Abstract
In this study, a dispersive solid-phase extraction (DSPE) pretreatment procedure using zeolite H-Beta as a sorbent was exploited for the determination of eight neonicotinoids in bottled water and honey products based on ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry analysis. The zeolite H-Beta was demonstrated to be a suitable sorbent for neonicotinoid insecticides, even after 10 recycles of reuse. The method performance was evaluated by the linearity (R2 ≥ 0.998), recovery (71–108%), precision (0.1–7.8%), limit of detection (0.05–0.1 ng/mL) and limit of quantification (0.1–0.2 ng/mL), which suggested excellent stability and high sensitivity with the use of the DSPE procedure. The method was further successfully applied in the test of neonicotinoid insecticides in 34 samples. Zeolite H-Beta shows promise as an efficient and practical material for monitoring neonicotinoid insecticides in bottled water and multiplex honey matrices.
1. Introduction
As broad-spectrum systemic insecticides, neonicotinoid insecticides have been authorized for use and operation on hundreds of farmland plants in more than 120 countries with the fastest-growing speed worldwide [1,2]. These pesticides are used to control aphids and other sap-sucking insects that can easily cause behavioral problems [3]. They selectively act on the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors of insects and cause the overexcitement of acetylcholine receptors. Neonicotinoids are nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists. They bind tightly to acetylcholine receptors in the central nervous system of insects, causing death at higher levels [4]. Neonicotinoids can penetrate into plant tissues and protect the entire crop. These neonicotinoids are also widely used in seed dressing [5]. However, recent studies have shown that these pesticides can cause a decline in pollen-transmitting organisms (e.g., the colony collapse of bees) and threaten human health [6]. Therefore, the use of neonicotinoids in the environment has been controlled by authorities to prevent the extinction of beneficial insects and guarantee human health [7]. The maximum residue limit (MRL) (50–200 μg/kg) of these substances in honey has been set up by the European Union and other international authorities [8]. In China, the detection of pesticide residues in honey usually follows the national standard GB23200.7-2016 [9]. Similar to this standard, other methods also involve careful sample preparation procedures, including analyte enrichment and cleanup of the extract [10]. A simple and fast method for the multiresidue detection of pesticides in honey with low cost and reusable materials is always preferable. This is also the goal of our study. Many studies reported the residue of neonicotinoids in surface waters and honey [1,5]. Previous literature has reported possible pharmaceutical and personal-care residues in bottled water [11,12,13]. The surface water is often contaminated by the use of pesticides in agricultural activities. As most of the bottled water is produced from the surface water, it probably contains these contaminants if the processing step is not performed well. Therefore, pesticide residue in bottled water produced from surface water and in honey products needs to be examined.
Solid-phase extraction (SPE) [14,15] and liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) [16,17] coupled with liquid chromatography (LC) [18,19,20], gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) [21], and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) [22,23] are frequently used to detect the residues of neonicotinoid insecticides in food, e.g., fruit, honey, milk, and vegetables. The SPE procedure includes conditioning, sample loading, rinsing, and elution, and the LLE procedures involve a large volume of organic solvents and often have low processing efficiency. Both of these methods are time-consuming and laborious. Dispersive solid-phase extraction (DSPE) is a part of the QuEChERS (quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe) procedure proposed by Anastassiades et al. in 2003 [24]. DSPE can also be independently used in sample extraction and cleanup, and it has been widely applied due to its simple procedure and low cost [25,26]. A large number of sorbents have been commercialized for testing in water or food [27,28], and there is still a demand for high-efficiency and low-cost sorbents. The research is challenging not only for adsorption but also for separation technology.
Zeolites, including natural minerals (such as natrolite, scolecite, clinoptilolite) and synthetic zeolites (such as A, X, ZSM-5, Beta), have been widely used as desiccants, catalysts, and soil amendments [29,30]. Its open frame is filled with crystalline aluminosilicate, which contains silica and alumina tetrahedrons connected by oxygen bridges [31,32]. Zeolite has attracted much attention as a sorbent due to its unique characteristics, including a high specific surface area, hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity, easy-to-adjust chemical properties, heat resistance, low cost, and eco-friendliness [33]. A variety of zeolites have found their application in adsorption, catalysis, construction, soil remediation, and energy storage [34]. The removal of various pollutants such as cephalexin [35], anionic dye [36], and environmental pollutants [37] by zeolites has been reported. In contrast, DSPE techniques using zeolites are rarely reported [10,38]. Various synthetic zeolites have been produced worldwide for industrial purposes, and the price is very competitive compared to that of the currently commercialized DSPE materials. Applying this environmentally friendly, low-cost material to detect pollutants in the environment and food is of great significance based on DSPE procedures. At the same time, the applicability of being a DSPE material needs to be justified because of the structural differences and different elemental compositions of each type of zeolite.
