Abstract
With the rapid development of global information technology, smart agriculture has gradually become an important force to promote agricultural modernisation. Taking Yangcheng Lake hairy crabs as the research object, this paper constructs a full-chain traceability process for hairy crabs integrating blockchain and Internet of Things technology in response to the demand for the enhancement of its brand value and market competitiveness. The model covers all aspects of breeding, processing, and transport to sales; realises end-to-end transparent regulation; effectively guarantees the authenticity and non-tamperability of information; and enhances consumers’ trust in the brand. At the technical level, this paper designs the ECMI (Enhanced Cuckoo Merkle Index) model, optimises the data storage and retrieval mechanism, and experimentally verifies the advantages of cuckoo filters over traditional Bloom filters in reducing false positives and improving query efficiency. This paper not only provides an efficient and safe traceability solution for the hairy crab industry in Yangcheng Lake but also provides technical support and practical cases for the further application of blockchain technology in smart agriculture, which is of great value for the realisation of the national rural revitalisation strategy.
1. Introduction
Smart agriculture is highlighted in China’s Rural Revitalisation Strategic Plan (2018–2022) as a key part of the country’s national strategic plan, aiming to improve agricultural productivity and food safety through technological innovation [1]. With consumers’ increasing concern for food quality and traceability [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10], Yangcheng Lake hairy crabs, as a high-quality regional brand, are facing the challenge of counterfeiting phenomenon for their market value and brand reputation [11,12,13]. This paper takes Yangcheng Lake hairy crabs as the research object and explores the application of blockchain technology in enhancing its brand value and market competitiveness to meet consumers’ demand for food safety and traceability. Through blockchain technology, the whole chain of traceability from breeding to sales is realised to ensure the authenticity and non-tamperability of information and enhance consumer trust.
The literature [14] focuses on the latest applications of blockchain technology in the agricultural sector, especially for fresh produce enterprises. The interactions between firms’ strategies of joining platform blockchain technology and channel invasion decisions are explored. The results show that the inclusion of blockchain technology can improve consumer trust and increase product demand. The study provides insights for fresh produce companies to make strategic decisions, highlighting the potential of blockchain technology to enhance supply chain management and increase consumer trust. The authors of [15] explore the application of blockchain technology in the supply chain of agricultural products and analyses the impact of companies joining blockchain on e-commerce platforms on their sales strategies. The study points out that blockchain technology enhances consumer trust by improving product traceability, which in turn may increase the demand for agricultural products. Meanwhile, whether enterprises set up third-party shops on e-commerce platforms and their adoption decisions of blockchain technology are influenced by consumers’ sensitivity and trust in product freshness. The authors of [16] focus on enterprises in the agricultural supply chain in Vietnam. It provides an in-depth analysis of the main barriers faced by enterprises in adopting blockchain technology and examines how the lack of government regulation, insufficient system scalability and speed, large resource and capital requirements, and lack of stakeholder trust combine to influence their strategic choices. In addition, the study proposes an order to prioritise these barriers to accelerate the adoption of blockchain technology in Vietnam’s agricultural supply chain. The authors of [17] delve into the role of blockchain technology in enhancing the performance of traceability systems in agri-food supply chains. By comprehensively analysing 78 relevant studies, it focuses on the application of BCT in tracking key food categories such as fruits, vegetables, meat, dairy products, and milk. It reveals how BCT-based traceability systems can achieve decentralisation, data immutability, transparency, and reliability while highlighting the key role of automated processes in monitoring real-time data and decision-making.
2. Filter Technical Analysis
2.1. Bloom Filter
In the field of data structure research, bitmap filters are an important technique whose origin dates back to the 1970s [18]. A Bloom filter consists of a Boolean array of length m bits and k independent hash functions, which uniquely identify elements, and fast querying is achieved by mapping elements to random locations in the array through the hash functions [19,20,21,22,23,24]. Its core advantage lies in the efficient mapping of elements using multiple hash functions while maintaining a low false positive rate. During insertion, elements are mapped to k positions of a Boolean array by k hash functions, and these positions are set to true. When querying, the existence of the element is determined by detecting the values of these positions. Figure 1 visualises the insertion process of elements x and y with three hash functions as an example, highlighting the efficiency and accuracy of Bloom filters when dealing with large amounts of data.
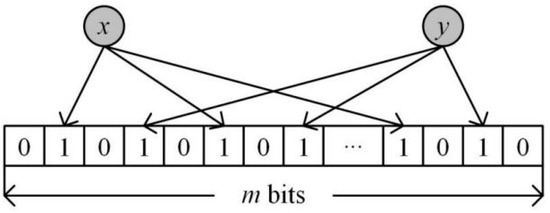
Figure 1.
