Abstract
The growth in the utilization and development of rail transport within urban networks is crucial for transitioning towards a more sustainable form of mobility. However, challenges related to discomfort and noise pollution arising from rail traffic must be addressed and mitigated to foster a harmonious coexistence between residents and trains. This study focuses on analyzing an experimental campaign conducted on the surface metropolitan network of Porto to study and identify the frequency content and pressure levels associated with light rail traffic. The presented experimental campaign holds significant relevance as it comprises various and distinct circulation conditions within the railway network, enabling a comprehensive characterization of railway noise. The collected data indicates a noticeable increase in sound pressure levels as the speed of circulation rises, particularly emphasizing the 1/3 octave band centered around 1000 Hz. The choice of tracks with components having a limited capacity for absorbing acoustic energy leads to a significant rise in noise levels compared to track solutions with elements exhibiting excellent acoustic energy absorption. Furthermore, the study highlights a substantial increase in noise levels (10 dBA) associated with small radius curves, even at low speeds. These findings underscore the importance of considering the track characteristics and geometric features in noise assessment within rail networks. Therefore, the insights gained from this experimental campaign contribute significantly to the understanding and comprehensive characterization of railway noise under diverse circulation conditions within the railway network.
1. Introduction
One of the primary objectives of modern society is to move towards a more environmentally and economically sustainable type of mobility. Rail transport appears to be the most efficient way of making this transition due to its low pollutant emissions and its capacity to transport a large number of people and goods. Thus, the growth of societies necessarily involves the use of this mode of transport; however, noise induced by rail traffic appears as a major problem that needs to be analyzed and solved. Several studies point to an increase in the number of people exposed to noise [1,2], and the problems that can result from this exposure have been the subject of study in several places, where there is a strong presence of urban railway traffic [3,4,5,6,7,8]. For the facts listed above, the experimental characterization of noise induced by rail traffic presents itself as an essential tool to characterize rail noise in all its dimensions to create measures to mitigate the natural effects of noise. The complete study of the noise problem implies the analysis of several aspects, namely, generation, propagation and reception. The characterization through in situ noise measurement in several types of scenarios, with different speeds, types of vehicles, types of tracks and different urban networks allows a clearer view of the sound pressure levels involved and, especially, the variations associated with the different circulation conditions mentioned above.
Taking these factors into account, several studies have addressed the issue to characterize and mitigate the noise levels existing in various locations on the European continent [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19]. The studies mentioned above reveal a clear connection between noise levels and frequency content, depending on specific traffic conditions. Factors like vehicle speed, vehicle characteristics, track solution, and other relevant aspects contribute to significant variations in the recorded noise levels. Based on the conclusions of this study, it is evident that the specific conditions of each location have a noticeable influence on noise levels. This paper presents the results obtained in an experimental campaign developed with the following objectives:
- To characterize the noise coming from the interaction between the track and the vehicle and the vehicle components;
- To identify its main frequency content;
- To assess the influence of different traffic conditions and types of tracks on noise levels.
Railway noise has several sources. It may originate, on the one hand, from the interaction of the track elements with the vehicle, or, on the other hand, it may originate from the components constituting the vehicle. Notwithstanding the various railway noise components, the noise generated by the wheel-rail interaction plays the most important role in noise generation. The variable that most affects the sound pressure levels and the origin of the noise is the velocity of circulation of the vehicles, as illustrated in Figure 1, where the main noise sources are shown as a function of circulation speed. The experimental characterization was carried out entirely on the railway tracks that are part of the surface metro network constitutes the Metro do Porto network, where the speed range is between 0 km/h and 80 km/h. Thus, as mentioned, the noise levels recorded are strongly influenced by rolling noise, as highlighted in Figure 1.
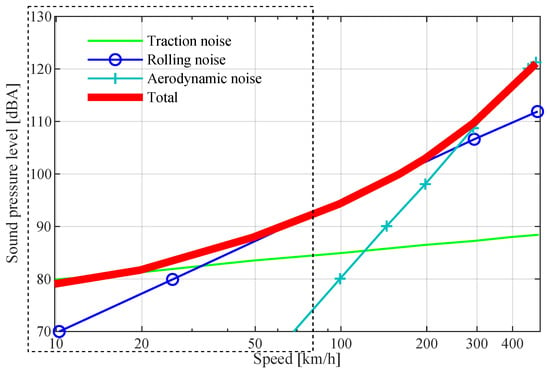
Figure 1.
Evolution of the contribution of the different sources as a function of the circulation velocity (adapted from [20]).
The aim of this experimental campaign and consequently of this article is to identify the noise sources within the speed range allowed on the surface metro network. As the noise depends on the speed of movement, the data collected concerns mainly the noise coming from rolling noise, as mentioned before. Rolling noise is associated with the interaction between track and vehicle, and results either from track or wheel irregularities or from the vibration of individual parts [21,22,23,24]. In addition to this, an attempt was also made to identify other particular cases of noise associated with track geometry and crossing bridges. The structure of the paper is as follows: Section 2, shows the main characteristics of the Porto surface metropolitan network and presents the experimental procedure for acoustic signal measurement; Section 3 presents an exhaustive analysis of the several circulation conditions, according to the collected data; finally, Section 4 summarises the main conclusions of this work.
