Abstract
Background: Short QT syndrome (SQTS) is a rare inheritable channelopathy characterized by a shortened corrected QT interval on an electrocardiogram and a significant risk of atrial and ventricular arrhythmias, potentially leading to sudden cardiac death. Despite advancements in our understanding of SQTS, knowledge gaps persist due to its extreme rarity. This scoping review aims to summarize the available knowledge on its clinical presentations, genetic mutations, and management strategies, while identifying areas for further investigation. Methods: This scoping review was conducted across the PubMed, Scopus, and Cochrane databases and identified relevant case reports, case series, and available studies on SQTS. We focused on articles that reported clinical outcomes, genetic mutations, diagnostic criteria, and management strategies, while excluding studies on the secondary causes of short QT intervals. Results: SQTS is present across a wide age range, from asymptomatic individuals to those experiencing syncope, palpitations, or sudden cardiac arrest. Common genetic mutations include KCNQ1, KCNH2, and KCNJ2. Management strategies vary, with some patients receiving implantable cardioverter defibrillators for secondary prevention and others treated pharmacologically, primarily with hydroquinidine. Our findings highlight the rarity and clinical variability of SQTS, underscoring the need for optimized diagnostic criteria and individualized management strategies. Conclusions: This review emphasizes the need for continued research to better understand the genetic basis of SQTS, optimize diagnostic tools, and improve treatment approaches. Large-scale studies and the integration of genetic and clinical data are critical to addressing the gaps in SQTS management and improving outcomes for patients with this potentially life-threatening arrhythmic disorder.
1. Introduction
Short QT syndrome (SQTS) is a rare and potentially life-threatening inheritable channelopathy characterized by abbreviated corrected QT (QTc) intervals on electrocardiograms (ECGs). First described in 2000, SQTS has since emerged as a distinct entity associated with increased risk for ventricular arrhythmias, syncope, and sudden cardiac death (SCD) in the absence of structural heart disease [1]. While our understanding of the syndrome has grown significantly over the past 20 years, knowledge gaps persist, especially regarding primary prevention.
Using the Schwartz criteria for long QT syndrome as an example [2], Gollob et al. proposed diagnostic criteria for SQTS based on ECG and clinical characteristics, family history, and genetic findings [3]. The clinical presentation of the syndrome is highly variable, ranging from asymptomatic individuals to those experiencing palpitations, syncope, or life-threatening arrhythmias, such as ventricular fibrillation (VF). Given this variability, the diagnosis of SQTS can be particularly challenging and often requires a high index of suspicion; the recent European Society of Cardiology (ESC) guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of SCD, published in 2022 [4], included updated diagnostic criteria for SQTS and suggested an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) for patients who are survivors of cardiac arrest or demonstrate a history of arrhythmic syncope. In terms of pharmaceutical options, hydroquinidine is recommended for the prevention of ventricular arrhythmias in high-risk SQTS patients who do not wish to have an ICD implanted [4]. A representative ECG of a patient with SQTS is shown in Figure 1, demonstrating their short QT (SQT) interval and repolarization abnormalities.
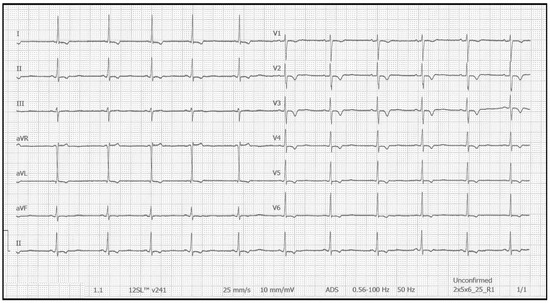
Figure 1.
Representative 12-lead ECG from a patient with SQTS, demonstrating a markedly shortened QT interval (QTc: 290 ms) and repolarization abnormalities.
Since the initial description of the syndrome, various gene mutations have been identified in SQTS patients, with seven types reported so far. SQTS 1–3 have been associated with mutations resulting in a gain of function for potassium channels, SQTS 4–6 with mutations causing loss of function for calcium channels, while the seventh subtype of SQTS is linked to a loss of function in the anion exchanger AE3 [5,6]. However, in a large proportion of SQTS cases, genetic testing is negative for known mutations, suggesting the presence of additional genetic contributors that are yet to be identified [4]. The close follow-up of these patients, with periodically repeated genetic testing for newly described mutations, as well as cascade screening and genetic counseling, are of paramount importance for a better understanding of these cases.
In an effort to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge on SQTS, we conducted a scoping review of the literature. Our aim was to summarize existing data on the clinical presentation, genetic basis, diagnostic criteria, management options, and outcomes for patients with SQTS; by identifying areas where knowledge is lacking, we hope to inform future research directions, with an eye to improve the treatment approaches for patients suffering from this rare but potentially life-threatening arrhythmic syndrome.
2. Materials and Methods
This scoping review of the literature was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR) (Supplementary Table S1). We searched the PubMed, Scopus, and Cochrane databases from their inception to January 5th, 2025, employing Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) terms such as “short QT syndrome”, “SQTS”, “short QT”, “QT shortening”, “QTc”, and “SQT”. No restrictions were placed in terms of time, while only English language articles were incorporated. Our search was designed to identify the available case reports, case series, and all other types of studies including patients with SQTS. Systematic reviews, narrative reviews, and expert opinions, as well as journal preprints and animal and cell model studies, were excluded. This scoping review was not registered in PROSPERO or other databases, as its nature is purely exploratory, rather than a systematic review with a predefined protocol.
All retrieved results were imported into reference management software for duplicate removal. Two independent reviewers scanned the results’ titles and abstracts for relevance (AB and AK). Eligible manuscripts then had their full text reviewed, while the PICO (Patients, Interventions, Control and Outcomes) process was used to construct data extraction tables from the retrieved studies. More detailed tables were also created to extract data from case reports and case series. Full-text reports were scanned for further references. A critical appraisal of the retrieved studies was not performed, since the goal of our search was to identify potential parameters of interest, rather than evaluate the level of evidence.
3. Results
Our search delivered a total of 1997 results, and, after duplicate removal, the titles and abstracts of 1724 references were screened for eligibility. A total of 1139 articles were initially excluded as irrelevant to the topic and, after full-text review, an additional 444 articles were rejected. We therefore included 141 references in our scoping review (Figure 2). In this review, specific emphasis was placed on SQTS, and references pertaining to secondary causes of SQT were deliberately excluded from the analysis in order to maintain a focused investigation on the primary genetic disorder.
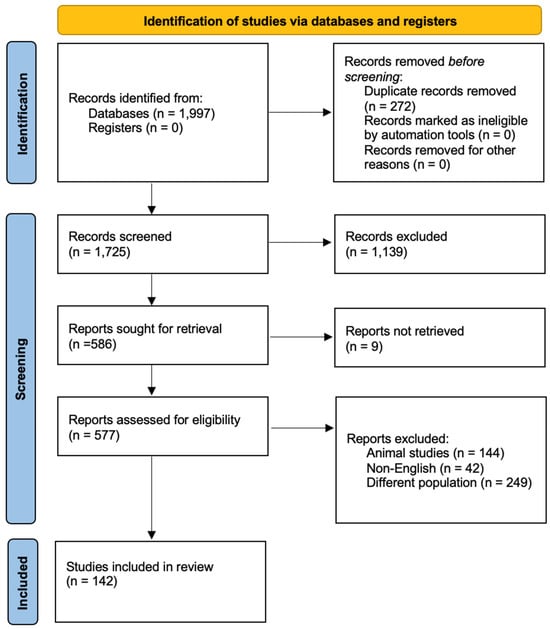
Figure 2.
PRISMA 2020 flow diagram illustrating the study selection process. This diagram outlines the identification, screening, eligibility assessment, and final inclusion of studies in this scoping review. A total of 1997 records were identified through database searches, with 273 duplicates then removed. After screening and an eligibility assessment, 141 studies were included in the final review. The exclusion criteria were non-English studies, animal studies, and studies focusing on different populations.
