Abstract
The calculation of effective doses is crucial in many medical and radiation fields in order to ensure safety and compliance with regulatory limits. Traditionally, Monte Carlo codes using detailed human body computational phantoms have been used for such calculations. Monte Carlo dose calculations can be time-consuming and require expertise in different processes when building the computational phantom and dose calculations. This study employs various machine learning (ML) algorithms to predict the organ doses and effective dose conversion coefficients (DCCs) from different anthropomorphic phantoms. A comprehensive data set comprising neutron energy bins, organ labels, masses, and densities is compiled from Monte Carlo studies, and it is used to train and evaluate the supervised ML models. This study includes a broad range of phantoms, including those from the International Commission on Radiation Protection (ICRP-110, ICRP-116 phantom), the Visible-Human Project (VIP-man phantom), and the Medical Internal Radiation Dose Committee (MIRD-Phantom), with row data prepared using numerical data and organ categorical labeled data. Extreme gradient boosting (XGB), gradient boosting (GB), and the random forest-based Extra Trees regressor are employed to assess the performance of the ML models against published ICRP neutron DCC values using the mean square error, mean absolute error, and R2 metrics. The results demonstrate that the ML predictions significantly vary in lower energy ranges and vary less in higher neutron energy ranges while showing good agreement with ICRP values at mid-range energies. Moreover, the categorical data models align closely with the reference doses, suggesting the potential of ML in predicting effective doses for custom phantoms based on regional populations, such as the Saudi voxel-based model. This study paves the way for efficient dose prediction using ML, particularly in scenarios requiring rapid results without extensive computational resources or expertise. The findings also indicate potential improvements in data representation and the inclusion of larger data sets to refine model accuracy and prevent overfitting. Thus, ML methods can serve as valuable techniques for the continued development of personalized dosimetry.
1. Introduction
In the field of nuclear medicine, the use of radioisotopes for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes was introduced in the 1960s. Safety prerequisites and compliance with regulatory limits led to the need to pre-calculate the dose distributions in the target organ and surrounding tissues. To calculate the dose received by the internal organs, a detailed model was introduced to estimate the diagnostic or therapeutic dose for both the organ and the entire body. This work resulted in the creation of an MIRD phantom (Medical Internal Radiation Dose Committee) [1] in conjunction with the state-of-the-art Monte Carlo N-Particle Transport code (MCNP). This model considers the full body size and shape, as well as physical characteristics, such as the density and elemental composition of organs [2]; furthermore, it has the advantage of using less computational memory. During the 1980s and 1990s, a second type of anthropomorphic phantom—known as the voxel-based phantom—was developed. This phantom takes advantage of sectional tomographic images to better represent the shape and size of organs, and it can include smaller organs in more detail. Additionally, a third type of phantom—known as the mesh-based or boundary representation (BREP) deformable phantom—was developed, which is also based on medical images. This phantom has higher resolution than the earlier phantoms and also possesses the ability to deform. All types of anthropomorphic phantoms are currently employed for research and operations in many radiological fields. Furthermore, all types have multiple versions available in different Monte Carlo codes, covering both gender and different age groups, as well as organ-specific models [3,4,5].
The concept of effective dose was set out by the International Commission for Radiation Protection (ICRP) [6,7]. It considers weighting factors for the selected organ tissue (radiation sensitivity) multiplied by radiation weighting factors associated with the radiation damage quality factor. The definition of the effective dose has great application potential, as it sets the dose limits for patients, workers, and the public [8]. Therefore, effective dose conversion coefficients (DCCs) have been calculated by employing all types of anthropomorphic phantoms and utilizing different Monte Carlo codes. This was achieved to accommodate the fact that defining an average person is difficult. Different locations use different types of population-based anthropomorphic phantoms [5] with the same elemental composition reference values [9,10] and varying physical characteristics, in terms of total weight, height, organ size, and shape, against the ICRP reference model.
Machine learning (ML) algorithms have been effectively applied in radiotherapy treatment planning [11], including for the segmentation and building of higher-resolution anthropomorphic tomography-based phantoms [5]. These applications depend on large amounts of evaluated data, increased computer capacity, and the development of powerful ML algorithms. One of the main advantages of ML is that it provides fast and accurate results, enabling rapid predictions [12].
This pilot study attempted to predict organ doses using supervised ML methods through tabulating several published Monte Carlo calculations of neutron DCCs for different types of anthropomorphic phantoms. The construction of the used data set and the accuracy constraints of the ML models are presented, and the results regarding organ doses and effective doses for previously uncalculated anthropomorphic phantom data are compared to the neutron DCCs published by the International Commission for Radiation Protection (ICRP) [13,14].
