Simple Summary
We investigated the pathogenicity, antimicrobial resistance and multilocus sequence types of Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serovar Enteritidis isolated from fresh chicken meat, ready-to-eat chicken meat as well as from cloacal swabs of live chickens in some selected locations within the central region of peninsular Malaysia. After culture and serotype confirmation of the Salmonella isolates, the genomic DNA was extracted and whole-genome sequencing was conducted using the NextSeq 550 System (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). In silico serotypes were determined with the aid of SeqSero WGS in silico software version 2, while multilocus sequence types, as well as virulence and antimicrobial resistance determinants, were all determined using the BioEasy Epinod pipeline. The S. Enteritidis isolates were found to harbour several virulence genes, with multidrug-resistance characteristics. The results of this investigation indicate the potential risks both humans and livestock are exposed to due to this foodborne pathogen.
Abstract
This study was undertaken to determine the virulence, antimicrobial resistance and molecular subtypes of Salmonella in the Central Region of Peninsular Malaysia. A total of 45 Salmonella Enteritidis were detected from live chicken (cloacal swab), and chicken products (fresh and ready-to-eat meat) samples upon cultural isolation and serotyping. Similarly, an antimicrobial susceptibility test based on the Kirby Bauer disk diffusion method as well as antimicrobial resistance AMR genes, virulence determinants and multilocus sequence typing (MLST) typing were conducted after the Whole Genome Sequencing and analysis of the isolates. The results indicate that sequence types ST1925 (63.7%), and ST11 (26.5%) were the predominant out of the seven sequence types identified (ST292, ST329, ST365, ST423 and ST2132). The phenotypic antimicrobial profile corresponds to the genotypic characterization in that the majority of the isolates that exhibited tetracycline, gentamycin and aminoglycoside resistance; they also possessed the tetC and blaTEM β-Lactam resistance genes. However, isolates from cloacal swabs showed the highest number of resistance genes compared to the chicken products (fresh and ready-to-eat meat) samples. Furthermore, most of the virulence genes were found to cluster in the Salmonella pathogenicity island (SPI). In this study, all the isolates were found to possess SPI-1, which codes for the type III secretion system, which functions as actin-binding proteins (SptP and SopE). The virulence plasmid (VP) genes (spvB, spvC) were present in all genotypes except ST365. The findings of this study, particularly with regard to the molecular subtypes and AMR profiles of the Salmonella Enteritidis serotype shows multidrug-resistance features as well as genetic characteristics indicative of high pathogenicity.
1. Introduction
The Malaysian Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance (MyAp-AMR 2017–2021) was established to aggressively address the threat posed by the emergence of antimicrobial resistance among pathogens in the country. Among their activities was to study strains from human infections, food-producing animals, and raw retail meats and aquaculture [1]. This is a follow-up to the already functional National Surveillance of Antibiotic Resistance (NSAR) program which has been active in Malaysia since 1988 [2]. The MyAp-AMR program is aimed at controlling the emergence and further spread of AMR, by educating the relevant stakeholders in the health industry particularly the healthcare administrators, and the livestock and aquaculture subsector on the dangers and public health importance of AMR [1]. Among the priority pathogens are Salmonella, Campylobacter, Klebsiella, Staphylococcus, Escherichia coli and Streptococcus, among a host of other important foodborne pathogens [1]. The program integrated the National Surveillance and a “One Health” approach to determine the magnitude of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria spreading through the food chain that eventually result in diseases in humans and loss in productivity in livestock.
Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serovar Enteritidis is a serotype of global public health significance [3]. It is one of the most common strain responsible for human infection worldwide second to S. Typhimurium [4]. Infections are usually characterized by mild self-limiting gastroenteric manifestations. However, in severe cases the bacteria can cause meningoencephalitis, septic arthritis and other extraintestinal illnesses in infants and immunocompromised adults [5]. In resource-poor countries, S. Enteritidis is an important cause of morbidity and mortality in children. It is also frequently incriminated in foodborne outbreaks [6]. In recent years, the world has been witnessing the emergence of invasive nontyphoidal Salmonella lineages with an extended multidrug-resistance range [7,8,9]. The emergence, although variable, represents a major public health concern, especially in Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa [10,11,12].
Molecular typing of Salmonella has proven to be an important infection control tool as it helps in monitoring the prevalence of specific strains in a cluster of unrelated outbreaks or within human healthcare institutions. It also provide information on the genetic relatedness of strains that are useful for surveillance as well as during an epidemiological investigation of outbreaks [13]. Two of the most popular molecular typing methods used in Salmonella are the Pulse Field Gel Electrophoresis (PFGE) and the Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST). Although both techniques are robust and reliable, PFGE requires rigorous standardization protocols; while MLST can be used to generate unambiguous data from different laboratories and can be used to study evolutionary relationships between isolates across the globe [14,15]. Whole-genome MLST on the other hand can be used to generate isolate-specific genetic fingerprints suitable for assessing epidemiological relatedness based on single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), as well as insertions and deletions [15].
The isolation of Salmonella and other foodborne pathogens from human clinical samples, animals and food of animal origin have been consistently conducted and its trends monitored by the Malaysian Ministry of Health in collaboration with the Department of Veterinary Service, Malaysia. Recent reports by the National Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance NSAR indicate that there has been an increase in the antibiotic resistance profile of Salmonella spp., with multiple resistance (multidrug-resistance—MDR) to ciprofloxacin (3.4%) and ampicillin (25%) in humans [16]. Similarly, investigations conducted by the Department of Veterinary Services Malaysia (2013/2014) to determine the prevalence and antimicrobial patterns of Salmonella isolates from chicken meat within the Central region of Peninsular Malaysia revealed a high prevalence of Salmonella contamination with a variety of antimicrobial resistance profiles including MDR phenotypes among the Salmonella isolates [1].
