Abstract
Peri-implant bone loss and bone quality significantly affect the biomechanical stability and long-term success of dental implants. This study used finite element analysis to evaluate the stress distribution and deformation behavior of implants and alveolar bone according to bone loss (0–5 mm) and bone quality (normal and low). A finite element model was implemented based on a three-dimensional mandibular model. The mechanical properties of each component were assigned, and finite element analysis was performed using a static occlusal load. The results showed that progressive bone loss increased von Mises stresses in the implant fixture and surrounding bone, and low-quality bone showed a significant vulnerability to stress concentration. The 2 mm bone loss model showed the maximum stress in cortical bone, and from 3 mm onwards, the stress decreased due to extensive loss of cortical bone. This may be because extensive bone loss causes the implant to lose interface with cortical bone and contact only with cancellous bone. This study confirmed that bone loss and the vulnerability of bone quality may potentially affect implant failure. Continued research is needed to suggest customized implants based on the structural vulnerability of alveolar bone.
1. Introduction
Dental implants are osseointegrated structures that stably combine with the surrounding bone, so maintaining marginal bone is essential for implant treatment success and long-term stability [1]. Peri-implant bone loss is a multifactorial process that involves progressive bone loss caused by factors such as bone quality deterioration, surgical trauma, peri-implantitis, and occlusal overload [2,3,4].
A long-term follow-up study of implants revealed complications such as loss of marginal bone after the prosthetic stage [5]. These complications are caused by direct stress transmission due to the implant–bone interface and stress concentration due to differences in stiffness of the bone around the implant under various load conditions. Anatomically, unlike teeth, implants do not have a periodontal ligament, so stress is directly transferred to the bone around the implant [6]. Excessive stress leads to bone microcracks and negatively affects implant stability, leading to implant failure in the long term. Previous studies have shown that as peri-implant bone loss increases, the magnitude of stress within the implant increases [7,8,9]. Other studies have suggested that unfavorable stress distribution associated with peri-implant bone resorption may lead to vertical fractures of internally connected implants [10].
Bone quality can affect implant survival and surrounding bone maintenance [11]. It is important in high-risk patients with skeletal diseases characterized by decreased bone density and microstructural deterioration, such as osteoporosis [12,13]. The results of implant treatment are within a predictable range in normal-quality bone, but it is difficult to obtain the same results in bone with low-quality bone. In previous studies, if the bone quality is poor during implant placement surgery, the risk of bone damage increases compared to normal bone [14]. Romanos et al. [15] reported that bone quality was the most important factor for implant selection and initial stability. Chrcanovic et al. [16] reported that bone structure was the most important factor in selecting favorable patient treatment outcomes. Continuously monitoring and comparing marginal bone changes is essential to prevent implant failure and complications, and it can provide useful information when implanting low-quality bone. However, there is still a need for more research that continuously evaluates implant stability and marginal bone changes according to bone loss and bone quality in various clinical situations, and the results of existing studies are inconsistent. Lombardi et al. [17] reported that deep implant insertion and short abutment were associated with greater marginal bone loss during the first 6 months after prosthesis loading. In contrast, Pontes et al. [18] evaluated clinical and radiographic changes in bone around implants inserted at various bone levels and reported that the apical position of the implant did not affect the ridge loss. In addition, Nimbalkar et al. [19] summarized the factors influencing bone loss around implants and reported that low bone density was correlated with decreased implant stability and increased bone deformation. In contrast, Do et al. [20] summarized the influence of various potential risk factors on the incidence of late dental implant failure and reported that bone status (osteoporosis or osteopenia) was not significantly associated with late failure. The inconsistency in these research results is likely due to differences in study design, definition and assessment of bone quality, criteria for measuring implant stability, and analytical methods. In particular, there is a lack of a standardized approach to quantitatively assess the effect of bone quality on early implant stability and long-term marginal bone changes and the specific mechanisms by which the interaction between bone loss progression and bone quality affects the mechanical stress and strain distribution in the bone around implants have not been elucidated.
Finite element analysis (FEA) has been gaining attention as a noninvasive technique useful for analyzing the complex biomechanical behavior of the jawbone [21,22]. FEA is widely used in various fields of expertise and provides a realistic description that can reflect the complexity of actual clinical situations through stress and strain behavior [23]. FEA is also widely used in studies on the stability of dental implants, but most studies focus on the structural design of the implant itself, and the evaluation and analysis of the biomechanical behavior of bone tissue are relatively lacking [24,25,26,27].
This study aims to evaluate the biomechanical stability of implants and surrounding bone by analyzing how stress and strain applied to implants and surrounding bone change according to the amount of bone loss and bone quality. By investigating the differences in the principal strains of stress and fatigue failure ranges that appear in cortical and cancellous bones, we provide basic clinical data necessary to ensure the long-term stability of implants.
