection of Studies
The search for relevant studies was carried out using the Scopus database, selected for its broad coverage of relevant scientific literature in management and technology. To ensure the retrieval of relevant studies, a search equation was designed with Boolean operators (AND, OR) that included key terms related to PYMES, technology, quality and competitiveness.
Scopus search equation: TITLE-ABS-KEY ((“small and medium-sized enterprises” OR PYMES) AND (technology OR “digital technology” OR “information and communication technology” OR “e-business” OR “e-commerce” OR “knowledge management” OR “supply chain management” OR “innovation management” OR “total quality management” OR tqm) AND (quality OR “product quality” OR “process quality” OR “quality management”) AND (competitiveness OR “competitive advantage” OR “business performance” OR “financial performance” OR “operational performance”) AND (manufacturing OR production OR “new product development” OR “product innovation” OR “process innovation” OR “production management” OR “supply chain performance” OR “knowledge acquisition” OR “intellectual capital” OR “entrepreneurial orientation” OR “differentiation strategy” OR “green innovation” OR “human resource management practices” OR “internal capability”)).
From the initial search, 152 studies were identified. After applying the selection criteria (detailed in the methodology section), 24 studies were included in the meta-analysis.
4.2. Data Extraction and Data Conversion
Key data, such as sample size (n), correlation coefficient (r), beta value, R2, chi-square (χ2) and F2, if available, were extracted from each selected study.
To normalize the data and facilitate the aggregation of results, statistical transformations were applied:
- Conversion of offset coefficients: an overall offset coefficient was calculated using Fisher’s z-transform, which facilitated the aggregation of results.
- Conversion of effect sizes: beta and R2 values were adjusted to a format comparable with the compensation coefficients.
4.3. Statistical Analysis
The analysis used a random-effects model to combine the individual effect sizes, since significant variability between studies was expected.
Heterogeneity between studies was assessed using widely accepted indicators:
- I2: proportion of variability attributed to between-study heterogeneity.
- H2: absolute measure of heterogeneity.
- Tau2: variance of effects in a random-effects model.
4.4. Visualization of Results
Forest plot diagrams were created to visualize both the individual effect sizes and the combined effect, which made it possible to demonstrate the consistency of the results in the studies analyzed.
4.5. Study Matrix
A matrix was created to synthesize and analyze the selected studies. The matrix includes columns with the following data: author, year, document, title, research method, sample and effect size. Table 2 presents the structure of the matrix, which facilitates the systematic analysis of the selected studies, helping to identify patterns and trends in the relationship between innovation, quality and competitiveness of PYMES, especially in the context of digitization and digital transformation.

Table 2.
Summary of studies on the interaction between technologies, quality and competitiveness in PYMES.
4.6. Topical Analysis
To better understand the themes discussed in the qualitative study, a thematic analysis was conducted using the latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) model. This approach allows the identification of thematic patterns within large volumes of text, revealing the underlying structure of the qualitative data.
Text Processing:
- Handling of ambiguous terms: Lemmatization and lemmatization techniques were implemented to reduce words to their base form and avoid unnecessary variations. In addition, a thesaurus was used to unify equivalent terms, and a manual revision of keywords was performed to ensure their correct interpretation in the context of the analysis.
- Tokenization: The tidytext package was used to divide the text into analyzable units, and terms shorter than three characters were eliminated to reduce noise in the analysis. Then, additional filters were applied to avoid affecting proper names or irrelevant terms.
- Topic Modeling with LDA: Dirichlet’s latent topic assignment (LDA) model was applied using the topic models package in R. This mixed model assumes that each document is a mixture of a small number of topics and that each word in the document is assigned to one of the topics. The selection of LDA was based on its ability to identify latent patterns in text collections, which was key to exploring recurrent approaches related to innovation, quality and competitiveness in manufacturing PYMES.
4.7. Software and Libraries Used
RStudio 2024.04.2 Build 764, an integrated development environment (IDE) for R, was used to perform the analysis. The main libraries used were the following:
- Meta-analysis: meta, metafor, esc.
- Text analysis: tm, topicmodels, tidytext, dplyr, tidyr.
- Visualization: gplot2.