This study was undertaken to determine the virulence and antimicrobial resistance profile of Salmonella Enteritidis isolated from chicken and chicken products in Malaysia. It also sought to determine the serotype diversity of the isolates using Whole Genome Sequencing data. The results will benefit the current prevention and control efforts of the Malaysian Government by strengthening the knowledge and evidence base concerning the status of Salmonella in the sampled locations, with particular emphasis on S. Enteritidis which is one of the most prevalent strains causing invasive salmonellosis globally.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolates
The isolates used in this study were obtained from stock cultures from the Department of Veterinary Services (DVS) and Food Safety and Quality Division laboratories, Ministry of Health. They were isolated from faecal swabs, and fresh/ready-to-eat chicken meats (food) samples collected from April 2016 to November 2018, as part of the Salmonella collections for the National AMR surveillance program. The samples were obtained within the central region of Peninsular Malaysia that comprises the states of Selangor and Melaka. The faecal swabs were collected from poultry farms, while the chicken products (fresh meat samples and ready-to-eat chicken) were collected from retail stores and food vendors, respectively.
The 45 Salmonella isolates used in this study were obtained from ready-to-eat chicken meat at retail markets (n = 7), raw chicken meat (n = 11), and (n = 27) cloacal swabs. The procedure for the culture and isolation used in all the laboratories entails collecting sterile swabs, or 1 g of homogenized meat sample to be inoculated in 9 mL of buffered peptone water and incubated at 37 °C for 18–24 h [17]. Subsequently, 100 µL of the pre-enriched, buffered peptone water was transferred into another 10 mL of Rappaport-Vassiliadis (RVS) broth (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK) and incubated at 41 °C for 24 ± 2 h for selective enrichment. This was then followed by streaking of the RVS broth enrichment culture onto xylose lysine deoxycholate (XLD) agar (Oxoid, UK) and Brilliant Green agar (Oxoid, UK), and the plates were incubated for 24–48 h at 37 °C. The resultant presumptive Salmonella colonies grown on the XLD and Brilliant green agar (BGA) plates were then subcultured on nutrient agar plates for isolation of distinct colonies. Biochemical characterization (catalase, urease, SIM) and serotyping (slide agglutination with O and H antigen-specific sera) were performed at the District Laboratories under the jurisdiction of the Department of Veterinary Services, Malaysia, based on the OIE standard method. Additionally, Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922) was included in the study as a negative control.
2.2. Phenotypic Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
The S. Enteritidis positive isolates were subjected to an antimicrobial susceptibility test by the Kirby–Bauer disc diffusion method on Mueller Hinton agar (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) using nine antibiotic discs (Oxoid LTD, UK): ampicillin (Amp), chloramphenicol (C), gentamicin (CN), streptomycin (S), sulfamethazine/trimethoprim (SXT), tetracycline (TE), ceftiofur (EFT), cefotaxime (CTX), and ciprofloxacin (CIP). These drugs are part of the Malaysia Ministry of Health Medicines Formulary (Formulari Ubat Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia) and are among the drugs commonly used in healthcare clinics in Malaysia [18]. Results were interpreted following the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute guidelines (CLSI 2018, 4th Ed) [19] while Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 was used as control.
2.3. Whole Genome Sequencing
About 2 mL of an overnight culture of the Salmonella isolates were centrifuged at 5000× g for 10 min and the genomic DNA was extracted from the resultant pellet using QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (Qiagen). The Nextera™ DNA Flex Library Prep Kit was used for the preparation of the genomic libraries and the Whole Genome Sequencing was performed on the NextSeq 550 System (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). The good-quality sequencing reads were then assembled using SPAdes (SPAdes version 3.9.0) to obtain contigs [20]. All the assembled contig sequences from the 45 Salmonella isolates as well as Escherichia coli K12 as control were subjected to comparative studies using the EPInod pipeline developed by BioEasy Sdn Bhd.
2.4. In Silico Serotype Prediction Using SeqSero
The serotype of the isolates was determined with the aid of SeqSero WGS in silico software version 2. The software allows for the serotype prediction from raw reads and genome assemblies. The software uses a k-mer-based algorithm which allows for the rapid serotype prediction from WGS data, and is built with additional sequence markers for the identification of Salmonella species and subspecies.
2.5. Determination of Salmonella Virulence and Resistance Determinants
The genome virulence factor analysis against the major Salmonella virulence factors was performed via the BLAST program (BLAST 2.5.0+) against the virulence factor database (VFDB) with the aid of EPInod software (BioEasy, Sdn Bhd). The genome comparison analysis was streamlined via the Abricate program against ResFinder and Card (Abricate–Version 0.8). The assembled contig sequences were subjected to comparative analyses using the EPInod, which included the Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST), and virulence factor (VF) detection. The presence of the Salmonella virulence determinants was investigated by targeting some major gene determinants: the cell invasion protein, transmembrane proteins, secretion-system effector proteins and the putative transcriptional regulator protein, and in addition, the immune evasion, host-colonization factor and the type 1 fimbria adherence determinant [21]. Similarly, virulence genes were identified by mapping the Illumina raw reads against chromosomal and plasmid virulence genes deposited in the Virulence Factor Database for Salmonella (VFDB).
