Abstract
Background/Objectives: Isthmin-1 (ISM1) is a secreted protein involved in immune regulation, inflammation, and angiogenesis. Although ISM1 has been implicated in chronic inflammatory conditions, its clinical relevance in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) remains unknown. This study aimed to evaluate serum ISM1 levels in RA patients and assess their associations with disease activity, autoantibody status, and inflammatory markers. Methods: This cross-sectional study included 90 RA patients fulfilling the 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria and 30 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. Serum ISM1 concentrations were measured using ELISA. Disease activity was assessed using DAS28-CRP and DAS28-ESR. Statistical analyses included group comparisons, correlation testing, multivariate linear regression, and ROC curve analysis to evaluate the predictive performance of ISM1 for remission or low disease activity. Results: Serum ISM1 levels were significantly lower in RA patients than in controls (454 ± 378 vs. 972 ± 809 ng/L, p < 0.001). ISM1 concentrations were inversely correlated with CRP, ESR, and both DAS28 indices. Multivariate regression confirmed independent associations between lower ISM1 concentrations and higher disease activity. ISM1 levels were significantly reduced in RF- and anti-CCP-positive patients, as well as in treatment-naïve early RA. ROC analysis identified a cut-off value of 673.73 ng/L for predicting remission or low disease activity, with an AUC of 0.713 (95% CI: 0.596–0.820), 100% specificity, and 38.9% sensitivity. Conclusions: This study is the first to demonstrate that serum ISM1 is independently associated with disease activity and autoantibody positivity in RA. High ISM1 levels may serve as a specific indicator of clinical remission or low disease activity, supporting its potential as a non-invasive biomarker for disease monitoring.
Keywords:
rheumatoid arthritis; Isthmin-1; disease activity; autoantibodies; DAS28; biomarker; adipokine 1. Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by synovial inflammation, joint destruction, and systemic complications, significantly affecting patients’ quality of life [1]. Disease pathogenesis involves complex interactions between genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and immune system dysregulation, leading to inflammation and autoantibody production [2]. Despite advances in therapeutic strategies, achieving sustained remission remains challenging, necessitating the identification of novel biomarkers for improved management of disease activity and progression.
Isthmin-1 (ISM1) is a secreted protein originally identified in the midbrain–hindbrain boundary of Xenopus embryos, playing roles in developmental biology [3]. Recent studies indicate ISM1 as an adipokine involved in metabolic processes, inflammatory regulation, and immune response modulation [4,5]. ISM1 is expressed across various tissues, including adipocytes, skin, mucosal surfaces, and immune cells such as NK, NKT, and Th17 cells, suggesting its potential multifaceted biological roles [6,7].
Emerging evidence highlights the association between ISM1 and several pathophysiological conditions, including glucose metabolism disorders, immune dysregulation, inflammation, and cancer progression [5,7]. ISM1 regulates glucose uptake via the translocation of glucose transporter GLUT4, enhancing glycolysis, and influencing inflammatory responses through the modulation of Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB) and inflammatory cytokines [4,8]. Furthermore, recent findings suggest ISM1’s role in aging-related cardiac dysfunction, exerting protective effects by enhancing glycolysis and activating SIRT1 deacetylase activity [4].
ISM1 exerts anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and anti-angiogenic effects through multiple mechanisms, including the suppression of NF-κB signaling, modulation of Th17 cell responses, enhancement of efferocytosis, and inhibition of endothelial proliferation [4,5,6,8,9]. These mechanisms are relevant to the pathogenesis of RA, which is characterized by synovial inflammation, immune dysregulation, and aberrant angiogenesis [1,10,11]. In view of this biological alignment, ISM1 may be considered a pathophysiological relevant molecule in RA. To our knowledge, serum ISM1 levels have not yet been clinically evaluated in RA, and their relationship with systemic inflammation, disease activity, or autoantibody status remains unexplored. Consequently, the present study hypothesized that serum ISM1 levels would be inversely associated with disease activity and immune activation in RA, potentially serving as a novel biomarker for disease monitoring.
