Research on the Vector Coherent Factor Threshold Total Focusing Imaging Method for Austenitic Stainless Steel Based on Material Characteristics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Test Principle
2.1. Total Focusing Method
2.2. VCF Threshold Imaging
3. Result Analysis and Discussion
3.1. Test Blocks and Experiments
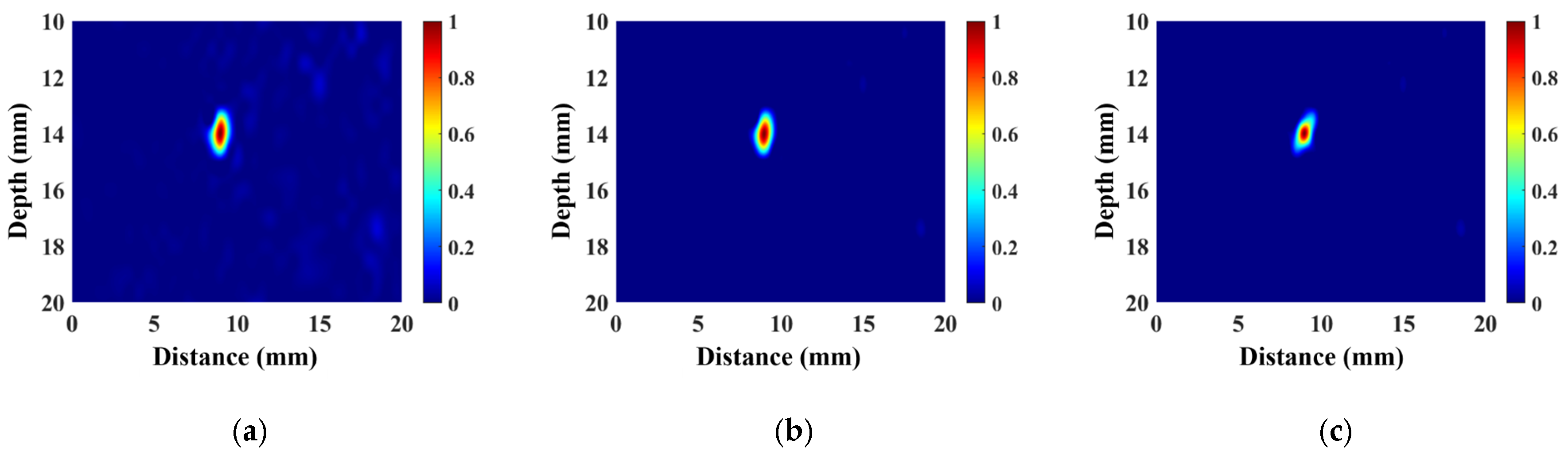
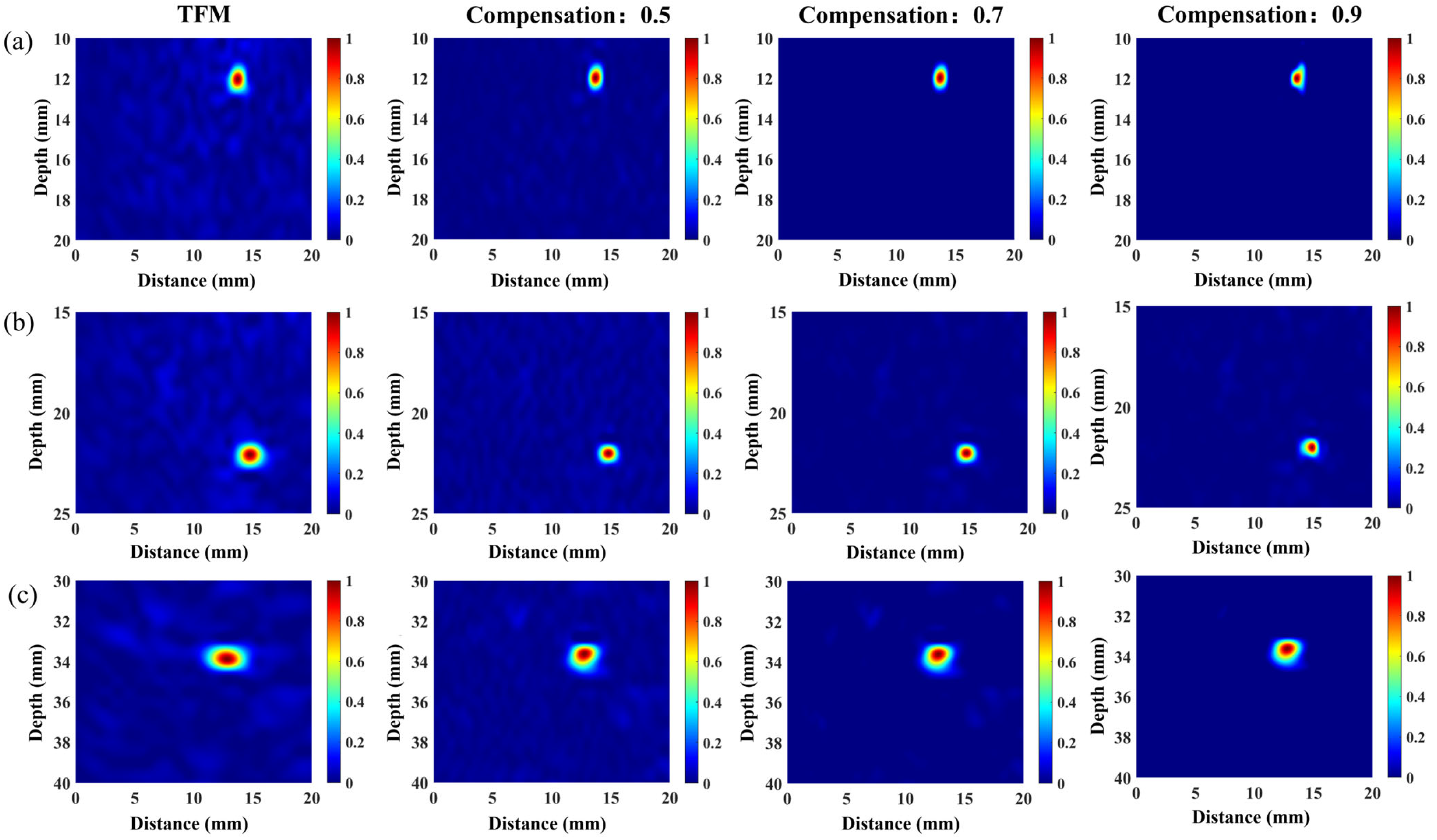
3.2. Simulated Analysis
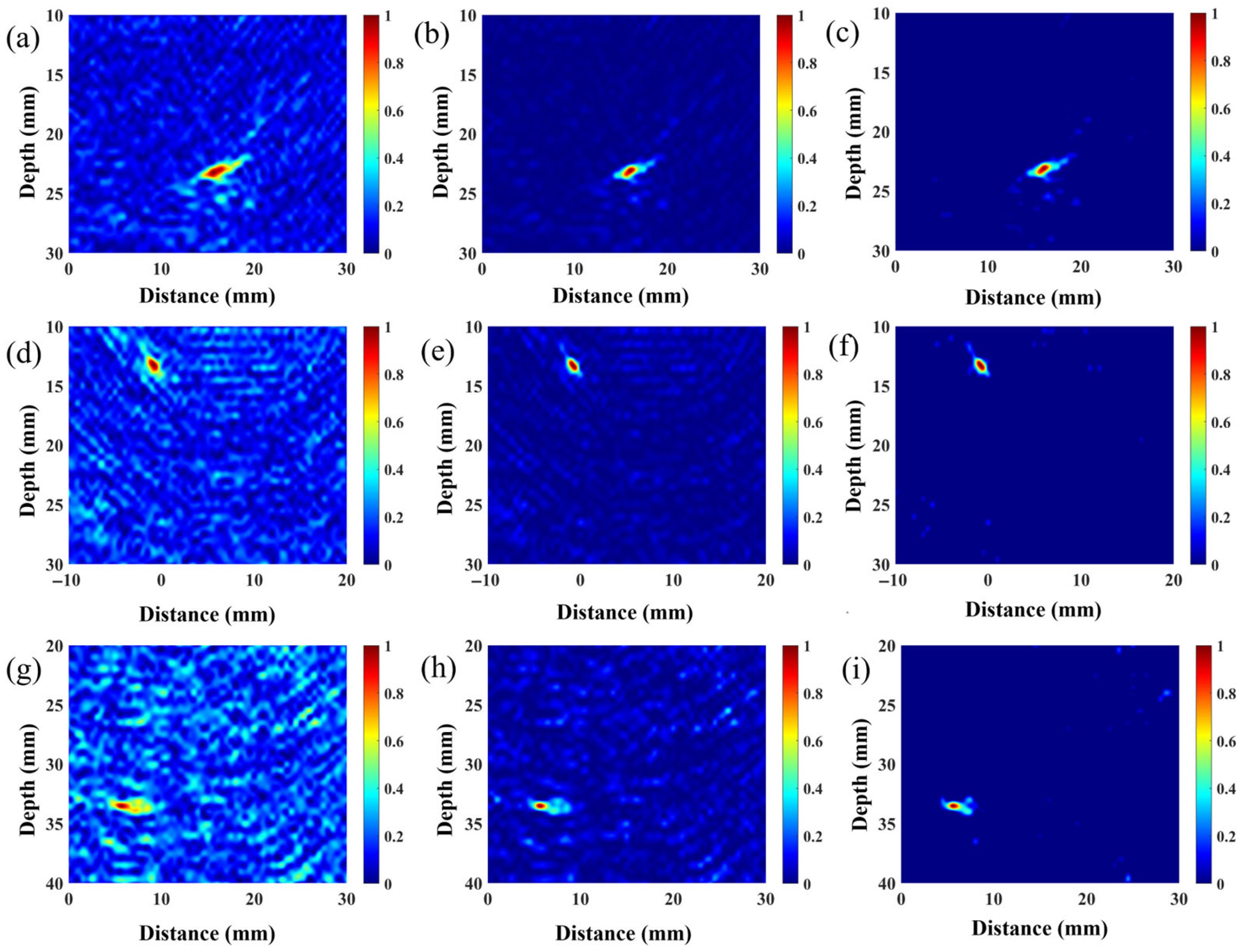
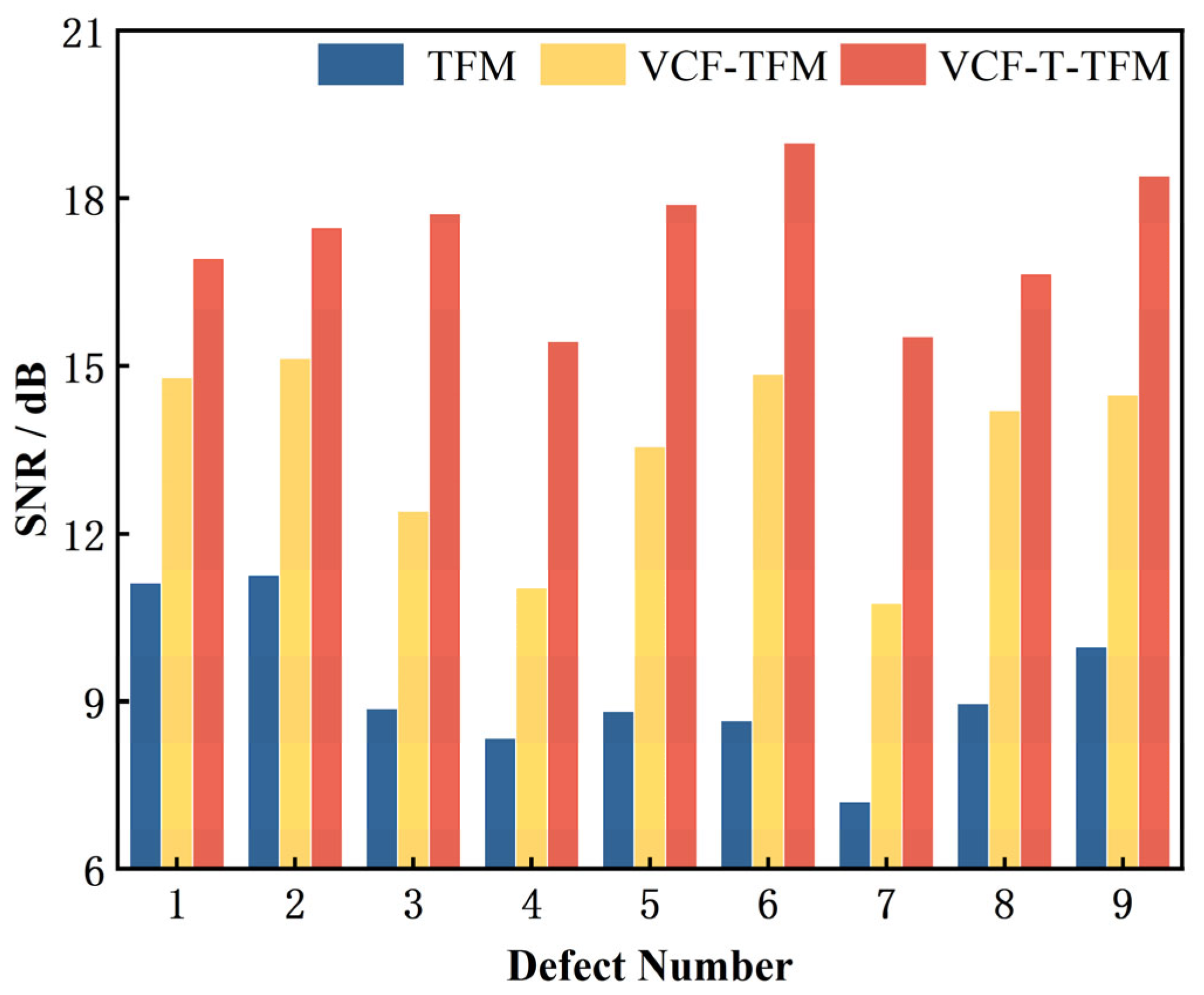
3.3. Experimental Result
4. Conclusions
- This study introduces the vector coherent factor threshold total focusing imaging method (VCF-T-TFM), incorporating material properties to enhance ultrasonic imaging in heterogeneous coarse-grained austenitic stainless steels. The efficacy of this approach in improving the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) was rigorously validated through combined simulation and experimental investigations.
