Abstract
While tank vehicles are in the process of transporting liquid chemicals, the transportation task may be delayed or terminated due to disruptions in the transportation network. To reduce transportation losses, it may be necessary to evaluate network performance to cope with emergencies in the transportation network. This study investigates the vulnerability of the road network for liquid chemical transportation (RNLCT) under both intentional and random attacks. We selected six network indices, including average degree, average path length, average betweenness of node and edge, average clustering coefficient, and network efficiency to analyze the topological structure of the network. A reverse greedy algorithm is applied to identify 40 key nodes for simulated intentional attacks. The results show that network efficiency drops by 57.3% under targeted attacks, compared to 37.8% under random attacks. Moreover, the proposed method outperforms the distance laplacian centrality, which leads to a 43.3% reduction, demonstrating its effectiveness in identifying key nodes and enhancing network robustness.
1. Introduction
The hazardous chemicals industry is an important manufacturing industry in China, closely related to the national economy, public safety, and sustainable development. Due to the intrinsic risks of hazardous chemical transport and its critical role in industrial supply chains, road-based chemical logistics has become a focal point in transportation safety management []. In 2022, the hazardous chemicals industry in China recorded a total cargo transportation volume of approximately 1.81 billion tons []. Among this, road transportation accounts for nearly 70% of the total freight volume across all modes of transport [].
In the context of increasing global concerns about hazardous material transportation safety, both developed and developing countries have strengthened research and regulation in this area. For most national traffic policies, their overall objective is to provide society with an economical and sustainable transportation network [,,]. With the continual growth in road-based transportation, a substantial amount of hazardous chemicals now circulates within urban road networks, effectively turning transport vehicles into mobile risk carriers [,,,].
As a representative hazardous liquid chemical, ammonia is liquid at a specific temperature and pressure. Its freight mode is mainly transported by tank truck. Liquid ammonia is corrosive and easy to volatilize, and its chemical accident rate is high. Transportation accidents may cause traffic congestion and delay or even fail to complete the transportation task []. These results will degrade the performance of the network []. These disruptions, often referred to as transportation network vulnerability, have been widely studied in terms of topological fragility and risk exposure [].
Recent studies have focused on evaluating network vulnerability under various failure scenarios, including random disruptions and targeted attacks [,,]. However, most existing research either lacks an emphasis on liquid chemical transportation or primarily addresses static properties without integrating dynamic disruption mechanisms or realistic routing constraints. Moreover, there remains a research gap in identifying critical nodes using computationally efficient algorithms that account for intentional attacks in realistic and large-scale networks.
From the perspective of safe transportation and management of liquid chemicals, assessing the interaction between failed nodes and their impact on network vulnerability can more effectively identify vulnerable links, provide references for transportation authorities to optimize road structures, and offer theoretical foundations for vehicle dispatching strategies. To address these gaps, this study applies complex network theory to analyze the vulnerability of road networks for liquid chemical transportation (RNLCT). By incorporating different attack strategies and considering network performance degradation under node failure, we aim to explore how intentional disruptions impact network integrity and to identify key nodes critical to maintaining network functionality.
This study is contextualized using the RNLCT of Jiangsu, China, which serves as a representative case due to its dense logistics infrastructure, high freight volume, and strategic economic position. These characteristics make Jiangsu an ideal setting to examine network-level vulnerabilities in critical transport systems, while the analysis is based on Jiangsu, the proposed methodology is generalizable and applicable to other regions with similar logistics and transport network structures.
There are 202 nodes and 597 edges in RNLCT. We collected the data of nodes and edges from the China liquid ammonia information website []. Highways occupy the main part of network routes, while ordinary roads occupy the remaining part. Using ArcGIS to process the road network map of RNLCT, the final network topology of RNLCT is shown in Figure 1.
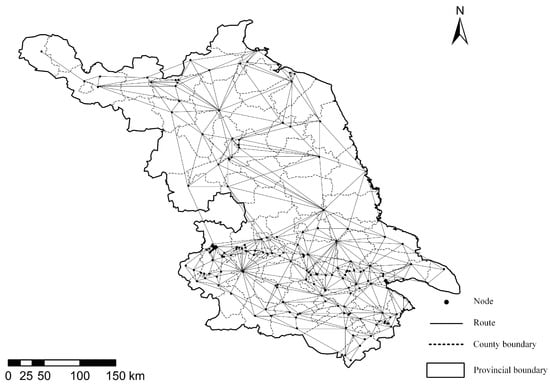
Figure 1.
Network topology of RNLCT.
Based on Figure 1, we can find that the network nodes and edges are densely distributed. If some nodes fail because of a liquid ammonia transportation accident, routes between other nodes will be significantly extended. To find the vulnerable links in the network and protect nodes based on the analysis results. We need to analyze the vulnerability of RNLCT by attacking the network with an intentional attack strategy. And then, we compare the result with random attack strategy. If there is a significant difference between the two, it indicates the effectiveness of intentional attacks and highlights the structural vulnerability of the targeted nodes. Compared with ordinary transportation networks, the characteristics of RNLCT can be summarized as follows:
- The network is far away from areas with high population densities, and the route of liquid ammonia usually passes through the suburbs, making it less susceptible to traffic from urban areas;
- In order to ensure the timeliness of road transportation of liquid ammonia, the lines with long travel time and good road conditions are usually selected;
- When road traffic accidents occur, network emergency response speed is faster due to the influence of the management mechanism.