3.1. Case Reports
Our search yielded 43 case reports on SQTS (Supplementary Table S2) [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49], with an average diagnosis age of around 25 years. Ten cases were reported to be asymptomatic; common symptoms included presyncope, syncope, and palpitations, with some cases presenting with aborted cardiac arrest. In total, 15 cases had a positive family history of SCD. Additional ECG abnormalities were observed, such as atrial fibrillation (AF), junctional rhythm, U-waves, ST-segment elevation, and early repolarization (ERP). A variety of diagnostic modalities were implemented for further investigation according to each individual case. Treatment strategies varied, with oral quinidine and b-blockers being commonly used pharmaceutical options and ICD implantation being frequently performed, mainly for secondary prevention. Regarding genetic testing, mutations in the genes KCNQ1, KCNH2, SCN5A, CACNA1C, CACNA2D1, KCNJ2, SCN10A, and SLC22A5 were identified in 19 cases. Genetic testing was not available or not performed in 16 cases and yielded negative results for known mutations or demonstrated variants of unknown significance (VUS) in 8 cases. Two patients had evidence of concomitant hypertrophic cardiomyopathy [18,42] and one patient developed arrhythmogenic ventricular cardiomyopathy [49]. The left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was reported to be reduced in one case [12]. Our search also revealed five case reports describing SQTS in the context of various syndromes or other genetic clinical conditions [10,24,25,28,33].
3.2. Case Series
Our review of the literature revealed 29 case series of patients with SQTS [1,5,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76]. In 2000, Gussak et al. [1] presented the first reported family with SQTS, which contained three affected members who demonstrated frequent AF episodes requiring cardioversion. Since then, a series of other affected families have been described, with SQTS manifesting across different age groups. Genetic testing was negative for known mutations in approximately half of these cases; when positive, the identified mutated genes included KCNQ1, KCNJ2, KCNH2, SLC4A3, KCNJ5, SCN10A, CACNA2D, and CACNB2d. The majority of reported patients presented with a positive family history for SCD, while their symptoms at initial presentation varied from palpitations and dyspnea to SCD. About 16% of the reported patients were asymptomatic.
The largest case series was published by El-Battrawy et al. [58], who described 17 patients within seven unrelated families, followed up with for an average of 13.5 years. SCD occurred in 71% of families, affecting men at a younger age, while AF or atrial flutter occurred in 53% of patients. Interventions included ICD implantation in 29% and oral hydroquinidine in 53% of cases, while the most common mutations identified were located in the KCNH2 and CACNB2b genes. Supplementary Table S3 describes the case series of patients with SQTS retrieved from the literature in more detail.
3.3. Studies
A total of 69 studies explored various facets of SQTS, including its prevalence in healthy populations, genetic testing, patient outcomes, drug efficacy, associations with other clinical conditions, and the findings from various diagnostic modalities [52,55,62,65,71,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137,138,139,140].
3.3.1. Studies Screening Healthy Populations or Medical Databases for SQTS
Our literature search revealed 22 studies focused on screening healthy individuals or medical databases to detect the presence of SQTS [65,88,89,90,92,93,94,99,103,106,108,114,120,123,125,130,132,133,134,135,139,140]. Iribarren et al. [106] analyzed 6.4 million ECGs, demonstrating a prevalence of very SQT (<300 ms) of 0.7 per 100,000 and a heightened multivariable-adjusted mortality risk (x2.6) over 8 years of follow-up. Estimates of SQT interval prevalence ranging from lower than 1% up to about 7–8% have been reported in different populations [65,93,94,99,108,120,132,140], although the true prevalence of SQTS, in contrast to SQT, is estimated to be less than 1 in 10,000. This is due to the fact that most individuals with a SQT interval do not meet the diagnostic criteria for SQTS. These findings highlight the importance of continued research in order to shed light on the actual prevalence, clinical implications, and optimal management strategies for this rare patient population. Details of the aforementioned studies are presented in Supplementary Table S4.
3.3.2. Genetic Testing in Patients with SQTS
A number of studies have focused on the genetic analysis of SQTS patients [55,62,77,107,115,121,122,136,137]. Brugada et al. [55] identified KCNH2 mutations in three families with SQTS, linking them to SCD for the first time. KCNH2 was also implicated by Hu et al. [107], with the identification of a KCNH2-T618I mutation associated with SQTS in 18 individuals across seven families, all experiencing SCD. Wu et al. [77] identified the R259H mutation in KCNQ1 associated with SQTS in the Chinese population. Antzelevitch et al. [137] observed SQT intervals in patients with Brugada syndrome (BrS), alongside their ST-segment elevation and SCD, which were linked to loss-of-function mutations in L-type calcium channel genes. Along the same lines, Burashnikov et al. [136] highlighted L-type calcium channel mutations in patients with BrS and SQTS. Harrell et al. [62] described two novel mutations (KCNH2-I560T and KCNQ1-V141M) in Japanese families, underlining the diverse clinical manifestations of SQTS. Christiansen et al. [121] indicated potentially disease-causing variants, notably SLC4A3, in 26% of patients with SQTS. However, Fukuyama et al. [115] and Blancard et al. [122] did not identify pathogenic variants in their SQTS cohorts.
In short, mutations identified in key genes such as KCNH2, KCNQ1, and L-type calcium channel genes have been associated with SQTS, although the molecular substrate remains unknown in the majority of cases [4]. In addition, these findings highlight the heterogeneous nature of SQTS and the importance of further investigations into the genetic etiology of the syndrome. Further research is also needed to fully understand its genotype–phenotype interplays and to develop targeted therapies for individuals with SQTS. Supplementary Table S5 presents details on the studies involving the genetic testing of patients with SQTS.
3.3.3. Studies Assessing Outcomes of Patients with SQTS
Studies reporting outcomes in patients with SQTS are summarized in Supplementary Table S6 [80,85,86,95,97,102,110,111,119,129]. Overall, the number of individuals with SQTS included in each study is small, and the reported rates of arrhythmic events attributable to SQTS are relatively low, with a significant proportion of patients experiencing inappropriate shocks and device-related complications [80,84,119,129].
3.3.4. Drug Therapy in Patients with SQTS
Few studies have evaluated the effect of antiarrhythmic medications on patients with SQTS (Supplementary Table S7a) [78,96,113,118,128]. Gaita et al. [113] assessed a series of antiarrhythmic regimens and reported that hydroquinidine prolonged the QT interval, suggesting that this could be a potential alternative or adjunct to ICD implantation. In line with this, quinidine has been shown to suppress IKr function, which may have therapeutic implications for the gain-of-function HERG mutations associated with SQTS [78]. Several studies have reported a favorable safety profile for hydroquinidine in SQTS [96,118], with indications of a lower incidence of life-threatening arrhythmias. Schimpf et al. suggested disopyramide as an alternative [128], demonstrating its ability to prolong the QT interval and ventricular effective refractory periods in SQTS patients with specific HERG gene mutations.
While available studies indicate that quinidine prolongs the QT interval and may reduce the incidence of ventricular arrhythmias in SQTS patients, this evidence is primarily based on small observational studies with limited follow-up. Disopyramide has also been proposed as an alternative treatment, particularly for those with specific HERG gene mutations. However, further research is needed to confirm the long-term efficacy and safety of these pharmacological approaches.
3.3.5. Studies Assessing Families of Sudden Cardiac Death Victims for the Presence of SQTS
Our search of the literature revealed a total of five studies screening families or cases of SCD for the presence of SQTS (Supplementary Table S7b) [71,83,101,105,131]. Wisten et al. [71] analyzed 181 young individuals with normal autopsy findings, identifying one family with SQTS; similarly, only one case of SQTS was found among 35 patients with unexplained cardiac arrest in the cohort study by Jiménez-Jáimez et al. [105]. Stepįeń-Wojno et al. [83] reported SQTS in 7% of 44 screened patients after SCD. Makarov et al. [131] observed a high frequency of SQT intervals in children from families with a history of sudden death; additionally, SQTS was diagnosed in only 1 family among the 109 referred with SCD and 52 probands with unexplained cardiac arrest [101].
Our review suggests a low prevalence of SQTS among individuals with unexplained cardiac arrest or normal autopsy findings, ranging from 1 to 7% in various cohorts. Further studies are needed for a better understanding of the relationship between SQTS and the risk of SCD.
3.3.6. Studies Demonstrating an Association Between SQT Intervals and Other Clinical Conditions
We identified three studies associating SQT intervals with various clinical conditions (Supplementary Table S7c) [100,104,127]. Teh et al. [127] examined 70 epilepsy patients, noting significantly shorter QTc intervals, especially in those with cryptogenic epilepsy, suggesting a possible connection between epilepsy and altered cardiac repolarization. Screening 150 patients with dilated cardiomyopathy for anti-KCNQ1 antibodies revealed 6% seropositivity and significantly shorter QT intervals [100]. Finally, Jørgensen et al. [104] observed shorter QTc intervals in males with Klinefelter syndrome. Further investigation may elucidate the potential clinical implications of the connection between SQTS and other clinical syndromes.
