Abstract
This work numerically evaluates the role of advancing velocity on the water entry of rigid wedges, highlighting its influence on the development of underpressure at the fluid–structure interface, which can eventually lead to fluid detachment or cavity formation, depending on the geometry. A coupled FEM–SPH numerical model is implemented within LS-DYNA, and three types of asymmetric impacts are treated: (I) symmetric wedges with horizontal velocity component, (II) asymmetric wedges with a pure vertical velocity component, and (III) asymmetric wedges with a horizontal velocity component. Particular attention is given to the evolution of the pressure at the fluid–structure interface and the onset of fluid detachment at the wedge tip and their effect on the rigid body dynamics. Results concerning the tilting moment generated during the water entry are presented, varying entry depth, asymmetry, and entry velocity. The presented results are important for the evaluation of the stability of the body during asymmetric slamming events.
1. Introduction
The phenomenon of a structure impacting on the water generally implies large forces due to the massive fluid volume displaced in a small time. The duration of the slamming event is in the order of milliseconds. These loads might damage the structure or, because of their short duration, excite a dynamic response of the local structure of the hull and cause vibrations. Non-symmetric impacts might further introduce a tilting moment and influence the impact dynamics and structural stability.
The first analytical solution to solve the impact dynamics of rigid bodies entering the water was presented by Von Karman [1], who developed a formula capable of predicting the maximum force acting on a rigid body entering the water, to make a stress analysis on the members connecting the fuselage with the floats of a seaplane. Many analytical methods have been proposed to extend Wagner’s method to different shapes (e.g., [2,3,4,5,6,7]) and most of them are very effective in predicting the water entry of simple-shaped structures impacting the surface with pure vertical velocity. Some of these solutions are even capable of accounting for oblique impacts (e.g., [8,9,10,11,12]). It is reported that particular conditions of entry velocity, deadrise angle, and tilt angle might lead the fluid to detach at the wedge apex, introducing difficulties in evaluating the pressure at the interface by analytical formulations. A typical water entry event that largely deviates from a symmetric case is ditching [13,14,15], where fluid detachment and cavitation arise if the advancing velocity is sufficiently large. Another area of interest for asymmetric impacts is the analysis of the response of planing hulls during the maneuvering operation since, depending on the conditions, restoring or capsizing moments can take place [16]. Xu [17] defined two types of asymmetric impact. Type A flow is the one when there is small asymmetry and the flow moves outward along the contour on both sides of the vertex. Type B flow occurs when there is large asymmetry and the flow detaches from the body contour at the vertex on one side. Chekin [18] concluded that there was only one unique combination of wedge angle and impact angle at which no separation of flow from the vertex would occur. For a given wedge shape and impact direction, any other impact angle would force separation. Defining U as the horizontal velocity and V as the vertical velocity, the advancing ratio at which the flow separation appears is less for bodies of larger deadrise angles. For small asymmetry impacts, the cavity flow during the water-entry is limited to a very small region. Furthermore, the flow that separates from the apex quickly re-attaches to the wedge. A symmetric body impacting with horizontal velocity will produce a flow similar to asymmetric impact with only vertical velocity when a tilting motion is not permitted. Judge et al. [8] performed experiments on wedges where asymmetry and horizontal impact velocity were present and compared the results with an analytical solution, showing good agreement for low angles of asymmetry and small advancing ratios.
Xu et al. [17] observed that the pressure near the tip of asymmetric wedges might attain negative values with respect to the gauge pressure, and hence be lower than the ambient pressure. They also observed that the peak pressure increases with the horizontal velocity, and with it, an increase in the wave elevation on the upstream side and a decrease on the downstream one. However, the simulations are based on the assumption of attached flow. In this work, we also consider the eventual detachment at the wedge tip, similarly to that described in [19] but utilizing a different numerical scheme. Semenov [20] studied the effect of the horizontal component of the entry velocity for various wedge orientations. Results show that certain configurations of the impact might induce a negative pressure along the whole wetted length of the downstream side of the wedge, leading to flow separation at the wedge apex. Semenov and coauthors [21,22,23] derived an analytical solution for the asymmetric/oblique water entry of a wedge which does not assume flow separation from the wedge vertex. It was shown that at some wedge orientations, the total force acting on the wedge side with the larger deadrise angle may become zero, a condition corresponding to flow separation.
Experimental evidence of the onset of cavity formation at high asymmetry ratios has been provided by Shams et al. [24], who studied asymmetric water impacts experimentally through particle image velocimetry.
