Abstract
As the term smart begins to move away from inflationary usage, mostly related to communication capabilities, and towards a more effective dimension, there is room for research into the systematic process of transforming the things that were not originally designed to be smart. Such a process is referred to as smartification, which evokes the digital refinement of an existing product by embedding digital technologies and smart services. The state of the art shows only a few articles that investigate such methodological approaches to provide smartness on several application domains (e.g., home appliances, buildings, cities), while the smart university domain has not been deeply faced up yet. Based on the hypothesis that a methodology synthesizes a set of suitable procedures oriented to simplify the process of measuring the degree of smartification, we propose in this work a methodology that uses technological and academic criteria for designing a tool to measure the smartification of universities. The main conclusions of this work are the following: (1) The review of the current state of the art related to smart universities and smartification reveals the need for a new vision for a more adequate and accurate assessment of the degree of smartness of universities; (2) A formal method based on Multiple-Attribute Decision Making and case study research aimed at assessing the degree of smartification within the scope of smart universities; (3) A demonstration of the feasibility and application of our method to quantify the smartification degree of the School of Computer Science (ESI) at the University of Castilla-La Mancha under the project Smart ESI; and (4) A valuable method that allows equal comparison between smart universities through a set of standardized indicators, which offers the opportunity to analyze in depth the strength and weakness, and potential achievements of any smart initiatives. To the authors’ knowledge, this is the first approach aimed at assessing the extent of the smartification process in smart universities through a formal method. The outcome of this research can benefit different stakeholders: university community, researchers, and, ultimately, the digital transformation of society.
1. Introduction
In twenty years of the Internet of Things (IoT) success story, we have witnessed the realization of the original concept, which empowered computers by giving them the means to see, hear and smell the world [1]. Advances in microelectronics and communications technologies have led to the emergence of a mass of sensing, computing and communication devices that are ubiquitous and indistinguishable from the explicit technology that people use. These devices, or things, have burst into multiple smart domains, such as cities, agriculture, or industry to develop the level of knowledge we possess of our environment, through the observation of a large number of phenomena, the collection of an unprecedented volume and variety of data, and the processing and analysis through advanced techniques of Artificial Intelligence (AI) or Big Data.
It is not so clear, however, what confers smartness to the IoT. In the smart cities domain, for example, the smartness condition may be just acquired by the fact of adopting actions oriented to increase the degree of urban development. In this context, initiatives such as providing grants to replace contaminant cars, to substitute bubbles in lampposts with LEDs, or more kilometers of bike lanes [2] are denominated smart in spite of they may completely lack the technology and services that provide a certain degree of smartness. Such initiatives generally overlook or do not draw enough attention to the need to incorporate Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) as part of the smart city materialization. Similarly to the smart cities domain, there is no common agreement on the definition under the term smart university and, also similarly to smart cities, it is commonly accepted that it differs from the traditional university in the employment of ICT, including automation, control and management systems, AI or IoT in order to accomplish the mission of the institution. Another example is found in the smart buildings domain. According to [3] a smart building is a set of communication technologies enabling different objects, sensors and functions within a building to communicate and interact with each other and also to be managed, controlled and automated in a remote way. Buildings represent one of the most critical infrastructures both in cities and in universities, due to the fact they concentrate the largest expenditure on utilities such as energy and water. In fact, it is also known that the energy consumption in buildings represents one of the largest shares of total consumption, around 40% in the EU according to the Directive 2010/31/EU [4]. In order to alleviate this issue, the EU has promoted policies over the last 50 years [5] that have progressively converged into the concept of Nearly Zero Energy Buildings (NZEB), which denotes buildings with a very high level of energy performance and that requires nearly zero or very low amounts of energy that can be covered, to a large extent, by energy from renewable sources.
To approach the concept of NEZB, IoT and IA enable the transformation of the existing buildings into smart buildings. Metallidou et al. review in [6] more than 20 research articles that propose strategies for energy savings in smart buildings through the automation and optimization of, for instance, the lighting, the HVAC (Heat and Ventilation Air Conditioning), fire prevention and air quality systems. Such systems are typically composed of devices that integrate multiple sensors and actuators, e.g., PIR, temperature, humidity, CO2, PMs (particulate matter), LEDs, and solenoid valves, and that implement user services based on AI techniques such as, for example, neural networks, agents or fuzzy logic to determine which are the user behaviors that, subject to environmental conditions and facility state parameters, incur superfluous energy consumption and how to adjust the system configuration accordingly to optimize its consumption while user safety and its comfortability are kept. For example, the simple observation of the occupation of the spaces and the user tracking may determine when the lights should be on and off in a room [2,7].
The previous examples provide samples of smartification processes by describing the digital refinement of an existing product by embedding digital technologies and smart services [8]. Although such works provide good demonstrations of smart initiatives, they overlook or, at least, do not address the question “how smart is that smart product/domain”, whose response provides an estimation of the degree of smartification, i.e., the quantity and quality of ICT resources employed, and how it impacts on a given domain. We rely on such assessment tools that can be built on a methodological foundation that allows for systematic replication of best practices in different domains. Precisely, based on this research hypothesis, we propose in this paper a methodology for evaluating the smartification process of small/medium-sized universities and campuses that will (1) simplify the time and effort of measuring the degree of smartification; (2) take advantage of lessons learned and best practices; and (3) provide a standardized tool for equitable comparison between smart universities based on technological and academic criteria. To the best of our knowledge, there is no other research work that investigates smart universities from this perspective. To this aim, Section 2 reviews the related works in methodologies for smartification and analyzes its suitability to the university domain. In Section 3, we describe the proposed methodology, the quantification method, dimensions and indicators. Section 4 presents the results of applying our methodology to the Smart ESI use case and Section 5 presents the discussion of the major outcomes of this analysis. Finally, Section 6 outlines the conclusions and directions for further research.
2. Related Works
The background of this work is based on smart campuses/universities and their smartification. Firstly, we describe examples of the design of smart universities and then, we review the works oriented to smartification. As far as the authors know, there exists no smartification process specifically designed for smart universities.
2.1. Smart University
The systematic review of literature on smart universities described in [9] reveals a plethora of works in a low maturity degree due to the lack of theoretical frameworks that enable them to reflect their specific circumstances. There exists a first group of works oriented to improving the education process in a more digital than smart way; thus, a smart university is a platform that acquires and delivers foundational data to drive the analysis and improvement of the teaching and learning environment [10]. Under this umbrella, we found a variety of platforms that increase the availability of data and resources and improve the user experience through, for instance, web-based tools, apps and conversational interfaces, following the changes promoted by new regulations, policies and social issues that are influencing the educational model [11], but excludes strategic aspects of the institution such as the governance, the environment and the efficiency in the resources management and the sustainability. An example of this first group is presented in [12], which describes a smart university as an organization composed of four smart axes—student, knowledge, interaction, and learning—to reflect the changing environment to which education processes are subjected due to informal learning methods and ubiquity of resources, students and teachers. The same criteria is followed in [13], where a smart classroom is defined as an intelligent class that incorporates learning methods and emerging information technologies with innovative teaching and new pedagogies. The same idea is reflected under the term smart campus which was coined in the 2000s: a video conference system for distribution of multimedia contents to the students [14].
