Effects of Ferulic Acid Esterase-Producing Lactic Acid Bacteria and Storage Temperature on the Fermentation Quality, In Vitro Digestibility and Phenolic Acid Extraction Yields of Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) Silage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. FAE-Producing LAB Strains
2.2. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing Analysis
2.3. Enzymatic Activity Assay
2.4. Sorghum Ensiling
2.5. Chemical Analysis
2.6. In Vitro Incubation and Degradability Measurements
2.7. Extraction and Determination of Phenolic Acids
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of FAE-Producing LAB Strains and Their Enzymatic Activity
3.2. Chemical Composition and Phenolic Acid Extraction Yields of Sorghum Prior to Ensiling
3.3. Fermentation Characteristics of Sorghum Silages
3.4. Chemical Composition of Sorghum Silages
3.5. In Vitro Incubation and Degradability Measurements
3.6. Phenolic Acid Extraction Yields of Sorghum Silage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tišma, M.; Planinić, M.; Bucić-Kojić, A.; Panjičko, M.; Zupančič, G.D.; Zelić, B. Corn silage fungal-based solid-state pretreatment for enhanced biogas production in anaerobic co-digestion with cow manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 253, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sifeeldein, A.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Dong, Z.; Chen, L.; Kaka, N.A.; Shao, T. Phylogenetic identification of lactic acid bacteria isolates and their effects on the fermentation quality of sweet sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) silage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Xie, Y.; Yu, Z.; Meng, G.; Wu, Z. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum expressing multifunctional glycoside hydrolases on the characteristics of alfalfa silage. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 7983–7995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; McKinnon, J.J.; Christensen, D.A. Hydroxycinnamic acids and ferulic acid esterase in relation to biodegradation of complex plant cell walls. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 85, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.B.; Jin, X.; Yang, H.J.; Li, S.L.; Jiang, L.S. Microbial release of ferulic and p-coumaric acids from forages and their digestibility in lactating cows fed total mixed rations with different forage combinations. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.B.; Wang, R.; Bo, Y.K.; Bai, S.; Yang, H.J. In situ rumen digestibility of ester-linked ferulic and p-coumaric acids in crop stover or straws in comparison with alfalfa and Chinese wild ryegrass hays. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2016, 212, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, G.; Kroon, P.A.; Faulds, C.B. Hairy plant polysaccharides: A close shave with microbial esterases. Microbiology 1998, 144, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soberon, M.A.; Cherney, J.H.; Liu, R.H.; Ross, D.A.; Cherney, D.J.R. Free ferulic acid uptake in lactating cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 6563–6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crepin, V.F.; Faulds, C.B.; Connerton, I.F. Functional classification of the microbial feruloyl esterases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 63, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; He, H.; Zhang, S.; Guo, T.; Kong, J. Characterization of feruloyl esterases produced by the four lactobacillus species: L. amylovorus, L. acidophilus, L. farciminis and L. fermentum, isolated from ensiled corn stover. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsereko, V.L.; Smiley, B.K.; Rutherford, W.M.; Spielbauer, A.; Forrester, K.J.; Hettinger, G.H.; Harman, E.K.; Harman, B.R. Influence of inoculating forage with lactic acid bacterial strains that produce ferulate esterase on ensilage and ruminal degradation of fiber. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2008, 145, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.P.; Prema, D.; Van Hamme, J.D.; Church, J.S.; Beauchemin, K.A. Fiber degradability, chemical composition and conservation characteristics of alfalfa haylage ensiled with exogenous fibrolytic enzymes and a ferulic acid esterase-producing inoculant. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 94, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comino, L.; Tabacco, E.; Righi, F.; Revello-Chion, A.; Quarantelli, A.; Borreani, G. Effects of an inoculant containing a Lactobacillus buchneri that produces ferulate-esterase on fermentation products, aerobic stability, and fibre digestibility of maize silage harvested at different stages of maturity. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 198, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, Z.G.; Szakacs, G.; Ashbell, G.; Hen, Y. The effect of temperature on the ensiling process of corn and wheat. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 90, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Drouin, P.; Lafrenière, C. Effect of temperature (5–25 °C) on epiphytic lactic acid bacteria populations and fermentation of whole-plant corn silage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, T.F.; Daniel, J.L.P.; Adesogan, A.T.; McAllister, T.A.; Drouin, P.; Nussio, L.G.; Huhtanen, P.; Tremblay, G.F.; Bélanger, G.; Cai, Y. Silage review: Unique challenges of silages made in hot and cold regions. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4001–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.T.; Xu, D.M.; Bai, J.; Li, F.H.; Adesogan, A.T.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, X.J.; Guo, X.S. Characterization and identification of ferulic acid esterase-producing Lactobacillus species isolated from Elymus nutans silage and their application in ensiled alfalfa. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolford, M.K.; Pahlow, G. The silage fermentation. In Microbiology of Fermented Foods; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 73–102. [Google Scholar]
- Donaghy, J.; Kelly, P.F.; McKay, A.M. Detection of ferulic acid esterase production by Bacillus spp. and lactobacilli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 50, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanis, A.; Kourkoutas, Y.; Tassou, C.C.; Chorianopoulos, N. Detection and identification of probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum strains by multiplex PCR using RAPD-derived primers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 25141–25153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.; Yang, H.J.; Li, D.H.; Wang, J.Q. A comparison of HPLC and spectrophotometrical methods to determine the activity of ferulic acid esterase in commercial enzyme products and rumen contents of steers. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2009, 153, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Li, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X. Interactive effect of inoculant and dried jujube powder on the fermentation quality and nitrogen fraction of alfalfa silage. Anim. Sci. J. 2017, 88, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, G.A.; Kang, J.H. Automated simultaneous determination of ammonia and total amino acids in ruminal fluid and in vitro media. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Sun, Z.; Gao, R.; Yu, Z. Lactic acid bacterial inoculant effects on the vitamin content of alfalfa and Chinese leymus silage. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Wen, A.; Desta, S.T.; Wang, J.; Shao, T. Effects of sodium diacetate on the fermentation profile, chemical composition and aerobic stability of alfalfa silage. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 30, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menke, K.H.; Raab, L.; Salewski, A.; Steingass, H.; Fritz, D.; Schneider, W. The estimation of the digestibility and metabolizable energy content of ruminant feedingstuffs from the gas production when they are incubated with rumen liquor in vitro. J. Agric. Sci. 1979, 93, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooke, J.A.; Hatfield, R.D. Biochemistry of Ensiling. In Silage Science and Technology; USDA-ARS/UNL Faculty: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2003; pp. 95–139. [Google Scholar]
- Filya, I.; Sucu, E.; Karabulut, A. The effect of Propionibacterium acidipropionici, with or without Lactobacillus plantarum, on the fermentation and aerobic stability of wheat, sorghum and maize silages. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 97, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaag, H.; Yuan, X.; Mala, A.; Bai, J.; Shao, T. Fermentation characteristics of Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus species isolated from sweet sorghum silage and their application as silage inoculants. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L.; Shaver, R.D.; Grant, R.J.; Schmidt, R.J. Silage review: Interpretation of chemical, microbial, and organoleptic components of silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooke, J.A.; Borman, A.J.; Armstrong, D.G. The effect of inoculation with Lactobacillus plantarum on fermentation in laboratory silos of herbage low in water-soluble carbohydrate. Grass Forage Sci. 1990, 45, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Shao, T. Effects of storage temperature and combined microbial inoculants on fermentation end products and microbial populations of Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.) silage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 125, 1682–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R.E.; Dickerson, J.T. Storage temperature effects on proteolysis in alfalfa silage. Trans. ASAE 1988, 31, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, Z.; Wang, X.; Tian, J. Effects of inoculants and environmental temperature on fermentation quality and bacterial diversity of alfalfa silage. Anim. Sci. J. 2018, 89, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Xu, S.; Wang, T.; Jia, T.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, Z. Effect of inoculants and storage temperature on the microbial, chemical and mycotoxin composition of corn silage. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, Z.G.; Muck, R.E. New trends and opportunities in the development and use of inoculants for silage. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 19, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, H.V.; Lafreniere, C.; Veira, D.M. A comparision of methods to determine dry matter in silages. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.D.; Olson, W.G.; Otterby, D.E.; Linn, J.G.; Hansen, W.P. Effects of temperature, moisture, and aeration on fermentation of alfalfa silage. J. Dairy Sci. 1989, 72, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ding, Z.; Ke, W.; Xu, D.; Zhang, P.; Bai, J.; Mudassar, S.; Muhammad, I.; Guo, X. Ferulic acid esterase-producing lactic acid bacteria and cellulase pretreatments of corn stalk silage at two different temperatures: Ensiling characteristics, carbohydrates composition and enzymatic saccharification. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Duniere, L.; Lynch, J.P.; McAllister, T.A.; Baah, J.; Wang, Y. Impact of ferulic acid esterase producing lactobacilli and fibrolytic enzymes on conservation characteristics, aerobic stability and fiber degradability of barley silage. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2015, 207, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Dunière, L.; Lynch, J.P.; Zaheer, R.; Turkington, K.; Blackshaw, R.E.; Lupwayi, N.Z.; O’Donovan, J.T.; Harker, K.N.; McAllister, T.; et al. Impact of ferulic acid esterase-producing lactobacilli and fibrolytic enzymes on ensiling and digestion kinetics of mixed small-grain silage. Grass Forage Sci. 2017, 72, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 ; LP23, Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant
; LP23, Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant  ; FAE, ferulic acid esterase. Means with difference superscripts (A–C) differ significantly from each other (p < 0.05). Error bars indicate standard error of means.
; FAE, ferulic acid esterase. Means with difference superscripts (A–C) differ significantly from each other (p < 0.05). Error bars indicate standard error of means.
 ; LP23, Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant
; LP23, Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant  ; FAE, ferulic acid esterase. Means with difference superscripts (A–C) differ significantly from each other (p < 0.05). Error bars indicate standard error of means.
; FAE, ferulic acid esterase. Means with difference superscripts (A–C) differ significantly from each other (p < 0.05). Error bars indicate standard error of means.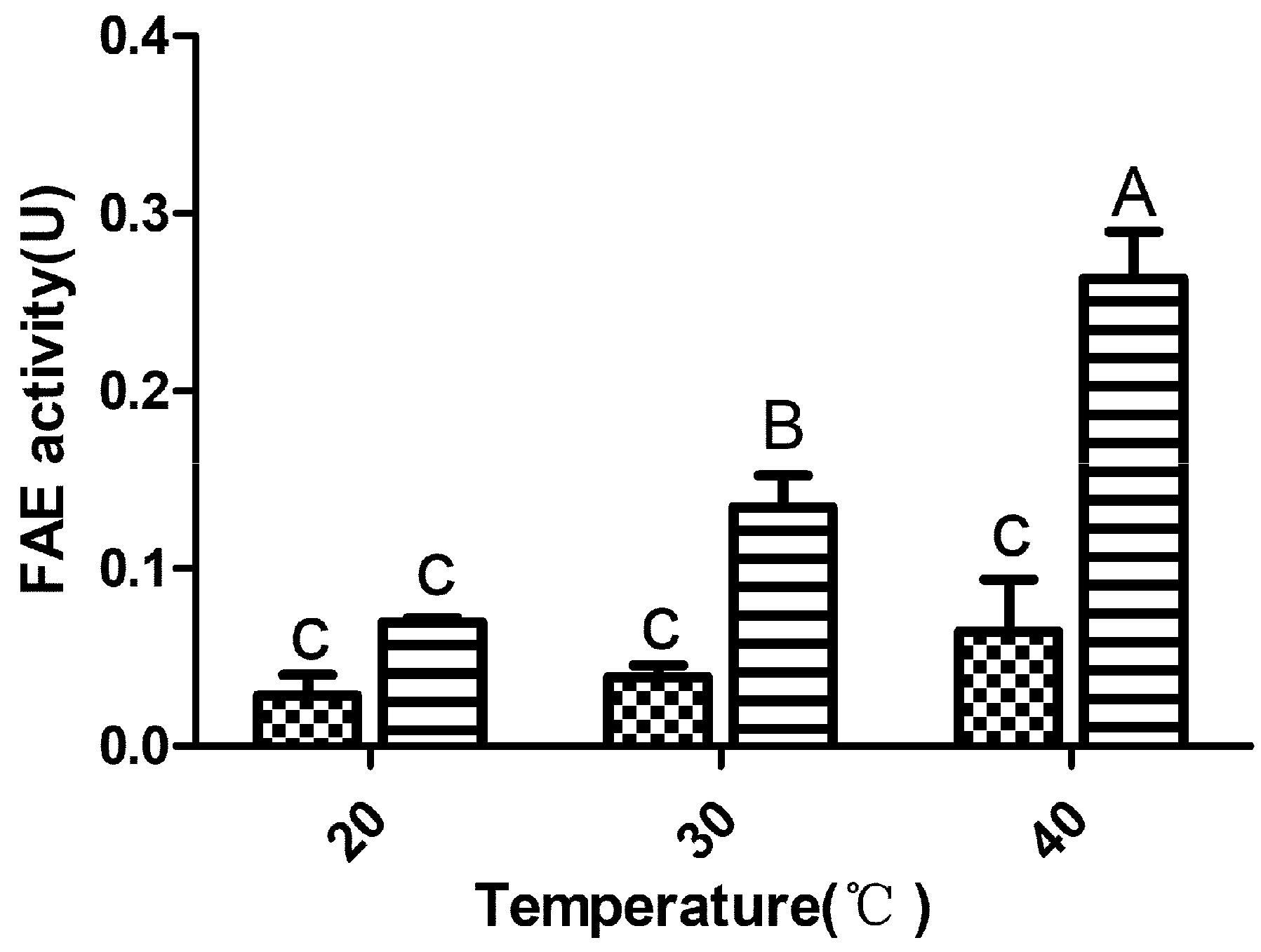
 ; LF18, Lactobacillus farciminis inoculant
; LF18, Lactobacillus farciminis inoculant  ; LP23, Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant
; LP23, Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant  . Means within the same temperature (a, b) or within the same inoculant (A, B) with difference superscripts differ significantly from each other (p < 0.05). Error bars indicate standard error of means.
. Means within the same temperature (a, b) or within the same inoculant (A, B) with difference superscripts differ significantly from each other (p < 0.05). Error bars indicate standard error of means.
 ; LF18, Lactobacillus farciminis inoculant
; LF18, Lactobacillus farciminis inoculant  ; LP23, Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant
; LP23, Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant  . Means within the same temperature (a, b) or within the same inoculant (A, B) with difference superscripts differ significantly from each other (p < 0.05). Error bars indicate standard error of means.
