Isolation, Pathogenicity and Genomic Analysis of Mannheimia haemolytica Strain XJCJMh1 in Bovine-Mycoplasma Co-Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Mycoplasma Bovis Detection
2.3. Isolation and Identification of Mannheimia haemolytica
2.4. Serotyping of Mannheimia haemolytica
2.5. Animal Pathogenicity Experiment
2.6. Histopathological Examination
2.7. Library Construction and Genome Sequencing, Assembly
2.8. Genomic Component Analysis and Functional Annotation
3. Results
3.1. Detection Results of Mycoplasma bovis
3.2. Isolation, Identification, and Microscopic Examination of Mannheimia haemolytica
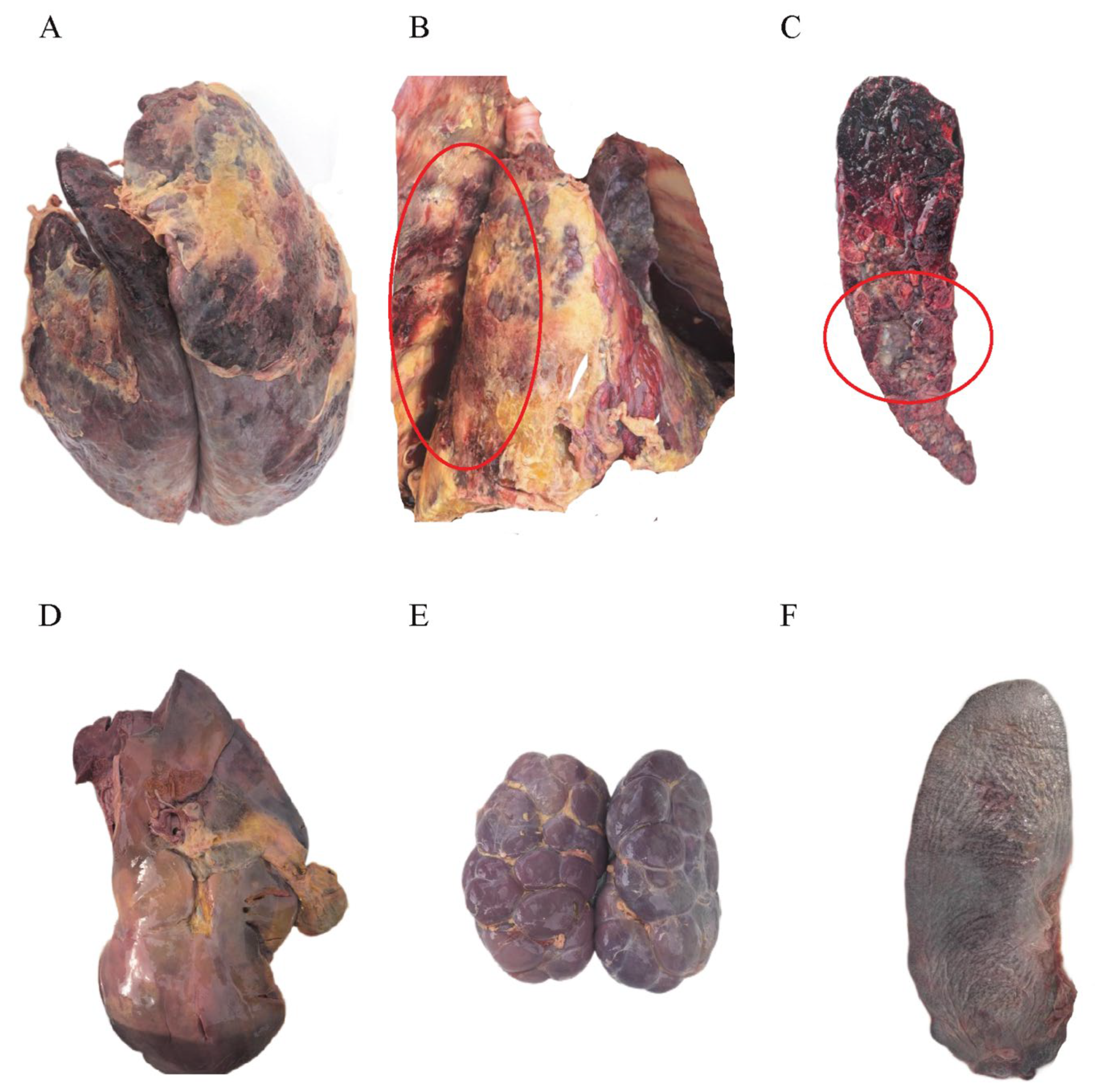
3.3. Postmortem Examination of Infected Cattle
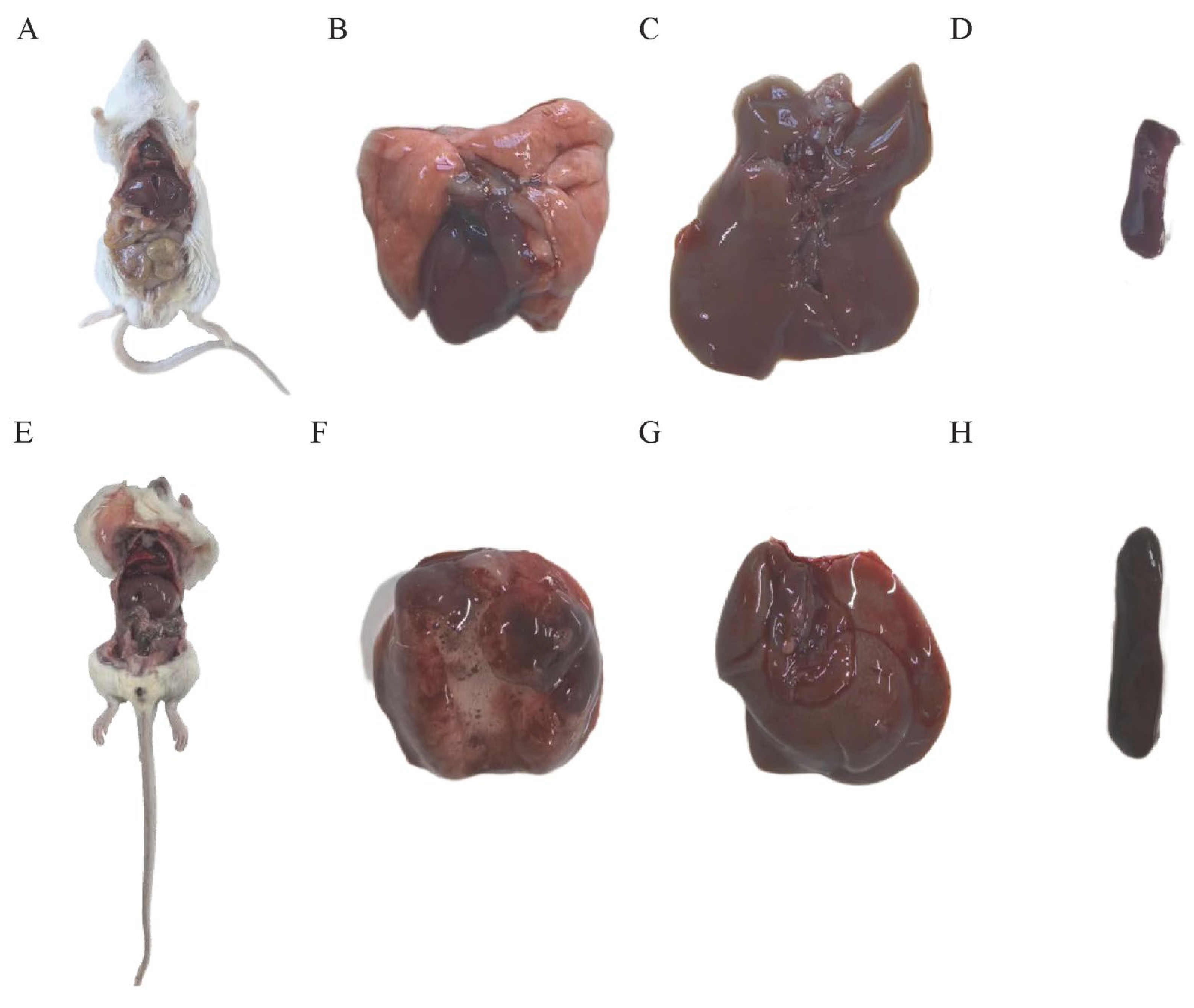
3.4. Mouse Lethality Assay
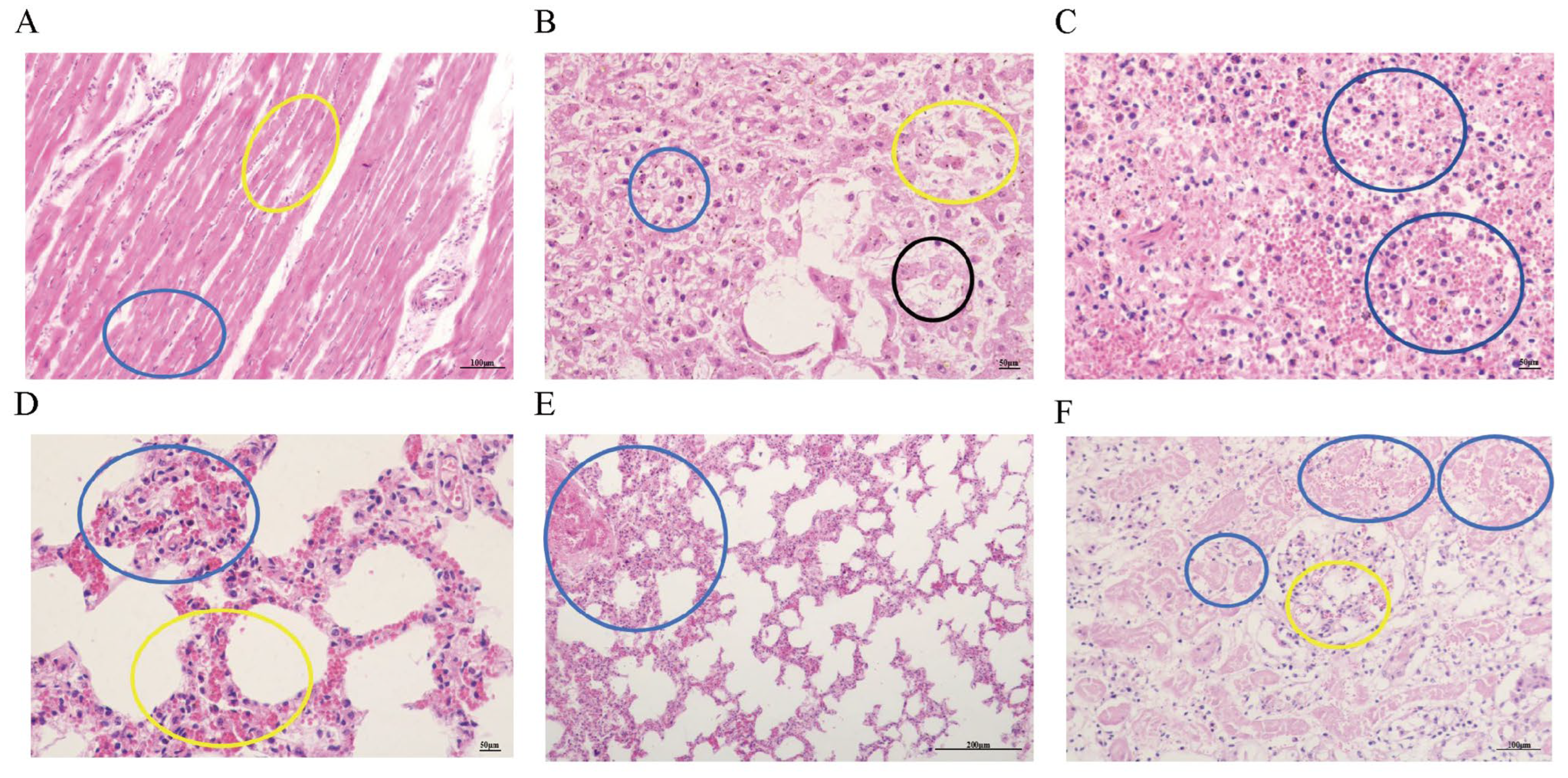
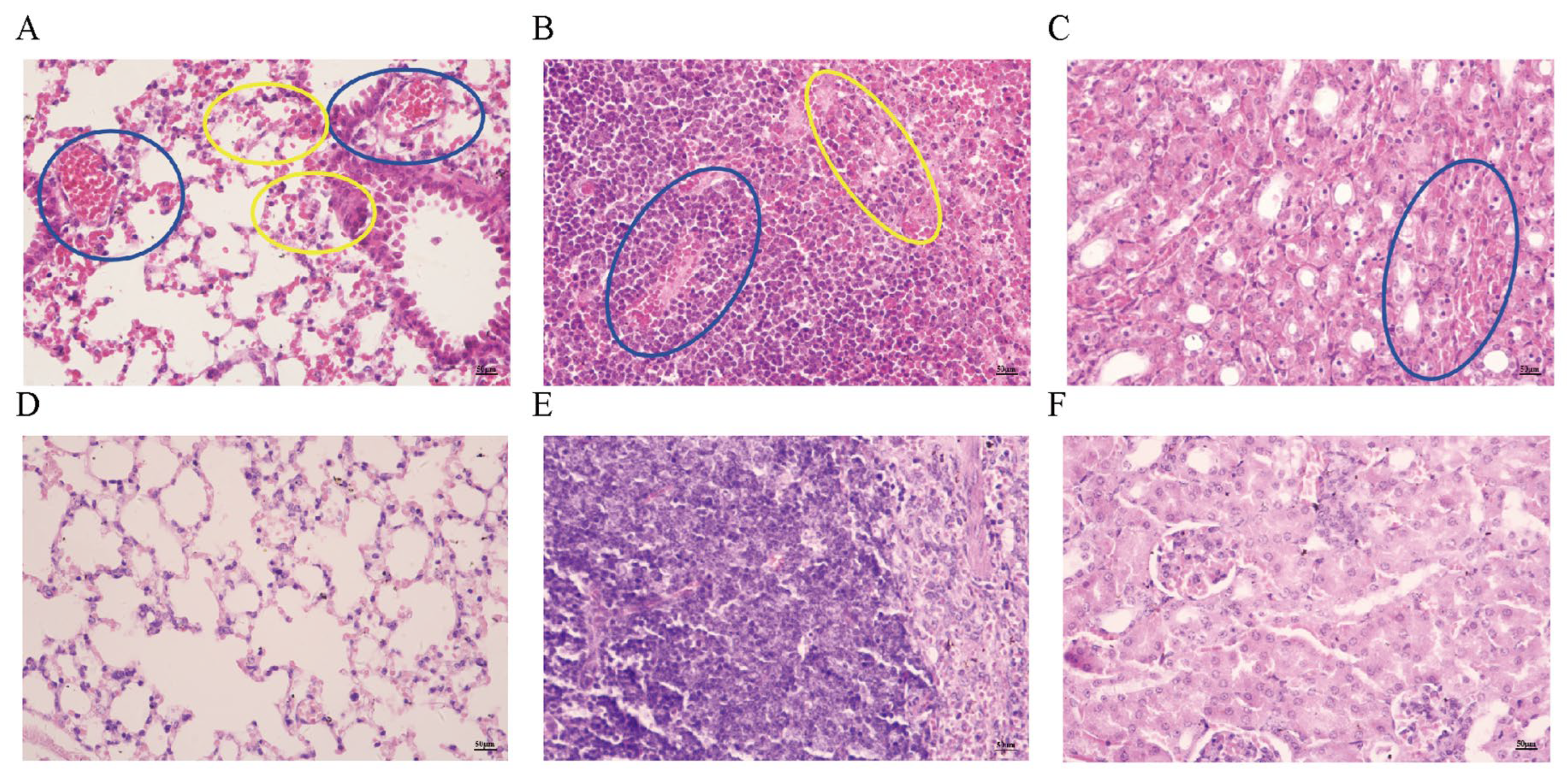
3.5. Observation of Pathological Tissue Sections
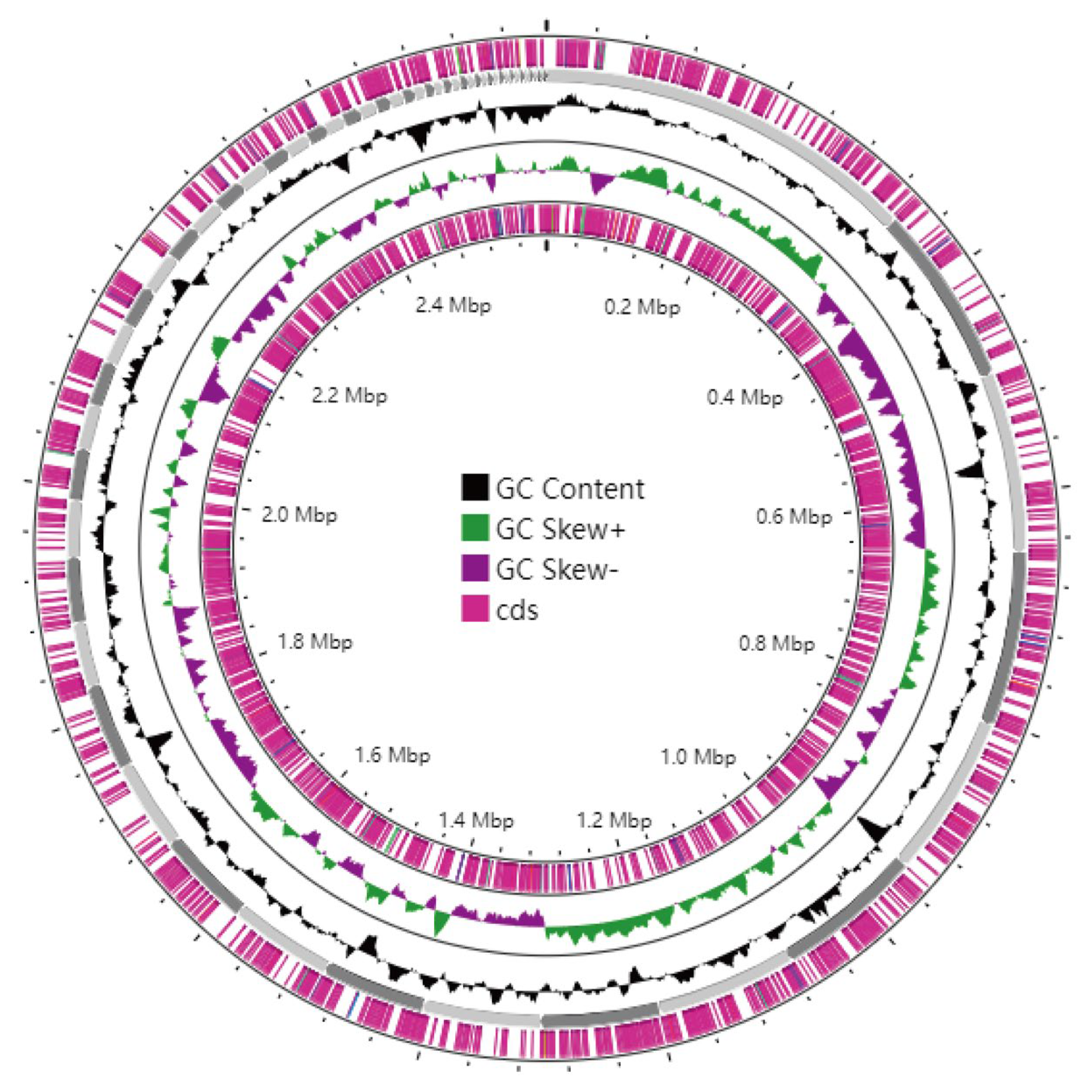
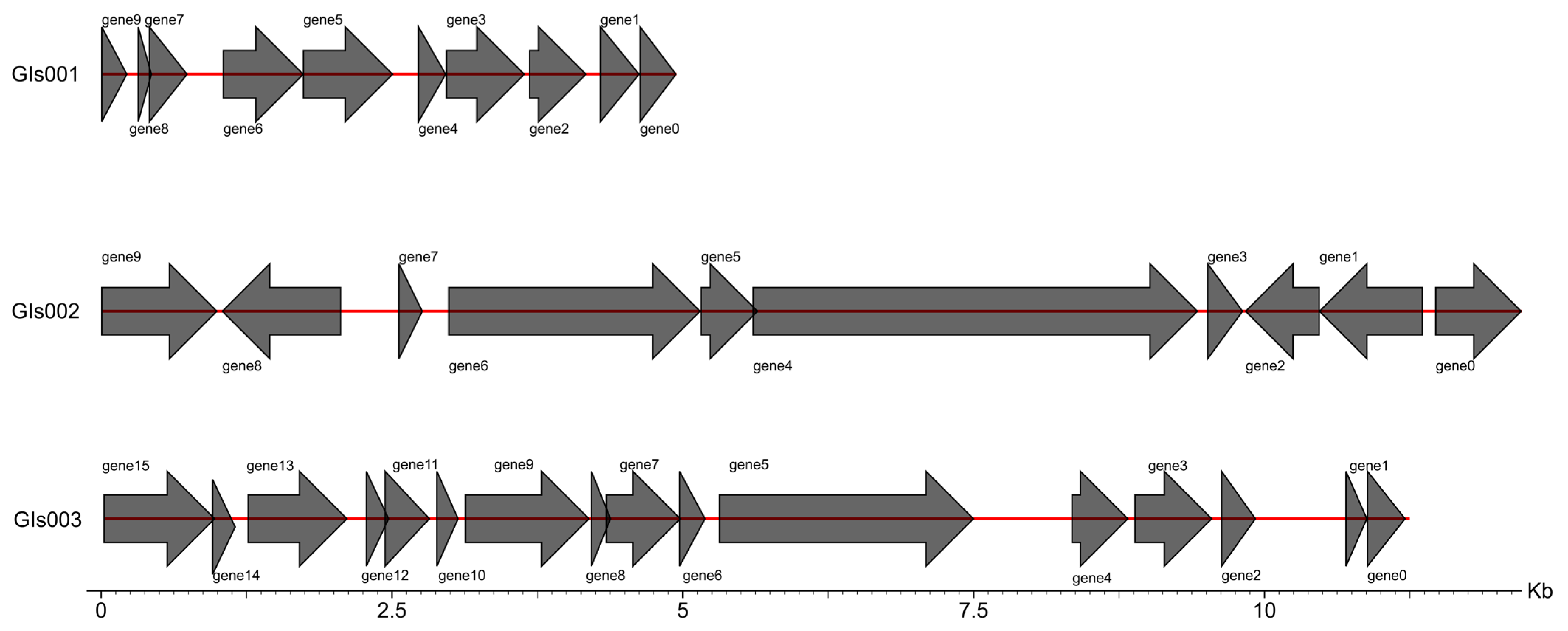
3.6. Genome Assembly and Whole-Genome Component Analysis Results
3.7. Gene Function Annotation and Prediction Results
3.8. Virulence and Drug Resistance Analysis Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamel, M.S.; Davidson, J.L.; Verma, M.S. Strategies for bovine respiratory disease (brd) diagnosis and prognosis: A comprehensive overview. Animals 2024, 14, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón Bernal, J.M.; Fernández, A.; Arnal, J.L.; Baselga, C.; Benito Zuñiga, A.; Fernández-Garyzábal, J.F.; Vela Alonso, A.I.; Cid, D. Cluster analysis of bovine respiratory disease (brd)-associated pathogens shows the existence of two epidemiological patterns in brd outbreaks. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 280, 109701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeris-Chacin, R.; Powledge, S.; McAtee, T.; Morley, P.S.; Richeson, J. Mycoplasma bovis is associated with mannheimia haemolytica during acute bovine respiratory disease in feedlot cattle. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 946792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeno-Martinez, R.E.; Glidden, N.; Mohan, S.; Davidson, J.L.; Fernández-Juricic, E.; Boerman, J.P.; Schoonmaker, J.; Pillai, D.; Koziol, J.; Ault, A.; et al. Identification of bovine respiratory disease through the nasal microbiome. Anim. Microbiome 2022, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosby, W.B.; Pinnell, L.J.; Richeson, J.T.; Wolfe, C.; Castle, J.; Loy, J.D.; Gow, S.P.; Seo, K.S.; Capik, S.F.; Woolums, A.R.; et al. Does swab type matter? Comparing methods for mannheimia haemolytica recovery and upper respiratory microbiome characterization in feedlot cattle. Anim. Microbiome 2022, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prysliak, T.; Vulikh, K.; Caswell, J.L.; Perez-Casal, J. Mannheimia haemolytica increases mycoplasma bovis disease in a bovine experimental model of brd. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 283, 109793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanelli, A.; Cirilli, M.; Lucente, M.S.; Zarea, A.A.K.; Buonavoglia, D.; Tempesta, M.; Greco, G. Fatal calf pneumonia outbreaks in italian dairy herds involving mycoplasma bovis and other agents of brd complex. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 742785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padalino, B.; Cirone, F.; Zappaterra, M.; Tullio, D.; Ficco, G.; Giustino, A.; Ndiana, L.A.; Pratelli, A. Factors affecting the development of bovine respiratory disease: A cross-sectional study in beef steers shipped from france to italy. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 627894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Hill, J.E.; Godson, D.L.; Ngeleka, M.; Fernando, C.; Huang, Y. The pulmonary virome, bacteriological and histopathological findings in bovine respiratory disease from western canada. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.; Ritchey, J.W.; Confer, A.W. Mannheimia haemolytica: Bacterial-host interactions in bovine pneumonia. Vet. Pathol. 2011, 48, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.R.; Brogden, K.A. Response of the ruminant respiratory tract to mannheimia (pasteurella) haemolytica. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, C.; Errington, J.; Foster, G.; Thacker, J.; Grace, O.; Baxter-Smith, K. Mannheimia haemolytica serovars associated with respiratory disease in cattle in great britain. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, A.; Ueno, Y.; Hoshinoo, K.; Okuno, M.; Uemura, R.; You, G.; Ogura, Y.; Takamatsu, D. Comprehensive serotyping of mannheimia haemolytica by a pcr system using the diversity of capsule biosynthesis genes. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozens, D.; Sutherland, E.; Lauder, M.; Taylor, G.; Berry, C.C.; Davies, R.L. Pathogenic mannheimia haemolytica invades differentiated bovine airway epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00078-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesse, F.F.A.; Amira, N.A.; Isa, K.M.; Maqbool, A.; Ali, N.M.; Chung, E.L.T.; Lila, M.A.M. Association between mannheimia haemolytica infection with reproductive physiology and performance in small ruminants: A Review. Vet. World 2019, 12, 978–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthalingam, S.; Goldy, A.; Bavananthasivam, J.; Subramaniam, R.; Batra, S.A.; Kugadas, A.; Raghavan, B.; Dassanayake, R.P.; Jennings-Gaines, J.E.; Killion, H.J.; et al. Pcr assay detects mannheimia haemolytica in culture-negative pneumonic lung tissues of bighorn sheep (ovis canadensis) from outbreaks in the western USA, 2009–2010. J. Wildl. Dis. 2014, 50, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klima, C.L.; Zaheer, R.; Briggs, R.E.; McAllister, T.A. A multiplex pcr assay for molecular capsular serotyping of mannheimia haemolytica serotypes 1, 2, and 6. J. Microbiol. Methods 2017, 139, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besemer, J.; Lomsadze, A.; Borodovsky, M. Genemarks: A self-training method for prediction of gene starts in microbial genomes. Implications for finding sequence motifs in regulatory regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 2607–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Bridges, S.; Magbanua, Z.V.; Peterson, D.G. Empirical comparison of ab initio repeat finding programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 2284–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, T.M.; Eddy, S.R. Trnascan-se: A program for improved detection of transfer rna genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagesen, K.; Hallin, P.; Rødland, E.A.; Staerfeldt, H.H.; Rognes, T.; Ussery, D.W. Rnammer: Consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal rna genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 3100–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, W.; Wan, I.; Jones, S.J.; Brinkman, F.S. Islandpath: Aiding detection of genomic islands in prokaryotes. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Liang, Y.; Lynch, K.H.; Dennis, J.J.; Wishart, D.S. Phast: A fast phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W347–W352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grissa, I.; Vergnaud, G.; Pourcel, C. Crisprfinder: A web tool to identify clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W52–W57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschenbroich, S.; Nemeth, N.; Rech, R.; Briggs, R.; Sanchez, S.; Brown, C. Mannheimia haemolytica a1-induced fibrinosuppurative meningoencephalitis in a naturally-infected holstein-friesian calf. J. Comp. Pathol. 