Simple Summary
The tropical rat mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) is a transmission vector of rickettsia pox and a potential vector of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS). This article reports the distribution and host selection of O. bacoti in Yunnan Province of Southwest China. The original data came from the investigations in 39 counties of Yunnan. The prevalence (PM), mean abundance (MA) and mean intensity (MI) were calculated to reflect the infestations of the dominant rat hosts with O. bacoti mites. The patchiness index and Taylor’s power law were used to measure the spatial distribution of the mites. A total of 4121 O. bacoti mites were identified from 15 species of small mammal hosts in 27 of the 39 investigated counties, and 99.20% of them (4088/4121) were found on rodents. The majority of total O. bacoti mites was found in the flatland landscape (91.28%) and indoor habitat (73.48%). Moreover, 51.78% and 40.09% of O. bacoti mites were identified from Rattus tanezumi and R. norvegicus, the two synanthropic rat species. The mites had some host-specificity, with a preference to two dominant hosts (R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus), and they were of aggregated distribution on R. tanezumi.
Abstract
(1) Background: As a species of gamasid mite, the tropical rat mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) is a common ectoparasite on rodents and some other small mammals. Besides stinging humans to cause dermatitis, O. bacoti can be a vector of rickettsia pox and a potential vector of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS). (2) Objective: The present study was conducted to understand the host selection of O. bacoti on different animal hosts and the distribution in different environmental gradients in Yunnan Province of Southwest China. (3) Methods: The original data came from the investigations in 39 counties of Yunnan, between 1990 and 2015. The animal hosts, rodents and some other small mammals were mainly trapped with mouse traps. The O. bacoti mites on the body surface of animal hosts were collected and identified in a conventional way. The constituent ratio (Cr), prevalence (PM), mean abundance (MA) and mean intensity (MI) were used to reflect infestations of animal hosts with O. bacoti mites. The patchiness index and Taylor’s power law were used to measure the spatial distribution pattern of O. bacoti mites on their hosts. (4) Results: A total of 4121 tropical rat mites (O. bacoti) were identified from 15 species and 14,739 individuals of hosts, and 99.20% of them were found on rodents. More than half of O. bacoti mites (51.78%) were identified from the Asian house rat (Rattus tanezumi), and 40.09% of the mites from the Norway rat (R. norvegicus) (p < 0.05). The infestations of R. tanezumi (PM = 7.61%, MA = 0.40 and MI = 5.31) and R. norvegicus (PM = 10.98, MA = 1.14 and MI = 10.39) with O. bacoti mites were significantly higher than those of other host species (p < 0.05). The infestations of two dominant rat hosts (R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus) with O. bacoti mites varied in different environmental gradients (latitudes, longitudes, altitudes, landscapes and habitats) and on different sexes and ages of the hosts. The prevalence of juvenile R. norvegicus rats with O. bacoti mites (PM = 12.90%) was significantly higher than that of adult rats (PM = 9.62%) (p < 0.05). The prevalence (PM = 38.46%) and mean abundance (MA = 2.28 mites/host) of R. tanezumi rats with O. bacoti mites in the high latitude were higher than those in the low latitudes (p < 0.05). The majority of the total collected 4121 O. bacoti mites was found in the flatland landscape (91.28%) and indoor habitat (73.48%) (p < 0.05). The PM (10.66%) and MA (0.49 mites/host) of R. tanezumi rats with O. bacoti mites were significantly higher in the indoor habitat than in the outdoor habitat (p < 0.05). The tropical rat mites showed an aggregated distribution pattern on their first dominant host, R. tanezumi. Conclusion: The tropical rat mite (O. bacoti) is a widely distributed species of gamasid mite in Yunnan Province, Southwest China, and its dominant hosts are two synanthropic species of rats, R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus. It is mainly distributed in the flatland landscape and indoor habitat. It has some host-specificity, with a preference to rodents, especially R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus. The O. bacoti mites are of aggregated distribution on R. tanezumi rats.
1. Introduction
As a worldwide species of gamasid mite, the tropical rat mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) is widely distributed in nearly all parts of the world, except the Arctic and Antarctic regions [1,2]. It is a common ectoparasite on rodents (rats, mice and voles) and some other small mammals (e.g., insectivores and tree shrews), frequently occurring on the body surface and in the nests of its hosts. Ornithonyssus bacoti is the most important species of gamasid mites associated with medicine, and nearly all its stages (larvae, protonymphs, deutonymphs and adults) in the life cycle can invade and sting animal hosts for blood meal [3,4,5]. The dermatitis caused by the stinging of O. bacoti mites is frequently reported throughout the world [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. Besides directly stinging humans, O. bacoti is associated with the transmission of some zoonoses. Together with another species of gamasid mite (Allodermanyssus sanguineus), the mite O. bacoti is the confirmed vector of rickettsia pox, caused by the pathogen Rickettsia akari [1,17,18]. Rickettsia pox is a zoonosis associated with rodents, and it is mainly prevalent in the United States, Canada, Russia, Ukraine, India and Egypt, etc. [17,19,20,21]. Besides being the intermediate host of the animal parasite Litomosoides carinii, the mite O. bacoti has been proved to be the potential vector of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) caused by hantavirus [22,23,24,25].
