Ice Elevation Change Based on GNSS Measurements along the Korth-Traverse in Southern Greenland
Abstract
1. Introduction
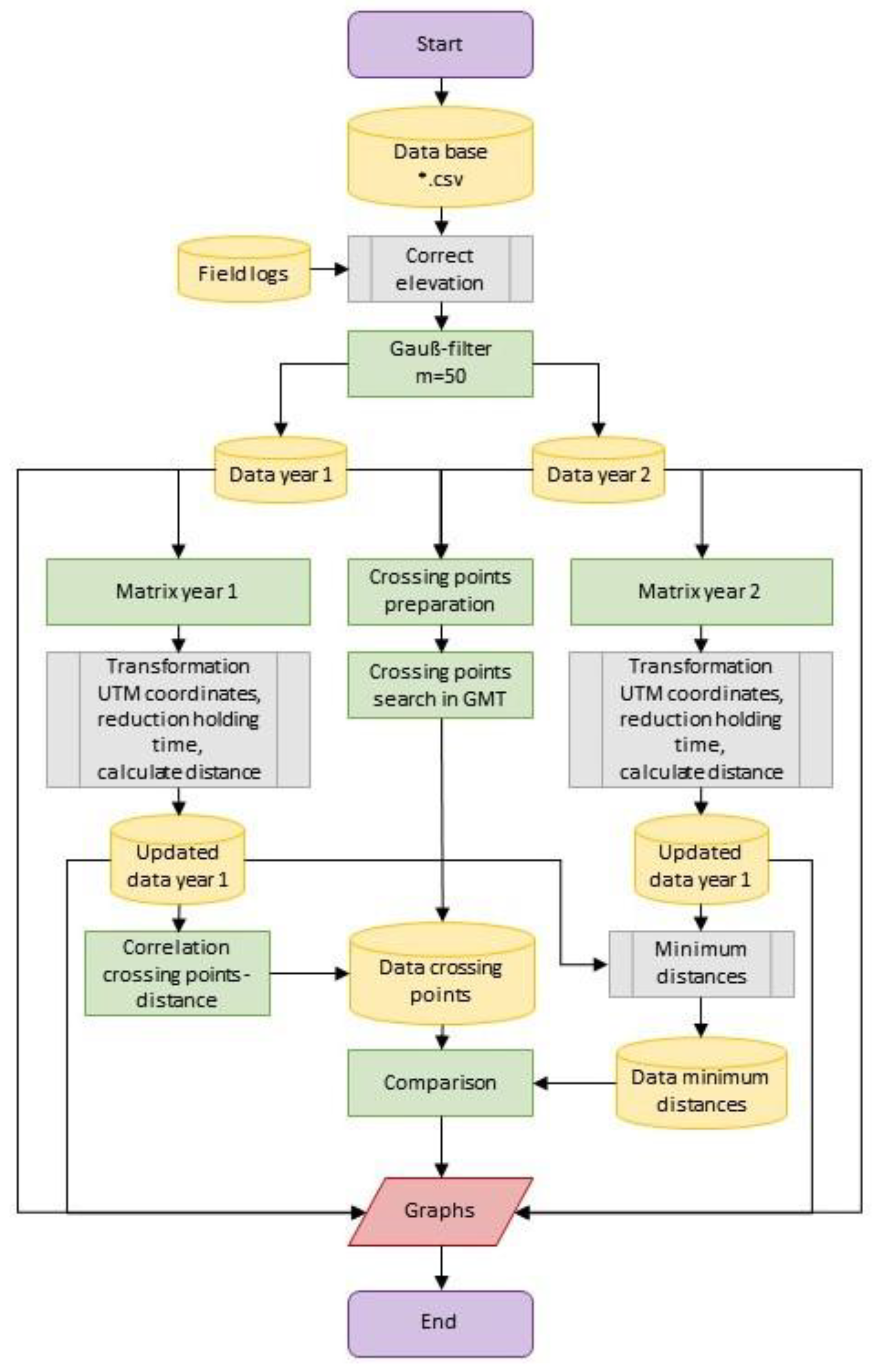
2. Materials and Methods
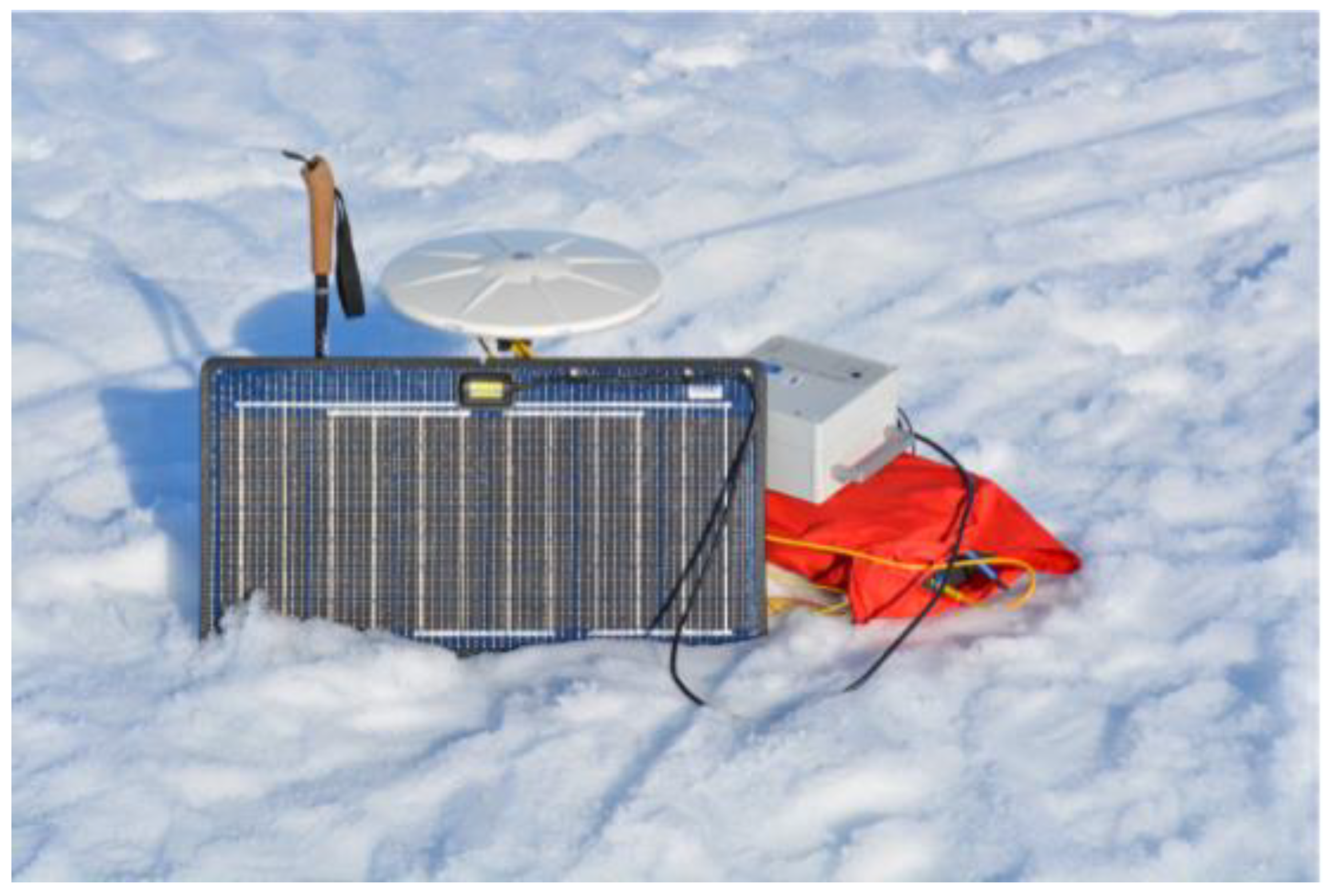
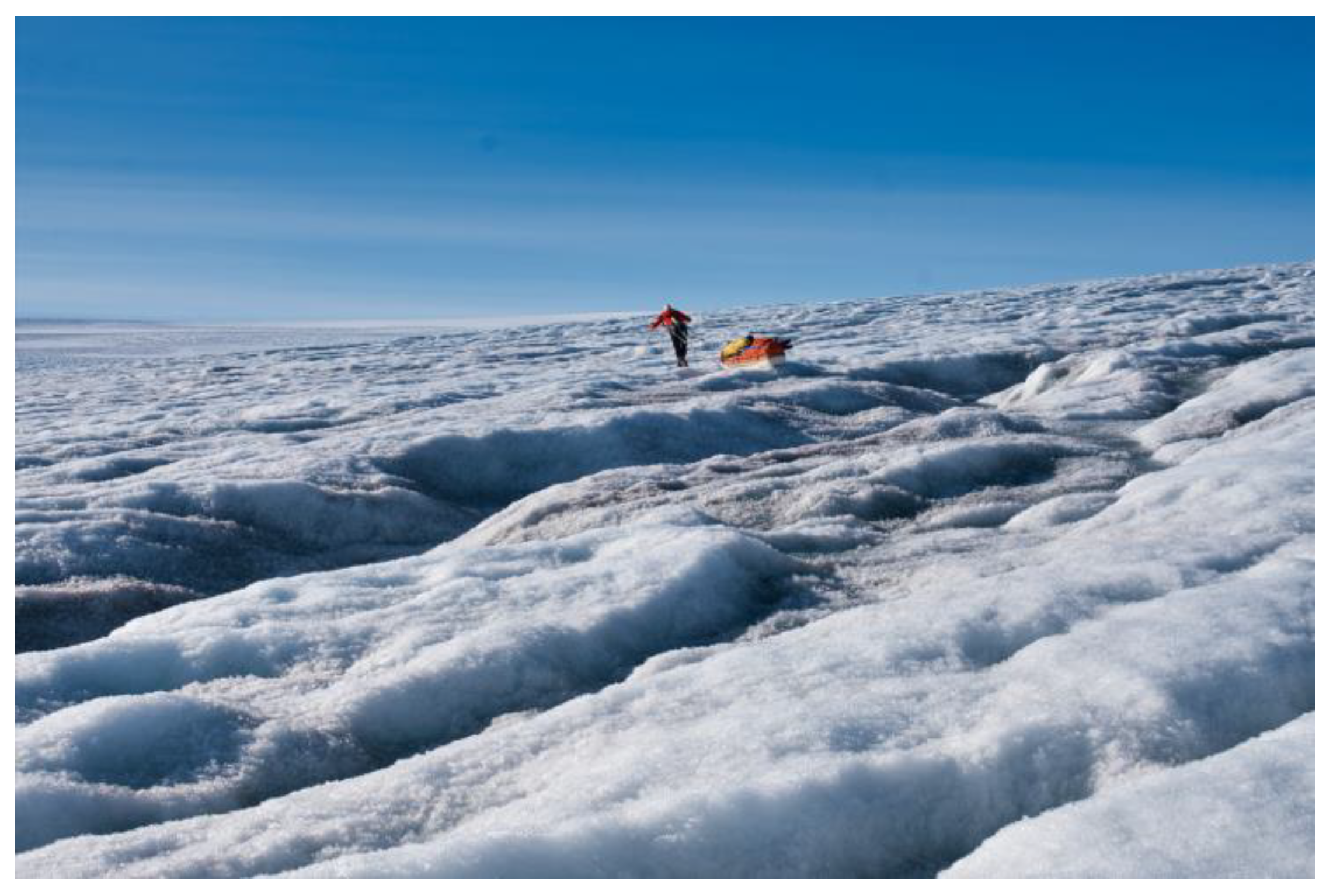
2.1. Static GNSS Measurements
2.2. Kinematic GNSS Measurements
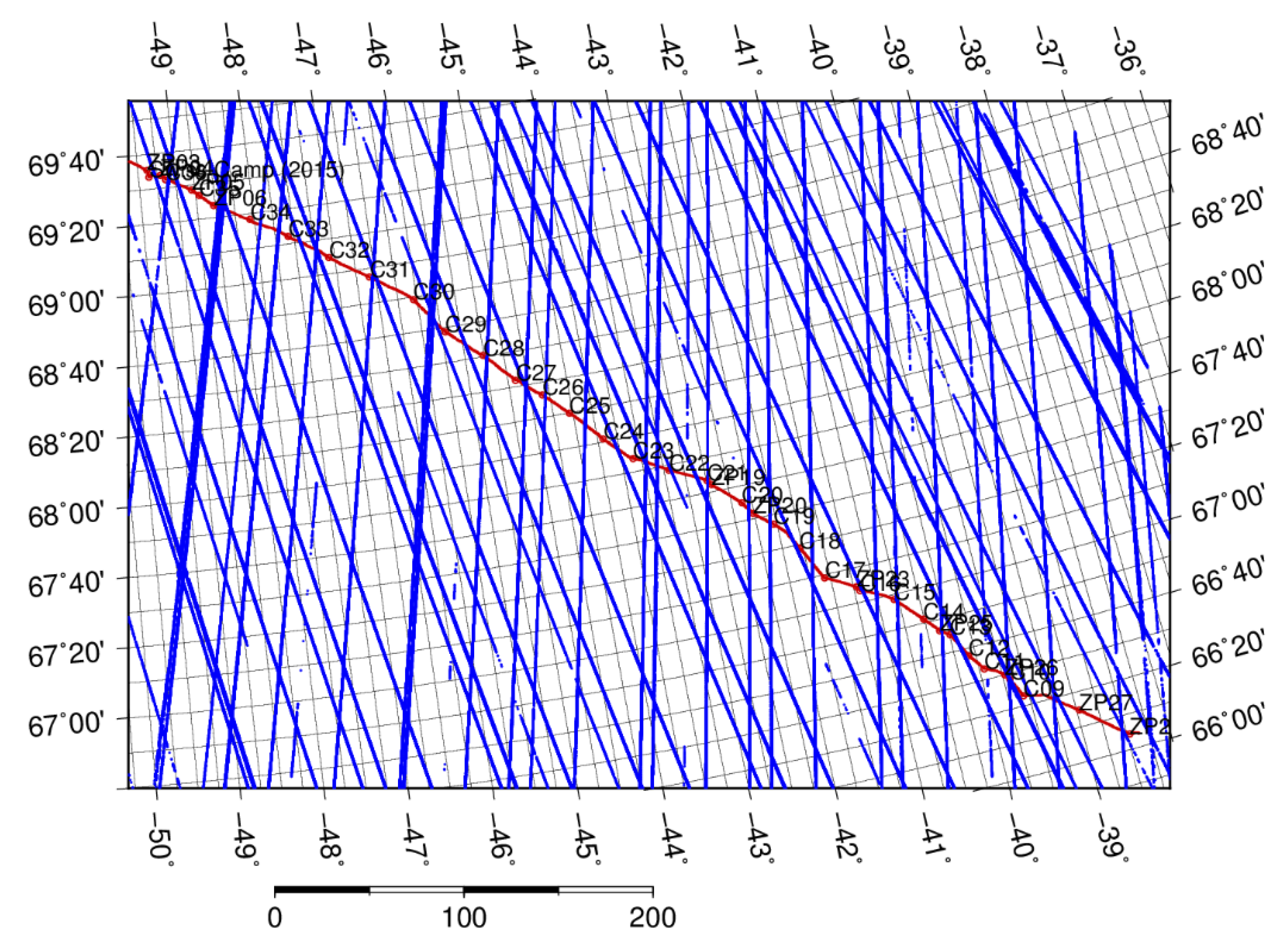
2.2.1. Crossing Point Comparison
2.2.2. Comparison of the Minimum Distances
3. Results
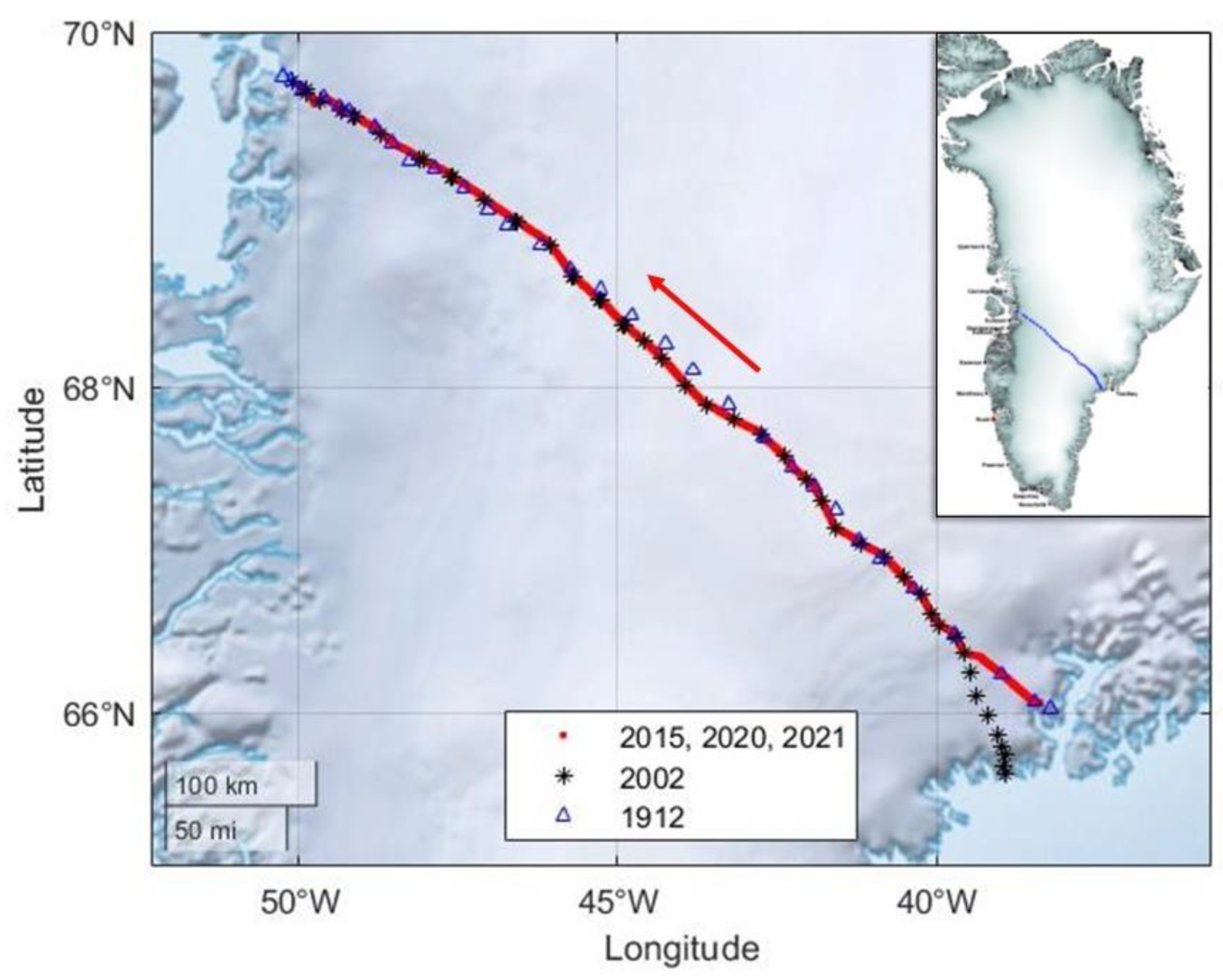
3.1. Static GNSS Measurements
3.2. Kinematic GNSS Measurements
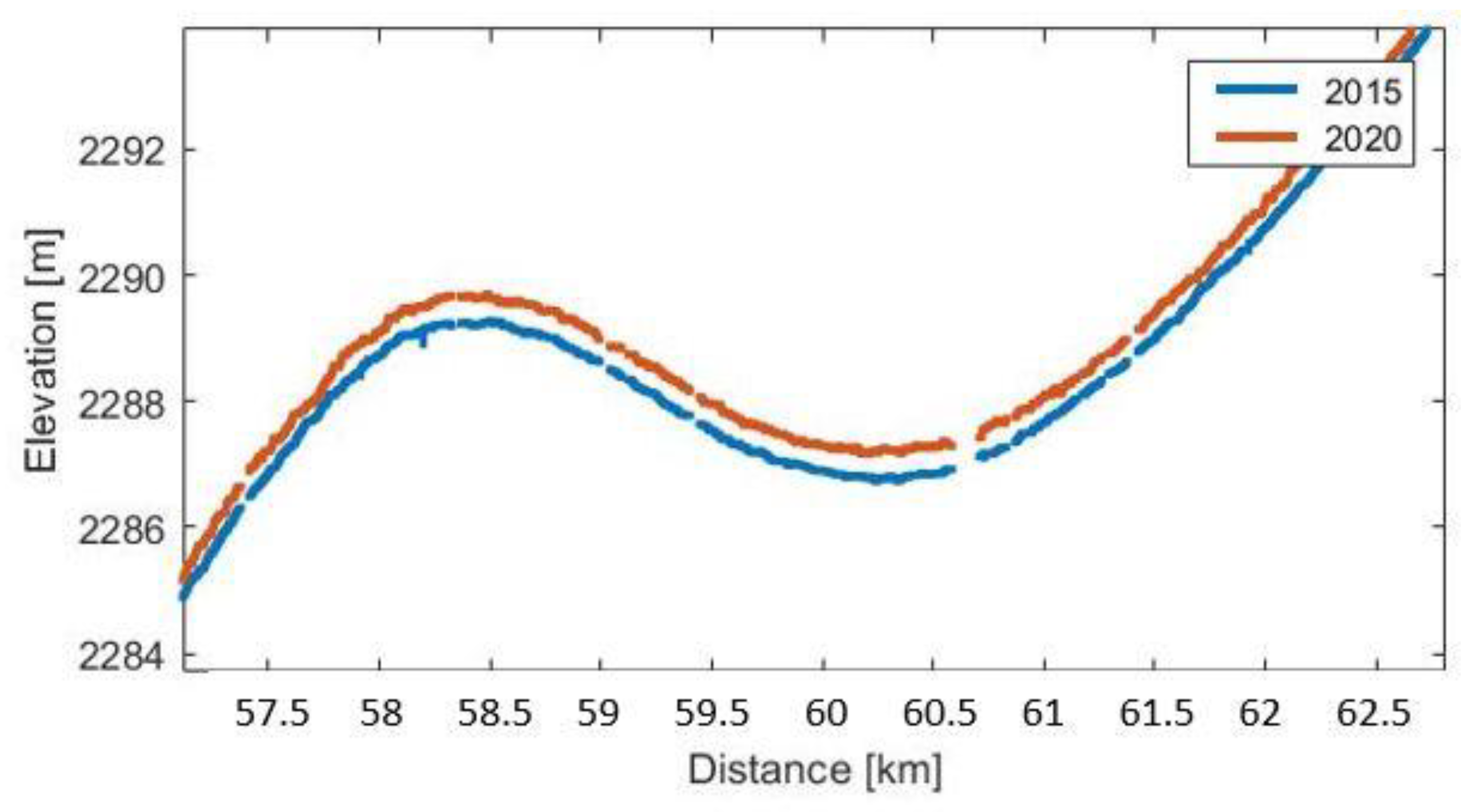
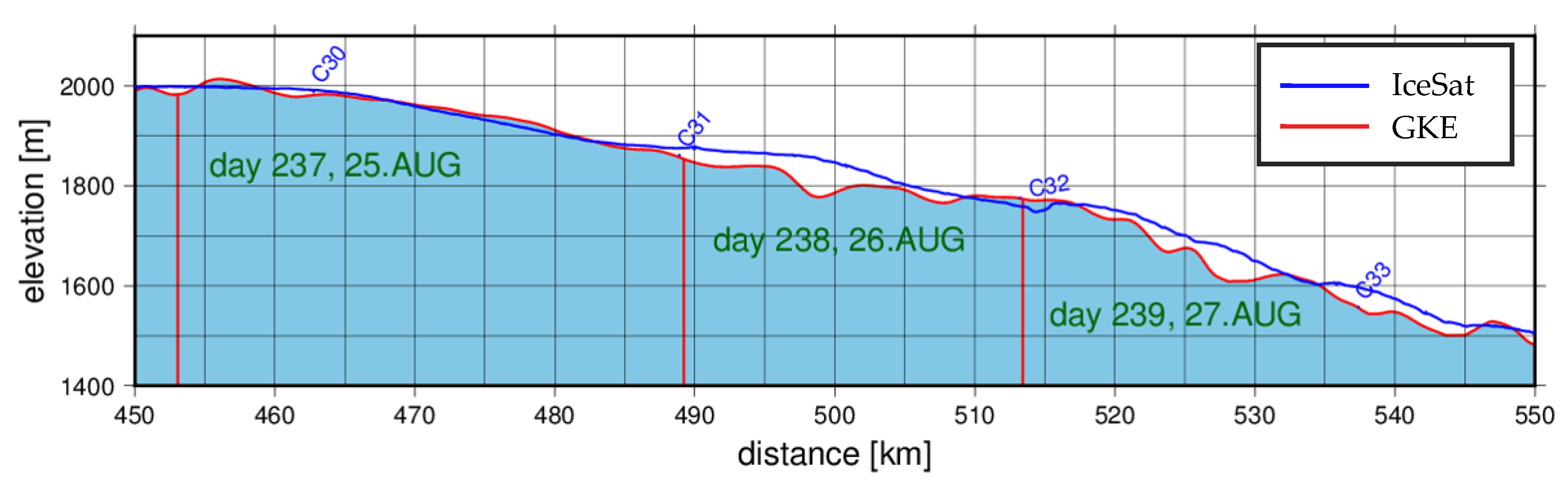
3.2.1. Profile Comparison
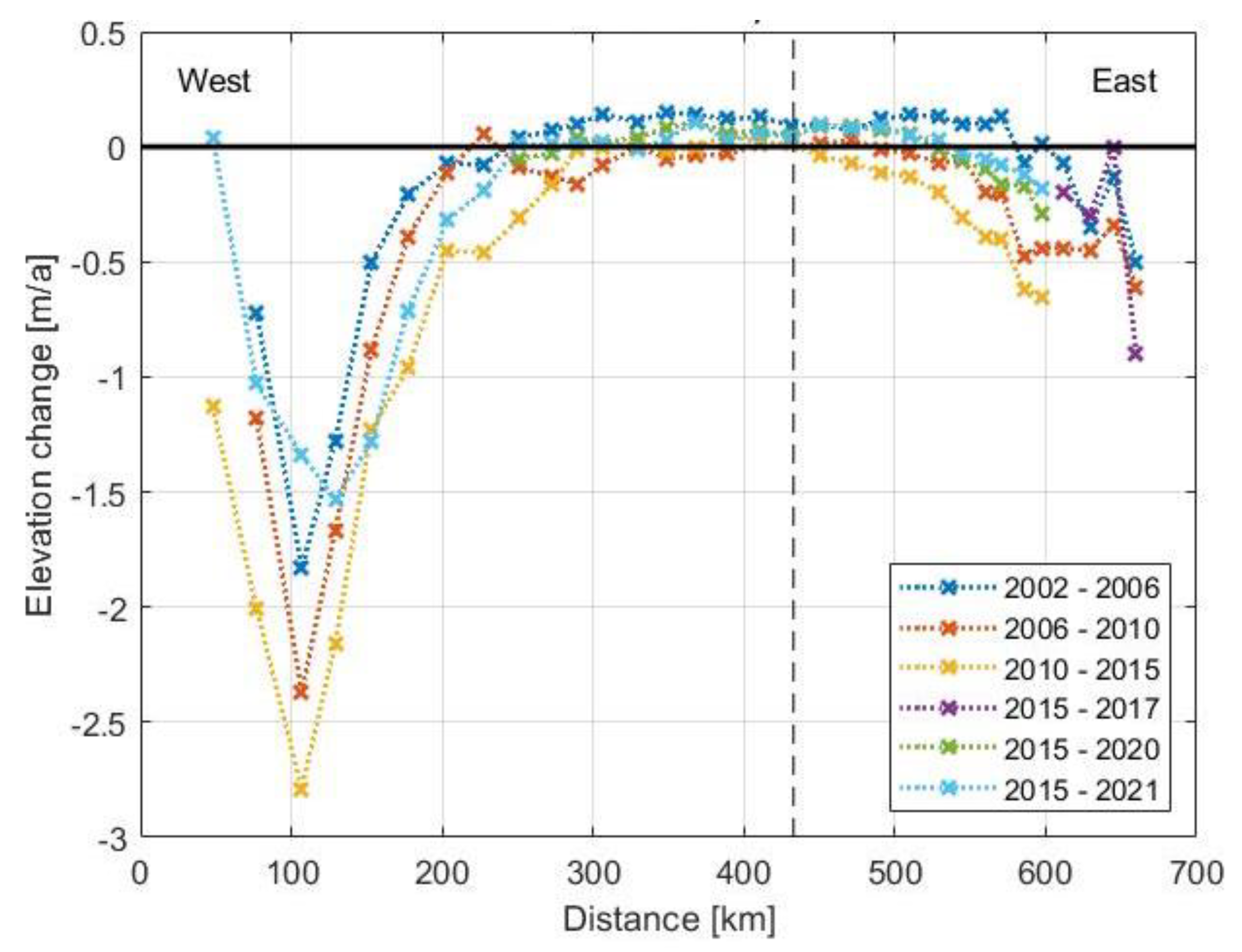
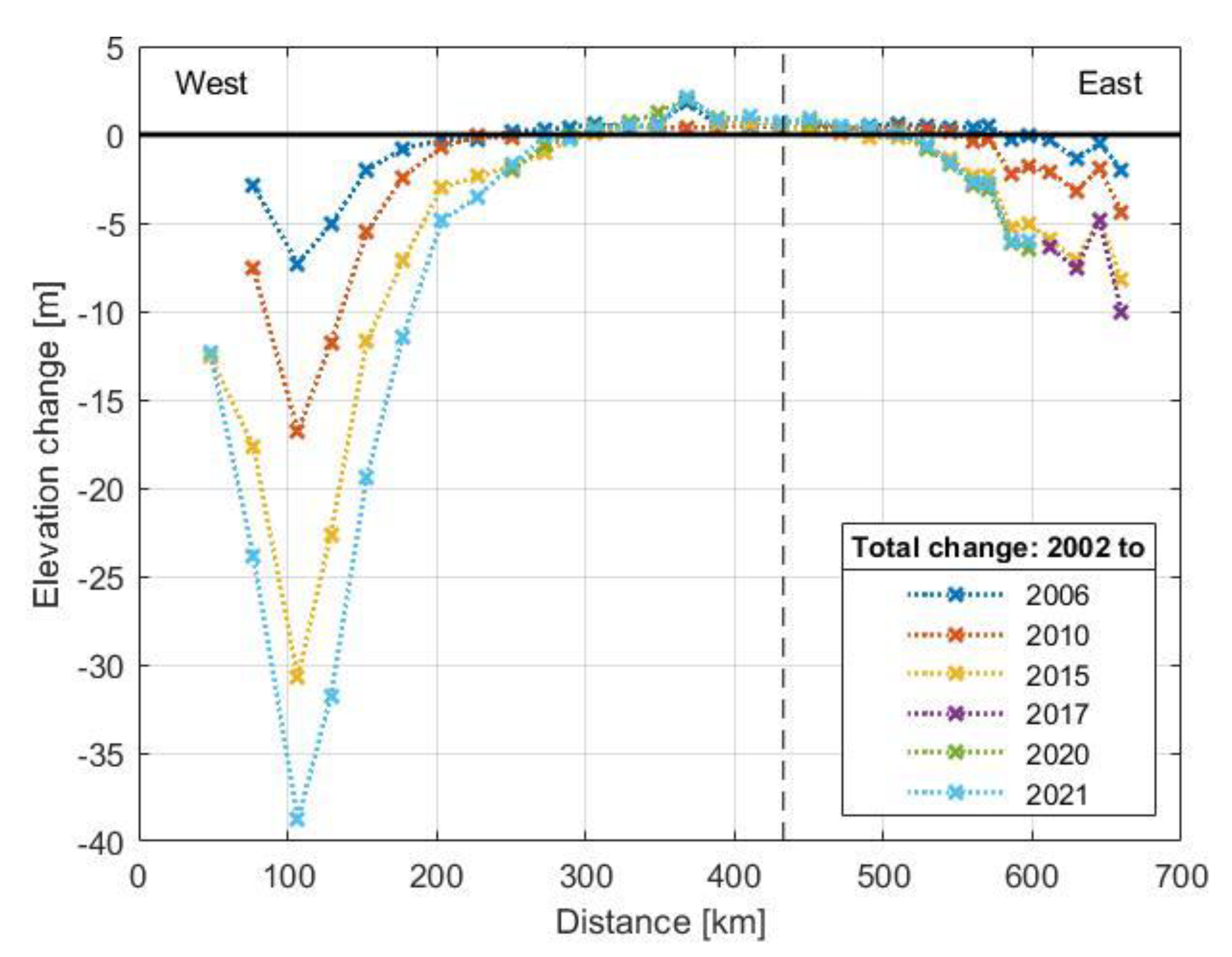
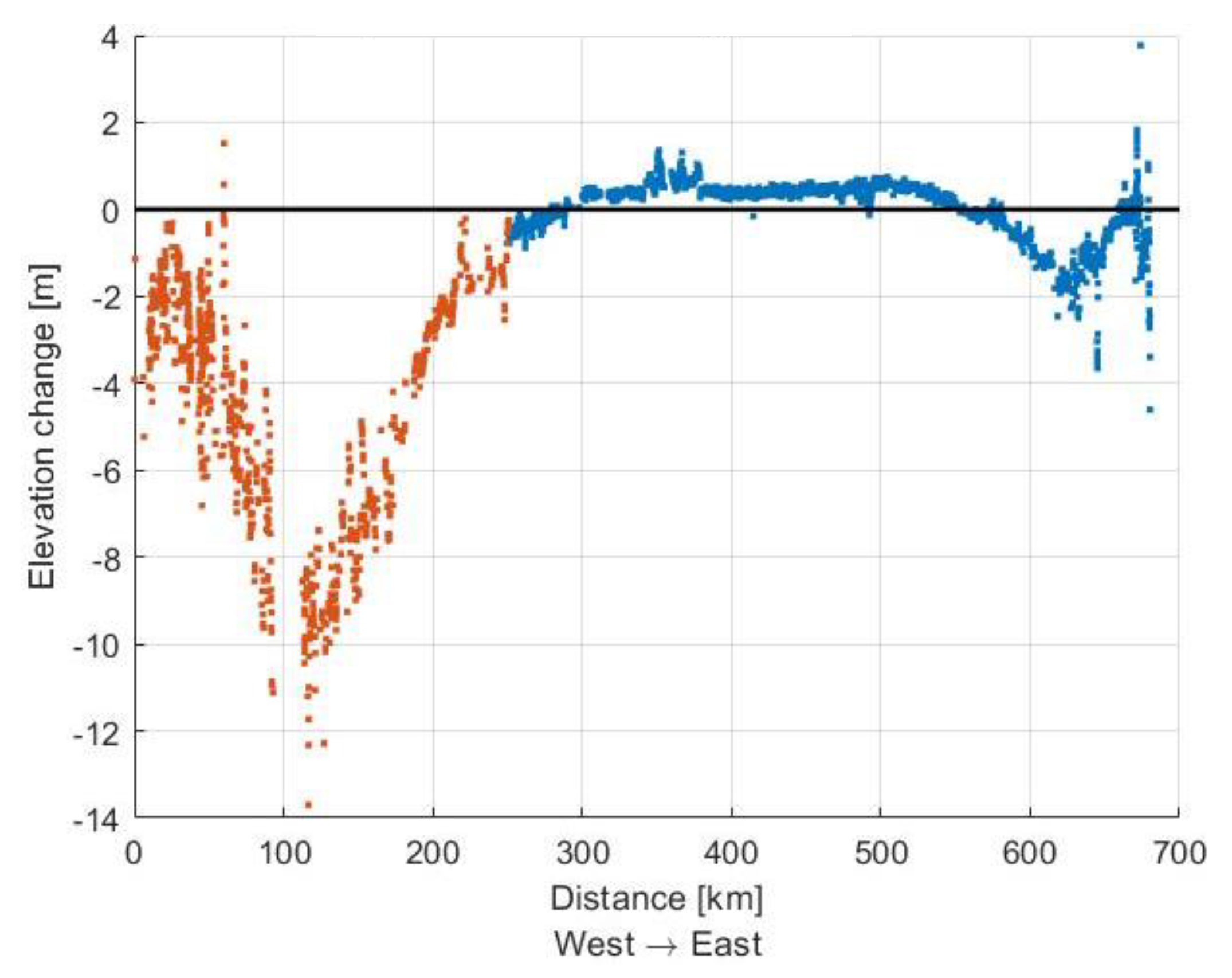
3.2.2. Elevation Change Comparison
3.2.3. Seasonal Changes during the Winter
3.2.4. Modification of Missing Parts
3.2.5. Accumulation and Ablation
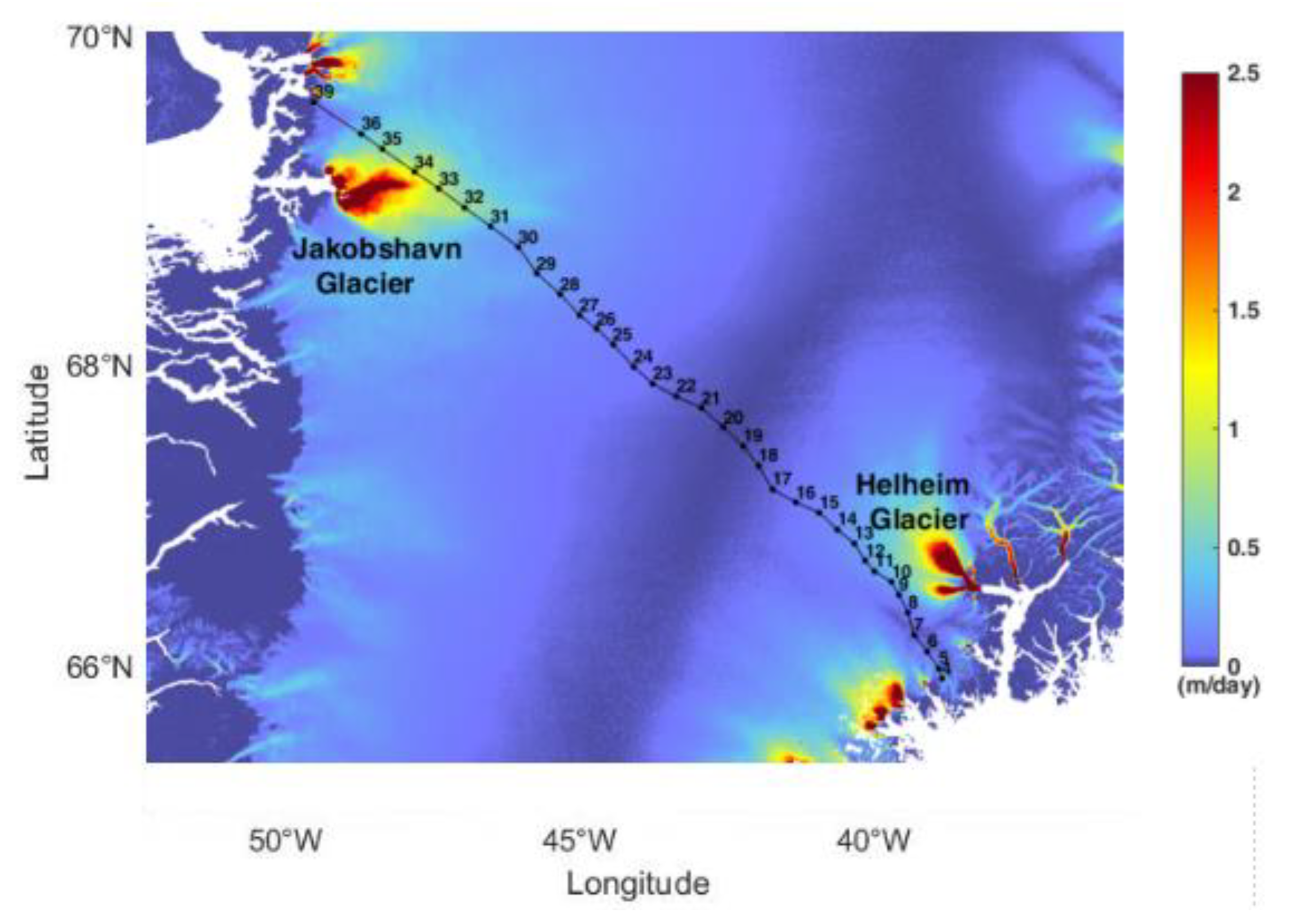
3.2.6. Comparison with Other Data
4. Discussion–Error Influences
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GIA | Glacial Isostatic Adjustment |
| GKE | Greenland Korth Expedition |
| GMT | Generic Mapping Tool |
| ITRF | International Terrestrial Reference Frame |
| NRCan | Natural Resources Canada |
| PPP | Precise Point Positioning |
| RINEX | Receiver Independent Exchange Format |
| UTM | Universal Transverse Mercator |
Appendix A
References