2. Methodology
Raw data were collected from published studies [13,14,15,16,17], and Python programming language was employed for ML models fitting and analysis. Table 1 shows the different types of anthropomorphic phantoms, the organs included in the study, and the target organs for the uncalculated neutron DCC in the anthropomorphic voxel phantom based on the population of Saudi Arabia [17]. This study included ICRP-110 voxel-based male and female phantoms, ICRP-116 mesh-based (a type of BREP deformable) male and female phantoms, the Visible Human Project VIP-man voxel-based phantom, and an MIRD mathematical-based phantom. Different general-purpose Monte Carlo codes were used, including the MCNP series, Geometry and Tracking 4 (GEANT4), FLUktuierend KAskade (FLUKA), and the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport Code System (PHITS). The inclusion criterion for selecting the data required for the anthropomorphic models was consistency in the calculated neutron energy bins. The data were organized vertically, with the neutron energy bins listed along with the corresponding organ labels, which were repeated for each of the 48 energy bin ranges (from 10−9 to 20 MeV). In addition, the associated data features, such as the weight of each organ in grams, the density in grams per cubic centimeters, and the calculated doses for anterior posterior (AP), posterior anterior (PA), and lateral (LAT) irradiation conditions were considered.

Table 1.
Different types of anthropomorphic phantoms, the organs included in the study, and the target organs for uncalculated neutron effective dose conversion coefficients.
Overall, the data included 5618 rows of vertically repeated neutron energy bins for all organs from all anthropomorphic models in the energy range from 10−9 to 20 MeV and 6 columns representing 6 features: organ label, organ mass, organ density, AP DCC, PA DCC, and LAT DCC. Data for the final shape are provided in an Excel file (Supplementary Material Table S1). The steps and processes (known as pipelines) in ML are well documented, and further details can be found in the study of Raschka and Mirjalili [18]. The most important steps are described as follows.
2.1. Data Preparation
The number of group labels investigated included 32 labeled organs generated from the 6 anthropomorphic phantoms. These data can be used in two ways: (1) employing only numerical data for prediction and (2) converting the labeled categorical data to encode false and true tables using the “one-hot-encoder” Python function to distinguish each group of labeled organs. The results from this step were added back into the original data file, and the organ column was replaced with 32 columns.
2.2. ML Model Selection
Extreme gradient boosting (XGB) and random forest models for tabulated data are preferred over artificial neural networks (ANNs) [19,20,21]. Three models were selected for fitting the pilot data: XGB, gradient boosting (GB), and the random forest-based Extra Trees regressor (EXTR). The detailed parameter options can be found in [22]. Default parameters were used, with a fixed number of estimators (n-estimator = 100), and the data (5168 × 38 after dropping the desired fitting target) were divided into a 75% sample for training and a 25% sample for testing.
2.3. Evaluation and Cross Validation
Table 2 shows a sample of the cross-validation scores of the ML models for the mean square error, mean absolute error, and R2, employing categorical labeled data for the EXTR-C, XGB-C, and GB-C ML models and numerical data for the EXTR, XGB, and GB ML models.

Table 2.
Cross-validation scores (fractional unit) of the ML models for mean square error, mean absolute error, and R2, employing categorical labeled data (for the EXTR-C, XGB-C, and GB-C ML models) and numerical data (for the EXTR, XGB, and GB ML models).
Figure 1 illustrates a sample of R2 values for the categorically labeled data models. In addition, the three models were compared in terms of k-fold accuracy for both the training and testing sets. The box plot in Figure 1 displays the results of the k-fold accuracy analysis with five cross-validations, showing the performance of all models for both types of data fitting, including the training and testing sets. In general, all three models performed well and demonstrated better results when fitting the categorical data. K-fold analysis can be used with large or small size data. However, while the hyperparameter tuning of any of the three models may lead to improved results, hyperparameters tuning except for k-fold analysis were avoided in this study, as it was found to potentially cause overfitting of the results. Future studies involving larger data sets should consider the use of hyperparameter tuning techniques.