Herein, an efficient DSPE method using zeolite H-Beta as a sorbent has been first explored and verified for the determination of neonicotinoids in water and honey products, which include dinotefuran, thiacloprid, thiamethoxam, flonicamid, imidaclothiz, clothianidin, imidacloprid, and acetamiprid. The parameters (amount of the zeolites, adsorption time, desorption solvent, desorption mode, and time) affecting the DSPE procedure performance have been optimized before the determination using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC–MS/MS). This research aims to provide a useful and economical sorbent that can be reused for detecting trace residues in bottled water and honey matrices.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
Silica gel powder (Qingdao Guichuang Fine Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., Qingdao, China) was used as the silica source. Sodium meta aluminate (NaAlO2, Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) was used as the aluminum source. The compositions of Na2O and Al2O3 in NaAlO2 were 39.5% and 48.0%, respectively, which were tested with ICP–OES. Tetraethyl ammonium hydroxide (TEAOH, 25%), the structure-directing agent, was supplied by Kente Catalysts Inc. (Hangzhou, China) Sodium hydroxide (NaOH, Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China) was used as the alkali source. Ultrapure water with a resistance of 18.2 MΩ.cm (25 °C) was obtained by Milli-Q Preference (Molsheim, France). Eight standards of neonicotinoid insecticides, namely, dinotefuran, thiacloprid, thiamethoxam, flonicamid, imidaclothiz, clothianidin, imidacloprid, and acetamiprid at the concentration of 100 mg/L in acetonitrile, were purchased from Alta Scientific Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China) and maintained at −18 °C, diluted with acetonitrile before analysis. HPLC-grade reagents purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany), including acetonitrile and methanol, were used for HPLC-MS/MS analysis. Glass microfiber filter (Grade G/F) with a diameter of 47 mm was purchased from Whatman International Ltd. (Maidstone, UK).
2.2. Instrumentation
The phase purity of the prepared H-Beta was confirmed using powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) on a Rigaku Ultima IV diffractometer with nickel-filtered Cu Kα radiation (λ = 0.15418 nm) at 30 kV and 30 mA. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images were obtained with a Hitachi S-4800 scanning electron microscope running at an accelerating voltage of 3 kV. The nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherm analysis of the zeolite H-Beta was performed at −196 °C on BELSORP-max equipment after degassing under a vacuum of 300 °C for 6 h. The specific surface area (SBET) calculation was based on the data in the p/p0 range of 0.01–0.15 by the Brunauer, Emmett, and Teller (BET) principle. The total pore volume (Vt) was estimated from the amount of nitrogen adsorbed when p/p0 was 0.99. The SiO2/Al2O3 molar ratio was quantified using inductively coupled plasma–atomic emission spectrometry (ICP–AES) on a Thermo IRIS Intrepid II XSP after dissolving the samples in HF solution.
2.3. HPLC-MS/MS Analysis
The samples were analyzed with a column (ACQUITY BEH-C182.1 × 100 mm, id: 1.7 μm, Waters, Milford, IN, USA) which was equipped on the Waters H-Class UPLC system (Waters, Milford, IN, USA) tandem QqQ mass spectrometer (AB4500, AB SCIEX, Framingham, MA, USA) with an electrospray ionization (ESI) source. Water with 0.1% formic acid (FA) and 10 mM ammonium acetate (A), and methanol (B) were used as mobile phase. The sample was eluted at a flow rate of 0.4 mL/min with binary mobile phase as follows: initial equilibration at 5% B was maintained for 1.2 min and linearly ramped to 95% in the next 3.3 min, maintained at 95% B for 1.5 min, returned to 5% B within 0.8 min and kept for 1.2 min before the next analysis. The injected volume of 3 μL was used. Samples were analyzed under the column temperature of 45 °C.
Data for eight insecticides were acquired on a mass spectrometer under positive multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode after separation. The main parameters of the ESI source were as follows: ion-spray voltage: 5500 V; source temperature: 450 °C; collision gas: 5 psi, curtain gas, gas 1, and gas 2 of the ion source were all 45 psi. Nitrogen was generated (CLAIND, Italy) for nebulization. The m/z of precursor ions and fragments acquired under the MRM mode which were used to identify and quantify the target analytes are given in Table S1.
