Nickel Binding Affinity with Size-Fractioned Sediment Dissolved and Particulate Organic Matter and Correlation with Optical Indicators
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Sampling Site and Samples Collection
2.2. AEOM Extraction and Separation
2.3. UV/Vis and Fluorescent Measurement
2.4. Optical Indicator
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. DOC and Ni Concentrations and Mass Fractions in DOM and AEOM
3.2. [Ni]/[DOC] Ratio
3.3. DOM and AEOM Optical Indicators
3.4. Correlation between [Ni]/[DOC] Ratios and Optical Indicators
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, Y.; Wan, Y.; Camara, A.Y.; Li, H. Effects of the addition and aging of humic acid-based amendments on the solubility of Cd in soil solution and its accumulation in rice. Chemosphere 2018, 196, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Chen, M.; Schlautman, M.A.; Hur, J. Dynamic exchanges between DOM and POM pools in coastal and inland aquatic ecosystems: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551–552, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Hur, J. Pre-treatments, characteristics, and biogeochemical dynamics of dissolved organic matter in sediments: A review. Water Res. 2015, 79, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Shen, Z.; Chen, J.; Feng, C. Characterization and spacial distribution variability of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in the Yangtze Estuary. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdige, D.J.; Komada, T. Sediment pore waters. In Biogeochemistry of Marine Dissolved Organic Matter, 2nd ed.; Chapter 12; Academic Press: Burlington, VT, USA, 2015; pp. 535–577. [Google Scholar]
- Aiken, G.R.; Hsu-Kim, H.; Ryan, J.N. Influence of Dissolved Organic Matter on the Environmental Fate of Metals, Nanoparticles, and Colloids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3196–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Guo, X.; Yin, S.; Tian, C.; Li, Y.; Shen, Z. Heavy metal partitioning of suspended particulate matter–water and sediment–water in the Yangtze Estuary. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.A.; Hamilton–Taylor, J.; Bieroza, M.; Zhang, H.; Davison, W. Improving and testing geochemical speciation predictions of metal ions in natural waters. Water Res. 2014, 67, 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Houghton, E.M.; Houghton, C.J.; Guo, L. Variations in size and composition of colloidal organic matter in a negative freshwater estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, J.; Lee, B.-M.; Shin, K.-H. Spectroscopic characterization of dissolved organic matter isolates from sediments and the association with phenanthrene binding affinity. Chemosphere 2014, 111, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Bravo, A.G.; Skyllberg, U.; Björn, E.; Wang, D.; Yan, H.; Green, N.W. Influence of dissolved organic matter (DOM) characteristics on dissolved mercury (Hg) species composition in sediment porewater of lakes from southwest China. Water Res. 2018, 146, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baken, S.; Degryse, F.; Verheyen, L.; Merckx, R.; Smolders, E. Metal complexation properties of freshwater dissolved organic matter are explained by its aromaticity and by anthropogenic ligands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2584–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, S.Y.; Kim, S.Y. Hydroclimatic controls on dissolved organic matter (DOM) characteristics and implications for trace metal transport in Hwangryong River Watershed, Korea, during a summer monsoon period. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2007, 21, 3025–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Ma, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, F.; Han, X.; Li, M.; Ni, J. Optical property of dissolved organic matters (DOMs) and its link to the presence of metal ions in surface freshwaters in China. Chemosphere 2017, 188, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amery, F.; Degryse, F.; Degeling, W.; Smolders, E.; Merckx, R. The copper-mobilizing-potential of dissolved organic matter in soils varies 10-fold depending on soil incubation and extraction procedures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2277–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amery, F.; Degryse, F.; Cheyns, K.; De Troyer, I.; Mertens, J.; Merckx, R.; Smolders, E. The UV-absorbance of dissolved organic matter predicts the fivefold variation in its affinity for mobilizing Cu in an agricultural soil horizon. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 59, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Fujii, M.; Terao, K.; Jiwei, R.; Lee, Y.P.; Yoshimura, C. Correlations between aromaticity of dissolved organic matter and trace metal concentrations in natural and effluent waters: A case study in the Sagami River Basin, Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yue, D.; Liu, J.; Nie, Y. Size fractionation of organic matter and heavy metals in raw and treated leachate. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2527–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Wu, W.; Liu, H. Metal sorption on soils as affected by the dissolved organic matter in sewage sludge and the relative calculation of sewage sludge application. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, K.; Chon, K.; Cho, J. Characterization of size fractionated dissolved organic matter from river water and wastewater effluent using preparative high performance size exclusion chromatography. Org. Geochem. 2017, 103, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, A.J.; Vale, P.; Whelan, J.; Constantino, C.; Dotro, G.; Campo, P.; Cartmell, E. Distribution of trace metals (Cu, Pb, Ni, Zn) between particulate, colloidal and truly dissolved fractions in wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.-H.; Chiu, T.-P.; Huang, W.-S.; Chen, T.-C.; Yeh, Y.-L. Cadmium (Cd) and Nickel (Ni) Distribution on Size-Fractioned Soil Humic Substance (SHS). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Xiao, M.; Mostofa, K.M.; Xu, S.; Wang, Z. Spatial Variations of Trace Metals and Their Complexation Behavior with DOM in the Water of Dianchi Lake, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, A.M.; Kraus, T.E.; Pellerin, B.A.; Fleck, J.A.; Downing, B.D.; Bergamaschi, B.A. Optical properties of dissolved organic matter (DOM): Effects of biological and photolytic degradation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 1015–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, M.; Yang, L.; Hur, J. Lipid biomarkers and spectroscopic indices for identifying organic matter sources in aquatic environments: A review. Water Res. 2017, 112, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Hur, J. Utilization of UV-Vis spectroscopy and related data analyses for dissolved organic matter (DOM) studies: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilainen, A.; Gjessing, E.T.; Lahtinen, T.; Hed, L.