2. Materials and Methods
This cross-sectional study aimed to evaluate serum ISM1 levels and their relationship with disease activity in RA patients. The study protocol was reviewed and approved by the University Non-Interventional Research Ethics Committee (approval number: 20.05.2024/24299). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to enrolment.
A total of 120 participants were enrolled, including 90 patients diagnosed with RA according to the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria and 30 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. RA patients were further stratified into moderate-to-high (DAS28-CRP ≥ 3.2, n = 54; DAS28-ESR ≥ 3.2, n = 59) and remission-to-low disease activity groups (DAS28-CRP < 3.2, n = 36; DAS28-ESR < 3.2, n = 31). Patients were also categorized according to disease duration as early RA (≤12 weeks; n = 30) and established RA (>12 weeks; n = 60).
Fasting blood samples were collected to measure biochemical parameters including glucose, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), urea, creatinine, uric acid, total protein, albumin, hemoglobin (Hb), white blood cells (WBCs), lymphocytes (Lym), platelets, C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), rheumatoid factor (RF), and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies. Serum ISM1 concentrations were measured using a commercially available Human ISM1 ELISA Kit (catalogue no.: 201-12-4050; Sunred Biological Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), following the manufacturer’s instructions. The assay range was 10–3000 ng/L, with a minimum detectable concentration (sensitivity) of 9.625 ng/L. The intra-assay coefficient of variation (CV) was <10%, and the inter-assay CV was <12%.
Descriptive statistics are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD), median, IQR (interquartile range: 25th–75th percentiles), and 95% confidence interval (CI). Normality of data distribution was assessed using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Between-group comparisons were performed using an independent samples t-test, chi-square test, or Mann–Whitney U test, as appropriate. Comparisons involving more than two groups were analyzed using the Kruskal–Wallis test, followed by post hoc pairwise analyses with the Dwass–Steel–Critchlow–Fligner method. Correlations between serum ISM1 levels and clinical parameters were assessed using Spearman’s rank correlation analysis. Effect sizes were calculated using Cohen’s d for group comparisons. Effect sizes (Cohen’s d) were interpreted according to conventional thresholds, small (≥0.20), moderate (≥0.50), large (≥0.80), and very large (≥1.30), to provide additional context regarding the magnitude of group differences. Statistical significance was defined as p-values less than 0.05. Data analyses were performed using Jamovi version 2.3.28 (The Jamovi project, 2024). Post hoc power analysis was performed using G*Power version 3.1.9.2 (Franz Faul, Universität Kiel, Kiel, Germany), a freely available statistical software for power calculations. The analysis targeted the primary comparison of serum ISM1 levels between RA patients and healthy controls. Based on the observed effect size (Cohen’s d = 1.00), group sample sizes (n = 90 for RA; n = 30 for controls), and a two-tailed significance level (α = 0.05), the resulting statistical power was 0.997 (99.7%), indicating a highly adequate sample size for detecting the observed group difference.
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
Demographic, clinical, and laboratory parameters were compared between RA patients and healthy control subjects (Table 1). There were no significant differences in age, gender distribution, body mass index (BMI), and routine biochemical parameters such as glucose, AST, ALT, urea, creatinine, uric acid, total protein, albumin, WBCs, lymphocyte count, and platelet count between RA patients and controls (p > 0.05 for all comparisons). However, Hb levels were significantly lower (12.8 ± 1.51 (12.8) vs. 13.5 ± 0.38 (13.6) g/dL, p = 0.001), while inflammatory markers, CRP (13.7 ± 20.3 (7.18) vs. 4.57 ± 1.30 (4.0) mg/L, p = 0.004) and ESR (30.1 ± 18.4 (29) vs. 16.7 ± 3.55 (16) mm/h, p < 0.001), were significantly higher in the RA group compared with controls. Serum ISM1 levels were significantly lower in RA patients compared to controls (454 ± 378 (342) vs. 972 ± 809 (678) ng/L, p < 0.001).

Table 1.
Comparison of demographic, clinical, and laboratory parameters between control and RA groups.
3.2. ISM1 Levels and Autoantibody Status
RF-positive patients had significantly reduced ISM1 levels (mean ± SD, 383 ± 286 ng/L; median (IQR), 312 (160) ng/L) compared to RF-negative patients (mean ± SD, 589 ± 487 ng/L; median (IQR), 421 (384) ng/L; p = 0.004), with a moderate effect size (Cohen’s d = 0.56).