In this work, we conducted a vulnerability analysis of the real-world liquid chemical transportation network in Jiangsu, China, and identified the network’s key nodes and its robustness. The main contributions of this work include
- This work constructs and analyzes a real-world road network for liquid chemical transportation in Jiangsu, China, which provides a practical case study illustrating the implementation of the method on a real-world logistics network;
- A vulnerability assessment framework is proposed to evaluate the performance of the transportation network under intentional attacks, focusing on the degradation of network connectivity;
- Several standard network metrics, including average degree, average path length, node and edge betweenness, clustering coefficient, and network efficiency, are adopted from the literature to examine the topological characteristics of the transportation network;
- A reverse greedy algorithm (ARG) is employed to identify 40 nodes whose removal leads to the greatest degradation in the network’s connectivity and performance under simulated attack scenarios;
- A comparative analysis between intentional attacks and random failures is conducted, showing that targeting nodes with higher importance rankings results in more pronounced network degradation compared to random node removals.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 describes a related literature review on network analysis for road transportation and vulnerability analysis. Section 3 presents the vulnerability analysis indicators for the RNLCT, analyzes its topological characteristics, and identifies key nodes in the network using the ARG algorithm. Section 4 combines intentional and random attack strategies to attack the network, and then analyzes the vulnerability of RNLCT. Section 5 summarizes this work and suggests several future research directions.
2. Related Work
This section reviews prior studies from three aspects: network analysis for road transportation, vulnerability of road transportation networks, and greedy strategies for network vulnerability. These works provide a foundation for understanding how transportation networks respond to disruptions and risks. In addition, we highlight the necessity of analyzing the vulnerability of RNLCT.
2.1. Network Analysis for Road Transportation
We distinguish road transportation networks by the types of goods transported [,]. We divide it into two types: general goods and hazardous chemicals, and then, describe their related research separately.
Road transportation network analysis plays a critical role in understanding and optimizing the movement of general goods across complex infrastructure systems. In recent years, researchers have applied both traditional modeling approaches and emerging data-driven techniques to capture and predict network performance.
Extensive efforts have been devoted to the analysis of road transportation networks for general goods, covering key aspects such as network sensitivity, abstraction, prediction, and resilience. For example, Zhu et al. proposed a road network abstraction method that scientifically and systematically selects a representative road network from the original full-size network to achieve both representativeness and computation efficiency in various transportation and traffic analysis applications []. In terms of traffic prediction, Ma et al. proposed a convolutional neural network-based method to learn traffic as images and predict large-scale, network-wide traffic speed with high accuracy []. Further advancing predictive capabilities, Xu et al. proposed a new traffic network state prediction model for freeways based on a generative adversarial framework to predict future traffic network states []. From a network resilience perspective, Jia et al. proposed a dynamic cascading failure model to analyze the network performance of a general goods transportation network []. Complementing this, Majumdar et al. introduced long short-term memory networks for the prediction of congestion propagation across a road network []. These studies collectively emphasize traffic state analysis and predictive modeling of transportation networks, yet primarily focusing on general goods.
Due to the high risk and potential consequences of accidents, the road transportation of hazardous chemicals requires more rigorous network analysis than that of general goods. Recent studies have explored various modeling and data-driven approaches to optimize routing decisions and assess network vulnerability.
For hazardous chemicals transportation networks, Shen and Wei applied the extreme gradient boosting algorithm to analyze accident data across seven regions in China []. Noguchi et al. employed network theory to examine liquefied petroleum gas transportation accidents in Japan, incorporating environmental factors into a transportation accident network to sample accident scenarios []. These studies highlight the relevance of network-based approaches in assessing accident impacts. Given the severe and often unpredictable consequences of hazardous chemical accidents, which may disrupt critical links in the network, evaluating network performance and identifying vulnerable components is essential. In this context, Song et al. developed a bi-objective optimization model for hazardous freight in rail–truck networks, minimizing both risk and cost while incorporating practical constraints, such as traffic regulations, alternative routes, and train schedules [].
Recent studies on road transportation networks have primarily focused on network efficiency, performance, traffic load, and accidents involving hazardous chemicals. For general freight networks, researchers often emphasize traffic indices to improve operational efficiency and environmental quality, whereas studies on hazardous chemicals transportation tend to prioritize accident rates and environmental risk factors. Given that emergencies are typically unpredictable and can severely disrupt network structure, this study simulates targeted disruptions through intentional attacks to systematically evaluate network vulnerability.
2.2. Vulnerability of Road Transportation Network
In the transportation network of dangerous chemicals, vulnerability is usually defined as a weak link that may lead to network failure, and vulnerability is an inherent attribute of any system []. Vulnerability is used to describe the susceptibility, powerlessness, and marginal state of physical and social systems to injury and to guide the normative analysis of actions to improve well-being by reducing risk [,,].
Assessing the vulnerability of transportation networks constitutes a fundamental step toward enhancing their resilience in the face of natural disasters and extreme events. Recent research efforts have increasingly emphasized the identification of critical infrastructure components and the evaluation of potential disruptions, aiming to support robust emergency response strategies and efficient post-disaster recovery planning.
For a weak component or geographical location whose failure would cause major damage. It describes the characteristics of vulnerable objects []. Tang and Huang proposed a Bayesian network method for seismic vulnerability assessment of an urban road network considering spatial seismic hazard with different levels of ground motion intensities, vulnerability of the components and effect of structural damage of components within the road network to the network functionality []. Cantillo et al. proposed a transportation network vulnerability assessment model, which can determine the key links of developing high impact disaster response actions []. Understanding disruption types is vital for assessing transportation network vulnerability. Recent studies analyze scenarios such as natural disasters, system failures, and intentional attacks to support resilience planning.