3.3.7. Findings of Various Diagnostic Modalities Among Patients with SQTS
Eleven studies explored the diagnostic modalities used in patients with SQTS (Supplementary Table S8) [52,79,81,82,85,98,109,116,117,124,138]. Echocardiographic abnormalities, including a reduced LVEF and significant myocardial contraction dispersion, were reported by Frea et al [116]. Exercise testing revealed that these patients had shorter QT intervals both at rest and during peak exercise, with a limited QT adaptation to heart rate [109]. Negative T-wave alternans suggested limited risk stratification [98], while increased transmural dispersion of repolarization was observed through 24-h ECG Holter monitoring [52].
Additional ECG findings included shorter Jpoint-Tpeak intervals in symptomatic patients [138], while Watanabe et al. [79] and Tülümen et al. [81] identified ERP and PQ segment depression, respectively, as potential markers of SQTS-associated arrhythmic events. Suzuki et al. [82] highlighted the utility of Jpoint-Tpeak intervals in children, while Extramiana et al. [117] recommended patient-specific QT correction formulas over Bazett’s. In summary, echocardiography, exercise testing, 24-h ECG Holter monitoring, and ECG markers (e.g., ERP, PQ depression, Jpoint-Tpeak intervals) offer valuable diagnostic insights in SQTS patients.
3.3.8. Other Advances in Research on SQTS
Our search revealed four additional studies involving patients with SQTS [87,91,112,126]. Viskin et al. [126] reported significantly shorter QTc in males with idiopathic VF compared to healthy males (371 ± 22 ms vs. 385 ± 19 ms, p = 0.034), with no such differences observed in females. Rollin et al. [87] highlighted shorter atrial and ventricular repolarization refractory periods during EP studies, aiding in the differentiation of SQTS from normal cases. Garvey et al. [112] evaluated cardiac sympathetic denervation in eight children with life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias (one with SQTS), noting significant improvement and reduced ICD discharges in treated patients. Finally, Pasero et al. [91] explored artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms in ECG analysis and found shallow neural networks effective in identifying SQTS patients less likely to experience life-threatening arrhythmias, paving the way for AI-based risk stratification. The aforementioned studies are presented in Supplementary Table S9.
3.4. Summary of Findings
Given the heterogeneity of the reported studies, we summarized the key clinical and management-related aspects of SQTS, including patient demographics, diagnostic criteria, treatment strategies, and outcomes. Table 1 provides an overview of the main findings derived from the reviewed reports, highlighting the complexity of diagnosis, risk stratification, and management approaches in SQTS.

Table 1.
Summary of key findings from studies on short QT syndrome.
4. Discussion
The findings of our scoping review underline the high complexity and rarity of SQTS, a condition that poses significant diagnostic and management challenges to clinicians due to its diverse clinical presentations, underlying genetic heterogeneity, and associated risk of SCD. Notably, these aspects have also been described in younger populations with SQTS, further emphasizing the importance of early recognition and risk stratification [141]. SQTS presents with diverse phenotypes, from asymptomatic to SCD, spanning infancy to late adulthood; the threshold for diagnosis can vary, making it essential to have a high index of suspicion, particularly in individuals with a family history of SCD or unexplained syncope. At the same time, beyond SQT interval changes, various accompanying ECG alterations have been described, such as ERP, tall/peaked T waves, ST-segment deviations, and other concomitant channelopathies [142]. AF is common in patients with SQTS, with prevalence estimates ranging between 30% and 60% across various studies, depending on the size and genetic background of the cohort [63,68,88]. SQTS often coexists with cardiomyopathies or systemic syndromes, adding complexity to its diagnosis and management [143]. This variability in clinical presentation, from asymptomatic individuals to those experiencing life-threatening arrhythmias such as VF, further complicates the diagnostic process and necessitates a thorough and multifaceted approach.
An extremely low prevalence of SQTS and high mortality rate have previously been reported, although the true incidence of SCD throughout the spectrum of SQTS remains difficult to assess. As such, while ESC guidelines recommend ICD implantation for patients who are survivors of cardiac arrest or have experienced arrhythmic syncope, the role of ICDs in asymptomatic patients with SQTS remains controversial, given the risks associated with device implantation and the significantly high possibility of inappropriate shocks. Concerning pharmacological therapy, quinidine is promising in prolonging QT intervals and reducing arrhythmias, but its use requires caution due to its potentially serious side effects (e.g., gastrointestinal disorders, cinchonism, and hepatotoxicity) [144]. Other antiarrhythmic drugs have been tested with variable success, and the optimal pharmacological management of SQTS remains an area of active investigation, significantly hampered by the small numbers of affected individuals. Further research is also warranted to establish the clinical significance of the associations between SQT intervals and other clinical syndromes such as cardiomyopathies, which could potentially influence the diagnosis and management of SQTS.
Genetic testing serves as a valuable tool for shedding light on the molecular mechanisms underlying SQTS, identifying mutations in genes like KCNH2, KCNJ2, and KCNQ1, which result in a gain of function for potassium channels, leading to accelerated repolarization of the cardiac action potential. Less commonly, mutations in CACNA1C, CACNB2, CACNA2D1 (calcium channel genes), and SLC4A3 (anion exchanger gene) have been identified. However, less than half of all SQTS cases can be attributed to known mutations, highlighting the need for future research to elucidate the genetic basis of the syndrome. Based on current evidence, only a subset of genes have been confirmed to be strongly associated with SQTS; according to the Clinical Genome Resource (ClinGen), genes such as KCNH2, KCNQ1, KCNJ2, and SLC4A3 are considered to have sufficient evidence for their inclusion in genetic testing panels. In contrast, genes like CACNA1c, CACNB2b, and CACNA2D1 have limited or disputed evidence regarding their role in SQTS, indicating the need for further validation before their routine inclusion in diagnostic evaluations (ClinGen, www.clinicalgenome.org, accessed on 26 January 2025). While our review focuses on gene–disease associations in SQTS, we acknowledge that variant classification follows the ACMG 5-tier system [145], with several mutations in KCNH2, KCNQ1, KCNJ2, and SLC4A3 being classified as pathogenic or likely pathogenic in databases such as ClinVar and ClinGen. Diagnostic modalities such as echocardiography, exercise testing, and ECG monitoring may aid in its comprehensive assessment, though limitations such as small sample sizes and diagnostic variability must be acknowledged.
We purposefully excluded references pertaining to secondary causes of SQT from the present scoping review. However, secondary causes of SQT, including electrolyte imbalances, drug-induced effects, or other genetic conditions (e.g., primary carnitine deficiency) [146,147,148], should be taken into consideration by clinicians encountering patients with SQT.
Despite the comprehensive nature of our review, certain limitations must be acknowledged. First, the rarity of SQTS and small sample sizes in the majority of the reported studies pose significant challenges, limiting our ability to draw safe conclusions. Updated ESC criteria for the diagnosis of SQTS [4] offer some guidance, but advancements in medical care over the past few decades may also impact reported outcomes, making it difficult to attribute these changes solely to the natural course of the disease. Second, this review does not systematically reassess the pathogenicity classification of all reported variants based on ACMG criteria, as this would require a structured genetic database analysis beyond the scope of a scoping review. Evolving medical technologies and genetic testing methods, as well as AI, could definitely impact the reported outcomes.
In this context, several key areas for future research can be suggested. Large, multicenter registries of SQTS patients are needed to collect comprehensive data on its clinical presentation, genetic mutations, management strategies, and outcomes. Such registries would provide valuable insights into the natural history of SQTS and help identify predictors of adverse events. As a next step, one could highlight the need for randomized controlled trials to evaluate the efficacy and safety of different pharmacological therapies in SQTS patients. Finally, advances in genetic research could allow us to explore new mutations associated with SQTS and provide a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the syndrome. Integrating genetic data with clinical phenotypes could lead to more personalized approaches to SQTS management.
