Mucopolysaccharidosis: What Pediatric Rheumatologists and Orthopedics Need to Know
Abstract
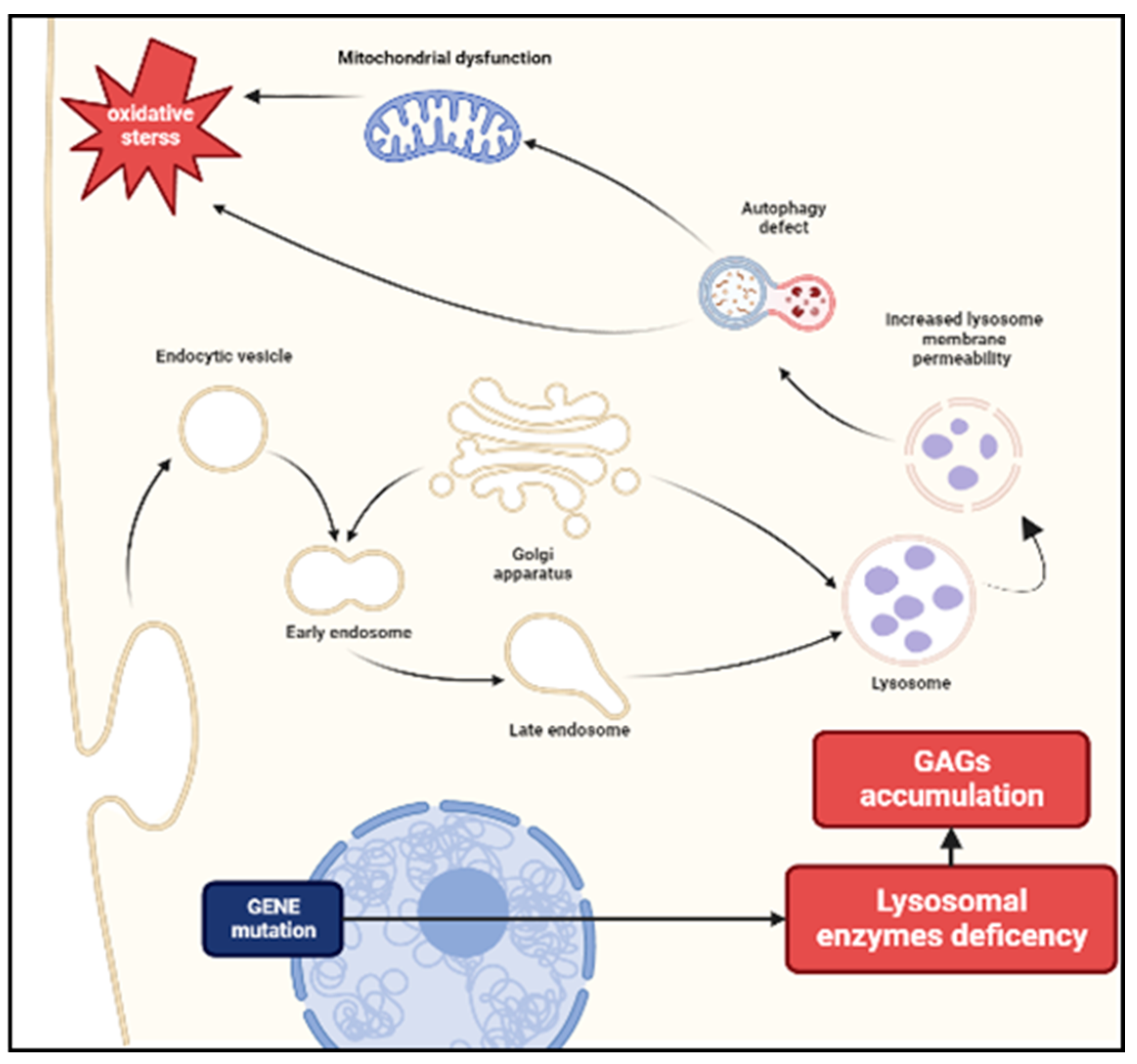
1. Introduction
2. Pathogenesis and the Role of Inflammation
3. Musculoskeletal Manifestations in MPS
3.1. Arthropathy and related issues
3.1.1. Joint Stiffness and Contractures
3.1.2. Joint Stiffness and Contractures
3.1.3. Trigger Digits and Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
3.2. Skeletal Involvement
3.2.1. Kyphosis
3.2.2. Hip Dysplasia
3.2.3. Genu Valgum
3.2.4. Spinal Cord Compression
3.2.5. Consideration on Surgery in MPS
3.2.6. Short Stature
3.3. Musculoskeletal Biomarkers
3.4. Bone Status in MPS
4. Other Manifestations of Attenuated MPS
5. Diagnosis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muenzer, J. Overview of the Mucopolysaccharidoses. Rheumatology 2011, 50 (Suppl. 5), v4–v12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, K.L.; Flanigan, K.M. Update in the Mucopolysaccharidoses. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2021, 37, 100874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimaz, R.; Vijay, S.; Haase, C.; Coppa, G.V.; Bruni, S.; Wraith, E.; Guffon, N. Attenuated Type I Mucopolysaccharidosis in the Differential Diagnosis of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: A Series of 13 Patients with Scheie Syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2006, 24, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Michaud, M.; Belmatoug, N.; Catros, F.; Ancellin, S.; Touati, G.; Levade, T.; Gaches, F. Mucopolysaccharidosis: A review. Rev. Med. Interne 2020, 41, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baehner, F.; Schmiedeskamp, C.; Krummenauer, F.; Miebach, E.; Bajbouj, M.; Whybra, C.; Kohlschütter, A.; Kampmann, C.; Beck, M. Cumulative Incidence Rates of the Mucopolysaccharidoses in Germany. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2005, 28, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimaz, R.; La Torre, F. Mucopolysaccharidoses. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2014, 16, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, L.; Ellaway, C.; Foster, H.E.; Giugliani, R.; Goizet, C.; Goring, S.; Hawley, S.; Jurecki, E.; Khan, Z.; Lampe, C.; et al. Understanding the Early Presentation of Mucopolysaccharidoses Disorders. J. Inborn Errors Metab. Screen. 2018, 6, 2326409818800346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze-Frenking, G.; Jones, S.A.; Roberts, J.; Beck, M.; Wraith, J.E. Effects of Enzyme Replacement Therapy on Growth in Patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2011, 34, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, L.A. Pathogenesis of Skeletal and Connective Tissue Involvement in the Mucopolysaccharidoses: Glycosaminoglycan Storage Is Merely the Instigator. Rheumatology 2011, 50 (Suppl. 5), v13–v18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoka-Winiarska, V.; Jurecka, A.; Emeryk, A.; Tylki-Szymańska, A. Osteoimmunology in Mucopolysaccharidoses Type I, II, VI and VII. Immunological Regulation of the Osteoarticular System in the Course of Metabolic Inflammation. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrovic, S.; Gouze, H.; Gossec, L.; Schaeverbeke, T.; Fautrel, B. Mucopolysaccharidoses Seen in Adults in Rheumatology. Jt. Bone Spine 2017, 84, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, R.; Brown, J.R.; Al-Mafraji, K.; Lamanna, W.C.; Beitel, J.R.; Boons, G.-J.; Esko, J.D.; Crawford, B.E. Disease-Specific Non-Reducing End Carbohydrate Biomarkers for Mucopolysaccharidoses. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, H.A.; Holley, R.J.; Langford-Smith, K.J.; Wilkinson, F.L.; van Kuppevelt, T.H.; Wynn, R.F.; Wraith, J.E.; Merry, C.L.R.; Bigger, B.W. Heparan Sulfate Inhibits Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cell Migration and Engraftment in Mucopolysaccharidosis I. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 36194–36203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer, C.A.; Scudder, S.L.; Lin, Y.; Dozier, L.E.; Phan, D.; Allen, N.J.; Patrick, G.N.; Esko, J.D. Neurodevelopmental Changes in Excitatory Synaptic Structure and Function in the Cerebral Cortex of Sanfilippo Syndrome IIIA Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, N.S.; Mancera, R.L. The Structure of Glycosaminoglycans and Their Interactions with Proteins. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des. 2008, 72, 455–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holley, R.J.; Deligny, A.; Wei, W.; Watson, H.A.; Niñonuevo, M.R.; Dagälv, A.; Leary, J.A.; Bigger, B.W.; Kjellén, L.; Merry, C.L.R. Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I, Unique Structure of Accumulated Heparan Sulfate and Increased N-Sulfotransferase Activity in Mice Lacking α-l-Iduronidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 37515–37524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futerman, A.H.; van Meer, G. The Cell Biology of Lysosomal Storage Disorders. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, V.G.; Gazarini, M.L.; Rodrigues, L.C.; da Silva, F.H.; Han, S.W.; Martins, A.M.; Tersariol, I.L.S.; D’Almeida, V. Evidence of Lysosomal Membrane Permeabilization in Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I: Rupture of Calcium and Proton Homeostasis. J. Cell Physiol. 2010, 223, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, V.G.; Martins, A.M.; Micheletti, C.; D’Almeida, V. Mutational and Oxidative Stress Analysis in Patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I Undergoing Enzyme Replacement Therapy. Clin. Chim. Acta 2008, 387, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippon, L.; Vanzin, C.S.; Biancini, G.B.; Pereira, I.N.; Manfredini, V.; Sitta, A.; do Carmo R. Peralba, M.; Schwartz, I.V.D.; Giugliani, R.; Vargas, C.R. Oxidative Stress in Patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II before and during Enzyme Replacement Therapy. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 103, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfi, A.; Richard, M.; Gandolphe, C.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Thérond, P.; Scherman, D. Neuroinflammatory and Oxidative Stress Phenomena in MPS IIIA Mouse Model: The Positive Effect of Long-Term Aspirin Treatment. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 103, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalfa, C.; Verpelli, C.; D’Avanzo, F.; Tomanin, R.; Vicidomini, C.; Cajola, L.; Manara, R.; Sala, C.; Scarpa, M.; Vescovi, A.L.; et al. Glial Degeneration with Oxidative Damage Drives Neuronal Demise in MPSII Disease. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reolon, G.K.; Reinke, A.; de Oliveira, M.R.; Braga, L.M.; Camassola, M.; Andrades, M.E.; Moreira, J.C.F.; Nardi, N.B.; Roesler, R.; Dal-Pizzol, F. Alterations in Oxidative Markers in the Cerebellum and Peripheral Organs in MPS I Mice. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2009, 29, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lever, R.; Page, C. Glycosaminoglycans, Airways Inflammation and Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 14, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.J.; Matsumoto, M.; Patel, S.; Lee, L.; Guan, J.-L.; Li, S. Role of Cell Surface Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans in Endothelial Cell Migration and Mechanotransduction. J. Cell Physiol. 2005, 203, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampe, C.S.; Eisengart, J.B.; Lund, T.C.; Orchard, P.J.; Swietlicka, M.; Wesley, J.; McIvor, R.S. Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I: A Review of the Natural History and Molecular Pathology. Cells 2020, 9, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termeer, C.; Benedix, F.; Sleeman, J.; Fieber, C.; Voith, U.; Ahrens, T.; Miyake, K.; Freudenberg, M.; Galanos, C.; Simon, J.C. Oligosaccharides of Hyaluronan Activate Dendritic Cells via Toll-like Receptor 4. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonaro, C.M.; D’Angelo, M.; He, X.; Eliyahu, E.; Shtraizent, N.; Haskins, M.E.; Schuchman, E.H. Mechanism of Glycosaminoglycan-Mediated Bone and Joint Disease: Implications for the Mucopolysaccharidoses and Other Connective Tissue Diseases. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polgreen, L.E.; Vehe, R.K.; Rudser, K.; Kunin-Batson, A.; Utz, J.J.; Dickson, P.; Shapiro, E.; Whitley, C.B. Elevated TNF-α Is Associated with Pain and Physical Disability in Mucopolysaccharidosis Types I, II, and VI. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2016, 117, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, H.; Ellison, S.M.; Holley, R.J.; O’Leary, C.; Liao, A.; Asadi, J.; Glover, E.; Ghosh, A.; Jones, S.; Wilkinson, F.L.; et al. Haematopoietic Stem Cell Gene Therapy with IL-1Ra Rescues Cognitive Loss in Mucopolysaccharidosis IIIA. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 12, e11185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ausseil, J.; Desmaris, N.; Bigou, S.; Attali, R.; Corbineau, S.; Vitry, S.; Parent, M.; Cheillan, D.; Fuller, M.; Maire, I.; et al. Early Neurodegeneration Progresses Independently of Microglial Activation by Heparan Sulfate in the Brain of Mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB Mice. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandolfo, O.; Parker, H.; Bigger, B. Innate Immunity in Mucopolysaccharide Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broz, P.; Dixit, V.M. Inflammasomes: Mechanism of Assembly, Regulation and Signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, N.; Jeltema, D.; Duan, Y.; He, Y. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonaro, C.M.; Ge, Y.; Eliyahu, E.; He, X.; Jepsen, K.J.; Schuchman, E.H. Involvement of the Toll-like Receptor 4 Pathway and Use of TNF-Alpha Antagonists for Treatment of the Mucopolysaccharidoses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliyahu, E.; Wolfson, T.; Ge, Y.; Jepsen, K.J.; Schuchman, E.H.; Simonaro, C.M. Anti-TNF-Alpha Therapy Enhances the Effects of Enzyme Replacement Therapy in Rats with Mucopolysaccharidosis Type VI. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishita, K.; Petty, R.E. Musculoskeletal Manifestations of Mucopolysaccharidoses. Rheumatology 2011, 50 (Suppl 5), v19–v25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghadam, S.H.; Ghahvechi, M.; Mozafari, F.; Sayarifard, F.; Mousavi, M.-S.; Rostami, R.; Ziaee, V. Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I in Children, a Forgotten Diagnosis Responsible for Undiagnosed Musculoskeletal Complaints: Report of Two Cases. Acta Med. 2019, 62, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vijay, S.; Wraith, J.E. Clinical Presentation and Follow-up of Patients with the Attenuated Phenotype of Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I. Acta Paediatr. 2005, 94, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewska, K.; Wolski, J.; Gaffke, L.; Cyske, Z.; Pierzynowska, K.; Węgrzyn, G. Misdiagnosis in Mucopolysaccharidoses. J. Appl. Genet. 2022, 63, 475–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.P.; Biswas, S.N.; Ray, S.; Dey, S.K. Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I Disguised as Rickets. BMJ Case Rep. 2016, 2016, bcr2016215416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, J.; Inbar-Feigenberg, M.; Raiman, J.; Bisch, M.; Chakraborty, P.; Mitchell, J.; Di Geso, L. Ultrasound Findings of Finger, Wrist and Knee Joints in Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2021, 133, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ty, J.M.; James, M.A. Failure of Differentiation: Part II (Arthrogryposis, Camptodactyly, Clinodactyly, Madelung Deformity, Trigger Finger, and Trigger Thumb). Hand Clin. 2009, 25, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rosso, A.; Cerinic, M.M.; De Giorgio, F.; Minari, C.; Rotella, C.M.; Seghieri, G. Rheumatological Manifestations in Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2006, 2, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, K.K. Orthopaedic Aspects of Mucopolysaccharidoses. Rheumatology 2011, 50 (Suppl. 5), v26–v33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaño, A.M.; Tomatsu, S.; Gottesman, G.S.; Smith, M.; Orii, T. International Morquio a Registry: Clinical Manifestation and Natural Course of Morquio a Disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2007, 30, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, E.; Lee, S.; Chong, S.; Park, J.H. Atlantoaxial Instability Treated with Free-Hand C1-C2 Fusion in a Child with Morquio Syndrome. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 1785–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northover, H.; Cowie, R.A.; Wraith, J.E. Mucopolysaccharidosis Type IVA (Morquio Syndrome): A Clinical Review. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1996, 19, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welman, T.; Young, K.; Larkin, J.; Horwitz, M.D. Trigger Finger from Ocean Rowing: An Observational Study. Hand 2022, 17, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-R.; Lee, S.-H. Ultrasonographic Assessment of Clinically Diagnosed Trigger Fingers. Rheumatol. Int. 2010, 30, 1455–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzewicz, M.; Wolf, J.M. Trigger Digits: Principles, Management, and Complications. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2006, 31, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muenzer, J.; Wraith, J.E.; Clarke, L.A. International Consensus Panel on Management and Treatment of Mucopolysaccharidosis I Mucopolysaccharidosis I: Management and Treatment Guidelines. Pediatrics 2009, 123, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- al-Qattan, M.M.; Thomson, H.G.; Clarke, H.M. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome in Children and Adolescents with No History of Trauma. J. Hand Surg. Br. 1996, 21, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, A.; Dowling, G.; Johnstone, B.; Kornberg, A.; Coombs, C. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome in Children with Mucopolysaccaridoses. J. Child Neurol. 