To date, there have been a lot of studies on the tropical rat mite, O. bacoti. Early on in the 1940s, some scholars began to feed O. bacoti in the laboratory and designed some special devices suitable for O. bacoti and some other sucking mites [26,27]. Many previous publications on O. bacoti and some other species of gamasid mites were about the mites’ ultrastructure [1,8,28,29,30], chromosome karyotype, gene sequencing, phylogeny and control [1,29,31,32,33,34], but only few studies were about the mite ecology. To date, there have been no systematically ecological studies on O. bacoti in Yunnan Province of Southwest China. Between 1990 and 2015, our research group made a long-term field investigation and accumulated abundant original data on gamasid mites in Yunnan. To take advantage of the previous investigation, the present paper analyzed the distribution and host selection of O. bacoti in Yunnan for the first time, which is an attempt to get more knowledge about O. bacoti and to enrich the ecological information of the mite.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Identification of Ornithonyssus bacoti and Its Animal Hosts
The original data came from a long-term field investigation in 39 counties of Yunnan Province in Southwest China, between 1990 and 2015, and the investigated 39 counties were shown in Figure 1, in Results. A stratified sampling investigation was made in different geographical localities, latitudes, longitudes, altitude, landscapes and habitats. To capture animal hosts, mouse traps were placed in the indoor and outdoor habitats of each investigation site, in the evening, and then checked the following morning. The indoor habitats covered houses, barns, stables, etc., and the outdoor habitats covered paddy fields, cornfields, bush habitats, woodlands, etc. [35]. Each trapped host was euthanized through anesthesia with ether (cotton balls soaked with ether), within a closed container. Under the anesthesia, the gamasid mites on the body surface of each host were all collected and then preserved in Eppendorf tubes with 70% of ethanol. After the mite collection, each animal host was identified into species according to its morphological features [4,36,37]. Through the dehydration and clarification, the collected gamasid mites were mounted onto glass slides with Hoyer’s medium and they were then identified into species under microscopes [38,39]. Based on the identification of gamasid mites, the tropical rat mite (O. bacoti) was chosen as the target of the present study. In the animal euthanasia, most rodent pests in agriculture and forestry were anaesthetized to death because the local government encourages people to kill and eradicate them. Some non-pest small mammals (e.g., weasels, moles and some squirrels) were anaesthetized only for two to five minutes, according to their body size, and they were finally released to the wild when they woke up. The capturing of rodents and other small mammals was officially permitted by the local authority of wildlife service in Yunnan Province, China. The use of animals (including animal euthanasia) for research was officially approved by the Animals’ Ethics Committee of Dali University, and the permitted number was DLDXLL2020-1104. The specimens of voucher mites and representative animal hosts are deposited in the specimen repository of the Institute of Pathogens and Vectors, Dali University, Yunnan, China.
2.2. Infestation Statistics
In a conventional way, the constituent ratio (Cr), prevalence (PM), mean abundance (MA) and mean intensity (MI) were calculated to reflect the infestations of dominant hosts with tropical rat mites (O. bacoti) [4,40,41,42]. In the present study, Cr represents the percentage of O. bacoti mites, PM the percentage of infested hosts by the mites, MA the number of the mites on each examined host and MI the number of the mites on each infested host.
2.3. Analysis on Host Selection and Distribution
The infestations of dominant animal hosts with O. bacoti mites were compared on different sexes and ages of the hosts to reflect the host selection of the mites. The infestations were compared in different latitudes and longitudes, to reflect the mite’s horizontal distribution, and compared in different altitudes, to reflect the mite’s vertical distribution. The latitudes and longitudes were divided into three gradients, and the altitudes were divided into four gradients. The three latitude gradients include <24° N, 24° N–26° N and >26° N, and the four longitude gradients are <100° E, 100° E–102° E, 102° E–104° E and >104° E. The four altitude gradients are <1000 m, 1000–2000 m, 2001–3000 m and >3000 m.
2.4. Analysis of Spatial Distribution Pattern
The patchiness index (m*/m) and Taylor’s power were used to measure the spatial distribution pattern of tropical rat mites (O. bacoti) among different individuals of its dominant hosts [43,44]. The formulae of patchiness index and Taylor’s power are listed as follows.
In the above formulae, m*/m = patchiness index, m = mean of O. bacoti mites on its dominant hosts and σ2 = variance of the mites; lg a = intercept on the Y-axis, and b = the slope or regression coefficient. When m*/m > 1, a > 1 and b > 1 or a > 1, b = 1, the spatial distribution pattern is determined as the aggregated distribution; when m*/m = 1, a = 1 and b = 1, the random distribution; when m*/m < 1, a < 1, b < 1, the uniform (or even) distribution [45,46].
2.5. Analysis on Interspecific Association
Based on a contingency table (see Table 10 in Results), the association coefficient (V) was used to measure the interspecific association between the tropical rat mite (O. bacoti) and some other related species of gamasid mites on the dominant animal hosts. In the contingency table, O. bacoti was defined as “species X”, while the other related mite species was defined as “species Y”. The association coefficient (V) is as follows.
In the above formula, V = the association coefficient between species X and Y; a = the host individuals on which species X and Y simultaneously occur; b = the host individuals on which species Y occurs, but species X does not occur; c = the host individuals on which species X occurs, but species Y does not occur; and d = the host individuals on which both species X and Y do not occur. When V > 0 and p < 0.05, the interspecific relationship between species X and Y is determined as the positive association; when V < 0 and p < 0.05, we have the negative association; P is the significance probability in Chi-square test (χ2).
2.6. Significance Test
Chi-square test (χ2) was used to test the significance of Cr, PM and V. Nonparametric test was used to test the significance of MA and MI. All the statistical analyses were performed with R software version 3.5.3.
3. Results
3.1. Abundance of Ornithonyssus bacoti
A total of 139,111 gamasid mites were collected from 74 species and 17,638 individuals of animal hosts, rodents and some other small mammals, in 39 counties of Yunnan. Of 139,111 collected gamasid mites, 137,210 of them were identified as 156 species and 39 genera in 13 families, and the remaining 1901 mites remained unidentified because of blemished, obscure and damaged structures or suspected new species. A total of 4121 tropical rat mites (O. bacoti) were identified from 15 species and 14,739 individuals of hosts, and they accounted for only 2.96% (4121/139,111) of the total mites. The identified 4121 O. bacoti mites were distributed in 27 counties (Figure 1).