In a second group, we find smart universities that are modeled following the design principles of a smart city and underwriting the sentence “behind every smart city is a smart university” quoted by Dr. Simon Easson of IBM. Such approaches are oriented to have better control of a broader range of aspects such as governance, wellness, management, or energy management processes [11,15]. One common characteristic is the adoption of IoT, with a mass of sensing/acting pervasive, hyperconnected things at any time, any place, with any-other-thing and anyone, increase our knowledge of the university environment and make possible the definition of an intelligent decision making process on top of it. As we describe in [2], a smart city refers to a city that monitors and integrates conditions of its critical infrastructures, e.g., roads, bridges, tunnels, rail/subways, airports, seaports and communications, to better optimize its resources, plan its maintenance activities, and monitor security aspects while the services to its citizens are maximized. In essence, a campus/university can be viewed as a mock-up of a city, with some obvious differences, as described in [16]: smaller size, infrastructure management (generally, public buildings in campuses/universities in contrast with private buildings in cities) and homogeneity and autonomy in campuses/universities that enable to force the adoption of technologies and specific architectures. This approach is used in [9,16,17,18,19], which identify firstly a set of smart dimensions for the universities and, secondly, for each one to identify intelligent, value-added services and, in some cases metrics and KPIs for different stakeholders. There is no agreement on the smart dimensions and services that are provided by the smart universities, as shown in Table 1, which presents a summary of smart universities modeled under this perspective: in the first column, we show a name to denote the smart dimension and in the second column we provide multiple designations that refer to the same dimension; then, in the third column, we show some common smart services (in gray color) provided by at least two universities in each dimension; and, finally, the fourth column shows other services that are implemented only by one university in one dimension.

Table 1.
Examples of Smart Universities designed as smart cities: dimensions and services.
In a third group of works, we find strategies defined merely from a technology viewpoint, which are oriented to optimize the efficiency in buildings, since they represent one of the most critical infrastructures in buildings. This is the case described in [20,21], where the authors present an iterative methodology to make buildings smart and resilient.
2.2. Smartification
Although the concept has been in the air for many years, the first definition of smartification was achieved in [8] in 2019, as the “digital refinement of an existing product by embedding digital technologies and smart services”. Such refinement pursues to become traditional objects or systems into smart versions of themselves that will, ultimately, provide a better function towards addressing human needs. We find two ways towards the smartification: ad-hoc and methodological. In the first group, we find works that describe the smartification process applied to a specific product. This is the case of the work presented in [22], where the authors describe the furniture smartification process, e.g., a table, a chair, by means of the addition to the original piece of the capabilities of sensing/acting, processing, and communication as well as actions to be undertaken when a certain condition occurs and sitting thus the basis for proactive behavior. For example, a chair becomes a smart chair able to monitor the heart rate of the person sited, to process its ECG measurements, or to detect long periods of inactivity. For the authors of [23], the concept of smartification is centered on providing horizontal interoperability through the smart application domains. They claim that, in spite of the great diversity of application domains, there exists a common need for all of them, which is to provide a smart service, interoperable and with QoS requirements. To this end, the authors identify the QoS properties that IoT communication protocols should satisfy, e.g., reliability, scalability, security, interoperability and availability, and then review the mechanisms implemented by three communication standards commonly used in IoT (3GPP, IEEE 802.11ax, IEEE 802.15.4) to fulfill such properties.
Differently from the previous works, there exists a second group that includes works that define a method for implementing smartification, in such a way the process can be systematically replicated on different smart domains. These works are based on, in turn, two approaches: research based on case studies and layered design. The next subsection provides insights into works that describe methodologies for smartification.
2.2.1. Methodologies for Smartification
As far as the authors know, there exist very few articles dealing with the problem of methodologies for smartification and none of them deal with the smart education domain. Next, we analyze two methodologies based on the case studies research, that are specifically relevant to the context we are addressing (the Eisenhardt Method and the Porsche Consulting Methodology), the classical development software methodologies and approaches based on Multiple-Attribute Decision Making.
The Eisenhardt Method [24] describes a process for theory building from multiple case studies. The method consists of eight stages: (1) Definition of the research question: the method attempts to answer research questions for which there is only a little or conflicting prior theory and/or empirical evidence, and so no obvious answers; (2) Selecting cases: the method focuses on the selection of the theoretical (not random) sampling from the population, this means electing carefully those cases where, with a higher probability, the focal phenomenon will occur and where the similarities and differences among cases will improve the theory building with the aim to extract the generalization of the cases. This stage is essential to yield a successful outcome of the method and there exists different techniques to accomplish the case selection, e.g., matched pair, polar types, and racing; however, as mentioned in the cited paper, it is generally accepted the selection based on the appreciation; (3) Crafting instruments and protocols: to identify multiple methods of data collection to be used, including both qualitative and quantitative methods; (4) Entering the fieldenables to identify the overlappings between the data analysis and the data collection and to provide flexibility to the data collection methods, for example, by introducing adjustments into the data and even new methods of data collection if needed; (5) Analyzing Within-Case Datais the task focused on the analysis of data, which is the core of the theory building and at the same time the most difficult part since the literature provides not many works oriented to examine the techniques used for this analysis; however, a recommendation is to address a within-case analysis, which typically involves detailed case study write-ups often in a simply pure descriptions way. Next, it follows a cross-case search for patterns, for example, by selecting categories or dimensions, and then looking for within-group similarities coupled with intergroup differences; (6) the shaping hypothesis consists of the definition of the constructs, as the essential components of a theory, and the measures, as the units that quantitatively evaluate the emergent theory. In this step, theoretical arguments that explain the validity and coherence of the resulting theory should be provided, where the explanations may be based on the data, logic, and research in other disciplines, like cognitive science and biology; (7) Enfolding literature is the constant refinement of the resulting theory through comparisons between the emergent concepts, theory or hypothesis with the existing literature: what is similar or different and why as the foundation for the generalization; (8) Reaching closure is the final step because the previous steps ranging from 4 to 7 could be into a loop and it is necessary to find the conditions to stop adding cases and compare against the existing literature.
Based on the Eisenhardt method, the work described in [8] attempts to answer the question How can a methodology for the smartification of products be designed? The authors selected 13 case studies aimed at describing the process of development of smart products by different industries and grouped them between two categories: B2B (Business-to-Business) and B2C (Business-to-Customer). For the phase of data collection, they used description documents and data sheets of each product as a primary source of data, and then they added interviews with users of the products to incorporate their perspectives. As a result of the data analysis, the authors identified a morphology consisting of 8 digital features and a total of 26 digital functions, which were found in the thirteen cases. For a product to be considered “smart” it must fit at least one function in each feature. A larger number of functions and a higher degree of product intelligence. From these outcomes, the authors define a methodology for manufacturing smart products by means of the link between the smart product’s objective and its digital functions. The methodology consists of three steps: (1) to establish the strategy portfolio; (2) to combine the objective and digital features of the smart product into the so-called “user stories”, one for each digital feature, that is expressed with the structure: “As <user> I want <feature, function> to achieve <objective>”; and (3) refinement of the “user story” by adding restrictions and other considerations to, finally obtain the description of a product development’s starting point.
The Porsche Consulting Method. The company Porsche Consulting GmbH [25] proposed a smartification methodology focused on the smart buildings domain also based on the research of case studies. This domain is elected basically for the urgent need for optimization of indoor spaces for 68% of the world’s population living in urban areas by 2050. The authors pose that the current state-of-the-art on this topic lacks widely shared and accepted visions and upside potential offered to various stakeholders and instead, it consists of a set of disconnected applications with different degrees of technological maturity (e.g., security, heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and lighting). To overcome this problem, Porsche Consulting proposes a smartification methodology based on six recommended steps: (1) Collection is the selection of the case studies from well-probed pilots in this or another markets; (2) Evaluation of each case study based on its business impact analysis and its feasibility; (3) Derivation from the previous analysis to determine the position of the company in the smart building ecosystem; (4) Definition of the smartification road map for achieving the target position in terms of development, operation and commercialization, ranging from investment policies up to the hiring of expert personnel in specific areas; (5) Alignment consists of checking the smartification strategy and coincides with the organization’s other strategic perspectives (e.g., corporate strategy, business unit strategy, and functional strategies) to detect potential conflicts and tackle them with appropriate solutions; and (6) Smart take off, consists of transferring the strategic initiatives to specific work packages with responsibilities and timelines.