- Wolff, E.; Fung, I.; Hoskins, B.; Mitchell, J.F.B.; Palmer, T.; Santer, B.; Shepherd, J.; Shine, K.; Solomon, S.; Trenberth, K.; et al. Climate Change, Evidence, and Causes. An Overview from the Royal Society and the US National Academy of Sciences, Update 2020; Royal Society and US National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hestmark, G. Fridtjof Nansen and the Geology of the Arctic. Earth Sci. Hist. 1991, 10, 168–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abplanalp, A. Alfred de Quervain. Available online: https://blog.nationalmuseum.ch/en/2020/02/de-quervain-greenland-1912 (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Hobbs, W.H. Lauge Koch. In Encyclopaedia Arctica; Dartmouth College Library: Hanover, NH, USA, 1864. [Google Scholar]
- Wegener, E.; Loewe, F. Greenland Journey, The Story of Wegener’s German Expedition to Greenland in 1930–31 as told by Members of the Expedition and the Leader’s Diary; Translated from the Seventh German Edition by Winifred M. Deans; Blackie Son Ltd.: London, UK, 1939. [Google Scholar]
- Bjørk, A.A.; Kjær, K.A.A. The Greenland Ice Sheet—80 Years of Climate Change Seen from the Air; Natural History Museum of Denmark, Faculty of Science, University of Copenhagen: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2014; 180p, ISBN 978-87-87519-46-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bjørk, A.A.; Kjær, K.H.; Korsgaard, N.J.; Khan, S.A.; Kjeldsen, K.K.; Andresen, C.S.; Box, J.E.; Larsen, N.K.; Funder, S. An aerial view of 80 years of climate-related glacier fluctuations in southeast Greenland. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technical Report. Greenland Bases. Air Force Historical Research Agency. Available online: https://www.afhra.af.mil/ (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- Jensen, J.F.; Krause, T. Wehrmacht occupations in the new world: Archaeological and historical investigations in Northeast Greenland. Polar Record 2011, 48, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, T.; Hogg, A.E.; Mottram, R. Ice-sheet losses track high-end sea-level rise projections. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020, 10, 879–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouginot, J.; Rignot, E.; Bjørk, A.A.; van den Broeke, M.; Millan, R.; Morlighem, M.; Noël, B.; Scheuchl, B.; Wood, M. Forty-six years of Greenland Ice Sheet mass balance from 1972 to 2018. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 9239–9244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwally, H.J.; Abdalati, W.; Herring, T.; Larson, K.; Saba, J.; Steffen, K. Surface Melt-Induced Acceleration of Greenland Ice-Sheet Flow. Science 2002, 297, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelka, K.; Šedina, J.; Pavelka, K. Knud Rasmussen Glacier Status Analysis Based on Historical Data and Moving Detection Using RPAS. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelka, K.; Šedina, J.; Matoušková, E.; Hlaváčová, I.; Korth, W. Examples of different techniques for glaciers motion monitoring using InSAR and RPAS. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 52, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bash, E.; Moorman, B.; Gunther, A. Detecting Short-Term Surface Melt on an Arctic Glacier Using UAV Surveys. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasgen, I.; Wouters, B.; Gardner, A.S.; King, M.D.; Tedesco, M.; Landerer, F.W.; Dahle, C.; Save, H.; Fettweis, X. Return to rapid ice loss in Greenland and record loss in 2019 detected by the GRACE-FO satellites. Commun. Earth Amp Environ. 2020, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezděk, A.; Kostelecký, J.; Sebera, J.; Hitziger, T. GNSS Profile from the Greenland Korth Expeditions in the Context of Satellite Data. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffeler, M. Eishöhenänderung in Grönland zwischen 1912 und 2010. Master’s Thesis, Beuth Hochschule für Technik Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Korth, W.; Hitziger, T.; Hofmann, U.; Pavelka, K. Monitoring of surface ice height changes in Greenland. Berichte zur Polar-und Meeresforschung 716, Polar Systems under Pressure. In Proceedings of the 27th International Polar Conference, Rostock, Germany, 25–29 March 2018; Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research: Bremerhaven, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shupe, M.D.; Rex, M.; Blomquist, B.; Persson, P.O.G.; Schmale, J.; Uttal, T.; Althausen, D.; Angot, H.; Archer, S.; Bariteau, L.; et al. Overview of the MOSAiC expedition: Atmosphere. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2022, 10, 00060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.; Lewińska, P.; Smith, W.A.P.; Hancock, E.R.; Dowdeswell, J.A.; Rippin, D.M. Unravelling the long-term, locally heterogenous response of Greenland glaciers observed in archival photography. Cryosphere 2022, 16, 2449–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewinska, P.; Głowacki, O.; Moskalik, M.; Smith, W.A.P. Evaluation of structure-from-motion for analysis of small-scale glacier dynamics. Measurement 2021, 168, 108327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Han, S.; Bu, J.; An, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, C.; Tabibi, S.; Cheong, J.W. Spaceborne GNSS Reflectometry. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerova, G.; Douša, J.; Dimitrova, T.; Stoycheva, A.; Václavovic, P.; Penov, N. GNSS Storm Nowcasting Demonstrator for Bulgaria. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwedczuk, K.; Cienkosz, D.; Apollo, M.; Borowski, L.; Lewinska, P.; Guimarães Santos, C.A.; Eborka, K.; Kulshreshtha, S.; Romero-Andrade, R.; Sedeek, A.; et al. Challenges related to the determination of altitudes of mountain peaks presented on cartographic sources. Geodetski Vestnik 2022, 66, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zheng, F.; Yang, C.; Nie, G.; Li, S. Analyses of GLONASS and GPS+GLONASS Precise Positioning Performance in Different Latitude Regions. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godah, W.; Szelachowska, M.; Ray, J.D.; Krynski, J. Comparison of Vertical Deformation of The Earth’s Surface Obtained Using GRACE-Based GGMS And GNNS Data—A Case Study Of South-Eastern Poland. Acta Geodyn. Geomater. 2020, 17, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesselbarth, A. Statische und Kinematische GNSS-Auswertung Mittels Precise Point Positioning (PPP); Verlag der Bayerischen Akademie der Wissenschaften: München, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Altamimi, Z.; Métivier, L.; Rebischung, P.; Rouby, H.; Collilieux, X. ITRF2014 plate motion model. Geophys. J. Int. 2017, 209, 1906–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näke, L. Vergleich kinematischer GNSS-Daten aus Ostgrönland. Bachelor-Thesis, Brandenburg University of Technology Cottbus, Senftenberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hitziger, T.; Korth, W. Einfluss der lokalen Eistopographie auf die Qualität von Oberflächenhöhen aus Satellitendaten. In Proceedings of the Internationale Geodätische Woche Obergurgl 2019, Obergurgl, Austria, 10–16 February 2019; Hanke, K., Weinold, T., Eds.; Wichmann Verlag: Berlin/Offenbach, Germany, 2019; pp. 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Hitziger, T.; Näke, L. Vergleich kinematischer GNSS-Daten des grönländischen Eisschildes. In Proceedings of the Internationale Geodätische Woche Obergurgl, Obergurgl, Austria, 7–13 February 2021; Weinold, T., Ed.; Wichmann Verlag: Berlin/Offenbach, Germany, 2021; pp. 201–206. [Google Scholar]