Similarly, anti-CCP-positive patients showed significantly lower ISM1 concentrations (mean ± SD, 385 ± 247 ng/L; median (IQR), 329 (171) ng/L) compared to anti-CCP-negative individuals (mean ± SD, 750 ± 637 ng/L; median (IQR), 437 (697) ng/L; p = 0.007), accompanied by a large effect size (Cohen’s d = 1.09).
Furthermore, patients who were double-positive for RF and anti-CCP antibodies also exhibited significantly lower serum ISM1 levels (mean ± SD, 333 ± 176 ng/L; median (IQR), 303 (150) ng/L) compared to double-negative patients (mean ± SD, 653 ± 518 ng/L; median (IQR), 443 (539) ng/L; p < 0.001), with a large effect size (Cohen’s d = 0.95) (Table 2). As summarized in Table 2, the observed effect sizes ranged from moderate (RF-positive vs. negative) to large (anti-CCP and double-positive vs. double-negative), underscoring the clinical relevance of ISM1 reductions in autoantibody-positive RA.

Table 2.
Serum ISM1 levels according to autoantibody status in RA patients.
3.3. ISM1 Levels According to Disease Activity
Serum ISM1 levels differed significantly among RA patients stratified by disease activity and healthy controls (Table 3, Figure 1). Healthy individuals exhibited markedly higher ISM1 concentrations (mean ± SD, 972 ± 809 ng/L; median (IQR), 678 (710) ng/L) compared to RA patients with moderate-to-high disease activity defined by DAS28-CRP ≥ 3.2 (mean ± SD, 315 ± 125 ng/L; median (IQR), 311 (184) ng/L; p < 0.001), with a very large effect size (Cohen’s d = 1.34). A significant difference was also observed between the high activity group and patients in remission or with low disease activity (DAS28-CRP < 3.2: 663 ± 515 ng/L; median (IQR), 407 (584) ng/L; p = 0.002), with a large effect size (Cohen’s d = 1.03). Although ISM1 levels appeared to be reduced in the low activity group compared with healthy controls, this difference did not reach statistical significance (p = 0.104; Cohen’s d = 0.47).

Table 3.
Serum ISM1 levels in control subjects and rheumatoid arthritis patients stratified by disease activity.

Figure 1.
Serum ISM1 levels in healthy controls and RA patients stratified by disease activity (DAS28-CRP); boxplot showing serum ISM1 levels (ng/L) in healthy controls (n = 30) and RA patients stratified by DAS28-CRP scores: remission/low (n = 36) and moderate/high activity (n = 54). The Kruskal–Wallis test revealed significant differences (χ2 = 34.0, p < 0.001; ε2 = 0.285). Post hoc analysis showed lower ISM1 levels in the moderate/high group compared to both controls (p < 0.001) and the remission/low group (p = 0.002); the difference between the controls and the remission/low group was not significant (p = 0.104).
Similarly, when disease activity was assessed using DAS28-ESR, patients with moderate-to-high activity (≥3.2) had significantly lower serum ISM1 levels (mean ± SD, 317 ± 116 ng/L; median (IQR), 306 (165) ng/L) compared to those in remission or with low disease activity (<3.2: 716 ± 539 ng/L; median (IQR), 475 (654) ng/L; p < 0.001), with a large effect size (Cohen’s d = 1.22). The high activity group also showed significantly lower ISM1 levels compared to the healthy controls (p < 0.001; Cohen’s d = 1.37), whereas the difference between the low activity group and the controls was not statistically significant (p = 0.334; Cohen’s d = 0.37).
These differences were confirmed using the Kruskal–Wallis test (χ2 = 34.0, p < 0.001; ε2 = 0.285), with post hoc pairwise comparisons conducted via the Dwass–Steel–Critchlow–Fligner method. Collectively, these findings indicate a strong inverse relationship between serum ISM1 levels and RA disease activity, particularly when assessed using inflammatory indices such as CRP and ESR, and demonstrate that the observed differences are not only statistically significant but also clinically meaningful. As summarized in Table 3, effect sizes were large to very large across disease activity strata, further supporting the clinical impact of ISM1 suppression in active RA.
