Craniofacial Cephalometric Morphology in Caucasian Adult Patients with Cleft Palate Only (CPO)
Abstract
1. Introduction
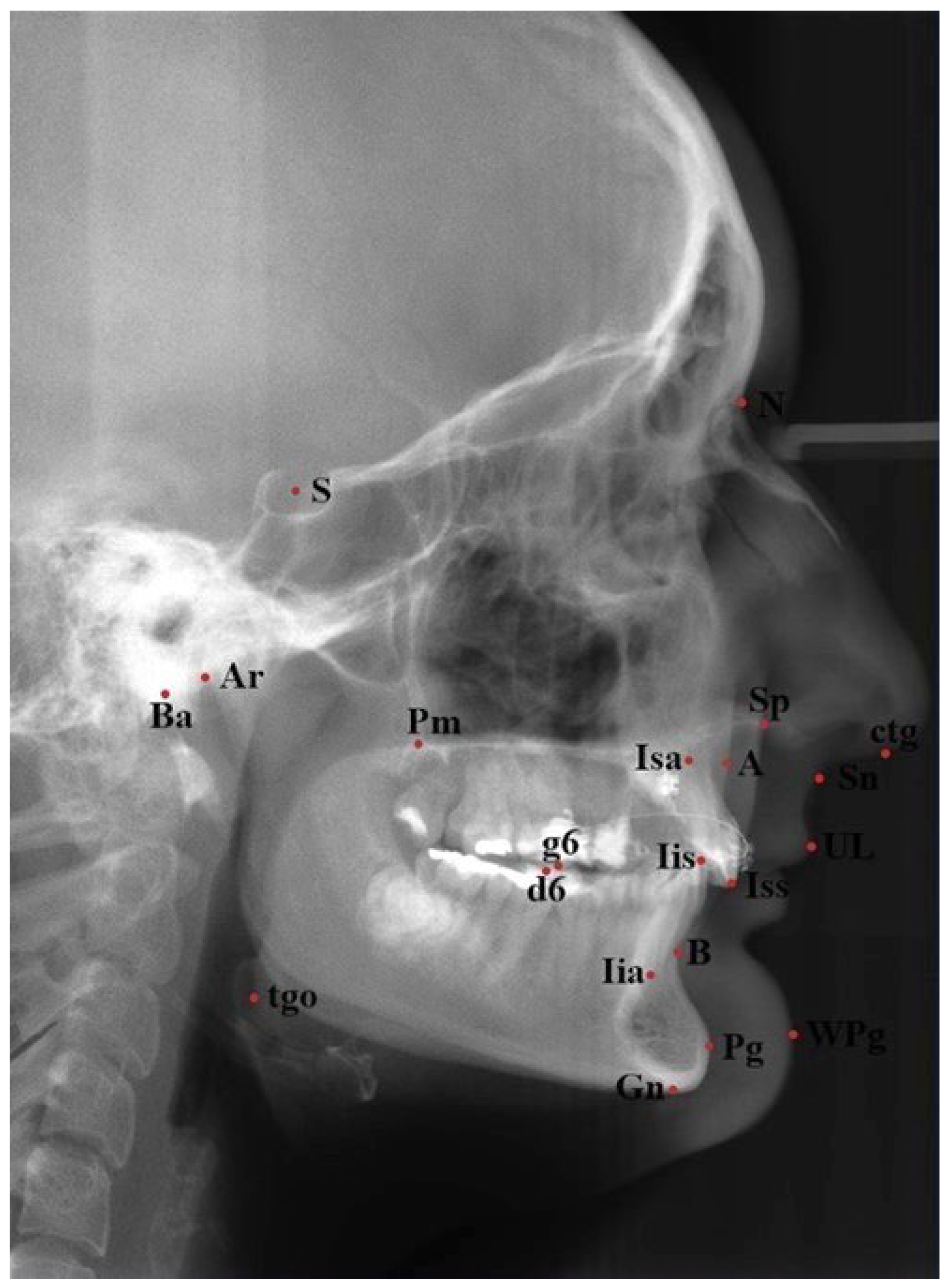
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoon, Y.J.; Perkiomaki, M.R.; Tallents, R.H.; Barillas, I.; Hererera-Guido, R.; Fong, C.T. Transverse craniofacial featueres and their genetic predisposition in families with nonsyndromatic unilateral cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate-Craniofacial J. 2004, 41, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkoukani, M.A.; Lawrence, L.A.; Liebertz, D.J.; Svider, P.F. Cleft palate: A clinical review. Birth Defects Res. Part C Embryo Today Rev. 2014, 102, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawiślak, A.; Woźniak, K.; Jakubowska, A.; Lubiński, J.; Kawala, B.; Znamirowska-Bajowska, A. Polymorphic variants in VAX1 gene (RS7078160) and BMP4 gene (RS762642) and the risk of non-syndromic ortofacial clefts in the polish population. Med. Wieku Rozw. 2014, 181, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, F.C. The genetic of cleft lip and palate. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1970, 22, 336–352. [Google Scholar]
- Madachi, K.; Takagi, R.; Asahito, Y.; Kodama, R.; Ominato, A.; Iila, K.; Ono, K.; Saito, I. Cephalometric evaluation after two-stage palatoplasty combined with a Hotz plate: A comparative study between the modified Furlow and Widmaier-Perko methods. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, K.; Haruyama, N.; Nomura, S.; Murata, N.; Yoshizaki, K.; Mitsuyasu, T.; Nakano, H.; Nakamura, S.; Mori, Y.; Takahashi, I. Characteristics of craniofacial morphology and factors affecting them in patients with isolated cleft palate. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, M.E.B.; Cordeiro, N.B.D.R.; Veras, S.R.D.A.; de Melo, E.M.C.; Vale, D.M.V.D.; Gurgel, L.G.F.; da Figueira, M.A.S. Malocclusion in Children Aged 8 to 10 Years Old with Operated Isolated Cleft Palate. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2021, 32, e156–e159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heliövaara, A.; Ranta, R.; Rauito, J. Craniofacial cephalometric morphology in six-year-old girls with submucous cleft palate and isolated cleft palate. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2003, 61, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azouz, V.; Ng, M.; Patel, N.; Murthy, A.S. Low incidence of maxillary hypoplasia in isolated cleft palate. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 42, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diah, E.; Lo, L.J.; Huang, C.S.; Sudjatmiko, G.; Susanto, I.; Chen, Y.R. Maxillary growth of adult patients with unoperated cleft: Answers to the debates. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2007, 60, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da-Silva, E.O.; Batista, J.E.; Medeiros, M.A.; Fonteles, S.M. Craniofacial anthropometric studies in Waardenburg syndrome type I. Clin. Genet. 