Bloom filter data structure example.
Bloom filters are an efficient data structure designed to quickly determine whether an element belongs to a particular set. At its core is a bit array of length m. Element features are mapped to the bit array by k hash functions to achieve constant time complexity queries. On insertion, element features are mapped and set to 1. On query, feature values are mapped, and the bit array is checked; if they are all 1, then they may exist. Otherwise, it is determined that they do not exist. Eigenvalue extraction can be achieved by independent hash functions or by splitting a single hash. By adjusting m and k, the Bloom filter minimises the false positive rate and optimises the spatial efficiency. When designing a Bloom filter for storing n data items, the optimal values of m and k can be calculated by the following mathematical formula to ensure that the false positive rate is minimised while minimising the space occupation.
Bloom filters have significant advantages in terms of storage and query efficiency. Taking the example of storing 10 billion pieces of data (i.e., n = 1010), if the false positive rate p is set to be no more than 3%, according to the theoretical calculation, the value of m/n is about 7.30. The theoretical optimal value for k is about 5.06, but in practice, the smallest integer larger than this value should be chosen, i.e., k should be taken to be 6. Therefore, the number of hash functions should be set to be 6 in practice, and at this time, the value of m/n is about 4.16, resulting in a value of m of approximately 4.16 × 1010 bits. Converted to bytes, this is 5.2 × 109 bytes, which is equivalent to 4.84 GB, and this amount of storage can be easily stored in the server’s memory. In contrast, if the method of recording the hash value of each data item is used, with each hash value occupying 32 bytes, the overhead of storing 10 billion pieces of data would be 3.2 × 1011 bytes, or about 298.02 GB, which is typically beyond the storage capacity of typical server memory.
2.2. Cuckoo Filter
A cuckoo hash table is a highly optimised hash table structure whose main advantage is its ability to efficiently handle the insertion and query process of a single element [25,26,27,28,29]. In a cuckoo hash table, for any given element x, its mapping to the hash table follows a specific mapping rule that ensures an even distribution of elements. However, a so-called storage conflict occurs when an element is mapped to a bucket that is already full. At this point, a strategy must be adopted to redistribute the conflicting elements to ensure the stability and efficiency of the system. As shown in Figure 2a, when the expected positions of element x in all sub-hash tables are occupied, a mechanism called ‘kick-out’ is triggered. This mechanism first removes the conflicting element a from its current sub-hash table and tries to reinsert it into the next sub-hash table. If successive sub-hash tables are full, the process is repeated until a suitable storage location is found. If no available storage location is found after successive attempts, this indicates that the storage capacity of the hash table has reached its design limit. In this case, the system must be expanded to accommodate the growing demand for element storage in order to maintain the performance and scalability of the hash table.
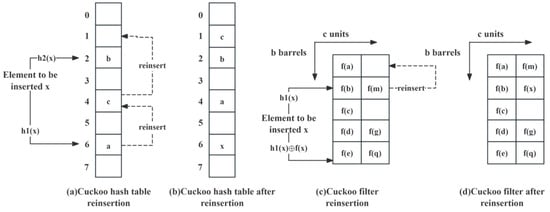
Figure 2.
Cuckoo hash tables and cuckoo filters.
A cuckoo filter is an approximate membership test data structure based on cuckoo hashing [30,31,32,33,34,35]. Unlike the traditional cuckoo hash table, the cuckoo filter improves on the storage strategy by saving space by not storing the complete elements but only keeping the fingerprint information of the elements. The architecture of this design enables a substantial reduction in the necessary storage space for cuckoo filters while concurrently sustaining a high level of query performance. However, the reliance on fingerprint data for element identification within the cuckoo filter does introduce a potential for misclassification. Specifically, there exists a risk that elements not actually present in the filter might be erroneously recognised as existing members. Despite this possibility, the rate of such errors is controllable and is confined within established theoretical limits.
As shown in Figure 2c, the cuckoo filter structure relies on a hash table consisting of b buckets. Each bucket contains c cells dedicated to storing the fingerprint information of an element. When an element x is inserted, it is mapped to two different buckets using two hash functions. Each bucket holds at most c elements. To locate the buckets and obtain the fingerprint information, the cuckoo filter uses two hash functions: h1(x) and the fingerprint hash function f(x). Specifically, if the fingerprint of an element x is f(x), its corresponding two bucket positions index1 and index2 are calculated by the following formula:
By knowing the position of one bucket and its fingerprint, the position of another bucket can be deduced using the operation of different-or (XOR). This approach simplifies the computation process. Figure 2c demonstrates its insertion mechanism, similar to the cuckoo hash table, which involves a reinsertion process to improve storage efficiency. By optimising this process, the storage space can be maximised. This design not only improves the performance of the filter but also ensures that a low probability of misclassification is maintained with limited resources. The method finds a good balance between space efficiency and operational complexity and is suitable for a variety of application scenarios. In addition, for the case of fingerprint length e, the misjudgement rate p can be calculated by the formula .