In this manuscript, we initially define the problem of asymmetric water impacts in Section 2 and we detail the numerical model utilized for the analysis in Section 3. Asymmetric water entry events are then divided into categories and studied separately in Section 4, Section 5 and Section 6, to finally draw some final remarks in Section 7.
2. Problem Statement: Water Entry of Asymmetric Wedges
In the most general case, wedges enter the water with combined vertical and horizontal velocity components, whose ratio defines the advancing ratio , and are not symmetric due to an initial tilt angle . As mentioned in the introduction, this kind of impact might introduce ventilation into the fluid flow [8] due to fluid detachment at the wedge tip. A sketch of the problem is shown in Figure 1: a wedge with nominal deadrise angle enters the water at the velocity and is rotated by a tilt angle with respect to the water surface.
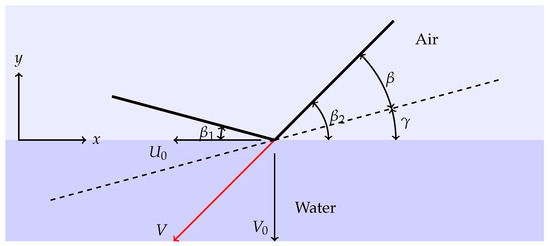
Figure 1.
Sketch of the asymmetric impact of a wedge.
In the following, the analysis will always refer to wedges designed as symmetric structures with nominal deadrise angle but rotated by a tilt angle , hence presenting different deadrise angles on the two sides ( and ). We also define the advancing ratio as the ratio between the horizontal velocity and the vertical velocity . Utilizing such definitions, we here classify the water entry event into three main categories:
- and —symmetric wedge with an horizontal velocity component;
- and —asymmetric wedge with pure vertical velocity;
- —asymmetric wedge with an horizontal velocity component.
In the case of vertical impact, fluid detachment is prone to happen only if the condition is met. In the presence of a horizontal velocity component, it is reported in the literature [20] that the flow separation from the wedge vertex may occur when , being is the leeward-side deadrise angle, and the water-entry angle, as in these cases, the pressure near the tip might become negative [25]. Although this phenomenon is well known, it is usually neglected due to the difficulties in treating the fluid detachment. This work instead focuses on those cases where the fluid detaches at the wedge vertex.
3. Coupled FEM/SPH Numerical Model
In this study, we assume that cavitation at the wedge vertex does not occur and flow separation depends on the flow characteristics enabling ventilation. Gravity is always neglected, while the entry velocity and tilt motion either follow the actual impact dynamics or is set to a constant value, for in the latter case the solution is self-similar in time, hence the results might be normalized by the entry depth. In the case of full fluid–structure interaction simulations (hence modelling the whole impact dynamics) the solution is not self-similar in time not only because of the role of acceleration but also because the tilt motion modifies the deadrise angle. As a result, the jet of water piling up over the counter-clock side thickens, while in the opposite side, the water is pushed by the rotating wedge and the free surface profile near the wedge deforms significantly.
The 2D numerical model, presented in Figure 2, is based on the SPH solutor available within the commercial software LS-DYNA. In all the numerical solutions, the fluid is modelled by SPH particles with a constant diameter of mm covering a region m wide and m deep. Non-reflecting boundaries define the bounding box. The fluid is modelled through an equation of state following the Gruneisen model and the fluid particles are solved utilizing the SPH-enhanced fluid formulation (FORM = 16). Both wedge’s sides are m long and are modelled as a rigid shell composed by 100 elements on each side, leading to an average of four SPH particles that make contact with a single element in the wet region. Such a strategy allows to smooth out the marked pressure fluctuations otherwise attained at the fluid–structure interface. Deadrise angle, initial rotation, and entry velocities are parametrically varied, while the wedge mass is 100 kg per unit width.
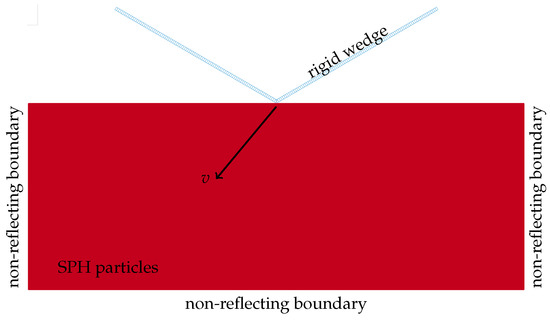
Figure 2.