Multiple-Criteria Decision Making. Multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) seeks to determine the best alternative by considering more than one criterion in the selection process. According to [26], the MCDM problems can be classified into two main branches: Multiple-Attribute Decision Making (MADM), which concentrates on ranking and scoring a limited number of alternatives that are characterized by multiple, usually conflicting attributes, whilst Multi-Objective Decision Making (MODM) problems involve evaluating alternatives that have been non-predetermined through competing objectives that are required to be optimized simultaneously. The MADM process requires identifying the alternatives, identifying the distinct attributes or criteria (qualitative or quantitative) that will be used to compare alternatives and specifying a method formal to determine what is the contribution of each alternative to a certain attribute. We find in MADM a valuable method for designing rankings targeted to smart cities attending to a wide range of technological criteria, such as we described in [2]. Our ranking contemplates explicitly 38 ICT indicators related to a smartness dimension, so that the smartness degree of the individual initiatives and of the overall smart city may be effectively measured.
Methodologies based on layered software design. The work presented in [27] superficially explores classical approaches to software development as methods for smartification of smart cities. The authors argue that each individual smart city application can be developed independently top-down, bottom-up, as an extension-oriented approach, as an off-the-shelf application or on the basis of open data as a starting point. The work, as the authors mention, is not complete and lacks in providing evidence to demonstrate why these methodologies fit well with the particularities of smart cities.
3. A Methodology for the Smartification of Universities and Campuses
This section describes a methodology for assessing the “smartification” of universities and campuses, based on the theoretical foundations of both Multiple Attribute Decision Making (MADM) and case study research. The case study review is used to extract knowledge from the literature through an iterative method that computes a final setup (defined by a set of dimensions, services and indicators). This final setup feeds the framework that is built on MADM principles for the computation of the smartification degree of a smart university when examined according to the proposed methodology. We present first in this section the methodology, and secondly, a method for the data collection from the case study research.
The goal of our methodology is twofold: on one hand, we formulate a theoretical framework for the quantification of the smartification in the smart university domain that could be translated, with minimal changes, to any smart domain; on the other hand, we enable a strategy for the equal comparison between smart universities according to a wide set of academics and technological criteria.
3.1. Smartification Framework Description
Let us start with the definition of a set of n smart universities (alternatives) to be evaluated against a set of m dimensions . We denote as to the p services provided for each university in each dimension . For each dimension , we may compute the set of core services as the intersection of the services corresponding to that dimension across the universities in as follows:
Note that p may differ across different but the size of is the same for all universities in a certain dimension since it corresponds to the common set of services. A service defined for the university and the dimension has associated a set of q specific indicators , where each indicator is defined by the tuple , . The first value represents one and only one observed value of the indicator x, which represents the contribution to the service k in the university i in dimension j, with . The second value of the tuple is the weight, i.e., a score that represents the relative importance of the indicator x to the service k, so that we can have preferred indicators over other indicators. Similarly, for a given service , the set of core indicators is computed as the intersection of the indicators corresponding to the service across the universities in as follows:
Now, let us define the smartness dimension aimed at evaluating specifically the ICT usage and smartness degree associated with a certain university across all its dimensions, to attempt answering the question how smartness the university is. Thus, is a transversal dimension to , because the smart infrastructure is shared by the different dimensions accomplished within the university. The dimension of a university i is measured through a set of λ ICT/smartness indicators denoted by . Such indicators may be used to measure horizontally any dimension, and thus they are defined similarly to the rest of indicators, i.e., , this means that, the smartness indicator takes one observed value for the university i with a score of . Note that the weight of the smartness indicator is always the same for all universities.
Theory of Smartification
Based on the previous formulation, we define two decision matrices:
: Service matrix to account the contribution of each service k to the dimension j and university i. To this end, we use the set of core services, i.e., the ones that are common for a specific dimension in all universities. Thus, the matrix may be computed as follows:
: Smartness matrix to account the contribution of each smartness indicator in the dimension j and at the university . Thus, the matrix is computed as follows:
Given the matrix , whose elements represent the contribution of the set of services k to a specific dimension j of a university i, and the matrix , whose elements provide the contribution of each smartness indicator y to a specific dimension j of a university i, with and , we define the degree of smartification of a university i that is denoted by and is computed as:
The value accounts for how smart the university i is, aggregating the weighted measures for a set of common indicators that are provided for a common set of services developed across multiple dimensions and, aggregating also the weighted measures for a set of common smartness indicators. Additionally, note that provides a standardized value that enables the comparison between universities transversely across dimensions. This means that it provides the score of a university (alternative) i against the set of common attributes (dimensions and services), which represents the overall contribution of i so may be ordered into a ranking such that or holds. The method of computation of the value of drops within the category of compensatory methods, specifically, the Weighted Sum Model (WSM) [28].
3.2. A Graphical Example
A representation of the matrices and are shown in Figure 1 (note, however, that they could be non-square matrices). They take a shape tridimensional, where the axis x represents the set of dimensions , the axis y represents the set of universities so the row i of the matrix identifies the university i. Specifically for , the axis z represents the weighted aggregated value for a set of q common indicators defined for a set of k common services, denoted as , for all the universities and dimensions; and, for , the axis z represents the weighted aggregated value for a set of λ common smartness indicators defined through universities and dimensions.
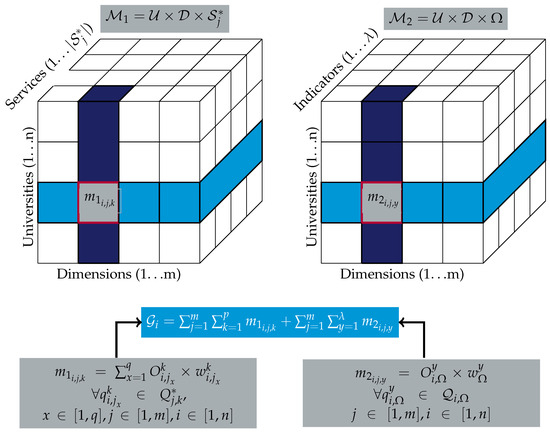
Figure 1.
A graphical representation of the smartness degree .
In order to compute , the values in the fixed row i through the columns and depth (axis y and z) are all aggregated. An example of dimensions may be taken from the first column of Table 1, where we show the set of common dimensions investigated on multiple smart universities. Additionally, the set of common services for a specific dimension j may be taken from the third column of the Table, where we have presented a common set of services in the specific dimension for the set of smart universities considered. Finally, for each common service, k within we identify a set of q indicators denoted as that represent common parameters to be measured in each service.
3.3. Iterative Method for Data Collection
We describe in Section 2.2.1 two methods for building theory from the research of case studies, the Eisenhardt and the Porsche Consulting Methods. One of the most critical steps in both methods, due to the potential impact on results to be provided, is how properly to collect the set of representative cases to capture enough similarities and differences between them to extract the general information of the cases. This is especially relevant in the scope that we are addressing in this paper, smart universities, since there exist multiple names for the same concept (as demonstrated in Table 1) and there is a very prolific literature of case studies. With this aim in mind, we propose an iterative method for data collection that feeds the model described in this section. Figure 2 shows a flow diagram with the process description.