2. Materials and Methods
To analyze the stability of the implant and bone tissue based on bone quality and peri-implant bone loss, two bone models with different material properties (normal bone and low-quality bone) and six models with levels of bone loss (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 mm) were constructed.
To reflect the anatomical structure of the bone, a three-dimensional (3D) model of the mandible was segmented from oral and maxillofacial computed tomography (CT) using medical image processing software (Mimics 26.0, Materialise Corporation, Leuven, Belgium). Using 3D modeling software (3-matic Research 18.0, Materialise Corporation, Leuven, Belgium), the mandibular region of the molar area was reconstructed by dividing it into cortical bone and cancellous bone, and then the implant fixture was implanted. The thickness and shape of the cortical and cancellous bone layers were configured based on actual anatomical proportions, with the cancellous bone positioned in the center and surrounded by a 2 mm thick cortical bone layer [28]. The implant is a type that is internally connected at the bone level and consists of a crown, cement, abutment, screw, and fixture model. The fixture was designed with a diameter of 4.0 mm and a length of 10.0 mm (Figure 1a). The peri-implant bone loss model implemented vertical bone loss based on a baseline model with standard bone height. By reducing the bone height in 1 mm increments, models with bone loss levels of 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 mm were created (Figure 1b) [29,30,31].
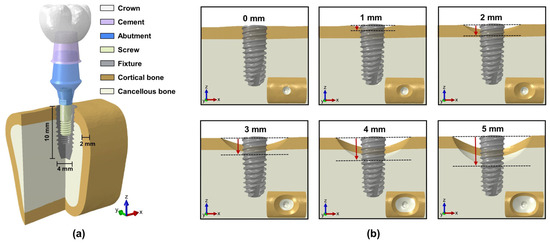
Figure 1.
Three-dimensional model: (a) composition of implants and bone; (b) peri-implant bone loss.
The mesh consists of four-node tetrahedral elements, and the mesh convergence test was conducted by gradually reducing the mesh size according to previous studies [32]. Considering computational efficiency and result convergence, the mesh size was determined to be appropriate for FEA (Figure 2a). Table 1 lists the element size, number of nodes, and number of elements for each structure.
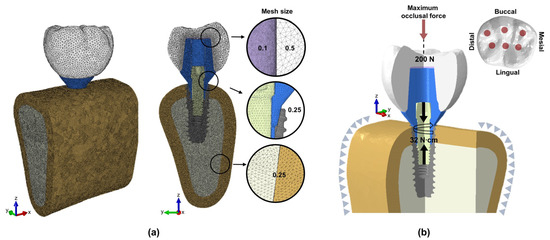
Figure 2.
Finite element model: (a) surface and volume mesh; (b) loading and boundary conditions.

Table 1.
Number of nodes, number of elements, and mesh size of the composition model.
The finite element model with surface and volume meshes was transferred to the FEA software (Abaqus version 6.14-3, Dassault Systèmes Simulia Corporation, Johnston, RI, USA) to perform static simulations. The implant components and bone tissue were assumed to be isotropic, homogeneous, and linearly elastic [33]. The normal bone model was set to have a general elastic modulus, and the low-quality bone model reflected a state of reduced bone strength, such as osteoporosis [34]. In the implant components, the crown type is all-ceramic, the cement type is temporary cement, and the abutment, screw, and fixture are selected as titanium [35,36,37]. The material properties assigned to the implant components and bone tissue are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Material properties of the composition model.
To implement the state where the surrounding tissues support the mandible, the cross-sections on both sides of the bone model were fixed in all directions to limit displacement. Each implant component and the implant–bone interface were set to a bonded condition. The implant–bone interface condition is assumed to be complete osseointegration. The loading condition was applied in two steps (Figure 2b). In the first step, the torque wrench was defined as the sum of the forces generated at the top and bottom of the screw during tightening. The torque wrench was set to 32 N∙cm, and an appropriate preload was applied to the top and bottom surfaces of the screw [38]. In the second step, a maximum occlusal force of 200 N was applied in the tooth axial direction to the occlusal surface of the crown [39,40]. A total of 50 nodes were applied to six occlusal points (mesial buccal cusp, distal buccal cusp, distal cusp, mesial fossa, distal fossa, and central fossa), with 4 N per node.
3. Results
To evaluate the mechanical stability of the implant fixture in bone tissue, the maximum von Mises stress and stress distribution were analyzed, and to evaluate the biomechanical effect in the bone tissue around the implant, the maximum von Mises stress and fatigue failure analysis was performed. In the fatigue failure criterion (>3000 µε), the bone remodeling rate cannot keep up with the microdamage rate. In other words, microfractures continue to occur, and the bone healing mechanism loses the time and ability to recover them [41].