3. ECMI Model
As delineated in Figure 3, the present study introduces an innovative model, denoted as ECMI (Enhanced Cuckoo Merkle Index). This model is engineered to refine the mechanisms of data storage and retrieval within the blockchain ecosystem, with a particular emphasis on two fundamental processes: the initial encoding and storage of data fingerprints and the subsequent retrieval and validation of these fingerprints in response to user query demands. The ECMI model distinguishes itself from the conventional blockchain verification protocols, which are typically anchored in Merkle tree structures, by incorporating advanced cuckoo filter technology. This strategic integration not only augments the efficiency of data storage but also significantly amplifies the efficacy of the query verification process. Moreover, the cuckoo filter ensures a consistent and predictable query response time, a critical parameter in high-performance computing environments.
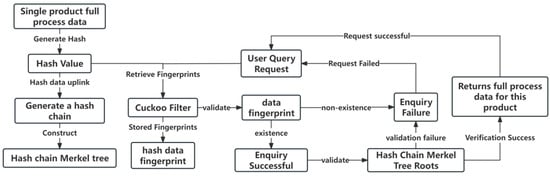
Figure 3.
ECMI model.
The ECMI model exemplifies a paradigm of high operational efficiency while concurrently sustaining an exceedingly low false positive rate, a testament to its robustness and reliability in data integrity verification. The detailed elucidation of these two processes is presented in the ensuing sections, providing a comprehensive understanding of the model’s operational dynamics and its implications for the field of blockchain technology.
Considering the storage cost associated with storing all the data on the chain, the ECMI model adopts an efficient strategy: only the hash values obtained by hashing the full-process data of a single product are stored. These hash values are further processed through the cuckoo filter to generate data fingerprints, which are stored in the cuckoo filter. Meanwhile, the uplinked block data consist of these hash values to form a hash chain, and the corresponding hash chain Merkle tree is constructed based on this. The hash values that are stored on the blockchain are organised into a hash chain, which is a series of linked hash values that represent the data’s journey from their origin to the current state. From these hash values, a Merkle tree is constructed. This tree structure is fundamental for the blockchain’s ability to verify data integrity efficiently. The Merkle tree allows for the validation of data without the need to process the entire dataset, thus saving computational resources and time.
When a user initiates a product traceability query request, the ECMI model first retrieves the fingerprint in the cuckoo filter. If the fingerprint does not exist, the query request is determined to be a failure, and the corresponding failure response is returned to the user. If the fingerprint is found, the model proceeds with a verification process using the Merkle tree. This involves validating the hash value against the Merkle tree to ensure the data’s integrity and authenticity. The verification process is made more efficient by the fact that the data uploaded to the blockchain is compact (32 bytes post-hashing), leading to a reduced number of layers in the Merkle tree. This optimisation allows for swift verification, even with extensive datasets. Upon successful verification, the ECMI model retrieves and returns the complete process data associated with the product, ensuring that the user receives comprehensive and verified information. Conversely, if the verification fails, the system returns a failure response, indicating potential issues with data integrity.
4. Experimental Validation
4.1. Experimental Purpose
In the current era of information explosion, especially in the case of the rapid expansion of the amount of data related to a single commodity, it becomes particularly important to achieve the traceability of the whole process of commodities. In order to meet this demand, this paper adopted a traceability method based on hash operation. Specifically, the full-process information of a single commodity was processed by a hash function, which generated a 32-byte hash value, and this hash value was stored on the blockchain. This practice of storing hash values on the chain not only significantly reduced the storage cost required to upload the full amount of data on the chain but also improved the security of the data. In order to verify the authenticity and integrity of the traceability data, we only needed to compare the hash value stored on the chain with the corresponding index hash value in the server or local storage. The index hash value is the database index value that is the same as the hash value stored on the blockchain. By hashing all the commodity information stored in the database, if the resulting hash value matches the hash value stored on the chain, the authenticity and integrity of the commodity production and processing data can be confirmed. Once the data are verified to be correct, the whole process of production information of the commodity can be queried and traced by the consumer user, which increases the transparency and trust.