. Means within the same temperature (a, b) or within the same inoculant (A, B) with difference superscripts differ significantly from each other (p < 0.05). Error bars indicate standard error of means.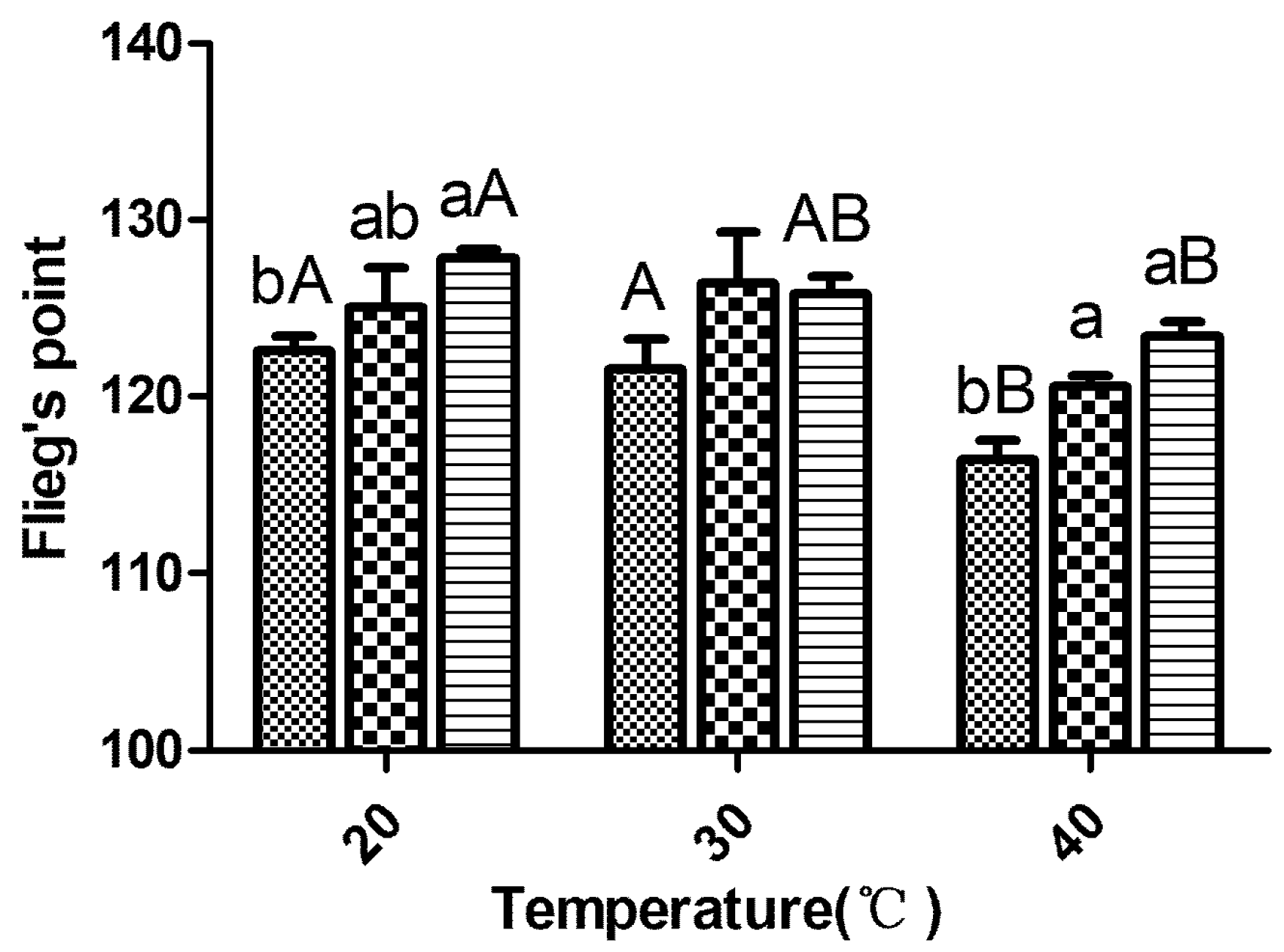
 ; LF18, Lactobacillus farciminis inoculant
; LF18, Lactobacillus farciminis inoculant  ; LP23, Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant
; LP23, Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant  . Means within the same temperature (a, b) or within the same inoculant (A, B) with difference superscripts differ significantly from each other (p < 0.05). Error bars indicate standard error of means.
. Means within the same temperature (a, b) or within the same inoculant (A, B) with difference superscripts differ significantly from each other (p < 0.05). Error bars indicate standard error of means.
 ; LF18, Lactobacillus farciminis inoculant
; LF18, Lactobacillus farciminis inoculant  ; LP23, Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant
; LP23, Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant  . Means within the same temperature (a, b) or within the same inoculant (A, B) with difference superscripts differ significantly from each other (p < 0.05). Error bars indicate standard error of means.