2. Experimental Approach
2.1. Measurements Sites Conditions
The results presented, as mentioned, are part of an extensive experimental campaign carried out in the metropolitan area of Porto. Given its extension and variability of traffic conditions, 15 measurement sites were considered to cover various types of tracks that run through the urban mesh. The chosen locations allow the acquisition to be the most reliable and realistic of the noise emitted directly from the source without obstacles or other constraints that might interfere with the measurements.
As mentioned, the Porto surface metro network presents, in its extension, different types of circulation conditions, so it is important to define its main characteristics. It should be highlighted that four different types of track make up the rail network. The type of track influences noise emission, due to the way it is built or to the capacity of its materials to absorb the sound energy generated by passing trains. The types of tracks are listed below and a photograph of each is shown. For the sake of clarity and readability, each type of track has been given a designation, which is explained and will be used in the comparative analyses in the following sections. Finally, a particular type of noise will also be compared, the noise generated by rail traffic on bridges, since the light traffic network includes a metallic bridge.
- Track whose rails are embedded in the grass is the most absorbent (Type I), Figure 2a;
- Ballast track (Type II), Figure 2b;
- Slab track (Type III), Figure 2c;
- Track where the rails are embedded in the pavement (Type IV), Figure 2d;
- Track whose rails are connected to wooden sleepers, with the presence of large metal plates for pedestrian crossings, Figure 2e.
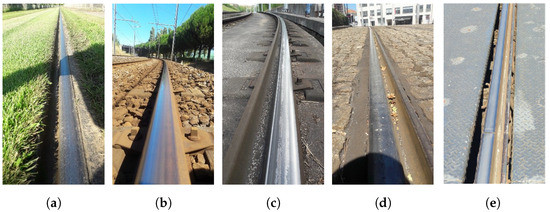
Figure 2.
Photographs of the type of tracks: (a) Type I; (b) Type II; (c) Type III; (d) Type IV; (e) Bridge.
In addition to the characteristics of the infrastructure of each measurement site and the circulation speeds, in the Porto metro network two different types of vehicles circulating, namely Eurotram and Flexity Swift, whose photographs can be found in Figure 3a,b. Both vehicles are supplied by Bombardier. Due to its nature, the Eurotram is a vehicle with lightweight characteristics and essentially for urban use, while the Flexity Swift is intended for longer journeys, applying to suburban connections [25]. Both vehicles are about 35 m long and two units can be coupled together. The Eurotram vehicle reaches a speed of 80 km/h, while the Flexity Swift unit has a top speed of 100 km/h. As already mentioned, in the case of the Porto network the vehicles reach maximum speeds of about 80 km/h.
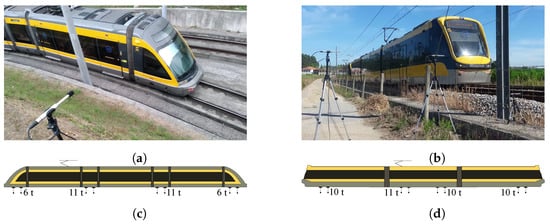
Figure 3.
Representation of vehicles operating in the metropolitan area of Porto: (a) Photograph of the vehicle Eurotram; (b) Photograph of the vehicle Flexity Swift; (c) Schematic representation of the vehicle load distribution Eurotram; (d) Schematic representation of the vehicle load distribution Flexity Swift.
In terms of the mechanical properties of the vehicles, Eurotram is composed of 5 modules, 4 bogies and 16 wheels per tram, whose loads are shown in Figure 3c. In the case of the Flexity Swift vehicle, it is composed of 3 modules, 4 bogies and and 16 wheels per tram whose the maximum axle loads are illustrated in Figure 3d.
2.2. Acoustic Measurements
The acquisition of the signal requires four microphones Behringer type ECM 8000 were connected to a Focusrite Scarlett 4Pre USB for the signal acquisition, as is shown in Figure 4. The post-processing of the data was performed in Matlab using the ITA-Toolbox 7.6 functions [26].
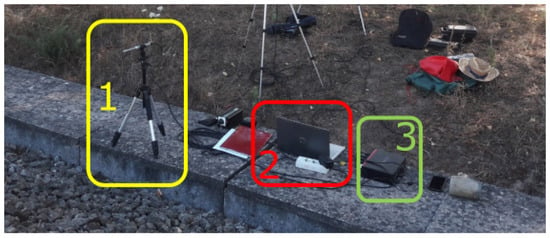
Figure 4.
Experimental setup for the acoustic signal acquisition; (1) Behringer ECM 8000 microphone, (2) computer, (3) Focusrite Sclarett 4Pre USB acquisition unit.
The definition of the measurement setups was made taking into account the specific constraints of each test site. The measurement setup included, on one hand, microphones placed as close as possible to the track, and, on the other hand, microphones placed in more distant locations where it is plausible the existence of passers-by and buildings. The microphone closest to the track is named M1 and so on along the array of receivers, being, therefore, the last microphone placed further away from the track named M4. In this way, the comparative analyses in the following section will be made for receivers occupying the same relative position. In practical terms, the microphone set comprises one microphone which is about 1.50 m from the outside of the vehicle and the others about 1.50 m from each other. In some locations, given the characteristics of the measurement site, it was possible to place microphones at about 80 cm from the rail. In the following analyses in the following sections, microphones at a distance of about 6 m and 7.5 m from the track were used. Both microphones were placed at a height of 1.50 m as illustrated in Figure 5.