3.4. ISM1 Levels According to Disease Duration
Serum ISM1 levels also varied significantly according to disease duration in RA patients compared with healthy controls (Figure 2). The Kruskal–Wallis test indicated a significant overall difference among the three groups (χ2(2) = 21.9, p < 0.001; ε2 = 0.184). Healthy controls exhibited markedly higher serum ISM1 levels (median (IQR), 678 (710) ng/L) than both early RA patients (≤12 weeks) (347 (142) ng/L; p < 0.001) and established RA patients (>12 weeks) (341 (256) ng/L; p < 0.001). However, no statistically significant difference in ISM1 concentrations was observed between the early and established RA groups (p = 0.962). These results suggest that the reduction in serum ISM1 levels occurs early in the disease course and remains stable over time, irrespective of the duration of the disease. Importantly, patients in the early RA group (≤12 weeks) included in our study were treatment-naïve, having not received any cDMARDs or biologic agents at the time of serum sampling. This strengthens the interpretation that the observed reduction in ISM1 levels in this group may reflect the natural pathophysiological alterations associated with untreated early disease, rather than being confounded by therapeutic interventions. Therefore, ISM1 suppression appears to occur early in the disease course, independent of pharmacologic modulation.
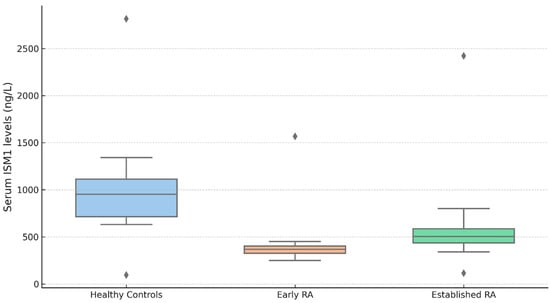
Figure 2.
Serum ISM1 levels in healthy controls and RA patients by disease duration; Serum ISM1 levels (ng/L) in healthy controls (n = 30), early RA (≤12 weeks; n = 30), and established RA (>12 weeks; n = 60). The Kruskal–Wallis test showed significant group differences (χ2 (2) = 21.9, p < 0.001; ε2 = 0.184). The post hoc Dwass–Steel–Critchlow–Fligner test revealed lower ISM1 levels in both RA groups vs. controls (p < 0.001), with no difference between RA subgroups (p = 0.962). Data are shown as the median (IQR); outliers are displayed as individual points. Serum ISM1 levels–median (IQR): healthy controls: 678 (710), early RA (≤12 weeks): 347 (142), established RA (>12 weeks): 341 (256).
3.5. Correlation Between Serum ISM1 Levels and Inflammatory and Disease Activity Markers
Spearman’s rank correlation analysis demonstrated significant inverse associations between serum ISM1 levels and markers of systemic inflammation and disease activity in RA patients (Table 4). ISM1 concentrations showed a moderate negative correlation with ESR (rs = −0.291, p = 0.001) and CRP (rs = −0.342, p < 0.001). Furthermore, serum ISM1 levels were negatively correlated with disease activity scores, including DAS28-ESR (rs = −0.385, p < 0.001) and DAS28-CRP (rs = −0.405, p < 0.001). These findings indicate that lower ISM1 levels are associated with higher levels of systemic inflammation and increased clinical disease activity in RA.

Table 4.
Spearman correlation between serum ISM1 levels and inflammatory and hematological markers.
To further investigate the independent association between serum ISM1 levels and disease activity, we conducted two separate multivariate linear regression models incorporating demographic (age, gender, BMI) and inflammatory covariates (hemoglobin, CRP, and ESR) (Table 5). In the first model, DAS28-CRP emerged as a significant independent predictor of lower serum ISM1 levels (β = −147.76, 95% CI: −217.80 to −77.72, p < 0.001), while the other covariates did not reach statistical significance. In the second model, in which DAS28-ESR was used instead of DAS28-CRP, DAS28-ESR remained a strong inverse predictor (β = −151.32, 95% CI: −216.52 to −86.13, p < 0.001), with other covariates again remaining non-significant.