1993, 41, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikakis, K.A.; Larson, O.; Karsten, A. Minimal incision palatoplasty with or without muscle reconstruction in patients with isolated cleft palate: A cast and medical records analysis. Eur. J. Orthod. 2018, 40, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heliövaara, A.; Rautio, J. Craniofacial and pharyngeal cephalometric morphology in seven-year-old boys with unoperated submucous cleft palate and without a cleft. Cleft Palate-Craniofacial J. 2009, 46, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonarakis, G.S.; Watts, G.; Daskalogiannakis, J. The need for orthognathic surgery in nonsyndromic patients with repaired isolated cleft palate. Cleft Palate-Craniofacial J. 2015, 52, e8–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, B.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Jing, H.; Hu, J. A comparative cephalometric study for adult operated cleft palate and unoperated cleft palate patients. J. Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg. 2015, 43, 1218–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Shi, B.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Q. The comparative study of craniofacial structural characteristic of individuals with different types of cleft palate. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2007, 59, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, E.; Kreiborg, S.; Jensen, B.L.; Fogh-Andersen, P. Comparison of craniofacial morphology in infants with incomplete cleft lip and infants with isolated cleft palate. Cleft Palate J. 1982, 19, 258–266. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, W.K.; Witzel, M.A. Cleft palate repair: Von Langenbeck Technique. In Multidisciplinary Management of Cleft Lip and Palatel; Bardach, J., Morris, H.L., Eds.; W.B. Saunders Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1990; p. 303. [Google Scholar]
- Segner, D.; Hasund, A. Individualisierte Kefalometrie; Dietmar Segner Verlag: Hamburg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Cicchetti, D.V.; Domenic, V. Guidelines, criteria, and rules of thumb for evaluating normed and standardized assessment instruments in psychology. Psychol. Assess. 1994, 6, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, A.; Diwakar, N.R.; Jayanthi, K.; Hema, H.M.; Deepukrishna, S.; Ghaste, S.R. The reliability of cephalometric measurements in oral and maxillofacial imaging: Cone beam computed tomography versus two-dimensional digital cephalograms. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2016, 27, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trpkova, B.; Major, P.; Prasad, N.; Nebbe, B. Cephalometric landmarks identification and reproducibility: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1997, 112, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, A. Update on the Wits appraisal. Angle Orthod. 