2.4. Preparation of Zeolite H-Beta Sorbent
The preparation of zeolite H-Beta was carried out according to the method proposed by Kuechl [39]. Typically, NaOH, NaAlO2, and TEAOH in the amounts of 0.916, 1.808, and 33.975 g, respectively, were dissolved in 42.725 g of H2O. Then, 23 g of silica gel powder was added under stirring. After stirring for 2 h, the obtained mixed solution was heated for 2 days in a Teflon-lined stainless autoclave at 145 °C. The intermediate solid product was formed after crystallization, which was cooled to room temperature in the autoclave and rinsed with deionized water. Then, the removal of the structure-directing agent was carried out through drying overnight at 100 °C and calcination at 550 °C for 6 h. The calcined sample was ion-exchanged in 1 mol/L ammonium chloride at 85 °C for 2 h with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:50. The residual solid material was converted into H-form Beta by calcination again at 550 °C for 6 h.
2.5. DSPE Process
In this method, the sorbent was dispersed in the sample solution, adsorbing impurities or targets, and then using a suitable solvent to desorb the targets. Figure 1 shows the detailed steps of the DSPE procedure from sample to extraction and then to qualitative and quantitative analysis of the targets. The time for a single sample preparation was around 15–20 min. First, the honey product was diluted into solution according to “2.6 Sample Collection” before the DSPE procedure. A sample solution (40 mL) was added into the 50 mL centrifuge tube, and then 50 mg of zeolite H-Beta was put into the tube. To adsorb the target analytes completely, the tubes were vortexed at 2500 rpm for 7 min. Subsequently, the zeolite H-Beta was divided from the aqueous phase by centrifugation at 3200× g for 3 min. The sorbent remained for desorption. The desorption of neonicotinoid insecticides from the sorbent was conducted with 2 mL of acetonitrile (0.5% ammonium hydroxide) under a vortex for 1 min and ultrasonication for 1 min. The eluent was separated from zeolite H-Beta by centrifugation for 3 min at 3200× g. The supernatant was passed through a 0.22 μm membrane filter before transferring to the vial for UHPLC–MS/MS analysis.
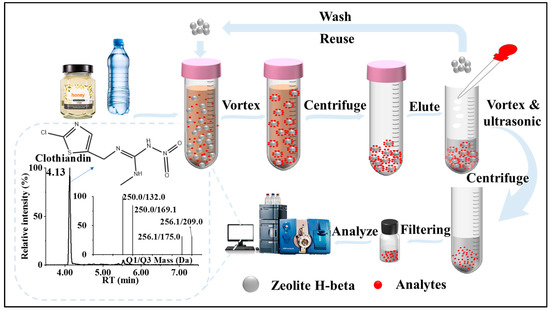
Figure 1.
DSPE procedures for the determination of eight neonicotinoid insecticides in bottled water and honey using zeolite H-Beta as the adsorbent.
2.6. Sample Collection
All bottled water and honey products were randomly purchased from several stores in Shanghai, China. The detailed information on real samples of nineteen honey and ten water samples can be found in the supplementary data (Table S2). Water samples were preserved in a 4 °C freezer before the DSPE procedure. Each honey sample was diluted 20-fold with ultrapure water, filtered through a glass microfiber filter, and kept at 4 °C before further steps.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Prepared Zeolite H-Beta
The obtained zeolite H-Beta was characterized by XRD, N2 adsorption–desorption, SEM, and ICP–OES (Figure 2). Compared with the XRD pattern of zeolite H-Beta reported by Kuechl [39] and Li et al. [40], the well-resolved diffraction peaks in the XRD patterns of the prepared zeolite H-Beta demonstrated representative Bragg reflections corresponding to typical BEA zeolite H-Beta topologies, without any impure crystalline phase (Figure 2A), indicating the successful synthesis of zeolite H-Beta. A typical IV isotherm was observed, with a steep N2 uptake in the relative pressure p/p0 below 0.1 and a slight rise in the p/p0 range between 0.1 and 0.9, corresponding to micropore filling and capillary condensation of N2 among the interparticle voids, respectively. A large micropore surface area (Smic) of 530.6 m2/g and micropore pore volume (Vmic) of 0.21 cm3/g were obtained. The existence of interparticle mesopores can be indicated from the high specific surface area (SBET) of 600 m2/g and external surface area (Sext) of 69.4 m2/g, total pore volume (Vt) of 0.36 cm3/g, and mesoporous volume (Vmeso) of 0.15 cm3/g, which can be ascribed to the small crystal size of the prepared H-Beta. The SEM images showed a uniform ellipsoid morphology of zeolite H-Beta, with a particle size of ~200 nm (Figure 2C,D). The ICP–OES result displayed the molar ratio of 36 for theSiO2/Al2O3in zeolite H-Beta.