Table 5.
Multivariate linear regression analysis of serum ISM1 levels in RA patients.
3.6. Predictive Value of Serum ISM1 Levels for Low Disease Activity
To determine the potential clinical utility of ISM1 as a biomarker for disease activity stratification, a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) for distinguishing patients in remission or with low disease activity was 0.713, with a 95% CI of 0.596–0.820, indicating moderate discriminatory performance.
At the optimal cut-off value of 673.73 ng/L, serum ISM1 levels demonstrated a sensitivity of 38.9% (95% CI: 23.1–56.5) and a specificity of 100.0% (95% CI: 93.4–100.0). The corresponding positive predictive value was 100.0% (95% CI: 76.8–100.0), and the negative predictive value was 71.1% (95% CI: 59.5–80.9). These results suggest that high serum ISM1 levels are highly specific for identifying patients with low disease activity or in remission, albeit with limited sensitivity. The ROC curve corresponding to this analysis is presented in Figure 3.
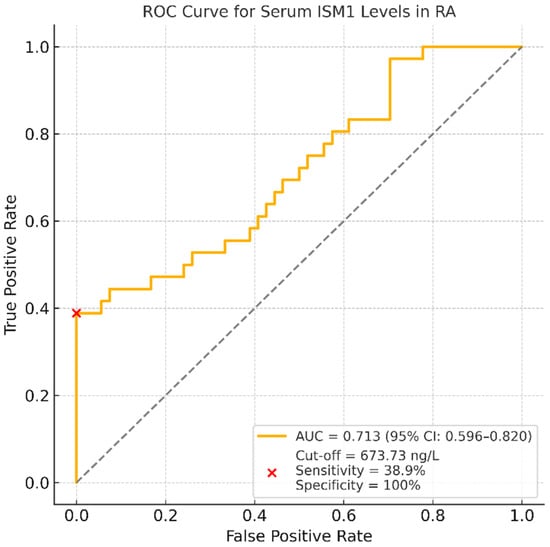
Figure 3.
ROC curve for serum ISM1 levels distinguishing RA patients in remission or with low disease activity from those with moderate-to-high disease activity; the AUC was 0.713 (95% CI: 0.596–0.820). At the optimal cut-off value of 673.73 ng/L, serum ISM1 levels showed a sensitivity of 38.9% and a specificity of 100.0%. These findings suggest that higher ISM1 levels may help identify patients with controlled disease activity, albeit with limited sensitivity.
4. Discussion
In this cross-sectional study, we provide the first clinical evidence that serum ISM1 levels are significantly reduced in RA patients compared to healthy controls. Moreover, ISM1 levels were inversely associated with DAS28-CRP and DAS28-ESR scores, CRP, ESR, and autoantibody positivity. These associations remained significant after adjustment for demographic and hematologic variables in multivariate regression models, suggesting an independent relationship between ISM1 and disease activity. Notably, ISM1 suppression was also evident in treatment-naïve patients with early RA, indicating that its downregulation occurs early in the disease course, possibly preceding pharmacologic intervention.
ISM1 is increasingly recognized as a secreted protein with multifaceted roles in immune modulation and inflammation. It has been shown to suppress NF-κB signaling and reduce pro-inflammatory cytokine production in models of acute and chronic lung injury, as well as modulate tissue repair and fibrosis [9,12]. In RA, aberrant activation of the NF-κB pathway contributes to synovial inflammation, immune cell recruitment, and cytokine amplification, particularly in Th17-mediated responses [10]. Therefore, the observed reduction in ISM1 levels in RA patients, particularly those with active disease, may reflect a loss of endogenous anti-inflammatory counter-regulation. Additionally, ISM1 has been implicated in endothelial function, oxidative stress, and glucose metabolism—processes that are also disrupted in RA pathophysiology [13,14,15]. Taken together, these mechanistic insights support a potential role for ISM1 not only as a biomarker of systemic inflammation but also as a contributor to RA pathogenesis.