1988, 58, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Xu, X.; Ahmatjian, A.; Bing, S. The Craniofacial Morphology in Adult Patients with Unoperated Isolated Cleft Palate. Bone Res. 2013, 1, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, C.; Schreuder, W.H.; Shi, J.; Shi, B.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, Y. Cephalometric analysis of craniofacial morphology and growth in unrepaired isolated cleft palate patients. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smahel, Z.; Hradiský, D.; Müllerová, Z. Multivariate comparison of craniofacial morphology in different types of facial clefts. Acta Chir. Plast. 1999, 41, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Janiszewska-Olszowska, J.; Grocholewicz, K.; Mazur, M.; Jedliński, M. Influence of Primary Palatal Surgery on Craniofacial Morphology in Patients with Cleft Palate Only (CPO)-Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Filho, O.G.; Rosa, L.A.; Lauris Rde, C. Influence of isolated cleft palate and palatoplasty on the face. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2007, 15, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Xu, X.; Shi, B.; Zheng, Q.; Li, J. Is Cleft Severity Correlated with Intrinsic Growth Pattern? Observation From Unoperated Adult Patients with Submucous Cleft Palate. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2017, 28, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Nakamura, A.; Michi, K.-I.; Go-Ming, W.; Kan, L.; Wei-Liu, Q. Cephalometric Analysis of Maxillofacial Morphology in Unoperated Cleft Palate Patients. Cleft Palate-Craniofacial J. 1992, 29, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanna, N.K.; AlMuzaini, A.A.; Mupparapu, M. Imaging in Orthodontics. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 65, 623–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.K.; Chen, Y.; Almalki, A.; Sivamurthy, G.; Kafle, D. Cephalometric Analysis in Orthodontics Using Artificial Intelligence-A Comprehensive Review. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 1880113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochhar, A.S.; Nucci, L.; Sidhu, M.S.; Prabhakar, M.; Grassia, V.; Perillo, L.; Kochhar, G.K.; Bhasin, R.; Dadlani, H.; d’Apuzzo, F.J. Reliability and Reproducibility of Landmark Identification in Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Patients: Digital Lateral Vis-A-Vis CBCT-Derived 3D Cephalograms. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Liu, B.; Luo, Z.; Ma, H.; Sun, M.; Wang, Y.; Yin, N.; Tang, X.; Song, T. Using a New Deep Learning Method for 3D Cephalometry in Patients with CleftLip and Palate. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2023. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, H.S.; Hyun, C.M.; Baek, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Seo, J.K. A semi-supervised learning approach for automated 3D cephalometric landmark identification using computed tomography. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Abbreviation | Mean Value | Interpretation | Special Significance in Cleft Palate (Only) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SNA | 82 | Sagittal maxillary position referring to cranial base. | Negative—indicates sagittal maxillary deficiency. |
| SNB | 80 | Sagittal position of the mandibular alveolar part referring to cranial base. | Reduced in mandibular deficiency. |
| ANB | 2 | Sagittal relation between the maxilla and mandible. | Negative in sagittal maxillary deficiency referring to mandible, reduces with age due to normal growth. |
| SNPg | 82 | Sagittal position of the chin referring to cranial base. | Reduced in mandibular deficiency. |
| NL-NSL | 8 | Vertical maxillary inclination relative to cranial base. | Reduced in vertical maxillary deficiency. |
| ML-NSL | 28 | Vertical mandibular inclination relative to cranial base. | Increased in posterior rotation of the mandible. |
| ML-NL | 20 | Vertical jaw relation. | Increased in posterior rotation of the mandible and in vertical maxillary deficiency. |
| NS-Ba | 130 | Inclination of the clivus to cranial base. | _ |
| Gn-tgo-Ar | 122 | Gonial angle. | Increased in severe mandibular deficiency with posterior rotation |
| H | 9.2 | Angle between the line upper lip—soft-tissue chin relative to line NB—inclination of the soft tissue profile. | Reduced in upper lip retrusion associated by maxillary deficiency, reduces with normal growth. |
| 1+:1- | 133 | Angle between the long axes of upper and lower central incisors. | _ |
| 1+:NA | 21 | Upper incisor inclination to NA line. | Increased with protrusion of upper incisors (compensatory to sagittal maxillary deficiency). |
| 1+:NB | 24 | Lower incisor inclination to NB line. | Reduced with retrusion of the lower incisors (compensatory to sagittal jaw discrepancy) |
| Nasolabial angle | 110 | Angle between nasal base and upper lip. | Increased in sagittal maxillary deficiency. |
| Index | 80 | Proportion between the upper and lower face height (in percentage). | Reduced in vertical maxillary and midface deficiency, reduced in posterior mandibular rotation. |
| Pg:NB (mm) | 2.3 | Distance between the point Pg and NB line. Describes chin prominence. | Reduced in mandibular Deficiency |
| 1+:NA mm | 4 | Distance between the incisal edge of the upper central incisor and NA line. | Increased in protrusion of upper incisors (compensatory to sagittal maxillary deficiency). |
| 1-:NB mm | 3.8 | Distance between the incisal edge of the lower central incisor and NB line. | Reduced in retrusion of lowers incisor (compensatory to sagittal jaw discrepancy). |