Two-dimensional numerical model with highlighted boundary and initial conditions.
The numerical results will be compared against established analytical solutions. It has already been shown that the numerical scheme utilized within this work is in line with the analytical predictions provided by Wagner’s model for the case of pure vertical velocity [26,27] which, in turn, was shown to provide results in line with experimental results conducted on rigid wedges [28,29,30,31]. In Wagner’s expanding plate model, which has been formulated for symmetric impacts only, the pressure distribution along the wedge edge is given by:
while the Modified Logvinovich Model (MLM), before flow separation, reads [32]
where defines the wet portion of the edge. Within this scheme, x is an abscissa oriented horizontally, i.e., following the direction of the free surface, and r is a function of the entry depth and equals . In the case of constant entry velocity, the horizontal projection of the wet length reads . MLM can be also utilized to study asymmetric impacts. However, a simplified method considering an equivalent deadrise angle equal to the average of the left- and the right-side deadrise angles is sufficiently accurate to predict the overall impact dynamics [32]. Within this numerical scheme, the distribution of the non-dimensional hydrodynamic pressure , which is given by , over the horizontal abscissa x is given by
The normalized pressure distribution for varying deadrise angle is shown in Figure 3.
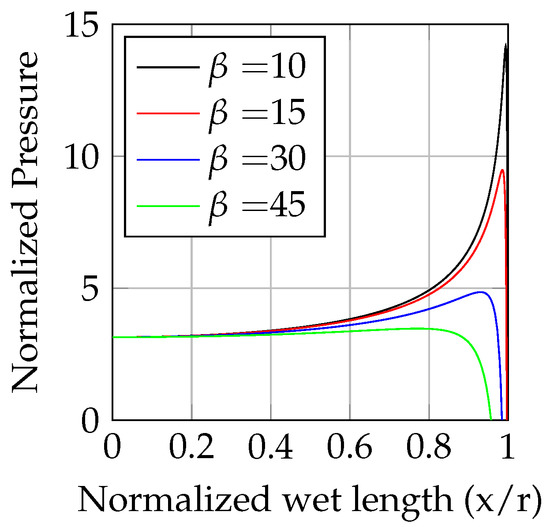
Figure 3.
Evolution of the normalized pressure along the wetted edge for variable deadrise angles.
Following Wagner’s solution, the vertical force (per unit width) of the wedge can then be estimated as follows:
This shows that the ratio between the vertical force and the entry depth, which in the case of constant velocity equals , is
which is time-independent, being a function of the deadrise angle only. Here, vertical force, horizontal force, and tilting moment will be normalized as
4. Symmetric Wedges with Horizontal Velocity Component— and
In this section, we investigate the effect of a horizontal velocity component on the pressure distribution over a rigid wedge. At first, we concentrate on rigid wedges with constant velocity and null tilt motion, since such approximation leads to a self-similar solution and the impact time can be taken out of the analysis.
As a general result, the horizontal velocity component alters the fluid motion beneath the wedge up to the point a cavity is formed. Indeed, a threshold value of it exists for the onset of cavity formation. Figure 4 shows three images of the cavity predicted by the numerical solutions on a wedge with and varying advancing ratios . Notably, fluid detachment is attained as exceeds 2 and the void region increases with the advancing ratio.
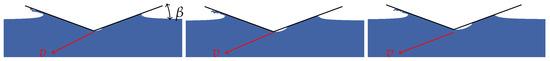
Figure 4.
Fluid detachment at the vertex of a wedge for varying advancing ratio (left to right).
Indeed, pressure drops to zero in the dry region, the extension of which increases with the advancing ratio . Figure 5 details the predicted pressure distribution over a symmetric wedge with deadrise angle entering the water with varying advancing ratios . These examples report wedges running at a constant speed and the tilt motion is inhibited. Each graph reports the normalized pressure over the normalized wet portion of the wedge at various instants of the impact. Notably, the solution remains self-similar for all the advancing ratios considered, as the normalized pressure and void region are not influenced by the entry depth. Interestingly, the leeward wedge side remains completely dry as exceeds 2.