2007, 22, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Heest, A.E.; House, J.; Krivit, W.; Walker, K. Surgical Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Trigger Digits in Children with Mucopolysaccharide Storage Disorders. J. Hand Surg. Am. 1998, 23, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viskochil, D.; Muenzer, J.; Guffon, N.; Garin, C.; Munoz-Rojas, M.V.; Moy, K.A.; Hutchinson, D.T. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome in Mucopolysaccharidosis I: A Registry-Based Cohort Study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2017, 59, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ponti, G.; Donsante, S.; Frigeni, M.; Pievani, A.; Corsi, A.; Bernardo, M.E.; Riminucci, M.; Serafini, M. MPSI Manifestations and Treatment Outcome: Skeletal Focus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Li, Y.W.; Wang, T.R.; Hsu, J.C. Bony Changes in Common Mucopolysaccharidoses. Acta Paediatr. Sin. 1996, 37, 178–184. [Google Scholar]
- Tandon, V.; Williamson, J.B.; Cowie, R.A.; Wraith, J.E. Spinal Problems in Mucopolysaccharidosis I (Hurler Syndrome). J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1996, 78, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisstein, J.S.; Delgado, E.; Steinbach, L.S.; Hart, K.; Packman, S. Musculoskeletal Manifestations of Hurler Syndrome: Long-Term Follow-up after Bone Marrow Transplantation. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2004, 24, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.P.; Patra, S.; Biswas, S.N.; Barman, H. Attenuated Form of Type II Mucopolysaccharidoses (Hunter Syndrome): Pitfalls and Potential Clues in Diagnosis. BMJ Case. Rep. 2018, 2018, bcr2018224392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żuber, Z.; Jurecka, A.; Różdżyńska-Świątkowska, A.; Migas-Majoch, A.; Lembas, A.; Kieć-Wilk, B.; Tylki-Szymańska, A. Ultrasonographic Features of Hip Joints in Mucopolysaccharidoses Type I and II. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, K.K.; Steinman, S.; Mubarak, S.J. Cervical Stenosis and Spastic Quadriparesis in Morquio Disease (MPS IV). A Case Report with Twenty-Six-Year Follow-Up. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2009, 91, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazawa, T.; Yasunaga, Y.; Ikuta, Y.; Harada, A.; Kusaka, O.; Sukegawa, K. Femoral Head Dysplasia in Morquio Disease Type A: Bilateral Varus Osteotomy of the Femur. Acta Orthop. Scand. 2001, 72, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.; Brady, P.; O’Meara, A.; Moore, D.; Dowling, F.; Fogarty, E. Mobility in Hurler Syndrome. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2008, 28, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odunusi, E.; Peters, C.; Krivit, W.; Ogilvie, J. Genu Valgum Deformity in Hurler Syndrome after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Correction by Surgical Intervention. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1999, 19, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, G.A.; Southorn, T.; Eastwood, D.M.; Bache, C.E. Lower Extremity Deformity Management in MPS IVA, Morquio-Brailsford Syndrome: Preliminary Report of Hemiepiphysiodesis Correction of Genu Valgum. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2016, 36, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Waal Malefijt, M.C.; van Kampen, A.; van Gemund, J.J. Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients with Inherited Dwarfism—A Report of Five Knee Replacements in Two Patients with Morquio’s Disease Type A and One with Spondylo-Epiphyseal Dysplasia. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2000, 120, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauchard, N.; Garin, C.; Jouve, J.L.; Lascombes, P.; Journeau, P. Perioperative Medullary Complications in Spinal and Extra-Spinal Surgery in Mucopolysaccharidosis: A Case Series of Three Patients. JIMD Rep. 2014, 16, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachur, E.; Del Maestro, R. Mucopolysaccharidoses and Spinal Cord Compression: Case Report and Review of the Literature with Implications of Bone Marrow Transplantation. Neurosurgery 2000, 47, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, G.W.; Meagher, J.N.; Burkhart, J. Spinal Pachymeningitis Secondary to Mucopolysaccharidosis. Case Report. J. Neurosurg. 1974, 41, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, S.H.; Casal, M.L.; Malhotra, N.R.; Ficicioglu, C.; Smith, L.J. Pathogenesis and Treatment of Spine Disease in the Mucopolysaccharidoses. Mol. Genet Metab. 2016, 118, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, G.; Maximova, N.; Zennaro, F.; Gregori, M.; Tamaro, P. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Effects on Spinal Cord Compression in Hurler. Pediatr. Transplant. 2014, 18, E96–E99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, A.; Heyde, C.