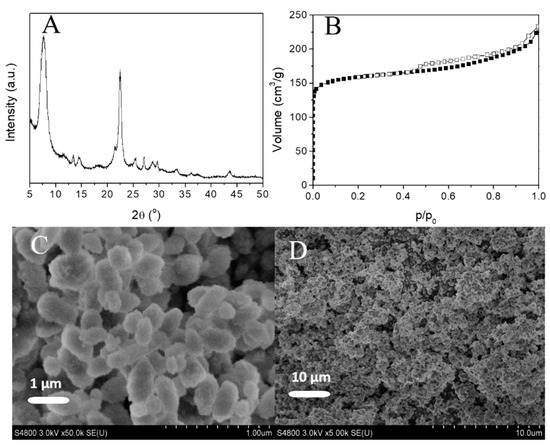
Figure 2.
XRD pattern (A), N2 adsorption–desorption isotherm (B), and SEM images with different magnifications (C,D) of the prepared zeolite H-Beta.
3.2. Optimization of DSPE Conditions
Several factors can influence the performance of zeolite H-Beta as a DSPE material. The analyte should be absorbed as much as possible by the sorbent and completely desorbed. The DSPE conditions, including the amount of sorbent, adsorption time, solution pH, and two desorption parameters (solvent and mode), were studied and optimized in our work. The blank sample solution was spiked with eight neonicotinoids at a concentration of 0.5 ng/mL for the optimizations. This concentration was around the middle range for the instrument analysis.
3.2.1. Effect of the Amount of Zeolite H-Beta
In our study, five dosages of the zeolite H-Beta sorbent (25, 50, 75, 100, and 125 mg) were evaluated on the extraction of the analytes. The results indicated an upward trend for the extraction efficiency of the eight neonicotinoids with the amount of zeolite H-Beta increasing from 25 to 50 mg (Figure 3A). Except for acetamiprid and thiacloprid, the recoveries of the other six neonicotinoids decreased by 6.5–10.7% when 75 mg of zeolite H-Beta was used. The extraction efficiencies remained stable with a further increase in the zeolite H-Beta dosage. When the amount of zeolite H-Beta increased to 125 mg, the recovery of acetamiprid dropped by approximately 7%. Obviously, as the amount increased, the elution efficiency decreased under the limited solvent. Therefore, 50 mg of zeolite H-Beta was selected for further use. Previous literature reported UiO-66 of 40 mg as dSPE material for the preconcentration of neonicotinoid insecticides in water [6]. Sorbents made of pure SDS (175 mg surfactant/g alumina) and mixed SDS–TBA (80 mg SDS and 0.05 mg TBA/g alumina) were selected for the extraction of pesticides from water [28]. The use of 50 mg of zeolite H-Beta was comparably less and could result in acceptable recoveries.
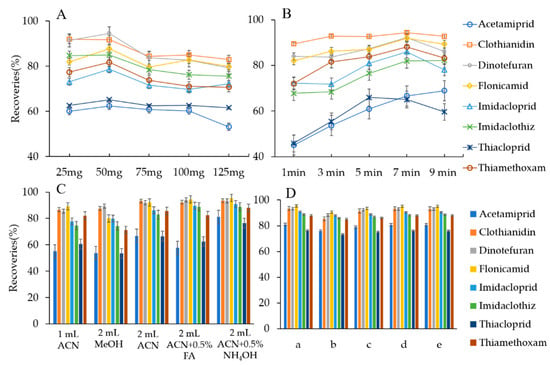
Figure 3.
Effect of the amount of zeolite H-Beta (A), adsorption time (B), desorption solvent (C), desorption mode and time (D) on neonicotinoids (a: vortex 10 min and ultrasonication 10 min; b: vortex 10 min; c: ultrasonication 10 min; d: vortex 5 min and ultrasonication 5 min; e: vortex 1 min and ultrasonication 1 min).
3.2.2. Effect of the Adsorption Time
DSPE is based on partition and repartition of the targets between the sorbent and solvents. In this study, the time of adsorbing analytes was conducted from 1 to 9 min. As shown in Figure 3B, the equilibrium between the sorbent and the solution was established within 7 min, which significantly reduced the enrichment time compared with that of SPE. Clothianidin, dinotefuran, and flonicamid reached equilibrium within 1 min, and the recoveries were maintained between 80% and 95% with extending time. The extraction efficiency of acetamiprid and thiacloprid was significantly lower than that of the other neonicotinoids and required at least 5 min for recoveries over 60%. Finally, 7 min of adsorption time was applied to obtain high efficiency for adsorption.