The purpose of this experiment was to make an in-depth comparison of the performance of Bloom and cuckoo filters under fixed data storage capacity, especially their false alarm rates when processing large-scale datasets. Through the comparison test under the same data volume condition, it aimed to clarify which filter performed better in reducing false positives and improving query efficiency. This experiment is hoped to provide empirical evidence for the efficient query of blockchain technology in the field of commodity traceability.
4.2. Experimental Procedure and Analysis of Results
In this experiment, a data volume with a scale of millions was selected for storage, and up to ten million query operations were performed on the data to ensure that the obtained experimental results are highly authentic and reliable. In order to further verify the consistency of the data, the experiment was repeated and executed 100 times, and the arithmetic average of the experimental results was used for further in-depth analyses and verification. The following are the specific implementation steps of the experiment:
The compilation and testing of this experiment was carried out under Windows system; the specific configuration of computer hardware and software is shown in Table 1. The code execution result of the cuckoo filter algorithm is shown in Figure 4, which is implemented in Go language and compiled and tested using goland compiler. In the experiment, we set the bucket size to 8 and the fingerprint length to 20, and we stored more than one million elements. The elements stored in the experiment were randomly generated data in Go language and hash values of 32-byte size obtained after hashing operation. Under these parameter configurations, the actual storage space occupied by the cuckoo filter is 2560 KB, while the original data, i.e., 106 32-byte hash values, has an actual storage space of about 31,250 KB. Through the efficient data compression mechanism of the cuckoo filter, the data storage space was significantly reduced to 8.192% of the original data storage space, which significantly reduced the storage requirements.

Table 1.
Computer hardware and software configuration table.
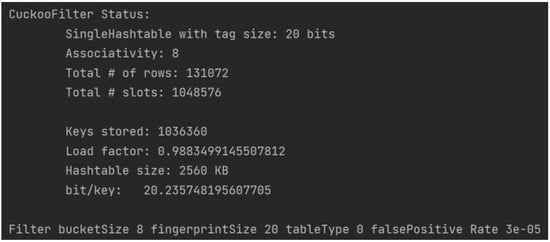
Figure 4.
Cuckoo Filter code run results.
In this experiment, since the actual number of elements stored in each cuckoo filter was variable, in order to ensure the scientificity and validity of the subsequent experiments, this paper adopted the arithmetic average of the number of stored elements in one hundred experiments of the cuckoo filter as well as the misjudgement rate as the parameter values of the Bloom filter implementation function, where the actual stored element n was about 1,036,384 and the misjudgement rate p was 3 × 10−5. The experimental results are shown in Figure 5. Further, in order to achieve the same misjudgement rate p = 3 × 10−5 in the Bloom filter as in the cuckoo filter, the number k of the Bloom filter’s hash function was computed for the theoretical case given the number of data elements n = 1,036,384.
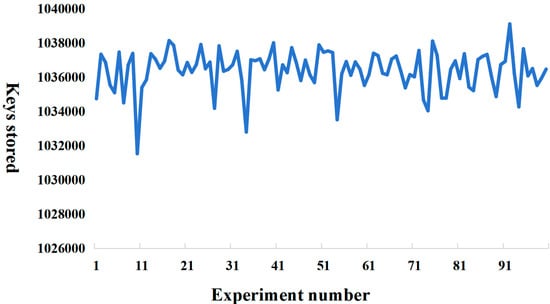
Figure 5.
Cuckoo filter element storage.
The theoretical value of k was found to be 15.02 according to the Bloom filter mathematical formula; however, in view of the integer requirement for the number of hash functions in practical applications, an upward rounding approach was taken. Therefore, it was determined that the optimal number of hash functions k should be 16 in the theoretical case, which means that 16 different hash functions need to be integrated into the Bloom filter’s hash function library to handle the insertion and query operations of elements. As the size of the stored data grows, the required value of k will also rise, which makes it extremely difficult to find the optimal value of k in practical scenarios, especially in scenarios that require efficient queries and low false positive rate control. In view of this, this paper designed a set of controlled experiments by selecting the same number of hash functions as the cuckoo filter, i.e., k = 2. At the same time, in order to ensure the consistency of the experimental conditions, the experiments set the storage size of the Bloom filter to be the same as that of the cuckoo filter so as to evaluate the misclassification rates of the two filters under the same resource constraints.