In conclusion, SQTS is a rare but serious condition with significant implications for affected individuals. This scoping review highlights our current understanding of SQTS, emphasizing the importance of accurate diagnosis, risk stratification, and individualized management. Despite significant advances, many questions remain unanswered, and the need for continued research to improve the outcomes for patients with this uncommon but potentially life-threatening syndrome is of paramount importance.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jpm15030105/s1, Table S1: Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) Checklist; Table S2: Case reports comprising patients with short QT syndrome; Table S3: Table presenting available case series involving families or distinct cases with short QT syndrome; Table S4: Studies assessing healthy populations or health databases for the presence of short QT syndrome; Table S5: Studies implementing genetic testing in patients with short QT syndrome; Table S6: Studies assessing outcomes in patients with short QT syndrome; Table S7a: Studies assessing the effects of pharmaceutical interventions among patients with short QT syndrome; Table S7b: Studies comprising identification of short QT syndrome cases among families with history of sudden cardiac arrest or sudden cardiac death; Table S7c: Studies demonstrating association of short QT with other clinical conditions; Table S8: Studies involving implementation of various diagnostic modalities among patients with short QT syndrome; Table S9: Studies involving other advances in research regarding short QT syndrome.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.B and A.G.; methodology, A.B.; software, A.B. and G.Z.; validation, C.P. and G.G.; formal analysis, A.B. and G.Z.; investigation, A.B., A.G., A.K., L.F. and V.V.; resources: A.B.; data curation: A.B.; writing—original draft preparation: A.B. and I.P.; visualization: A.B. and A.G.; supervision: A.G., G.G., C.P. and V.V.; project administration: A.G.; funding acquisition: not applicable. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SQTS | Short QT syndrome |
| QTc | Corrected QT |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| SCD | Sudden cardiac death |
| VF | Ventricular fibrillation |
| ESC | European Society of Cardiology |
| ICD | Implantable cardioverter defibrillator |
| SQT | Short QT |
| AF | Atrial fibrillation |
| ERP | Early repolarization |
| LVEF | Left ventricular ejection fraction |
| BrS | Brugada syndrome |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
References
- Gussak, I.; Brugada, P.; Brugada, J.; Wright, R.S.; Kopecky, S.L.; Chaitman, B.R.; Bjerregaard, P. Idiopathic short QT interval: A new clinical syndrome? Cardiology 2000, 94, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, P.J.; Moss, A.J.; Vincent, G.M.; Crampton, R.S. Diagnostic criteria for the long QT syndrome. An update. Circulation 1993, 88, 782–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollob, M.H.; Redpath, C.J.; Roberts, J.D. The short QT syndrome: Proposed diagnostic criteria. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeppenfeld, K.; Tfelt-Hansen, J.; de Riva, M.; Winkel, B.G.; Behr, E.R.; A Blom, N.; Charron, P.; Corrado, D.; Dagres, N.; de Chillou, C.; et al. 2022 ESC Guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3997–4126. [Google Scholar]
- Thorsen, K.; Dam, V.S.; Kjaer-Sorensen, K.; Pedersen, L.N.; Skeberdis, V.A.; Jurevičius, J.; Treinys, R.; Petersen, I.M.B.S.; Nielsen, M.S.; Oxvig, C.; et al. Loss-of-activity-mutation in the cardiac chloride-bicarbonate exchanger AE3 causes short QT syndrome. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschwitz, L.S.; El-Battrawy, I.; Schlentrich, K.; Besler, J.; Veith, M.; Roterberg, G.; Liebe, V.; Schimpf, R.; Lang, S.; Wolpert, C.; et al. Differences in Short QT Syndrome Subtypes: A Systematic Literature Review and Pooled Analysis. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ploneda-Valencia, R.G.; Ortiz-Solis, W.A.; Ruiz-Gonzalez, G.; Santiago-Garcia, A.K.; Rivera-Rodríguez, L.; Nava-Townsend, S.; Márquez, M.F.; Levinstein-Jacinto, M. Supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and sinus node dysfunction as a first manifestation of short QT syndrome in a pediatric patient. Case Report. J. Electrocardiol. 2022, 74, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grytsay, O.N.; Skybchyk, Y.V.; Shorikova, D.V.; Shorikov, E.I. Clinical Cases of Life—Threatening Arrhythmias: Long and Short Qt Syndromes. Wiad. Lek. 2022, 75, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramoğlu, M.G.; Karagözlü, S.; Uçar, T.; Tutar, E. Aborted cardiac arrest during sport activity in a teenager diagnosed with short QT syndrome. Cardiol. Young. 2020, 30, 886–889. [Google Scholar]
- Endres, D.; Decher, N.; Röhr, I.; Vowinkel, K.; Domschke, K.; Komlosi, K.; Tzschach, A.; Gläser, B.; Schiele, M.A.; Runge, K.; et al. New Cav1.2 Channelopathy with High-Functioning Autism, Affective Disorder, Severe Dental Enamel Defects, a Short QT Interval, and a Novel CACNA1C Loss-Of-Function Mutation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Pan, W.; Jiang, C.; Fu, G.; Sun, Y.; Hu, D. Implantable cardioverter defibrillator replacement guided by T wave safety margin in a short QT syndrome patient. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2019, 42, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugliese, D.N.; Reiffel, J.A. Implantable Cardioverter-defibrillator Therapy for Syncope: An Educational Example of a Multicomponent Electrocardiographic Differential Diagnosis and the Application of Clinical Trial Data to an Individual Patient. J. Innov. Card. Rhythm Manag. 2019, 10, 3860–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, Y.; Watanabe, A.; Morita, H.; Nishii, N.; Nakamura, K.; Ito, H. Successful radiofrequency catheter ablation of a premature ventricular contraction triggering ventricular fibrillation in a patient with short QT syndrome. Heart Case Rep. 2019, 5, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Gong, T.; Chen, X.; Zhang, P.; Su, L.; Fu, G.; et al. Patient-Specific and Gene-Corrected Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes Elucidate Single-Cell Phenotype of Short QT Syndrome. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakatsuki, D.; Iso, Y.; Mase, H.; Kurata, M.; Kyuno, E.; Shimojima, H.; Asano, T.; Sambe, T.; Suzuki, H. Sudden cardiac arrest during marathon training in a young adult with short QT syndrome. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2018, 18, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stolfo, G.; Palumbo, P.; Castellana, S.; Mastroianno, S.; Biagini, T.; Palumbo, O.; Leone, M.P.; De Luca, G.; Potenza, D.R.; Mazza, T.; et al. Sudden cardiac death in J wave syndrome with short QT associated to a novel mutation in Na(v) 1.8 coding gene SCN10A: First case report for a possible pharmacogenomic role. J. Electrocardiol. 2018, 51, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, A.; Rivolta, I.; Villa, C.; Chisci, E.; Beghi, M.; Cornaggia, C.M.; Giovannoni, R.; Combi, R. A Novel KCNJ2 Mutation Identified in an Autistic Proband Affects the Single Channel Properties of Kir2.1. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Barajas-Martinez, H.; Zhu, D.; Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Zhuang, R.; Shi, J.; Wu, X.; Tao, Y.; Jin, W.; et al. Novel trigenic CACNA1C/DES/MYPN mutations in a family of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with early repolarization and short QT syndrome. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sharma, P.K.; Awasthy, N. Bystander Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation Saves Life in a Patient with Short QT Syndrome. Indian Pediatr. 2016, 53, 933–934. [Google Scholar]