Numerous studies have investigated the vulnerability of transportation networks under various types of disruptions, with a particular focus on hazardous materials and environmental risks. Zhong et al. conducted a quantitative vulnerability analysis on road networks for hazardous goods transportation, proposing an iterative and a step-by-step algorithm to compute correlation coefficients and link impact strengths []. Building on the environmental dimension of hazardous goods transport, Machado et al. incorporated environmental risk factors into a multi-criteria vulnerability assessment framework for highway and trunk road networks []. To address scenarios involving simultaneous link disruptions, Xu et al. developed an optimization-based approach to derive the upper and lower bounds of network vulnerability []. Extending the scope to natural hazards, Zhang et al. introduced a data-driven method for evaluating network vulnerability and accessibility under landslide-induced disruptions []. In a more infrastructure-specific context, Lu et al. proposed an accessibility-based model that incorporates structural attributes such as road alignment and facility types (e.g., bridges, tunnels) []. Most recently, Nie et al. advanced the research by developing an adaptive topological optimization model for urban road networks, integrating population density data to construct a composite vulnerability index, and analyzing network robustness under various attack scenarios and user information levels [].
2.3. Greedy Strategy for Network Vulnerability
Greedy algorithms have been widely adopted in the network vulnerability assessment to efficiently identify critical components by iteratively optimizing local criteria across various infrastructure systems. In their framework for assessing road network vulnerability, Starita and Scaparra addressed the model’s computational complexity by incorporating a greedy strategy, which identifies the most damaging link failures by sequentially building a disruption set based on the greedy rationale that removing high-flow arcs most effectively increases system-wide congestion []. Pu et al. introduced a greedy attack strategy for power grid vulnerability assessment, where the most critical links are identified by greedily selecting those with the highest rank according to a novel link centrality metric that uniquely combines both topological and electrical properties of the network []. Li et al. developed an edge importance greedy strategy that iteratively expands a set of known important nodes by greedily selecting the adjacent node with the highest connection score, which is based on a metric of edge importance []. Extending greedy strategies to the vulnerability analysis of hypergraphs, Wang et al. developed a greedy algorithm, which identifies critical nodes by iteratively selecting the one with the highest marginal benefit, but replaces slow simulations with a fast and accurate influence evaluation function []. Li et al. proposed a failure propagation graph-based greedy search algorithm to identify critical branches for reinforcement, which iteratively applies a greedy strategy by selecting the single branch that yields the maximum cascading risk reduction from a candidate set intelligently pruned by a novel failure propagation graph [].
These works have applied greedy strategies across a variety of network types to efficiently identify critical nodes or links. These approaches commonly rely on iterative selection based on locally defined metrics such as flow, connectivity, or risk contribution to approximate vulnerable components under different disruption scenarios. The effectiveness and adaptability of greedy algorithms make them a practical choice for large-scale network vulnerability analysis.
The necessity of this study arises from three key considerations. First, the high-risk nature of RNLCT requires a risk-oriented perspective that goes beyond general transport analysis. Second, the theory of network vulnerability provides a strong analytical foundation for such an assessment. Third, greedy algorithms have demonstrated practical effectiveness in addressing similar problems. By combining these elements, this research applies a tailored greedy strategy-based vulnerability analysis to RNLCT, contributing to more effective risk management and infrastructure resilience.
3. Methodology
This section introduces the methodology used to analyze the topological structure of the RNLCT and identify key nodes in the network. First, a set of network characteristic indicators is computed to understand the structural properties of the RNLCT. Then, an importance index system for nodes is constructed by combining multiple structural metrics. Finally, an ARG algorithm is applied to determine the most critical nodes whose failure would significantly affect network connectivity and efficiency. The research framework of this paper is shown in Figure 2.
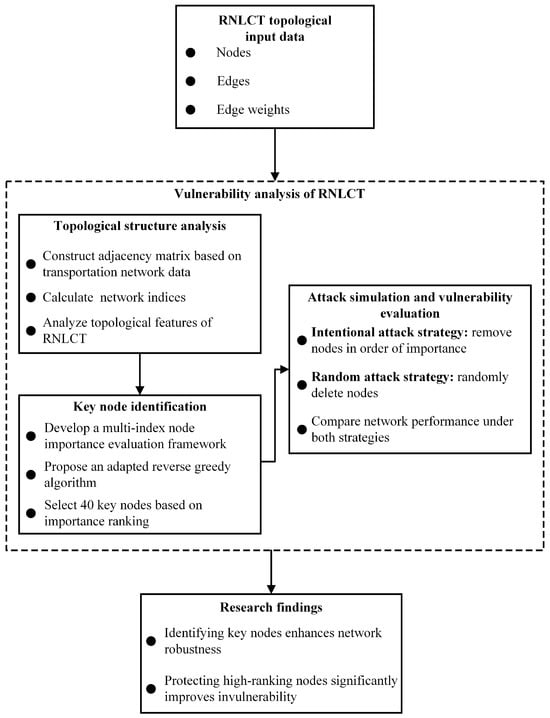
Figure 2.
Research framework of RNLCT.
Considering the characteristics of the RNLCT, we assume the following properties:
- The network does not consider the direction of edges;
- The nodes and edges of the network have the same level;
- The shortest path lengths of edges in the network are the straight-line distance between nodes.