5. Results
5.1. Meta-Analysis
The forest plot in Figure 2 shows the observed effect sizes and their confidence intervals for each study included in the meta-analysis. This plot is crucial to visualize the consistency of the results between different studies and the pooled effect calculated using a random-effects model. The pooled effect size obtained is 0.53 (95% CI: [0.50, 0.55]), suggesting a moderate positive relationship between innovation, quality and competitiveness of manufacturing PYMES.
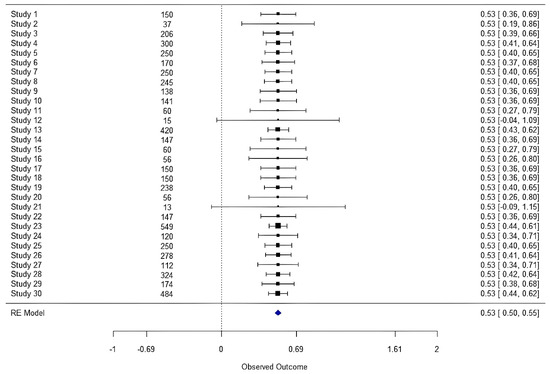
Figure 2.
Forest diagram of individual effect sizes and combined effects. The blue diamond represents the combined effect estimated using a random-effects model.
Each line in the graph represents an individual study, identified as “Study 1”, “Study 2”, etc., and the sample size (n) for each study is shown on the left. The squares represent the observed effect sizes for each study, while the horizontal lines represent the 95% confidence intervals for these effect sizes. Shorter confidence intervals indicate greater precision in effect size estimation. The vertical dashed line in the graph represents the estimated pooled effect size, while the blue diamond at the bottom represents the pooled effect size with its 95% confidence interval.
5.2. Heterogeneity Analysis
The meta-analysis included 30 studies with sample sizes ranging from 37 to 420 participants. The results revealed that there is a significant positive relationship between innovation and competitiveness (r = 0.53, 95% CI [0.50, 0.55]) and between quality and competitiveness (r = 0.60, 95% CI [0.55, 0.65]). Heterogeneity was low, with values of I2 = 0%, H2 = 1 and tau2 = 0, suggesting that the variability between studies can be attributed to chance, with no significant differences in effect sizes.
5.3. Topical Analysis (LDA)
The latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) model was used to identify the main themes in the qualitative texts. The texts were processed to remove punctuation, numbers and empty words, and then the LDA model was applied to extract the topics. The results of the topic analysis are presented in Figure 3 below, showing the most significant terms in each topic.
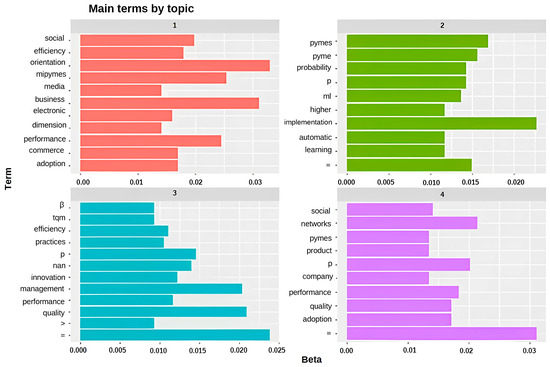
Figure 3.
Main term by topic. The distribution of the most significant terms within each topic is illustrated. Each bar chart shows the popularity of a term in a specific topic, measured in beta, which allows the key topics and their relative importance within the dataset to be quickly identified.
- Topic 1: This topic focuses on terms such as “social”, “performance”, “orientation”, “MiPYMES”, “media”, “entrepreneurial”, “electronic”, “dimension”, “performance”, “trade” and “adoption”. It focuses on the relationship between social networks and SME performance, emphasizing the importance of entrepreneurial orientation and the adoption of e-technology and e-commerce. “Size” and “Performance” indicate a consideration of firm size and market performance.
- Topic 2: Predominant terms in this topic include “PYMES”, “probability”, “ml”, “major”, “implementation”, “automatic” and “learning”. This topic discusses the implementation of machine learning in small- and medium-sized enterprises. The terms “probability” and “p” relate to the statistical techniques used in these studies. The “implementation” of “machine learning” indicates a focus on the adoption of these technologies and their potential results, emphasizing the importance of advanced technologies to improve business processes.