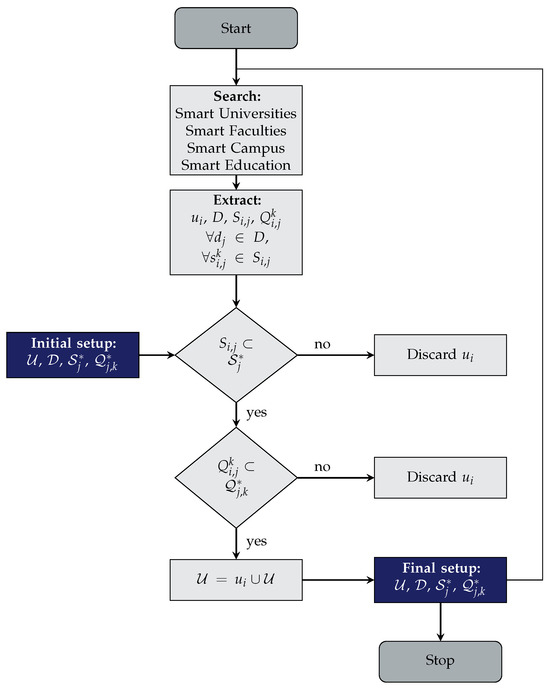
Figure 2.
Flow diagram to compose the Final Setup.
We start with an Initial Setup composed of a set of universities (), dimensions (), the core services for each dimension () and, for each service, the set of common indicators that are able to measure the degree of achievement of each service according to a given weight. This setup is built by means of an exercise of systematic review of the literature, through the search of keywords in scientific database as smart university, smart faculty, smart campus, and smart education, and extracting from them the mentioned sets, i.e., (). The iterative method proposed is aimed at determining if a university i may be orthogonally measured through the framework described, if the university i uses the same services and indicators to measure a specific dimension as the other universities in set (). If this is the case, the university i is added to the set .
Note that the selection of case studies may be conducted, however, in multiple ways. Note also that, in order to evaluate a sole smart university independently, it is not necessary to restrict agreeing on dimensions, services, and indicators since the purpose is not the comparison between universities.
4. Smart ESI: A New Model of School
In this section, we face the technical and formal definition of a smart campus following the methodological perspective shown in the previous section. Firstly, we start with a brief description of the university context; second, we present the Smart ESI project, the mission, objectives and design principles. Next, we describe the project from a merely technical perspective for later, finally, to show the results of the application of the methodology proposed.
4.1. The Context
The University of Castilla-La Mancha (UCLM) is one of the 50 public Spanish universities and the one in the autonomous region of Castilla-La Mancha. UCLM holds the 18th position out of 72 Spanish universities evaluated by U-Ranking (https://www.u-ranking.es/, accessed on 8 October 2023) and is within the range [701–800] out of ≥2500 universities evaluated by ARWU (https://www.shanghairanking.com/rankings/arwu/2021, accessed on 8 October 2023). The School of Computer Science, ESI from now on, is one of the university campuses of the UCLM that has been developing training and research work in the field of Computer Engineering since 1989. ESI currently has around 80 teachers for 700 students. The activity in the ESI takes place in several buildings: Fermín Caballero Building with its annexed modules A and B, which are organized in the following categories: administration, management and direction teachers offices, conference (multipurpose) rooms with a maximum capacity for 180 people, classrooms with an average capacity of 60 people and laboratories with an average capacity of 40 people. Figure 3 shows the buildings’ distribution and Table 2 presents the main spaces for activities on each floor of the three buildings.
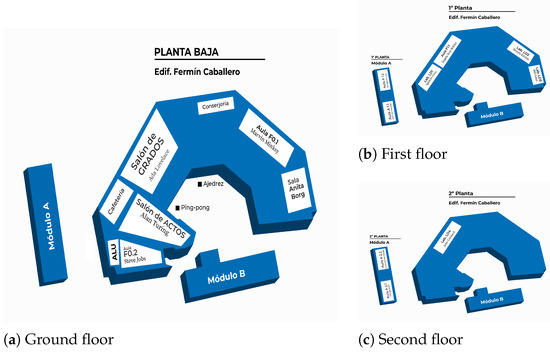
Figure 3.
Plans of ESI: Fermín Caballero Building and Modules A and B.

Table 2.
Summary of infrastructures at ESI campus through the three buildings.
4.2. Smart ESI: Mission, Objectives and Design Principles
The university, as an institution, plays a fundamental role in our society by promoting its advancement and development through the generation and transfer of knowledge. In this sense, we conceived the smart ESI project to address the responsibility and challenge of bringing the R&D&I activities developed at the ESI closer to the university community and society in general. To this end, the smart ESI project (https://esi.uclm.es/index.php/programas-singulares/smartesi/, accessed on 8 October 2023) proposes using the entire campus infrastructure as a mock-up to build a smart city model on which to define a set of advanced and specialized services, aimed at increasing our knowledge about the School and its environment, and with the ultimate goal of improving its operation, sustainability and efficiency. The smart ESI project has two main objectives:
- To offer the ESI, and the university community in general, an agile and flexible framework for the cohesion and demonstration of cutting-edge technologies (e.g., IoT, renewable energies, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, augmented reality or computer vision), research and innovation carried out by the different research groups.
- To provide society with a catalog of intelligent services that can be articulated via the previous framework, aimed at increasing the level of knowledge about the different elements and spaces of the school, its conditions and state, and its environment.
Smart ESI project carries out the smartification of our school by providing it with the technological means necessary for the realization of the smart city concept. We pose the process of smartification to be: (1) transversal, based on the collaboration of the research groups that ESI holds; (2) transparent through the use of open data; (3) scalable, so it can be extended gradually through the paradigm of services; (4) measurable where the progress may be quantified thanks to a set of indicators; (5) hyper-technological, making intensive use of enabling and cutting-edge technologies (not for nothing ESI is a school of technology); (6) value-added services-based, that provides added value, through relevant, advanced, specific services for heterogeneous users.
4.3. System Architecture
The system architecture of the Smart ESI project from a technological perspective is presented in Figure 4. This is a layered architecture that may be summarized as (from bottom to up): (1) physical layer infrastructure, that comprises the sensing and acting devices as well as the interconnection devices through multiple networks; (2) data integration platform, that provides functionalities for the data integration, filtering, persistent storing and processing with data analytics techniques; and (3) applications and user interfaces, which provide information access through the services paradigm, via multiple (graphical) user interfaces and heterogeneous devices.
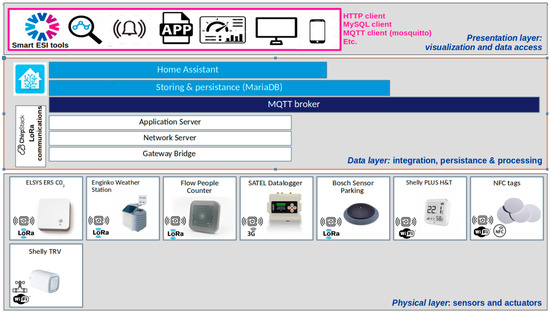
Figure 4.
Overall Architecture of the Smart ESI case use.
4.3.1. Physical Layer: Sensors and Actuators
At the moment of writing these lines, we have deployed a total of 59 devices, with sensing/action and communication capabilities, on the ESI campus in order to monitor the comfort of classrooms, lecture halls and laboratories, parking space occupancy, weather and energy expenditure. For incident management, we used a total of 28 NFC tags that were recorded with the appropriate information and deployed in the classrooms of Module B. Table 3 shows the total number of devices.