2.6. Multilocus Sequence Typing—MLST
The Multilocus Sequence Typing and characterization was performed after PCR amplification and sequencing using the reported conventional primers targeting the seven housekeeping genes: aroC, dnaN, hemD, hisD, purE, sucA, and thrA [22]. The sequence type for each isolate was assigned based on the set of alleles derived from the seven loci. The goeBURST Minimum Spanning Tree expansion was also used to visualize the possible evolutionary relationships between isolates using the PHYLOViZ software v2.0 online software [23].
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles
Twenty-nine (62.3%) of the 45 S. Enteritidis isolates were found to be resistant to one or more antimicrobials tested, while sixteen (37.7%) were susceptible to all the antimicrobials tested. The percentage of resistance to each of the tested antimicrobial drugs is presented in Table 1. Samples that showed multidrug resistance against Amp, CN, TE and S were all obtained from cloacal swabs from poultry farms in Selangor. However, 54% of the isolates exhibiting tetracycline resistance were from cloacal samples from poultry farms in Melaka.

Table 1.
S. Enteritidis isolates showing resistance to antimicrobial drugs tested.
3.2. Phenotypic and WGS Serotype Prediction
The traditional Kauffman–White scheme for serotyping found that all 45 isolates belong to the S. Enteritidis serogroup based on the O and H antigens (Table 2). While the SeqSero2 (SeqSero2 v1.1.0) serotype prediction showed 89.9% concordance with the traditional method while being discordant on the serotypes of four isolates. The SeqSero2 identified the four isolates of S. Ohio (S72-cloacal swab), S. Weltevreden (S77-cloacal swab) and S. Kentucky (S81-cloacal swab), while S63 (cloacal swab) was found to have the antigenic formula (8: z4, z24) which corresponds to either S. Albany or S. Duesseldorf, because both of these share the same antigenic formula as detected by the SeqSero2 software. Furthermore, the WGS in silico analysis identified one unique isolate with antigenic formula I 4:b:-(S87-cloacal swab), which is not listed in the Kauffmann White Scheme.

Table 2.
In silico WGS and phenotypic Salmonella serotypes.
3.3. Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Virulence Factor Determinants
The Whole Genome Sequence data from the positive Salmonella isolates were examined for the possession of antimicrobial resistance genes and virulence factor determinants. Overall, the most common resistance genes detected were pmr c, pmr e, pmr f and aac (6’)-Iy (Table 3). Similarly, the Salmonella isolates were also screened for virulence genes. A total of 122 virulence-factor determinants were detected in this study using the WGS. Notable among the common Salmonella virulence genes detected are plasmid-encoded fimbriae chaperone protein PefD, type III secretion-system effector SpvC, phosphothreonine lyase Spv, resistance to complement killing Rck, type III secretion-system effector SseK1, SPI-2-encoded T3SS, as well as InvA, and Spa, among others.

Table 3.
Distribution of antimicrobial resistance AMR genes in Salmonella Enteritidis isolates based on the antimicrobial susceptibility test AST.
3.4. Multilocus Sequence Typing of S. Enteritidis Isolates
The MLST analysis identified seven sequence types based on the MLST database results (Table 4). The most commonly detected allelic profiles were ST1925 (63%) and ST11 (26.5%). Other sequence types identified are ST292, ST329, ST365, ST423 and ST2132, which were observed in each of the three categories of samples studied (ready-to-eat chicken meat, fresh chicken meat, and cloacal swab). In the goEBURST dataset, lowering the level to seven results in detachment into five distinct groups with three singletons (STs 2132, 329 and 423), while STs 2132, 292 and 365 clustered together (Figure 1).

Table 4.
MLST sequence types of Salmonella Enteritidis isolates.
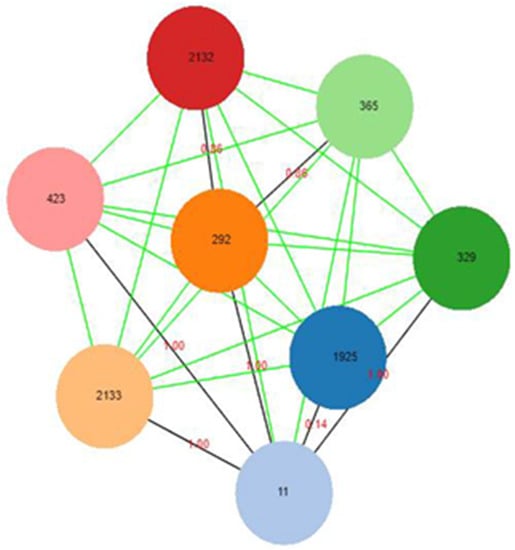
Figure 1.
MLST Clonal Complex defined by goeBURST for Salmonella Enteritidis isolates. Each coloured node represents a clone in relation to their absolute distance, with ST11 being more closely related to ST1925.
This implies that the connection between the detached nodes had at least seven differences. Similarly, the sample data set was used to generate a graph with an nLV (N Locus Variant) of level seven, which identifies sets of closely related nodes; and the results indicate that all the allele profiles with distances equal or below six were all connected.