. Means within the same temperature (a, b) or within the same inoculant (A, B) with difference superscripts differ significantly from each other (p < 0.05). Error bars indicate standard error of means.
| Item | Temperature | Inoculant | SEM | Significance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | LF18 | LP23 | I | T | I × T | |||
| pH | 20 °C | 3.92 aB | 3.81 b | 3.72 bC | 0.01 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.705 |
| 30 °C | 3.93 aB | 3.82 b | 3.77 bB | |||||
| 40 °C | 4.04 aA | 3.90 b | 3.86 bA | |||||
| Lactic acid (g kg−1DM) | 20 °C | 47.9 bB | 54.1 abAB | 63.5 aA | 0.82 | 0.005 | <0.001 | 0.111 |
| 30 °C | 60.7 A | 58.6 A | 62.4 A | |||||
| 40 °C | 43.3 bC | 44.0 abB | 48.1 aB | |||||
| Acetic acid (g kg−1 DM) | 20 °C | 14.7 aA | 13.6 aA | 10.0 bB | 0.33 | 0.326 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 30 °C | 14.9 aA | 13.8 abA | 10.8 bAB | |||||
| 40 °C | 7.1 bB | 8.7 abB | 12.4 aA | |||||
| Propionic acid (g kg−1 DM) | 20 °C | ND C | ND | ND C | 0.18 | 0.602 | <0.001 | 0.537 |
| 30 °C | 1.3 aB | 1.0 b | 0.4 cB | |||||
| 40 °C | 1.9 A | 3.2 | 2.4 A | |||||
| Butyric acid (g kg−1 DM) | 20 °C | ND | ND | ND | - | - | - | - |
| 30 °C | ND | ND | ND | |||||
| 40 °C | ND | ND | ND | |||||
| Lactic acid: Acetic acid ratio | 20 °C | 3.26 bB | 4.12 b | 6.39 aA | 0.20 | 0.209 | 0.399 | 0.002 |
| 30 °C | 4.13 bAB | 4.25 b | 5.89 aA | |||||
| 40 °C | 6.69 A | 5.19 | 3.89 B | |||||
| NH3-N (g kg−1 TN) | 20 °C | 22.9 aC | 17.7 bC | 16.5 bC | 0.27 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 30 °C | 28.8a B | 21.1 bB | 21.9 bB | |||||
| 40 °C | 40.7 aA | 27.3 bA | 27.0 bA | |||||
| Item | Temperature | Inoculant | SEM | Significance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | LF18 | LP23 | I | T | I × T | |||
| DM (g kg−1 FM) | 20 °C | 371.1 | 362.7 | 357.9 | 1.88 | 0.218 | 0.729 | 0.524 |
| 30 °C | 369.8 | 370.2 | 358.4 | |||||
| 40 °C | 364.9 | 357.9 | 364.6 | |||||
| WSC (g kg−1 DM) | 20 °C | 39.0 A | 41.2 A | 42.8 A | 0.42 | 0.010 | <0.001 | 0.053 |
| 30 °C | 32.0 bB | 35.4 abB | 38.4 aA | |||||
| 40 °C | 32.4 B | 35.7 B | 31.7 B | |||||
| CP (g kg−1 DM) | 20 °C | 109.8 A | 109.9 A | 109.7 A | 0.34 | 0.262 | <0.001 | 0.195 |
| 30 °C | 109.4 A | 105.6 B | 105.9 B | |||||
| 40 °C | 104.7 B | 105.6 B | 104.1 B | |||||
| aNDF (g kg−1 DM) | 20 °C | 572.9 B | 564.6 | 557.4 C | 1.40 | 0.014 | <0.001 | 0.273 |
| 30 °C | 585.2 aA | 569.3 b | 571.5 bB | |||||
| 40 °C | 585.2 A | 579.2 | 585.5 A | |||||
| ADF (g kg−1 DM) | 20 °C | 314.1 | 313.0 | 308.0 B | 1.59 | 0.754 | 0.023 | 0.293 |
| 30 °C | 319.1 | 315.5 | 314.0 B | |||||
| 40 °C | 315.4 | 328.0 | 327.1 A | |||||
| HC (g kg−1 DM) | 20 °C | 258.8 | 251.6 | 249.5 | 1.95 | 0.040 | 0.347 | 0.889 |
| 30 °C | 266.1 | 253.8 | 257.5 | |||||
| 40 °C | 269.8 | 251.2 | 258.4 | |||||
