Abstract
Introduction: Forensic identification practice requires a multitude of methods for positive identification, among which the facial reconstruction occupies a high place. For this to be done in the best way possible, it is mandatory that each population have their own database regarding soft tissue thickness. Objective: The present research is focused on creating such a database for the Romanian adult population and on exploring the statistical distribution and correlation of craniometric landmarks, overall, and in groups defined according to sex and weight categories. This might provide support in estimating the values of missing landmarks or other variables (e.g., age, sex) for unidentified bodies. Methods: Twelve craniometric landmarks were measured on 100 cadavers less than 24 h after death. Results and discussions: Of the 12 anatomical landmarks, only one appears to manifest statistically significant differences between sexes, and seven landmarks appear to vary significantly among the weight categories. Additionally, some evidence of interpopulation differences in the average soft tissue thicknesses were observed by the comparison of these data with similar studies from Caucasian groups with different geographic origin. Additionally, correlations between facial landmarks were examined, overall and between sexes.
1. Introduction
The thickness of the soft tissues at the level of the facial massif represents an important landmark in anthropological forensic practice, especially for the possibility of performing cranio-facial reconstruction. Cranio-facial reconstruction is a useful technique and is used in the field of forensic anthropology, the result of which is the creation of an image starting from the skull arranged for anthropological analysis [1,2]. It has multiple important uses, primarily when the forensic anthropologist has only one skull at his disposal that cannot give you much information about the person to whom it belonged; it is also important in the investigations of victims of genocide, and victims of mass disasters (wars, natural or intentional accidents, etc.) [2,3,4].
The history of cranio-facial reconstruction places it somewhere in the early nineteenth century; however, the method became notorious with the works of Gerasimov (1968). In its primary stages, cranio-facial reconstruction was a more artistic method, depending on the researcher’s skills as a sculptor. Additionally, the cranio-facial reconstruction method began by modeling clay or plasticine to restore the depth of soft tissue on the skull of the deceased. This tissue depth (thickness of the cranio-facial soft tissues) is established by measuring it at certain points and interpreting those measurements. The key to cranio-facial reconstruction lies in the understanding that each head/skull has distinct features that gives the individuality of a person. It is also important for each population to hold such values of soft tissue thickness, as each population is characterized by unique and individual traits [4,5].
The points measured to estimate the values of the thickness of the facial soft tissues are called craniometric landmarks (or facial landmarks) These landmarks are key points of the face with a certain biometric and geometric significance. These can have a skeletal or a soft tissue base, depending on where it is located, on the bone or directly on the skin. In the first case, they are called craniometric landmarks of hard tissue, and in the second case, they are called craniometric landmarks of soft tissue [4,5,6,7].
The establishing of the soft tissue thicknesses values, as well as the relationship between soft and hard tissue, can be made by means of radiological data—X-ray, computed tomography, nuclear magnetic resonance, ultrasound—which can be in vivo, or on cadaveric material, the last one being a direct method via needle puncture [1,8,9,10,11,12]. International literature is characterized by vast research regarding soft tissue thicknesses values. Thus, a number of countries (France, Brazil, Portugal, etc.) have conducted and are conducting numerous research to establish soft tissue thicknesses values and to develop methods for craniofacial reconstruction (based on computed-tomography images, cadavers, X-ray, etc.), specific to each population [1,8,9,10,11,12,13].
Despite all these developments, the Romanian population does not have any research data regarding the soft tissue thicknesses values to allow for an accurate craniofacial reconstruction. The importance of these data for Romania is, first, for the alignment at the international standard of the forensic identification process, and, second, to help the development of research in forensics. Another important aspect is the fact that Romania is a country with a predisposition for disasters with multiple victims because it is a country with an important seismic activity.
This study examines the distribution of values and the relationships among twelve craniometric landmarks for a dataset containing information on 100 Romanian adults. Data centrality, overall and on sexes, is compared with results from previous studies on similar populations (Caucasians) and data collection techniques. Identifying the landmarks with significant differences between sexes and among weight categories can provide valuable support in estimating the missing values when data collection is incomplete and/or the bodies are unidentified. Thus, the main purpose of this study was to develop and propose standard values for the thickness of cranio-facial soft tissues for the adult population of Romania.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of the Study Sample, Criteria for Inclusion and Exclusion
In order to estimate the standard values for the thickness of the facial soft tissues of the adult population of Romania, an exploratory study with a descriptive experimental approach was developed on 100 subjects consisting of cadaveric bodies of adult deceased persons who were subjected to forensic autopsy in a delimited territory on the North-East region of Romania. The type of study was a prospective one.