Figure 6 illustrates the results of the Bloom filter running with the same fixed parameter settings for k = 2. Specifically, the Bloom filter inserted n = 1,036,384 storage elements, performed 10 million query operations, and operated on 2560 KB of storage. Figure 7 then shows the false positive rates of the Bloom filter and the cuckoo filter in one hundred independent experiments and calculates the arithmetic mean of their respective false positive rates. The Bloom filter had a false positive rate of 8.75 × 10−3, and the cuckoo filter had a false positive rate of 3 × 10−5. Based on the above data, it was calculated that the probability of a false positive for the Bloom filter was approximately 292 times higher than the probability for the cuckoo filter. Accordingly, it can be concluded that the false positive rate of the cuckoo filter is significantly lower than that of the Bloom filter under the same experimental conditions. Further, considering the continuous growth of the data volume in practical applications, the Bloom filter usually has two solutions in order to maintain a low false positive rate: The first solution is to increase the k value, i.e., to expand the hash function library of the algorithm, but in practical applications, this solution is more difficult to implement, and it is difficult to ensure the continuous expansion of the hash function, so this solution is discarded. The second scheme is to reduce the false positive rate by increasing the storage space. Based on this, this paper further carried out experiments on Bloom filter storage space expansion.
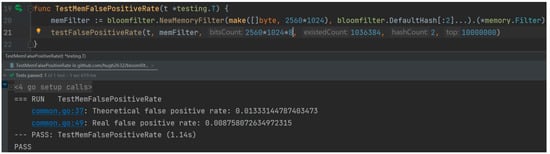
Figure 6.
Bloom filter code run results.
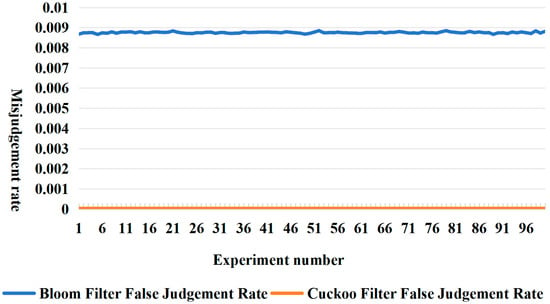
Figure 7.
Misjudgement rate.
As shown in Figure 8, the experimental operation of gradually expanding the storage space of the Bloom filter was carried out until the storage space was expanded to 17 times the original capacity in order to reduce the false judgement rate to the level of p = 3 × 10−5. Considering that the original data consisted of 106 32-byte hash values, its actual occupied storage space was 31,250 KB; in the previous experiments, the cuckoo filter reduced the storage space to 2560 KB, which was only 8.192% of the storage space of the original data, by means of efficient data compression techniques. If the Bloom filter adopts an expansion strategy to reduce the misclassification rate, the storage space needs to be increased to 139.26% of the original capacity, which obviously violates the high compression ratio and space efficiency principles that the Bloom filter was designed for. In view of the dual demands of the application scenarios explored in this paper for low misjudgement rate and data compression storage, the cuckoo filter, with its excellent compression performance and low misjudgement rate, became the preferred choice for constructing the model, which contrasted with the reduction in storage efficiency that the Bloom filter may face after expansion.
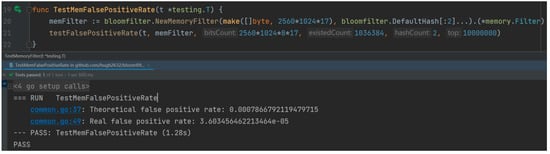
Figure 8.
Results of the expanded Bloom filter operation.
5. Hairy Crab Full-Chain Traceability
5.1. Construction of Traceability Information Table for Each Link of Traceability Process
Building a full-chain traceability process for hairy crabs is a key step in ensuring food safety and enhancing consumer trust. The model covers every link from breeding, processing, and transport to sales and collects and integrates information directly related to hairy crabs, such as the breeding environment, feed use, disease control, processing and packaging, quality inspection, logistics and distribution, and market sales data. Through this model, we are able to comprehensively assess and reduce potential quality and safety risks in the supply chain as well as promote close co-operation among all parties in the supply chain to jointly promote the efficient and sustainable development of the hairy crab industry. This not only enhances consumer trust in hairy crab products but also provides a solid foundation for the long-term prosperity of the hairy crab industry. In this paper, Yangcheng Lake hairy crabs are taken as the research object, and the blockchain uplink data design is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Traceability information table for each link.
5.2. Hairy Crab Full-Chain Traceability Process
This paper proposes a full-chain traceability process for hairy crabs that integrates blockchain and IoT technologies in order to achieve end-to-end transparent regulation from the original breeding to the terminal sales. As shown in Figure 9, the integrated architecture of the model and its specific implementation details are elaborated on in this paper.