Previous studies have characterized ISM1 as a novel adipokine, widely expressed in adipose, immune, and epithelial tissues, with roles in metabolism, inflammation, and angiogenesis [5,16]. It enhances glucose uptake, regulates lipid metabolism, and suppresses inflammatory responses by modulating NF-κB activation [9,17]. Consistent with these functions, in our study, we found that ISM1 levels negatively correlated with CRP and ESR, and positively correlated with hemoglobin. These findings support ISM1’s role as a modulator of immune and inflammatory responses in RA [6,9].
The inverse association between ISM1 and disease activity was particularly evident in patients with moderate-to-high disease activity. Moreover, our ROC analysis demonstrated that serum ISM1 levels ≥ 673.73 ng/L predicted remission or low disease activity with excellent specificity (100%) and positive predictive value (100%), although sensitivity was modest (38.9%). These findings further support the notion that elevated ISM1 levels may serve as a reliable indicator of controlled disease states in RA.
Despite the fact that serum ISM1 levels exhibited high specificity (100%) in identifying RA patients with remission or low disease activity, the sensitivity was comparatively low (38.9%) at the proposed cut-off value. This finding suggests that ISM1 may be more appropriate as a complementary biomarker rather than a primary screening tool in clinical practice. Its high specificity could support decision-making in selected clinical contexts, such as confirming remission or evaluating treatment response in conjunction with established indices like DAS28.
Furthermore, ISM1 levels were markedly lower in patients who were RF- and anti-CCP-positive, indicating a potential link between ISM1 and autoantibody-mediated immune mechanisms. Experimental studies suggest that ISM1 may influence immune tolerance by inducing apoptosis in proinflammatory macrophages, enhancing adiponectin release, and suppressing NF-κB signaling [9,18,19]. These pathways are integral to autoimmunity and chronic inflammation, reinforcing the relevance of ISM1 suppression in autoantibody-positive RA.
While the findings establish robust inverse correlations between serum ISM1 levels and inflammatory markers such as CRP, ESR, and DAS28 indices, the directionality of this relationship remains uncertain. The role of ISM1 downregulation in driving inflammation remains to be elucidated; it is unclear whether it plays an active role or merely reflects a secondary consequence of heightened immune activation in RA. Preclinical studies have demonstrated that inflammatory stimuli, including LPS exposure, can suppress ISM1 expression [9], thus suggesting that systemic inflammation may result in a reduction in ISM1 levels. In contrast, ISM1 has also been reported to attenuate inflammatory signaling via the inhibition of NF-κB, enhancement of efferocytosis, and modulation of proinflammatory cytokines [9,19]. Consequently, ISM1 suppression in RA may serve as both an indicator and a mediator of the inflammatory burden.
The fact that ISM1 levels did not differ between early and established RA, but were significantly reduced in active disease, suggests that ISM1 reflects disease burden rather than the duration of the disease. This is further supported by the presence of low ISM1 levels in treatment-naïve patients, indicating that the observed suppression is not merely a consequence of immunosuppressive therapy. These findings point to the potential utility of ISM1 as a dynamic, non-invasive biomarker for monitoring RA activity.
Beyond inflammation, ISM1 has also been implicated in angiogenesis, a key pathological feature in RA. Angiogenesis contributes to pannus formation and persistent synovial inflammation. Interestingly, ISM1 exhibits anti-angiogenic properties by inducing endothelial cell apoptosis and inhibiting neovascularization [20,21]. It is overexpressed in glomerulopathy models and impairs podocyte viability, suggesting its broader role in vascular integrity [11,13]. Although angiogenesis is essential for pannus expansion in RA [11], the role of ISM1’s anti-angiogenic activity within the inflammatory joint microenvironment remains unclear. Further studies are warranted to determine whether the suppression of ISM1 contributes to pathological angiogenesis in RA or represents a compensatory response [22].
Given the large effect sizes observed in our comparisons, ISM1 alterations appear to be clinically meaningful. The inclusion of effect size metrics such as Cohen’s d in our analysis further emphasizes the clinical relevance of ISM1 alterations in RA, beyond mere statistical significance. In light of its anti-inflammatory functions and ability to modulate NF-κB pathways, ISM1 may hold therapeutic potential in RA. Current research on NF-κB-targeted therapies underscores the importance of endogenous regulators such as ISM1 [23,24,25,26]. Whether ISM1 can be leveraged as a therapeutic agent or serve as a companion biomarker for targeted treatment strategies remains a promising area for future research.