- Simulation studies employed three austenitic stainless-steel weld specimens exhibiting graded heterogeneity. These studies compared the defect imaging performance of the VCF-T-TFM in carbon steel versus austenitic stainless steel across regions of differing heterogeneity, specifically analyzing the impact of tissue heterogeneity on the imaging SNR. Results demonstrate that, in contrast to homogeneous media, the VCF-T-TFM effectively suppresses backscattered structural noise within heterogeneous regions of coarse-grained materials. Furthermore, the analysis revealed a correlation between the optimal coarse-grain coherence compensation value and the degree of material heterogeneity.
- Experimental validation involved ultrasonic testing of nine side-drilled-hole (SDH) defects at various locations within austenitic stainless-steel weld test blocks. Conventional denoising techniques without coarse-grain compensation achieved a maximum SNR improvement of 5.24 dB. In comparison, the proposed VCF-T-TFM, by incorporating coarse-grain coherent compensation, significantly enhanced defect detectability, suppressing structural noise inherent to coarse-grain structures. This yielded a substantial SNR improvement of up to 10.34 dB, representing a 97.3% enhancement over the uncompensated conventional approach.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TFM | Total Focusing Method |
| VCF | Vector Coherent Factor |
| EBSD | Electron Backscatter Diffraction |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
References
- Rokhlin, S.I.; Bolland, T.K.; Adler, L. High-frequency Ultrasonic Wave Propagation in Polycrystalline Materials. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1992, 91, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.T.; Yan, S.G.; Zhang, B.X. Acoustic Simulation and Total Focusing Method Defect Detection in Austenitic Stainless Steel Welds. J. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 42, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Leymarie, N.; Imperiale, A.; Fortuna, T.; Edouard, D. Comparisons of Ray and Finite Element Simulations of Ultrasonic Wave Fields in Smoothly Inhomogeneous Austenitic Welds of Thick-walled Components. NDT E Int. 2024, 147, 103177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.G.; Wu, W.; Ouyang, X.Q. Ultrasonic Testing Analysis of 304 Stainless Steel Crystal Grain Diffusion Properties. Nondestruct. Test. 2010, 32, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Bloxham, H.A.; Velichko, A.; Wilcox, P.D. Combining Simulated and Experimental Sata to Simulate Ultrasonic Array Data from Defects in Materials with High Structural Noise. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2016, 63, 2198–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.D.; Huang, H.D.; Wang, Q.; Chen, T.; Wu, L.L. Detection of the Defects in Austenitic Stainless Steel Weld by Using the Ultrasonic Total Focus Imaging. J. China Univ. Metrol. 2021, 32, 472–479. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. Complementarity of Phased-Array Technology and Total Focusing Method. Nondestruct. Test. Technol. 2017, 41, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ponseenivasan, S.; Kumar, A.; Rajkumar, K.V. Anisotropy Corrected FMC/TFM Based Phased Array Ultrasonic Imaging in an Austenitic Buttering Layer. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.Y.; Su, J.K.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.F.; Jin, S.J.; Yang, H.M.; Lin, L. Defect Detection of BOSS Welds in Nuclear Power Plant by Ultrasonic Total Focusing Method. Nondestruct. Test. Technol. 2023, 47, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho, J.; Fritsch, C. Phase Coherence Imaging of Grained Materials. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2011, 58, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, S.K.; Lu, C.; Li, Q.F. Shear Wave Full-skip Total Focusing Method of Upper Surface-breaking Cracks Based on Circular Statistic Vector Threshold Weighting. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2023, 44, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. Modeling of Ultrasonic Testing and Noise Suppression Using Phase Coherence Imaging Algorithm in Heavy-Walled Cast Austenitic Stainless Steel. Ph.D. Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bilodeau, M.; Quaegebeur, N.; Berry, A.; Masson, P. Correlation-based Ultrasound Imaging of Strong Reflectors with Phase Coherence Filtering. Ultrasonics 2022, 119, 106631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesage, J.C.; Marvasti, M.; Farla, O. Vector Coherence Imaging for Enhancement of Small Omni-directional Scatterers and Suppression of Geometric Reflections. NDT E Int. 2021, 123, 102502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.X.; Chen, M.; Kong, Q.R.; Xiao, L.Z.; Lu, C.; Chen, Y. Phased Array Ultrasonic Sector Scan Imaging of Helicopter Damper Bolts Based on Vector Coherence Factor. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.Y.; Wang, X.K.; Hua, L.; Li, Y.X. TFM Imaging of Aeroengine Casing Ring Forgings with Curved Surfaces using Acoustic Field Threshold Segmentation and Vector Coherence Factor. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2022, 35, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, V.T.; Higuti, R.T.; Kitano, C.; Martinez-Graullera, O. Instantaneous Phase Threshold for Reflector Detection in Ultrasonic Images. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2014, 61, 1204–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, B.; Painchaud-April, G.; Le Duff, A.; Belanger, P. Lightweight and Amplitude-Free Ultrasonic Imaging Using Single-Bit Digitization and Instantaneous Phase Coherence. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2022, 69, 1763–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazulin, E.G. Using coherence factor to improve the quality of reflector images in ultrasonic testing. Russ. J. Nondestruct. 