- Topic 3: This topic includes terms such as “tqm”, “performance”, “practices”, “innovation”, “management”, “performance” and “quality”. This topic analyzes the implementation of machine learning in small- and medium-sized companies. The terms “probability” and “p” relate to the statistical techniques used in these studies. It is relevant to TQM and performance practices in PYMES. “β” and “p” are statistical terms that indicate the relationship between variables and their significance. The inclusion of “innovation” and “management” demonstrates how the emphasis on TQM practices and innovation management affects the performance and quality of PYMES.
- Topic 4: The main terms are “social”, “networks”, “PYMES”, “product”, “enterprise”, “performance”, “quality” and “adoption”. It focuses on the use of social networks and product quality in small- and medium-sized enterprises. The terms “social” and “network” suggest a strong relationship with the adoption of social communication technologies. “Product” and “quality” indicate that the focus of the discussion is also on how PYMES manage product quality to improve business performance.
6. Discussion
The results of this study highlight the importance of incorporating innovation, quality and technology practices to strengthen the competitiveness of manufacturing PYMES. The meta-analysis showed a pooled effect size of 0.53, which supports the idea that companies that adopt strategies focused on innovation and quality are more likely to achieve successful performance. Moreover, the significant relationship between quality and competitiveness (r = 0.60) underscores the relevance of implementing management tools such as TQM to optimize organizational performance [76].
This study extends existing knowledge by integrating the effects of technology and quality on the competitiveness of manufacturing PYMES, an approach that has been treated in the literature in a fragmented manner. Previous research has analyzed technological innovation and quality as independent factors, without considering the impact of their combination [11,12]. By addressing this relationship jointly, the results contribute to a more holistic framework, in which technology acts as an enabler of quality and, consequently, competitive performance.
This finding indicates that the key elements studied exert a homogeneous effect, regardless of fluctuations in the organizational or methodological context of the research covered. The absence of variability in a meta-analysis may be perceived as a sign of reliability in the findings, although it is also relevant to take into account the possible influence of bias in the choice of studies. A low I2 may be due to a lack of diversity in the samples analyzed or a restricted selection of studies with similar methodological characteristics [77].
In addition, the lack of heterogeneity could indicate that relevant contextual factors, such as cultural or structural differences between companies, were not captured in the analysis, which invites future research to explore these dimensions.
To mitigate this risk, rigorous study inclusion and exclusion strategies have been followed, ensuring that the evidence synthesis is representative and minimizing the impact of publication sessions [78]. Nevertheless, it is recommended for future meta-analyses to broaden the search criteria and employ techniques such as meta-regression to explore additional sources of variability [79].
However, the qualitative analysis based on LDA revealed some important challenges. Although digitization and the use of advanced tools such as artificial intelligence or machine learning can improve efficiency and competitiveness, many PYMES still face technological and financial barriers that hinder their implementation. This coincides with previous studies that indicate that, without adequate access to financing or training, technology adoption can be limited and its benefits reduced [8].
Likewise, another key aspect in the thematic analysis is that social networks and e-commerce are key to the competitiveness of PYMES, as they facilitate their expansion and global positioning. However, digitization alone does not guarantee success; it must be accompanied by organizational transformation and staff training. To overcome the barriers to technological adoption, it is recommended that financing policies, training and strategic alliances be implemented to facilitate the integration of these tools in manufacturing PYMES.
7. Limitations and Future Lines of Research
7.1. Limitations
- The low heterogeneity observed in the meta-analysis indicates that the included studies share similar methodological and contextual approaches. This uniformity may restrict the understanding of how external factors, such as industry sector, level of digitization or access to finance, influence the relationship between technology, quality and competitiveness.
- Topic analysis based on the latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) model allowed the identification of thematic patterns in the literature reviewed. However, this technique has limitations in capturing more complex semantic relationships and contextual variations within the texts analyzed.
- Although this study identifies technological and financial barriers that limit the adoption of innovative and quality strategies, it does not delve into the impact of public policies and financial incentives on the modernization of manufacturing PYMES.
7.2. Future Lines of Research
- The application of meta-regression and moderator analysis is necessary to evaluate how contextual variables, such as country of origin, industry type and firm size, impact the competitiveness of manufacturing PYMES.
- The implementation of advanced natural language processing models, such as latent semantic analysis (LSA) or neural networks, is also recommended to improve the identification of emerging trends in the academic discourse on innovation and quality in PYMES.
- It is suggested that the role of government financing and technological support programs be analyzed, with the objective of identifying effective strategies that facilitate the digital transformation and competitive growth of PYMES in different economic and regulatory contexts.