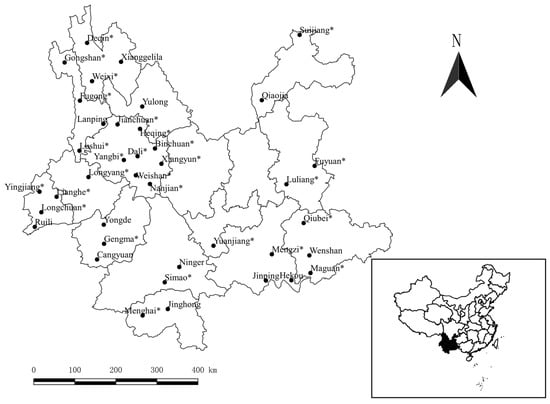
Figure 1.
The 39 investigated counties and 27 counties with tropical rat mites (Ornithonyssus bacoti) collected (marked with “*”) in Yunnan Province, Southwest China (1990–2015).
3.2. Host Selection of Ornithonyssus bacoti
The identified 4121 O. bacoti mites came from 15 species, 8 genera and 4 families of animal hosts in 3 orders, Rodentia, Soricomorpha and Scandetia. On the order level of animal hosts, 99.20% of O. bacoti mites (4088/4121) were found on the order Rodentia, which was significantly higher than that on Soricomorpha and Scandetia (p < 0.05). The percentages of O. bacoti mites found on the family Muridae (4088/4121 = 99.20%) and the genus Rattus (3953/4121 = 95.92%) were the highest of four host families and eight genera (p < 0.05). On the species level of hosts, the majority of O. bacoti mites was identified from two dominant rat hosts, with 51.78% of the mites on the Asian house rat (Rattus tanezumi) and 40.09% of the mites on the Norway rat (R. norvegicus) (p < 0.05). Of the 15 species of hosts, the infestations of the dominant rat hosts (R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus) with O. bacoti mites were significantly higher than those of other 13 species of hosts (p < 0.05) (Table 1). Positive linear correlations existed among PM, MA and MI, with r = 0.685 between MA and MI, r = 0.646 between MA and PM and r = 0.332 between MI and PM (p < 0.05) (Figure 2).

Table 1.
Infestations of two dominant rat hosts (Rattus tanezumi and R. norvegicus) with tropical rat mites (Ornithonyssus bacoti) in Yunnan Province, Southwest China (1990–2015).
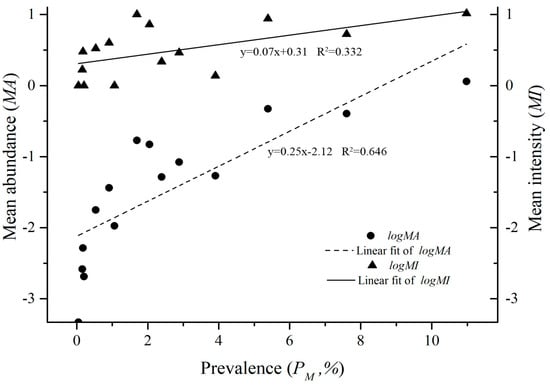
Figure 2.
The linear regression between PM, MA and MI of 15 host species with O. bacoti mites in Yunnan Province, Southwest China (1990–2015).
Different sexes and ages of two dominant rat hosts (R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus) showed some differences in the infestations with O. bacoti mites. The infestations of male rats (R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus) with O. bacoti mites were slightly higher than those of female rats, but the differences were of no statistical significance (p > 0.05) (Table 2 and Table 3). The prevalence of juvenile R. norvegicus rats with the mites (PM = 12.90%) was significantly higher than that of adult rats (PM = 9.62%) (p < 0.05). The mean abundance (MA mites/host) and mean intensity (MI mites/host) of juvenile R. norvegicus rats with the mites were slightly higher than those of adult rats, but the differences were of no statistical significance (p > 0.05). The infestations of juvenile R. tanezumi rats with the mites (PM, MA and MI) were also slightly higher than those of adult rats, but the differences were of no statistical significance (p > 0.05) (Table 2 and Table 3).

Table 2.
Infestations of different sexes and ages of R. tanezumi rats with O. bacoti mites in Yunnan Province, Southwest China (1990–2015).

Table 3.
Infestations of different sexes and ages of R. norvegicus rats with O. bacoti mites in Yunnan Province, Southwest China (1990–2015).
3.3. Horizontal Distribution of Ornithonyssus bacoti
The infestations of two dominant rat hosts (R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus) with O. bacoti mites showed some differences in different latitudes and longitudes (horizontal distribution). The PM (38.46%) and MA (2.28 mites/host) of R. tanezumi with O. bacoti mites, together with MA (2.04 mites/host) of R. norvegicus with the mites, were higher in the high latitude (>26° N) than in other latitudes (p < 0.05) (Table 4 and Table 5). The MA (0.63 mites/host) of R. tanezumi rats with the mites was higher in the longitude <100° E than in other three longitudes (p < 0.05), and the PM (16.81%) and MA (2.10 mites/host) of R. norvegicus with the mites were higher in the longitude 100° E–102° E than in other three longitudes (p < 0.05) (Table 4 and Table 5).

Table 4.
Infestations of R. tanezumi rats with O. bacoti mites in different latitudes and longitudes of Yunnan Province, Southwest China (1990–2015).

Table 5.
Infestations of R. norvegicus rats with O. bacoti mites in different latitudes and longitudes of Yunnan Province, Southwest China (1990–2015).