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and the protocol was approved by the Ethic Committee of “Grigore T. Popa” Medicine and Pharmacy University.
The inclusion criteria were represented by corpses with characteristics of skeletal maturity, with the absence of cranio-facial malformations or other modifications of the facial massif that could have influenced the measurements made. The cadaveric bodies with an PMI (postmortem interval) of more than 24 h or in an advanced state of decomposition were excluded from the study, including those that had traumatic marks at the level of the facial massif.
2.2. Recording Information in the Database
For the analyzed study group, regarding the personal data, we recorded the sex, age, height measured postmortem and the constitution of the cadaver according to body mass index (BMI) (underweight means a BMI < 18.5; normal weight means a BMI between 18.5 and 24.9; and overweight that means a BMI > 25).
2.3. Working Methodology
As a working methodology, the authors conducted the study on cadaveric material, having at their disposal deceased persons whose autopsy is mandatory and is carried out completely. The corporeal material included in the study is an important source of research in forensic anthropology, as it allows researchers to work on known parameters, in this case, the waist, sex and known age of deceased people.
The study was conducted on 100 bodies, including 52 males and 48 females aged between 22 and 85 years. As a working material in the study, the cadaveric bodies and one skin thickness measuring instrument length 0–30 mm, with the possibility of measuring up to 30 mm (Figure 1), were used. The instrument used for measuring is a manual caliper, which has a needle with which it pricks, the sting at the level of the craniometric landmarks being performed perpendicularly. The craniometric landmarks were located via palpation.

Figure 1.
Skin thickness measuring instrument length 0–30 mm.
Measurements, which were taken in horizontal (supine) position, were made at the level of 12 craniometric landmarks of the facial massif, of which 8 on the midline, respectively, of 4 bilateral craniometric landmarks (left side, respectively, on the right side). Table 1 is a description of the craniometric landmarks included in the present study [7,13].

Table 1.
Description of craniometric landmarks used for the measurements.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The distribution of facial landmarks and other personal data was examined using Exploratory Data Analysis for the entire dataset, between sexes, and within three weight categories. Correlations among landmarks were computed on the entire dataset and on sexes. Inferential statistics techniques, such as the Fisher’s exact test, the Mann–Whitney (Wilcoxon) test, and the Kruskal–Wallis test, helped assess the variability of facial landmarks among categories/groups defined by sex or by weight category. All tests were non-parametric since the distributions of all facial landmarks are not normal, as reported by the Shapiro–Wilk test of normality (see Section 3).
Data were prepared and analyzed with R programming language [14]. The tidyverse ecosystem of packages (dplyr, tidyr, readr, stringr) [15] was the main tool for data preparation tasks. Exploratory data analysis relied mainly on two packages, gtsummary [16] and ggplot2 [17] (which is part of the tidyverse). Table 2 and Table 3 were generated with packages gtsummary and flextable [18].

Table 2.
Descriptive characteristics of parameters studied in relation to sex.

Table 3.
Descriptive characteristics of parameters studied in relation to BMI categories.
All statistical tests were performed in base R. The correlation plot was produced with the corrplot package [19]. Statistical test results and charts were obtained using the ggstatsplot package [20] which computes and displays the following parameters for each test: the statistics, the p-value, the effect size, and the 95% confidence interval of the effect size.
3. Results
Figure 2 presents the overall distribution (as density curves) of all numerical variables in the 100-case dataset. Some variables, such as glabella and l_mid_supraorbital are more concentrated around their central values, whereas others, such as nasion and supraglabella, are more scattered. The Shapiro–Wilk test of normality (not shown) reveals that age_years is the only numeric variable with a normal distribution. This determines the types of tests to be chosen when assessing the statistical significance of the differences among groups or the correlation among variables.