2017, 53, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, C.; Robert, S.; Miorelli, R.; Lesselier, D. Optimization algorithms for ultrasonic array imaging in homogeneous anisotropic steel components with unknown properties. NDT E Int. 2020, 116, 102327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedade, L.P.; Painchaud-April, G.; Le Duff, A.; Belanger, P. Minimum Transmission Events for Fast Ultrasonic TFM Imaging: A Comparative Study. NDT E Int. 2022, 128, 102627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Shi, S.Q.; Sun, X.; Ma, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Liu, L.L.; Jin, S.J. Resolution Enhancement of Total Focusing Imaging Combining with Autoregressive Spectral Extrapolation. J. Mech. Eng. 2020, 56, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cruza, J.F.; Camacho, J.; Fritsch, C. Plane-wave phase-coherence Imaging for NDE. NDT E Int. Indep. Nondestruct. Test. Eval. 2017, 87, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, B.; Painchaud-April, G.; Le Duff, A.; Belanger, P. Ultrasonic Multi-view Data Merging using the Vector Coherence Factor. NDT E Int. 2023, 136, 102805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E494-05; Standard Practice for Measuring Ultrasonic Velocity in Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2005.
- Li, W. Non-Destructive Testing Manual, 2nd ed.; Chapter Ten; Machinery Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 43–44. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Z.D.; Yang, Z.; Meng, X.F.; Guo, Q.Q.; Huang, S.X.; Yang, X.G. Hot deformation behavior and hot rolled properties of Gd-rich 316 L austenitic stainless steel neutron shielding material for spent nuclear fuel storage and transportation. Mater. Charact. 2024, 218, 114493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Luo, Z.B.; Zhou, Q.; Zou, L.J.; Lin, L. Modeling of Ultrasonic Propagation in Heavy-walled Centrifugally Cast Austenitic Stainless Steel Based on EBSD Analysis. Ultrasonics 2015, 59, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Drinkwater, B.D.; Wilcox, P.D.; Hunter, A.J. Defect detection using ultrasonic arrays: The multi-mode total focusing method. NDT E Int. 2010, 43, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