- An intentional attack will affect the nodes of RNLCT, attack the key nodes that destroy the network first, and the attack process will not affect the liquid ammonia transported, nor will it cause explosion, poisoning, and other derived accidents.
Regarding Property 3, the edge length in the RNLCT network are defined as the straight-line distance between nodes. This simplifies network construction and highlights key structural features without modeling full transport routes. This approach is reasonable because the transported chemical, anhydrous ammonia, is delivered under time constraints by licensed carriers. In general, longer straight-line distances imply longer actual routes, which are more prone to delays or disruptions. Therefore, longer edges indicate higher transport risk, while some short edges may connect important nodes, their significance is reflected through node-level metrics, such as degree and betweenness centrality. Edge length and node importance are thus evaluated from different but complementary perspectives.
Based on the topological structure of the RNLCT, we design two node attack strategies, intentional and random, and compare the resulting changes in network performance. This analysis helps identify weak links within the network and provides a basis for proposing targeted optimization strategies aligned with real-world conditions.
3.1. Topological Structure Analysis of RNLCT
The computational experiments are performed on a PC equipped with an Intel Core i5 CPU (2.5 GHz) and 16 GB of RAM. By building the adjacency matrix of RNLCT, each programming index of the network is solved by using MATLAB R2023b.
The RNLCT is defined as , where V is the set of nodes, E is the set of edges, and D represents the corresponding edge lengths. The RNLCT is simplified as an undirected connected network by building corresponding indexes combined with the special conditions of liquid ammonia road transportation. The symbol description of each characteristic index is shown in Table 1 and Table 2 present their definitions and equations in the context of the RNLCT.

Table 1.
Description of parameters.

Table 2.
Description of parameters.
By programming the network index, various characteristic index values of RNLCT are obtained as shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Characteristic index values of RNLCT.
According to the results presented in Table 3, the RNLCT network exhibits a relatively dense structure with an average degree of about 5.9, indicating that each node is well connected. The very short average path length suggests a highly compact network facilitating rapid communication between nodes, characteristic of small-world networks. Low average node and edge betweenness values imply that the network is fairly evenly distributed without over-reliance on specific nodes or edges, enhancing robustness. A moderate clustering coefficient indicates notable local clustering or community structure within the network. However, the relatively low network efficiency suggests there is still room for improvement in overall information transfer efficiency, particularly for long-distance connections. Compared with other transportation networks of the same size [], RNLCT demonstrates unique structural features.
3.2. Key Nodes Identification
Identifying and selecting key nodes is important for vulnerability analysis of networks. Not all nodes are equal in large-scale complex networks. In RNLCT, key nodes play a central role in the whole network. In the process of transporting liquid ammonia, the emergencies will lead to the failure of key nodes in the network, which will lead to the loss of local connectivity of the road network. The smooth operation of key nodes and road segments helps to ensure the efficiency of transportation and improve the accuracy of performance analysis of the road transportation network.
3.2.1. Node Importance Index System Construction
Traditional key node identification methods are usually determined by a single index []. Based on this, we propose improvement measures. We consider the degree, betweenness and complementary graph network efficiency (the network formed after the node fails) as the basis for determining the key nodes of the network. Based on the previous equations, the distribution of each index in RNLCT can be obtained, as shown in Figure 3.
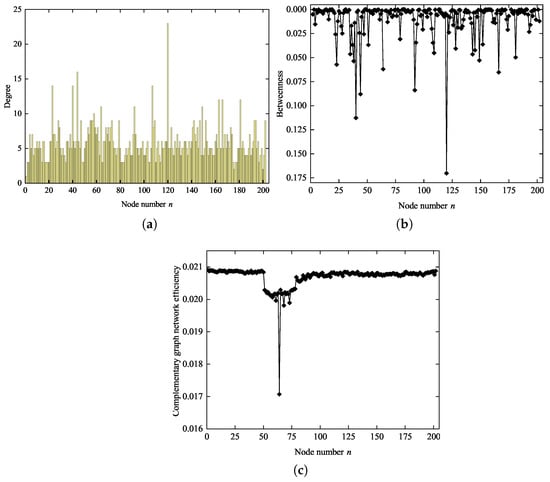
Figure 3.
Three indexes of nodes in RNLCT: (a) degree of each node; (b) betweenness of each node; (c) complementary graph network efficiency after removing each node.
As shown in the three subfigures of Figure 3, the RNLCT network displays clear heterogeneity. Figure 3a shows that most nodes have low degrees, while a small number of nodes, such as those around node 120, have significantly higher degrees and form hub nodes. Figure 3b indicates that these high-degree nodes often also have high betweenness centrality, suggesting they play important roles as bridges in the network. Figure 3c highlights a key observation: the sensitivity of network efficiency to node removal is not entirely determined by node degree or betweenness. For example, removing nodes near node 65 results in the largest decrease in network efficiency, even though these nodes do not have the highest degree or betweenness. This suggests that some nodes, while not prominent hubs, are still critical to maintaining the overall efficiency and connectivity of the network.
However, it is not enough to use these three indicators as the basis for identifying key nodes. In order to establish a complete evaluation index system of node importance, the selected index needs to be representative and comprehensive, not only to reflect the importance of node’s topology in the network, but also to contact the actual network of RNLCT.