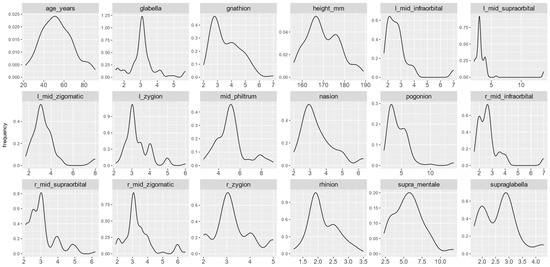
Figure 2.
Overall distribution of each numeric variable.
Table 2 and Table 3 provide descriptive statistics by grouping the results by sex (Table 2) and weight category (Table 3). The last column in both tables refers to the p-value of the statistical tests concerning group differences (Wilcoxon rank sum test and Kruskal–Wallis test).
Table 2 provides the descriptive statistics when grouping the results by sex. Last column in the table contains the p-value of the statistical tests concerning group differences (the Wilcoxon rank sum test). Of the 100 (deceased) people in the dataset, 48 were females and 52 males. Overall median age was 52 years (54 for females and 52 for males). The difference on age distribution between females and males was not statistically significant (p-value = 0.4). By contrast, Table 2 suggests that the differences on height between females and males are statistically significant (p-value < 0.001).
According to Table 2, only one landmark appeared to manifest statistically significant differences between sexes, i.e., nasion. For l_mid_zygomatic, at 0.05 significance level (alpha), the difference is not significant. Because the Shapiro–Wilk normality test reports W = 0.896, p-value < 0.001 for nasion, and W = 0.755, p-value < 0.001 for zygomatic, the statistical differences between sexes on both variables were assessed with the non-parametric Mann–Whitney test—see Figure 3.
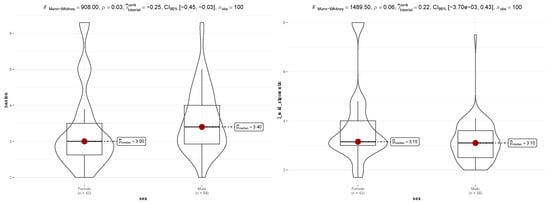
Figure 3.
Non-parametric tests for assessing the differences between sex on nasion (left) and l_mid_zigomatic (right).
For variable nasion (Figure 3 (left)), the Mann–Whitney test assesses the null hypothesis that, for randomly selected values of nasion for females (X) and values of nasion for males (Y), the probability of X being greater than Y is equal to the probability of Y being greater than X. The p-value (0.03) is smaller than the 0.05, and the effect size is medium (−0.25 CI95% [−0.45, −0.03]); thus, there is sufficient evidence to reject H0. Nasion median is larger for males than females (3.49 vs. 3.00) and the differences between the two distributions are statistically significant. As for variable l_mid_zygomatic (Figure 3 (right)), not only the p-value exceeds 0.05, but also the 95% confidence interval of the effect size covers the value of zero; therefore, the differences between sexes for l_mid_zygomatic are not significant.
Next, the mean values of the facial landmarks were compared with values found in other studies concerning similar populations using the same method of data collection. Figure 4 displays the comparative average facial soft tissue thicknesses measured using needle puncture methods on female and male cadavers from three different geographic origins, Portugal, Romania, and Spain, based on the paper published by [9,21]. The chart includes eight landmarks, since only these are common in both our study and the study concerning Portugal and Spain [9].
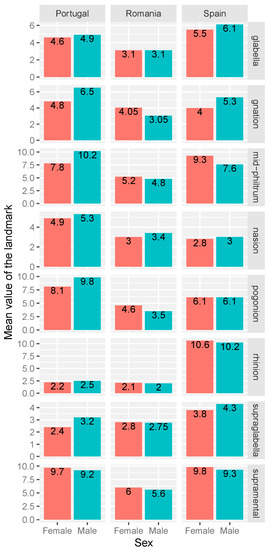
Figure 4.
Comparison of average facial soft tissue thicknesses measured using needle puncture methods on cadavers from groups with different geographic origin.
Based on another paper concerning the population of Brazil [22], Figure 5 compares the mean values (of the the same eight-landmark set) between Brazil and Romania, without grouping according to sex (as the data on sex were not available for Brazil).