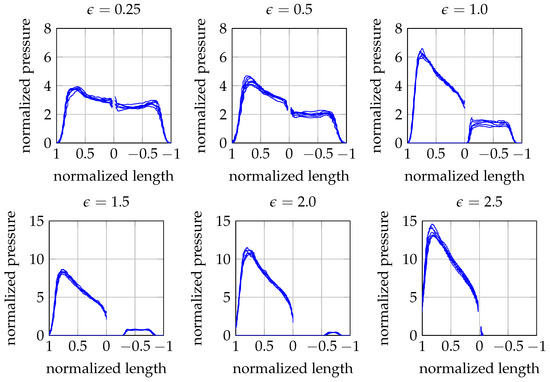
Figure 5.
Normalized pressure versus wet portion of a wedge () at various instants of the impact for varying .
The self-similarity of the results allows for the effect of the advancing ratio on the pressure distribution along the body to be compared. Figure 6 reports results similar to the ones presented in Figure 5, but stacked on a single graph to ease their comparison. Results about and wedges with varying advancing ratios are presented. In the case of pure vertical impact, such deadrise angles experience a hydrodynamic load that is almost constant over the entire wet surface, as also predicted by the Wagner’s solution reported in Figure 3. However, when a horizontal velocity component is introduced, the pressure on the right side (that is, the windward side) is found to increase almost linearly moving from the vertex to the free edge, while it remains constant on the leeward side, except for the region experiencing fluid detachment. The graph reports a single solution for each case due to the self-similarity of the results. In the case of , fluid detachment initiates when becomes greater than 1 and the magnitude of the void region with respect to the overall wet length increases with the advancing ratio, to eventually remain fully dry when is greater than 2. Notably, for both the deadrise angles considered, the cavity incipient condition is met as soon as , while the cavity is completely formed as soon as , a result which matches with the analytical predictions [25], validating the capability of the numerical model to correctly capture the cavity formation event. The pressure on the windward side is found to increase with the horizontal component while it decreases on the opposite side. At the higher advancing ratio considered in this study (), the left side never makes contact with the fluid. Figure 6 also highlights, with particular reference to the case, how the pile-up on the windward side of the wedge increases with the advancing ratio, while it decreases on the leeward side. These results should be ascribed to the increasing horizontal component of the velocity.
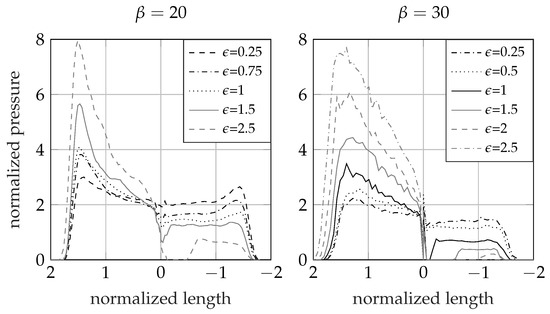
Figure 6.
Normalized pressure versus normalized wetted surface on a symmetric wedge with (left) and (right), entering the water with different advancing ratios .
Having imposed a constant entry velocity further allows normalizing the impact forces and the tilting moment, whose magnitude remain constant during the whole impact event. The normalized results for all cases considered are collected in Figure 7. The normalized horizontal force is found to linearly increase with the advancing ratio, as the horizontal velocity component increases with it—while both the vertical force and the momentum remain constant (hence proportional to the vertical force only)—to eventually diverge as exceeds 2, which is the full cavity generation condition.
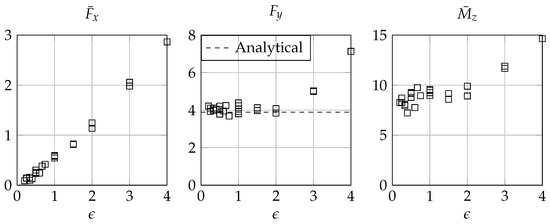
Figure 7.
Normalized horizontal force, vertical force, and momentum versus advancing ratio .
5. Asymmetric Wedges with Pure Vertical Velocity— and
This section firstly proposes to adapt simple analytical formulations to investigate the impact dynamics of asymmetric wedges. Later, the hydrodynamic pressure evaluated numerically will be compared against Wagner’s solution to assess its validity in asymmetric water impacts.
5.1. Impact Dynamics of Asymmetric Wedges
The impact dynamics of the asymmetric wedge impacting with pure vertical velocity will be here approximated through Wagner’s formula, by adjusting the added mass term to account for the different deadrise angles, hence the wet length, of the two sides of the wedge. The mass of the expanding plate in Wagner’s approach is here approximated by
And the impact dynamics is estimated utilizing Equation (4) by substituting the term with
The comparison between analytical predictions and the numerical results shows a fairly good match during the initial stage of the water entry, to slightly diverge after the peak acceleration is reached. Such a difference should be ascribed to the tilt motion which modifies the deadrise angle over time, an effect that is not accounted for in the analytical model. As an example, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11 show the comparison between numerical results and analytical predictions of the impact dynamics of a wedge varying tilt angle and entry velocity.