4. Discussion
To date, serological typing of Salmonella remains the most popular tool for characterization during surveillance and epidemiological investigations [24]. However, molecular techniques are beginning to gain popularity as substitutes to the traditional Kauffman–White method. In this study, both the traditional and molecular (SeqSero2) methods were employed for the serotyping of the Salmonella isolates. The SeqSero2 was found to be a good alternative to the phenotypic serotyping, with 89.9% of the results in full agreement. This finding conforms with previous reports by Diep et al. and Ferrato et al. [24,25]. Both Diep et al. and Ferrato et al. used Check & Trace Salmonella™, a commercial DNA Microarray System to determine serotype designation of Salmonella isolates from clinical samples as well as the WGS-based serotype prediction tool (SeqSero) utilized in this study, and suggested that SeqSero is a very reliable replacement for the traditional serotyping method where WGS is implemented. The in silico method in this investigation showed improved performance over the traditional method by accurately predicting the antigenic formulae of the Salmonella serotypes in a manner consistent with the traditional phenotypic serotyping, albeit with some disparity. However, the claim for superiority for SeqSero2 can be affected by the fact that the same antigenic formula can be shared by strains from different subspecies, as observed with Albany and Dusseldorf (8: z4, z24) in this study. Similarly, SeqSero was not able to identify some Salmonella subspecies accurately because they differ only by minor epitopes which were often not available in the software [24]. Nevertheless, in comparison, this technique is much faster than the traditional phenotypic method, which usually requires a couple of days to complete or even longer when dealing with rare serotypes.
The emergence of multiple-drug-resistant, and highly pathogenic S. Enteritidis, signifies a serious threat to public health and food safety. Hence, in addition to identifying the serotypes, we sought to understand the genetic variability and virulence characteristics of the Salmonella isolates. This is because S. Enteritidis is a major zoonotic pathogen that constitutes a serious public health problem globally, especially with the rapid development and emergence of multidrug-resistant strains [5,26]. The strain is a common food contaminant, and has been incriminated in several outbreaks in Malaysia in recent years [11]. Moreover, human infections are being repeatedly reported, with chicken and chicken products being one of the most common sources of infection [11,27,28]. Therefore, it has become paramount to investigate and understand the potential role of chicken (meat and meat products) in the dissemination of Salmonella species.
The phenotypic AMR analysis showed that isolates from ready-to-eat meat samples (chicken meat products) were resistant to only tetracycline (5/7), while isolates from raw chicken meat and cloacal swab samples were resistant to multiple antimicrobials including tetracycline (4/11; 11/27), and ampicillin (0/11; 6/27) predominating. While varying levels of AMR resistance was observed among the isolates in both Selangor and Melaka, it is interesting to note that all the isolates that exhibited multidrug resistance were isolated from cloacal swabs samples collected from poultry farms in Selangor, with the majority of the isolates from Melaka showing resistance to tetracycline. This finding is similar to the findings of Ibrahim et al., where they investigated the prevalence of antimicrobial resistant Salmonella in the East Coast of the peninsular Malaysia [29]. S. Enteritidis isolates in Selangor have been reported to exhibit high resistance against several antimicrobials including penicillin, erythromycin and vancomycin [30,31,32,33]. However, in this study, resistance was observed against ampicillin, gentamicin, and tetracycline. Even though numerous potential vehicles of transmission for Salmonella are abound, commercial chicken meat has been identified as one of the most crucial food vehicles for these organisms [34]. The result from this study is therefore a further testament to the role of poultry in the spread of resistant Salmonella in Malaysia.
Animals and foods of animal origin, especially if prepared under poor hygienic conditions, can serve as a source of Salmonella. Therefore, it is not uncommon to observe a similar frequency of AMR from different sources, as observed in the present study. All the isolates from the ready-to-eat chicken meat in Selangor showed resistance to only tetracycline, except for one isolate that showed resistance to sulfamethazine/trimethoprim. Many studies have observed the rate at which foodborne pathogens are acquiring resistance to tetracycline and other commonly used antimicrobials in the food chain, which is a cause for concern. In the same vein, Zakaria et al. have also reported a high rate of tetracycline resistance among Salmonella isolated from poultry meat [8]. S. Enteritidis isolates have also been reported to show increasing resistance to the commonly used antimicrobials in livestock. In this study, the highest level of resistance was observed with tetracycline, followed by ampicillin. Although, we cannot say exactly what was responsible for the resistance observed in this study, since our analysis does not include determining the mechanism of the resistance. Nonetheless, previous studies have reported that widespread development of resistance against tetracycline is thought to be the result of pumping of the drug out of the extracellular space before it reaches its site of activity or due to changes in cellular permeability [35]. This is similar to an earlier report by Ngoi et al. in Malaysia, where 51% and 52% resistance was observed for tetracycline and streptomycin, respectively [36]; while a considerably low resistance was observed for CN, SXT, and S. This may imply that the drugs (gentamicin, sulfamethazine/trimethoprim, and streptomycin) may still have considerable activity against Salmonella as observed in the present study. On the other hand, the high level of resistance observed for tetracycline, ampicillin and streptomycin is in contrast to a similar study conducted in India, where the absence or low rate of resistance to ampicillin, and tetracycline was recorded [37]. Furthermore, relatively low resistance to CTX and other third-generation cephalosporins was found in the present study. This outcome confirms earlier reports from Malaysia and China [36,38].