2013, 149, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesheuvel, M.M.; van Schaik, G.; Meertens, N.M.; Peperkamp, N.H.; van Engelen, E.; van Garderen, E. Emergence of fatal mannheimia haemolytica infections in cattle in the netherlands. Vet. J. (Lond. Engl. 1997) 2021, 268, 105576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanzlicek, G.A.; White, B.J.; Mosier, D.; Renter, D.G.; Anderson, D.E. Serial evaluation of physiologic, pathological, and behavioral changes related to disease progression of experimentally induced mannheimia haemolytica pneumonia in postweaned calves. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2010, 71, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzon, A.; Miramontes, C.; Weimer, B.C.; Profeta, R.; Hoyos-Jaramillo, A.; Fritz, H.M.; Pereira, R.V. Comparison of virulence and resistance genes in mannheimia haemolytica and pasteurella multocida from dairy cattle with and without bovine respiratory disease. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e0120025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidanemariam Gelaw, A.; Bihon, W.; Faranani, R.; Mafofo, J.; Rees, J.; Madoroba, E. Complete genome sequence of mannheimia haemolytica strain mh10517, isolated from sheep in south africa. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e00129-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi, A.; Fazzio, L.; Fernandez, J.; Sisti, F. Draft genome sequence of mannheimia haemolytica strain oliden, isolated from a calf lung infection in argentina. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2024, 13, e0099723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Chang, Y.; Brun, Y.V.; Howell, P.L.; Burrows, L.L.; Liu, J. Pily1 regulates the dynamic architecture of the type iv pilus machine in pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepenbrink, K.H.; Sundberg, E.J. Motility and adhesion through type iv pili in gram-positive bacteria. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2016, 44, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hounsome, J.D.; Baillie, S.; Noofeli, M.; Riboldi-Tunnicliffe, A.; Burchmore, R.J.; Isaacs, N.W.; Davies, R.L. Outer membrane protein a of bovine and ovine isolates of mannheimia haemolytica is surface exposed and contains host species-specific epitopes. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 4332–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Grenier, D.; Yi, L. Regulatory mechanisms of the luxs/ai-2 system and bacterial resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01186-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertani, B.; Ruiz, N. Function and biogenesis of lipopolysaccharides. EcoSal Plus 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.N.; Tan, Y.; Xiao, X.C.; Li, Q.; Wu, Q.; Peng, Y.Y.; Ren, J.; Dong, M.L. Deletion of tlr4 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 1610–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, F.; Gyles, S.; Atapattu, D.; Maheswaran, S.K.; Czuprynski, C.J. Prior exposure to mannheimia haemolytica leukotoxin or lps enhances beta(2)-integrin expression by bovine neutrophils and augments lkt cytotoxicity. Microb. Pathog. 2003, 34, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troxell, B.; Hassan, H.M. Transcriptional regulation by ferric uptake regulator (fur) in pathogenic bacteria. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.; Pedersen, A.G.; Davies, R.L.; Kuhnert, P.; Frey, J.; Christensen, H.; Bisgaard, M.; Olsen, J.E. Evolution of the leukotoxin promoter in genus mannheimia. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhat, N.; Ali, A.; Bonomo, R.A.; Khan, A.U. Efflux pumps as interventions to control infection caused by drug-resistance bacteria. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 2307–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Z.; Plésiat, P.; Nikaido, H. The challenge of efflux-mediated antibiotic resistance in gram-negative bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 337–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Primer Name | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Product Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| UrvC | F:TAATTTAGAAGCTTTAAATGAGCGC | 238 |