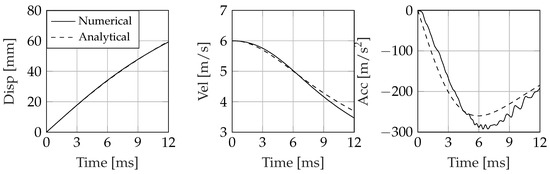
Figure 8.
Impact dynamics of an asymmetric wedge entering the water at 6 m/s. Deadrise angle , tilt angle 5.
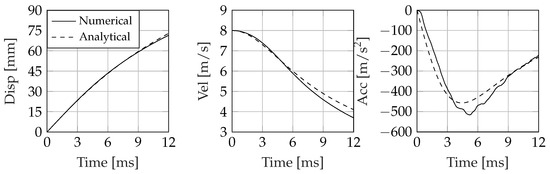
Figure 9.
Impact dynamics of an asymmetric wedge entering the water at 8 m/s. Deadrise angle , tilt angle 5.
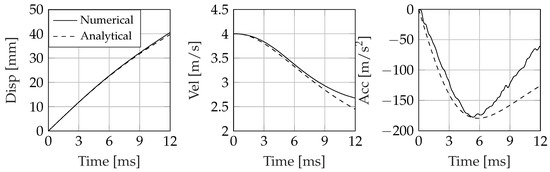
Figure 10.
Impact dynamics of an asymmetric wedge entering the water at 4 m/s. Deadrise angle , tilt angle 15.
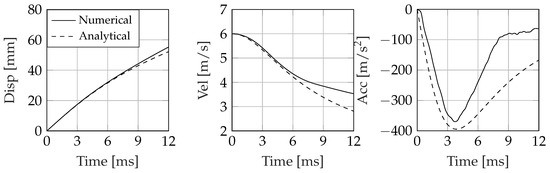
Figure 11.
Impact dynamics of an asymmetric wedge entering the water at 6 m/s. Deadrise angle , tilt angle 15.
5.2. Hydrodynamic Pressure
It has been found that the impact dynamics during the initial stages of the water entry process can be effectively predicted by a simple modification of the expanding plate model. To evaluate the effect of the tilt angle on the pressure distribution, we now concentrate on the hydrodynamic pressure at the interface and compare the results against Wagner’s predictions.
Figure 12 shows the effect of the tilt angle on the pressure distribution for the case of a wedge with constant entry velocity and null tilt motion. In such a condition, the solution is found to remain self-similar in time and the trend of the hydrodynamic pressure follows Wagner’s prediction on each side of the wedge. The pileup coefficient [33] is not influenced by the initial tilt angle and it remains approximately constant to , matching with the analytical value predicted for symmetric wedges.
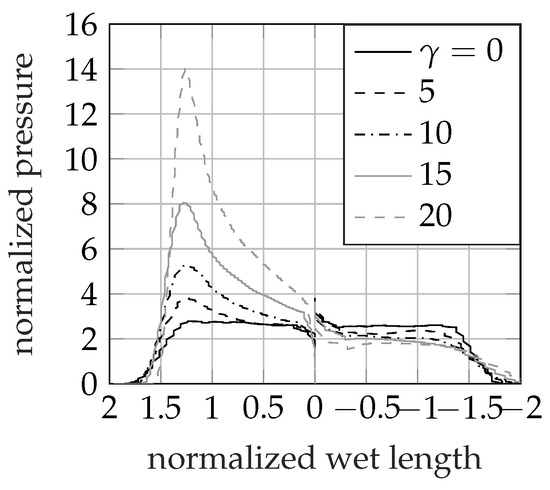
Figure 12.
Effect of the initial tilt angle on the pressure distribution on a wedge entering the water with pure vertical velocity for varying initial tilt angle.
Indeed, if the velocity is not prescribed a priori, the simulation loses the self-similarity and the solution changes over time. Figure 13 reports, as an example, the time evolution of the pressure at the fluid–structure interface of a wedge with deadrise angle entering the water with an initial tilt angle of and initial velocity of 6 m/s. The hydrodynamic pressure compares well during the initial stage of the impact but soon diverges in both sides, to eventually switch the side experiencing the higher pressure. As already mentioned before, such a difference should be ascribed to the tilt motion, which is not taken into account in the analytical model. Please note that the sudden pressure jump at the keel, the magnitude of which increases with , is a graphical artefact introduced by the normalization of the results.