3.4. Vertical Distribution of Ornithonyssus bacoti
The infestations of two dominant rat hosts (R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus) with O. bacoti mites showed some differences in different altitudes (vertical distribution). The PM (27.27%) and MA (0.82 mites/host) of R. tanezumi rats with O. bacoti mites were highest above 3000 m, but MI (7.62 mites/host) was highest below 1000 m (p < 0.05). The PM (13.40%), MA (0.77 mites/host) and MI (5.74 mites/host) of R. norvegicus rats with the mites were highest at 1000–2000 m (p < 0.05) (Table 6).

Table 6.
Infestations of R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus rats with O. bacoti mites in different altitudes of Yunnan Province, Southwest China (1990–2015).
3.5. Landscape and Habitat Distribution of Ornithonyssus bacoti
The majority of total collected 4121 O. bacoti mites was found in the flatland landscape (1894/2075 = 91.28%) and indoor habitat (3028/4121 = 73.48%) (p < 0.05). The infestations of two dominant rat hosts (R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus) with O. bacoti mites showed some differences in two kinds of landscapes (mountainous and flatland landscapes), but the differences were of no statistical significance (p > 0.05) (Table 7). The infestations of R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus with the mites also showed some differences in two kinds of habitats. The PM (10.66%) and MA (0.49 mites/host) of R. tanezumi rats with the mites were significantly higher in the indoor habitat than in the outdoor habitat (p < 0.05). The PM (11.50%), MA (1.30 mites/host) and MI (11.31 mites/host) of R. norvegicus rats with the mites were higher in the indoor habitat than in the outdoor habitat, but the differences were of no statistical significance (p > 0.05) (Table 8).

Table 7.
Infestations of R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus rats with O. bacoti mites in different landscapes of Yunnan Province, Southwest China (1990–2015).

Table 8.
Infestations of R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus rats with O. bacoti mites in different habitats of Yunnan Province, Southwest China (1990–2015).
3.6. Spatial Distribution Pattern and Interspecific Association
A total of 5285 Asian house rats (R. tanezumi), the first dominant host of the tropical rat mites (O. bacoti), were captured in 35 of 39 investigated counties, but there were only 24 counties where R. tanezumi harbored O. bacoti mites. To establish a linear regression equation based on Taylor’s power law, the 24 counties were recombined as four “sample units”, according to their adjacent locations, and then the mean (m) and variance (σ2) of O. bacoti mites on R. tanezumi rats in each sample unit were calculated (Table 9). According to the calculated m and σ2, a linear regression equation was established as lg σ2 = lg 39.30 + 1.42 lg m, where both a (39.30) and b (1.42) were beyond 1 (a > 1, b > 1), the border value for determining the aggregated distribution. The calculated patchiness index (m*/m) in each sample unit was also higher than 1 (m*/m > 1), the border value for determining the aggregated distribution (Table 9). On the body surface of R. tanezumi rats, there were a lot of L. nuttalli mites (the other species of gamasid mites) that co-occurred with O. bacoti mites, and therefore the interspecific association between O. bacoti and L. nuttalli was studied. The result showed that there was a slight negative association between O. bacoti and L. nuttalli (V = −0.0794, V < 0, p < 0.05) (Table 10).

Table 9.
The mean (m), variance (σ2) and patchiness index (m*/m) of O. bacoti mites on R. tanezumi rats in each recombined sample unit of Yunnan, Southwest China (1990–2015).

Table 10.
The contingency table for measuring the interspecific association between O. bacoti mites and L. nuttalli mites on the body surface of R. tanezumi rats in Yunnan, Southwest China (1990–2015).
4. Discussion
In laboratories, the tropical rat mite (O. bacoti) is often found on the experimental rats and mice, and it does a great harm to experimental animals [6,47,48]. Therefore, it is important to make a systematic study on O. bacoti. Some previous ecological studies of gamasid mites mainly focused on some local species surveys, faunal studies and community investigations [4,36,49]. Although some local investigations on the fauna and community of gamasid mites included the constituent ratio of O. bacoti, there were few independent and systematic studies of O. bacoti [16,38,50]. The present study systematically analyzed the distribution and host selection of O. bacoti in Yunnan Province of Southwest China for the first time. The original data came from a long-term investigation between 1990 and 2015, and the investigated 39 counties covered the different localities of Yunnan Province, Southwest China. The tropical rat mite (O. bacoti) was found in 27 of 39 investigated counties (Figure 1), and it suggests that O. bacoti is a widely distributed species of gamasid mites in Yunnan.
The present study showed that 99.20% of tropical rat mites (O. bacoti) were found on rodents (the order Rodentia), even though three orders of hosts (Rodentia, Soricomorpha and Scandetia) harbored the mites. Although O. bacoti mites occurred on different categories of hosts (15 species, 8 genera, 4 families and 3 orders), most of them were identified from two dominant rat species, the Asian house rat (R. tanezumi) and the Norway rat or brown rat (R. norvegicus). The infestations of R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus with O. bacoti mites were significantly higher than those of other 13 host species. The results suggest that O. bacoti has some host-specificity and it has a preference to R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus in Yunnan. The higher prevalence (PM) of juvenile R. norvegicus rats with O. bacoti mites than that of adult rats (Table 2) may imply the preference of the mites to juvenile hosts. Rodents are closely related to human beings, and they are the infection source and reservoir hosts of many zoonotic diseases [18,51]. The rodent-preference of O. bacoti would increase the potential risk of the mite’s attacking humans and spreading some zoonoses. The Asian house rat (R. tanezumi) and the Norway rat (R. norvegicus) are two major species of rodents associated with human settlements in Yunnan Province and some other places of China [52,53]. Rattus tanezumi (often called R. flavipectus in China) is widely distributed in the vast areas south of the Yangtze River, in Southern China. It is a very common rodent species in residential areas (especially the indoor habitats) in Central and Southern Yunnan [54,55]. Rattus norvegicus is widely distributed in the whole China, and it is also a very common rodent species in residential areas (especially the indoor habitats) in Yunnan, often co-occurring in the same areas with R. tanezumi [35,56,57,58]. The previous studies revealed that the main hosts of O. bacoti included some synanthropic rats and mice with humans (especially R. norvegicus) and experimental rats and mice [3,7,18]. The most commonly used laboratory rat is descended from R. norvegicus, which retains many biological characteristics of its ancestor R. norvegicus [59,60]. The frequent occurrence of O. bacoti on R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus would highly increase the risk of the mites’ attacking humans and spreading some zoonoses.