The phenotypic and genotypic AMR profiling in the present study corresponds with the tetracycline resistance gene (tetC), the aac (6’) that confers resistance to aminoglycosides including gentamicin and the blaTEM β-lactam resistance gene. In each of the aforementioned resistance genes, isolates from cloacal swabs showed the highest amount of resistance followed by raw chicken meat and ready-to-eat meat. As earlier mentioned, S. Enteritidis is an enteric pathogen, which implies that animal faeces is always going to be an important source. Animals acquire infection by eating materials (e.g., feed, water, pasture grass) contaminated with faeces of other infected animals. Additionally, the level of Salmonella in livestock varies depending on the endemicity, production system and whether adequate control measures are in place. This result agrees with Kagambega et al. who detected a high prevalence of S. Enteritidis in the production of animals slaughtered for human consumption [39]. However, many discordant results were also recorded with the genetic evaluation proving to be superior and more robust compared to the phenotypic characterizations. While none of the isolates was positive for the mcr colistin resistance gene, the detection of the Pmrcef genes which are responsible for the mediation of resistance to colistin should be worrisome [26]. The pmrA-activated pmrC gene encodes an inner membrane protein that is required for the incorporation of phosphoethanolamine into lipid A and for polymyxin B resistance [40]. Colistin is a highly potent drug for the treatment of the majority of the multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria [41]. It is considered the last-line choice of drug for the management of severe infection due to Gram-negative bacteria. Therefore, the emergence of resistance is viewed as a serious health problem. The presence of AMR genes dfrA15, sul1, sul2, aadA1, aadA2, CpxR, floR and qnr in these study isolates, have earlier been reported in S. Enteritidis [42,43].
Salmonella has been reported to acquire virulence from other species through horizontal gene transfer [44]. The acquisition of these virulence gene clusters is said to be the major driving force in the evolution and emergence of highly pathogenic strains [45,46]. Most of the virulence genes are located in a cluster referred to as the Salmonella Pathogenicity Island (SPI) within the chromosome [21]. In this study, all the isolates were found to possess SPI-1 that codes for the type III secretion system, which functions as the actin-binding proteins (SptP and SopE). This actin-binding protein is essential during the transportation and uptake of the bacterium by the cells. In addition, the 40 kb SPI-2 locus that encodes the second type III secretion system was also detected, and this is important for the survival of the bacteria in epithelial cells and macrophages [47,48]. In addition to the SPI 1 and SPI 2 locus, the mgtC gene and the plasmid-encoded fimbriae chaperone gene PefD were also detected in this study. These genes are responsible for the growth of the bacteria in an Mg2+-limiting environment such as phagosomes, and the adhesion of S. Enteritidis to the small intestine, respectively. This finding is in concordance with previous reports where they identified that the Salmonella pathogenicity islands are chromosomal clusters of horizontally acquired virulence genes [49,50,51]. Furthermore, 88% of the isolates were found to possess the plasmid virulence (spv) locus. Notably among these are spvB and spvC, which are responsible for the multiplication of intracellular Salmonella [52]. A similar finding has also been reported where experiments show that the simultaneous administration of spvB and spvC are capable of conferring sufficient virulence to Salmonella species in mice [53]. The detection of virulence genes within these pathogenicity islands implies that the S. Enteritidis isolates found in this study are highly virulent and poses a potential threat of worse disease outcome in susceptible humans and animals.
According to the MLST analysis, the S. Enteritidis study isolates were typed into seven genotypes, with the majority of the isolates clustering into ST1925 (63%) followed by ST11 (26.5%), with ST292 (raw chicken meat), ST329 (cloacal swabs), ST365 (read-to-eat chicken meat), ST423 (raw chicken meat) and ST2132 (cloacal swab) occurring singly in each case. Earlier reports indicate that among S. Enteritidis worldwide, ST11 is the predominant sequence type, accounting for 89% of the sequence types in the EnteroBase database [54]. Similarly, according to the goeBurst analysis, these sequence types share some genetic features by their close relationship. This observation is supported by an earlier report where ST1925 is said to be a variant of the ST11 sequence type [55]. The multilocus sequence types of S. Enteritidis previously reported in Malaysia include ST11 and ST1925, isolated from poultry [56]. However, in neighbouring Singapore, ST11 and ST1925 were reported from Salmonella isolated from retail food and wild birds [57]. Moreover, ST11 has been reported as one of the most common genotypes of S. Enteritidis in Queensland, Australia [58]. Other novel ST types detected in this study are ST292, ST329, ST423 and ST2132. The distribution of these rare sequence types may signify the role of human travel and trade in exotic animal species from endemic regions in the spread of AMR-resistant Salmonella subtypes, which could pose an important health hazard. Likewise, the detection of these novel STs constitute a serious public health challenge because earlier studies that detected Salmonella (S. Albany, S. Ohio, and S. Kentucky) harbouring resistance to cephalosporins and macrolide antibiotics were found to also belong to these sequence types [57,59]. In addition, the isolates showing resistance to multiple antimicrobials clustered in the novel ST2132 as well as the predominant ST11 sequence types. However, an endemic Salmonella genotype reported in Asia, ST34 [37], was not observed in this study. Each of the aforementioned sequence types has been repeatedly reported in food, poultry and human clinical samples from the United Kingdom and the United States [57,59,60].
5. Conclusions
The study provides an appraisal of the AMR, virulence determinants and the MLST subtypes of S. Enteritidis isolates circulating in Malaysia. It is important to highlight that although resistance to some of the antimicrobials tested was observed, none of the isolates was found to show resistance to colistin as no mcr gene was detected. We also noticed that the isolates possess a number of Salmonella virulence determinants which is an indication that they are highly pathogenic, hence possessing a serious threat to humans. Further, the in silico serotype prediction proved to be a good alternative to the traditional Kauffman–White Scheme for serotyping of Salmonella by providing good insights into the genetic determinants of Salmonella.