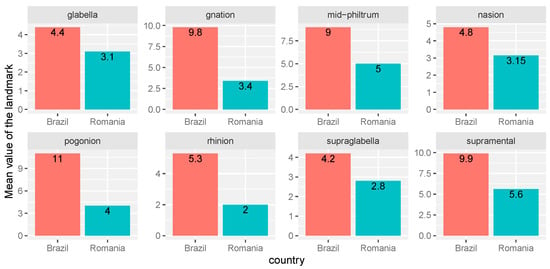
Figure 5.
Comparison between Romanian and Brazilian adult population using the same method for the measurements.
The next topic of interest for the Romanian dataset was to assess if the distribution of values referring to the facial landmarks varies significantly among weight categories. Table 3 contains the descriptive statistics of the “Romanian” dataset variables, overall and grouped by the three weight categories. The last column in Table 3 refers to the p-value of the statistical tests concerning the differences among categories. Since, in this study, three weight categories were included, and the distribution of facial landmarks was non-normal, the Kruskal–Wallis test was preferred (instead of ANOVA).
The overweight group was smaller since it is represented by only 8 observatios, compared to 50 observations for the underweight group, and 42 for the normal weight group. The median age was considerable larger for the overweight group (67 vs. 52 for both underweight and normal weight groups). Nevertheless, as the last column in the table shows, the differences among the three groups, as assessed through the non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis test, do not appear to be statistically significant (p-value = 0.8).
Regarding the sex vs. weight category frequency table, Table 3 shows that the overall females/male’s proportion (42/58) is preserved by the underweight group but reversed in the overweight group. The Fisher’s exact test assessed as non-significant the association between weight category and sex.
Seven landmarks appear to vary significantly among the three weight categories: supraglabella, glabella, nasion, rhinion, gnation, r_mid_infraorbital, l_mid_zygomatic, whereas for supramentale, the difference is close to the significance level (p-value = 0.051).
Another subject of interest was to examine the bivariate correlation among numerical variables, so that whenever the value of a given facial landmark is missing, it could be inferred based on its association with other landmarks and/or additional personal variables. As the distribution of all variables (except age years) is not normal, the non-parametric Spearman coefficient was preferred instead of the parametric (Pearson) one. Figure 6 displays the correlation plot, as produced by the corrplot package.
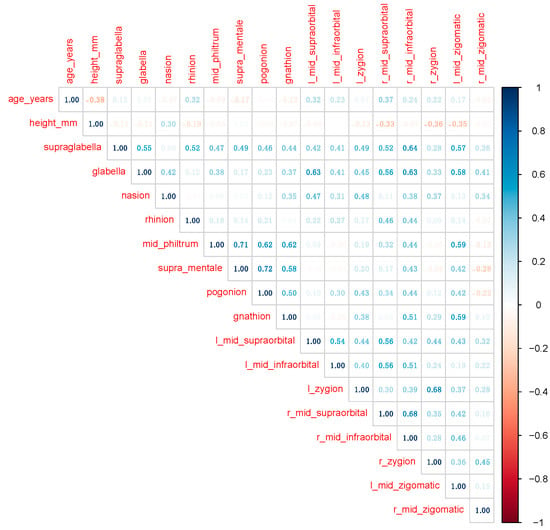
Figure 6.
Non-parametric correlation among numerical variables.
The largest positive correlation coefficients were recorded for the following pairs of variables: pogonion and supra_mentale (0.72); mid_philtrum and supra_mentale (0.71); r_mid_infraorbital and r_mid_supraorbital (0.68); l_zygion and r_zygion (0.68); r_mid_infraorbital and supraglabella (0.64); glabella and l_mid_supraorbital (0.63); glabella and r_mid_infraorbital (0.63); mid_philtrum and pogonion (0.62); gnathion and mid_philtrum (0.61).
Negative correlations were considerable weaker. The largest negative values of the Spearman correlation coefficient were recorded between the following pairs: age_years and height_mm (−0.38); height_mm and r_zygion (−0.36), height_mm and l_mid_zigomatic (−0.35); height_mm and r_mid_supraorbital (−0.33).