-E.; Völker, A.; Schumann, E.; Heinz von der Höh, N. Treatment of Severe Kyphoscoliosis in Children with Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I (Pfaundler-Hurler Syndrome) Using the Growing Rod Technique: A Case Series with Mid-Term Results. World Neurosurg. 2020, 139, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohrmann, T.; Muschol, N.M.; Sehner, S.; Punke, M.A.; Haas, S.A.; Roeher, K.; Breyer, S.; Koehn, A.F.; Ullrich, K.; Zöllner, C.; et al. Airway Management and Perioperative Adverse Events in Children with Mucopolysaccharidoses and Mucolipidoses: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2020, 30, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveri, C.P.; Kaplan, F.S.; Fallon, M.D.; Bayever, E.; August, C.S. Hurler Syndrome with Special Reference to Histologic Abnormalities of the Growth Plate. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1991, 269, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldenhoven, M.; Sakkers, R.J.B.; Boelens, J.; de Koning, T.J.; Wulffraat, N.M. Musculoskeletal Manifestations of Lysosomal Storage Disorders. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1659–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polgreen, L.E.; Miller, B.S. Growth Patterns and the Use of Growth Hormone in the Mucopolysaccharidoses. J. Pediatr. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 3, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guffon, N.; Journeau, P.; Brassier, A.; Leger, J.; Chevallier, B. Growth Impairment and Limited Range of Joint Motion in Children Should Raise Suspicion of an Attenuated Form of Mucopolysaccharidosis: Expert Opinion. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2019, 178, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viskochil, D.; Clarke, L.A.; Bay, L.; Keenan, H.; Muenzer, J.; Guffon, N. Growth Patterns for Untreated Individuals with MPS I: Report from the International MPS I Registry. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2019, 179, 2425–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polgreen, L.E.; Bay, L.; Clarke, L.A.; Guffon, N.; Jones, S.A.; Muenzer, J.; Flores, A.L.; Wilson, K.; Viskochil, D. Growth in Individuals with Attenuated Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I during Untreated and Treated Periods: Data from the MPS I Registry. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2022, 188, 2941–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baronio, F.; Zucchini, S.; Zulian, F.; Salerno, M.; Parini, R.; Cattoni, A.; Deodato, F.; Gaeta, A.; Bizzarri, C.; Gasperini, S.; et al. Proposal of an Algorithm to Early Detect Attenuated Type I Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS Ia) among Children with Growth Abnormalities. Medicina 2022, 58, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura-Utsunomiya, A. Bone Biomarkers in Mucopolysaccharidoses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Franceschi, L.; Roseti, L.; Desando, G.; Facchini, A.; Grigolo, B. A Molecular and Histological Characterization of Cartilage from Patients with Morquio Syndrome. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2007, 15, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jiang, Z.; Byers, S.; Casal, M.L.; Smith, L.J. Failures of Endochondral Ossification in the Mucopolysaccharidoses. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2020, 18, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, S.H.; O’Donnell, P.J.M.; Kang, J.L.; Malhotra, N.R.; Dodge, G.R.; Pacifici, M.; Shore, E.M.; Haskins, M.E.; Smith, L.J. Delayed Hypertrophic Differentiation of Epiphyseal Chondrocytes Contributes to Failed Secondary Ossification in Mucopolysaccharidosis VII Dogs. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2015, 116, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.; Mills, P.; Davison, J.; Cleary, M.; Gissen, P.; Banushi, B.; Doykov, I.; Dorman, M.; Mills, K.; Heywood, W.E. Free Urinary Glycosylated Hydroxylysine as an Indicator of Altered Collagen Degradation in the Mucopolysaccharidoses. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2020, 43, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonaro, C.M.; D’Angelo, M.; Haskins, M.E.; Schuchman, E.H. Joint and Bone Disease in Mucopolysaccharidoses VI and VII: Identification of New Therapeutic Targets and Biomarkers Using Animal Models. Pediatr. Res 2005, 57, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, T.C.; Doherty, T.M.; Eisengart, J.B.; Freese, R.L.; Rudser, K.D.; Fung, E.B.; Miller, B.S.; White, K.K.; Orchard, P.J.; Whitley, C.B.; et al. Biomarkers for Prediction of Skeletal Disease Progression in Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I. JIMD Rep. 2021, 58, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, E.B.; Johnson, J.A.; Madden, J.; Kim, T.; Harmatz, P. Bone Density Assessment in Patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis: A Preliminary Report from Patients with MPS II and VI. J. Pediatr. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 3, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Shih, S.-C.; Chuang, C.-K.; Chen, M.-R.; Niu, D.-M.; Lin, S.-P. Assessment of Bone Mineral Density by Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry in Patients with Mucopolysaccharidoses. Orphanet J. Rare. Dis. 2013, 8, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiral, J.; Sanchez, J.M.; Gonzalez, M.A. Stress Fracture of the Femoral Neck in a Young Adult with Maroteaux-Lamy Syndrome. Acta Orthop. Belg. 1992, 58, 91–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, T.; Nishimura, G.; Tsukune, Y.; Dezawa, A.; Miki, H. Progressive Bone Resorption after Pathological Fracture of the Femoral Neck in Hunter’s Syndrome. Pediatr. Radiol. 1999, 29, 914–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polgreen, L.E.; Thomas, W.; Fung, E.; Viskochil, D.; Stevenson, D.A.; Steinberger, J.; Orchard, P.; Whitley, C.B.; Ensrud, K.E. Low Bone Mineral Content and Challenges in Interpretation of Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry in Children with Mucopolysaccharidosis Types I, II, and VI. J. Clin. Densitom. 2014, 17, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kor, D.; Bulut, F.D.; Kılavuz, S.; Şeker Yılmaz, B.; Köşeci, B.; Kara, E.; Kaya, Ö.; Başaran, S.; Seydaoğlu, G.; Önenli Mungan, N. Evaluation of Bone Health in Patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis. J. Bone. Miner. Metab. 2022, 40, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Longo, A.; Piozzi, E.; Schweizer, F. Ocular Features in Mucopolysaccharidosis: Diagnosis and Treatment. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenzl, C.R.; Teramoto, K.; Moshirfar, M. Ocular Manifestations and Management Recommendations of Lysosomal Storage Disorders I: Mucopolysaccharidoses. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2015, 9, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, J.L.; Biswas, S.; Wraith, E.; Lloyd, I.C. Mucopolysaccharidoses and the Eye. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2006, 51, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M.; Arn, P.; Giugliani, R.; Muenzer, J.; Okuyama, T.; Taylor, J.; Fallet, S. The Natural History of MPS I: Global Perspectives from the MPS I Registry. Genet. Med. 2014, 16, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.A.; Beck, M.; Clarke, J.T.R.; Cox, G.F. Childhood Onset of Scheie Syndrome, the Attenuated Form of Mucopolysaccharidosis I. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2010, 33, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunlin, E.; Wang, R. Cardiac Issues in Adults with the Mucopolysaccharidoses: Current Knowledge and Emerging Needs. Heart 2016, 102, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boffi, L.; Russo, P.; Limongelli, G. Early Diagnosis and Management of Cardiac Manifestations in Mucopolysaccharidoses: A Practical Guide for Paediatric and Adult Cardiologists. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fesslová, V.; Corti, P.; Sersale, G.; Rovelli, A.; Russo, P.; Mannarino, S.; Butera, G.; Parini, R. The Natural Course and the Impact of Therapies of Cardiac Involvement in the Mucopolysaccharidoses. Cardiol. Young 2009, 19, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretto, A.; Bosatra, M.G.; Marchesini, L.; Tesoro, S. Anesthesiological Risks in Mucopolysaccharidoses. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braunlin, E.A.; Harmatz, P.R.; Scarpa, M.; Furlanetto, B.; Kampmann, C.; Loehr, J.P.; Ponder, K.P.; Roberts, W.C.; Rosenfeld, H.M.; Giugliani, R. Cardiac Disease in Patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis: Presentation, Diagnosis and Management. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2011, 34, 1183–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampmann, C.; Lampe, C.; Whybra-Trümpler, C.; Wiethoff, C.M.; Mengel, E.; Arash, L.; Beck, M.; Miebach, E. Mucopolysaccharidosis VI: Cardiac Involvement and the Impact of Enzyme Replacement Therapy. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2014, 37, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yund, B.; Rudser, K.; Ahmed, A.; Kovac, V.; Nestrasil, I.; Raiman, J.; Mamak, E.; Harmatz, P.; Steiner, R.; Lau, H.; et al. Cognitive, Medical, and Neuroimaging Characteristics of Attenuated Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2015, 114, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, K.I.; Fagondes, S.C.; Giugliani, R.; Hardy, K.A.; Lee, K.S.; McArdle, C.; Scarpa, M.; Tobin, M.J.; Ward, S.A.; Rapoport, D.M. Respiratory and Sleep Disorders in Mucopolysaccharidosis. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2013, 36, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigoldi, M.; Verrecchia, E.; Manna, R.; Mascia, M.T. Clinical Hints to Diagnosis of Attenuated Forms of Mucopolysaccharidoses. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, S.; Lavery, C.; Broomfield, A. The Diagnostic Journey of Patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis I: A Real-World Survey of Patient and Physician Experiences. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2016, 8, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimberti, C.; Madeo, A.; Di Rocco, M.; Fiumara, A. Mucopolysaccharidoses: Early Diagnostic Signs in Infants and Children. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomatsu, S.; Okamura, K.; Maeda, H.; Taketani, T.; Castrillon, S.V.; Gutierrez, M.A.; Nishioka, T.; Fachel, A.A.; Orii, K.O.; Grubb, J.H.; et al. Keratan Sulphate Levels in Mucopolysaccharidoses and Mucolipidoses. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2005, 28, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomatsu, S.; Gutierrez, M.A.; Ishimaru, T.; Peña, O.M.; Montaño, A.M.; Maeda, H.; Velez-Castrillon, S.; Nishioka, T.; Fachel, A.A.; Cooper, A.; et al. Heparan Sulfate Levels in Mucopolysaccharidoses and Mucolipidoses. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2005, 28, 743–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federico, A.; Capece, G.; Cecio, A.; D’Auria, N.; Di Iorio, G.; Ronsisvalle, L.; Di Natale, P. Sanfilippo B Syndrome (MPS III B): Case Report with Analysis of CSF Mucopolysaccharides and Conjunctival Biopsy. J. Neurol. 1981, 225, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Rojas, M.-V.; Vieira, T.; Costa, R.; Fagondes, S.; John, A.; Jardim, L.B.; Vedolin, L.M.; Raymundo, M.; Dickson, P.I.; Kakkis, E.; et al. Intrathecal Enzyme Replacement Therapy in a Patient with Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I and Symptomatic Spinal Cord Compression. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2008, 146A, 2538–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Mason, R.W.; Giugliani, R.; Orii, K.; Fukao, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Orii, T.; Tomatsu, S. Glycosaminoglycans Analysis in Blood and Urine of Patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 125, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.E. Urine Analysis in the Diagnosis of Mucopolysaccharide Disorders. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 1998, 35, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalingam, K.; Janani, S.; Priya, S.; Elango, E.M.; Sundari, R.M. Diagnosis of Mucopolysaccharidoses: How to Avoid False Positives and False Negatives. Indian. J. Pediatr. 2004, 71, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longdon, K.; Pennock, C.A. Abnormal Keratan Sulphate Excretion. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 1979, 16, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linker, A.; Evans, L.R.; Langer, L.O. Morquio’s Disease and Mucopolysaccharide Excretion. J. Pediatr. 1970, 77, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, L.A.; Atherton, A.M.; Burton, B.K.; Day-Salvatore, D.L.; Kaplan, P.; Leslie, N.D.; Scott, C.R.; Stockton, D.W.; Thomas, J.A.; Muenzer, J. Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I Newborn Screening: Best Practices for Diagnosis and Management. J. Pediatr. 2017, 182, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donati, M.A.; Pasquini, E.; Spada, M.; Polo, G.; Burlina, A. Newborn Screening in Mucopolysaccharidoses. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimaz, R.; Coppa, G.V.; Koné-Paut, I.; Link, B.; Pastores, G.M.; Elorduy, M.R.; Spencer, C.; Thorne, C.; Wulffraat, N.; Manger, B. Joint Contractures in the Absence of Inflammation May Indicate Mucopolysaccharidosis. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2009, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Disease | OMIM | Enzyme Deficiency | Gene (Locus) | Inheritance | Incidence (1/100,000 Live Births) | GAG | CNS | Approved Therapy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPS I | α-L-Iduronidase | IDUA (4p16.3) | AR | 0.69–1.66 | Dermatan sulfate, heparan sulfate | + | Laronidase | |
| Type Hurler | 607,014 | +++ | ||||||
| Type Scheie | 607,016 | − | ||||||
| Type Hurler/Scheie | 607,016 | +/− | ||||||
| MPS II (Hunter syndrome) | 309,900 | Iduronate sulphate sulphatase | IDS (Xq28) | X-Linked recessive | 0.3–0.71 | Dermatan sulfate, heparan sulfate | + | Idrosulfase |
| MPS III (Sanfilippo syndrome) | AR | Heparan sulfate | +++ | NA | ||||