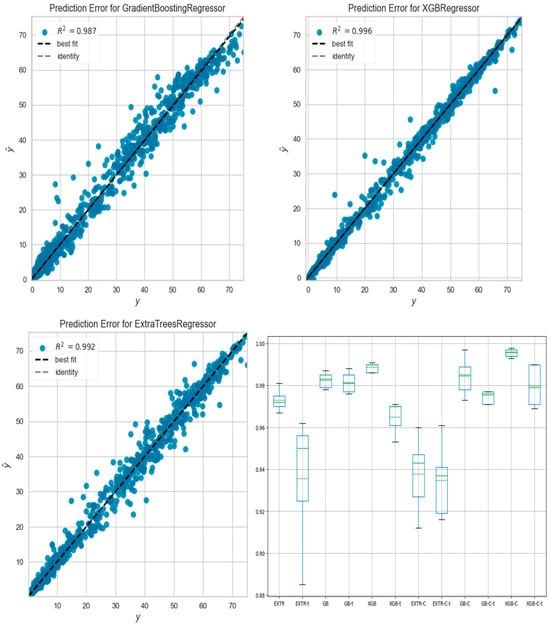
Figure 1.
R2 values for the categorical labeled data training set for the EXTR-C, XGB-C, and GB-C models, both actual (y) and predicted (ŷ) units in pSv. The box plot in the lower right corner of the figure shows the results for the k-fold accuracy analysis with five cross-validations for all models on the training set for numerical data (EXTR, GB, XGB), categorical data (EXTR-C, GB-C, XGB-C), testing set for numerical data (EXTR-t, GB-t, XGB-t) and categorical data (EXTR-C-t, GB-C-t, XGB-C-t).
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 2 shows a comparison of the XGB, GB, and EXTR models. These models used both numerical and categorical data (XGB-C, GB-C, and EXTR-C) to predict doses for the target voxel-based anthropomorphic phantom. Selected organ doses for the colon and red bone marrow (RBM) at different irradiation positions (AP, PA, and LAT) were compared with the ICRP-116 mesh-based and ICRP-110 voxel-based anthropomorphic reference calculated the organ doses. The results obtained when using predictive ML models (numerical and categorical) overlapped with each other; however, a deviation in the results of some models was observed. For red bone marrow (RBM) AP irradiation conditions, the values for neutron energies lower than 1 eV had percentile differences that varied between 40% (for the EXTR, EXTR-C, and XGB-C models) and 87% (for GB, GB-C, and XGB). For higher neutron energies, the values varied between 3% and 27% for all of the models.
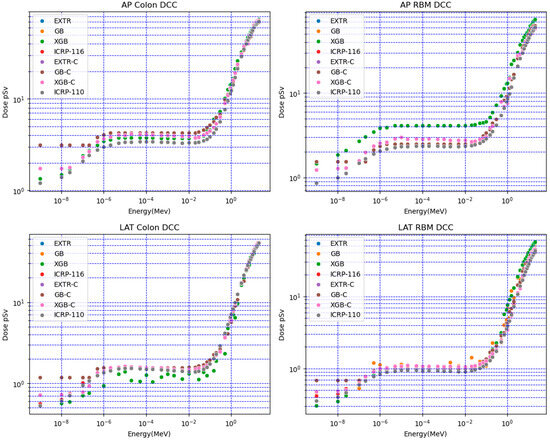
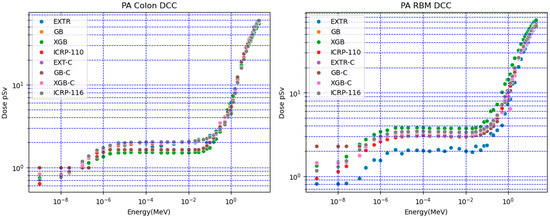
Figure 2.
Comparison of predicted doses for colon and red bone marrow (RBM) in different irradiation positions (AP, PA, and LAT) using the ICRP (116 mesh-based and 110 voxel-based) anthropomorphic reference.
The ML model predictions varied, and the EXTR-C and XGB-C models generally performed better than the other models; for example, for the colon LAT DCCs in Figure 2, the XGB model using numerical data presented signs of underestimation and overfitting. All ML models scored an average percentile difference of less than 9% with respect to ICRP-116 LAT DCCs.
The models employed for fitting categorical data (XGB-C, GB-C, and EXTR-C) showed reasonable agreement with the reference values of ICRP-116 and ICRP-110, considering the variation in the physical characteristics of the organ (assigned features weight and density) for the target voxel phantom. Notably, the results of ICRP-116 and ICRP-110 represented the average of several Monte Carlo codes calculations with a variation of 15% [13,14].