To find if there are major variations on the correlation between females and males, Table 4 presents the Spearman correlation coefficients (absolute values) larger than 0.50 (corr_overall), and the same coefficient for female group (corr_females) and the male group (corr_males). The last column (ratio_ls) is the ratio between the larger and the smaller coefficient of both sexes and assesses the gap of the correlations between sex.

Table 4.
Spearman correlation coefficients larger than 0.50, overall, and by sex.
Generally, for the largest values of the correlation coefficient, the gap between sexes is small. The largest gaps were recorded for the gnation-pogonion pair of variables (ratio_ls = 2.36), for gnation-mid_philtrum (ratio_ls = 1.94) and for the (gnation, supra_mentale) pair (ratio_ls = 1.91).
4. Discussion
One of the main problems regarding the forensic anthropological methods of cranio-facial identification is the reliance on the use of the average values of the thickness of the soft tissues as control in the techniques of three-dimensional and two-dimensional facial approximations [8,23].
The importance of the present study lies in the fact that it creates a dataset for facial soft tissue thicknesses for the North-East region of Romania, a country that does not have such a dataset. In our study, we observed that there are no significant differences between men and women and the values found increase significantly for overweight people, compared to underweight and normal weight that show similar values. The particularity of the study consists of creation of this dataset with good results involving the facial soft tissue thicknesses values and the instrument used for measurements taken.
As we mentioned in introduction part, there are numerous methods which are used for establishing values for soft tissue thicknesses. Some of these methods are invasive, including needle puncture on cadavers, and some of them are non-invasive, using imagistic methods (X-ray, computed tomography, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, etc.) [1,8,9,10,11,12,13,24,25].
Regarding the needle puncture method, which was also used in the present study, it was the first method used to measure facial soft tissue thicknesses by Welcker in 1883, and has suffered some modifications since then [26,27]. In comparison with the imagistic methods, the needle puncture method has some advantages, especially regarding the fact that it enables direct physical measurements on the subject and the possibility of palpation the craniometric landmarks for a better visualization of them. However, some disadvantages of the method do exist, those regarding the impossibility of keeping the data material for other measurements or the appearance of postmortem changes. According to the literature, the postmortem changes do not affect the values of soft tissue thicknesses [9,11,22]. Additionally, the Australian research group mentions the fact the there are no differences between the measurements made on cadavers and the measurements made using the ultrasound method on living persons [1,11]. Another postmortem modification is rigor mortis. Concerning rigor mortis, there are some studies which conclude that there is no modification in soft tissue thicknesses measurement during the stages of this cadaveric change. In our study, we chose the needle puncture method because the cadaver is always a good study material, and it gives you the advantages of having the whole cadaver with known important parameters (age, sex, weight, etc.). Another motivation in favor of choosing the needle puncture method is the fact that it is cheaper, easy to use and does not depend on the imaging technique, since there are situations sometimes in which the computed-tomographic images do not include the entire cephalic extremity.
There are researchers that use different instruments as material, such as a tweezer needle or soot needle with subsequent measurement on the osteometric board, or fine steel markers with stops and silicone calipers [9,11,22]. In our study, we used an instrument for measuring skin thickness length 0–30 mm. This type of instrument helps us to measure the length directly when we insert the needle. In this way, we have prevented any possible error caused by handling the rubber stops while removing the needle. Therefore, we can state that in the present study, the tool we used to measure the thickness of soft tissues brings a novelty in the field. It is important to note that our study sample consists of fresh cadavers which have not been embalmed. This characteristic brings more credibility for our results, because according to the literature, embalming causes increases in tissue thickness, and after the tissues become fully embalmed, most tissues decrease in thickness [23,24,25].
Taking into account the phenotypic variation observed in European and South American populations, and considering that the effectiveness of the probability of obtaining the likeness of a person is related to access to data collected from genetically related individuals, this paper tries to contribute with data on the average thicknesses of soft tissues for the adult population of Romania, for which, until this study, there were no publicly available records of this nature. The analysis of central tendency of landmark values for the entire dataset was complemented with the examination of differences among two types of groups. First, it was examined whether knowing the sex of the body provides a better estimation of the facial landmark. Next, this study considered the constitutional aspect of individuals according to the BMI (body mass index) in relation to facial landmarks, since previous studies provide data on BMI relationship with the anthropometric characteristics.