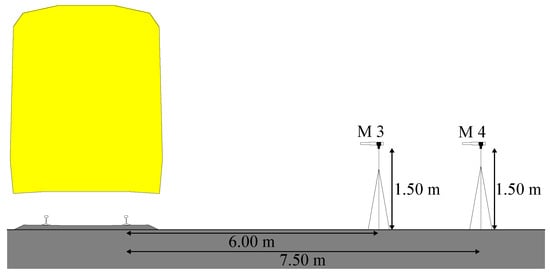
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram showing the position of the microphones in relation to the track.
3. Effects of Different Parameters on Sound Pressure Level
As outlined previously, the primary objective of this study is to characterize and analyze the noise levels and frequency content generated by railway traffic on the Porto metropolitan surface line. Given the specific operating conditions of the metro network, which include diverse types of vehicles, distinct track solutions, and unique track geometries with particular characteristics, along with a range of speeds integrated into these operational conditions, it becomes feasible to conduct a comparative analysis based on these described aspects. Therefore, the analysis conducted takes advantage of the context of the metro network to determine noise levels based on these specificities. With the available data, it is possible to compare the following aspects:
- Dependence of emitted noise on tram type;
- Influence of traffic speed on different types of tracks;
- Influence of track type on sound pressure levels;
- Influence of track geometry on sound pressure levels;
- Influence of vehicles in acceleration phase and with zero acceleration;
- Influence of bridge noise.
The calculation of the indicator (equivalent short-term continuous sound level), which represents the energy of the acoustic signal at the various receivers during a period that corresponds to the passage of the vehicle, is very useful for understanding how the different traffic conditions influence the noise levels. As a unique value, this indicator gathers all the information present in the collected signal and facilitates analysis. For this reason, for each of the scenarios under analysis, the corresponding is presented for the receiver furthest from the road. is calculated as presented in Equation (1), where is the acoustic signal under analysis, is the reference pressure and and correspond to the time defined by the 20 dB maximum level.
3.1. Tram Type Analysis
As mentioned, any variation in traffic conditions may lead to a change in the noise levels generated by the circulating vehicle. In this section, we perform a comparative analysis of the sound pressure levels generated by the two types of vehicles circulating in the metropolitan network of Porto, which were presented in Section 2. For that purpose, and to have similar conditions for each vehicle, we will consider two different types of tracks, Type II (ballast) and Type III (slab). In each case, similar circulation speeds will be used. In Figure 6, the records are compared for a speed of 58 km/h. As can be seen, the sound pressure levels in both receivers and for each train type are very similar. The Eurotram vehicle records the maximum sound pressure levels for 1000 Hz, whereas from 4000 Hz onwards, there is a slight increase in the sound pressure levels of the Flexity Swift vehicle compared to the Eurotram vehicle. The value for the Flexity Swift vehicle is 87 dBA and 87 dBA for the Eurotram vehicle, corroborating what had already been concluded, that the behavior of both vehicles is very similar.
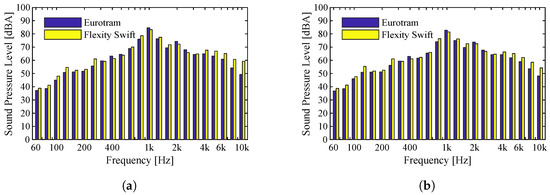
Figure 6.
Comparison of sound pressure levels (dBA) for Flexity Swift and Eurotram vehicles traveling at 58 km/h on a Type II track: (a) Microphone 1; (b) Microphone 2.
In Figure 7, the sound pressure levels are illustrated for a speed of 30 km/h. The conclusions that can be drawn when comparing the two types of vehicles are very similar to those recorded for the previous case (speed of 58 km/h), although a considerable change in the noise spectra is registered at both microphones. Indeed, it seems that the peak registered at 1000 Hz is no longer evident, with the spectrum plots showing an almost flat sound level between 200 Hz and 1000 Hz. This is an interesting change from the previous results, clearly showing the influence of vehicle speed on the emitted spectrum. In general, the sound pressure levels for the same speed and in the case of a straight track are very similar for both vehicles. It thus seems that, in the case of a straight track, and with vehicles and tracks in good condition, the speed of circulation is the variable that most influences the noise levels. Once again, the spectra are very similar, and so are the values of the indicator, giving a value of 82 dBA for the Flexity Swift vehicle and 84 dBA for the Eurotram vehicle.
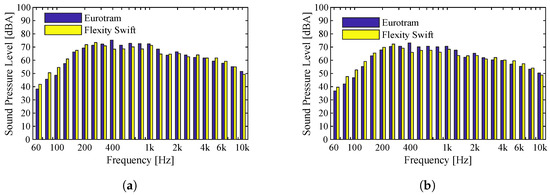
Figure 7.
Flexity Swift and Eurotram vehicles traveling at 30 km/h on a Type II track: (a) Microphone 1; (b) Microphone 2.
Finally, Figure 8 presents the comparison for the two vehicles traveling at about 40 km/h on a Type III track. Unlike the previous analyses, the sound pressure levels generated by the passage of the two vehicles seem to be quite distinct. In this case, the Eurotram vehicle has higher sound pressure levels than the Flexity Swift vehicle (up to 10 dBA), namely for frequencies above 2000 Hz. The explanation for this evidence is not entirely clear, but different reasons could cause it, from vehicle load distribution to geometrical or mechanical characteristics. For Type III, the values of the sound pressure levels are slightly higher and, as such, are reflected in the value of the indicator, obtaining a value of 79 dBA for the Flexity Swift vehicle and a value of 87 dBA for the Eurotram vehicle.