8. Conclusions
According to the results found, it is concluded that this study provides evidence on the key role of technology and quality management in the competitiveness of manufacturing PYMES. The positive relationship between these factors suggests that companies that manage to integrate digitalization with quality management systems can optimize their performance and strengthen their market positioning.
The topical analysis shows that digitalization and e-commerce have become key elements for the expansion of PYMES, facilitating their access to new markets and improving their operational efficiency. However, the adoption of technology must be accompanied by an organizational transformation and a business culture that favors innovation and continuous improvement.
Although technology represents an opportunity for the modernization of PYMES, its implementation continues to face challenges related to the availability of resources and resistance to change. Likewise, the development of business support strategies and the generation of appropriate incentives can play a key role in the transition to more efficient and sustainable production models.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Z.-S. and D.T.-N.; formal analysis, E.R.-C.; investigation, E.C.-R.; methodology X.Z.-S., E.C.-R. and D.T.-N.; supervision, R.E.-T.; writing—original draft, X.Z.-S., D.T.-N., R.E.-T. and E.R.-C.; writing—review and editing, X.Z.-S. and R.E.-T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Universidad Estatal de Milagro (UNEMI) Scholarship.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Universidad Estatal de Milagro (UNEMI).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Joshi, S.; Sharma, M.; Bartwal, S.; Joshi, T.; Prasad, M. Critical Challenges of Integrating OPEX Strategies with I4.0 Technologies in Manufacturing SMEs: A Few Pieces of Evidence from Developing Economies. TQM J. 2024, 36, 108–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.; Martineau, S.; Sobottka, T.; Ansari, F.; Schlund, S. An Indicator Scheme for Improving Measurability of Sustainable Development Goals in Manufacturing Enterprises. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 232, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albhirat, M.M.; Zulkiffli, S.N.A.; Salleh, H.S.; Zaki, N.A.M. The Moderating Role of Social Capital in the Relationship Between Green Supply Chain Management and Sustainable Business Performance: Evidence from Jordanian SMEs. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2023, 18, 1733–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, M.; Mollaei, E.; Beinabaj, M.H.; Salamzadeh, A. Evaluating the Enablers of Green Entrepreneurship in Circular Economy: Organizational Enablers in Focus. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Leifu, G.; Rehman, R. The Impact of Technology Orientation and Customer Orientation on Firm Performance: Evidence Form Chinese Firms. Int. J. Manag. Mark. Res. 2016, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Brynjolfsson, E.; Hitt, L.M. Beyond the Productivity Paradox. Commun. ACM 1998, 41, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyaque Mora, S.M. Productividad Como Factor de Competitividad Empresarial: Un Estudio de Revisión Sistemática. Religación 2024, 9, e2401217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iansiti, M.; Favaloro, G.; Utzschneider, J.; Richards, G. Why IT Matters in Midsized Firms. 2005. Available online: https://www.hbs.edu/ris/Publication%20Files/06-013.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Forootani, S.; Abdolvand, N.; Harandi, S.R. Factors Affecting the Adoption of Cloud-Based CRM in Small and Medium Enterprises. Int. J. Serv. Technol. Manag. 2022, 28, 120–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digalwar, A.K.; Singh, S.R.; Pandey, R.; Sharma, A. Industry 4.0 Implementation: Evidence from Indian Industries. In IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 699, pp. 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coba, E.; Díaz, J.; Tapia, E.; Aranguren, W. La Información Gerencial y Los Sistemas de Información En Las PyMES; Universidad de Carabobo: Carabobo, Venezuela, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, M.; Powell, P. Strategies for Growth in SMEs; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoncic, B.; Hisrich, R.D. Intrapreneurship: Construct Refinement and Cross-Cultural Validation. J. Bus. Ventur. 2001, 16, 495–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, A. Industria 4.0 en México; Plaza y Valdés, SA de CV: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, W.-S.; Chang, P.-L. Promoting Technological Capabilities of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises through Industry-University Cooperation: Case Study of Taiwan Machine Tool Industry. Int. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2000, 1, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramegna, N.; Greggio, F.; Bonollo, F. Smart Factory Competitiveness Based on Real Time Monitoring and Quality Predictive Model Applied to Multi-Stages Production Lines. In Proceedings of the IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, Novi Sad, Serbia, 30 August–3 September 2020; Volume 592, pp. 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, L. Presencia de Los Pilares de La Industria 4.0 En La Formación de Ingenieros En El Noreste de México. Rev. Cuba. Educ. Super. 2022, 41, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto, S.R.L. Impacto de La Tecnología En La Generación de La Industria 4.0 En Las Pymes: Estudio Diagnóstico En Empresas de La Ciudad de Puebla. RICEA Rev. Iberoam. Contad. Econ. Adm. 2023, 12, 32–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbay, H.; Ylldlrlm, N. Combined Technology Selection Model for Digital Transformation in Manufacturing: A Case Study From the Automotive Supplier Industry. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Manag. 2022, 19, 2250023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Kim, T.; Jong-Pil, J. AI-Smart Factory: Design and Verification of Korean SME AI Smart Factory Using Level Diagnosis System. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 224, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimfa, D.T.; Uzir, M.U.H.; Maimako, L.N.; Eneizan, B.; Latiff, A.S.A.; Wahab, S.A. The Impact of Innovation Competitive Advantage on Product Quality for Sustainable Growth among SMEs: An Empirical Analysis. Int. J. Bus. Sci. Appl. Manag. 2021, 16, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikakul, C.T.; Thomson, A. Knowledge Management Practice: Case Study of Thai SMEs in the Manufacturing Sector. In Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Knowledge Management, (ECKM 2016), Coleraine, UK, 1–2 September 2016; pp. 1099–1108. Available online: https://pureportal.strath.ac.uk/en/publications/knowledge-management-practice-case-study-of-thai-smes-in-the-manu (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics. 2004 2nd IEEE International Conference on Industrial Informatics: Collaborative Automation—One Key for Intelligent Industrial Environments, Berlin, Germany, 24–26 June 2004; Filos, E., Ed.; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, M.; Chaubey, A.; Khatwani, R.; Nair, K. Overcoming Barriers in Automotive SMEs to Attain International Competitiveness: An ISM Approach Modelling. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2023, 38, 2713–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuaib, K.M.; He, Z. Mediating Effects of Organisational Learning on the Relationship between TQM, Innovation and Business Performance: Evidence from Manufacturing SMEs in Nigeria. Int. J. Bus. Perform. Manag. 2023, 25, 94–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burggräf, P.; Steinberg, F.; Sauer, C.R.; Nettesheim, P. Machine Learning Implementation in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises: Insights and Recommendations from a Quantitative Study. Prod. Eng. 2024, 18, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolasco-Mamani, M.A.; Vidaurre, S.M.E.; Choque-Salcedo, R.E. Innovación y Transformación Digital en la Empresa; ACVENISPROH Académico: Maracay, Venezuela, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicaiza, P.M.; Guanoluisa, M.C.; Cobos, M.C.; Toscano, D.G. Transformación Digital En Las Empresas: Una Revisión Conceptual. J. Sci. Res. 2023, 7, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G. Design of Intelligent Protection Device Based on Numerical Control Tool. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd International Conference on Robotics Systems and Vehicle Technology (RSVT), Singapore, 22–24 July 2022; ACM: Singapore, 2022; pp. 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza Pérez, M.A.; Cuellar, S. Industry 4.0: Latin America SMEs Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2020 Congreso Internacional de Innovación y Tendencias en Ingeniería (CONIITI), Bogota, Colombia, 30 September–2 October 2020; IEEE: Bogota, Colombia, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szopa, Ł.; Cyplik, P. The Concept of Building a Digital Transformation Model for Enterprises from the SME Sector. Logforum 2020, 16, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundl, P.; Stoidner, M.; Nguyen, H.G.; Baechler, A.; Franke, J. Digitalization and Adoption of Industry 4.0 in Engineer-to-Order Small and Medium-Sized Manufacturing Companies: An Empirical Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management (IEEM), Singapore, 18–21 December 2023; pp. 