For effective dose calculations, categorical data for organ dose prediction were considered using three linear ML models (XGB-C, GB-C, and EXTR-C). The calculation methods described in ICRP-103 and ICRP-116 using a function for the neutron energy radiation weighting factor dependency were adopted. ICRP-103 recommends a radiation-sensitive assigned weighting factor for 14 organs (Table 1) with the remaining tissues segmented in the Saudi voxel anthropomorphic phantom.
Figure 3 shows the results of the neutron effective dose CC for the AP, PA, and LAT irradiation conditions compared with ICRP-116. The comparison results, obtained through dividing the ML model-predicted value by the ICRP-116 values, are shown in Figure 3 (right lower corner graph). The PA had the largest deviation, which was followed by the AP and LAT. The major contributors to the received dose in organs depend primarily on the position of the organ relative to the irradiation source and the mean position volume of the organ within the phantom. Therefore, differences can be expected when comparing with the agreed reference anthropomorphic phantom provided by the ICRP. Figure 3 shows the PA effective dose calculations for the FAX voxel-based phantom using the ICRP-103 radiation weighting factors [23] and the Zubal voxel-based phantom [24]. The deviation was larger than the Saudi voxel-based ML model-predicted neutron effective dose CC versus the ICRP reference values. The use of different neutron radiation weighting factors and different numbers of organs in the calculations may explain the larger deviation for the FAX voxel phantom and, to a lesser extent, Zubal voxel-based phantoms, compared to that in the current study. Despite the possible sources of variation, the present results indicate that the ML model predictions were within the range of expected differences given the large variations between neutron effective doses from different anthropomorphic phantoms [13,14,15,16,17,23,24].
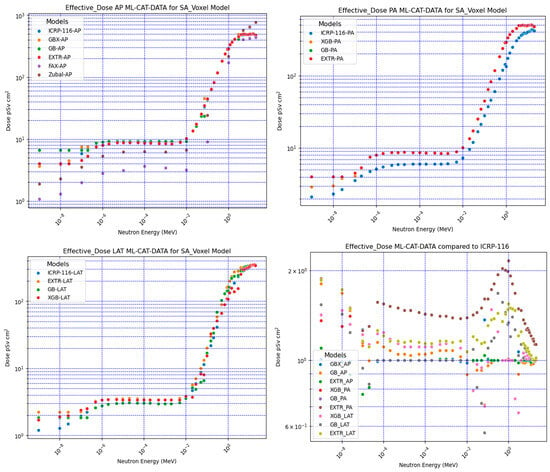
Figure 3.
ML prediction using categorical data (ML-CAT-DATA) for the Saudi voxel phantom (SA-Voxel model) neutron effective dose CC for AP, PA, and LAT irradiation conditions compared with ICRP-116.
The prediction of the categorical data models for the neutron effective dose exhibited reasonable results, considering the differences in the voxel phantom based on the Saudi population for organ sizes and assigned physical characteristics for weights and densities.
Finally, the size of the row data used in this study (5618 rows × 6 columns) was within the medium range. Therefore, while the interpretations of the current results show reasonable agreement with the expected neutron DCC trend, the results may be improved further through increasing the size of the sample.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we presented a method for constructing a data set which enables ML-based prediction from previously calculated Monte Carlo neutron DCCs from different types of anthropomorphic phantoms. The results of the ML models were in agreement with the ICRP values at medium neutron energies but presented large deviations at lower energies and relatively acceptable deviation at higher energy ranges; however, these observed differences were expected and fell within a reasonable range. Although the current study covered more than 75% of the published calculated neutron effective DCCs, the overall number of such studies remains low. Therefore, to eliminate the possibility of overfitting, the size of the data set could be increased in future investigations through including more simulation studies or applying ML models to photon DCCs, for which more investigations of anthropomorphic phantoms have been conducted on a larger scale.
Better fitting results were obtained with categorical arranged data than when using numerical data; however, numerical data offer the possibility to predict one or multiple organs and one or multiple energy bins.