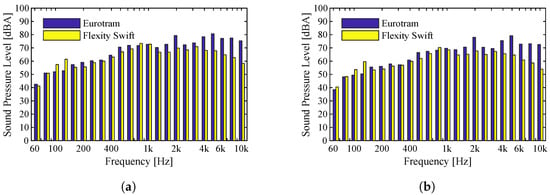
Figure 8.
Flexity Swift and Eurotram vehicles traveling at 40 km/h on a Type III track: (a) Microphone 1; (b) Microphone 2.
3.2. Analysis of the Influence of Traffic Speed on Different Types of Tracks
In this section, we analyze the influence of speed on sound pressure levels. As explained in Figure 1, increasing traffic speed implies an increase in sound pressure levels. The first step was to analyze the Type II track where the vehicle Flexity Swift is operating. In this case, speeds vary from 64 km/h to the maximum speed recorded on the line, 82 km/h. As already mentioned, in Figure 9, we observe an increase in the sound pressure levels as the circulation speed increases. It is important to note that there is no significant change in the frequency content of the measured levels, and thus, despite the change in sound pressure levels, the maximum levels for each record are registered for the same frequency bands. Taking into account the different sound pressure levels it is expected that the values of the indicator will increase according to the velocity increase. Thus, for the vehicle circulating at 64 km/h and for the most distant receiver, a value of 85 dBA was obtained. For the vehicle circulating at 75 km/h, the value of is 93 dBA and, finally, for the vehicle with the highest velocity, the indicator value is 93 dBA.
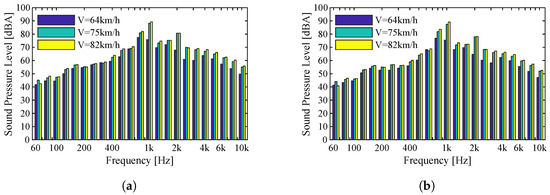
Figure 9.
Comparison between different speeds for the Flexity Swift vehicle operating on a Type II track: (a) Microphone 1; (b) Microphone 2.
The same type of analysis can be carried out for the Eurotram type vehicle. In this case, the speed varies between 40 km/h and 60 km/h. The results presented in Figure 10 show that, as concluded in the case of the Flexity Swift, the sound pressure levels increase as the speed increases, but the most prominent frequency content remains the same in the identified records. For the case under analysis, it is also expected that the value of is increasing with the velocity of circulation, however, with lower values than those analyzed, given the lower levels of sound pressure. Thus, for the vehicle circulating at 40 km/h, a value of 83 dBA was obtained, and for the other two cases, values of 86 dBA and 88 dBA for vehicles circulating at 50 km/h and 60 km/h were obtained, respectively.
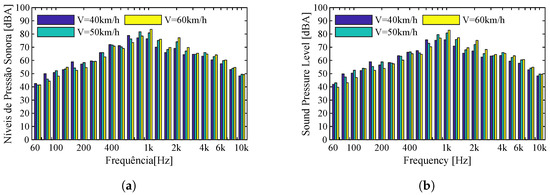
Figure 10.
Comparison between different speeds for the Eurotram vehicle operating on a Type II track: (a) Microphone 1; (b) Microphone 2.
Finally, the influence of speed is evaluated for the Type I track. The records presented in Figure 11 relate to the passage of a vehicle Eurotram. A slight increase in the sound pressure levels is observed with the increase in the speed of circulation; however, contrary to what was recorded for the ballasted track, this increase is not significant. There is a very close proximity between the sound pressure levels for speeds of 39 km/h and 50 km/h In this case, given the proximity of the two spectra analyzed, it is expected that the values of are also very close. Thus, a value of 76 dBA was obtained for the vehicle circulating at 39 km/h and a value of 77 dBA for the vehicle circulating at 50 km/h. The considerable difference (about 7 dBA) of this indicator concerning the previous case should be noted; it is strongly influenced by the type of track on which the records were made.
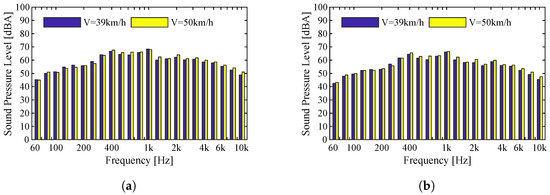
Figure 11.
Comparison between different speeds for the Eurotram vehicle operating on a Type I track: (a) Microphone 1; (b) Microphone 2.