Rattus tanezumi and R. norvegicus were two dominant rat hosts of O. bacoti mites, and therefore the present paper analyzed the infestations of the two host species with the mites in different horizontal gradients (latitudes and longitudes) and vertical gradients (altitudes). The results showed that the infestations of the rats (R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus) with O. bacoti mites showed some differences in different horizontal and vertical gradients. Some infestation indices (PM and MA) were higher in the high latitude (>26° N) and low longitudes (<100° E and 100° E–102° E) than in other latitudes and longitudes (Table 4 and Table 5). The PM and MA of R. tanezumi rats with the mites were highest above 3000 m, but MI was highest below 1000 m. The PM, MA and MI of R. norvegicus rats with the mites were highest at 1000–2000 m (Table 6). The results indicated an unstable fluctuation in different vertical gradients. The climates in Yunnan province greatly vary from region to region because of complex topography and altitude gradients. Even within the same latitude or longitude gradient zone, the climate at a mountainous site with higher altitude may be very different from that at a flatland site with lower altitude [61,62,63]. The different infestations of the rats (R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus) with O. bacoti mites in different horizontal and vertical gradients may be related to different climates (temperature, humidity and rainfall, etc.) in different geographical localities. However, it is difficult to explain the unstable fluctuation of the mite infestations in different horizontal and vertical gradients, and more research studies still remain to be conducted.
Located in the southwest of China, Yunnan is a mountainous province where mountainous landscapes with higher altitude and lower temperature account for 84% of the whole territory, and flatland landscapes with lower altitude and higher temperature are often embedded in mountainous landscapes [63,64]. Although the flatland landscape only takes a small portion of the whole territory, the majority of O. bacoti mites (91.28%) was found in the flatland landscape, and this suggests that O. bacoti is mainly distributed in the flatland landscape. The infestations of the rats (R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus) with the mites showed some differences in mountainous and flatland landscapes, but the differences were of no statistical significance (Table 7). In habitat distribution, 73.48% of O. bacoti mites were collected in the indoor habitat. The PM and MA of R. tanezumi rats with the mites were significantly higher in the indoor habitat than in the outdoor habitat (Table 8), indicating the preference of the mites for the indoor habitat. The previous study showed that the optimum temperature for the development of O. bacoti was about 25 °C ± 5 °C, and higher than 30 °C or lower than 20 °C was not suitable for the mites’ development [65]. The outdoor habitat in the present study involved a series of different sub-habitats, or microhabitats, such as cultivated farmlands (e.g., paddy fields and cornfields) and uncultivated bush areas and woodlands; the micro-climates in the outdoor habitat are often unstable. In comparison with the outdoor habitat, the indoor habitat is a relatively closed environment with a relatively stable and warm temperature and low humidity [65,66]. The stable and warm micro-climate with relatively low humidity in the indoor habitat may be more suitable to the growth and reproduction of O. bacoti mites. The frequent occurrence of O. bacoti in the indoor habitat would highly increase the risk of the mites’ invading and stinging humans. When rats and mice are not available for O. bacoti mites to suck the blood of, the mites in the indoor habitat may quickly move onto humans for the blood meal and then expand their range of activity [1,67,68].
The measurement of spatial distribution pattern of a certain population is one of important issues in arthropod ecology [69,70]. There are usually three types of spatial distribution patterns: uniform (or even) distribution, random distribution and aggregated distribution [52,71,72,73]. There are a variety of statistical methods to measure the spatial distribution pattern of a certain population, and the patchiness index and Taylor’s power law are two of them [43,44,74]. According to the statistics of the patchiness index and Taylor’s power law, tropical rat mites (O. bacoti) were determined to be of aggregated distribution on R. tanezumi, the first dominant host. The aggregated distribution indicates that the mite infestation is not even among different hosts. Some hosts may harbor a large number of mites, forming a clump of mites on their body surface, while some other hosts may have no or very few mites on their body surface. The aggregated distribution pattern of O. bacoti in the present study is consistent with that of some other ectoparasites, such as chigger mites; this is a common phenomenon in many parasites [38,52,71]. The aggregated distribution may be beneficial to the survival, mating and defense of the parasites [4,38,72,73].
The analysis of the interspecific relationship between any two different species is also an important issue in animal ecology [75,76]. The association coefficient (V) used in the present study is a simple way to measure the interspecific relationship between any two species [77,78,79,80]. The negative value of the association coefficient (V = −0.0794) may imply that there is a slight negative association between O. bacoti and L. nuttalli, but the value of “V = −0.0794” was very close to “0”, and more research is still needed.