3.2.2. Identifying Key Nodes Based on ARG Algorithm
To identify key nodes, we adopt the Approximate Reverse Greedy (ARG) algorithm, which iteratively removes the node with the least marginal contribution to overall network performance []. Unlike traditional strategies such as degree, betweenness, or eigenvector centrality that often overlook network dynamics or risk propagation, ARG directly targets overall network impact and offers a scalable heuristic for approximating node importance. Compared to exact optimization methods, ARG avoids combinatorial complexity while still delivering competitive results []. This makes it particularly suitable for the risk-sensitive and large-scale nature of RNLCT networks. The detailed procedure for the key node identification is depicted in Algorithm 1.
Subsequently, the top 40 nodes from the algorithm output are selected as key nodes, and their rankings are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Rank of key nodes in RNLCT.
Based on the node rankings in Table 4, analysis of their geographic and topological features shows that a node’s importance in the RNLCT network comes from a combination of factors: strategic location, high degree centrality, and its role as a bridge between regions, rather than any single attribute. The key nodes are primarily concentrated in two categories of strategically critical areas:
- Major hubs in the economically dense southern Jiangsu region: the top-ranked node, node 120, along with nodes 107, 149, and 152, are all located in the industrial corridor along the southern bank of the Yangtze River. As shown in Figure 1, these nodes have high degree centrality, acting as key hubs in the densest part of the network. Their high betweenness centrality highlights their role as major bridges for hazardous chemical transport between the provincial capital and key economic areas. Disrupting any of these nodes would severely impact the most active part of the provincial supply chain.
- Critical gateways and regional centers connecting north and south Jiangsu: nodes 44, 40, and 23 are especially important due to their strategic locations. Node 44, at the Yangtze River estuary, serves as a key gateway between southern and northern Jiangsu, and its loss would cut off a major transport route. Nodes 40 and 23 also play crucial roles in central Jiangsu, linking the developed south with the larger northern area. Other nodes, like node 12 in the northwest, act as important regional hubs and main connections to neighboring provinces such as Shandong and Anhui.
| Algorithm 1 ARG Algorithm |
| Input: Network adjacency matrix A; Output: Node sequence ;
|
In summary, the most critical nodes in the RNLCT network are those that combine strategic geographical positions such as regional centers and river crossings with strong topological features including high degree and betweenness centrality. These nodes act either as key hubs within dense industrial zones or as essential bridges connecting otherwise separated economic areas. As a result, they represent potential single points of failure, whose disruption could trigger significant cascading effects throughout the entire network.
4. Simulation Experiments
This section presents the simulation results of the road network vulnerability under intentional and random attacks. By modeling the RNLCT and applying the ARG algorithm, key nodes are identified and analyzed. The effectiveness of intentional attack strategies is evaluated by tracking changes in network performance indicators. Subsequently, a comparative analysis with random attack strategies is conducted to further highlight the importance of protecting critical nodes.
4.1. Network Performance Under Intentional Attacks
Combined with vulnerability analysis indicators and identified key nodes, RNLCT is modeled and simulated to analyze the impact of network node failure on the global network under deliberate attack. The specific process of vulnerability analysis is as follows:
- The network is intentionally attacked based on the rank of key nodes until all key nodes fail;
- Calculates the performance indexes of the network after each node failure;
- Summarize the index value and compare with the network performance change under random attack strategy.
The failure node distribution under intentional attack is shown in Figure 4.
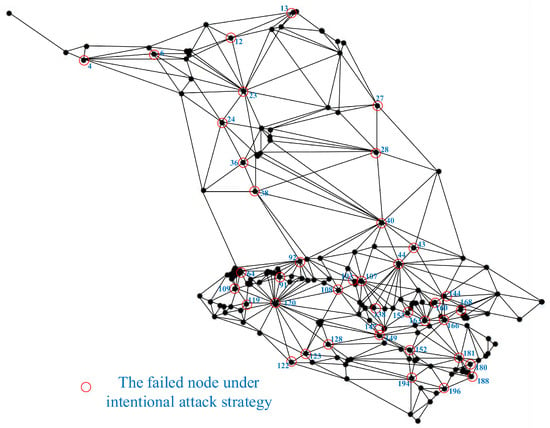
Figure 4.
Network nodes intentionally attacked in RNLCT.
According to the rank of key nodes, attack the key nodes in the network from back to front, invalidate the nodes, and destroy the connectivity of the network. We assume that the initial performance of the RNLCT is 1, intentionally attacking 40 key nodes and causing them to fail. After that, we analyze the relationship between network performance degradation and the number of key nodes attacked. The network performance under intentional attack strategy is shown in Figure 5.
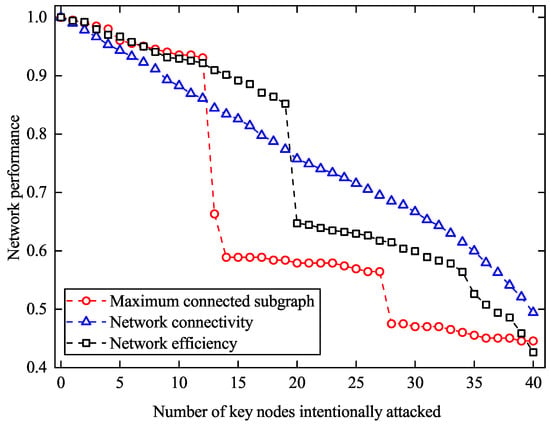
Figure 5.
Network performance under intentional attacks on key nodes.