This study demonstrated that ML can be an efficient tool for dose prediction, depending on the number of available Monte Carlo studies covering different anthropomorphic phantoms. In many cases, such Monte Carlo dose calculations are time-consuming, require expertise, and require the computational capacity to incorporate a large number of voxels. Therefore, ML methods offer the possibility of dose prediction when rapid results are required. ML has some additional advantages in terms of flexibility in accommodating different data; however, it should be considered that ML models are very sensitive to irregularities in the data, such as the number of energy bins considered in the Monte Carlo calculations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app14135740/s1, Table S1: Anthropomorphic Phantom’s Data.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Snyder, W.S.; Ford, M.R.; Warner, G.G.; Fisher, H.L., Jr. Estimates of Absorbed Fractions for Monoenergetic Photon Sources Uniformly Distributed in Various Organs of a Heterogeneous Phantom; Oak Ridge National Lab: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, R.W.; Wessels, B.W.; Loevinger, R.; MIRD Committee. The MIRD perspective 1999. J. Nucl. Med. 1999, 40, 3S–10S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abadi, E.; Segars, W.P.; Tsui, B.M.; Kinahan, P.E.; Bottenus, N.; Frangi, A.F.; Maidment, A.; Lo, J.; Samei, E. Virtual clinical trials in medical imaging: A review. J. Med. Imaging 2020, 7, 042805–042845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Yeom, Y.S.; Petoussi-Hen, N.; Zankl, M.; Bolch, W.E.; Lee, C.; Choi, C.; Nguyen, T.T.; Eckerman, K.; Kim, H.S.; et al. ICRP publication 145: Adult mesh-type reference computational phantoms. Ann. ICRP 2020, 49, 13–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Gao, N.; Wu, B.; Chen, Z.; Xu, X.G. A review of computational phantoms for quality assurance in radiology and radiotherapy in the deep-learning era. J. Radiat. Prot. Res. 2022, 47, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection. Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection; ICRP Publication 26; ICRP Publication: Oxford, UK, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection. 1990 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection; ICRP Publication 60; The International Commission on Radiological Protection: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- McCollough, C.H.; Schueler, B.A. Calculation of effective dose. Med. Phys. 2000, 27, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.A. Photon, Electron, Proton and Neutron Interaction Data for Body Tissues: ICRU Report 46; International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Zankl, M.; Schlattl, H.; Petoussi-Henss, N.; Hoeschen, C. Electron specific absorbed fractions for the adult male and female ICRP/ICRU reference computational phantoms. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, 4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Lam, S.; Cai, J.; Yang, R. A review on application of deep learning algorithms in external beam radiotherapy automated treatment planning. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 580919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, W.; Lin, X.; Yi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Qu, L.; Zhuo, W.; Liu, H. Fast prediction of patient-specific organ doses in brain CT scans using support vector regression algorithm. Phys. Med. Biol. 2024, 69, 025010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICRPP. Adult reference computational phantoms. ICRP Publication 110. Ann. ICRP. 2009, 39, 1. [Google Scholar]
- ICRP. Conversion Coefficients for Radiological Protection Quantities for External Radiation Exposures. ICRP Publication 116. Ann. ICRP 2010, 40, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Bozkurt, A.; Chao, T.C.; Xu, X.G. Fluence-to-dose conversion coefficients from monoenergetic neutrons below 20 MeV based on the VIP-man anatomical model. Phys. Med. Biol. 2000, 45, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakimabad, H.M.; Motavalli, L.R.; Shahri, K.K. Assessment of neutron fluence to organ dose conversion coefficients in the ORNL analytical adult phantom. J. Radiol. Prot. 2009, 29, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, A.K.; Hussein, M.A.; Altaher, K.M.; Farid, K.Y.; Amer, M.; Aldhafery, B.F.; Alghamdi, A.A. Fluence-to-effective dose conversion coefficients from a Saudi population based phantom for monoenergetic photon beams from 10 keV to 20 MeV. J. Radiol. Prot. 2014, 35, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raschka, S.; Mirjalili, V. Python Machine Learning: Machine Learning and Deep Learning with Python, Scikit-Learn, and TensorFlow 2; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Deka, B.; Maji, P.; Mitra, S.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Bora, P.; Pal, S. Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference, PReMI 2019, Tezpur, India, 17–20 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Geurts, P.; Ernst, D.; Wehenkel, L. Extremely randomized trees. Mach. Learn. 2006, 63, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, S.; Valdes, G. Machine learning for radiation outcome modeling and prediction. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, e178–e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. JMLR 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Cordeiro, T.P.V.; Silva, A.X.; Crispim, V.R. Calculation of conversion coefficients for effective dose for neutrons using a female voxel anthropomorphic model and the MCNPX code. In Proceedings of the INAC 2009: International Nuclear Atlantic Conference. Innovations in Nuclear Technology for a Sustainable Future, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 27 September–2 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Alghamdi, A.A.; Ma, A.; Tzortzis, M.; Spyrou, N.M. Neutron-fluence-to-dose conversion coefficients in an anthropomorphic phantom. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2005, 115, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).