Table 3.
Summary of devices deployed on Smart ESI campus. Legend: S: Sensor; A: Actuator. LTR: Left to Right; RTL: Right to Left. Loc: Location: F: Fermín Caballero Building; B: Module B; O: Outdoor.
We define three separate networks for supporting the operation of the devices in Table 3: LoRa, WiFi and 3G network, whose details are described next.
The LoRa network is composed by LoRa devices and the LoRaWAN Gateway UG67 of Milesight LoRaWAN Gateway UG67 (https://www.milesight-iot.com/lorawan/gateway/ug67, accessed on 8 October 2023), which is located on the false ceiling on the ground floor of the Fermin Caballero building. Some sensors need to be activated and minimally configured (e.g., transmission period, activation type) through an app provided by the manufacturer that connects to the device generally via NFC. Most of the LoRa sensors are equipped with power supplies that, according to the manufacturer, provide lifetimes very long (around several years). The weather station, installed on the roof of a building, is also equipped with a solar panel to recharge its batteries. For security reasons, prior to deployment, LoRa devices are connected to the gateway via their DevEUI and AppKey identifiers, to ensure that only the registered devices will be able to transmit data to the network. LoRa devices transmit periodically data towards the gateway in one only hop, covering distances not larger than 200 m. The data transmitted are received by the gateway, which acts as a LoRa/IP gateway by retransmitting all data towards an IP server that is located within the data center in our school. We did not detect packet losses in this network due to the low traffic generated and the fact that the devices used a low duty cycle (DC), in compliance with the ETSI EN300.220 standard, which states that a DC can range from 0.1% to 10% in each subband.
The WiFi network. On the other hand, the WiFi devices were connected to a wireless network separated from the one usually used for teaching and research. This network was specifically designed by UCLM-TIC services for IoT connection devices purposes. To ensure complete coverage throughout the campus and for security reasons, the technical services of the UCLM enabled this network as a virtual network in each access point (AP) and defined an appropriate IP address block from which to assign addresses to WiFi devices requesting connection. Thus, the data transmitted by the WiFi devices achieves the paired AP, which forwards the data to the IP server, possibly in more than one hop.
3G network. For energy consumption monitoring purposes, we acquired professional devices, versatile and robust, which are intended for tertiary and industrial buildings and designed to operate in multiple failure situations, e.g., data transmission failures. These devices are the Sennet IoT DL271 Datalogger Long Net and 2 Sennet IoT Xtend M6, designed and manufactured by the Spanish company Satel Iberia, and shown in Figure 5. The IoT DL271 Datalogger is a measurement concentrator that allows us to configure and deploy a complete monitoring system for a building. In our use case, the purpose of this device will be the energy monitoring of the Smart ESI campus, including the three buildings and the data center, which is one of the most energy consumers. This datalogger includes a display and keypad, RFNet radio frequency, 3G/GPRS router, Ethernet, RS232 and RS485 serial interfaces, digital inputs and outputs and it integrates 3 three-phase electrical analyzers (or 9 single-phase analyzers) in the same equipment, and it has the capacity to manage up to 100 m by radio frequency. It has an SD card for data storage in the event that the network is not available, which automatically will resend data when enabled. The second one is the Sennet IoT Xtend M6, which consists of 6 expansion modules to extend with one only click the range of the datalogger to a total of 15 three-phase analyzers. At the moment of writing these lines, these devices were turned off for maintenance purposes.

Figure 5.
Sennet IoT DL271 Datalogger Long Net (the first device on the left) and 2 Sennet IoT Xtend M6.
4.3.2. Data Layer: Integration, Persistence and Storing
The Data Layer is implemented by a server whose software architecture is depicted in Figure 4. This layer provides functionalities for data integration, persistent storing, processing, and multiple interfaces for data access. Such functionalities are supplied by the next software stack, from bottom to up: MQTT, Chirpstack, and Home Assistant. These three components were installed as Docker containers in the server, in order to ease the installation. The first two components are related to the data collection proceeding from the WiFi and Lora devices, while the last one is in charge of the storing, processing and data access interface. Next, we provide the implementation details.
Message Queue Telemetry Transport (MQTT) is a protocol for IoT device communication based on the publish/subscribe model. The broker or MQTT server was installed in the server and, therefore, assumes the role of the subscriber while the WiFi devices act as MQTT clients, or publishers, that connect to the MQTT server with a given topic. MQTT runs over TCP/IP, thus supporting reliable bidirectional communications. Data collected by the WiFi devices are encapsulated into an MQTT message, which aggregates two headers, a fixed one, with a length of 5 bytes, and an optional header of variable length to a payload with a maximum of 256 Mbits. MQTT does not provide any mechanism for data security, so the data is transmitted raw to the server.
ChirpStack is the protocol stack that allows the management of LoRaWAN communications. The protocol stack includes three major components, from bottom to up: (1) a Gateway Bridge, which interfaces with the UG67 LoRa gateway to collect all messages forwarded from there; (2) a Network Server, which filters duplicate messages from other gateways, and (3) an Application Server, which interacts with the MQTT server by forwarding all LoRa data to the TCP/IP network. The architecture of Chirpstack is represented in Figure 4.
Home Assistant is a free and open-source software platform for home automation designed to be a central control system (hub) for smart home devices with a focus on local control and privacy. One of the main advantages of Home Assistant is that offers the capability of controlling a very large number of devices (sensors and actuators) manufactured by a large number of companies through multiple supported wireless communication protocols such as WiFi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and Z-Wave. Additionally, it enables the possibility of connecting with other devices by writing customized integrations. All these devices communicate with the controller both to receive management commands and to transmit periodically their data, which are stored in a database (MariaDB in our implementation). Home Assistant also provides the capability of managing the data provided by devices through the mechanism of automation, which are scripts that implement some functionality and that are triggered when a certain event occurs (e.g., the temperature is higher 25 C). On the other hand, Home Assistant offers a web-based user interface that may be easily designed as a dashboard, called Lovelace, by means of different cards to display information and control devices. Additionally, it can be accessed through voice commands via a supported virtual assistant such as Google Assistant or Amazon Alexa.
In our case study, most of the devices we deployed in our school were not supported by Home Assistant, so it was necessary to write integrations for them. Such integrations consisted of processing the data, by providing the suitable format to the received data, according to the instructions given by the manufacturer (see an example in Figure 6).
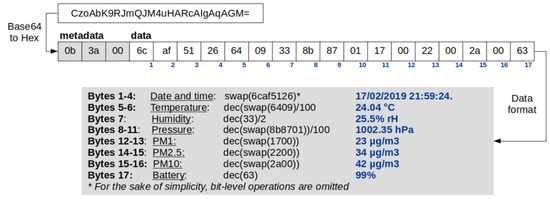
Figure 6.
Enginko MCF-LW12TERPM weather station packet decode.