- Stempfhuber, W.; Korth, W.; Hitziger, T. Glacier surface and mass balance variation in Alaska and southern Greenland. Berichte zur Polar- und Meeresforschung 716, Polar Systems under Pressure. In Proceedings of the 27th International Polar Conference, Rostock, Germany, 25–29 March 2018; p. 176. [Google Scholar]
- Korth, W.; Hitziger, T. Geodätisches Monitoring des Klimawandels in Grönland. In Forum: Zeitschrift des BdVI, 45. Jahrgang, Heft 1/2019; Universitätsbibliothek der LMU München: München, Germany, 2019; pp. 26–37. ISSN 0342-6165. [Google Scholar]
- Joughin, I. Greenland rumbles louder as glaciers accelerate. Science 2006, 311, 1719–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewert, H. Auswertung von IceSat-Laseraltimeterdaten zur Untersuchung Glaziologischer Fragestellungen in Polaren Gebieten. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Abshire, J.B.; Sun, X.; Riris, H.; Sirota, J.M.; McGarry, J.F.; Palm, S.; Yi, D.; Liiva, P. Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) on the ICESat Mission: On-orbit measurement performance. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Year | Scientific Director | Method of Measurement | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1912 | A. de Quervain | barometric | 39 camps; accuracy in the coastal area +/−3–5 m |
| 2002 | W. Korth | GPS static | 34 positions; +/−3 cm |
| 2006 | W. Korth | GPS static | 34 positions; +/−3 cm |
| 2010 | W. Korth | GNSS static | 34 positions; +/−2 cm |
| 2012 | W. Korth | GNSS static | only east coast; 17 positions +/−2 cm |