Figure 3 shows the maximum von Mises stress values and stress distribution areas of the implant fixture according to bone quality and peri-implant bone loss. The maximum von Mises stress of the implant fixture was higher in low-quality bone than in normal bone, regardless of the amount of bone loss. The stress of the fixture gradually increased as bone loss increased in both normal and low-quality bone. The highest von Mises stress was observed in the model with 5 mm of bone loss in low-quality bone, and the stress value was 218.05 MPa. In the normal bone, when bone loss occurred from 0 mm to 5 mm, the maximum stress value of the fixture showed a stress increase rate of approximately 36.95%, and in the low-quality bone, it showed an increase rate of approximately 74.90%. This indicates that the stress increase in the fixture due to bone loss was more pronounced in low-quality bone. The maximum von Mises stress difference between normal and low-quality bone was minimal when bone loss was 0 to 2 mm. However, when bone loss exceeded 3 mm, the stress difference between the two bones became significant. This indicates that a significant difference in stress distribution occurs when bone loss exceeds a certain level. As bone loss progresses, the vulnerability of defective bone may become more prominent.
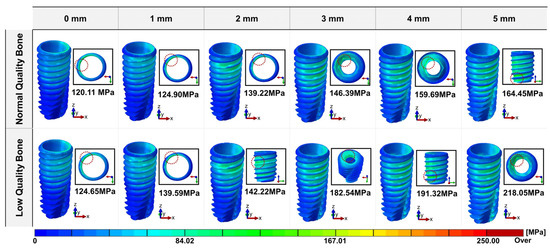
Figure 3.
Distribution area and maximum value of the von Mises stress of the implant fixture.
Figure 4 shows the maximum von Mises stress values and stress distribution areas of cortical and cancellous bone according to bone quality and peri-implant bone loss. The highest von Mises stress in the cortical bone surrounding the implant was observed when the bone loss was 2 mm in the low-quality bone, with a stress value of 60.88 MPa. Regardless of the amount of bone loss, the stress value of the cortical bone was higher in the low-quality bone than in the normal-quality bone. As bone loss progressed from 0 mm to 2 mm, the maximum von Mises stress of the cortical bone gradually increased. In the normal-quality bone, the stress increased from 21.45 MPa to 47.33 MPa; in the low-quality bone, the stress increased from 22.29 MPa to 60.88 MPa. When bone loss progressed to 3 mm or more, the cortical bone surrounding the implant was lost, and the maximum von Mises stress of the cortical bone rapidly decreased. The highest von Mises stress in cancellous bone was observed when the bone loss was 5 mm in the low-quality bone, with a stress value of 60.88 MPa. Similar to cortical bone, the maximum von Mises stress in cancellous bone was higher in the low-quality bone than in the normal bone model, regardless of the amount of bone loss. However, the difference in stress values between the normal- and low-quality bone was not significant overall. The maximum von Mises stress of cancellous bone increased slightly as bone loss progressed from 0 mm to 2 mm and from 3 mm to 5 mm, but the difference was insignificant. As bone loss progressed from 2 mm to 3 mm, the stress value of cancellous bone increased rapidly from 5.10 MPa to 9.85 MPa in normal bone and from 5.96 MPa to 10.58 MPa in low-quality bone, compared to other bone loss increase sections.
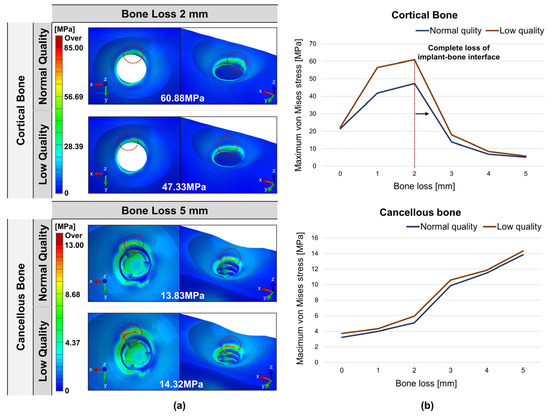
Figure 4.
Distribution of von Mises stress in cortical and cancellous bone: (a) maximum von Mises stress value and location; (b) von Mises stress values according to bone loss.