6. Study Limitation
This study was not able to discuss adequately the epidemiological aspect of the S. Enteritidis isolates obtained because we did not have full access to the sampling and sources of the samples.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.Z., L.H. and N.A.; methodology, Z.S., N.M.S. and R.M.A.; software sequence analysis and interpretation, Z.Z., N.M.S. and B.G.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.Z. and B.G.; writing—review and editing, Z.Z., B.G., L.H., N.A., Z.S., N.M.S., R.M.A., S.A.H. and S.A.B.; funding acquisition, Z.Z.; supervision, Z.Z. and L.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Universiti Putra Malaysia Matching Grant (No 9300438) and Bioeasy Sdn Bhd (No 9300920).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study. This research uses isolates obtained from existing culture collection from the National AMR Surveillance.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/biosample?Db=biosample&DbFrom=bioproject&Cmd=Link&LinkName=bioproject_biosample&LinkReadableName=BioSample&ordinalpos=1&IdsFromResult=674970 (accessed on 26 October 2021)).
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the contribution of the Ministry of Health and the Department of Veterinary Services, Malaysia for the donation of isolates as well as expertise during the course of this research, and BioEasy Sdn Bhd for the analysis of the WGS data. This research was funded by UPM-Bioeasy Sdn Bhd Matching Grant 6300920 and UPM Putra Grant 9300438.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
References
- Ministry of Health Malaysia (MOH). Malaysian Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance (MyAP-AMR) 2017–2021; Published by Ministry of Health, Malaysia and Ministry of Agriculture & Agro-Based Industry Malaysia. 2017. Available online: https://www.moh.gov.my/moh/resources/Penerbitan/Garis%20Panduan/Garis%20panduan%20Umum%20(Awam)/National_Action_Plan_-_FINAL_29_june.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2021).
- Institute of Medical Research (IMR). Malaysia National Antibiotic Resistance Surveillance Report. 2017. Available online: Chrome-extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj/viewer.html?pdfurl=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.imr.gov.my%2Fimages%2Fuploads%2FNSAR%2FNSAR_2017%2FNSAR_report_2017-edited-31.1.2019.pdf&clen=1427117&chunk=true (accessed on 26 October 2021).
- Whistler, T.; Sapchookul, P.; McCormick, D.W.; Sangwichian, O.; Jorakate, P.; Makprasert, S.; Jatapai, A.; Naorat, S.; Surin, U.; Koosakunwat, S.; et al. Epidemiology and antimicrobial resistance of invasive non-typhoidal salmonellosis in rural Thailand from 2006–2014. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanis, E.; Lo Fo Wong, D.M.A.; Patrick, M.E.; Binsztein, N.; Cieslik, A.; Chalermchaikit, T.; Aidara-Kane, A.; Ellis, A.; Angulo, F.J.; Wegener, H.C. Web-based surveillance and global Salmonella distribution, 2000–2002. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulhaleem, N.; Garba, B.; Younis, H.; Mahmuda, A.; Hamat, R.A.; Majid, R.B.A.; Lung, L.T.T.; Unyah, N.Z.; Sattar, A.; Saidu, B. Current trend on the economic and public health significance of salmonellosis in Iraq. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2019, 7, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, F.; von Kalckreuth, V.; Aaby, P.; Adu-Sarkodie, Y.; El Tayeb, M.A.; Ali, M.; Aseffa, A.; Baker, S.; Biggs, H.M.; Bjerregaard-Andersen, M.; et al. Incidence of invasive Salmonella disease in sub-Saharan Africa: A multicentre population-based surveillance study. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e310–e323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, J.J.; MacLennan, C.A. Invasive Nontyphoidal Salmonella Disease in Africa. EcoSal Plus 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, Z.; Hassan, L.; Ahmad, N.; Husin, S.A.; Ali, R.M.; Sharif, Z.; Sohaimi, N.M.; Garba, B. Discerning the Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence, and Phylogenetic Relatedness of Salmonella Isolates Across the Human, Poultry, and Food Materials Sources in Malaysia. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, Z.; Hassan, L.; Sharif, Z.; Ahmad, N.; Ali, R.M.; Husin, S.A.; Hazis, N.H.; Binti, A.; Sohaimi, N.F.M.; Bakar, S.A.; et al. Analysis of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis isolates from chickens and chicken meat products in Malaysia using PFGE, and MLST. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keddy, K.H.; Musekiwa, A.; Sooka, A.; Karstaedt, A.; Nana, T.; Seetharam, S.; Nchabaleng, M.; Lekalakala, R.; Angulo, F.J.; Klugman, K.P. Clinical and microbiological features of invasive nontyphoidal Salmonella associated with HIV-infected patients, Gauteng Province, South Africa. Medicine 2017, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Munusamy, C.; Tan, Y.-C.; Muthuvelu, S.; Hashim, R.; Chien, S.-L.; Wong, M.-K.; Khairuddin, N.A.; Podin, Y.; Lau, P.S.-T.; et al. Invasive Salmonella infections among children in Bintulu, Sarawak, Malaysian Borneo: A 6-year retrospective review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phu Huong Lan, N.; Le Thi Phuong, T.; Nguyen Huu, H.; Thuy, L.; Mather, A.E.; Park, S.E.; Marks, F.; Thwaites, G.E.; Van Vinh Chau, N.; Thompson, C.N.; et al. Invasive Non-typhoidal Salmonella Infections in Asia: Clinical Observations, Disease Outcome and Dominant Serovars from an Infectious Disease Hospital in Vietnam. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcenas, R.C. Molecular Methods for Healthcare-Acquired Infections. In Diagnostic Molecular Pathology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 163–177. [Google Scholar]