From the point of view of the constitutional aspect, in the present study, we have divided the constitutional type of the individuals included in the study group into three categories (underweight with a BMI < 18.5, normal weight with a BMI between 19–2.5 and overweight with a BMI > 25) according to the specialized literature [9,22,24].
Given that the physiognomy of individuals changes depending on their nutritional state, it is significant to have access to this type of data. Additionally, the constitutional aspect of the deceased person is important to be considered to establish the average values of the thickness of the soft tissues of the face.
According to the results (Table 2), in the case of the adult population of modern, present-day Romania, in the North-East region of Romania, it is noticed that there are only small and statistically unsignificant differences between males and females in the case of the craniometric landmarks considered in the present study. The most representative differences are found corresponding to the craniometric landmark nasion, with the statistical analysis showing that in males the thickness of the soft tissue is higher than in females (Figure 3). In some cases, it has even been revealed that females have soft tissue thicknesses at certain craniometric landmarks slightly higher than males; however, they do not show statistically significant differences. Overall, Romania’s adult population presents the thickest average values for rhinion. Thus, we can state that for most of the differences between the craniometric landmarks under discussion, they are not statistically significant.
Regarding the average values of the thickness of soft tissues in the craniometric landmarks measured on the Romanian population, it is observed, according to Table 3, that there are statistically significant differences between the constitutional types for the craniometric landmarks gnathion, supraglabella, nasion, rhinion, right mid-infraorbital, left mid-zygomatic and glabella. Their values are increased as the constitutional type becomes more overweight, which is also confirmed in the literature for other populations described. The lowest values, regardless of the constitutional type, are observed at the level of the craniometric landmarks glabella and rhinion, the differences among BMI categories being statistically not significant for rhinion. For gnathion, supraglabella, left zygon, right zygon, left mid-zygomatic, right mid-zygomatic, and left_mid-infraorbital, there are similar values for the first two constitutional types (underweight and normal weight), values that increase significantly for people of overweight constitution. On the other hand, the value of the craniometric mid-philtrum landmark is less sensitive to the constitutional type, which can be explained by the fact that the difference in the thickness of the soft tissue depending on the constitutional type is seen more at the dimensions of the nose, respectively of the nasal opening. Following the analysis of the measurements made on cadaveric bodies, it is also observed that there are no differences between the values of the craniometric landmarks arranged on the side of the face; therefore, at least on cadaveric bodies, the facial asymmetry regarding the adult population of Romania is not highlighted.
Figure 4 and Figure 5 show a comparison between the values of the thickness of the soft tissue of the craniometric landmarks arranged medial between the population of Romania (the present study) and the Portuguese, Spanish and Brazilian populations, on which similar studies have been carried out using the method of puncture on corpses [8,9,11,22,23,24].
Regarding the comparison made between the average values of the thickness of soft tissues between the adult population of Romania, respectively, the Spanish and Portuguese adult population (Figure 4), we can notice some differences. For the craniometric landmarks nasion, gnathion (especially for the females) and supraglabella, small differences are revealed between the adult population of Romania and Spain, while for the craniometric landmarks glabella, mid-philtrum, pogonion, rhinion and supramental there are relatively large differences between the two populations. Analyzing the comparison made between the adult population of Romania and the adult population of Portugal, we can notice small differences between the craniometric landmarks glabella, nasion, rhinion and supraglabella, while for gnathion, mid-philtrum and supramental, we can notice larger differences.
Analyzing Figure 5, we can see large differences between the craniometric landmarks considered (glabella, gnathion, mid-philtrum, nasion, pogonion, rhinion, supraglabella, respectively supramental). We noticed that Brazilians have significantly higher average values than the Romanian population. Even though the Brazilian population is white, it is part of the American population, being part of the Hispanic group. Our comparison between the Romanian and Brazilian populations confirms the results of a study showing that multiple facial anthropometric measurements are significantly higher in African Americans and Hispanics than in Caucasians [25]. According to the literature and with each specific population study carried out, it is revealed that ethnicity has an impact on the aspects of the face and certainly on the thickness of the facial soft tissues [24,25,26,27].