Figure 5 show the distribution and volume fraction of the fatigue failure area of cortical and cancellous bone according to bone quality and peri-implant bone loss. The fatigue failure area was distributed around the cancellous bone surrounding the implant. In all models, the fatigue failure area of low-quality bone was wider than that of normal-quality bone. The volume fraction in the fatigue failure range of cortical bone was maintained at 0% in all bone loss sections. There was little difference between normal and low-quality bone, which increased slightly when bone loss progressed from 0 mm to 2 mm in low-quality bone. The volume fraction in the fatigue failure range in normal-quality cancellous bone was almost 0%. As bone loss increased, the volume fraction in the fatigue failure range also increased, but the difference was minimal. The volume fraction in the fatigue fracture range in low-quality cancellous bone increased with increasing bone loss. The maximum volume fraction in low-quality bone condition was 19.60% at 5 mm bone loss, showing a significantly higher strain than normal-quality bone.
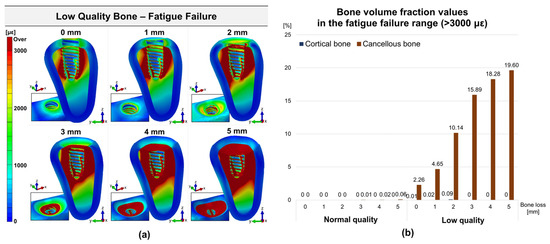
Figure 5.
Distribution and volume fraction of fatigue failure area in cortical and cancellous bone: (a) principal strain distribution in low-quality bone; (b) volume fraction values according to bone loss.
4. Discussion
This study investigated biomechanical factors by analyzing stress and strain applied to implants and surrounding bone according to bone loss and quality. The results showed that the stability of implants was significantly affected by the amount of bone loss and bone quality surrounding them, suggesting that the anatomical and structural characteristics of bone play an important role in implant success and long-term survival.
Implant complications are generally classified into biological and technical complications, but in actual clinical practice, complex interactions between human tissue and the mechanical components of the implant occur. Biological problems can cause technical defects, and conversely, technical defects can lead to biological problems, so one problem or defect can escalate into another clinical complication [42]. Since these interactions vary depending on the biological conditions of each patient, it is necessary to understand the biomechanical characteristics of the bone tissue surrounding the implant and comprehensively consider various factors. In particular, the structural characteristics and quality of the bone play an important role in the implant withstanding and dispersing external stress, and if the bone quality is low, stress may be concentrated, and bone loss may accelerate [43]. This may negatively affect the implant’s stability and ultimately lead to implant failure. Therefore, to prevent excessive bone loss and identify its causes, it is necessary to analyze various factors that act in clinical practice from various angles [19].
Marginal bone loss of approximately 1.5–2 mm around the implant neck during the first year after implant placement is considered a physiological response, and additional bone loss of less than 0.2 mm per year after that is within the clinically acceptable range and is considered a positive outcome [31]. However, the criteria presented in each study are different and lack consistency [44,45,46]. The level of bone loss that can be used to predict implant failure has not been appropriately defined. In this regard, a systematic approach that clearly distinguishes between physiological and pathological loss of marginal bone around implants and closely evaluates continuous bone changes is emphasized.
Our results showed that as bone loss around the implant increased, the maximum von Mises stress in the implant fixture and surrounding bone tissue tended to increase, consistent with previous research results showing that marginal bone loss around the implant compromises implant stability. A previous study evaluating the stress distribution during occlusal loading on implant-supported prostheses using different amounts of bone loss and materials demonstrated statistically significant differences in the stresses in all relevant structures when the bone level was reduced by 2 and 4 mm [11]. Another previous study investigating the effect of microthreads on the stress distribution in the bone around implants with different bone levels demonstrated a progressive increase in the stresses in the bone around implants with increased depth of bone resorption [47]. Additionally, another previous study determining the effect of prosthetic materials and crown/implant (C/I) ratios on short implants with marginal bone resorption demonstrated that the stresses in the implants ranged from 50 to 105 MPa in non-resorbable models, whereas in resorbable models, the values ranged from 168 to 322 MPa [48]. This stress increase phenomenon was observed throughout the entire structure and may be due to the reduced implant support capacity caused by bone loss. Since bone loss around the implant reduces the contact area between the implant and bone, thereby reducing the load-bearing area and effectively increasing the lever arm length of the implant fixture, the stress increase was found to accelerate when marginal bone loss began [9]. This trend was more pronounced in patients with low-quality bone. Low-quality bone has a relatively limited ability to disperse load, leading to an increased bone stress concentration around the implant and significantly impacting its initial stability. In low-quality bone, a high stress concentration occurs even when initial bone loss occurs, so the resulting stress concentration increases the structural burden on the implant and surrounding tissues. In an environment where low-quality bone exists, the stress distribution around the implant is formed unfavorably, which promotes microdamage and fatigue destruction of bone tissue [49].