| Wits (mm) | 0 | Distance between perpendicular projections of points A and B on the occlusal plane. | Negative value in maxillary deficiency. |
| Variable | Group | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control Group (n = 28) | Study Group (n = 28) | |||
| SNA (°) | mean ± SD | 80.97 ± 3.54 | 77.18 ± 4.36 | p = 0.001 * |
| Median | 80.7 | 77.2 | ||
| Quartiles | 78.7–83.62 | 74.8–79.2 | ||
| SNB (°) | mean ± SD | 78.17 ± 3.87 | 79.15 ± 5.43 | p = 0.857 |
| Median | 78.15 | 77.95 | ||
| Quartiles | 76.42–80.7 | 76.77–80.65 | ||
| ANB (°) | mean ± SD | 2.92 ± 2.71 | −1.97 ± 4.8 | p < 0.001 * |
| Median | 2.95 | −1.75 | ||
| Quartiles | 0.98–4.68 | −4.05–1.35 | ||
| SNPg (°) | mean ± SD | 79.43 ± 3.9 | 80.51 ± 5.67 | p = 0.928 |
| Median | 80.3 | 79.9 | ||
| Quartiles | 77.3–82.15 | 78.22–82.32 | ||
| NSBa (°) | mean ± SD | 130.08 ± 5.91 | 130.33 ± 6.14 | p = 0.902 |
| Median | 130.6 | 129.95 | ||
| Quartiles | 126.33–133.27 | 127.17–132.92 | ||
| GntgoAr (°) | mean ± SD | 123.08 ± 7.42 | 127.45 ± 9.1 | p = 0.088 |
| Median | 122.95 | 126.1 | ||
| Quartiles | 118.83–125.75 | 119.8–134.62 | ||
| NL-NSL (°) | mean ± SD | 7.45 ± 3.62 | 11.53 ± 5.43 | p = 0.004 * |
| Median | 7.5 | 11.95 | ||
| Quartiles | 4.53–9.32 | 7.18–15.45 | ||
| ML-NSL (°) | mean ± SD | 30.7 ± 7.16 | 33.83 ± 8.63 | p = 0.142 |
| Median | 29.7 | 32.7 | ||
| Quartiles | 26.6–34.95 | 29.82–37.42 | ||
| ML-NL (°) | mean ± SD | 23.23 ± 7.22 | 22.35 ± 9.24 | p = 0.941 |
| Median | 22.25 | 21.6 | ||
| Quartiles | 18.55–28.95 | 15.52–28.58 | ||
| H | mean ± SD | 9.82 ± 5.37 | 7.78 ± 5.42 | p = 0.068 |
| Median | 9.15 | 5.95 | ||
| Quartiles | 6.57–13.35 | 3.8–11.1 | ||
| +:1- angle (°) | mean ± SD | 132.66 ± 14.08 | 135.59 ± 13.17 | p = 0.413 |
| Median | 131 | 131.65 | ||
| Quartiles | 122.88–139 | 126.35–143.52 | ||
| 1+:NA angle (°) | mean ± SD | 20.09 ± 10.41 | 26.87 ± 9.97 | p = 0.035 * |
| Median | 21.25 | 27.2 | ||
| Quartiles | 17.5–26.52 | 20.15–34.55 | ||
| 1-:NB angle (°) | mean ± SD | 24.42 ± 7.6 | 19.23 ± 8.22 | p = 0.025 * |
| Median | 25.95 | 19.95 | ||
| Quartiles | 19.68–30.05 | 16.7–24.88 | ||
| Nasolabial angle (°) | mean ± SD | 109.83 ± 11.12 | 102.64 ± 18.62 | p = 0.152 |
| Median | 110.6 | 105.9 | ||
| Quartiles | 104.77–117.75 | 92.23–116 | ||
| Pg:NB [mm] | mean ± SD | 1.69 ± 1.58 | 1.9 ± 1.52 | p = 0.566 |
| Median | 1.35 | 1.8 | ||
| Quartiles | 0.5–2.68 | 0.9–2.47 | ||
| 1+:NA [mm] | mean ± SD | 2.48 ± 3.09 | 4 ± 2.39 | p = 0.018 * |
| Median | 2.05 | 3.3 | ||
| Quartiles | 1.03–3.45 | 2.28–6.08 | ||
| 1-:NB [mm] | mean ± SD | 2.71 ± 2.23 | 2.26 ± 2.39 | p = 0.928 |
| Median | 2.1 | 2.6 | ||
| Quartiles | 1.1–3.2 | 0.92–3.55 | ||
| Index | mean ± SD | 78.46 ± 8.49 | 77.78 ± 12.02 | p = 0.441 |
| Median | 78.8 | 74.3 | ||
| Quartiles | 72.45–83.75 | 71.05–82.72 | ||
| Wits [mm] | mean ± SD | 0.39 ± 2.76 | −4.02 ± 4.63 | p < 0.001 * |
| Median | 0.6 | −3.1 | ||
| Quartiles | −1.08–2.22 | −6.17–−1.15 | ||