From the results in Figure 5, we can find that the value of the maximum connected subgraph and network efficiency decrease rapidly in the early stage. After 13 key nodes failing, the value of the maximum connected subgraph dropped from 0.93 to 0.66. The value of network efficiency also dropped from 0.85 to 0.65 attributed to 19 key nodes failed. After that, the tendency to decrease tends to be stable. Therefore, the maximum connected subgraph has similar characteristics with the trend of network connectivity. In contrast, the tendency of network connectivity is relatively slow. After 40 key nodes failed, the value of three indexes fell below 0.5, which means the network composed of the remaining nodes is difficult to implement the normal liquid ammonia transportation plan. Node 120 and 44 are close to the node dense area and bear the traffic load from the surrounding area. The operation of these two nodes makes the network maintain a normal state at the beginning of intentional attack. After removing the 40 key nodes, the network efficiency drops to 0.43, representing a 57.3% decrease compared to the complete network.
These results highlight the RNLCT network vulnerability to intentional attacks on structurally important nodes, where a few failures can lead to significant degradation in both connectivity and efficiency.
4.2. Comparison with Random Attack Strategy
To compare and analyze the changes in network performance under intentional attack, a random attack strategy is adopted for the nodes in the network. After maintaining 40 key nodes, attack the remaining 162 nodes randomly, and analyze the impact of 40 failed random nodes on the performance of the RNLCT. Changes in network performance under random attacks are shown in Figure 6.
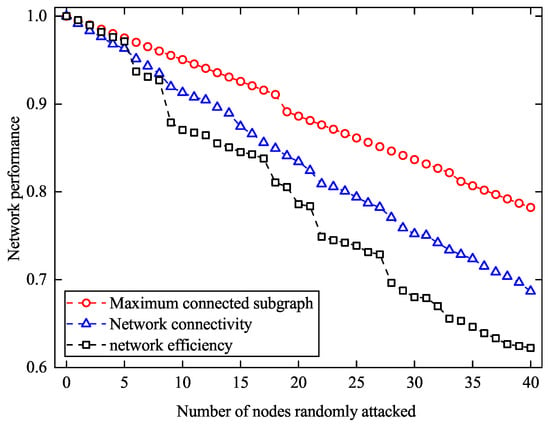
Figure 6.
Network performance under random attacks.
According to Figure 6, we can obtain that the downward trend of the three indicators is stable. After 40 random nodes fail, the network efficiency value remains at 0.62 and the maximum connected subgraph value is 0.78, which means that the network still maintains most of its functions. Intentional attack strategy can achieve the same effect if only 20 nodes fail. That is, after protecting the key nodes, the network has some destructiveness. The tendency of three index values has similar characteristics, which indicates that the selected random nodes are less important in the network. After removing 40 random nodes, the network efficiency decreases to 0.62, representing a 37.8% reduction compared to the complete network.
In contrast, under intentional attacks where key nodes are removed in order of importance (as shown in Figure 5), the network experiences sharp declines after removing only a small number of nodes. For example, removing just 12 targeted nodes can reduce the size of the maximum connected subgraph to around 0.6, and network efficiency drops even more drastically. This stark contrast highlights the highly uneven role of different nodes in the network, while many nodes have limited structural importance, a few serve as central hubs or bridges that are critical for maintaining overall connectivity and communication efficiency.
From a performance perspective, the analysis reveals that random attacks tend to preserve network integrity due to their low probability of affecting high degree or high betweenness nodes. The gradual performance degradation under random failure suggests redundancy and alternative paths exist within the network. However, the dramatic impact of targeted attacks underscores a vulnerability rooted in structural heterogeneity, where a small number of nodes disproportionately influence global performance. These findings emphasize the need for protective strategies focusing on the structural core of the network to enhance its resilience.
4.3. Comparison with Existing Key Node Identification Methods
To validate the performance and effectiveness of the proposed algorithm, we perform a comparative analysis against a state-of-the-art key node identification method. A primary benchmark selected for this comparison is the recently introduced distance laplacian centrality (DLC) []. DLC is a centrality measure that assesses node importance from a graph energy perspective. Its core principle is to evaluate a node’s criticality based on its contribution to the structural stability of the network. Specifically, node importance is quantified by the relative decrease in the network’s total distance Laplacian energy following the removal of that node. A greater reduction in energy indicates a more critical role of the node in maintaining the global connectivity and distance-dependent structure of the network.
Moreover, DLC effectively captures global network characteristics by incorporating the concept of transfer degree, defined as the sum of a node’s shortest path distances to all other nodes. Figure 7 presents the network performance under intentional attacks based on the DLC method.
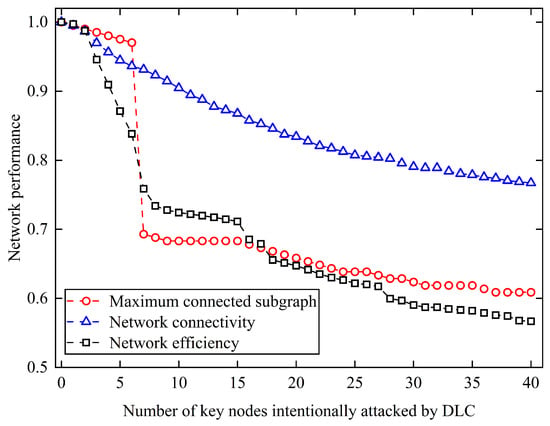
Figure 7.
Network performance under intentional attacks on key nodes by DLC.