3.3. Analysis of the Influence of Track Type on Sound Pressure Levels
Given the different types of tracks that make up the surface metro network, the following analysis is of particular importance, since the intention is to analyze the influence of track characteristics on noise levels. It is expected that the Type I track (grassed track), due to its construction and acoustic absorption characteristics, will present the lowest levels of sound pressure [13]. On the contrary, in the Type III track (slab track), it is expected that the noise levels are much higher given the inability of the track to absorb part of the sound energy. The records presented here correspond to the passage of vehicles of the Eurotram type, whose speed of circulation is, in this case, around 40 km/h. As we can see in Figure 12, the sound pressure levels vary significantly for the different types of tracks, particularly at higher frequencies. The grassed track (Type I), as mentioned, due to its intrinsic characteristics of sound absorption, presents sound pressure levels below 70 dBA unlike what happens to the other two types of track. For Type I and Type II tracks the frequency spectrum is very similar, except for the sound pressure levels which are slightly higher in the ballasted track in the whole frequency range. There is an increase in noise levels up to 1000 Hz and then a decrease in the higher frequency bands. In the case of track Type III (slab track), the sound pressure levels in a frequency band extending from 2000 Hz to 12.5 kHz often exceed 60 dBA. The large difference between the three types of tracks under analysis lies precisely in the frequency range mentioned. This trend is justified by the acoustic characteristics of the tracks, as previously discussed. The slab track is not able to absorb part of the sound energy that is generated and allows it to reach the receivers. In the frequency spectrums, it is clear the difference between the various types of the track about the indicator this difference is also quite notorious, differing from each other by about 4 dBA. For the Type I track, the indicator value is 77 dBA, for the ballasted track (Type II), the indicator value is 83, and for the Type III track, the value is 87 dBA.
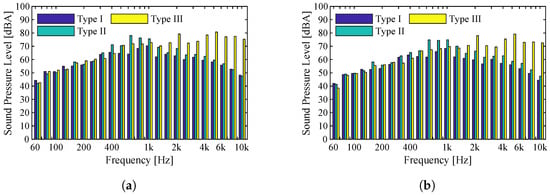
Figure 12.
Comparison of sound pressure levels for three different types of the track (I, II, III) for a Eurotram vehicle operating at 40 km/h: (a) Microphone 1; (b) Microphone 2.
3.4. Analysing the Influence of Track Geometry on Sound Pressure Levels
In the following section, the aim is to analyze the influence of the track geometry in terms of noise emissions. For that purpose, the data concerning the passage of Eurotram vehicles on the Type IV track will be analyzed. In both sections of the track (straight and curved), the vehicle circulates at a reduced speed of about 20 km/h. It should be noted that the curve has a very small radius, about 50 m, as illustrated in the Figure 13.

Figure 13.
Site illustration with curved track geometry and the corresponding signalling (+) of the measurement location.
The presence of the curve leads to a substantial increase in noise levels in the whole frequency range. This is due to the contact between the wheel flange and the rail. The wheel is restricted in its movement by the presence of the rail, generating an increase in noise levels. Despite this phenomenon, there is no squeal. The squeal localized noise mechanism is common in situations such as this, but, in this case, this phenomenon is not recorded due to the reduced speed of circulation, one of the mechanisms used to avoid the appearance of this localized phenomenon. In practical terms and as illustrated in Figure 14, sound pressure levels in the straight case are 60 dBA. In the case of the curved trajectory, as already mentioned, up to 10 dBA higher sound pressure levels are observed, reaching 70 dBA. Regarding the indicator, the difference between the two cases analyzed lies at 10 dBA, similar to what was observed for the general frequency spectrum. Therefore, the indicator’s value for the straight track is 74 dBA, while for the section of track on a curve, a value of 84 dBA is recorded.
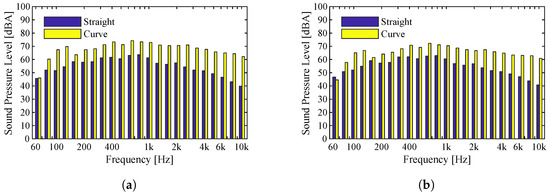
Figure 14.
Comparison of sound pressure levels of a straight measuring section and a measurement on a curved section for a Eurotram vehicle on a Type IV track: (a) Microphone 1; (b) Microphone 2.
Since the differences between straight and curved alignment are so evident, the analysis of the spectrograms illustrated Figure 15 can be useful to allow a more detailed analysis of this case. As can be seen in the spectrograms corresponding to receivers M3 and M4 the energy corresponding to the passage of the vehicles is higher in the curved alignment compared to the straight alignment, exciting a wider range of frequencies. Moreover, the passage of the vehicles in the curved section presents very noticeable energy peaks, unlike the spectra referring to the straight alignment, which are more diffuse. In these peaks, one can perceive that the highest noise levels (about 80 dBA) correspond to the passage of the wheels on the measurement section. Finally, the spectra analysis allows corroborating the non-existence of squeal, since this type of noise is easily identified in the spectrograms due to its harmonic character.
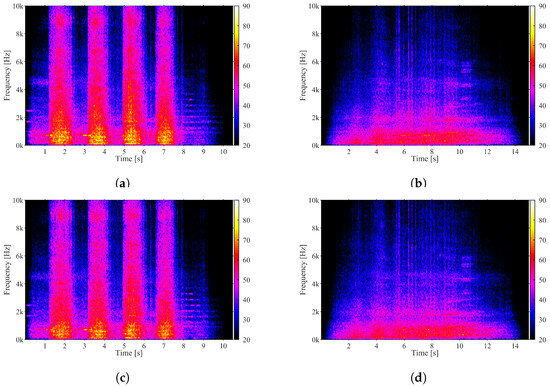
Figure 15.
Spectrograms of the vehicles passing on the curved measuring section and on the straight section: (a) Microphone 3—curved track; (b) Microphone 3—straight track; (c) Microphone 4—curved track; (d) Microphone 4—straight track.