| 2015 | W. Korth | GNSS kinematic and static | continuous profile; spot spacing 2–6 m; 700 km; +/−3 cm |
| 2017 | W. Korth | GNSS kinematic | continuous pr.; spot spacing 2–6 m; approx. 180 km; +/−3 cm |
| 2020 | T. Hitziger | GNSS kinematic | continuous pr.; spot spacing 2–6 m; approx. 500 km; +/−3 cm |
| 2021 | T. Hitziger/J. Heim | GNSS kinematic | continuous pr.; spot spacing 2–6 m; approx. 680 km; +/−3 cm |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hitziger, T.; Näke, L.; Pavelka, K. Ice Elevation Change Based on GNSS Measurements along the Korth-Traverse in Southern Greenland. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12066. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312066
Hitziger T, Näke L, Pavelka K. Ice Elevation Change Based on GNSS Measurements along the Korth-Traverse in Southern Greenland. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(23):12066. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312066
Chicago/Turabian StyleHitziger, Thomas, Luisa Näke, and Karel Pavelka. 2022. "Ice Elevation Change Based on GNSS Measurements along the Korth-Traverse in Southern Greenland" Applied Sciences 12, no. 23: 12066. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312066
APA StyleHitziger, T., Näke, L., & Pavelka, K. (2022). Ice Elevation Change Based on GNSS Measurements along the Korth-Traverse in Southern Greenland. Applied Sciences, 12(23), 12066. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312066