These results have important clinical implications in osteoporotic patients with low bone quality, supporting the importance of a treatment approach that minimizes marginal bone loss during implant placement in patients with low-quality bone, as discussed in previous studies [30]. When planning implants for patients with osteoporosis, several important clinical considerations are necessary [50,51,52,53]. An accurate assessment of the patient’s bone quality is necessary to establish a customized treatment plan that matches the characteristics of the bone. In the prosthesis design stage, designing to minimize stress concentration around the implant is important. The structural burden can be reduced by utilizing a multi-implant system or distributing the load evenly through an occlusal adjustment. It is also an effective approach to improve the quality and quantity of bone by performing bone grafting or bone augmentation, if necessary. This can optimize the implant placement environment and improve initial stability.
This study found conflicting results in the maximum von Mises stress and volume fraction of the fatigue failure area of cortical and cancellous bone. These differences may be due to the difference in elastic modulus between cortical and cancellous bone, implying that bone type responds to stress differently [54]. Cortical bone has a relatively high elastic modulus, which provides great resistance to initial load and is essential for initial implant stability, especially because it plays a structural support role around the implant neck [33]. The results of this study showed that the maximum von Mises stress increased significantly when the initial bone loss of 1 mm occurred in cortical bone. This suggests that cortical bone increases initial stability by distributing the load around the implant and playing a supporting role. However, when the bone loss progressed to 3 mm or more, the supporting ability of cortical bone was rapidly lost, and the stress decreased significantly. This emphasizes that it is important to manage cortical bone loss so that it does not exceed a certain level clinically for long-term implant stability [55]. Conversely, cancellous bone has a lower elastic modulus than cortical bone, so it responds more flexibly to the initial load [56]. The cancellous bone acts as the main supporting structure after the support ability of cortical bone is lost. In this study, cancellous bone stress rapidly increased when bone loss progressed from 2 mm to 3 mm and then gradually increased as it progressed to 5 mm. In particular, in the initial bone loss section, the stress in the cortical bone was higher than that in the cancellous bone. However, as cortical bone loss worsened, the cancellous bone acted as the main supporting structure, and the stress increased.
In the volume fraction of the fatigue failure area, the cortical bone did not show a fatigue failure area regardless of bone quality. In contrast, cancellous bone showed a pattern in which the fatigue failure area increased as bone loss increased in low-quality bone. Although the maximum von Mises stress value of cancellous bone is lower than that of cortical bone, the fatigue failure volume fraction is higher because it is structurally porous and highly ductile, so it reacts more sensitively to fatigue load. Cortical bone distributes stress well, but cancellous bone accumulates even a small load when repeated and gradually increases the strain [11]. The contrasting responses of cortical bone and cancellous bone provide an important point for discussion on the stability of bone around implants. These differences provide important information for specifying cortical and cancellous bones’ effects in maintaining implant stability.
It is important to note that, in all models studied, the stresses in the fixture were significantly below the yield strength limit of the titanium [57,58]. The maximum von Mises stress values obtained in all models should not compromise the clinical success of the implant under static loading.
Although the finite element method is an effective method for solving biomechanical problems, there are some limitations in the analysis process of this study. First, this study simplified the connection method of the implant model. Since this approach is based on analyzing the stress and strain distribution trends between the implant and the surrounding bone, it is judged that it will not significantly affect the results. However, to more precisely reflect the implant system’s mechanical characteristics, the implant structure’s connection method must be specified, and additional modeling is necessary. Second, the load used in this study was set within the normal human occlusal range, but the oral occlusal process is an environment in which load time, distribution, and direction are complexly affected. Since the stress and strain distribution within the structure may vary depending on these load conditions, simulations that reflect dynamic and cyclic loads, such as fatigue analysis, are required to obtain more realistic results. Third, the study considered two main properties of bone material properties: stiffness and strain in different directions. However, more precise consideration of bone physiological properties, such as bone density and oral environment, can better reflect the actual oral situation. These properties are important in determining how bone tissue responds to applied loads. Unlike in vivo or laboratory experiments, FEA focuses on predicting mechanical properties. However, the oral cavity is a complex environment where various factors, such as biomechanical behavior, interact. Although this study contributed to analyzing the biomechanical interaction between implants and surrounding bone, future studies need to more faithfully reproduce the actual oral environment through more sophisticated modeling and simulations that reflect in vivo conditions.