3.5. Comparative Analysis of Vehicles in Acceleration Phase and with Zero Acceleration
The traction noise, coming from the vehicle engines, influences the perceived noise decisively. Here, the purpose is to analyze the real influence of this component on the recorded sound pressure levels. To this end, the recordings are compared for the two types of vehicles under analysis circulating at similar speeds. Two sets of measurements were performed, the first in a place near a station, therefore with the train still accelerating, and the second in a place where the vehicles have reached maximum speed, and thus are no longer accelerating. Figure 16 corresponds to results measured for the Flexity Swift vehicle traveling at 77 km/h, and reveals a strong difference between the two measurement cases. In the case where the vehicle is accelerating, sound pressure levels are up to 10 dBA higher than in the case where the vehicle is not accelerating, but this increase is concentrated mostly in frequency bands close to 1000 Hz. In the case of Figure 17, the sound pressure levels recorded are for the Eurotram vehicle traveling at a speed of 58 km/h. In the case of this vehicle, engine noise has a more predominant influence on the overall noise levels. Higher sound pressure levels are observed over the whole frequency range for the vehicle that is accelerating, most notably in the frequency band close to 1000 Hz. Analyzing the value shows the difference between the vehicles with acceleration and with zero acceleration, although the differences between the two spectra are more evident at point frequencies, especially for the Flexity Swift vehicle. The value for the accelerating Flexity Swift vehicle is 90 dBA, while the same vehicle with no acceleration presents a value of 79 dBA. For the accelerating Eurotram vehicle the value is 84 dBA, whereas the non-accelerating vehicle has a value of 76 dBA.
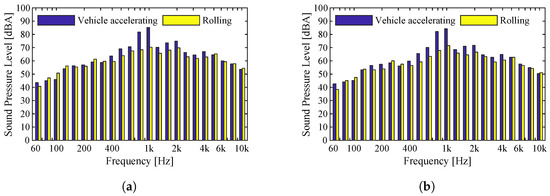
Figure 16.
Comparison of sound pressure levels for the Flexity Swift vehicle traveling on a Type II track, under acceleration and at null acceleration, for a speed of 77 km/h: (a) Microphone 1; (b) Microphone 2.
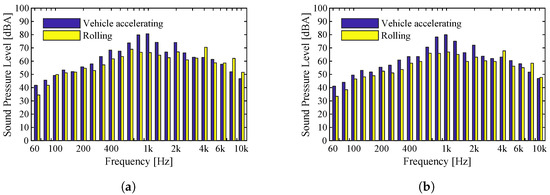
Figure 17.
Comparison of sound pressure levels for the Eurotram vehicle traveling on a Type II track, under acceleration and at null acceleration, for a speed of 58 km/h: (a) Microphone 1; (b) Microphone 2.
Complementarily, the spectrograms of the M4 receiver are shown in Figure 18 and Figure 19, which show data of the Flexity Swift and Eurotram vehicles, respectively. As can be seen, during the passage of vehicles through the measurement section, vehicles that are accelerating emit noise in the 1000 Hz band, which does not arise when passing vehicles with zero acceleration. This evidence is easily observed in the spectrograms with yellow coloration.
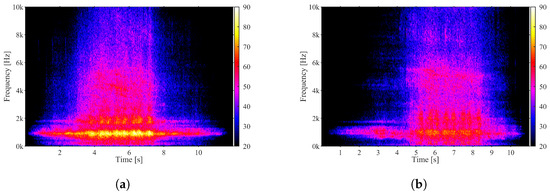
Figure 18.
Spectrograms of a Flexity Swift vehicle passing the measuring section at acceleration and null acceleration: (a) Microphone 4—accelerating; (b) Microphone 4—null acceleration.
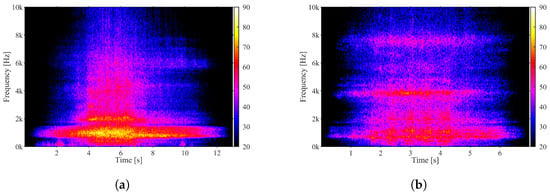
Figure 19.
Spectrograms of a Eurotram vehicle passing the measuring section at acceleration and at null acceleration: (a) Microphone 4—accelerating; (b) Microphone 4—null acceleration.
3.6. Comparative Analysis between Rolling Noise and Bridge Noise
In this section, it is intended to characterize the noise levels generated by the crossing of a superstructure. In this case, the passing of the vehicles over a metallic bridge crossing the Douro river which is part of the metro network was analyzed. The noise due to traffic on bridges is one of the particular types of noise associated with rail traffic, and according to the literature [22,27], the reasons for the development of this type of noise are related to two mechanisms. Firstly the vibrations that are transmitted to the elevated structure when vehicles pass over it. Since they are usually large structures, these vibrations are then radiated by the structure in the form of noise, which can reach quite high sound levels on several occasions. Secondly, how the rail is fastened to the superstructure plays a fundamental role since it influences the vibration of the rail which, according to the same authors, may have higher vibration levels than a current track. In this example, for a vehicle of the Eurotram type, at a speed of approximately 20 km/h, the records are compared with other types of track, considered to be conventional, in this case, Type I, Type III and Type IV. In Figure 20, it can firstly be observed that two tracks of similar construction, namely Type I and Type IV, present very different levels of sound pressure, with the absorption capacity and the restriction of movement of the rail having a dominant influence on the noise levels. However, the most pertinent observation is the fact that the noise levels at the bridge crossing are substantially higher than the noise levels recorded for the other track types under analysis. It can be concluded that the records presented corroborate what had been previously identified, with the crossing over the metal bridge generating noise levels that are up to 10 dBA higher than those recorded on conventional tracks. It should be noted that the maximum levels of sound pressure are around 70 dBA, although all the records correspond to low-speed crossings, around 20 km/h. Finally, it should be noted that there is a large difference, about 20 dBA between the records of the grass track and the records of the metal bridge crossing. The differences registered with the analysis of the frequency spectrums are also evident in the values of the indicator. For the Type I track the value is 71 dBA, for the Type III track the value of the indicator is 75 dBA, for Type IV track a value of 76 dBA is recorded and finally for the metallic bridge, a value of 85 dBA was obtained. As mentioned, the crossing of the metal bridge originates noise values much higher than those recorded for the other tracks for vehicles traveling at the same velocity. This discrepancy is evident in the values of the indicator , which are about 10 dBA higher compared to the other examples.