Nevertheless, although the study was cross-sectional in design, the post hoc power analysis confirmed adequate statistical power (99.7%) for the primary outcome, supporting the reliability of our findings regarding ISM1 levels in RA.
This study has several limitations that should be acknowledged. First, due to its cross-sectional design, causal inferences regarding the relationship between ISM1 and RA disease activity cannot be drawn. Second, although treatment-naïve patients were included in the early RA group, we did not stratify established RA patients based on their current or prior medication exposure, which may potentially influence serum ISM1 levels. Third, multivariate analyses did not include treatment status, RF/anti-CCP titers, or other potentially relevant immunological parameters due to missing data and limited sample size. Additionally, serum ISM1 measurements were not complemented with synovial fluid levels or tissue expression analyses, which could have provided further mechanistic insights. Future longitudinal and multicenter studies with larger and demographically diverse RA cohorts, incorporating serial ISM1 measurements and comprehensive immunophenotyping, will be essential to validate our findings and to clarify the clinical relevance of ISM1 in RA.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this is the first clinical study to demonstrate that serum ISM1 levels are significantly reduced in RA patients and independently associated with disease activity, as measured using DAS28-CRP and DAS28-ESR, after adjustment for key inflammatory and demographic variables. Additionally, ISM1 levels were inversely associated with autoantibody positivity (RF and anti-CCP), although these relationships require confirmation in multivariate settings. ISM1 suppression was evident even in treatment-naïve early RA patients, suggesting that its downregulation occurs early in the disease course.
Importantly, ROC analysis revealed that serum ISM1 levels ≥ 673.73 ng/L could predict remission or low disease activity with excellent specificity (100%) and positive predictive value (100%). Although sensitivity was limited, this threshold may support the potential role of ISM1 as a clinically meaningful complementary indicator of controlled disease. Supported by strong effect sizes, predictive performance, and multivariate modelling, these findings highlight ISM1’s potential as a non-invasive biomarker for disease monitoring in RA. Given its established anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory functions, ISM1 may also represent a novel target for future therapeutic research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.O.; methodology, B.O., A.K., and R.F.A.; validation, B.O., N.G., and S.S.K.; formal analysis, B.O. and A.K.; investigation, B.O. and R.F.A.; resources, R.F.A.; data curation, I.G., G.Y., M.G., and Y.D.; writing—original draft preparation, B.O.; writing—review and editing, B.O., A.K., and S.S.K.; visualization, Y.D.; supervision, N.G. and S.S.K.; project administration, B.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Non-Interventional Research Ethics Committee of Firat University (protocol code: 24299; date of approval: 20 May 2024).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study are not publicly available due to ethical and privacy restrictions but may be provided by the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Rheumatology Unit staff at Firat University Hospital for their support during patient recruitment and laboratory procedures.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| DAS28 | Disease Activity Score in 28 Joints |
| DMARDs | Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| ESR | Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| ISM1 | Isthmin-1 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor kappa B |
| NK | Natural Killer cells |
| NKT | Natural Killer T cells |
| RA | Rheumatoid Arthritis |
| RF | Rheumatoid Factor |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| Th17 | T helper 17 cells |
| anti-CCP | Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide |
References