4.3.3. Presentation Layer: Visualization and Data Access
As depicted at the upper layer of the Smart ESI architecture shown in Figure 4, this layer is composed of the user tools aimed at accessing, post-processing and visualization of the data stored at the underlying layer by means of multiple heterogeneous devices, such as PCs, laptops, mobile phones, and screens. Due to the fact that Home Assistant provides a web-based interface, users access data mainly via any web browser. There exist, however, different ways to access information, so we divide the tools at this layer into two categories: (1) Smart ESI-specific tools developed as part of the project. This is currently a work-in-progress because many applications are being developed as Final Degree Projects and Master’s Thesis with the support of professors of the school; and (2) standard protocols and common software tools as HTTP, MySQL and MQTT clients. In the first category drops a vast number of Smart ESI-specific applications (generally applications built to work on mobile phones or apps) developed on top of the standard protocols/tools of the second category, and designed to provide some functionality. For example, one of these apps is the incident management app, which is designed to manage the different events that can occur in a classroom, such as the PC not working or the lights being off. This app allows the technical staff to be immediately alerted of an incident detected in the classroom where the professor is teaching so that it can be corrected as soon as possible. This app reads the information associated with each incident from a pre-recorded NFC tag, which is attached to the back of an icon representing the type of incident detected. Figure 7 shows a strip of 7 icons representing 7 different incidents, each with a corresponding NFC tag on the back. This strip is printed and plastified, and set at some place in the classroom (at the wall, normally close to other sensors). The professor simply activates NFC on their cell phone, gets their mobile phone close to the corresponding NFC tag, adds a comment (if necessary) and sends the information through the app.
Figure 7.
Icons for the incident management app. The legend at the bottom of the figure is written in Spanish, and it means: Activate NFC and bring the cell phone close to the icon where the incident occurred.
In addition to the web interface provided by Home Assistant, technical and research personnel can access the server through MySQL-based tools to perform database queries. These queries have different purposes, such as performing maintenance and research tasks using different data processing and analysis techniques. As an example, in Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14 we show different parameters measured through the sensors deployed on different buildings of our school. Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11 show the temperature, humidity, CO2 and battery level, respectively, reported by the four Elsys ER2 CO2 sensors installed in the four classrooms of Module B building (see Table 2) during the period 1 January 2023 to 30 August 2023. According to Spanish Directive 486/1997 (B.O.E.: https://www.boe.es/boe/dias/1997/04/23/pdfs/A12918-12926.pdf, accessed on 8 October 2023), by which the minimum safety and health provisions in workplaces are established, the temperature of the premises where sedentary work is carried out shall be between 17 C and 27 C. It can be observed that the temperature takes values that are mostly in this range with the exception of some days in December and in the non-teaching and vacation periods. On the other hand, it is known that humidity decreases when the temperature grows, as shown in Figure 9. It is especially interesting, the variation of CO2 in the four classrooms depicted in Figure 10. Note that the minimum value reported by these sensors is around 400 ppm, which means that there is no activity in the classrooms, while they achieve maximum values of around 3000 ppm when larger is the concentration of people. Figure 11 presents the battery level of the four sensors and shows a very low consumption of battery during the 8-month period. In Figure 12 and Figure 13, we show the temperature and humidity values reported by the 14 Shelly Plus H&T (see Table 3) installed on different dependencies of the main building of our school, during the periods 19 June 2023 to 30 August 2023 (for 7 sensors) and 20 July 2023 to 30 August 2023 (for the other 7 sensors). Note that in this particular period of time considered, the temperatures are exceptionally high considering that in this period there is no regular activity in classrooms and laboratories and, therefore, the air-conditioning is not activated. Of particular interest are the temperature and humidity associated with the data center (see red lines in Figure 12 and Figure 13), which are always kept within the ranges of 23–25 °C and 40–50%, respectively, in compliance with the recommendations made by the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE), for an optimal and maximum uptime and hardware life. Finally, we show in Figure 14 the outdoor temperature reported by the Enginko MCF-LW12TERPM weather station installed on the roof of the main building, during the period 1 January 2023 to 30 August 2023 and we compare it with the temperature reported by the State Meteorological Agency (Agencia Estatal de Meteorología, AEMET), which is an agency of the Government of Spain responsible for providing weather forecast and warnings of hazardous weather. As observed, the temperature value reported by our weather station is slightly higher than the temperatures reported by AEMET, especially in summer, due likely to the location of the station, situated on the roof in an area with no shadows.
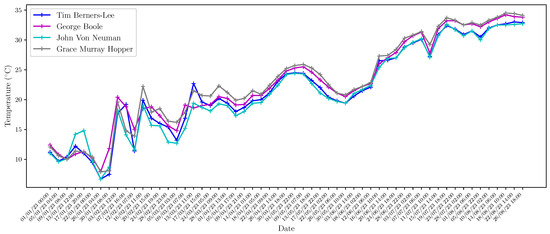
Figure 8.
Temperature measured by Elsys ER2 CO2 sensors in the four classrooms of the Module B building during the period 1 January 2023 to 30 August 2023.
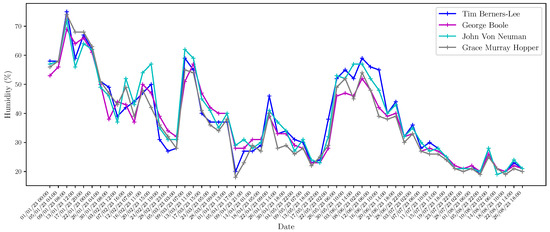
Figure 9.
Humidity measured by Elsys ER2 CO2 sensors in the four classrooms of the Module B building during the period 1 January 2023 to 30 August 2023.
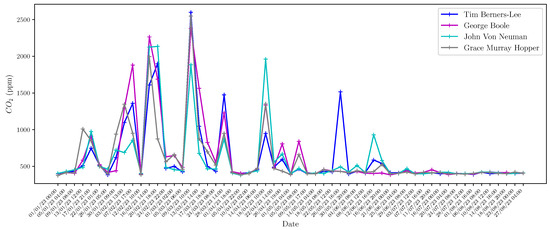
Figure 10.
CO2 levels measured by Elsys ER2 CO2 sensors in the four classrooms of the Module B building during the period 1 January 2023 to 30 August 2023.
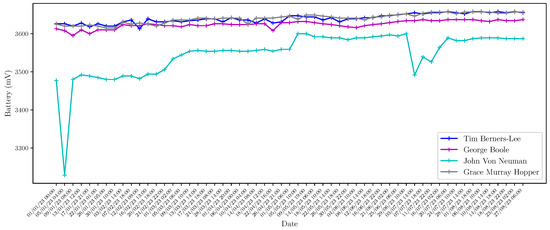
Figure 11.
Battery level reported by Elsys ER2 CO2 sensors during the period 1 January 2023 to 30 August 2023.
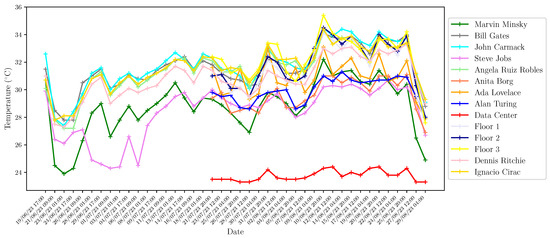
Figure 12.
Temperature measured by the 14 Shelly Plus H&T sensors in different dependencies of Fermin Caballero building during the period 19 June 2023 to 30 August 2023.
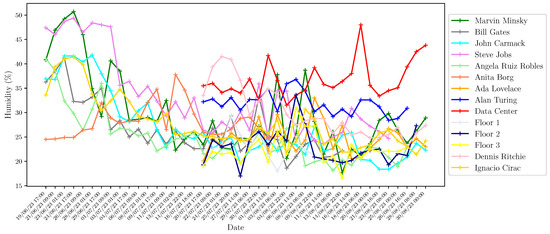
Figure 13.
Humidity measured by the 14 Shelly Plus H&T sensors in different dependencies of Fermin Caballero building during the period 19 June 2023 to 30 August 2023.
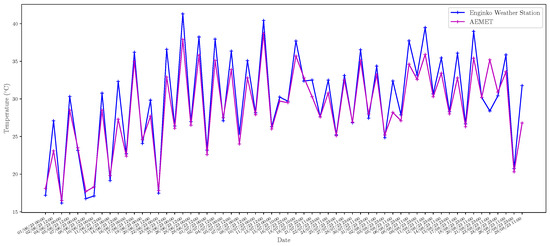
Figure 14.