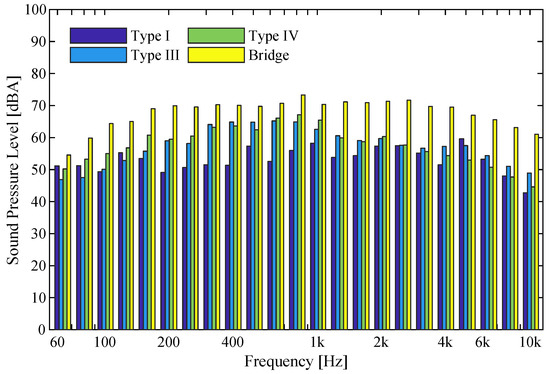
Figure 20.
Comparison between the sound pressure levels of the Eurotram vehicle traveling at approximately 20 km/h on Type I, III and IV tracks and on a metal frame bridge.
4. Conclusions
This study contributes to the characterization of noise levels generated by light rail traffic, focusing specifically on the surface metro network in Porto. The paper examines the noise spectrum of trams during their passage and explores the effects of different circulation conditions on the noise spectrum and levels at a specific location.
In general, the Eurotram type of vehicle exhibits higher noise levels compared to the Flexity Swift vehicle under similar running conditions. Regardless of the vehicle type, an increase in speed tends to result in higher noise levels, although there is no significant change in the distribution of noise levels among frequency bands. The study also highlights that more reflective tracks, such as slab tracks or tracks with rails embedded in cobbles, lead to higher sound pressure levels due to their low sound energy absorption capacity.
The study also noted a substantial impact of track geometry on sound pressure levels. Moreover, a distinct rise in noise was evident during the passage over a sizable metallic structure. This increase can be attributed to the vibrations within the structure, translating into acoustic noise in the surrounding environment. In summary, the type of platform (track + surface) and speed significantly impact noise levels, as evidenced by diverse records collected under various traffic conditions.
Regarding the frequency content, the most important range is around 1000 Hz, with maxima reaching around 80 dBA, depending on the circulation speed. The collected data, summarized in the preceding paragraphs, align with findings from other authors. While acknowledging the non-repeatability of conditions at data collection sites, the sound pressure values based on track type and circulation speed closely resemble those reported in other works [9,10,11,12,14].
It is emphasized that specific conditions at each measurement site and the characteristics of circulating vehicles play a pivotal role in noise levels and should be considered in the analysis [15,17,18,28]. Moreover, considering the extensive coverage of the surface metro network throughout Porto’s urban area, the obtained data allow for inferring the noise levels experienced by the population due to this type of traffic noise.
In conclusion, while the collected data are crucial for analyzing and understanding noise levels under different circulation conditions, identifying noise sources would enhance the clarity of railway noise analysis, beyond focusing solely on specific points near the railway track.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, J.L., P.A.C. and L.G.; methodology, J.L., P.A.C. and L.G.; software, J.L., validation, J.L., P.A.C. and L.G.; formal analysis, J.L., P.A.C. and L.G.; investigation, J.L.; resources, J.L., P.A.C. and L.G.; data curation, J.L.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L.; writing—review and editing, P.A.C. and L.G.; visualisation, J.L., P.A.C. and L.G.; supervision, P.A.C. and L.G.; project administration, P.A.C. and L.G.; funding acquisition, J.L., P.A.C. and L.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is financially supported by: Base Funding—UIDB/04708/2020 with DOI 10.54499/UIDB/04708/2020 (https://doi.org/10.54499/UIDB/04708/2020) and Programmatic Funding—UIDP/04708/2020 with DOI 10.54499/UIDP/04708/2020 (https://doi.org/10.54499/UIDP/04708/2020) of the CONSTRUCT—Instituto de I&D em Estruturas e Construções—funded by national funds through the FCT/MCTES (PIDDAC); FCT/MCTES through national funds (PIDDAC) under the R&D Unit Institute for Sustainability and Innovation in Structural Engineering (ISISE), under reference UIDB/04029/2020 (doi.org/10.54499/UIDB/04029/2020), and under the Associate Laboratory Advanced Production and Intelligent Systems ARISE under reference LA/P/0112/2020. Project POCI-01-0247-FEDER-033990 funded by FEDER funds through COMPETE2020—Programa Operacional Competitividade e Internacionalização (POCI); Project PTDC/ECI-EGC/3352/2021, funded by national funds through FCT/ MCTES; National funds (PIDDAC) through FCT/MCTES; Individual Grant: SFRH/BD/148367/2019.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors. The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Blanes, N.; Marín, A.; Maria José Ramos, U. Noise Exposure Scenarios in 2020 and 2030 Outlooks for EU 28; Technical Report; EEA (European Environment Agency): Kjeller, Norway, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- EEA (European Environment Agency). Environmental Noise in Europe—2020; Technical Report; EEA (European Environment Agency): Luxembourg, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.; Marquis-Favre, C.; Champelovier, P. Assessment of annoyance due to urban road traffic noise combined with tramway noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 141, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maigrot, P.; Parizet, E.; Marquis-Favre, C. Annoyance due to combined railway noise and vibration: Comparison and testing of results from the literature. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 165, 107324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidlöf-Gunnarsson, A.; Ögren, M.; Jerson, T.; Öhrström, E. Railway noise annoyance and the importance of number of trains, ground vibration, and building situational factors. Noise Health 2012, 14, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandrock, S.; Griefahn, B.; Kaczmarek, T.; Hafke, H.; Preis, A.; Gjestland, T. Experimental studies on annoyance caused by noises from trams and buses. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 313, 908–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallas, M.A.; Philipps-Bertin, C.; Maldonado, M.; Legouis, T.; Champelovier, P.; Chiello, O.; Lambert, J.; Le Houëdec, D.; Lelong, J. Bruits et Vibrations Dus Aux Tramways: émission et Perception; Rapport de Recherche; IFSTTAR—Institut Français des Sciences et Technologies des Transports, de l’Aménagement et des Réseaux: Bouguenais, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Licitra, G.; Fredianelli, L.; Petri, D.; Vigotti, M.A. Annoyance evaluation due to overall railway noise and vibration in Pisa urban areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 1315–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallas, M.A.; Lelong, J.; Chatagnon, R. Tram noise emission: Spectral analysis of the noise source contributions. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallas, M.A.; Perrier, R. Nearfield noise source localisation with constant directivity arrays: A comparison-Application to tram noise. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics NAG/DAGA 2009, Rotterdam, The Netherland, 23–26 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pallas, M.A.; Lelong, J.; Chatagnon, R. Characterisation of tram noise emission and contribution of the noise sources. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, S. Reductions in environmental noise emissions from Dublin’s light rail system following a rail grinding campaign on embedded track. In Proceedings of the Euronoise, Crete, Greece, 27–31 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Handbook Green Track Network Track Greening Design, Implementation, Maintenance; Eurailpress: Hamburg, Germany, 2016.
- Torres, J.; Olafsen, S.; Fernandez Espejo, T. Noise from urban transport, noise emission of trams. In Proceedings of the INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings, Madrid, Spain, 16–19 June 2019; Spanish Acoustical Society (SEA): Madrid, Spain, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sobota, A.; Żochowska, R.; Szczepański, E.; Gołda, P. The influence of tram tracks on car vehicle speed and noise emission at four-approach intersections located on multilane arteries in cities. J. Vibroengineering 2018, 20, 2453–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panulinova, E.; Harabinova, S. Quantification of acoustic risk from the tram ride in track curves. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Mangalore, India, 27–29 July 2022; IOP Publishing: Košice, Slovakia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Němec, M.; Danihelová, A.; Gergeľ, T.; Gejdoš, M.; Ondrejka, V.; Danihelová, Z. Measurement and Prediction of Railway Noise Case Study from Slovakia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pultznerova, A.; Eva, P.; Kucharova, D.; Argalasova, L. Railway noise annoyance on the railway track in Northwest Slovakia. Noise Health 2018, 20, 90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iannace, G.; Amadasi, G.; Trematerra, A.; Bevilacqua, A. City-Train noise reduction in urban area by using acoustic mini-screens made of metamaterials. In Proceedings of the INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings, Tokyo, Japan, 20–23 August 2023; Institute of Noise Control Engineering: Chiba, Japan, 2023; Volume 268, pp. 5909–5919. [Google Scholar]
- Hemsworth, B. Development of Action Plans for Railways Environmental Noise Directive Development of Action Plans for Railways; International Union of Railways: Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Selig, E.T.; Waters, J.M. Track Geotechnology and Substructure Management; Thomas Telford: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, D. Railway Noise and Vibration: Mechanisms, Modelling and Means of Control; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, D.; Zhang, X.; Ntotsios, E.; Squicciarini, G. A comparison of the noise and vibration performance of slab and ballasted track designs. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Railway Technology: Research, Development and Maintenance (RAILWAYS 2018), Sitges, Spain, 3–7 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Grassie, S.; Kalousek, J. Rail corrugation: Characteristics, causes and treatments. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J. Rail Rapid Transit 1993, 207, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veículos. Available online: https://www.metrodoporto.pt/pages/308 (accessed on 18 July 2022).
- Berzborn, M.; Bomhardt, R.; Klein, J.; Richter, J.G.; Vorländer, M. The ITA-Toolbox: An open source MATLAB toolbox for acoustic measurements and signal processing. In Proceedings of the 43th Annual German Congress on Acoustics, Kiel, Germany, 6–9 March 2017; Volume 2017, pp. 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Janssens, M.; Thompson, D. A calculation model for the noise from steel railway bridges. J. Sound Vib. 1996, 193, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papánová, Z.; Papán, D.; Ižvolt, L.; Dobeš, P. Modernization of Heavy Loaded Tram Radial Effect on Noise and Vibration. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).