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. An overview of the methods used in the characterisation of natural organic matter (NOM) in relation to drinking water treatment. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birdwell, J.E.; Engel, A.S. Characterization of dissolved organic matter in cave and spring waters using UV–Vis absorbance and fluorescence spectroscopy. Org. Geochem. 2010, 41, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguet, A.; Vacher, L.; Relexans, S.; Saubusse, S.; Froidefond, J.-M.; Parlanti, E. Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderibigbe, D.O.; Giwa, A.-R.A.; Bello, I.A. Characterization and treatment of wastewater from food processing industry: A review. Imam J. Appl. Sci. 2017, 2, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopal, R.; Saady, N.M.C.; Torrijos, M.; Thanikal, J.V.; Hung, Y.-T. Sustainable agro-food industrial wastewater treatment using high rate anaerobic process. Water 2013, 5, 292–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, J.; Lee, D.-H.; Shin, H.-S. Comparison of the structure, spectroscopic and phenanthrene binding characteristics of humic acids from soils and lake sediments. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, J.R.; Stubbins, A.; Ritchie, J.D.; Minor, E.C.; Kieber, D.J.; Mopper, K. Absorption spectral slopes and slope ratios as indicators of molecular weight, source, and photobleaching of chromophoric dissolved organic matter. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weishaar, J.L.; Aiken, G.R.; Bergamaschi, B.A.; Fram, M.S.; Fujii, R.; Mopper, K. Evaluation of specific ultraviolet absorbance as an indicator of the chemical composition and reactivity of dissolved organic carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4702–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapworth, D.J.; Kinniburgh, D. An R script for visualising and analysing fluorescence excitation–emission matrices (EEMs). Comput. Geosci. 2009, 35, 2160–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Her, N.; Amy, G.; McKnight, D.; Sohn, J.; Yoon, Y. Characterization of DOM as a function of MW by fluorescence EEM and HPLC-SEC using UVA, DOC, and fluorescence detection. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4295–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrin, A.; Roulier, J.-L.; Coquery, M. Colloidal and truly dissolved metal (oid) fractionation in sediment pore waters using tangential flow filtration. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 31, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zou, L.; Guan, D.; Li, W.; Jiang, H. Molecular weight-dependent spectral and metal binding properties of sediment dissolved organic matter from different origins. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.-S.; Huang, W.-S.; Hsu, L.-F.; Yeh, Y.-L.; Chen, T.-C. Fluorescence of Size-Fractioned Humic Substance Extracted from Sediment and Its Effect on the Sorption of Phenanthrene. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, T.A.; Loi, V.D.; Thao, T.T. Partition of heavy metals in a tropical river system impacted by municipal waste. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 1907–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wen, B.; Zhang, S.; Shan, X.-Q. Distribution of heavy metals in water and soil solutions based on colloid-size fractionation. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2003, 83, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenming, X.; Zhang, S.; Lin, R.; Mingyue, Y.; Weiming, S.; Zhang, H.; Weihua, L. Evaluating soil dissolved organic matter extraction using three-dimensional excitation-emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 968–973. [Google Scholar]
- Ilina, S.M.; Lapitskiy, S.A.; Alekhin, Y.V.; Viers, J.; Benedetti, M.; Pokrovsky, O.S. Speciation, size fractionation and transport of trace elements in the continuum soil water–mire–humic lake–river–large oligotrophic lake of a Subarctic watershed. Aquat. Geochem. 2016, 22, 65–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yu, G.; Yang, L.; Jiang, H. Combination of two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy and parallel factor analysis to characterize the binding of heavy metals with DOM in lake sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 263, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
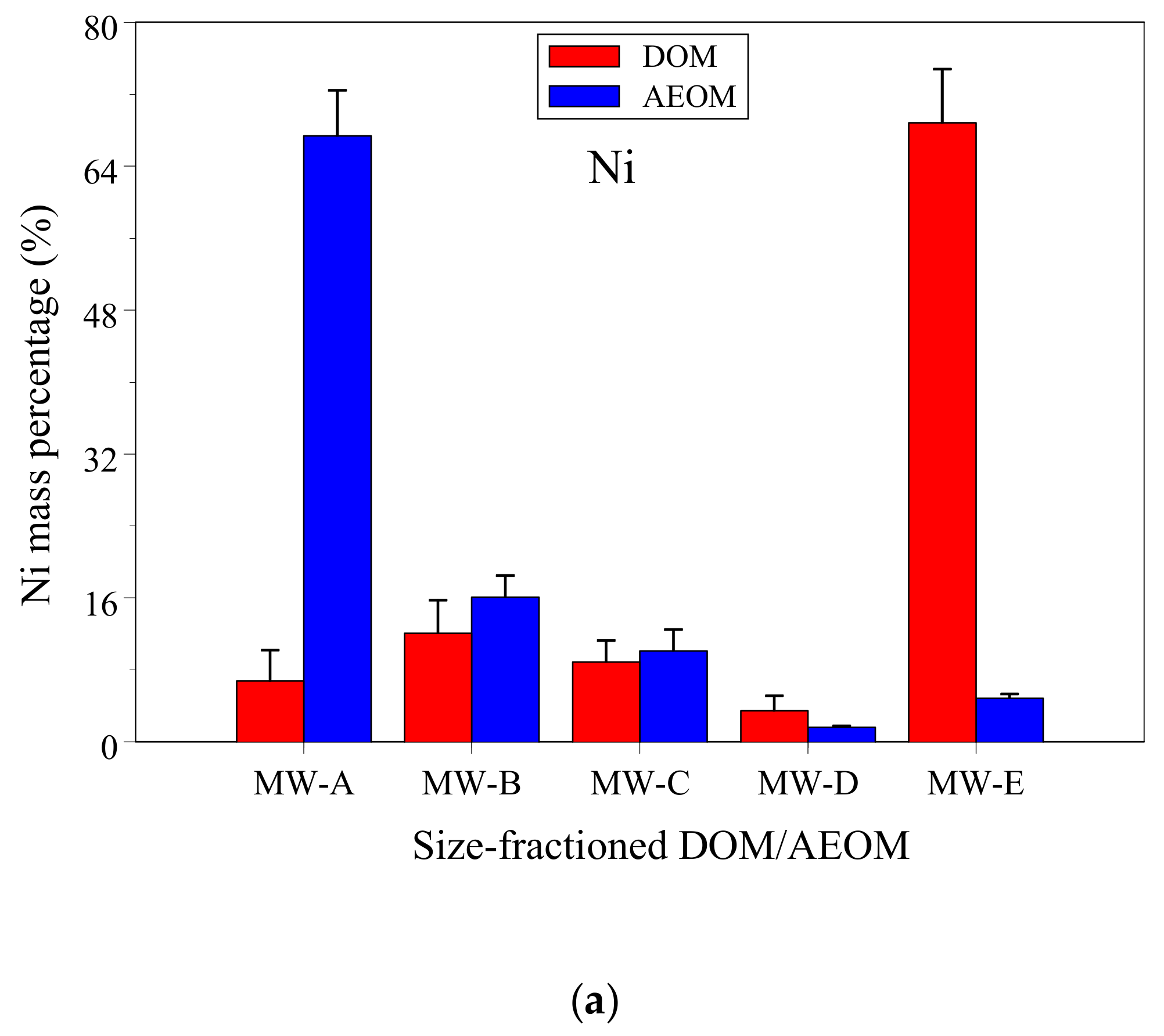
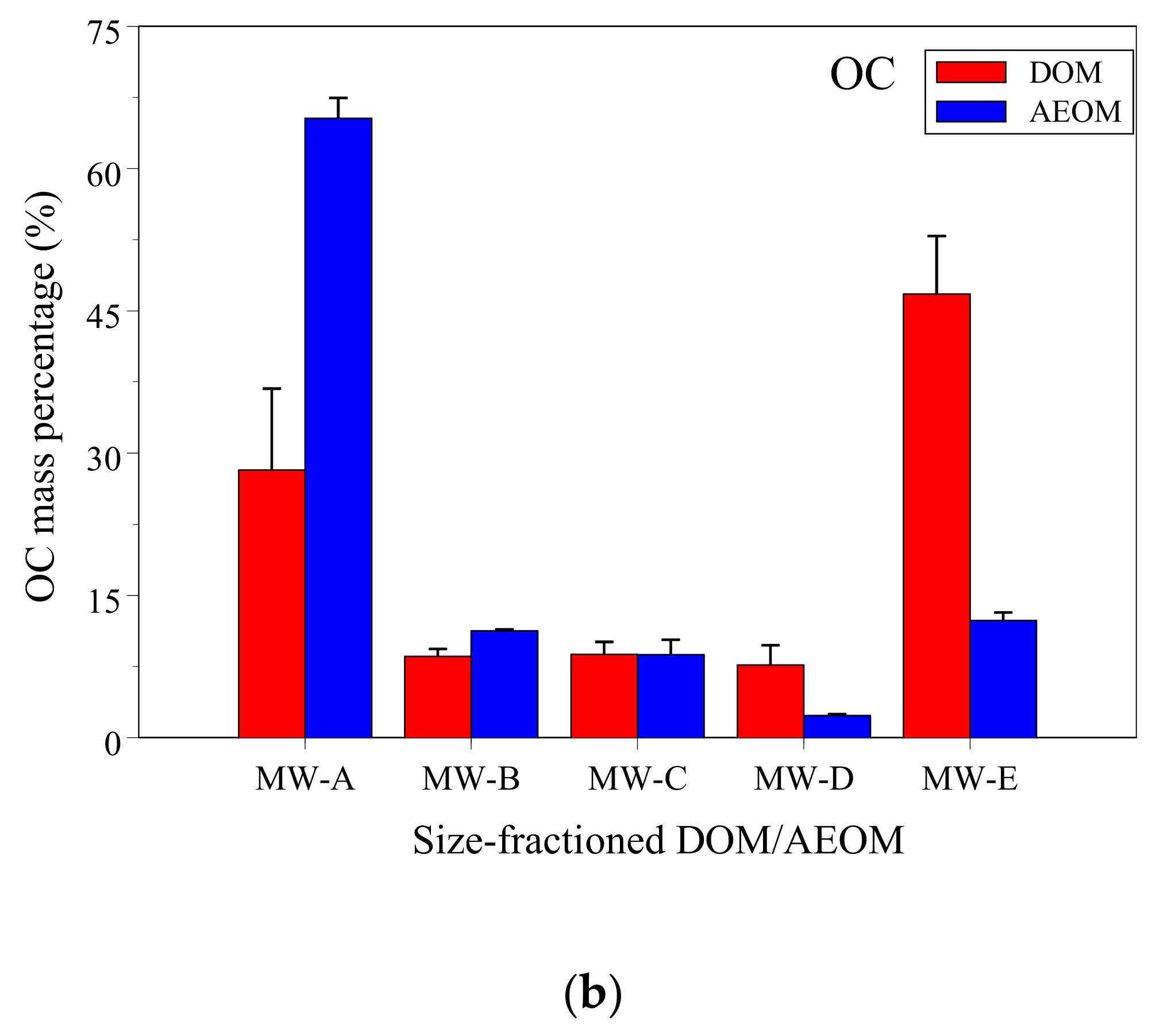