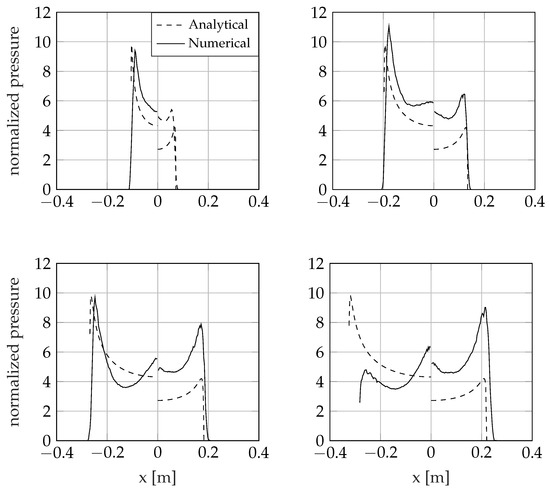
Figure 13.
Asymmetric wedge entering the water at 6 m/s with pure vertical velocity. Deadrise angle , tilt angle 5. Pressure distribution at 4, 8, 12, and 16 ms from the impact.
The presented results show that, on one side, an eventual asymmetry during the water impact does not have a remarkable effect on the impact dynamics and on the maximum impact force, since the peak force is attained in the early stage of the impact, prior to a substantial tilt motion. On the other side, the tilt motion is found to largely alter the hydrodynamic pressure distribution at the larger entry depths.
The next section presents some numerical solutions for asymmetric wedges entering the water with combined vertical and horizontal velocity to investigate the combined influence of tilt angle and horizontal component.
6. Asymmetric Wedges with Horizontal Velocity Component—
In this section, asymmetric wedges with combined vertical and horizontal impact velocities are studied, which represents a combination of the impact conditions studied in Section 4 and Section 5. The analysis considers only the cases where the advancing ratio is in the same direction of the tilt angle (left direction in Figure 1, and counter-clock wise rotation). Advancing ratio, deadrise angle, and tilt angle have been parametrically varied in the numerical analysis, but only some reference cases are reported here for brevity.
As an example, two cases representative of incipient cavity formation are presented: Figure 14 compares the numerical results and analytical predictions of the pressure over a wedge with an initial tilt angle of entering the water with vertical velocity m/s and horizontal velocity m/s. Figure 15 shows a wedge with a deadrise angle of and tilt angle of entering the water with vertical velocity m/s and horizontal velocity m/s ( = 1).
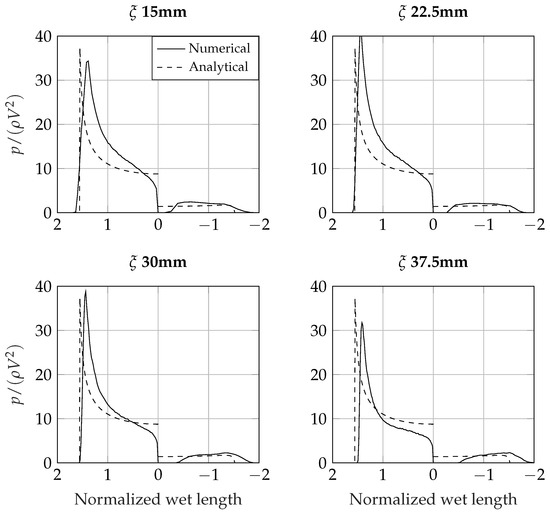
Figure 14.
Asymmetric wedge entering the water at 4 m/s (y) + 2 m/s (x). Deadrise angle , tilt angle 15.
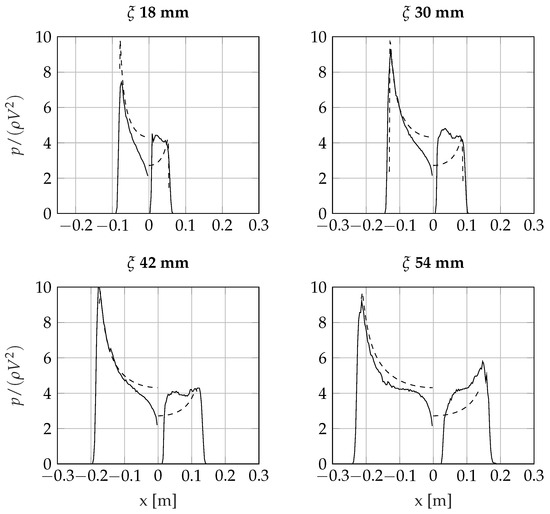
Figure 15.