Inferring the values of facial landmarks (when they are missing) based on data centrality (overall, and on groups defined by sex and weight category) could be enhanced or complemented by examining the correlation among landmarks and with other numeric variables. Figure 6 shows the correlations among numerical variables in the dataset, whereas Table 4 focuses on the variability of the strongest correlation coefficients between sexes.
In Figure 6, we can observe good correlation between the craniometric landmarks which are in the midline with the ones that are bilateral but on the same floor of the face (upper floor of the face); we can also observe that the vertical dimensions from the lower floor of the face are generally with largest positive correlation with each other. The correlation analysis we performed does not show good correlation between the age and the soft tissue at different craniometric landmarks; this aspect is in contradiction with the literature, which states that growth changes are age-dependent [26].
The correlation analysis present in this study requires, however, further research in which we would like to perform some mathematical models and some regression equations to be able to predict the soft-tissue depth at specified areas of the face based on craniometric dimensions. On the other hand, we wanted to highlight the fact that if one of the craniometric landmarks is not measured, it is possible to calculate another based on this correlation between them. This aspect is extremely important in facial reconstructive surgery. For the same importance, based on Figure 6, Table 4 shows us the sex difference between the craniometric landmarks that present a good correlation.
From the abovementioned, it follows that it is very important to establish the geographical origin of the skull used for cranio-facial reconstruction, here referring to a very correct analysis of the facial profile (the shape of the skull, face, orbits, jaws, etc.) [27,28,29]. The present study refers only to the adult population of Romania, with the values determined in this work not being considered in order to perform cranio-facial reconstruction in children (juvenile). Our study highlights the presence of inter-population variations as well as the need to carry out as many population-specific studies as possible. The resulting variations on the adult population of Romania between the sex and the weight categories may be a consequence of the size of the dataset; however, future research directions will be made, with the addition of new observations, and these differences will be reassessed. Additionally, because the age range of the study sample is quite large and the age is an important factor that affects facial soft tissue thicknesses, the present study has some limitations regarding age differences. This aspect will be corrected through another study, a more complex one with a larger size of the dataset. The present study can also be considered a preliminary study, necessary for a population of Eastern Europe, especially in the given context, the presence of the conflict in Ukraine and the subsequent need to identify the victims of this conflict.
5. Conclusions
Cranio-facial reconstruction is sometimes used as the only method of establishing the identity of an individual; therefore, it is especially important to have databases on the thickness of soft tissues, with these measurements being indispensable for performing cranio-facial reconstructions, regardless of the method used for it.
The present study provides a database for the thickness of soft tissue for 12 craniometric landmarks (8 on the midline, respectively 4 bilaterally) and represents the first of its kind for the adult population of Romania. It makes important contributions in the field of forensic anthropology, and implicitly in the field of cranio-facial reconstruction. The statistical analysis of the measurements performed shows that there are no major differences between the sex for the thickness of the soft tissue at the facial level, so that for a cranio-facial reconstruction, unique values can be used.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.D. and D.B.I.; methodology, M.M.D., D.B.I. and S.I.D.; software, M.F. and N.R.; validation, M.F. and N.R.; resources, M.M.D., S.D., C.F. and T.I.; data curation, M.F., N.R., A.S. and C.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M.D., S.D., N.G. and I.H.; writing—review and editing, M.M.D., C.F. and D.B.I.; supervision, D.B.I. and S.I.D.; project administration, M.M.D., D.B.I. and I.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by University of Medicine and Pharmacy “Grigore T. Popa” Iasi, Grant number 7373/30.04.2020 title Forensic Human Identification: multifactorial features in forensic anthropology using craniometry for Romanian population.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of Institute of Legal Medicine Iasi and University of Medicine and Pharmacy “Grigore T. Popa” Iasi, Romania.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to Romania legislation regarding the manipulation of cadavers.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Stephan, C.N.; Preisler, R. In vivo facial soft tissue thicknesses of adult Australians. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 282, e1–e220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diac, M.M.; Earar, K.; Damian, S.I.; Knieling, A.; Iov, T.; Shrimpton, S.; Castaneyra-Ruiz, M.; Wilkinson, C.; Bulgaru Iliescu, D. Facial reconstruction: Anthropometric studies regarding the morphology of the nose for Romanian adult population I: Nose width. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Gupta, V.; Vij, H.; Vij, R.; Tyagi, N. Forensic Facial Reconstruction: The final frontier. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2015, 9, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, C. Computerized Forensic Facial Reconstruction a Review of Current Systems. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2005, 1, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verze, L. History of facial reconstruction. Acta Biomed. 2009, 80, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, C. Forensic Facial Reconstruction; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 6–27. [Google Scholar]