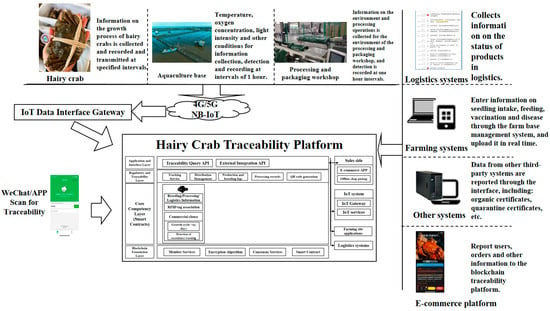
Figure 9.
Hairy crab whole-chain traceability process.
Figure 9 illustrates the various aspects of the process and the data flow path. In the aquaculture stage, an array of IoT sensors is deployed to capture key environmental parameters in real time, including water temperature, dissolved oxygen content, and light intensity. These parameters are transmitted via high-speed mobile communication networks (e.g., 4G/5G or NB-IoT) to the blockchain platform for data uploading operations. The non-tamperability of blockchain technology ensures the authenticity and integrity of the data, providing solid data support for the subsequent production and regulatory processes. At the processing and packaging stage, environmental monitoring sensors are used to oversee the quality of the processing environment, ensuring that each batch of hairy crabs is finely processed under standardised conditions. All relevant processing data are uploaded to the blockchain platform through the IoT interface, building an open and transparent production and processing record chain. The logistical tracking system is responsible for recording and updating the transport status of hairy crabs in real time. Through the application of blockchain technology, the logistical information is made non-tamperable and transparent, enabling consumers and regulators to access the transport track of the product that has been maliciously tampered with, which greatly enhances the credibility of the product. Consumers can access the blockchain platform by scanning the 2D traceability code on the product packaging to obtain information on the full life cycle of hairy crabs from farming to sales, including farming production parameters, processing environment, and logistical status. This not only enhances consumer trust but also advances the transparency of supply chain management.
5.3. Hairy Crab Traceability Platform
As shown in Figure 10, the architecture of the hairy crab traceability platform proposed in this paper is shown. The architecture is hierarchically divided according to functional requirements, including the blockchain foundation layer, the core capability layer, the regulation and traceability layer, and the application and interface layer. In the blockchain foundation layer, this system adopts an open source project as the underlying architecture in order to build a traceability application platform that is both secure and efficient. This layer provides a series of basic capability services, including user authentication, data encryption, consensus mechanism, and the operating environment of smart contracts, providing a solid basic capability service for the entire traceability system. The core capability layer is responsible for providing the execution environment of smart contracts and strictly verifying the data before uploading to the chain to ensure that all information meets the preset contract standards. Based on the established smart contract, this layer automatically executes relevant algorithms and refuses to uplink data that do not meet the specifications, thus ensuring the accuracy and compliance of the data. The supervision and traceability layer assumes the key role of data management and platform configuration and realises functions such as user login, channel management, smart contract release and upgrade, and transaction and query. This layer not only ensures the flexibility and scalability of the platform operation but also provides regulators with the necessary tools to achieve the effective monitoring of the entire traceability process. Finally, the application and interface layer serves as a bridge for the interaction between the system and the outside world, providing functions such as the management of breeding bases, the querying of product traceability information, the integration and display of IoT data, and integration interfaces with external systems. This layer unifies the access points of external data and provides traceability information services externally, enabling consumers, regulators, and other relevant parties to conveniently access the whole life cycle information of hairy crabs.
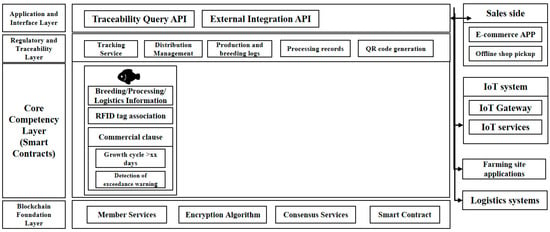
Figure 10.
Hairy crab traceability platform architecture.
To sum up, this traceability process realises the efficient synergy of all links in the hairy crab supply chain through information sharing and transparent management. This not only greatly enhances the brand influence and food safety level but also significantly strengthens consumers’ trust in the products and the market competitiveness of the products, providing strong technical support for the sustainable development of the hairy crab industry.