As illustrated in Figure 7, the removal of key nodes identified by the DLC method results in a notable decline in network performance across all three evaluated metrics. Specifically, network efficiency decreases significantly as more critical nodes are removed, dropping to 0.57 after the top 40 nodes are attacked, which corresponds to a 43.3% reduction compared to the intact network. The maximum connected subgraph size also exhibits a sharp decrease in the early stages of the attack. After removing the first 6–8 key nodes, a dramatic fragmentation occurs, reducing the size of the largest connected component to approximately 68.8% of its original value. This indicates that the attacked nodes play a central role in preserving the overall structural integrity of the network. In addition, network connectivity, which reflects the proportion of connected node pairs, shows a relatively moderate yet steady decline, decreasing to approximately 76.7% after 40 nodes are removed. This suggests that although some pairwise connections remain, the global structure becomes increasingly sparse and less robust.
The comparative results reveal that intentional attacks targeting key nodes can cause severe damage to the network, leading to a sharp decline in performance and a higher risk of overall network failure. This poses a significant threat to transportation enterprises where timeliness and safety are critical. Simulation results further demonstrate that the proposed reverse greedy algorithm outperforms the recently proposed DLC method in identifying structurally critical nodes. Given the uncertainty of node failure in time and location, prioritizing the protection of a small subset of key nodes (e.g., nodes 120, 44, 107, 40, 23) identified by our method can serve as an effective strategy to enhance network resilience. In contrast, attempting to maintain all nodes uniformly would impose excessive costs and operational burdens on the enterprise.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
This paper investigates the vulnerability of the RNLCT network under both intentional and random attacks, revealing its structural weaknesses and offering insights for targeted improvements. For more effective network analysis, we used the ARG algorithm to identify key nodes. In the process of vulnerability analysis, we used two different attack strategies. In real circumstances, RNLCT is constrained by the geographic location of liquid ammonia producers and demand enterprises. This makes the network denser in the south and sparser in the north, leading to an unbalanced distribution of structural importance. The southern network also has a quantitative advantage in the distribution of key nodes. Under such conditions, the optimization adjustment of network routes will focus more on the south, while the northern network routes will consider their capacity to transfer loads.
Theoretically, this study contributes to the understanding of resilience in geographically constrained industrial logistics networks, demonstrating the utility of combining centrality metrics with simulated attack scenarios. Practically, the findings provide a decision-making reference for infrastructure planning, emergency response, and regional coordination of hazardous chemical transport.
Although this study focuses on Jiangsu, China, the proposed model is designed in a modular and data-driven manner, which allows for generalization to other countries or regions. Specifically, the model requires information on node locations (e.g., logistics centers, production hubs, and transit depots), the functional relationships between nodes (e.g., transport corridors or risk-weighted edges), and regional freight movement patterns. With such data, the network can be reconstructed and evaluated using the same methodology. For instance, the model could be readily adapted to analyze the RNLCT in other industrialized regions, where freight networks also play a critical role in regional economic integration.
For future research, several directions are worth exploring to enhance the realism and applicability of the model. Future studies could incorporate operational and risk-based indicators, such as the amount of hazardous material transported, traffic flow, and accident records, to evaluate node criticality more comprehensively. The vulnerability framework may also be improved by introducing more diversified attack strategies, including hybrid and edge-focused disruptions. Incorporating time-dependent failure probabilities and stochastic cascading effects can further enable a more realistic simulation of failure dynamics. These extensions would improve the model’s applicability for both policy-making and real-world risk assessment.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft, R.C.; software, R.C.; methodology, R.C.; data curation R.C.; writing—review and editing, F.Z.; project administration, F.Z.; funding acquisition, F.Z.; formal analysis, F.Z.; validation, F.Z.; supervision, F.Z.; conceptualization F.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 72271051) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 2232018H-07).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the anonymous referees for their invaluable comments on an earlier version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- China Statistical Yearbook 2023. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ndsj/2023/indexeh.htm (accessed on 22 May 2024).
- Analysis of the Current Status of China’s Hazardous Chemicals Logistics Market and Key Enterprises in 2023. Available online: https://www.huaon.com/channel/trend/979510.html (accessed on 21 April 2024).