3.2.3. Effect of the Desorption Solvent, Mode, and Time
Acetonitrile and methanol, as the most common eluents, have good compatibility with different pesticides. In our study, acetonitrile (ACN), methanol (MeOH), ACN with 0.5% (v/v) FA, and ACN with 0.5% (v/v) ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH) were examined for the desorption efficiency of the eight neonicotinoids from the zeolite H-Beta sorbent. The results indicated that 2 mL of ACN exhibited a better elution efficiency than 2 mL MeOH did, which may be due to its greater polarity. Meanwhile, the introduction of NH4OH significantly improved the recoveries of acetamiprid and thiacloprid. It can be seen from Figure 3C that ACN with 0.5% NH4OH (2 mL) could desorb all targets with acceptable recoveries. It was therefore chosen as the eluent for the subsequent works. We examined different combinations of vortex and ultrasonication time. As shown in Figure 3D, the recoveries of the eight neonicotinoids did not change dramatically with different desorption modes and time. Therefore, to reduce the time for sample preparation, 1 min of vortexing and 1 min of ultrasonication time were applied in the following procedure.
3.2.4. Matrix Effects
The matrix effect (ME) comes from the ionization process, where interferences in the matrix can inhibit or enhance the ionization efficiency of the analyte [41]. It can lead to errors in the quantitation of pesticides and should be considered when significant suppression or enhancement occurs [42]. Our study investigated the matrix effect of the target compounds in bottled water and honey products based on the ratio of the peak area between standards in the blank matrix solution and standards in the solvent. The blank matrix solution was obtained following the proposed DSPE scheme, where no studied pesticides were detected. For water samples, the matrix effects for all target compounds were between −2.7% and +3.6%, which are ignorable for the accurate quantification by LC-MS/MS analysis based on the standards proposed by Mol et al. [43]. However, in honey products, the matrix effects were +51.6% and −29.9% for imidacloprid and thiacloprid, respectively. Further rinsing steps were studied to remove the matrix effect of the DSPE materials after adsorption. Five solvents of 5 mL were examined by 1 min of vortex, and centrifugation at 3200× g for 2 min. As shown in Figure 4, an acceptable ME of all targets (within ±20%) could be achieved by introducing a rinsing procedure with water containing 10% (v/v) methanol. Thus, it was selected as the washing solvent to decrease the matrix effect in honey.
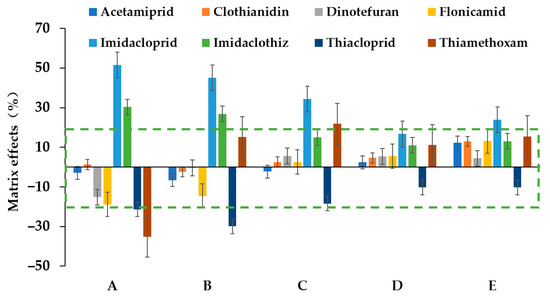
Figure 4.
Matrix effects in honey products with different rinsing solvents ((A), petroleum ether; (B), hexane; (C), water; (D), 10% MeOH in water; (E), 30% MeOH in water). DSPE conditions: sample volume, 40 mL; the dosage of the sorbents, 50 mg; desorption solvent, 2 mL 0.5% (v/v) ammonium hydroxide in acetonitrile; desorption mode and time, 1 min of vortex, and 1 min of ultrasonication (The dashed box indicates that the matrix effect was within ±20%).
3.3. Reusability of the Sorbent
To reuse the zeolite H-Beta as DSPE material in the cleanup procedure, the regeneration of the used zeolite H-Beta was developed. In our study, 0.5% (v/v) NH4OH in ACN (5 mL) was employed to eliminate the residual pollution on the zeolite H-Beta from the previous sample preparation during regeneration. The procedure for cleaning included vortexing at 2000 r/min for 5 min and ultrasonication for 5 min, followed by centrifugation at 3200× g for 5 min, discarding the supernatant, repeating the procedure once, and air-drying overnight in a fume hood after the last centrifugation. To examine the regeneration effect, the last supernatant was used for UHPLC–MS/MS analysis. When the recoveries for all the targets were below 1%, zeolite H-Beta was considered successfully regenerated. As shown in Figure 5, the recoveries remained nearly stable between 75.6% and 90.1% for 10 cycles of the reuse procedure, indicating the continuous stability and excellent reusability of zeolite H-Beta as a sorbent. Therefore, the established DSPE method is promising as an environment friendly and cost-effective method with sufficient accuracy.