| Author | Year | Characterictics of Subjects | Cephalometric Measurements | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Subjects with CPO | Origin | Gender | Mean Age (Age Range) | Characteristics of Malformation | |||
| Cao C et al. [29] | 2017 | 40 | Chinese | F/M | CPO (25.43 ± 7.18, sCPO 24.32 ± 6.22) | CPO, sCPO | S-N, S-Ba/S-N, N-Ba/S-N, ANS-Me/S-N, Ba-PMP/S-N, Ba-ANS/S-N, A-PMP/S-N, PMP-ANS/S-N, ANS-N/S-N, R-PMP/S-N, Ar-Go/S-N, Pog-Go/S-N, N-Me/S-N, < Ba-N-ANS, <S-N-ANS, <S-N-A, <S-N-B, <S-N-Pog, <N-S-PMP, <Ar-Go-Gn, <A-N-B |
| Antonarakis G.S. et al. [14] | 2015 | 189 | Caucasian, Asian, African | F/M | Minimum age of 15 years | CPO | maxillary length, maxillary protrusion, maxillary height, maxillary inclination |
| Xu Y. et al. [25] | 2014 | 30 | Chinese | F/M | Over 18 | CPO | S-N, S-Ba, N-Ba, NSBa, Pmp-Ba, Pmp-S, ANS-Pmp, N-ANS, Pmp-NSL, SNA, Lo-Lo’, Mo-Mo’, Apt-Apt’, Mx-Mx’, Zyg-Zyg’, Gn-Go, Cd-Go, Gn-Cd, Ii-Pgn, SNB, SnPg, SN/GoPgn, ANSPmp/Go-PGn, Cd-Cd’, Go-Go’, ANB |
| Ye Z et al. 2013 [24] | 2013 | 37 | Chinese | F/M | 22.19 ± 6.57 | CPO | N-S/mm, N-Ba/mm, S-Ba/mm, Ba-S-N/°, ANS-Me, N-ANS, N-Me, S-Ptm, Pog-Go, Ar-Go, R-PMP, Ba-PMP, PMP-ANS, PMP-A, ∠SNA, ∠SNB, ∠ANB, Ba-N-ANS, Ba-N-A, S-N-ANS, S-N-Pog, SN-PP, MP-SN, Ar -Go-Me, N-ANS/N-Me, R-PMP/N-ANS |
| Diah E et al. [10] | 2007 | 92 | Indian | F/M | 21.6 (range 16–47 years) | UCL, UCLP, BCLP, CPO | SNA |
| Smahel Z et al. [26] | 1999 | 34 complete CPO + 34 incomplete CPO + 17 sCPO | Czech | M | (20–40) | UCL, UCLP, BCLP, CPO | SNA, SNB, ANB, Spp-Spa, S-Go%N-Me, Is-NPo, overjet, Ls-EL |
| Yoshida H et al. [30] | 1992 | 14 | Chinese | F/M | 13–28 | CPO | SNA, ANS-Ptm, N-ANS, SNB, mandibular plane angle, facial angle, ANB, U1-SN |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zawiślak, A.; Wędrychowska-Szulc, B.; Grocholewicz, K.; Janiszewska-Olszowska, J. Craniofacial Cephalometric Morphology in Caucasian Adult Patients with Cleft Palate Only (CPO). Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13122058
Zawiślak A, Wędrychowska-Szulc B, Grocholewicz K, Janiszewska-Olszowska J. Craniofacial Cephalometric Morphology in Caucasian Adult Patients with Cleft Palate Only (CPO). Diagnostics. 2023; 13(12):2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13122058
Chicago/Turabian StyleZawiślak, Alicja, Barbara Wędrychowska-Szulc, Katarzyna Grocholewicz, and Joanna Janiszewska-Olszowska. 2023. "Craniofacial Cephalometric Morphology in Caucasian Adult Patients with Cleft Palate Only (CPO)" Diagnostics 13, no. 12: 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13122058
APA StyleZawiślak, A., Wędrychowska-Szulc, B., Grocholewicz, K., & Janiszewska-Olszowska, J. (2023). Craniofacial Cephalometric Morphology in Caucasian Adult Patients with Cleft Palate Only (CPO). Diagnostics, 13(12), 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13122058