5. Conclusions
The tropical rat mite (O. bacoti) is a widely distributed species of gamasid mite in Yunnan Province, Southwest China, and its dominant hosts are two synanthropic species of rats, R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus. It is mainly distributed in the flatland landscape and indoor habitat. It has some host-specificity, with a preference to rodents, especially R. tanezumi and R. norvegicus. The O. bacoti mites are of aggregated distribution on R. tanezumi rats.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, resources, supervision, validation, and writing—review & editing, X.-G.G.; supervision, D.-C.J.; data curation, formal analysis, software, visualization, and writing—original draft, P.-W.Y.; investigation, R.F., C.-F.Z., Z.-W.Z. and K.-Y.M.; methodology, X.-B.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81960380 and 81672055), to Xian-Guo Guo, and the Innovation Team of Vector Biology, Dali University (No. ZKLX2019104).
Data Availability Statement
The experimental data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author request.
Acknowledgments
Up until now, more than 60 people have joined this study, including field investigation, collection of gamasid mites, specimen making and identification of the mites. Here we would like to express our sincere thanks to the following people, who have made special contributions to the field investigation and laboratory work: Qiao-Hua Wang, Yong Zhang, Cong-Hua Gao, Nan Zhao, Jian-Chang He, Guo-Li Li, Xue-Song He, Yun-Ji Zou, De-Cai Ouyang and Shuang-Lin Wang, some colleagues and college students.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Beck, W.; Folster-Holst, R. Tropical Rat Mites (Ornithonyssus bacoti)—Serious Ectoparasites. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2009, 7, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, W.; Pantchev, N. Parasitäre Zoonosen: Bild-Text-Atlas; Schlütersche: Rostock, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, A.; Venkataramana, K.; Fölster-Holst, R.; Beck, W. Epizootiology, Treatment and Control of Tropical Rat-Mite Infestation in a Breeding Colony of Swiss Mice under Temperate Climate of Nilgiris Hill-India. Anim. Sci. 2013, 7, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.Q.; Guo, X.G.; Speakman, J.R.; Dong, W.G. Analysis of Gamasid Mites (Acari: Mesostigmata) Associated with the Asian House Rat, Rattus tanezumi (Rodentia: Muridae) in Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 1967–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, W. Occurrence of a House-Infesting Tropical Rat Mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) on Murides and Human Beings. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2008, 6, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.L.; Hwang, S.J.; Kwon, S.B.; Kim, D.W.; Jun, J.B.; Cho, B.K. Outbreak of Rat Mite Dermatitis in Medical Students. Int. J. Dermatol. 1998, 37, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creel, N.B.; Crowe, M.A.; Mullen, G.R. Pet Hamsters as a Source of Rat Mite Dermatitis. Cutis 2003, 71, 457–461. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, P.M.; Welzel, J.; Maass, M.; Schramm, U.; Wolff, H.H. Tropical Rat Mite Dermatitis: Case Report and Review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 27, 1465–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumcuoglu, Y.; Buchheim, E. Dermatitis Caused by the Tropical Rat Mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) in Switzerland. Case Report. Schweiz. Med. Wochenschr. 1983, 113, 793–795. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, S.; Yeruham, I.; Braverman, Y. Dermatitis in Humans Associated with the Mites Pyemotes tritici, Dermanyssus gallinae, Ornithonyssus bacoti and Androlaelaps casalis in Israel. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2002, 16, 442–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skirnisson, K. The Tropical Rat Mite Ornithonyssus bacoti Attacks Humans in Iceland. Laeknabladid 2001, 87, 991–993. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, W.; Pfister, K. Occurrence of a House-Infesting Tropical Rat Mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) on Murides and Human Beings in Munich: 3 Case Reports. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2004, 116, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baumstark, J.; Beck, W.; Hofmann, H. Outbreak of Tropical Rat Mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) Dermatitis in a Home for Disabled Persons. Dermatology 2007, 215, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiechter, R.; Grimm, F.; Müller, G.; Schnyder, M. Cumulation of Ornithonyssus bacoti (Tropical Rat Mite) Infestations of Pet Rodents and Their Owners in the Canton of Zürich and Graubünden. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2011, 153, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cafiero, M.; Raele, D.; Mancini, G.; Galante, D. Dermatitis by Tropical Rat Mite, Ornithonyssus bacoti (Mesostigmata, Macronyssidae) in Italian City-Dwellers: A Diagnostic Challenge. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 30, 1231–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ovidio, D.; Noviello, E.; Santoro, D. Prevalence and Zoonotic Risk of Tropical Rat Mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) in Exotic Companion Mammals in Southern Italy. Vet. Dermatol. 2018, 29, 522-e174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, W.K.; Loftis, A.D.; Szumlas, D.E.; Abbassy, M.M.; Helmy, I.M.; Hanafi, H.A.; Dasch, G.A. Rickettsial Pathogens in the Tropical Rat Mite Ornithonyssus bacoti (Acari: Macronyssidae) from Egyptian Rats (Rattus spp.). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2007, 41, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, P.J.; Nath, A.J. Record of Tropical Rat Mite, Ornithonyssus bacoti (Acari: Mesostigmata: Macronyssidae) from Domestic and Peridomestic Rodents (Rattus rattus) in Nilgiris, Tamil Nadu, India. J. Arthropod Borne Dis. 2016, 10, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, D.H. Rickettsiae. In Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.; Baron, S., Ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996; Chapter 38. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, S.; Essbauer, S.S.; Mayer-Scholl, A.; Poppert, S.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Klempa, B.; Henning, K.; Schares, G.; Groschup, M.H.; Spitzenberger, F.; et al. Multiple Infections of Rodents with Zoonotic Pathogens in Austria. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibler, J.H.; Zakhour, C.M.; Gadhoke, P.; Gaeta, J.M. Zoonotic and Vector-Borne Infections among Urban Homeless and Marginalized People in the United States and Europe, 1990–2014. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.A.; Kershaw, W.E. Host-Parasite Relations in Cotton Rat Filariasis. II: The Quantitative Transmission of Litomosoides carinii to Delhi and Carworth Strains of White Rats, Including the Effect of Age. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1976, 70, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renz, A.; Wenk, P. Intracellular Development of the Cotton-Rat Filaria Litomosoides carinii in the Vector Mite Ornithonyssus bacoti. Trans. R Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 75, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notarnicola, J.; Bain, O.; Navone, G.T. Two New Species of Litomosoides (Nematoda: Filarioidea) in Sigmodontines (Rodentia: Muridae) from Rio de La Plata Marshland, Argentina. J. Parasitol. 2000, 86, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, S.; Pfarr, K.M.; Hoerauf, A. Infection of the Intermediate Mite Host with Wolbachia-depleted Litomosoides sigmodontis Microfilariae: Impaired L1 to L3 Development and Subsequent Sex-Ratio Distortion in Adult Worms. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.W. The Laboratory Rearing of the Tropical Rat Mite, Liponyssus bacoti (Hirst). J. Parasitol. 1946, 32, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, D.S. An Apparatus for Collecting Blood-Sucking Mites. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1946, 40, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, E.; Baker, C. Observations on the Micromorphology of the Tropical Rat Mite Ornithonyssus bacoti (Hirst) as Revealed by Scanning Electron Microscopy. J. South Afr. Vet. Assoc. 1996, 67, 128–132. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, J.M.; Mascarelli, P.E.; Trull, C.L.; Maggi, R.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Bartonella henselae Infections in an Owner and Two Papillon Dogs Exposed to Tropical Rat Mites (Ornithonyssus bacoti). Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, A.J.; Islam, S.; Sahu, S. Use of Scanning Electron Microscopy to Confirm the Identity of Tropical Rat Mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti): The Cause of Rat Mite Dermatitis. J. Parasit. Dis. 2016, 40, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieri-Bastos, F.A.; Labruna, M.B.; Marcili, A.; Durden, L.A.; Mendoza-Uribe, L.; Barros-Battesti, D.M. Morphological and Molecular Analysis of Ornithonyssus spp. (Acari: Macronyssidae) from Small Terrestrial Mammals in Brazil. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2011, 55, 305–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, R.; Hu, L. De Novo RNA-seq and Functional Annotation of Ornithonyssus bacoti. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 75, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, D.; Gong, X.; Hu, L. Study on the Relationship between Microbial Composition and Living Environment in Important Medical Mites Based on Illumina Miseq Sequencing Technology. J. Med. Entomol. 2020, 57, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, W.Y.; Wang, R.L.; Niu, D.L. Divergent Domains of 28S Ribosomal RNA Gene: DNA Barcodes for Molecular Classification and Identification of Mites. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Guo, X.G.; Fan, R.; Zhao, C.F.; Mao, K.Y.; Zhang, Z.W.; Zhao, Y. Ecological Analysis of Gamasid Mites on the Body Surface of Norway Rats (Rattus norvegicus) in Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Biologia 2019, 75, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.P.; Guo, X.G.; Qian, T.J.; Wu, D.; Men, X.Y.; Dong, W.G. Distribution of Gamasid Mites on Small Mammals in Yunnan Province, China. Insect Sci. 2007, 14, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.Y.; Guo, X.G.; Jin, D.C. A New Species of Laelaps Koch (Acari: Laelapidae) Associated with Red Spiny Rat from Yunnan Province, China. Pak. J. Zool. 2018, 50, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.Y.; Guo, X.G.; Song, W.Y.; Hou, P.; Zou, Y.J.; Fan, R.; HE, X.S. Analysis of Ectoparasites (Chigger Mites, Gamasid Mites, Fleas and Sucking Lice) of the Yunnan Red-Backed Vole (Eothenomys miletus) Sampled Throughout Its Range in Southwest China. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2015, 29, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, P.Y.; Guo, X.G.; Song, W.Y.; Hou, P.; Zou, Y.J.; Fan, R. Ectoparasitic Chigger Mites on Large Oriental Vole (Eothenomys miletus) across Southwest, China. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritzi, C.M.; Whitaker, J.O. Ectoparasites of Small Mammals from the Newport Chemical Depot, Vermillion County, Indiana. Northeast. Nat. 2003, 10, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storm, J.J.; Ritzi, C.M. Ectoparasites of Small Mammals in Western Iowa. Northeast. Nat. 2008, 15, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.Z.; Guo, X.G.; Speakman, J.R.; Zuo, X.H.; Wu, D.; Wang, Q.H.; Yang, Z.H. Abundances and Host Relationships of Chigger Mites in Yunnan Province, China. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2013, 27, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L.R. Aggregation, Variance and the Mean. Nature 1961, 189, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuno, E. Sampling and Analysis of Insect Populations. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1991, 36, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.E. Parasite Prevalence and the Size of Host Populations: An Experimental Test. J. Parasitol. 2005, 91, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.G.; Qian, T.J.; Meng, X.Y.; Dong, W.G.; Shi, W.X.; Wu, D. Preliminary Analysis of Chigger Communities Associated with House Rats (Rattus flavipectus) from Six Counties in Yunnan, China. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2006, 11, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J. New Building, Old Parasite: Mesostigmatid Mites—An Ever-Present Threat to Barrier Rodent Facilities. ILAR J. 2008, 49, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlesworth, E.N.; Clegern, R.W. Tropical Rat Mite Dermatitis. Arch. Dermatol. 1977, 113, 937–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.G.; Dong, W.G.; Men, X.Y.; Qian, T.J.; Wu, D.; Ren, T.G.; Qin, F.; Song, W.Y.; Yang, Z.H.; Fletcher, Q.E. Species Abundance Distribution of Ectoparasites on Norway Rats (Rattus norvegicus) from a Localized Area in Southwest China. J. Arthropod Borne Dis. 2016, 10, 192. [Google Scholar]