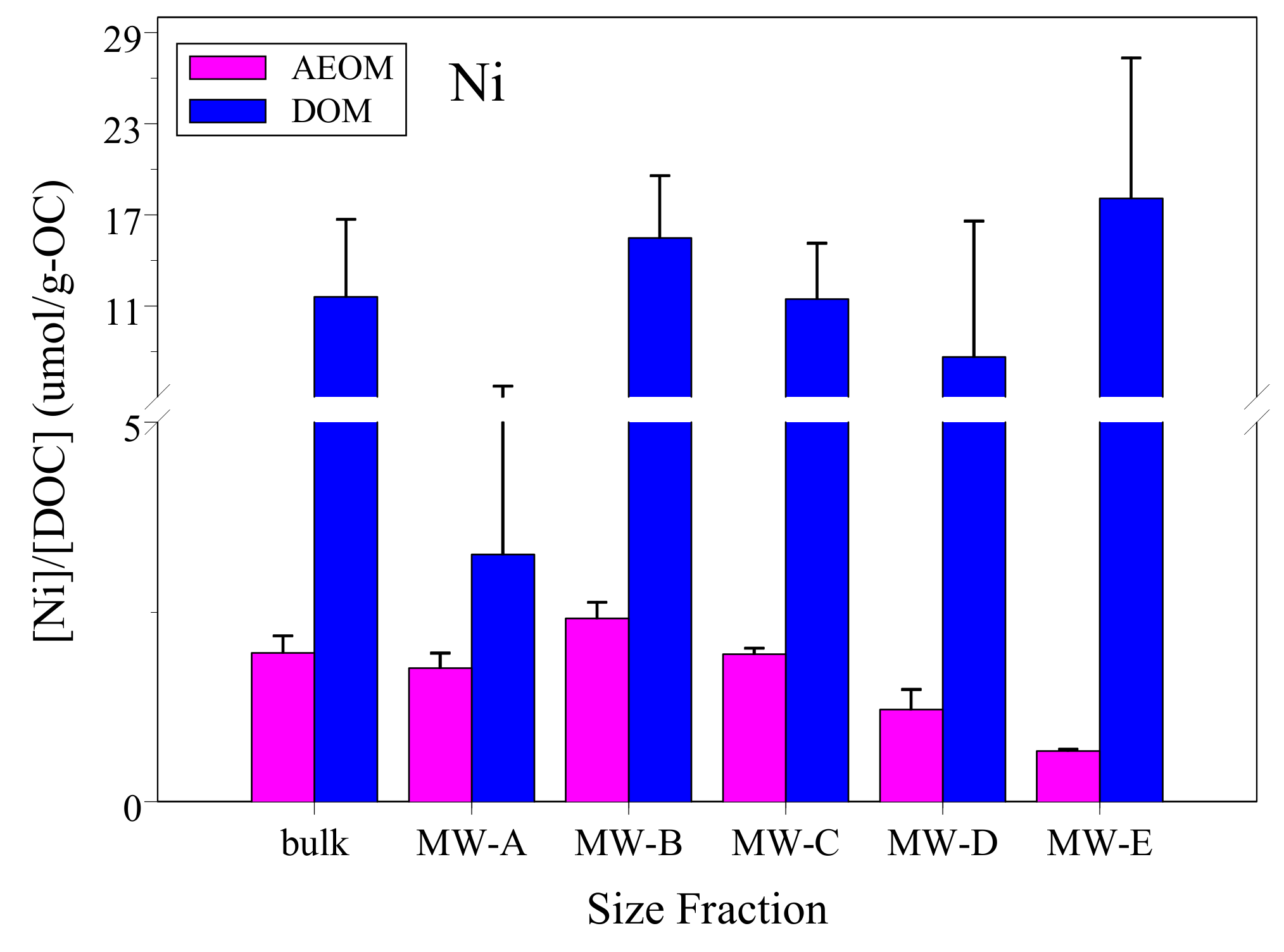

| Samples | DOM | AEOM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOC (mg/L) | Ni (μg/L) | DOC (mg/L) | Ni (µg/L) | |
| Bulk | 8.3 ± 0.4 a | 5.56 ± 2.16 | 739 ± 33 | 85 ± 7 |
| MW-A | 24.8 ± 6.9 | 4.49 ± 3.77 | 5040 ± 231 | 520 ± 82 |
| MW-B | 8.4 ± 0.8 | 7.56 ± 1.75 | 966 ± 3 | 137 ± 12 |
| MW-C | 9.6 ± 1.6 | 6.23 ± 1.49 | 834 ± 141 | 95 ± 19 |
| MW-D | 9.3 ± 2.4 | 3.46 ± 3.44 | 247 ± 16 | 17 ± 3 |
| MW-E | 6.3 ± 1.0 | 6.71 ± 3.96 | 145 ± 9 | 6.0 ± 0.0 |
| SUVA254 | FI | BIX | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SUVA254 | −0.93 *** | −0.85 *** | |
| FI | −0.41 | 0.92 *** | |
| BIX | −0.31 | −0.03 |
| Samples | SUVA254 | FI | BIX |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Ni]/[DOC]AEOM | 0.87 *** | −0.87 *** | −0.92 *** |
| [Ni]/[DOC]DOM | −0.13 | 0.40 | 0.17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng-Wen, C.; Liang-Fong, H.; Hsiang-Chun, T.; Yung-Yu, L.; Wei-Shiang, H.; Ting-Chien, C. Nickel Binding Affinity with Size-Fractioned Sediment Dissolved and Particulate Organic Matter and Correlation with Optical Indicators. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8995. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10248995
Cheng-Wen C, Liang-Fong H, Hsiang-Chun T, Yung-Yu L, Wei-Shiang H, Ting-Chien C. Nickel Binding Affinity with Size-Fractioned Sediment Dissolved and Particulate Organic Matter and Correlation with Optical Indicators. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(24):8995. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10248995
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng-Wen, Chuang, Hsu Liang-Fong, Tsai Hsiang-Chun, Liu Yung-Yu, Huang Wei-Shiang, and Chen Ting-Chien. 2020. "Nickel Binding Affinity with Size-Fractioned Sediment Dissolved and Particulate Organic Matter and Correlation with Optical Indicators" Applied Sciences 10, no. 24: 8995. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10248995
APA StyleCheng-Wen, C., Liang-Fong, H., Hsiang-Chun, T., Yung-Yu, L., Wei-Shiang, H., & Ting-Chien, C. (2020). Nickel Binding Affinity with Size-Fractioned Sediment Dissolved and Particulate Organic Matter and Correlation with Optical Indicators. Applied Sciences, 10(24), 8995. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10248995