Asymmetric wedge entering the water at 4 m/s (y) + 4 m/s (x). Deadrise angle , tilt angle 5.
In the case shown in Figure 15, the high horizontal velocity component induces the fluid to detach from the wedge tip, as visible in Figure 16, reporting the fluid velocity. Since air is not considered in the numerical model, the numerical solution might not represent the real behaviour of the fluid. Nevertheless, the results show that even if there is a region where the pressure drops to zero, the maximum pressure compared well with Wagner’s model, even if the overall shape changed: the maximum pressure on the leeward face is now located where the fluid reattach to the wedge rather than in the fluid jet.
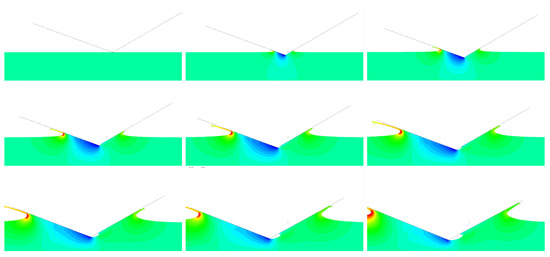
Figure 16.
Velocity field in the fluid. Asymmetric wedge entering the water with combined horizontal (4 m/s) and vertical (4 m/s) velocity. Deadrise angle , tilt angle 5.
Overall, the results show that the combination of leeward deadrise angle and advancing ratio resulting in incipient cavity formation is , and full cavity formation is attained when . These results are in line with the ones obtained for the symmetric wedges with horizontal velocity component presented in Section 4.
7. Conclusions
This work demonstrates that the proposed numerical solution scheme based on a coupled FEM–SPH approach allows for prediction of the hydrodynamic pressure during asymmetric water entry of rigid bodies and also in the case of cavity formation at the wedge vertex. The following three cases were considered: symmetric wedges entering the water with a velocity vector with components normal and tangential to the fluid surface, asymmetric wedges falling vertically, and, finally, the combination of asymmetry and a generic velocity vector. In the first scenario, the results show that the horizontal component of the velocity influences the fluid motion beneath the wedge and that a threshold value of the ratio between the horizontal and the vertical velocity components exists, leading to the onset of the cavity formation. This threshold depends on the deadrise angle. Cavity formation has an influence on the impact forces and on the tilting moment that increases significantly for advancing ratios above the threshold. On the other side, in pure vertical entry events, it is found that an asymmetry in terms of the initial tilt angle does not affect the maximum hydrodynamic load. This is very important because, as a consequence, the impact dynamics can be effectively predicted by simply introducing the tilt angle in the analytical formulations developed for symmetric impacts. However, the tilt motion alters the hydrodynamic pressure distribution at the larger entry depths. Finally, the combination of the two conditions shows that the maximum pressure is comparable to Wagner’s solution, even if the pressure distribution is very different and presents zero pressure zones. As in the symmetric case, the cavity formation presents a threshold, which, in this case, is a function of the deadrise angle and the advancing ratio. As a further step, the proposed numerical scheme can be coupled with FEM to determine the effect of asymmetry on the hydro-elastic behaviour of flexible structures.
Author Contributions
R.P. contributed to carrying out the simulations and the data analysis. He is the main writer of the paper. G.M. contributed to the redaction of the manuscript and was responsible for the supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study could be available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Von Karman, T. The Impact on Seaplane Floats, during Landing. NACA-TN-321, October 1929. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/19930081174 (accessed on 30 January 2021).