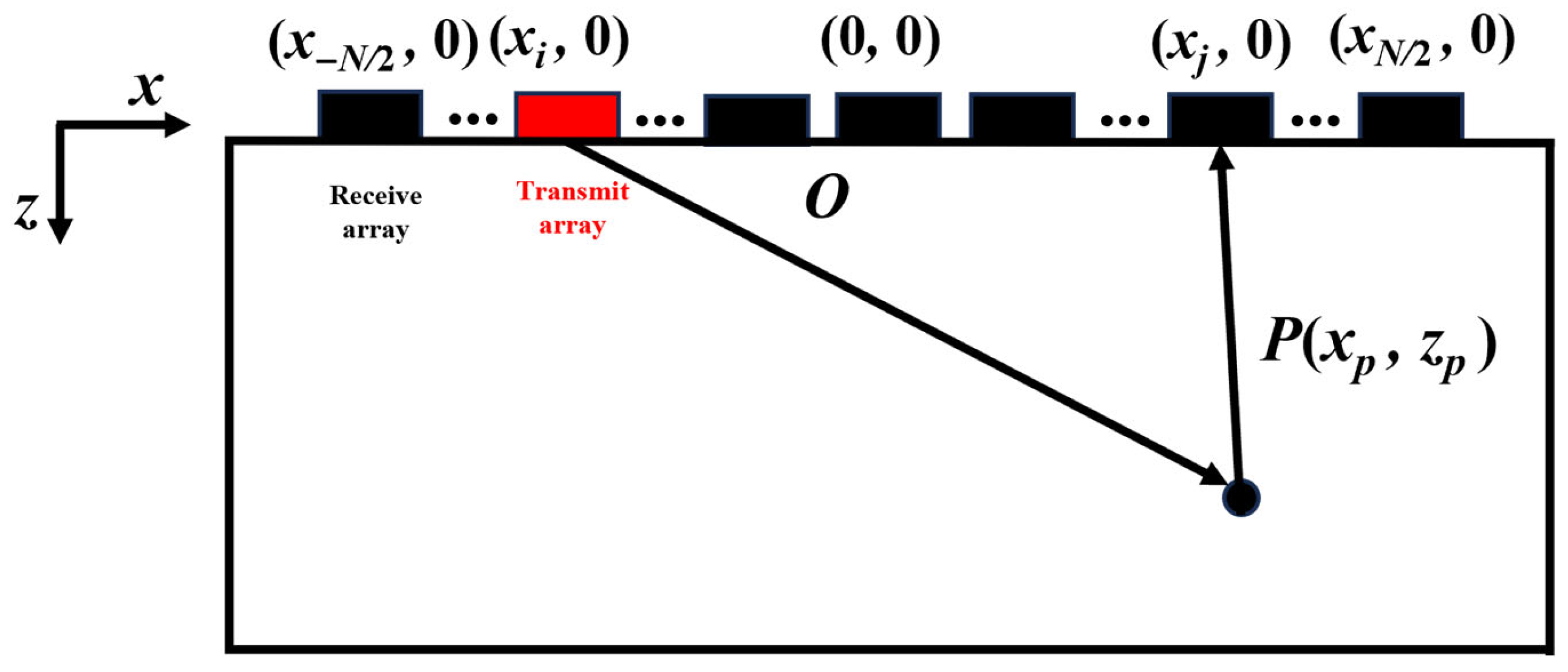
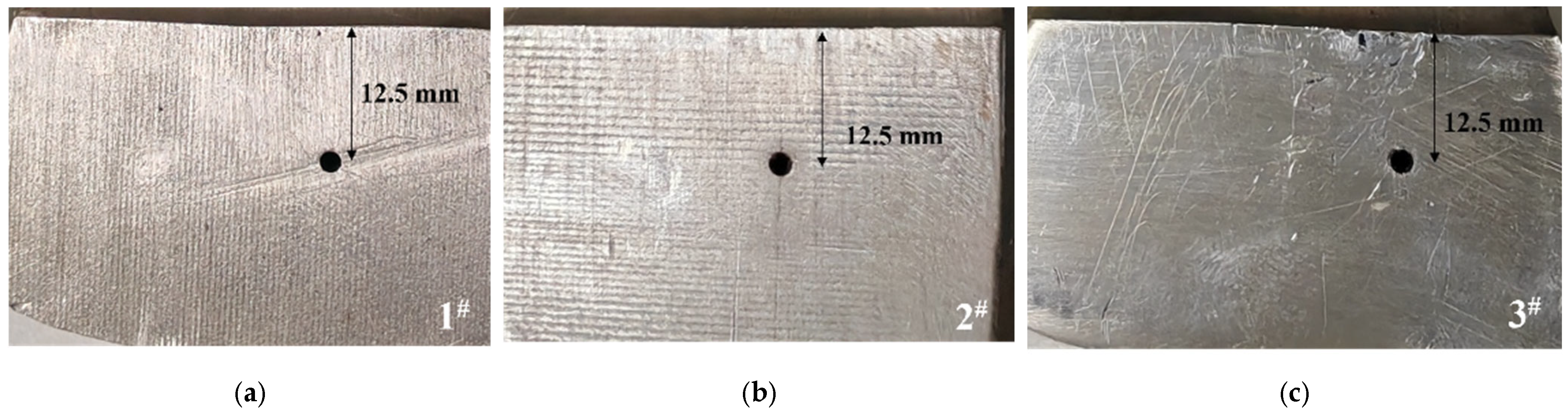
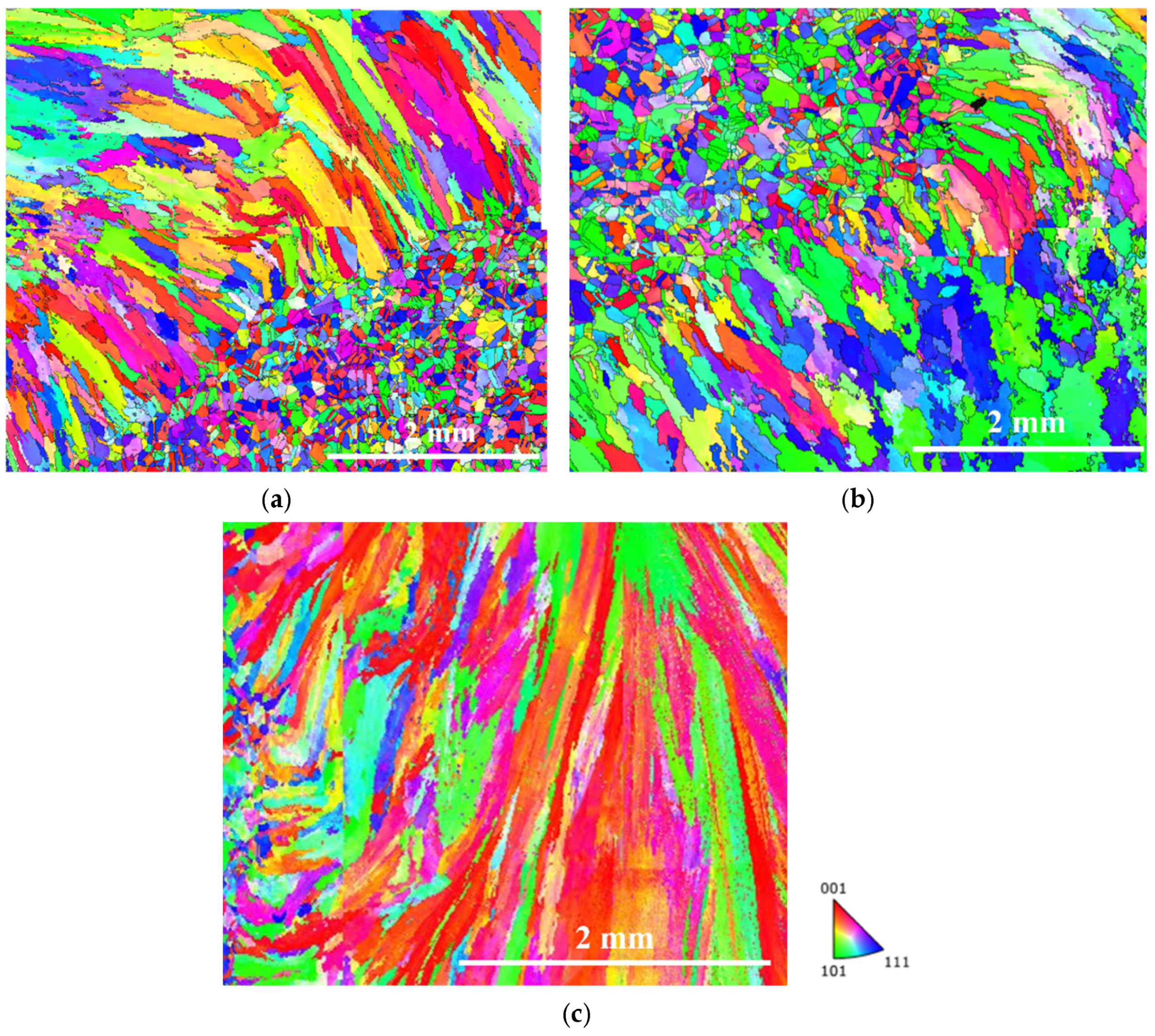
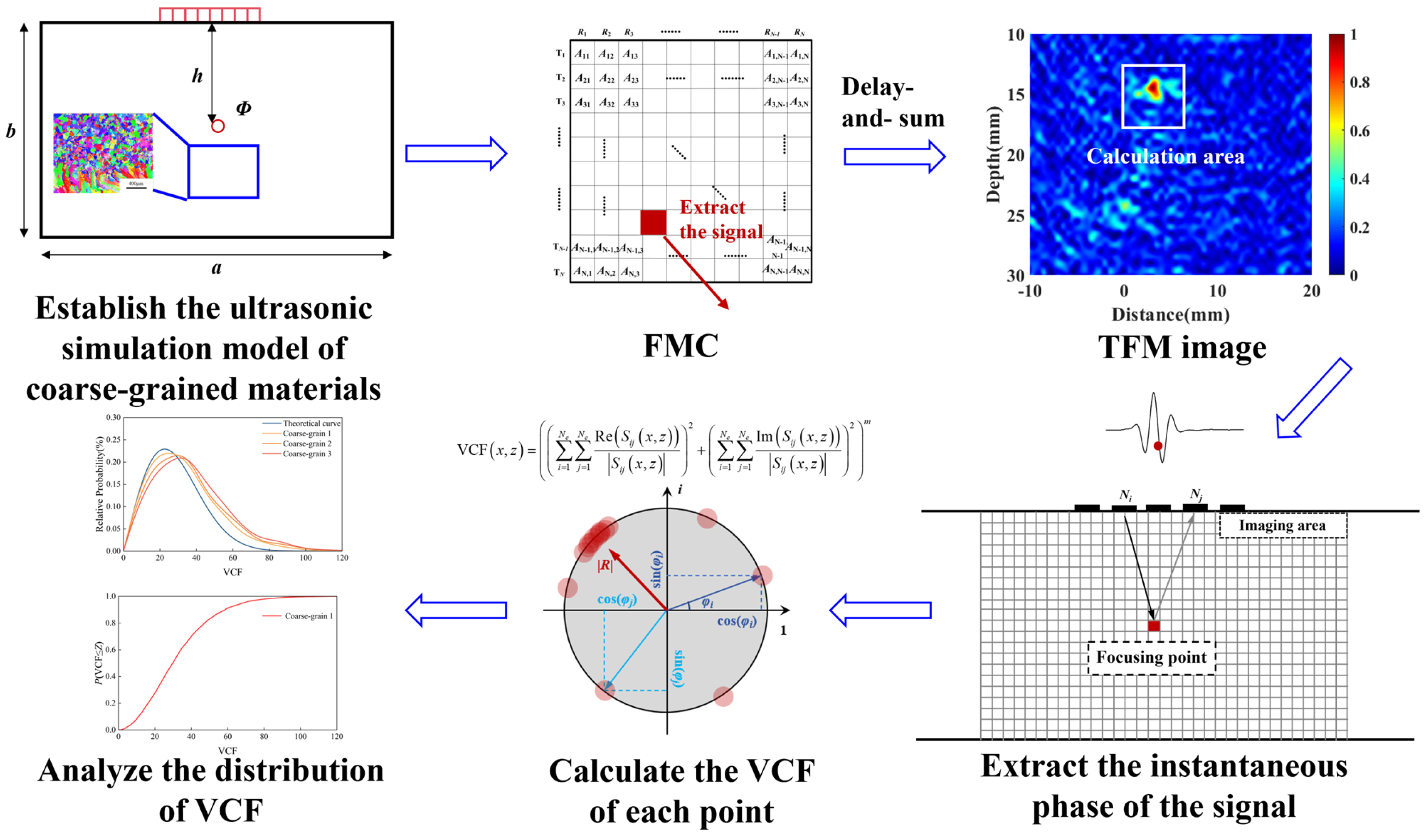


| Test Block Number | Material | Welding Procedure |
|---|---|---|
| 1# | Z2CN18-10-M | Plasma arc welding |
| 2# | Z2CN18-10-M | Plasma arc welding |
| 3# | X2CrNiMo18-12 (nitrogen-controlled) | Narrow gap automatic welding |
| Test Block Number | Longitudinal Wave Velocity (m/s) | Attenuation Coefficient (dB/mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 1# | 5826.5~5860.3 | 0.15~0.19 |
| 2# | 5769.2~5836.3 | 0.16~0.21 |
| 3# | 5624.3~5706.8 | 0.18~0.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, T.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Peng, G. Research on the Vector Coherent Factor Threshold Total Focusing Imaging Method for Austenitic Stainless Steel Based on Material Characteristics. Metals 2025, 15, 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080901
Zhao T, Liu Z, Zhang D, Wang J, Peng G. Research on the Vector Coherent Factor Threshold Total Focusing Imaging Method for Austenitic Stainless Steel Based on Material Characteristics. Metals. 2025; 15(8):901. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080901
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Tianwei, Ziyu Liu, Donghui Zhang, Junlong Wang, and Guowen Peng. 2025. "Research on the Vector Coherent Factor Threshold Total Focusing Imaging Method for Austenitic Stainless Steel Based on Material Characteristics" Metals 15, no. 8: 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080901
APA StyleZhao, T., Liu, Z., Zhang, D., Wang, J., & Peng, G. (2025). Research on the Vector Coherent Factor Threshold Total Focusing Imaging Method for Austenitic Stainless Steel Based on Material Characteristics. Metals, 15(8), 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080901