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2205–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pera, E.M.; Kim, J.I.; Martinez, S.L.; Brechner, M.; Li, S.-Y.; Wessely, O.; De Robertis, E. Isthmin is a novel secreted protein expressed as part of the Fgf-8 synexpression group in the Xenopus midbrain–hindbrain organizer. Mech. Dev. 2002, 116, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.-P.; Hu, Y.-X.; Teng, T.; Wang, S.-S.; Tang, Q.-Z. Isthmin-1 Improves Aging-Related Cardiac Dysfunction in Mice through Enhancing Glycolysis and SIRT1 Deacetylase Activity. Aging Dis. 2024, 15, 2682–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menghuan, L.; Yang, Y.; Qianhe, M.; Na, Z.; Shicheng, C.; Bo, C.; XueJie, Y. Advances in research of biological functions of Isthmin-1. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 17, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle-Rios, R.; Maravillas-Montero, J.L.; Burkhardt, A.M.; Martinez, C.; Buhren, B.A.; Homey, B.; Gerber, P.A.; Robinson, O.; Hevezi, P.; Zlotnik, A. Isthmin 1 is a secreted protein expressed in skin, mucosal tissues, and NK, NKT, and th17 cells. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014, 34, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liang, X.; Ni, J.; Zhao, R.; Shao, S.; Lu, S.; Han, W.; Yu, L. Effect of ISM1 on the immune microenvironment and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 681240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakhawat, H.M.; Hazrat, Z.; Zhou, Z. Isthmin—A multifaceted protein family. Cells 2022, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.; Xu, S.; Lam, T.Y.W.; Liao, W.; Wong, W.S.F.; Ge, R. ISM1 suppresses LPS-induced acute lung injury and post-injury lung fibrosis in mice. Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firestein, G.S.; McInnes, I.B. Immunopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunity 2017, 46, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Deng, R. Angiogenesis as a potential treatment strategy for rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 910, 174500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugasundaram, M.; Xu, S.; Yang, Y.; Tee, J.H.; Lam, T.Y.W.; Ge, R. Ism1 deficiency in mice exacerbates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis with enhanced cellular senescence and delayed fibrosis resolution. hLife 2024, 2, 342–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahiri, V.; Caron, J.; Roger, E.; Desterke, C.; Ghachem, K.; Mohamadou, I.; Serre, J.; Prakoura, N.; Fellahi, S.; Placier, S. The angiogenesis inhibitor Isthmin-1 (Ism1) is Overexpressed in experimental models of Glomerulopathy and impairs the viability of Podocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Zhang, X.; Hu, C.; Ma, Z.-G.; Wang, S.-S.; Teng, T.; Zeng, X.-F.; Tang, Q.-Z. Isthmin-1 alleviates cardiac ischaemia/reperfusion injury through cGMP-PKG signalling pathway. Cardiovasc. Res. 2024, 120, 1051–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian Herlitz-Cifuentes, H.; Carola Fernandez Garces, P.; Ivone Lamperti Fernandez, L.; Alberto Guzman-Gutierrez, E. Effect of systemic inflammation on the function of insulin and glucose metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2016, 12, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Zhang, X.; Hu, C.; Teng, T.; Tang, Q.-Z. A brief overview about the adipokine: Isthmin-1. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 939757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.-Y.; Wei, H.-J.; Tang, Y.-Y. Isthmin: A multifunctional secretion protein. Cytokine 2024, 173, 156423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, T.Y.W.; Nguyen, N.; Peh, H.Y.; Shanmugasundaram, M.; Chandna, R.; Tee, J.H.; Ong, C.B.; Hossain, M.Z.; Venugopal, S.; Zhang, T.; et al. ISM1 protects lung homeostasis via cell-surface GRP78-mediated alveolar macrophage apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2019161119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, J.H.; Vijayakumar, U.; Shanmugasundaram, M.; Lam, T.Y.W.; Liao, W.; Yang, Y.; Wong, W.S.F.; Ge, R. Isthmin-1 attenuates allergic Asthma by stimulating adiponectin expression and alveolar macrophage efferocytosis in mice. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.-C.; Chang, J.-H.; Jin, J. Regulation of nuclear factor-κB in autoimmunity. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.; Lee, Y.F.; Ge, R. Novel endogenous angiogenesis inhibitors and their therapeutic potential. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 1177–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osório, L.; Wu, X.; Zhou, Z. Distinct spatiotemporal expression of ISM1 during mouse and chick development. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 1571–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.; Zheng, J.; Lu, J.; Shen, H.-L. NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 6998–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarov, S.S. NF-κB in rheumatoid arthritis: A pivotal regulator of inflammation, hyperplasia, and tissue destruction. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2001, 3, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrington, F.D.; Carmody, R.J.; Goodyear, C.S. Modulation of NF-κB signaling as a therapeutic target in autoimmunity. J. Biomol. Screen. 2016, 21, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).