- Nikfarjam, M.; Koto, J.; Yaakob, O.B.; Seif, M.S.; Aref, A. Pressure Distribution at Water Entry of a Symmetrical Wedge. J. Ocean Mech. Aerosp. 2014, 12, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.X.; Sun, H.; He, Y.S. Numerical simulation and experimental study of water entry of a wedge in free fall motion. J. Fluids Struct. 2004, 19, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovol’skaya, Z.N. On some problems of similarity flow of fluid with a free surface. J. Fluid Mech. 2006, 36, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korobkin, A.A. Second-order Wagner theory of wave impact. J. Eng. Math. 2006, 58, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Liu, Y.; Yue, D.K.P. On the water impact of general two-dimensional sections. Appl. Ocean. Res. 1999, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistin, D.; Iafrati, A. Hydrodynamic loads during water entry of two-dimensional and axisymmetric bodies. J. Fluids Struct. 2003, 17, 643–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, C.; Troesch, A.; Perlin, M. Initial water impact of a wedge at vertical and oblique angles. J. Eng. Math. 2004, 48, 279–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korobkin, A.A. Inclined entry of a blunt profile into an ideal fluid. Fluid Dyn. 1988, 23, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seif, M.S.; Mousaviraad, S.M.; Sadathosseini, S.H. The effect of asymmetric water entry on the hydrodynamic impact. Int. J. Eng. Trans. A Basics 2004, 17, 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- Algarín, R.; Tascón, O. Hydrodynamic Modeling of Planing Boats with Asymmetry and Steady Condition. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on High Performance Marine Vehicles (HIPER 11), Naples, Italy, 18–19 September 2011; Volume 2, pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, T.; Repalle, N.; Pistani, F.; Thiagarajan, K. An experimental study of slamming impact during forced water entry. In Proceedings of the 17th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference, Auckland, New Zealand, 5–9 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Spinosa, E.; Iafrati, A. Experimental investigation of the fluid-structure interaction during the water impact of thin aluminium plates at high horizontal speed. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2021, 147, 103673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iafrati, A.; Grizzi, S. Cavitation and ventilation modalities during ditching. Phys. Fluids 2019, 31, 052101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iafrati, A.; Grizzi, S.; Olivieri, F. Experimental Investigation of Fluid–Structure Interaction Phenomena During Aircraft Ditching. AIAA J. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardi, G.; Iafrati, A. Water impact of an asymmetric floating wedge. J. Eng. Math. 2004, 49, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Duan, W.; Wu, G. Numerical simulation of oblique water entry of an asymmetrical wedge. Ocean. Eng. 2008, 35, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekin, B.S. The entry of a wedge into an incompressible fluid. J. Appl. Math. Mech. 1989, 53, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krastev, V.K.; Facci, A.L.; Ubertini, S. Asymmetric water impact of a two dimensional wedge: A systematic numerical study with transition to ventilating flow conditions. Ocean Eng. 2018, 147, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, Y.A.; Yoon, B.S. Onset of flow separation for the oblique water impact of a wedge. Phys. Fluids 2009, 21, 112103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Semenov, Y.A.; Iafrati, A. On the nonlinear water entry problem of asymmetric wedges. J. Fluid Mech. 2006, 547, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, Y.A.; Wu, G.X. Asymmetric impact between liquid and solid wedges. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2013, 469, 20120203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goman, O.G.; Semenov, Y.A. Oblique entry of a wedge into an ideal incompressible fluid. Fluid Dyn. 2007, 42, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, A.; Jalalisendi, M.; Porfiri, M. Experiments on the water entry of asymmetric wedges using particle image velocimetry. Phys. Fluids 2015, 27, 027103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.D.; Duan, W.Y.; Wu, G.X. Simulation of water entry of a wedge through free fall in three degrees of freedom. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2010, 466, 2219–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panciroli, R.; Abrate, S.; Minak, G.; Zucchelli, A. Hydroelasticity in water-entry problems: Comparison between experimental and SPH results. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panciroli, R. Water entry of flexible wedges: Some issues on the FSI phenomena. Appl. Ocean Res. 2013, 39, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panciroli, R.; Porfiri, M. Evaluation of the pressure field on a rigid body entering a quiescent fluid through particle image velocimetry. Exp. Fluids 2013, 54, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panciroli, R.; Abrate, S.; Minak, G. Dynamic response of flexible wedges entering the water. Compos. Struct. 2013, 99, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panciroli, R.; Porfiri, M. Analysis of hydroelastic slamming through particle image velocimetry. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 347, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalisendi, M.; Zhao, S.; Porfiri, M. Shallow water entry: Modeling and experiments. J. Eng. Math. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Zhao, L.; Shen, J. A modified Logvinovich model for hydrodynamic loads on an asymmetric wedge entering water with a roll motion. J. Mar. Sci. Appl. 2011, 10, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panciroli, R.; Pagliaroli, T.; Minak, G. On Air-Cavity Formation during Water Entry of Flexible Wedges. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).