| CE (g kg−1 DM) | 20 °C | 293.5 | 291.3 | 288.4 | 1.78 | 0.556 | 0.379 | 0.232 |
| 30 °C | 296.2 | 294.4 | 292.3 | |||||
| 40 °C | 277.0 | 295.4 | 291.8 | |||||
| ADL (g kg−1 DM) | 20 °C | 20.6 B | 21.7 B | 19.5 C | 0.58 | 0.317 | <0.001 | 0.396 |
| 30 °C | 26.8 B | 25.2 B | 25.9 B | |||||
| 40 °C | 38.4 A | 32.6 A | 35.3 A | |||||
| Ash (g kg−1 DM) | 20 °C | 90.0 | 93.3 A | 91.6 | 0.33 | 0.034 | 0.438 | 0.564 |
| 30 °C | 89.3 | 90.6 B | 92.2 | |||||
| 40 °C | 89.7 | 91.1 B | 91.2 | |||||
| Weight loss (g kg−1 FM) | 20 °C | 28.9 a | 13.8 b | 13.6 b | 1.05 | 0.005 | 0.309 | 0.106 |
| 30 °C | 24.6 | 14.6 | 13.1 | |||||
| 40 °C | 14.4 | 15.5 | 14.5 | |||||
| DM loss (g kg−1 DM) | 20 °C | 40.7 | 47.9 | 60.3 | 4.73 | 0.538 | 0.788 | 0.561 |
| 30 °C | 40.1 | 29.1 | 58.5 | |||||
| 40 °C | 42.6 | 62.0 | 43.7 | |||||
| Item | Temperature | Inoculant | SEM | Significance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | LF18 | LP23 | I | T | I × T | |||
| DMD (%) | 20 °C | 47.71 | 47.42 | 48.78 | 0.78 | 0.866 | 0.485 | 0.966 |
| 30 °C | 49.1 | 49.35 | 49.15 | |||||
| 40 °C | 48.9 | 51.53 | 50.5 | |||||
| NDFD (%) | 20 °C | 35.61 | 36.96 | 34.52 | 0.30 | 0.042 | 0.876 | 0.018 |
| 30 °C | 34.30 ab | 33.30 b | 38.34 a | |||||
| 40 °C | 35.59 ab | 33.40 b | 37.36 a | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, W.; Wu, Z.; Yu, Z. Effects of Ferulic Acid Esterase-Producing Lactic Acid Bacteria and Storage Temperature on the Fermentation Quality, In Vitro Digestibility and Phenolic Acid Extraction Yields of Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) Silage. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010114
Xie Y, Guo J, Li W, Wu Z, Yu Z. Effects of Ferulic Acid Esterase-Producing Lactic Acid Bacteria and Storage Temperature on the Fermentation Quality, In Vitro Digestibility and Phenolic Acid Extraction Yields of Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) Silage. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(1):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010114
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Yixiao, Jingui Guo, Wenqi Li, Zhe Wu, and Zhu Yu. 2021. "Effects of Ferulic Acid Esterase-Producing Lactic Acid Bacteria and Storage Temperature on the Fermentation Quality, In Vitro Digestibility and Phenolic Acid Extraction Yields of Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) Silage" Microorganisms 9, no. 1: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010114
APA StyleXie, Y., Guo, J., Li, W., Wu, Z., & Yu, Z. (2021). Effects of Ferulic Acid Esterase-Producing Lactic Acid Bacteria and Storage Temperature on the Fermentation Quality, In Vitro Digestibility and Phenolic Acid Extraction Yields of Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) Silage. Microorganisms, 9(1), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010114