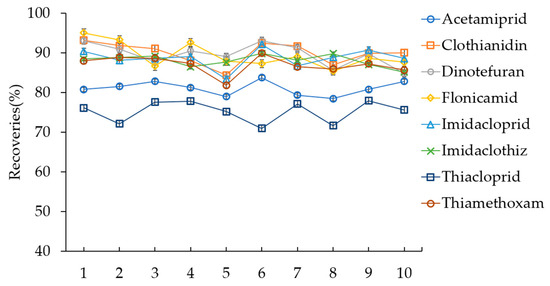
Figure 5.
The recoveries for reuse of zeolite H-Beta in DSPE after repeated regeneration.
3.4. Method Validation
In our study, the method performance was evaluated in terms of linearity, limits of detection (LOD), limits of quantification (LOQ), and accuracy according to the guidelines of SANTE/2020/12830 under the optimized DSPE conditions described above. The standards dissolved in solvents at six concentration levels were used to calculate the linear equation and correlation coefficiency for accurate quantification. Excellent linearity and coefficients (R2 ≥ 0.9982) were obtained in a range from 0.1 to 200 ng/mL for all eight analytes (Table S1). The sensitivity of the method was evaluated by the validation of LODs and LOQs of eight insecticides, at 0.05 or 0.1 ng/mL (LODs), and 0.1 or 0.2 ng/mL (LOQs) for bottled water; and 0.5 or 1.0 ng/g (LODs), and 1.0 or 2.0 ng/g (LOQs) for honey products. Spiking experiments in water and honey for all target compounds at concentrations of 0.2, 1, and 10 ng/mL showed satisfactory recoveries between 70.9% and 108.4% (Table S3). The relative standard deviations (RSDs) of all analytes ranged between 0.1% and 7.7% for intraday precision and 0.3% and 7.8% for interday precision. The RSDs of the retention time of each analyte within ±1.0% were observed after five repeated analyses of fortified bottled water and honey products for five consecutive days. All the evaluated parameters suggested that the developed DSPE scheme was of high accuracy, acceptable reproducibility and practicality for the simultaneous analysis of the eight insecticides in bottled water and honey products. According to SANTE/2020/12830, a recovery of 70–120% with RSDs lower than 20% was considered acceptable, and our result is also comparable with that of the DSPE method reported by Arnnok [10].
3.5. Method Application
The collected samples, including 10 bottles of water and 24 honey products from stores, were tested according to the proposed DSPE–UHPLC–MS/MS method. No neonicotinoid pesticides were found in any bottled water. It could either be a demonstration of good manufacturing practice for these products or be a result of not enough samples being collected. However, the residue of thiamethoxam was detected in one honey sample at 1.8 ng/g, and the residue of acetamiprid in five honey samples was detected in higher levels than the LOQ (1.0, 1.4, 1.6, 5.5, and 9.4 ng/g). Imidacloprid was identified in three honey samples (1.0, 1.0, and 4.8 ng/g). These results demonstrated the practicability of our developed method. The presence of imidacloprid and acetamiprid in honey from different manufacturers and other reports [1,10] indicate that high caution should be taken for the use of neonicotinoids.
Compared with the National Standard GB23200.7-2016, the time for single sample preparation has been shortened by more than 80%, and the consumption of organic solvents has been significantly reduced from 140 to 2 mL. Moreover, the DSPE procedure proposed by Salisaeng [38] consumes 10.6 mL of organic solvent and takes about 80 min for sample preparation. The method reported by Arnnok [10] takes 60–80 min for sample preparation. Our method achieves satisfactory reusability compared with that of their proposed methods.