| R:CATATCTAGGTCAATTAAGGCTTTG | ||
| gcp | F:TGGGCAATACGAACTACTCGGG | 227 |
| R:CTTTAATCGTATTCGCAG | ||
| Hyp | F:CATTTCCTTAGGTTCAGC | 306 |
| R:CAAGTCATCGTAATGCCT | ||
| Core2 | F:GGCATATCCTAAAGCCGT | 106 |
| R:AGAATCCACTATTGGGCACC | ||
| TupA | F:TGAGAATTTCGACAGCACT | 78 |
| R:ACCTTGGCATATCGTACC |
| Components of the Genome | Number |
|---|---|
| Gene | 2664 |
| Tandem repeat, TR | |
| Tandem repeat sequence | 85 |
| Minisatellite DNA | 64 |
| Microsatellite DNA | 8 |
| Dispersed repetitive sequences | |
| LTR sequences | 102 |
| DNA transposons | 35 |
| Longinterspersed nuclear | 36 |
| elements, LINE | 2 |
| Short interspersed nuclear | 5 |
| elements, SINE | 1 |
| Rolling circle, RC | |
| Unknown | 52 |
| RNA ncRNA | 6 |
| tRNA | 6 |
| 5S rRNA | 2 |
| 16S rRNA | 16 |
| 23S rRNA | 3 |
| sRNA | 20 |
| Genomics Islands, GIs | 20 |
| Prophage | |
| CRISPR |
| VF Category | Virulence Factors | Related Genes |
|---|---|---|
| Adherence | Type IV pili | pilQ |
| Exopolysaccharide | mrsA/glmM, pgi | |
| Streptococcal enolase | Eno | |
| IlpA | IlpA | |
| OmpA | pomA | |
| HMW1/HMW2 | HD_RS07760 | |
| EF-Tu | tufA | |
| Biofilm | AI-2 | luxS |
| Effector delivery system | T6SS-II | clpV |
| Nutritional/Metabolic factor | Fur | Fur |
| Iron/manganese transport | sitC, sitA | |
| HitABC | hitA, hitB | |
| HxuABC | hxuC, hxuB | |
| Achromobactin | DDA3937_RS07710 | |
| Heme biosynthesis | hemE, hemA, hemN, hemC, hemY, hemL, hemB, hemM | |
| Regulation | CsrA | csrA |
| ClpP | clpP | |
| Invasion | Capsular polysaccharide | rmlB, wecC, wbjD/wecB |
| K1 capsule | neuB | |
| LPS | acpXL | |
| Capsule | bexA, bexB’, bexC’, bexD’, lipA, hcsB’, rpe | |
| Stress survival | KatA | katA |
| Motility | Polar flagella | flmH |
| Exotoxin | Alpha-Hemolysin | hlyB, hlyD |
| Immune modulation | Hsp60 | htpB Hsp60 |