- Zou, Z.F.; Kang, S.P. Route optimization for hazardous chemicals transportation under time-varying conditions. Sustainability 2024, 16, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdica, K. An introduction to road vulnerability: What has been done, is done and should be done. Transp. Policy 2002, 9, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Wang, S.Z.; Su, J.F. Integrated production and transportation scheduling in e-commerce supply chain with carbon emission constraints. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2021, 16, 2554–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.H.; Cheng, W.Y.; Gai, W.M. Hazardous chemicals road transportation accidents and the corresponding evacuation events from 2012 to 2020 in China: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.F.; Wang, X.H.; Pei, J.J.; Xu, M.; Huang, X.W.; Luo, Y. Risk assessment of the areas along the highway due to hazardous material transportation accidents. Nat. Hazards 2018, 93, 1181–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janno, J.; Koppel, O. Operational risks in dangerous goods transportation chain on roads. LogForum 2018, 14, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundin, J.; Antonsson, L. Road tunnel restrictions–Guidance and methods for categorizing road tunnels according to dangerous goods regulations (ADR). Safety Sci. 2019, 116, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornalchyk, Y.; Afonin, M.; Postranskyy, T.; Boikiv, M. Risk assessment during the transportation of dangerous goods considering the functional state of the driver. Transp. Probl. 2021, 16, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhou, J.; Yang, D. Causation analysis of hazardous material road transportation accidents based on the ordered logit regression model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.R.; Chan, A.P.C.; Yuan, J.; Xia, B.; Skitmore, M.; Li, Q.M. Recent advances in modeling the vulnerability of transportation networks. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2015, 21, 06014002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starita, S.; Scaparra, M.P. Assessing road network vulnerability: A user equilibrium interdiction model. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2021, 72, 1648–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.H.; Li, J.P.; Yuen, K.F.; Mao, X. Towards vulnerability urban road networks: Adaptive topological optimization and network performance analysis. J. Transp. Geogr. 2025, 126, 104237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Pan, Q.; Tang, J. HEDV-Greedy: An advanced algorithm for influence maximization in hypergraphs. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, D.; Fang, J.; Zhang, X.; Tse, C.K. Failure propagation graphs for studying cascading failure propagation in power networks. IEEE Syst. J. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liquid Ammonia Transportation Network in Jiangsu Province. Available online: http://www.yean.cn/ (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Holeczek, N. Hazardous materials truck transportation problems: A classification and state of the art literature review. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2019, 69, 305–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Miller-Hooks, E.; Denny, K. Assessing the role of network topology in transportation network resilience. J. Transp. Geogr. 2015, 46, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Chiu, Y.C.; Chen, Y.C. Road network abstraction approach for traffic analysis: Framework and numerical analysis. IET Int. Transp. Syst. 2017, 11, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.L.; Dai, Z.; He, Z.B.; Ma, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.P. Learning traffic as images: A deep convolutional neural network for large-scale transportation network speed prediction. Sensors 2017, 17, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.W.; Peng, P.; Wei, C.C.; He, D.F.; Xuan, Q. Road traffic network state prediction based on a generative adversarial network. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 14, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.F.; Li, F.Y.; Yang, L.L.; Luo, Q.Y.; Li, Y.X. Dynamic cascading failure analysis in congested urban road networks with self-organization. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 17916–17925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, S.; Subhani, M.M.; Roullier, B.; Anjum, A.; Zhu, R.B. Congestion prediction for smart sustainable cities using IoT and machine learning approaches. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 64, 102500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Wei, S. Application of XGBoost for Hazardous Material Road Transport Accident Severity Analysis. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 206806–206819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, H.; Hienuki, S.; Fuse, M. Network theory-based accident scenario analysis for hazardous material transport: A case study of liquefied petroleum gas transport in japan. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2020, 203, 107107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Yu, L.; Li, S. Route optimization of hazardous freight transportation in a rail-truck transportation network considering road traffic restriction. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 423, 138640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, P.; Cheng, Y. Concepts and assessment methods of vulnerability. Prog. Geogr. 2008, 27, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Adger, W.N. Vulnerability. Glob. Environ. Change 2006, 16, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Wang, M. Transportation functionality vulnerability of urban rail transit networks based on movingblock: The case of Nanjing metro. Physica A 2019, 535, 122367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.M.; Tong, Q.Q.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Q. Risk assessment of express delivery service failures in china: An improved failure mode and effects analysis approach. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2021, 16, 2490–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, L.G.; Jenelius, E. Vulnerability and resilience of transport systems—A discussion of recent research. Transp. Res. Part Policy Pract. 2015, 81, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Huang, S.P. Assessing seismic vulnerability of urban road networks by a Bayesian network approach. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2019, 77, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantillo, V.; Macea, L.F.; Jaller, M. Assessing vulnerability of transportation networks for disaster response operations. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2019, 19, 243–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.L.; Wang, J.; Yip, T.L.; Gu, Y.M. An innovative gravity-based approach to assess vulnerability of a Hazmat road transportation network: A case study of Guangzhou, China. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 62, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, E.R.; do Valle Júnior, R.F.; Fernandes, L.F.S.; Pacheco, F.A.L. The vulnerability of the environment to spills of dangerous substances on highways: A diagnosis based on Multi Criteria Modeling. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 62, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.D.; Chen, A.; Yang, C. An optimization approach for deriving upper and lower bounds of transportation network vulnerability under simultaneous disruptions of multiple links. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2017, 23, 645–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, H.; Li, Z.N.; Zhang, G.H.; Ma, D.T. Assessing potential likelihood and impacts of landslides on transportation network vulnerability. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 82, 102304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.C.; Xu, P.C.; Zhang, J.X. Infrastructure-based transportation network vulnerability modeling and analysis. Phys. A 2021, 584, 126350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, C.; Wu, P.; Xia, Y. Vulnerability assessment of power grids against link-based attacks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2020, 67, 2209–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yin, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, N. Mining algorithm of relatively important nodes based on edge importance greedy strategy. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girvan, M.; Newman, M.E.J. Community structure in social and biological networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7821–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Zhao, M.W.; Liu, H.K.; Xu, X.M. Networked characteristics of the urban rail transit networks. Phys. A 2013, 392, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.; Alam, S. A complex network approach towards modeling and analysis of the Australian Airport Network. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2017, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latora, V.; Marchiori, M. Efficient behavior of small-world networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 198701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccaletti, S.; Latora, V.; Moreno, Y.; Chavez, M.; Hwang, D.U. Complex networks: Structure and dynamics. Phys. Rep. 2006, 424, 175–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Chen, D.; Ren, X.L.; Zhang, Q.M.; Zhang, Y.C.; Zhou, T. Vital nodes identification in complex networks. Phys. Rep. 2016, 650, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morone, F.; Makse, H.A. Influence maximization in complex networks through optimal percolation. Nature 2015, 524, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Lang, C.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, L. Identifying critical nodes in complex networks based on distance Laplacian energy. Chaos Solitons Fract. 2024, 180, 114487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).