- Wiesner, M.; Zaidi, M.B.; Calva, E.; Fernández-Mora, M.; Calva, J.J.; Silva, C. Association of virulence plasmid and antibiotic resistance determinants with chromosomal multilocus genotypes in Mexican Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium strains. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, P.F.; Tyson, G.H.; Kabera, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Folster, J.P.; Ayers, S.L.; Lam, C.; Tate, H.P.; Zhao, S. Whole-genome sequencing for detecting antimicrobial resistance in nontyphoidal Salmonella. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 5515–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute for Medical Research. National Antibiotic Resistance Surveillance Report 2017; Institute for Medical Research: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.S.; Lim, T.H.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, B.Y.; Kwon, J.H.; Choi, S.W.; Noh, J.Y.; Hong, Y.H.; Lee, S.B.; et al. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella species isolated from chicken meats produced by different integrated broiler operations in Korea. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 2370–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsuddin, S.; Akkawi, M.E.; Zaidi, S.T.R.; Ming, L.C.; Manan, M.M. Antimicrobial drug use in primary healthcare clinics: A retrospective evaluation. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 52, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubbers, B.V.; Papich, M.G.; Schwarz, S.; Bowden, R.; Dubraska, B.S.; Diaz-Campos, V.; Fielder, M.; Langston, C.; Li, X.-Z.; Martinez, M.N.; et al. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals A CLSI supplement for global application. In Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated From Animals; NCCLS: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018; ISBN 9781684400102. [Google Scholar]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andesfha, E.; Indrawati, A.; Mayasari, N.L.P.I.; Rahayuningtyas, I.; Jusa, I. Detection of Salmonella pathogenicity island and Salmonella plasmid virulence genes in Salmonella Enteritidis originated from layer and broiler farms in Java Island. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2019, 6, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, K.P.; Ho, W.S.; Gan, H.M.; Chai, L.C.; Thong, K.L. Global MLST of Salmonella Typhi revisited in post-genomic era: Genetic conservation, population structure, and comparative genomics of rare sequence types. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, A.P.; Vaz, C.; Monteiro, P.T.; Melo-Cristino, J.; Ramirez, M.; Carriço, J.A. PhyloViZ: Phylogenetic inference and data visualization for sequence based typing methods. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diep, B.; Barretto, C.; Portmann, A.-C.; Fournier, C.; Karczmarek, A.; Voets, G.; Li, S.; Deng, X.; Klijn, A. Salmonella Serotyping; Comparison of the Traditional Method to a Microarray-Based Method and an in silico Platform Using Whole Genome Sequencing Data. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrato, C.; Chui, L.; King, R.; Louie, M. Utilization of a molecular serotyping method for Salmonella enterica in a routine laboratory in Alberta Canada. J. Microbiol. Methods 2017, 135, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghapour, Z.; Gholizadeh, P.; Ganbarov, K.; Bialvaei, A.Z.; Mahmood, S.S.; Tanomand, A.; Yousefi, M.; Asgharzadeh, M.; Yousefi, B.; Kafil, H.S. Molecular mechanisms related to colistin resistance in enterobacteriaceae. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packierisamy, P.R.; Haron, R.; Mustafa, M.; Mahir, A.; Ayob, A.; Balan, V. Outbreak Caused by Food-Borne Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteriditis in a Residential School in Perak State, Malaysia in April 2016. Intl Food Research J. 2018, 25, 2379–2384. [Google Scholar]
- Johari, M.I.; Besari, A.M.; Wan Ghazali, W.S.; Yusof, Z. Disseminated Salmonella infection. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e226337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Hoong, L.W.; Siong, Y.L.; Mustapha, Z.; Zalati, C.W.S.C.W.; Aklilu, E.; Mohamad, M.; Kamaruzzaman, N.F. Prevalence of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Salmonella spp. and Escherichia coli Isolated from Broilers in the East Coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thung, T.Y.; Radu, S.; Mahyudin, N.A.; Rukayadi, Y.; Zakaria, Z.; Mazlan, N.; Tan, B.H.; Lee, E.; Yeoh, S.L.; Chin, Y.Z.; et al. Prevalence, Virulence Genes and Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles of Salmonella Serovars from Retail Beef in Selangor, Malaysia. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, A.A.; Abdi, A.A.; Awale, M.A.; Garba, B. Occurrence and phenotypic characterization of multidrug-resistant bacterial pathogens isolated from patients in a public hospital in Mogadishu, Somalia. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salihu, M.D.; Garba, B.; Isah, Y. Evaluation of microbial contents of table eggs at retail outlets in Sokoto metropolis, Nigeria. Sokoto J. Vet. Sci. 2015, 13, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salihu, M.D.; Magaji, A.A.; Garba, B.; Saidu, B.; Aliyu, M.; Suleiman, N.; Wurno, S.B. Bacteriological quality of raw meat displayed for sale at Sokoto, Sokoto state, Original article Bacteriological quality of raw meat displayed for sale at Sokoto, Sokoto state. Sci. J. Microbiol. 2013, 27, 134–139. [Google Scholar]