Temperature reported by the Enginko MCF-LW12TERPM weather station and AEMET during the period 1 January 2023 to 30 August 2023.
4.4. Method: Initial Setup and Computation of G
In order to quantify the degree of smartness of ESI campus (G) based on the method proposed, we have defined an initial setup with a set of dimensions of interest for our school and, for each one of them, a set of q indicators , and a set of λ smartness/ICT indicators to measure the level of advance performed in one or several services implemented. As shown in Table 4, we have defined a total of 79 indicators, λ = 33 indicators belong to the smartness/ICT dimension, and the rest of q = 46 indicators correspond to one of the smart universities dimensions identified previously in Table 1, i.e., smart learning, governance, environment, people, management, mobility and economy. The discussion on the appropriateness of the indicators is presented in Section 5. For each university i, dimension j and service k, an indicator x takes one and only one observed value , which represents the contribution performed by the university i in dimension j to service k. Similarly, for each university i, dimension an indicator y takes one and only one observed value . In order to make the values of the observations directly comparable among indicators, we compute the normalized values of such observations by using the decimal scaling normalization method [29] as follows:
where z is the smallest integer such that max(||) < 1 (and in a similar way for smartness indicators). Note that, therefore, the normalized values are within the range between . Note also that, the minimum/maximum value that may take an indicator should be taken into account for matching its value within this interval. For example, for the indicator , if the minimum value that the sensor may report is around 400, this value matches the value 0 in the interval. The same occurs with the indicators GRA and MAS, where the minimum value that they may take is 4 years.

Table 4.
The initial setup: set of dimensions , set of indicators and the corresponding smart service implemented (); at the end of the table the smartness indicators .
By using the normalized values of the observations, we may compute the matrices and as described in Section 3, by assuming a weight equal to 1 for most of the indicators in Table 5, except for those that represent a penalty on the overall score and are therefore intended to be reduced, i.e., OUT, GRA, MAS, PM2, CO2, POW, ENE, WAT, GAS and PRV, highlighted in gray color in the table, which use a weight equal to −1. The sum of all items in both matrices provides a value of = 22.054 for our school, which represents a numeric, standardized value of the smartification process performed in ESI and enables the fair comparison between other universities by using the same method. Note that + = 59 and that, therefore the value represents a 37.37% of achievement of the maximum smartification value.

Table 5.
Values and normalized values in range (−1,1) for the indicators. Legend: NA: Not available. Yes: 0.999. No: 0. Indicators in color gray use a weight = −1; rest of indicators use weight = 1.
5. Discussion
The review of related works completed in Section 2 suggests the need for a more rigorous and adequate vision for the evaluation of the smartification process, in any smart domain, that contributes to enriching the current state of the art: unlike the works presented in [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,30], which describe a variety of smart university initiatives, emphasizing either the digital transformation of content or processes, or the design of the smart university as a smart city, or from a purely technological perspective, our work presents a case study based on the smart ESI project and, additionally, a formal method of measuring its degree of transformation, i.e., its smartification. On the other hand, works describing smartification approaches, such as those described in [8,22,23], lack methodology, so we can argue that they are difficult to systematically exploit in other contexts. Our work described in [2], which presents a formal method to develop rankings for smart cities, is similar to this work as both leverage MADM for the description of the theoretical framework but lack in-depth analysis related to the domain of smart universities that includes, for example, academic indicators. The work described in [25] proposes a methodology for smartification of buildings, without providing evidence or demonstrations of its application in real-life scenarios. The proposed methodology has as its main objective to estimate a value of the effort performed by a university/campus to become a smart university, i.e., valor to measure the smartification process. It is important to note that such value should be understood in the context of the demonstration of the proposed methodology, not as an absolute result of its application. More importantly, the outcome of this research is oriented to understand better the strengths and weaknesses of the smartification process by focusing our attention on technological aspects without detracting from the academic and research and aspects, which make up the fundamental mission of universities.
We have considered seven dimensions that are commonly employed in the different initiatives related to smart universities/campuses that we have found in the state of the art, such as explained in Section 2: Smart Learning, Governance, Environment, People, Management, Mobility, Economy. To this set we have added an eighth dimension, the smartness dimension , that is related to measuring the quantity and quality of the ICT resources employed in the university that are transversal to the rest of the dimensions. The methodology proposed is centered on the selection of a large set of indicators associated with the seven dimensions, in order to obtain a standardized value aimed at measuring the overall development degree in universities, i.e., its smartification process. From the set of 79 indicators used in our methodology, λ = 33 are technological/smart indicators and q = 46 are indicators designed to collect diverse information on academic aspects, operations, results, infrastructure and environment, including the results of the Degree program.
Our research work addresses the question “how smart is the smart university”. In doing so, we have faced several difficulties that may limit the value of our research: (1) Lack of reference methods in the literature, which can provide the basis for elaborating a formal answer to this question. As we have reviewed in Section 2, the works that present smart initiatives are described from a technological rather than a methodological perspective and hardly quantify the value of their smartification; (2) Difficulty in measuring the real impact that smart university strategies have on the university community, resources (e.g., buildings) and the environment. In fact, we have defined two indicators, KPI (number of known metrics to determine the progress achieved) and AWK (average percentage of improvement achieved per KPI) that we considered necessary to measure the improvement but could not be easily assessed; (3) Subjectivity inherent to the method, as it depends on the indicators selected. However, due to the lack of a commonly accepted set of indicators for evaluation purposes in the research community, this subjectivity is not unique to our method, as in any ranking process it is necessary to select variables, construct indicators and weight them; these steps are usually applied on the basis of participatory or expert assessment methods. Conversely, the set of indicators can be easily extended by adding new indicators related to smart universities, even of a different nature (e.g., human factors), to improve the accuracy of the results. For a fair comparison, the only requirement is that all universities considered in the assessment have a valid value for the new indicator. Thus, we highlight another strength of this research, which is the possibility to fairly compare universities/campuses using the proposed method under a standardized set of indicators.
Theoretical and Practical Implications for Stakeholders
We complete the discussion with a description of the implications of this research work for the different stakeholders. The outcome of this research can benefit different stakeholders: on the one hand, the university community is composed of professors, students, administrative and technical staff, and managers. On the other hand, the work can tangentially benefit society, from citizens who can consult data from public APIs to companies engaged in the development of products and services in the field of IoT that can echo this research. Finally, the research community may find in this work a new research niche in methodological approaches for the quantification of the smartification process. For all stakeholders, there is an increase in knowledge in different scopes. Table 6 presents in the first column the stakeholders and in the second column the list of associated theoretical and practical implications of this work.

Table 6.
Summary of the theoretical and practical implications for stakeholders. Th: Theoretical; Pr: Practical implication.
6. Conclusions
There is not much research on formal methods to quantify the degree of smartification carried out by the so-called smart initiatives and, as far as the authors are aware, none of them has addressed the university environment. In this sense, this paper presents a novel formal method to quantify the degree of smartification in small universities or medium-sized campuses. The proposed formal method employs, firstly, case study research to extract knowledge from the literature on the most commonly used subdomains, services and indicators in the smart university context and, secondly, Multiple Attribute Decision Making (MADM) to quantify the degree of smartification of the universities (alternatives in terms of MADM) according to the criteria and attributes (indicators) obtained in the first step. To do so, we reviewed a collection of articles whose keywords refer to IoT and the domains of smart university/faculty/campus in order to obtain a broad set of indicators of different types, both academic, technological and related to smartness, that could globally score the effort made by a university on its way to smartification. By using this methodological perspective, we presented a detailed description of the Smart ESI project, an initiative to populate our School of Computer Science (ESI) at University Castilla-La Mancha with sensing and acting devices able to provide a large set of data about the School and its environment oriented to increase our knowledge and with the ultimate goal of improving its operation, sustainability and efficiency.