| LOS | LpxC, kdsA, kdsB, opsX/rfaC, galU, gmhA/lpcA, orfM, lpsA, htrB, rfaE, waaQ, lgtF, lpxD, lpxA, galE, lpxK, msbB, lsgA, lsgD, lsgE, lsgF, kdkA, wecA, rfaD, manB/yhxB, kpsF, HD_RS06500, lpxH |
| ARO Category | ARO Name |
|---|---|
| Tetracyclines | tetQ, tet44, tet34 |
| Fosfomycin | murA |
| Fluoroquinolones | gyrA, parE, mfd |
| Aminoglycosides | kdpE |
| Mupirocin | ileS |
| Acetanilidomycin | EF-TU |
| β-lactam | NmcR, PBP2, mecl |
| Lincosamides | clbA |
| Diaminopyrimidines | dfrD |
| Aminocoumarins | ParY |
| Sulfonamides | Sul2, leuO |
| Glycopeptides | VanTC, VanG, adeR, VanHO |
| Drug-resistant efflux pump | evgs, tetA(60), hmrM, CRP, mdtF, msrB, macA, oleC, tet(35), adeL, MexV, macB, lmrD, patA, tetA(60), rosB, qacH, tetA(48), cmeC, carA, sav1866, cpxA, rosA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, C.; Kareem, K.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, B.; Sheng, J. Isolation, Pathogenicity and Genomic Analysis of Mannheimia haemolytica Strain XJCJMh1 in Bovine-Mycoplasma Co-Infection. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102258
Liang C, Kareem K, Zhang L, Liang Y, Wu H, Li B, Sheng J. Isolation, Pathogenicity and Genomic Analysis of Mannheimia haemolytica Strain XJCJMh1 in Bovine-Mycoplasma Co-Infection. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(10):2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102258
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Chengzhe, Kashaf Kareem, Lichun Zhang, Yafei Liang, Huiying Wu, Beibei Li, and Jinliang Sheng. 2025. "Isolation, Pathogenicity and Genomic Analysis of Mannheimia haemolytica Strain XJCJMh1 in Bovine-Mycoplasma Co-Infection" Microorganisms 13, no. 10: 2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102258
APA StyleLiang, C., Kareem, K., Zhang, L., Liang, Y., Wu, H., Li, B., & Sheng, J. (2025). Isolation, Pathogenicity and Genomic Analysis of Mannheimia haemolytica Strain XJCJMh1 in Bovine-Mycoplasma Co-Infection. Microorganisms, 13(10), 2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102258