- Braden, C.R. Salmonella enterica Serotype Enteritidis and Eggs: A National Epidemic in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenover, F.C.; McGowan, J.E. Antimicrobial Resistance. Int. Encycl. Public Health 2008, 2008, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoi, S.T.; Lindstedt, B.A.; Watanabe, H.; Thong, K.L. Molecular characterization of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium isolated from human, food, and animal sources in Malaysia. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 66, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.; Sudhanthirakodi, S.; Chowdhury, G.; Joshi, S.; Anandan, S.; Ray, U.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Dutta, S. Antimicrobial resistance, plasmid, virulence, multilocus sequence typing and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis profiles of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium clinical and environmental isolates from India. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Ke, B.; Huang, Y.; He, D.; Li, X.; Liang, Z.; Ke, C. The molecular epidemiological characteristics and genetic diversity of Salmonella Typhimurium in Guangdong, China, 2007–2011. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagambèga, A.; Lienemann, T.; Aulu, L.; Traoré, A.S.; Barro, N.; Siitonen, A.; Haukka, K. Prevalence and characterization of Salmonella enterica from the feces of cattle, poultry, swine and hedgehogs in Burkina Faso and their comparison to human Salmonella isolates. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Hsu, F.F.; Turk, J.; Groisman, E.A. The PmrA-regulated pmrC gene mediates phosphoethanolamine modification of lipid A and polymyxin resistance in Salmonella enterica. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 4124–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, M.R.; Zakaria, Z.; Hassan, L.; Ahmad, N.I.; Faiz, N.M.; Garba, B. Rapid detection of colistin-resistant Enterobacterales using the resazurin reduction-based assay. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 26, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, M.R.; Doumith, M.; Do Nascimento, V.; Nair, S.; Ashton, P.M.; Jenkins, C.; Dallman, T.J.; Stevens, F.J.; Freedman, J.; Hopkins, K.L.; et al. Comparison of phenotypic and WGS-derived antimicrobial resistance profiles of Salmonella enterica serovars Typhi and Paratyphi. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 73, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, P.; Machado, J.; Sousa, J.C.; Peixe, L. Dissemination of sulfonamide resistance genes (sul1, sul2, and sul3) in Portuguese Salmonella enterica strains and relation with integrons. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäumler, A.J. The record of horizontal gene transfer in Salmonella. Trends Microbiol. 1997, 5, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groisman, E.A.; Ochman, H. Pathogenicity islands: Bacterial evolution in quantum leaps. Cell 1996, 87, 791–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asten, A.J.A.M.; Dijk, J.E. Distribution of classic virulence factors among Salmonella spp. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 44, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, J.E.; Hensel, M.; Gleeson, C.; Holden, D.W. Identification of a virulence locus encoding a second type III secretion system in Salmonella typhimurium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 2593–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garai, P.; Marathe, S.; Chakravortty, D. Effectors of Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 2: An Island crucial to the life of Salmonella. Virulence 2011, 2, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Blanc-Potard, A.B.; Groisman, E.A. The Salmonella selC locus contains a pathogenicity island mediating intramacrophage survival. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 5376–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, R.D.; Koronakis, V. Direct modulation of the host cell cytoskeleton by Salmonella actin-binding proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 2002, 12, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäumler, A.J.; Tsolis, R.M.; Bowe, F.A.; Kusters, J.G.; Hoffmann, S.; Heffron, F. The pef fimbrial operon of Salmonella typhimurium mediates adhesion to murine small intestine and is necessary for fluid accumulation in the infant mouse. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.; Puente, J.L.; Calva, E. Salmonella virulence plasmid: Pathogenesis and ecology. Pathog. Dis. 2017, 75, ftx070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, H.; Bacot, C.M.; Garlington, W.A.; Doyle, T.J.; Roberts, S.; Gulig, P.A. Virulence plasmid-borne spvB and spvC genes can replace the 90-kilobase plasmid in conferring virulence to Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium in subcutaneously inoculated mice. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 4652–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, P.M.; Nair, S.; Peters, T.M.; Bale, J.A.; Powell, D.G.; Painset, A.; Tewolde, R.; Schaefer, U.; Jenkins, C.; Dallman, T.J.; et al. Identification of Salmonella for public health surveillance using whole genome sequencing. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, R.M.A.; Hiley, L.; Rathnayake, I.U.; Jennison, A.V. Comparative genomics identifies distinct lineages of S. Enteritidis from Queensland, Australia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadee, P.; Patchanee, P.; Boonkhot, P.; Kittiwan, N.; Chotinun, S. Dissemination of Salmonella enterica Sequence Types Among Asean Economic Community Countries. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2015, 46, 707–719. [Google Scholar]
- Aung, K.T.; Chen, H.J.; Chau, M.L.; Yap, G.; Lim, X.F.; Humaidi, M.; Chua, C.; Yeo, G.; Yap, H.M.; Oh, J.Q.; et al. Salmonella in Retail Food and Wild Birds in Singapore—Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Sequence Types. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, L.R.; Van Der Graaf-Van Bloois, L.; Donado-Godoy, P.; León, M.; Clavijo, V.; Arévalo, A.; Bernal, J.F.; Mevius, D.J.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Zomer, A.; et al. Genomic characterization of extended-spectrum cephalosporin-resistant Salmonella enterica in the Colombian poultry chain. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Lei, C.W.; Kang, Z.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.N. IS26-Mediated Genetic Rearrangements in Salmonella Genomic Island 1 of Proteus mirabilis. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toboldt, A.; Tietze, E.; Helmuth, R.; Junker, E.; Fruth, A.; Malorny, B. Population structure of Salmonella enterica serovar 4,[5],12:b-strains and likely sources of human infection. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5121–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).