Our approach provides two important potential benefits: first, it is able to pinpoint the strengths and weaknesses of smart university initiatives; second, it suggests a preliminary study to develop tools based on standard indicators and common criteria that allow a fair comparison of such initiatives. In future work, we plan to automate the calculation process and tackle a large experiment involving a broad set of universities. As part of this work, we are already working on the development of web forms to facilitate data collection by university managers, through which they will be able to provide indicator values that can later be used for comparison among all universities participating in the experiment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.E., C.B.; methodology, S.E.; software, F.R., J.A.d.l.T.; validation, J.B. and J.C.; formal analysis, S.E.; investigation, F.R.; resources, J.B., C.B.; data curation, J.B.; writing—original draft preparation, S.E.; writing—review and editing, S.E.; visualization, J.C.; supervision, J.C.L.; project administration, J.C.L.; funding acquisition, C.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This paper is partially supported by European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement no. 857159, project SHAPES (Smart & Healthy Ageing through People Engaging in Supportive Systems). It is also funded by MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 under Grant TALENT-BELIEF (PID2020-116417RB-C44) and the Project MIRATAR TED2021-132149B-C41 funded by MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 and by European Union NextGenerationEU/PRTR.
Data Availability Statement
The processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also forms part of an ongoing study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ashton, K. That ‘Internet of Things’ Thing. RFID J. 1999, 22, 97–114. [Google Scholar]
- Escolar, S.; Villanueva, F.J.; Santofimia, M.J.; Villa, D.; del Toro, X.; López, J.C. A Multiple-Attribute Decision Making-based approach for smart city rankings design. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 142, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente-Peces, C. On the Energy Efficiency in the Next Generation of Smart Buildings—Supporting Technologies and Techniques. Energies 2019, 12, 4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 2010/31/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 May 2010 on the Energy Performance of Buildings (Recast). 2010. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2010/31/oj (accessed on 8 October 2023).
- Economidou, M.; Todeschi, V.; Bertoldi, P.; D’Agostino, D.; Zangheri, P.; Castellazzi, L. Review of 50 years of EU energy efficiency policies for buildings. Energy Build. 2020, 225, 110322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metallidou, C.K.; Psannis, K.E.; Egyptiadou, E.A. Energy Efficiency in Smart Buildings: IoT Approaches. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 63679–63699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daissaoui, A.; Boulmakoul, A.; Karim, L.; Lbath, A. IoT and Big Data Analytics for Smart Buildings: A Survey. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 170, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, G.; Zeller, V.; Hicking, J.; Bernardy, A. Introducing a methodology for smartification of products in manufacturing industry. Procedia CIRP 2019, 81, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckyardi, S.; Hurriyati, R.; Disman, D.; Dirgantari, P. A Systematic Review of the IoT in Smart University: Model and Contribution. Indones. J. Sci. Technol. 2022, 7, 529–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, C.; Kheirkhahzadeh, A.; Roth-Berghofer, T. Data Literacy in the Smart University approach. In Proceedings of the Learning Analytics and Knowledge Conference, Edinburgh, UK, 25–29 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Maresca, P.; Coccoli, M.; Guercio, A.; Stanganelli, L. Smarter universities: A vision for the fast changing digital era. J. Vis. Lang. Comput. 2014, 25, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areniz-Arévalo, Y.; Barrientos-Avendaño, E. Universidad inteligente: Oportunidades y desafíos desde la Industria 4.0. Rev. Ingenio 2019, 16, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargaoui, H.; Bdiwi, R. Smart classroom: Design of a gateway for ubiquitous classroom. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Web and Open Access to Learning (ICWOAL), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 25–27 November 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, A.; Sugino, N.; Suzuki, T.; Ishijima, S. A step towards the Smart Campus: A venture project based on distance learning by a hybrid video conferencing system. In Proceedings of the SMC 2000 Conference Proceedings, 2000 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, “Cybernetics Evolving to Systems, Humans, Organizations, and Their Complex Interactions”, Nashville, TN, USA, 8–11 October 2000; Volume 1, pp. 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandi, C.; Monti, L.; Ceccarini, C.; Salomoni, P. Smart Campus: Fostering the Community Awareness through an Intelligent Environment. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2020, 25, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Caramés, T.M.; Fraga-Lamas, P. Towards Next Generation Teaching, Learning, and Context-Aware Applications for Higher Education: A Review on Blockchain, IoT, Fog and Edge Computing Enabled Smart Campuses and Universities. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciá Pérez, F.; Berna-Martinez, J.; Fonseca, I. Modelling and Implementing Smart Universities: An IT Conceptual Framework. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-da Nóbrega, P.I.; Chim-Miki, A.F.; Castillo-Palacio, M. A Smart Campus Framework: Challenges and Opportunities for Education Based on the Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min-Allah, N.; Alrashed, S. Smart campus—A sketch. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 59, 102231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbán Pozas, B.; Muriel Holgado, B.; Lucas Bonilla, M.; Barroso Ramírez, S.; Bustos García de Castro, P. Iterative Optimization of a Social Inmotics-Based Method in Order to Make Buildings Smart and Resilient. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 82, 103876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbán Pozas, B.; Muriel Holgado, B.; Lucas Bonilla, M. Metodología para mejorar el confort y la calidad del aire en edificios públicos con tecnología de bajo coste = Methodology to improve comfort and air quality in public buildings with low-cost technology. An. De Edif. 2021, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis-Ferreira, F.; Sarraipa, J.; Goncalves, R. Smartification of Home Appliances for Safety Assessment and Risk Alert. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 207–211, In Proceedings of the 13th IFAC Workshop on Intelligent Manufacturing Systems IMS 2019, Oshawa, ON, Canada, 12–14 August 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, O.; Zeadally, S. Toward efficient smartification of the Internet of Things (IoT) services. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 92, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhardt, K.M. Building Theories from Case Study Research. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1989, 14, 532–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porsche Consulting. Too Smart to Use? How Increased User Involvement Is Key to Make Smart Building Concepts Thrive. 2022. Available online: https://newsroom.porsche.com/en/2022/company/porsche-consulting-too-smrt-to-use-smart-buildings-30459.html (accessed on 8 October 2023).
- Hwang, C.; Yoon, K. Multiple Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications—A State-of-the-Art Survey; Lecture Notes in Economics and Mathematical Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981; Volume 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, B.; Chalon, R.; Yin, C. Design Methodology for “Smartification” of Cities: Principles and Case Study. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 25th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design (CSCWD), Hangzhou, China, 4–6 May 2022; pp. 1486–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanakis, S.H.; Solomon, A.; Wishart, N.; Dublish, S. Multi-attribute decision making: A simulation comparison of select methods. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1998, 107, 507–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamani, G.; Parmar, R.; Ghodasara, Y. Data Normalization in Data Mining Using Graphical User Interface a Pre-Processing Stage. Gujarat J. Ext. Educ. 2022, 30, 106–109. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez Domínguez, A.; Barrena García, M.; García Rodríguez, P.; Montalbán Pozas, B.; Bustos García, P. SmartPolitech: Un experimento en inmótica social. In Proceedings of the XXII Jornadas de Ingeniería del Software y Base de Datos, La Laguna, Spain, 19–21 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).