6. Conclusions and Outlook
This paper constructs a whole-chain traceability process for hairy crabs from Yangcheng Lake for the needs of food safety and traceability in the context of smart agriculture. The process integrates blockchain and IoT technologies to achieve transparent supervision of all links from farming to sales, which effectively improves product trust and market competitiveness. Through an experimental analysis, the cuckoo filter outperforms the traditional Bloom filter in terms of data storage efficiency and query performance while maintaining a low misclassification rate. The proposal of the ECMI model further optimises the blockchain data storage and retrieval mechanism and significantly improves the storage efficiency of the data fingerprints through the cuckoo filter technology. The ECMI model not only provides Yangcheng Lake hairy crabs with a highly efficient and safe traceability solution, but it also provides empirical support for the wider application of blockchain technology in smart agriculture, which is of great significance for promoting agricultural modernisation.
The ECMI model, with its enhancements in data storage and query performance, presents a promising framework for blockchain-based traceability. However, as it transitions into practical applications and encounters the complexities of large-scale data management, it must navigate challenges related to scalability, system resource optimisation, dynamic data handling, and the strengthening of security and privacy measures. To surmount these obstacles, future research must delve into the advancement of data structures and algorithms, the strategic implementation of resource management, and the development of systems capable of real-time data manipulation. Concurrently, there is a critical need to enhance security protocols and privacy preservation techniques to safeguard the integrity of the data. Moreover, exploring cross-chain and multi-chain technologies will be pivotal for the ECMI model, enabling seamless and efficient data interchange across various blockchain networks [36,37,38,39,40,41,42]. This exploration is not only crucial for the model’s scalability but also for fostering a more interconnected and collaborative ecosystem within the realm of distributed ledger technology.
Looking ahead, the ECMI model’s evolution will likely play a transformative role in smart agriculture scenarios, such as precision farming, supply chain transparency, and food provenance verification. Its potential to streamline data management and enhance operational efficiencies could lead to more sustainable agricultural practices and improved consumer trust. Furthermore, as the model is refined and adapted to address the unique demands of diverse agricultural contexts, it could serve as a blueprint for blockchain integration in other sectors, heralding a new era of transparency and efficiency in global supply chains.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.T.; methodology, S.T.; software, S.T.; validation, S.T.; formal analysis, S.T.; investigation, S.T.; resources, S.T.; data curation, S.T.; writing—original draft preparation, S.T.; writing—review and editing, S.T.; visualization, S.T.; supervision, W.J.; project administration, W.J.; funding acquisition, W.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Key Research and Development Program of China grant number 2022YFB2703000 and the APC was funded by National Key Research and Development Program of China.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zeng, Y.W.; Song, Y.X.; Lin, X.Z. Ruminations on some issues of digital village construction in China. China Rural. Econ. 2021, 4, 21–35. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.; Huang, X.; Fang, H.; Wang, V.; Hua, Y.; Wang, J.; Yin, H.; Yi, D.; Yau, L. Blockchain Technology in Current Agricultural Systems: From Techniques to Applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 143920–143937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, M.; Yu, H.; Wang, M.; Xu, D.; Sun, C. A Trusted Blockchain-Based Traceability System for Fruit and Vegetable Agricultural Products. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 36282–36293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashar, D.; Jha, N.; Jha, S.; Lee, Y.; Joshi, G.P. Blockchain-Based Traceability and Visibility for Agricultural Products: A Decentralized Way of Ensuring Food Safety in India. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Zhang, H. Improving Agricultural Product Traceability Using Blockchain. Sensors 2022, 22, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, M.M.; Chang, Y.S. Traceability in a food supply chain: Safety and quality perspectives. Food Control. 2014, 39, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F. A supply chain traceability system for food safety based on HACCP, blockchain & Internet of things. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Service Systems and Service Management, Dalian, China, 16–18 June 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbene, F.; Gay, P.; Tortia, C. Traceability issues in food supply chain management: A review. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 120, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F. An agri-food supply chain traceability system for China based on RFID & blockchain technology. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Service Systems and Service Management (ICSSSM), Kunming, China, 24–26 June 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholten, H.; Verdouw, C.N.; Beulens, A.; Van der Vorst, G.A. Defining and Analyzing Traceability Systems in Food Supply Chains. In Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition, Advances in Food Traceability Techniques and Technologies; Espiñeira, M., Santaclara, F., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2016; pp. 9–33. ISBN 9780081003107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mileti, A.; Arduini, D.; Watson, G.; Giangrande, A. Blockchain Traceability in Trading Biomasses Obtained with an Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture. Sustainability 2023, 15, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xue, J.; Tang, J.; Jiang, T.; Chen, X.; Yang, J. Taste Attributes of the “June Hairy Crab” Juveniles of Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis) in Yangcheng Lake, China—A Pilot Study. Fishes 2022, 7, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fu, C.; Ding, G.; Fang, Y.; Yun, Y.; Norra, S. Effects of hairy crab breeding on drinking water quality in a shallow lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akella, G.K.; Wibowo, S.; Grandhi, S.; Mubarak, S. A systematic review of blockchain technology adoption barriers and enablers for smart and sustainable agriculture. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2023, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Cao, K. Interaction between joining platform blockchain technology and channel encroachment for fresh agricultural product firms. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2024, 31, 3565–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.; Tran, D.H.; Nguyen, P.H.; Lin, M.H. Interval-valued hesitant fuzzy DEMATEL-based blockchain technology adoption barriers evaluation methodology in agricultural supply chain management. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosona, T.; Gebresenbet, G. The role of blockchain technology in promoting traceability systems in agri-food production and supply chains. Sensors 2023, 23, 5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, B.H. Space/time tradeoffs in hash coding with allowable errors. Commun. ACM 1970, 13, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazelle, B.; Kilian, J.; Rubinfeld, R.; Tal, A. The bloomier filter: An efficient data structure for static support lookup tables. In Proceedings of the Fifteenth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, New Orleans, LA, USA, 11–13 January 2004; pp. 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Guo, D.; Ma, R.T.; Rottenstreich, O.; Luo, X. Optimizing bloom filter: Challenges, solutions, and comparisons. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 21, 1912–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkoma, S.; Rothenberg, C.E.; Lagerspetz, E. Theory and practice of bloom filters for distributed systems. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2011, 14, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geravand, S.; Ahmadi, M. Bloom filter applications in network security: A state-of-the-art survey. Comput. Netw. 2013, 57, 4047–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottenstreich, O.; Keslassy, I. The bloom paradox: When not to use a bloom filter. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2014, 23, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Wu, J.; Chen, H.; Yuan, Y.; Luo, X. The dynamic bloom filters. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2009, 22, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jia, W.; Gao, Z.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, Z. Cuckoo-Store Engine: A Reed–Solomon Code-Based Ledger Storage Optimization Scheme for Blockchain-Enabled IoT. Electronics 2023, 12, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Dai, W.; Wang, S.; Xi, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F. A Review of Cuckoo Filters for Privacy Protection and Their Applications. Electronics 2023, 12, 2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, H.; Xu, Y. SPACF: A secure privacy-preserving authentication scheme for VANET with cuckoo filter. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 10283–10295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reviriego, P.; Larrabeiti, D. Denial of service attack on cuckoo filter based networking systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 1428–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslow, A.D.; Jayasena, N.S. Morton filters: Fast, compressed sparse cuckoo filters. VLDB J. 2020, 29, 731–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Rawat, T.K. Optimal fractional delay-IIR filter design using cuckoo search algorithm. ISA Trans. 2015, 59, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reviriego, P.; Apple, J.; Larrabeiti, D.; Liu, S.; Lombardi, F. On the Privacy of Adaptive Cuckoo Filters: Analysis and Protection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2024, 19, 5867–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Andersen, D.G.; Kaminsky, M.; Mitzenmacher, M.D. Cuckoo filter: Practically better than bloom. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Networking Experiments and Techno-logies, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 9–12 December 2014; pp. 75–88. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Liao, L.; Jin, H.; Wu, J. The dynamic cuckoo filter. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Network Protocols, Toronto, ON, Canada, 10 October 2017; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, H.; Jin, H.; Reviriego, P. logarithmic dynamic cuckoo filter. In Proceedings of the 37th IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering, Chania, Greece, 19–22 April 2021; pp. 948–959. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.; Yang, T. Additive and subtractive cuckoo filters. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Quality of Service, Hang Zhou, China, 15–17 June 2020; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Lv, Z.; Alfarraj, O.; Tolba, A.; Yu, X.; Ren, Y. Secure cross-chain interaction solution in multi-blockchain environment. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, W.; Huang, S.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, G.; Han, W. An overview on cross-chain: Mechanism, platforms, challenges and advances. Comput. Netw. 2022, 218, 109378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Nie, T.; Sun, H.; Shen, D.; Yu, G. A survey on cross-chain technology: Challenges, development, and prospect. IEEE Access 2022, 11, 45527–45546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wu, B.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, K.; Li, H. A cross-chain trusted reputation scheme for a shared charging platform based on blockchain. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 7989–8000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falazi, G.; Breitenbücher, U.; Leymann, F.; Schulte, S. Cross-Chain Smart Contract Invocations: A systematic multi-vocal literature review. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 56, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, G.; Yuan, Y. Efficient cross-chain transaction processing on blockchains. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Sun, Y.; Ni, W.; Ding, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, W. Attacks against cross-chain systems and defense approaches: A contemporary survey. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2023, 10, 1647–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).