- Vezzetti, E.; Marcolin, F.; Tornincasa, S.; Moos, S.; Grazia Violante, M.; Dagnes, N.; Monno, G.; Uva, A.E.; Fiorentino, M. Facial Landmarks for Forensic Skull-Based 3D Face Reconstruction: A Literature Review. In Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality and Computer Graphics; De Paolis, L., Mongelli, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 9768, pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Pithon, M.M.; Debora Lais, R.R.; Leite de Santana, C.; Pedrosa Cruz, J.P. Soft tissue thickness in young north eastern Brazilian individuals with different skeletal classes. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2014, 22, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codinha, S. Facial soft tissue thicknesses for the Portuguese adult population. Forensic Sci. Int. 2009, 184, 80.e1–80.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotrashetti, V.S.; Mallapur, M.D. Radiographic assessment of facial soft tissue thickness in South Indian population—An anthropologic study. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2016, 39, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domaraki, M.; Stephan, C.N. Facial soft tissue thicknesses in Australian adult cadavers. J. Forensic Sci. 2006, 51, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyomarc’h, P.; Santos, F.; Dutailly, B.; Coqueugniot, H. Facial soft tissue depths in French adults: Variability, specificity and estimation. Forensic Sci. Int. 2013, 231, e1–e411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhine, J.S.; Campbell, H.R. Thicknesses of facial tissues in American blacks. J. Forensic Sci. 1980, 25, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. “R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing”. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. R Version 4.2.2. Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Whickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, L.; McGowan D’Agostino, L.; Francois, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjoberg, D.D.; Whiting, K.; Curry, M.; Lavery, J.A.; Larmarange, J. Reproducible summary tables with the gtsummary package. R J. 2021, 13, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gohel, D.; Skintzos, P. Flextable: Functions for Tabular Reporting. R Package Version 0.8.3. 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=flextable (accessed on 3 April 2023).
- Wei, T.; Simko, V. R Package ‘Corrplot’: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix (Version 0.92). 2021. Available online: https://github.com/taiyun/corrplot (accessed on 3 April 2023).
- Patil, I. Visualizations with statistical details: The ‘ggstatsplot’ approach. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillis, V.M.; Smuts, N.A. Facial reconstruction: Utilization of computerized tomography to measure facial tissue thickness in a mixed racial population. Forensic Sci. Int. 1996, 83, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad de Almeida, N.; Michel-Crosato, E.; Saavedra de Paiva, L.A.; Haye Biazevic, M.G. Facial soft tissue thickness in the Brazilian population: New reference data and anatomical landmarks. Forensic Sci. Int. 2013, 231, e1–e404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, C.N.; Sievwright, E. Facial soft tissue thickness (FSTT) estimation models-and the strength of correlations between craniometric dimensions and FSTTs. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 286, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Y.; Qiang, Y.; Liu, M.; Fulton, D.; Chen, T. Age and sex related measurement of craniofacial soft tissue thickness and nasal profile in the Chinese population. Forensic Sci. Int. 2011, 212, e1–e272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Landsittel, D.; Benson, S.; Roberge, R.; Shaffer, R. Facial anthropometric differences among gender, ethnicity and age groups. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2010, 54, 391–402. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, E.; Henneberg, M. Variation in soft-tissue thicknesses on the human face and their relation to craniometric dimensions. Am. J. Psys. Anthropol. 2002, 118, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, O.; Sipahioglu, S.; Hekimoglu, B. Facial soft tissue thicknesses database for craniofacial reconstruction in the Turkish adult population. Forensic Sci. Int. 2014, 242, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephan, C.N.; Meikle, B.; Freudenstein, N.; Taylor, R.; Claes, P. Facial soft tissue thicknesses in craniofacial identification: Data collection protocols and associated measurement errors. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 304, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, P.R.N. Bizygomatic diameter: The thickness of the soft tissue tissues over the zygions. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1969, 30, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).