- Righi, D.; Silvetti, M.S.; Drago, F. Sinus bradycardia, junctional rhythm, and low-rate atrial fibrillation in Short QT syndrome during 20 years of follow-up: Three faces of the same genetic problem. Cardiol. Young. 2016, 26, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergül, Y.; Özyılmaz, İ.; Onan, S.H.; Güzeltaş, A. Short QT syndrome in a 14-year-old patient: The first pediatric case from Turkey. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2015, 15, 590–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sadeghian, S.; Bozorgi, A.; Safkhani, Z. Short QT syndrome and idiopathic ventricular tachycardia in a 28-year-old young man: A potential disease-specific link? Europace 2014, 16, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavão, M.L.; Ono, V.C.; Arfelli, E.; Simões, M.V.; Marin Neto, J.A.; Schmidt, A. Sudden cardiac death and short QT syndrome. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2014, 103, e37–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltret, A.; Wiener-Vacher, S.; Denis, C.; Extramiana, F.; Morisseau-Durand, M.P.; Fressart, V.; Bonnet, D.; Chabbert, C. Type 2 short QT syndrome and vestibular dysfunction: Mirror of the Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome? Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 171, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, J.; Fuglsang-Frederiksen, A.; Brugada, R.; Pedersen, B.; Rubboli, G.; Johansen, P.; Beniczky, S. Heart rate variability analysis indicates preictal parasympathetic overdrive preceding seizure-induced cardiac dysrhythmias leading to sudden unexpected death in a patient with epilepsy. Epilepsia 2014, 55, e67–e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, M.; Ruan, Y.; Pandit, S.V.; Shah, K.; Berenfeld, O.; Blaufox, A.; Cerrone, M.; Noujaim, S.F.; Denegri, M.; Jalife, J.; et al. KCNJ2 mutation in short QT syndrome 3 results in atrial fibrillation and ventricular proarrhythmia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4291–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.; Hu, J.; Yu, J.; Brugada, R. Concomitant Brugada-like and short QT electrocardiogram linked to SCN5A mutation. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 20, 1189–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, T.; Makiyama, T.; Akao, M.; Ehara, E.; Ohno, S.; Iguchi, M.; Nishio, Y.; Sasaki, K.; Itoh, H.; Yokode, M.; et al. A novel gain-of-function KCNJ2 mutation associated with short-QT syndrome impairs inward rectification of Kir2.1 currents. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 93, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinushi, M.; Sato, A.; Iijima, K.; Suzuki, K.; Hiroshi, F.; Izumi, D.; Watanabe, H.; Kanae, H.; Aizawa, Y. Exercise-related QT interval shortening with a peaked T wave in a healthy boy with a family history of sudden cardiac death. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2012, 35, e239–e242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templin, C.; Ghadri, J.R.; Rougier, J.S.; Baumer, A.; Kaplan, V.; Albesa, M.; Sticht, H.; Rauch, A.; Puleo, C.; Hu, D. Identification of a novel loss-of-function calcium channel gene mutation in short QT syndrome (SQTS6). Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.; Guo, J. Inappropriate ICD discharge due to T-wave oversensing in a patient with short QT syndrome. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2010, 33, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villafane, J.; Young, M.L.; Maury, P.; Wolpert, C.; Anttonen, O.; Hamilton, R.; Kannankeril, P.J.; Fischbach, P.S. Short QT syndrome in a pediatric patient. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2009, 30, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooryck, C.; Stef, M.; Burgelin, I.; Simon, D.; Souakri, N.; Thambo, J.B.; Chateil, J.F.; Lacombe, D.; Arveiler, B. 2.3 Mb terminal deletion in 12p13.33 associated with oculoauriculovertebral spectrum and evaluation of WNT5B as a candidate gene. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2009, 52, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, H.; Sakaguchi, T.; Ashihara, T.; Ding, W.G.; Nagaoka, I.; Oka, Y.; Nakazawa, Y.; Yao, T.; Jo, H.; Ito, M.; et al. A novel KCNH2 mutation as a modifier for short QT interval. Int. J. Cardiol. 2009, 137, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efremidis, M.; Letsas, K.P.; Weber, R.; Gavrielatos, G.; Filippatos, G.S.; Sideris, A.; Kardaras, F. Recurrent syncope associated with a distinct ECG pattern consisting of short QT interval, early repolarization and atrioventricular block. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2009, 98, 807–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizobuchi, M.; Enjoji, Y.; Yamamoto, R.; Ono, T.; Funatsu, A.; Kambayashi, D.; Kobayashi, T.; Nakamura, S. Nifekalant and disopyramide in a patient with short QT syndrome: Evaluation of pharmacological effects and electrophysiological properties. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2008, 31, 1229–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichet, J.; Genee, O.; Pierre, B.; Babuty, D. Fatal QT interval. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2008, 26, 739.e5-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimpf, R.; Bauersfeld, U.; Gaita, F.; Wolpert, C. Short QT syndrome: Successful prevention of sudden cardiac death in an adolescent by implantable cardioverter-defibrillator treatment for primary prophylaxis. Heart Rhythm 2005, 2, 416–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirilmaz, A.; Ulusoy, R.E.; Kardesoglu, E.; Ozmen, N.; Demiralp, E. Short QT interval syndrome: A case report. J. Electrocardiol. 2005, 38, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.; Piper, D.R.; Diaz-Valdecantos, A.; Brugada, J.; Oliva, A.; Burashnikov, E.; Santos-de-Soto, J.; Grueso-Montero, J.; Diaz-Enfante, E.; Brugada, P.; et al. De novo KCNQ1 mutation responsible for atrial fibrillation and short QT syndrome in utero. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 68, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellocq, C.; van Ginneken, A.C.; Bezzina, C.R.; Alders, M.; Escande, D.; Mannens, M.M.; Baró, I.; Wilde, A.A. Mutation in the KCNQ1 gene leading to the short QT-interval syndrome. Circulation 2004, 109, 2394–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienciuk-Krajka, A.; Kukla, P.; Stec, S.; Raczak, G. Short QT syndrome presenting with atrial fibrillation and LV hypertrophy. Int. J. Cardiol. 2012, 156, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Schie, M.S.; Ramdat Misier, N.L.; van Leeuwen, W.J.; Taverne, Y.J.H.J.; de Groot, N.M.S. An unexpected finding by epicardial mapping: Atrial fibrillation in a 14-month-old patient with short QT syndrome. Heart Case Rep. 2023, 9, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlemez, S.; Çil, E.; Kula, S.; Oǧuz, A.D.; Tunaoǧlu, F.S. A diagnosis that escapes our attention: Short QT syndrome. Gazi Med. J. 2018, 29, 246–248. [Google Scholar]
- Spartalis, M.; Livanis, E.; Spartalis, E.; Tsoutsinos, A. Electrical storm in an acquired short QT syndrome successfully treated with quinidine. Clin. Case Rep. 2019, 7, 1617–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portugal, G.; Martins Oliveira, M.; Silva Cunha, P.; Ferreira, F.; Lousinha, A.; Fiarresga, A.; Nogueira Da Silva, M.; Cruz Ferreira, R. Short QT syndrome presenting as syncope: How short is too short? Rev. Port. Cardiol. 2014, 33, 649.e1–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morphet, J.A.M. The short QT syndrome and sudden infant death syndrome. Can. J. Cardiol. 2007, 23, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.J.; Atallah, J. Use of topical lidocaine in eliminating mechanically stimulated ventricular fibrillation in a patient with short QT syndrome. Heart Case Rep. 2019, 5, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, P.; Moreau, A.; Richard, S.; Janin, A.; Millat, G.; Bessière, F.; Delinière, A. Short QT interval as a harbinger of an arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy. Heart Case Rep. 2021, 7, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdis, D.; Saguner, A.M.; Medeiros-Domingo, A.; Schaller, A.; Balmer, C.; Steffel, J.; Brunckhorst, C.; Duru, F. Multiple clinical profiles of families with the short QT syndrome. Europace 2018, 20, f113–f121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosini, E.; Sicca, F.; Brignone, M.S.; D’Adamo, M.C.; Napolitano, C.; Servettini, I.; Moro, F.; Ruan, Y.; Guglielmi, L.; Pieroni, S.; et al. Genetically induced dysfunctions of Kir2.1 channels: Implications for short QT3 syndrome and autism-epilepsy phenotype. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 4875–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anttonen, O.; Väänänen, H.; Junttila, J.; Huikuri, H.V.; Viitasalo, M. Electrocardiographic transmural dispersion of repolarization in patients with inherited short QT syndrome. Ann. Noninvasive. Electrocardiol. 2008, 13, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basarici, I. Delayed diagnosis of short QT syndrome concealed by pacemaker implant due to sick sinus syndrome. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2020, 23, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohora, S.; Namboodiri, N.; Tharakan, J.; Vk, A.K.; Nayyar, S. Dilated cardiomyopathy with short QT interval: Is it a new clinical entity? Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2009, 32, 688–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugada, R.; Hong, K.; Dumaine, R.; Cordeiro, J.; Gaita, F.; Borggrefe, M.; Menendez, T.M.; Brugada, J.; Pollevick, G.D.; Wolpert, C.; et al. Sudden death associated with short-QT syndrome linked to mutations in HERG. Circulation 2004, 109, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bun, S.S.; Maury, P.; Giustetto, C.; Deharo, J.C. Electrical storm in short-QT syndrome successfully treated with Isoproterenol. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2012, 23, 1028–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinushi, M.; Sato, A.; Izumi, D.; Furushima, H. Nifekalant enlarged the transmural activation-recovery interval difference as well as the peak-to-end interval on surface ECG in a patient with short-QT syndrome. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2012, 23, 877–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Battrawy, I.; Besler, J.; Liebe, V.; Schimpf, R.; Tülümen, E.; Rudic, B.; Lang, S.; Wolpert, C.; Zhou, X.; Akin, I.; et al. Long-Term Follow-Up of Patients With Short QT Syndrome: Clinical Profile and Outcome. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e010073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Battrawy, I.; Lan, H.; Cyganek, L.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Buljubasic, F.; Lang, S.; Yücel, G.; Sattler, K.; Zimmermann, W.H.; et al. Modeling Short QT Syndrome Using Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e007394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaita, F.; Giustetto, C.; Bianchi, F.; Wolpert, C.; Schimpf, R.; Riccardi, R.; Grossi, S.; Richiardi, E.; Borggrefe, M. Short QT Syndrome: A familial cause of sudden death. Circulation 2003, 108, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustetto, C.; Scrocco, C.; Giachino, D.; Rapezzi, C.; Mognetti, B.; Gaita, F. The lack of effect of sotalol in short QT syndrome patients carrying the T618I mutation in the KCNH2 gene. Heart Case Rep. 2015, 1, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, D.T.; Ashihara, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Tominaga, I.; Mazzanti, A.; Takahashi, K.; Oginosawa, Y.; Abe, H.; Maemura, K.; Sumitomo, N.; et al. Genotype-dependent differences in age of manifestation and arrhythmia complications in short QT syndrome. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 190, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.; Bjerregaard, P.; Gussak, I.; Brugada, R. Short QT syndrome and atrial fibrillation caused by mutation in KCNH2. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2005, 16, 394–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.X.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Q.; Yu, K.; Zhu, C. Short QT syndrome: A case report and review of literature. Resuscitation 2006, 71, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriya, M.; Seto, S.; Yano, K.; Akahoshi, M. Two cases of short QT interval. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2007, 30, 1522–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirro, E.; De Francia, S.; Banaudi, E.; Riggi, C.; De Martino, F.; Piccione, F.M.; Giustetto, C.; Racca, S.; Agnoletti, G.; Di Carlo, F. Short QT syndrome in infancy. Therapeutic drug monitoring of hydroquinidine in a newborn infant. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 72, 982–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Priori, S.G.; Pandit, S.V.; Rivolta, I.; Berenfeld, O.; Ronchetti, E.; Dhamoon, A.; Napolitano, C.; Anumonwo, J.; di Barletta, M.R.; Gudapakkam, S.; et al. A novel form of short QT syndrome (SQT3) is caused by a mutation in the KCNJ2 gene. Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Campuzano, O.; Iglesias, A.; Grueso, J.; Bradley, D.J.; Kerst, G.; Shmorhun, D.; Brugada, J.; Brugada, R. Short QT and atrial fibrillation: A KCNQ1 mutation-specific disease. Late follow-up in three unrelated children. Heart Case Rep. 2015, 1, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Quan, X.Q.; Fromme, S.; Cox, R.H.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, L.; Guo, D.; Guo, J.; Patel, C.; Kowey, P.R.; et al. A novel mutation in the KCNH2 gene associated with short QT syndrome. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2011, 50, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Hoshina, S.; Ozawa, J.; Sato, A.; Minamino, T.; Aizawa, Y.; Saitoh, A. Short QT syndrome in a boy diagnosed on screening for heart disease. Pediatr. Int. 2014, 56, 774–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisten, A.; Boström, I.M.; Mörner, S.; Stattin, E.L. Mutation analysis of cases of sudden unexplained death, 15 years after death: Prompt genetic evaluation after resuscitation can save future lives. Resuscitation 2012, 83, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, K.; Parrott, A.; Spar, D.; Knilans, T.; Czosek, R.; Miller, E.; Anderson, J. A novel variant in KCNQ1 associated with short QT syndrome. Heart Case Rep. 2021, 7, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Trümmel, M.; Koehler, B. Shorter-than-normal QT interval and provocable right precordial ST segment elevation in three patients with suspicious arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. J. Fur Kardiol. 2011, 18, 326–328. [Google Scholar]
- Giustetto, C.; Gaita, F. Syncope in a Patient with a Short QT Interval. Syncope Cases 2007, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, J.R.; Lacunza, J.; García-Molina, E.; Oliva-Sandoval, M.J.; Valdes, M. Short QT and dilated cardiomyopathy. A phenotype with a good prognosis? Int. J. Cardiol. 2011, 151, 356–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaoǧlu, K.; Binnetoǧlu, K.; Altun, G.; Tuzcu, V. A 13-year-old boy with a short QT interval—Case report. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2012, 12, 275. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.J.; Huang, Y.; Fu, Y.C.; Zhao, X.J.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhu, Q.L.; Li, Y. Characterization of a Chinese KCNQ1 mutation (R259H) that shortens repolarization and causes short QT syndrome 2. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wolpert, C.; Schimpf, R.; Giustetto, C.; Antzelevitch, C.; Cordeiro, J.; Dumaine, R.; Brugada, R.; Hong, K.; Bauersfeld, U.; Gaita, F.; et al. Further insights into the effect of quinidine in short QT syndrome caused by a mutation in HERG. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2005, 16, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, H.; Makiyama, T.; Koyama, T.; Kannankeril, P.J.; Seto, S.; Okamura, K.; Oda, H.; Itoh, H.; Okada, M.; Tanabe, N.; et al. High prevalence of early repolarization in short QT syndrome. Heart Rhythm 2010, 7, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villafañe, J.; Atallah, J.; Gollob, M.H.; Maury, P.; Wolpert, C.; Gebauer, R.; Watanabe, H.; Horie, M.; Anttonen, O.; Kannakeril, P.; et al. Long-term follow-up of a pediatric cohort with short QT syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tülümen, E.; Giustetto, C.; Wolpert, C.; Maury, P.; Anttonen, O.; Probst, V.; Blanc, J.J.; Sbragia, P.; Scrocco, C.; Rudic, B.; et al. PQ segment depression in patients with short QT syndrome: A novel marker for diagnosing short QT syndrome? Heart Rhythm 2014, 11, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Horie, M.; Ozawa, J.; Sumitomo, N.; Ohno, S.; Hoshino, K.; Ehara, E.; Takahashi, K.; Maeda, Y.; Yoshinaga, M.; et al. Novel electrocardiographic criteria for short QT syndrome in children and adolescents. Europace 2021, 23, 2029–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stępień-Wojno, M.; Ponińska, J.; Rydzanicz, M.; Bilińska, M.; Truszkowska, G.; Baranowski, R.; Lutyńska, A.; Biernacka, E.K.; Stępińska, J.; Kowalik, I.; et al. Sudden cardiac arrest in patients without overt heart disease: A limited value of next generation sequencing. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2018, 128, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimpf, R.; Wolpert, C.; Bianchi, F.; Giustetto, C.; Gaita, F.; Bauersfeld, U.; Borggrefe, M. Congenital short QT syndrome and implantable cardioverter defibrillator treatment: Inherent risk for inappropriate shock delivery. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2003, 14, 1273–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimpf, R.; Antzelevitch, C.; Haghi, D.; Giustetto, C.; Pizzuti, A.; Gaita, F.; Veltmann, C.; Wolpert, C.; Borggrefe, M. Electromechanical coupling in patients with the short QT syndrome: Further insights into the mechanoelectrical hypothesis of the U wave. Heart Rhythm 2008, 5, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudic, B.; Tülümen, E.; Berlin, V.; Röger, S.; Stach, K.; Liebe, V.; El-Battrawy, I.; Dösch, C.; Papavassiliu, T.; Akin, I.; et al. Low Prevalence of Inappropriate Shocks in Patients With Inherited Arrhythmia Syndromes With the Subcutaneous Implantable Defibrillator Single Center Experience and Long-Term Follow-Up. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e006265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rollin, A.; Gandjbakhch, E.; Giustetto, C.; Scrocco, C.; Fourcade, C.; Monteil, B.; Mondoly, P.; Cardin, C.; Maupain, C.; Gaita, F.; et al. Shortening of the Short Refractory Periods in Short QT Syndrome. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabkin, S.W.; Tang, J.K.K. The Short QTc Is a Marker for the Development of Atrial Flutter and Atrial Fibrillation. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2020, 2858149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Providência, R.; Karim, N.; Srinivasan, N.; Honarbakhsh, S.; Vidigal Ferreira, M.J.; Gonçalves, L.; Marijon, E.; Lambiase, P.D. Impact of QTc formulae in the prevalence of short corrected QT interval and impact on probability and diagnosis of short QT syndrome. Heart 2018, 104, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickham, D.; Zarafshar, S.; Sani, D.; Kumar, N.; Froelicher, V. Comparison of three ECG criteria for athlete pre-participation screening. J. Electrocardiol. 2014, 47, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasero, E.; Gaita, F.; Randazzo, V.; Meynet, P.; Cannata, S.; Maury, P.; Giustetto, C. Artificial Intelligence ECG Analysis in Patients with Short QT Syndrome to Predict Life-Threatening Arrhythmic Events. Sensors 2023, 23, 8900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panicker, G.K.; Manohar, D.; Karnad, D.R.; Salvi, V.; Kothari, S.; Lokhandwala, Y. Early repolarization and short QT interval in healthy subjects. Heart Rhythm 2012, 9, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikoo, M.H.; Heiran, A.; Mashayekh, F.; Rezaianzadeh, A.; Shiravani, A.; Azadian, F. A descriptive report on short QT interval in Kherameh branch of the PERSIAN cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, A.; Hayashi, H.; Yoshino, T.; Kawaguchi, T.; Taniguchi, A.; Itoh, H.; Sugimoto, Y.; Itoh, M.; Makiyama, T.; Xue, J.Q.; et al. Clinical and electrocardiographic characteristics of patients with short QT interval in a large hospital-based population. Heart Rhythm 2012, 9, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, F.; Silvano, M.; Zorzi, A.; Bertaglia, E.; Siciliano, M.; Leoni, L.; De Franceschi, P.; Iliceto, S.; Corrado, D. Implantable cardioverter defibrillator therapy in young patients with cardiomyopathies and channelopathies: A single Italian centre experience. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2016, 17, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzanti, A.; Maragna, R.; Vacanti, G.; Kostopoulou, A.; Marino, M.; Monteforte, N.; Bloise, R.; Underwood, K.; Tibollo, V.; Pagan, E.; et al. Hydroquinidine Prevents Life-Threatening Arrhythmic Events in Patients With Short QT Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 3010–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzanti, A.; Kanthan, A.; Monteforte, N.; Memmi, M.; Bloise, R.; Novelli, V.; Miceli, C.; O’Rourke, S.; Borio, G.; Zienciuk-Krajka, A.; et al. Novel insight into the natural history of short QT syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maury, P.; Extramiana, F.; Giustetto, C.; Cardin, C.; Rollin, A.; Duparc, A.; Mondoly, P.; Denjoy, I.; Delay, M.; Messali, A.; et al. Microvolt T-wave alternans in short QT syndrome. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2012, 35, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubart, E.; Segal, R.; Yearovoi, A.; Fridenson, A.; Baumoehl, Y.; Leibovitz, A. QT interval disturbances in hospitalized elderly patients. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2009, 11, 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Seyler, C.; Wiedmann, F.; Schmidt, C.; Schweizer, P.A.; Becker, R.; Katus, H.A.; Thomas, D. Anti-KCNQ1 K⁺ channel autoantibodies increase IKs current and are associated with QT interval shortening in dilated cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 98, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Peters, S.; Thompson, T.; Morgan, N.; Maccicoca, I.; Trainer, A.; Zentner, D.; Kalman, J.M.; Winship, I.; Vohra, J.K. Familial cardiological and targeted genetic evaluation: Low yield in sudden unexplained death and high yield in unexplained cardiac arrest syndromes. Heart Rhythm 2013, 10, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Uhm, J.S.; Kim, M.; Kim, I.S.; Jin, M.N.; Yu, H.T.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Joung, B.; Pak, H.N.; et al. Long-term prognosis of short QT interval in Korean patients: A multicenter retrospective cohort study. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2021, 21, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser-Nielsen, L.V.; Tischer, S.G.; Prescott, E.B.; Rasmusen, H.K. Symptoms, diagnoses, and sporting consequences among athletes referred to a Danish sports cardiology clinic. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2017, 27, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, I.N.; Skakkebaek, A.; Andersen, N.H.; Pedersen, L.N.; Hougaard, D.M.; Bojesen, A.; Trolle, C.; Gravholt, C.H. Short QTc interval in males with klinefelter syndrome-influence of CAG repeat length, body composition, and testosterone replacement therapy. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2015, 38, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Jáimez, J.; Peinado, R.; Grima, E.Z.; Segura, F.; Moriña, P.; Sánchez Muñoz, J.J.; Mazuelos, F.; Cózar, R.; Gimeno, J.R.; Heras, R.P.; et al. Diagnostic Approach to Unexplained Cardiac Arrest (from the FIVI-Gen Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 116, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iribarren, C.; Round, A.D.; Peng, J.A.; Lu, M.; Klatsky, A.L.; Zaroff, J.G.; Holve, T.J.; Prasad, A.; Stang, P. Short QT in a cohort of 1.7 million persons: Prevalence, correlates, and prognosis. Ann. Noninvasive. Electrocardiol. 2014, 19, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pfeiffer, R.; Gollob, M.H.; Healey, J.; Harrell, D.T.; Makita, N.; Abe, H.; Sun, Y.; et al. The Phenotypic Spectrum of a Mutation Hotspot Responsible for the Short QT Syndrome. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2017, 3, 727–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrier, K.; Kwiatkowski, D.; Czosek, R.J.; Spar, D.S.; Anderson, J.B.; Knilans, T.K. Short QT Interval Prevalence and Clinical Outcomes in a Pediatric Population. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2015, 8, 1460–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustetto, C.; Scrocco, C.; Schimpf, R.; Maury, P.; Mazzanti, A.; Levetto, M.; Anttonen, O.; Dalmasso, P.; Cerrato, N.; Gribaudo, E.; et al. Usefulness of exercise test in the diagnosis of short QT syndrome. Europace 2015, 17, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustetto, C.; Schimpf, R.; Mazzanti, A.; Scrocco, C.; Maury, P.; Anttonen, O.; Probst, V.; Blanc, J.J.; Sbragia, P.; Dalmasso, P.; et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with short QT syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustetto, C.; Di Monte, F.; Wolpert, C.; Borggrefe, M.; Schimpf, R.; Sbragia, P.; Leone, G.; Maury, P.; Anttonen, O.; Haissaguerre, M.; et al. Short QT syndrome: Clinical findings and diagnostic-therapeutic implications. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 2440–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, E.M.; Papez, A.L.; Notrica, D.M.; Egan, J.C.; Molitor, M.; Cohen, M.I.; van Leeuwen, K. Thoracoscopic Cardiac Sympathetic Denervation: Adjunct Therapy for Secondary Prevention of Life-Threatening Ventricular Arrhythmias in Children. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. A 2018, 28, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaita, F.; Giustetto, C.; Bianchi, F.; Schimpf, R.; Haissaguerre, M.; Calò, L.; Brugada, R.; Antzelevitch, C.; Borggrefe, M.; Wolpert, C. Short QT syndrome: Pharmacological treatment. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 1494–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funada, A.; Hayashi, K.; Ino, H.; Fujino, N.; Uchiyama, K.; Sakata, K.; Masuta, E.; Sakamoto, Y.; Tsubokawa, T.; Yamagishi, M. Assessment of QT intervals and prevalence of short QT syndrome in Japan. Clin. Cardiol. 2008, 31, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, M.; Ohno, S.; Wang, Q.; Kimura, H.; Makiyama, T.; Itoh, H.; Ito, M.; Horie, M. L-type calcium channel mutations in Japanese patients with inherited arrhythmias. Circ. J. 2013, 77, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frea, S.; Giustetto, C.; Capriolo, M.; Scrocco, C.; Fornengo, C.; Benedetto, S.; Bianchi, F.; Pidello, S.; Morello, M.; Gaita, F. New echocardiographic insights in short QT syndrome: More than a channelopathy? Heart Rhythm 2015, 12, 2096–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Extramiana, F.; Maury, P.; Maison-Blanche, P.; Duparc, A.; Delay, M.; Leenhardt, A. Electrocardiographic biomarkers of ventricular repolarisation in a single family of short QT syndrome and the role of the Bazett correction formula. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Battrawy, I.; Besler, J.; Li, X.; Lan, H.; Zhao, Z.; Liebe, V.; Schimpf, R.; Lang, S.; Wolpert, C.; Zhou, X.; et al. Impact of Antiarrhythmic Drugs on the Outcome of Short QT Syndrome. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Battrawy, I.; Besler, J.; Ansari, U.; Liebe, V.; Schimpf, R.; Tülümen, E.; Rudic, B.; Lang, S.; Odening, K.; Cyganek, L.; et al. Long-term follow-up of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators in Short QT syndrome. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2019, 108, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhutia, H.; Malhotra, A.; Parpia, S.; Gabus, V.; Finocchiaro, G.; Mellor, G.; Merghani, A.; Millar, L.; Narain, R.; Sheikh, N.; et al. The prevalence and significance of a short QT interval in 18,825 low-risk individuals including athletes. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, M.K.; Kjær-Sørensen, K.; Clavsen, N.C.; Dittmann, S.; Jensen, M.F.; Guldbrandsen, H.; Pedersen, L.N.; Sørensen, R.H.; Lildballe, D.L.; Müller, K.; et al. Genetic analysis identifies the SLC4A3 anion exchanger as a major gene for short QT syndrome. Heart Rhythm 2023, 20, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blancard, M.; Debbiche, A.; Kato, K.; Cardin, C.; Sabrina, G.; Gandjbakhch, E.; Probst, V.; Haissaguerre, M.; Extramiana, F.; Hocini, M.; et al. An African loss-of-function CACNA1C variant p.T1787M associated with a risk of ventricular fibrillation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anttonen, O.; Junttila, M.J.; Rissanen, H.; Reunanen, A.; Viitasalo, M.; Huikuri, H.V. Prevalence and prognostic significance of short QT interval in a middle-aged Finnish population. Circulation 2007, 116, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anttonen, O.; Junttila, J.; Giustetto, C.; Gaita, F.; Linna, E.; Karsikas, M.; Seppänen, T.; Perkiömäki, J.S.; Mäkikallio, T.H.; Brugada, R.; et al. T-Wave morphology in short QT syndrome. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2009, 14, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.; Sadek, M.M.; Chan, A.Y.; Dell, E.; Rutberg, J.; Davis, D.; Green, M.S.; Spears, D.A.; Gollob, M.H. Patient Outcomes From a Specialized Inherited Arrhythmia Clinic. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2016, 9, e003440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viskin, S.; Zeltser, D.; Ish-Shalom, M.; Katz, A.; Glikson, M.; Justo, D.; Tekes-Manova, D.; Belhassen, B. Is idiopathic ventricular fibrillation a short QT syndrome? Comparison of QT intervals of patients with idiopathic ventricular fibrillation and healthy controls. Heart Rhythm 2004, 1, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, H.S.; Tan, H.J.; Loo, C.Y.; Raymond, A.A. Short QTc in epilepsy patients without cardiac symptoms. Med. J. Malays. 2007, 62, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Schimpf, R.; Veltmann, C.; Giustetto, C.; Gaita, F.; Borggrefe, M.; Wolpert, C. In vivo effects of mutant HERG K+ channel inhibition by disopyramide in patients with a short QT-1 Syndrome: A pilot study. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2007, 18, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.A.; Lapage, M.J.; Atallah, J.; Webster, G.; Miyake, C.Y.; Ratnasamy, C.; Ollberding, N.J.; Mohan, S.; Von Bergen, N.H.; Johnsrude, C.L.; et al. Outcomes of Pediatric Patients With Defibrillators Following Initial Presentation With Sudden Cardiac Arrest. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2021, 14, E008517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, L.M.; Kisileva, I.I.; Dolgikh, V.V.; Bimbaev, A.B.Z.; Bairova, T.A.; Drozdova, A.I. Assesment of parameters of QT interval in children and adolescents. Kardiologiya 2006, 46, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Makarov, L.M.; Chuprova, S.N.; Kiseleva, I.I. QT interval shortening in families with history of sudden death at young age. Kardiologiia 2004, 44, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Lubart, E.; Segal, R.; Megid, S.; Yarovoy, A.; Leibovitz, A. QT interval disturbances in elderly residents of long-term care facilities. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2012, 14, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kobza, R.; Roos, M.; Niggli, B.; Abächerli, R.; Lupi, G.A.; Frey, F.; Schmid, J.J.; Erne, P. Prevalence of long and short QT in a young population of 41,767 predominantly male Swiss conscripts. Heart Rhythm 2009, 6, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazeki, D.; Ninomiya, Y.; Ueno, K.; Yoshinaga, M. Tentative screening criteria for short QT interval in children and adolescents. Circ. J. 2018, 82, 2627–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, M.M.; Magliano, G.; Yap, Y.G.; Padula, M.; Morgia, V.; Postorino, C.; Liberato, F.; Leo, R.; Borzi, M.; Romeo, F. Distribution and Prognostic Significance of QT Intervals in the Lowest Half Centile in 12,012 Apparently Healthy Persons. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 98, 933–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burashnikov, E.; Pfeiffer, R.; Barajas-Martinez, H.; Delpón, E.; Hu, D.; Desai, M.; Borggrefe, M.; Hissaguerre, M.; Kanter, R.; Pollevick, G.D.; et al. Mutations in the cardiac L-type calcium channel associated with inherited J-wave syndromes and sudden cardiac death. Heart Rhythm 2010, 7, 1872–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antzelevitch, C.; Pollevick, G.D.; Cordeiro, J.M.; Casis, O.; Sanguinetti, M.C.; Aizawa, Y.; Guerchicoff, A.; Pfeiffer, R.; Oliva, A.; Wollnik, B.; et al. Loss-of-function mutations in the cardiac calcium channel underlie a new clinical entity characterized by ST-segment elevation, short QT intervals, and sudden cardiac death. Circulation 2007, 115, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anttonen, O.; Junttila, M.J.; Maury, P.; Schimpf, R.; Wolpert, C.; Borggrefe, M.; Giustetto, C.; Gaita, F.; Sacher, F.; Haissaguerre, M.; et al. Differences in twelve-lead electrocardiogram between symptomatic and asymptomatic subjects with short QT interval. Heart Rhythm 2009, 6, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi-Renani, S.; Soltani, D.; Farshbafnadi, M.; Shafiee, A.; Jalali, A.; Mohammadi, M.; Golestanian, S.; Kamalian, E.; Alaeddini, F.; Saadat, S.; et al. Prevalence and associated factors of ECG abnormality patterns indicative of cardiac channelopathies among adult general population of Tehran, Iran: A report from the Tehran Cohort Study (TeCS). BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2024, 24, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, G.; Bergonti, M.; Probst, V.; Morita, H.; Tfelt-Hansen, J.; Behr, E.R.; Kengo, K.; Arbelo, E.; Crotti, L.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; et al. aTrial arrhythmias in inhEriTed aRrhythmIa Syndromes: Results from the TETRIS study. Europace 2024, 26, euae288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzanti, A.; O’Rourke, S.; Ng, K.; Miceli, C.; Borio, G.; Curcio, A.; Esposito, F.; Napolitano, C.; Priori, S.G. The usual suspects in sudden cardiac death of the young: A focus on inherited arrhythmogenic diseases. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2014, 12, 499–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewi, I.P.; Dharmadjati, B.B. Short QT syndrome: The current evidences of diagnosis and management. J. Arrhythm. 2020, 36, 962–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollob, M.H. Short QT syndrome: Advancing our understanding of genetics and cardiac physiology. Heart Rhythm 2023, 20, 1144–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, I.S.; Jick, H.; Cohen, S.I. Adverse reactions to quinidine in hospitalized patients: Findings based on data from the Boston Collaborative Drug Surveillance Program. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 1977, 20, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodewyckx, P.; Issa, J.; Gaschignard, M.; Lamireau, D.; De Lonlay, P.; Servais, A.; Barth, M.; Courapied, S.; Morin, G.; Benbrik, N.; et al. Systemic primary carnitine deficiency induces severe arrhythmia due to shortening of QT interval. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2023, 140, 107733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, T.J.; John, K.; Jansen Van Rensburg, R.; Kyriakakis, C. Hypercalcaemia and a short QT interval. QJM 2020, 113, 55–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, M.; Malik, M.; Shah, R.R.; Valentin, J.P. Drug induced shortening of the QT/QTc interval: An emerging safety issue warranting further modelling and evaluation in drug research and development? J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2009, 59, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).