- Paramasvaran, S.; Sani, R.; Hassan, L.; Krishnasamy, M.; Jeffery, J.; Oothuman, P.; Salleh, I.; Lim, K.; Sumarni, M.; Santhana, R. Ectoparasite Fauna of Rodents and Shrews from Four Habitats in Kuala Lumpur and the States of Selangor and Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia and Its Public Health Significance. Trop. Biomed. 2009, 26, 303–311. [Google Scholar]
- Negm, M.W.; Mohamed, A.A.; El-Gepaly, H.M.K.; Abdelaziz, S.M. Mesostigmata Mites (Acari: Parasitiformes) Associated with Birds and Their Nests from Egypt. Turk. J. Zool. 2018, 42, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.Y.; Guo, X.G.; Ren, T.G.; Dong, W.G.; Song, W.Y. An Updated Distribution and Hosts: Trombiculid Mites (Acari: Trombidiformes) Associated with Small Mammals in Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 1923–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xu, Z. The Effect of Three Gorge Project on the Small Mammals in Yangtze River of China. Arch. Zool. Stud. 2018, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, A.M.; Singleton, G.R.; Prescott, C.V. Population Ecology of the Asian House Rat (Rattus tanezumi) in Complex Lowland Agroecosystems in the Philippines. Wildl. Res. 2015, 42, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Li, G.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Lu, L.; Liu, Q. Dispersal Route of the Asian House Rat (Rattus tanezumi) on Mainland China: Insights from Microsatellite and Mitochondrial DNA. BMC Genet. 2019, 20, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Zou, Y.; Fu, Z.F.; Plyusnin, A. Hantavirus Infections in Humans and Animals, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, B.; Kosoy, M.Y.; Maupin, G.O.; Tsuchiya, K.R.; Gage, K.L. Genetic and Ecologic Characteristics of Bartonella Communities in Rodents in Southern China. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2002, 66, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhenyu, L.; Gregg, W.P.; Dianmo, L. Invasive Species in China—An Overview. Biodivers. Conserv. 2001, 10, 1317–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbergh, J.G. Use of House Mice in Biomedical Research. ILAR J. 2000, 41, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, M.; Yu, H.T.; Bi, X.; Lai, Y.C.; Jiang, W.; Huang, L. Phylogeography of Chinese House Mice (Mus musculus musculus/castaneus): Distribution, Routes of Colonization and Geographic Regions of Hybridization. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 4387–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badgley, C. Tectonics, Topography, and Mammalian Diversity. Ecography 2010, 33, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangwala, I.; Miller, J.R. Climate Change in Mountains: A Review of Elevation-Dependent Warming and Its Possible Causes. Clim. Change 2012, 114, 527–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Ding, K.; Li, M.B.; Zhou, R.L. Spatial Distribution Modeling of Temperature Increase for the Uplifted Mountain Terrains and Its Characteristics in Southwest China. J. Mt. Sci. 2017, 14, 2270–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jen, M.N. Agricultural Landscape of Southwestern China: A Study in Land Utilization. Econ. Geogr. 1948, 24, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.F.; Wang, D.Q.; Gu, Y.M.; Meng, Y.C. Economic Insect Fauna of China. Fasc 40, Acari, Dermanyssoidea; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Habedank, B.; Betke, P. Aktuelle Nachweise der Tropischen Rattenmilbe, Ornithonyssus bacoti (Acari: Macronyssidae) in Wohnungen. DVG Tag. Bekämpfung Epidemiol. Parasitosen 2002, 19, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Mullen, G.R.; O’Connor, B.M. Mites (Acari). In Medical and Veterinary Entomology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 533–602. [Google Scholar]
- Varma, M. Ticks and Mites (Acari). In Medical Insects and Arachnids; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1993; pp. 597–658. [Google Scholar]
- Grenfell, B.T.; Dobson, A.P.; Moffatt, H. Ecology of Infectious Diseases in Natural Populations; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Grear, J.S.; Schmitz, O.J. Effects of Grouping Behavior and Predators on the Spatial Distribution of a Forest Floor Arthropod. Ecology 2005, 86, 960–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touati, L.; Figuerola, J.; Alfarhan, A.H.; Samraoui, B. Distribution Patterns of Ectoparasites of Glossy Ibis (Plegadis falcinellus) Chicks. Zoology 2015, 25, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, L.E.; Squires, J.R.; Oakleaf, R.J.; Wallace, Z.P.; Kennedy, P.L. Predicting Above-Ground Density and Distribution of Small Mammal Prey Species at Large Spatial Scales. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicacio, J.; Oliveira, I.D.; Uchoa, M.A.; Faccenda, O.; Abot, A.R.; Fernandes, M.G.; Garcia, F.R. Spatial Distribution and Control Levels of Anastrepha spp. (Diptera: Tephritidae) in Guava Orchards. Anais Acad. Bras. Ciências 2019, 91, e20180428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.H.; Guo, X.G.; Zhan, Y.Z.; Wu, D.; Yang, Z.H.; Dong, W.G.; Huang, L.Q.; Ren, T.G.; Jing, Y.G.; Wang, Q.H. Host Selection and Niche Differentiation in Sucking Lice (Insecta: Anoplura) among Small Mammals in Southwestern China. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 108, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elton, C.S. Animal Ecology; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the Amount of Ecologic Association between Species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurlbert, S.H. A Coefficient of Interspecific Assciation. Ecology 1969, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, T.M.; Gaston, K.J. A Critical Assessment of the Form of the Interspecific Relationship between Abundance and Body Size in Animals. J. Anim. Ecol. 1997, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, L.C. The Measurement of Interspecific Associaton. Ecology 1949, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, L.C. The Measurement of Partial Interspecific Association. Ecology 1957, 38, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).