4. Conclusions
In this work, zeolite H-Beta was synthesized, characterized, and successfully applied as a rapid, effective, and efficient DSPE material for eight neonicotinoid insecticides in bottled water and honey samples. The developed method proved to be simple and sensitive. Furthermore, it was environmentally friendly, as only 2 mL of organic solvent was used for a single sample, and economical, as its reusability was demonstrated, making it a highly promising material for detecting trace amounts of organic pollutants from bottled water and honey products.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app12094316/s1, Table S1: Parameters for UHPLC-MS/MS determination and the method performance in linearity, LODs and LOQs; Table S2: The detailed information of honey and bottled water; Table S3: Recoveries, intra-, and interday precisions of eight neonicotinoid insecticides in bottled waters and honey products.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.S. and B.B.; methodology, W.S. and S.W.; software, W.S. and N.W.; validation, N.W., T.Y. and C.K.; formal analysis, F.X. and C.K.; data curation, N.W. and T.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, W.S.; writing—review and editing, S.W. and C.K.; supervision, B.B.; project administration, F.X. and B.B.; funding acquisition, F.X. and B.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by Shanghai Agriculture Applied Technology Development Program, China (No: 2019-02-08-00-12-F01144).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
References
- Morrissey, C.A.; Mineau, P.; Devries, J.H.; Sanchez-Bayo, F.; Liess, M.; Cavallaro, M.C.; Liber, K. Neonicotinoid contamination of global surface waters and associated risk to aquatic invertebrates: A review. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J.E. Selective toxicity of neonicotinoids attributable to specificity of insect and mammalian nicotinic receptors. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2003, 48, 339–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeschke, P.; Nauen, R. Neonicotinoids—from zero to hero in insecticide chemistry. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 1084–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, G. A common pesticide decreases foraging success and survival in honey bees: Questioning the ecological relevance. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goulson, D. An overview of the environmental risks posed by neonicotinoid insecticides. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 50, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, S.; Hong, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Shao, Y.; She, Y.; Jin, F.; Jin, M.; et al. Metal-organic framework UiO-66 for rapid dispersive solid phase extraction of neonicotinoid insecticides in water samples. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1077–1078, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Anadón, A.; Wu, Q.; Qiao, F.; Ares, I.; Martinez-Larrañaga, M.; Yuan, Z.; Martínez, M.-A. Mechanism of Neonicotinoid Toxicity: Impact on Oxidative Stress and Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 58, 471–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Union Pesticide Database. Current MRLs Values. Active Substances Detail. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/pesticides/eu-pesticides-database/active-substances/ (accessed on 30 May 2021).
- GB23200.7—2016; Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China, Beijing, National Food Safety Standards-Determination of 497 Pesticides and Related Chemicalsresiduesin Honey, Fruit Juice and Wine Gaschromatography-Mass Spectrometry. 2016. Available online: http://down.foodmate.net/standard/yulan.php?itemid=50178 (accessed on 13 April 2022).
- Arnnok, P.; Patdhanagul, N.; Burakham, R. Dispersive solid-phase extraction using polyaniline-modified zeolite NaY as a new sorbent for multiresidue analysis of pesticides in food and environmental samples. Talanta 2017, 164, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paíga, P.; Santos, L.H.M.L.M.; Delerue-Matos, C. Development of a multi-residue method for the determination of human and veterinary pharmaceuticals and some of their metabolites in aqueous environmental matrices by SPE-UHPLC–MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 135, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwanz, T.G.; Carpilovsky, C.K.; Weis, G.C.C.; Costabeber, I.H. Validation of a multi-residue method and estimation of measurement uncertainty of pesticides in drinking water using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1585, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ye, D.; Li, X.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.; Du, J.; Tian, L.; Li, J.; et al. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in bottled water and assessment of the associated risks. Environ. Int. 2021, 155, 106651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidente, P.; Seccia, S.; Vanni, F.; Morrica, P. Analysis of nicotinoid insecticides residues in honey by solid matrix partition clean-up and liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1094, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muccio, A.D.; Fidente, P.; Barbini, D.A.; Dommarco, R.; Seccia, S.; Morrica, P. Application of solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry to the determination of neonicotinoid pesticide residues in fruit and vegetables. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1108, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, K.; Oulkar, D.P.; Dasgupta, S.; Patil, S.B.; Patil, S.H.; Savant, R.; Adsule, P.G. Validation and uncertainty analysis of a multi-residue method for pesticides in grapes using ethyl acetate extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1173, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farajzadeh, M.A.; Hojaghan, A.S.; Mogaddam, M. Development of Heat-Induced Homogeneous Liquid–Liquid Microextraction for Extraction and Preconcentration of Neonicotinoid Insecticides from Fruit Juice and Vegetable Samples. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 3738–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Cui, J.; Dong, A.J.; Zhao, H.T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xu, R.B.; Li, W.J. Multi-residue method for determination of seven neonicotinoid insecticides in grains using dispersive solid-phase extraction and dispersive liquid–liquid micro-extraction by high performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, C.; Zang, X.; Wang, Z. Extraction of neonicotinoid insecticides from environmental water samples with magnetic graphene nanoparticles as adsorbent followed by determination with HPLC. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, E.; Kobara, Y.; Baba, K.; Eun, H. Determination of Seven Neonicotinoid Insecticides in Cucumber and Eggplant by Water-Based Extraction and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Lett. 2015, 48, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, L.; Greulich, K.; Kempe, G.; Vieth, B. Residue analysis of 500 high priority pesticides: Better by GC-MS or LC-MS/MS? Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2010, 25, 838–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, S.; Hong, S.; Li, H.; Shao, Y.; She, Y.; Wang, J.; Jin, F.; Jin, M. One-pot synthesis of magnetic zeolitic imidazolate framework/grapheme oxide composites for the extraction of neonicotinoid insecticides from environmental water samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 4747–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, S.; Huai, Q.; Xu, D.; Zhang, H. Methylamine-modified graphene-based solid phase extraction combined with UPLC-MS/MS for the analysis of neonicotinoid insecticides in sunflower seeds. Talanta 2017, 162, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelangelo, A.; Lehotay, S.J.; Darinka, Š.; Schenck, F.J. Fast and Easy Multiresidue Method Employing Acetonitrile Extraction/Partitioning and “Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction” for the Determination of Pesticide Residues in Produce. J. Aoac Int. 2003, 86, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, L.; Chen, C.; Yang, Y. Suspension Dispersive Solid Phase Extraction for Preconcentration and Determination of Cobalt, Copper, and Nickel in Environmental Water by Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Anal. Lett. 2015, 48, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Niu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Ma, J.; Chen, L. Graphene oxide-based microspheres for the dispersive solid-phase extraction of non-steroidal estrogens from water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1368, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado-Sánchez, M.C.; Romero-González, R.; Rodríguez-Cáceres, M.I.; Durán-Merás, I.; Frenich, A.G. Rapid and sensitive on-line solid phase extraction-ultra high performance liquid chromatography-electrospray-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of pesticides in surface waters. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1305, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moral, A.; Sicilia, M.; Rubio, S.; Pérez-Bendito, D. Multifunctional sorbents for the extraction of pesticide multiresidues from natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 608, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.; Vidal, L.; Canals, A. Zeolite/iron oxide composite as sorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylenes from water samples prior to gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1458, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez, C.M.; Pariente, J.P. Zeolites and Ordered Porous Solids: Fundamentals and Applications; Editorial Universitat Politècnica de València: Valencia, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A.; Raja, G. Modification of Nanoclinoptilolite Zeolite with Hexadecyltrimethylammonium Surfactant as an Active Ingredient of Chromate-Selective Membrane Electrode. J. Chem. 2012, 2013, 685290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailu, S.L.; Nair, B.U.; Redi-Abshiro, M.; Diaz, I.; Tessema, M. Preparation and Characterization of Cationic Surfactant Modified Zeolite Adsorbent Material for Adsorption of Organic and Inorganic Industrial Pollutants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3319–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalakshmi, M.; Priya, S.V.; Arabindoo, B.; Palanichamy, M.; Murugesan, V. Photocatalytic degradation of aqueous propoxur solution using TiO2 and Hbeta zeolite-supported TiO2. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalló, D. Applications of Natural Zeolites in Water and Wastewater Treatment. In Natural Zeolites: Occurrence, Properties, Applications; David, L.B., Douglas, W.M., Eds.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 519–550. [Google Scholar]
- Mohseni-Bandpi, A.; Al-Musawi, T.J.; Ghahramani, E.; Zarrabi, M.; Mohebi, S.; Vahed, S.A. Improvement of zeolite adsorption capacity for cephalexin by coating with magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 218, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alver, E.; Metin, A. Anionic dye removal from aqueous solutions using modified zeolite: Adsorption kinetics and isotherm studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 200–202, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, M.; Selim, E.M.; Assaad, F.F. Removal Of Some Environmental Pollutants From Aqueous Solutions By Linde-Zeolite: Adsorption And Kinetic Study. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2012, 6, 1716–1724. [Google Scholar]
- Salisaeng, P.; Arnnok, P.; Patdhanagul, N.; Burakham, R. Vortex-Assisted Dispersive Micro-Solid Phase Extraction Using CTAB-Modified Zeolite NaY Sorbent Coupled with HPLC for the Determination of Carbamate Insecticides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2145–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuechl, D.E.; Benin, A.I.; Knight, L.M.; Abrevaya, H.; Wilson, S.T.; Sinkler, W.; Mezza, T.M.; Willis, R.R. Multiple paths to nanocrystalline high silica beta zeolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 127, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; An, T.; Yue, Y.; Bao, X. Carboxylic acids to butyl esters over dealuminated–realuminated beta zeolites for removing organic acids from bio-oils. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 33714–33725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soler, C.; Mañes, J.; Picó, Y. Routine application using single quadrupole liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry to pesticides analysis in citrus fruits. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1088, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, W.M.A.; Manini, P.; Andreoli, R. Matrix effects in quantitative pesticide analysis using liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2010, 25, 881–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwafune, T.; Ogino, T.; Watanabe, E. Water-Based Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Neonicotinoid Insecticides and Their Metabolites in Green Pepper/Tomato Samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).