5. Conclusions
This study assessed the biomechanical effects of peri-implant bone loss and bone quality on the stability of dental implants. The results simulated with finite element methods show that progressive bone loss exacerbates stress concentrations within the implant and surrounding bone tissue and that low-quality bone is significantly more susceptible to stress and fatigue failure. Cortical bone is identified as important for maintaining initial implant stability, and cancellous bone assumes a progressively more significant load-bearing role as bone loss progresses. These results highlight the importance of preserving marginal bone and optimizing implant design to alleviate stress concentrations, especially in patients with low-quality bone. It also provides clinical insight into improving the long-term stability of implants by considering the potential risk of implant failure due to anatomical and structural problems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Y. and Y.-D.K.; methodology, Y.Y.; validation, S.P., I.K. and J.-E.K.; formal analysis, E.K.; investigation, Y.Y. and J.-E.K.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Y. and Y.-D.K.; writing—review and editing, J.-E.K.; visualization, Y.-D.K.; supervision, Y.-D.K.; project administration, Y.-D.K.; funding acquisition, Y.-D.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by a research grant from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education of Korea (NRF-2023R1A2C1003876).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in the study are openly available in DataOn at https://doi.org/10.22711/idr/1061.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Galindo-Moreno, P.; León-Cano, A.; Ortega-Oller, I.; Monje, A.; O’Valle, F.; Catena, A. Marginal bone loss as success criterion in implant dentistry: Beyond 2 mm. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, e28–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bruyn, H.; Christiaens, V.; Doornewaard, R.; Jacobsson, M.; Cosyn, J.; Jacquet, W.; Vervaeke, S. Implant surface roughness and patient factors on long-term peri-implant bone loss. Periodontology 2017, 73, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caricasulo, R.; Malchiodi, L.; Ghensi, P.; Fantozzi, G.; Cucchi, A. The influence of implant-abutment connection to peri-implant bone loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokaya, D.; Srimaneepong, V.; Wisitrasameewon, W.; Humagain, M.; Thunyakitpisal, P. Peri-implantitis Update: Risk Indicators, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Eur. J. Dent. 2020, 14, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vervaeke, S.; Collaert, B.; Cosyn, J.; Deschepper, E.; De Bruyn, H. A multifactorial analysis to identify predictors of implant failure and peri-implant bone loss. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17 (Suppl. 1), e298–e307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jokar, H.; Rouhi, G.; Abolfathi, N. The Effects of Splinting on the Initial Stability and Displacement Pattern of Periodontio-Integrated Dental Implants: A Finite Element Investigation. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2020, 40, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linetskiy, I.; Demenko, V.; Linetska, L.; Yefremov, O. Impact of annual bone loss and different bone quality on dental implant success—A finite element study. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 91, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, L.; Mito, T.; Yoda, N.; Sato, E.; Shigemitsu, R.; Han, J.M.; Sasaki, K. Effect of peri-implant bone resorption on mechanical stress in the implant body: In vivo measured load-based finite element analysis. J. Oral Rehabil. 2020, 47, 1566–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, C.A.A.; Verri, F.R.; Noritomi, P.Y.; Kemmoku, D.T.; Souza Batista, V.E.; Cruz, R.S.; de Luna Gomes, J.M.; Pellizzer, E.P. Effect of bone quality and bone loss level around internal and external connection implants: A finite element analysis study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 125, 137.e1–137.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, S.A.; Souza Dos Santos Vianna, M.; Dedavid, B.A. Influence of bone insertion level of the implant on the fracture strength of different connection designs: An in vitro study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2014, 18, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsouknidas, A.; Lympoudi, E.; Michalakis, K.; Giannopoulos, D.; Michailidis, N.; Pissiotis, A.; Fytanidis, D.; Kugiumtzis, D. Influence of Alveolar Bone Loss and Different Alloys on the Biomechanical Behavior of Internal-and External-Connection Implants: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2015, 30, e30–e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merheb, J.; Temmerman, A.; Rasmusson, L.; Kubler, A.; Thor, A.; Quirynen, M. Influence of Skeletal and Local Bone Density on Dental Implant Stability in Patients with Osteoporosis. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2016, 18, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Moriyama, Y.; Takemura, Y.; Rokuta, M.; Ayukawa, Y. Influence of osteoporosis and mechanical loading on bone around osseointegrated dental implants: A rodent study. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 123, 104771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, F.; Ahmed, H.B.; Crespi, R.; Romanos, G.E. Role of primary stability for successful osseointegration of dental implants: Factors of influence and evaluation. Interv. Med. Appl. Sci. 2013, 5, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanos, G.E.; Delgado-Ruiz, R.A.; Sacks, D.; Calvo-Guirado, J.L. Influence of the implant diameter and bone quality on the primary stability of porous tantalum trabecular metal dental implants: An in vitro biomechanical study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2018, 29, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrcanovic, B.R.; Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. Bone Quality and Quantity and Dental Implant Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2017, 30, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, T.; Berton, F.; Salgarello, S.; Barbalonga, E.; Rapani, A.; Piovesana, F.; Gregorio, C.; Barbati, G.; Di Lenarda, R.; Stacchi, C. Factors Influencing Early Marginal Bone Loss around Dental Implants Positioned Subcrestally: A Multicenter Prospective Clinical Study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, A.E.; Ribeiro, F.S.; da Silva, V.C.; Margonar, R.; Piattelli, A.; Cirelli, J.A.; Marcantonio, E., Jr. Clinical and radiographic changes around dental implants inserted in different levels in relation to the crestal bone, under different restoration protocols, in the dog model. J. Periodontol. 2008, 79, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimbalkar, S.; Dhatrak, P.; Gherde, C.; Joshi, S. A review article on factors affecting bone loss in dental implants. Mater. Today-Proc. 2021, 43, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.A.; Le, H.S.; Shen, Y.W.; Huang, H.L.; Fuh, L.J. Risk Factors related to Late Failure of Dental Implant-A Systematic Review of Recent Studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.P.; Tan, K.B.; Liu, G.R. Application of finite element analysis in implant dentistry: A review of the literature. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 85, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, W.; Klein, D.; Karl, M. Effect of model parameters on finite element analysis of micromotions in implant dentistry. J. Oral Implantol. 2013, 39, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayabasi, O.; Yüzbasioglu, E.; Erzincanli, F. Static, dynamic and fatigue behaviors of dental implant using finite element method. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2006, 37, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goiato, M.C.; Andreotti, A.M.; Dos Santos, D.M.; Nobrega, A.S.; de Caxias, F.P.; Bannwart, L.C. Influence of length, diameter and position of the implant in its fracture incidence: A Systematic Review. J. Dent. Res. Dent. Clin. Dent. Prospects 2019, 13, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Goyal, P.; Jain, A.; Chopra, P. Effect of peri-implantitis associated horizontal bone loss on stress distribution around dental implants—A 3D finite element analysis. Mater. Today-Proc. 2020, 28, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Chopra, P.; Goyal, P.; Jain, A. Effect of vertical bone loss on stress distribution at the bone-implant interface around implants of varying diameters-an in silico 3D finite element analysis. Mater. Today-Proc. 2021, 45, 4581–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satpathy, M.; Duan, Y.; Betts, L.; Priddy, M.; Griggs, J.A. Effect of Bone Remodeling on Dental Implant Fatigue Limit Predicted Using 3D Finite Element Analysis. J. Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2022, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.H.; Peng, B.Y.; Wang, P.D.; Feng, S.W. Evaluation of the implant stability and the marginal bone level changes during the first three months of dental implant healing process: A prospective clinical study. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2020, 110, 103899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, F.; Derks, J.; Monje, A.; Wang, H.L. Peri-implantitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45 (Suppl 20), S246–S266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, T.J.; Yoon, J.; Misch, C.E.; Wang, H.L. The causes of early implant bone loss: Myth or science? J. Periodontol. 2002, 73, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y. A pilot study of a deep learning approach to detect marginal bone loss around implants. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Park, J.; Kang, I.; Lee, H.; Noh, G. Effects of assessing the bone remodeling process in biomechanical finite element stability evaluations of dental implants. Comput. Meth Prog. Bio 2022, 221, 106852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, J.F.; Verri, F.R.; Almeida, D.A.D.; Batista, V.E.D.; Lemos, C.A.A.; Pellizzer, E.P. Finite element analysis on influence of implant surface treatments, connection and bone types. Mat. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. 2016, 63, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Horita, S.; Murakami, K.; Tsutsumi, S.; Kirita, T. The effects of bone density and crestal cortical bone thickness on micromotion and peri-implant bone strain distribution in an immediately loaded implant: A nonlinear finite element analysis. J. Periodontal Implant Sci. 2016, 46, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaillancourt, H.; Pilliar, R.M.; Mccammond, D. Finite-Element Analysis of Crestal Bone Loss around Porous-Coated Dental Implants. J. Appl. Biomater. 1995, 6, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niinomi, M. Mechanical properties of biomedical titanium alloys. Mat. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. 1998, 243, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolidis, K.; Papadogiannis, D.; Papadogiannis, Y.; Gerasimou, P. Dynamic and static mechanical analysis of resin luting cements. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2012, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; de Ibarra, N.L.S.; Martín, I.M.; Rotaeche, L.S. Influence of Dental Implant Diameter and Bone Quality on the Biomechanics of Single-Crown Restoration. A Finite Element Analysis. Dent. J. 2021, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torcato, L.B.; Pellizzer, E.P.; Verri, F.R.; Falcón-Antenucci, R.M.; Santiago, J.F.; Almeida, D.A.D. Influence of parafunctional loading and prosthetic connection on stress distribution: A 3D finite element analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2015, 114, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Jo, M.; Sailer, I.; Noh, G. Effects of implant diameter, implant-abutment connection type, and bone density on the biomechanical stability of implant components and bone: A finite element analysis study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2022, 128, 716–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, H.M. The mechanostat: A proposed pathogenic mechanism of osteoporoses and the bone mass effects of mechanical and nonmechanical agents. Bone Miner. 1987, 2, 73–85. [Google Scholar]
- Mattheos, N.; Janda, M.; Acharya, A.; Pekarski, S.; Larsson, C. Impact of design elements of the implant supracrestal complex (ISC) on the risk of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis: A critical review. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2021, 32 (Suppl 21), 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragger, U.; Hirt-Steiner, S.; Schnell, N.; Schmidlin, K.; Salvi, G.E.; Pjetursson, B.; Matuliene, G.; Zwahlen, M.; Lang, N.P. Complication and failure rates of fixed dental prostheses in patients treated for periodontal disease. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2011, 22, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.B.; Wu, T.X.; Guo, Y.C.; Zhou, X.D.; Lei, Y.L.; Xu, X.; Mo, A.C.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yuan, Q. Marginal bone loss around non-submerged implants is associated with salivary microbiome during bone healing. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2017, 9, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravidà, A.; Samal, A.; Qazi, M.; Webber, L.P.; Wang, H.L.; Galindo-Moreno, P.; Borgnakke, W.S.; Saleh, M.H.A. Interproximal implant thread exposure after initial bone remodeling as a risk indicator for peri-implantitis. J. Periodontol. 2023, 94, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trombelli, L.; Farina, R.; Tomasi, C.; Vignoletti, F.; Paolantoni, G.; Giordano, F.; Ortensi, L.; Simonelli, A. Factors affecting radiographic marginal bone resorption at dental implants in function for at least 5 years: A multicenter retrospective study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2024, 35, 1406–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.H.; Peng, M.D.; Li, Q. The effect of implant neck microthread design on stress distribution of peri-implant bone with different level: A finite element analysis. J. Dent. Sci. 2020, 15, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ercal, P.; Taysi, A.E.; Ayvalioglu, D.C.; Eren, M.M.; Sismanoglu, S. Impact of peri-implant bone resorption, prosthetic materials, and crown to implant ratio on the stress distribution of short implants: A finite element analysis. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2021, 59, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.; Kang, I.; Noh, G.; Kwon, Y.D. Biomechanical analysis of alveolar bones with compromised quality supporting a 4-unit implant bridge; a possible association with implant-related sequestration (IRS). Clin. Oral Investig. 2024, 28, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera-Jimenez, J.F.; Burgueno-Barris, G.; Gomez-Gonzalez, S.; Lopez-Lopez, J.; Valmaseda-Castellon, E.; Fernandez-Aguado, E. Finite element analysis of narrow dental implants. Dent. Mater. 2020, 36, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcinelli, C.; Valente, F.; Vasta, M.; Traini, T. Finite element analysis in implant dentistry: State of the art and future directions. Dent. Mater. 2023, 39, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehboob, H.; Ouldyerou, A.; Ijaz, M.F. Biomechanical Investigation of Patient-Specific Porous Dental Implants: A Finite Element Study. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callea, C.; Ceddia, M.; Piattelli, A.; Specchiulli, A.; Trentadue, B. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) for a Different Type of Cono-in Dental Implant. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.Y.; Sun, Y.C.; Wang, C. Effect of Integration Patterns Around Implant Neck on Stress Distribution in Peri-Implant Bone: A Finite Element Analysis. J. Prosthodont. 2017, 26, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stefano, D.A.; Arosio, P.; Cappare, P.; Barbon, S.; Gherlone, E.F. Stability of Dental Implants and Thickness of Cortical Bone: Clinical Research and Future Perspectives. A Systematic Review. Materials 2021, 14, 7183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ausiello, P.; Tribst, J.P.M.; Ventre, M.; Salvati, E.; di Lauro, A.E.; Martorelli, M.; Lanzotti, A.; Watts, D.C. The role of cortical zone level and prosthetic platform angle in dental implant mechanical response: A 3D finite element analysis. Dent. Mater. 2021, 37, 1688–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervino, G.; Romeo, U.; Lauritano, F.; Bramanti, E.; Fiorillo, L.; D’Amico, C.; Milone, D.; Laino, L.; Campolongo, F.; Rapisarda, S.; et al. Fem and Von Mises Analysis of OSSTEM ((R)) Dental Implant Structural Components: Evaluation of Different Direction Dynamic Loads. Open Dent. J. 2018, 12, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayyad, A.A.; Abbas, N.A.; AbdelNabi, N.M.; Osman, R.B. Biomechanics of 3-implant-supported and 4-implant-supported mandibular screw-retained prostheses: A 3D finite element analysis study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 124, 68.e1–68.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).