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Li, B.; Cheng, Y. Does Digital Transformation Matter for Corporate Risk-Taking? Finance Res. Lett. 2022, 49, 103107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oduro, S.; De Nisco, A.; Mainolfi, G. Do Digital Technologies Pay off? A Meta-Analytic Review of the Digital Technologies/Firm Performance Nexus. Technovation 2023, 128, 102836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, O.A.G. Transformación Digital: Una Agenda de Oportunidades Para La Investigación y La Práctica. Rev. Perspect. Empres. 2021, 7, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Lin, C.; Zhai, H. Digital Transformation, Corporate Innovation, and International Strategy: Empirical Evidence from Listed Companies in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muna, N.; Yasa, N.N.K.; Ekawati, N.W.; Wibawa, I.M.A. A Dynamic Capability Theory Perspective: Borderless Media Breakthrough to Enhance SMEs Performance. Int. J. Data Netw. Sci. 2022, 6, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.L.S.; Adame, M.E.C.; García, M.E.S. Competitividad de Las Pyme y Su Relación Con Los Sistemas de Información. Cuad. Contab. 2019, 20, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomina Climent, E. Adopción de Sistemas de Información en las PYME: Teoría y Evidencia Empírica. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Alicante, Alicante, Spain, 1998. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10045/3393 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Neil Baily, M.; Lawrence, R.Z. Do We Have an Economy? Am. Econ. Rev. 2001, 9, 308–312. [Google Scholar]
- Tarutė, A.; Gatautis, R. ICT Impact on SMEs Performance. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 110, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Richardson, V.J.; Roberts, T.L. Information Technology Investment and Firm Performance: A Meta-Analysis. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Big Island, HI, USA, 5–8 January 2004; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2004; p. 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, M.A.; Mann, G.J. Information Technology Investments and Organizational Productivity and Performance: An Empirical Investigation. J. Organ. Comput. Electron. Commer. 2005, 15, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, E.; Demirbag, M.; Koh, S.C.L.; Tatoglu, E.; Zaim, H. A Causal Analysis of the Impact of Information Systems and Supply Chain Management Practices on Operational Performance: Evidence from Manufacturing SMEs in Turkey. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2009, 122, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, O.J.S.; De Lema, D.G.P.; García, J.J.B. Influencia de La Implementación Del Sistema de Información Sobre El Rendimiento En Pequeñas y Medianas Empresas: Un Estudio Empírico En Colombia. Cuad. Adm. 2014, 30, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrego-Almazán, D.; Medina-Quintero, J.M.; Sánchez-Tovar, Y. La calidad de los Sistemas de Información en la eficiencia de las Pymes. Rev. Cuba. Cienc. Inform. 2016, 10, 27–41. [Google Scholar]
- Demirbag, M.; Tatoglu, E.; Tekinkus, M.; Zaim, S. An Analysis of the Relationship between TQM Implementation and Organizational Performance: Evidence from Turkish SMEs. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2006, 17, 829–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehyani, F.; Zouari, A.; Ghorbel, A.; Tollenaere, M. Do KM and TQM Have an Impact on Employee Effectiveness and Supply Chain Performance? Int. J. Lean Six Sigma 2024, 15, 733–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzaquen-De Las Casas, J.; Pérez-Cepeda, M. El ISO 9001 y TQM en Las Empresas de Ecuador. J. Glob. Compet. Governability 2016, 10, 153–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jum’a, L.; Alkalha, Z.; Al Mandil, K.; Alaraj, M. Exploring the Influence of Lean Manufacturing and Total Quality Management Practices on Environmental Sustainability: The Moderating Role of Quality Culture. Int. J. Lean Six Sigma 2023, 14, 1626–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.L.S.; Adame, M.E.C.; Sánchez, B.T. Calidad Para La Competitividad En Las Micro, Pequeñas y Medianas Empresas, de La Ciudad de México. Rev. Venez. Gerenc. 2017, 22, 551–575. [Google Scholar]
- Calvo, J.C.A.; Ortiz, R.F.; Menorca, M.L.G. Technological Capacities and Quality Certifications. An Empirical Application to La Rioja Family SMEs. Cuad. Gest. 2004, 4, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camisón, C.; Boronat Navarro, M.; Villar López, A. Estructuras Organizativas, Estrategias Competitivas y Ventajas Estratégicas de Las PYMES. Econ. Ind. 2010, 375, 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio, A.; Aragón, A. Recursos Críticos y Estrategia En La Pyme Industrial. Rev. ICE Trib. Econ. 2009, 17, 193–212. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio, A.; Aragón, A. Recursos Estratégicos En Las Pymes. Rev. Eur. Dir. Econ. Empresa 2008, 17, 103–126. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, T.C. Total Quality Management as Competitive Advantage: A Review and Empirical Study. Strateg. Manag. J. 1995, 16, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OEA-GTZ. Gestión de La Calidad En Pequeñas y Medianas Empresas; Memoria del Proyecto Copatrocinado por OEA y GTZ; OEA: Bogotá, Colombia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilasocho, D.; Galeana, E.; Guerra, J. Factores Que Afectan La Competitividad de Las Pymes Agrocítricas Manufactureras En Michoacán. Dialnet 2014, 15, 45–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuner-Flores, M.R.; Mercado Salgado, P. Gestión de Calidad En PyMEs Manufactureras Certificadas Con ISO 9001-2000. Rev. Cent. Inv. 2011, 9, 79–97. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, S.-C.; Hung, S.-W.; Lin, M.-J.J. Are Alliances a Panacea for SMEs? The Achievement of Competitive Priorities and Firm Performance. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 2015, 26, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, R.; Lin, S. The Embedding Path of Design Innovation in Garment Enterprises’ High-Quality Development. J. Silk 2022, 59, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamatinulu; Dahlan, M.; Rauf, N.; Nusran, M. Interpretive structural modeling of performance improvement strategies on perspective of customers. Int. J. Tech. Phys. Probl. Eng. 2023, 15, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Niyi Anifowose, O.; Ghasemi, M.; Olaleye, B.R. Total Quality Management and Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises’ (SMEs) Performance: Mediating Role of Innovation Speed. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaleye, B.R.; Ali-Momoh, B.O.; Herzallah, A.; Sibanda, N.; Ahmed, A.F. Dimensional Context of Total Quality Management Practices and Organizational Performance of SMEs in Nigeria: Evidence from Mediating Role of Entrepreneurial Orientation. Int. J. Oper. Quant. Manag. 2021, 27, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Hamid, N.A.; Ahmad, A.N.A.; Nawi, M.N.M.; Rahman, N.A.A.A.; Hamid, N.A.A. The impact of tqm on business performances based on balanced scorecard approach in Malaysia SMEs. Int. J. Qual. Res. 2022, 16, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teplická, K.; Hurná, S. New Approach of Costs of Quality According Their Trend of during Long Period in Industrial Enterprises in SMEs. Manag. Syst. Prod. Eng. 2021, 29, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-C. The Effectiveness Analysis of the Practices in Five Quality Management Stages for SMEs. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 2020, 31, 955–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silviana; Hardianto, A.; Fuhaid, N.; Hermawan, D. Designing the Ergonomic Press and Molding Machine of Cassava Chips for Sustainable Development in Smes. Pertanika J. Sci. Technol. 2021, 29, 1595–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariastuti, N.L.P.; Pratikto, P.; Santoso, P.B.; Tama, I.P. Analyzing the Drivers of Sustainable Value Creation, Partnership Strategies, and Their Impact on Business Competitive Advantages of Small & Medium Enterprises: A PLS-Model. East.-Eur. J. Enterp. Technol. 2021, 2, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Rothstein, H.R. Introduction to Meta-Analysis; Nachdr.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hedges, L.V.; Olkin, I. Statistical Methods for Meta-Analysis. J. Educ. Stat. 1988, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W. Accuracy of Funding Information in Scopus: A Comparative Case Study. Scientometrics 2020, 124, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengadesh, S.; Chinna, P.R.; Aravindaraj, K. A Bibliometric Analysis of Research Trends in Goods Transportation Using the Scopus Database. Bus. Perspect. Res. 2023, 227853372211488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.E.; Pitsouni, E.I.; Malietzis, G.A.; Pappas, G. Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar: Strengths and Weaknesses. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Martín, A.; Orduna-Malea, E.; Thelwall, M.; Delgado López-Cózar, E. Google Scholar, Web of Science, and Scopus: A Systematic Comparison of Citations in 252 Subject Categories. J. Informetr. 2018, 12, 1160–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Timilsina, B. Sources of Sustainable Competitive Advantage and Direction of Development: A Study on Pharmaceutical SMEs. Acta Logist. 2023, 10, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring Inconsistency in Meta-Analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Sutton, A.J.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Terrin, N.; Jones, D.R.; Lau, J.; Carpenter, J.; Rucker, G.; Harbord, R.M.; Schmid, C.H.; et al. Recommendations for Examining and Interpreting Funnel Plot Asymmetry in Meta-Analyses of Randomised Controlled Trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, T.D.; Doucouliagos, H. Meta-Regression Analysis in Economics and Business; Routledge: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).