| Type III-A | 252,900 | Heparan-S-sulphate-sulphaminidase | SGSH (17q25.3) | 0.29–1.89 | ||||
| Type III-B | 252,920 | N-Acetyl-D-glucosaminidase | NAGLU (17q21.2) | 0.42–0.72 | ||||
| Type III-C | 252,930 | Acetyl-CoA-glucosaminide-N-acetyltransferase | HGSNAT (8p11.21) | 0.07–0.21 | ||||
| Type III-D | 252,940 | N-Acetylglucosaminine-6-sulphate-sulphatase | GNS (12q14.3) | 0.1 | ||||
| MPS IV (Morquio syndrome) | AR | 0.2–1.3 | − | |||||
| Type IV-A | 253,000 | Galactosamine-6-sulphate-sulphatase | GALNS (16q24.3) | 0.2–1.3 | A: Keratan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate | Elosulfase alpha | ||
| Type IV-B | 253,010 | β-galactosidase | GALNS (16q24.3) | 0.02–0.14 | B: Keratan sulfate | |||
| MPS VI (Maroteaux–Lamy syndrome) | 253,200 | Arylsulfatase B | ARSB (5q14.1) | AR | 0.36–1.3 | Dermatan sulfate, heparan sulfate | − | Galsulfase |
| MPS VII (Sly syndrome) | 253,220 | β-Glucuronidase | GUSB (7q11.21) | Automosal recessive | 0.05–0.29 | Dermatan sulfate, heparan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate | +/− | Vestronidase alpha |
| MPS IX (Hyaluronidase deficiency) | 601,492 | Hyaluronidase | Automosal recessive | <0.01 | Hyaluronan | − | NA | |
| MPS Type | Musculoskeletal Features |
|---|---|
| MPS I (Hurler, Hruler-Scheie, Scheie) | Dysostosis multiplex, short stature (disproportionate), joint contractures, carpal tunnel syndrome, trigger digits, odontoid hypoplasia, atlanto-axial instability, acetabular dysplasia, coxa valga, genu valgum |
| MPS II (Hunter) | Dysostosis multiplex, short stature (disproportionate), joint contractures, carpal tunnel syndrome, trigger digits, odontoid hypoplasia, atlanto-axial instability, acetabular dysplasia, coxa valga, genu valgum |
| MPS III (Sanfilippo) | Mild short stature and contractures (mainly elbow joint) |
| MPS IV (Morquio) | Severe skeletal dysplasia, dysostosis multiplex, short stature (disproportionate), joint hypermobility, odontoid hypoplasia, atlanto-axial instability, acetabular dysplasia, hip dislocations, coxa valga, genu valgum, pes planus, pectus carinatum |
| MPS VI (Maroteaux-Lamy) | Dysostosis multiplex, short stature (disproportionate), joint contractures, carpal tunnel syndrome, odontoid hypoplasia, atlanto-axial instability, acetabular dysplasia, coxa valga, genu valgum, trigger digits, pectus carinatum |
| MPS VII (Sly) | Dysostosis multiplex, short stature (disproportionate), joint contractures, odontoid hypoplasia, atlanto-axial instability, acetabular dysplasia, pectus carinatum |
| MPS IX (Hyaluronidase deficiency) | Short stature, periarticular soft tissue masses, nodular synovial masses, joint effusions, acetabular erosions |
| Inflammatory diseases | Inflammatory arthritis Scleroderma Dermatomyositis and polymyositis |
| Distal extremity conditions | Arthrogryposis Camptodactyly Clinodactyly Trigger finger (isolated) Carpal tunnel syndrome (isolated) |
| Osteochondrodysplasias | Epiphyseal dysplasia Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenital (including the X-linked form) Spondylometaphyseal dysplasia Dystrophic dysplasias Osteogenesis imperfecta Other dysplasias |
| Other metabolic diseases | Gaucher’s disease Fabry’s disease Pompe’s disease Rickets Hypophosphatasia Diabetic cheiroarthropathy |
| Miscellaneous | Legg-Perthes-Calvé disease Growing pains Amplified musculoskeletal pain syndrome (AMPS) Muscular dystrophy Polyneuropathy Ehler-Danlos syndrome |
| Features of Joint Involvement | MPS | JIA |
|---|---|---|
| Involved joints | DIP | PIP and MCP |
| Stiffness temporal pattern | Continuous | Morning 1 |
| Clinical signs | Stiffness and contracture 2 | Joint swelling, warmth, and tenderness |
| Inflammatory markers | Normal | Normal/raised |
| Response to anti-inflammatory drugs 3 | No | Yes |
| Neurological | ENT | GI | Cardiological | Ophthalmological | Hepato-Splenomegaly | Skin Involvement | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPS I H | Hydrocephalus Psychomotor retardation Behavior trouble Peripheral compression Atlanto-axial instability | Deafness (+++ H) Recurrent sinopulmonary infections Chronic rhinitis | Umbilical or inguinal hernias | Valve disease Cardiomyopathy Endocardial fibroelastosis Coronary heart disease | Corneal clouding Retinopathy Optical nerve compression | ++ | Thickened and rough skin texture Pebbly papules (rare) |
| MPS I S | - | - | ++ | ||||
| MPS I HS | Pachymeningitis cervicalis Typically normal intelligence | Umbilical or inguinal hernias | ++ | ||||
| MPS II | Neurocognitive decline Behavior trouble Some patients have normal intelligence | Deafness | - | Valve disease Cardiomyopathy Endocardial fibroelastosis Coronary heart disease | - | ++ | Pebbly papules |
| MPS III | Neurocognitive decline Behavior trouble Intellectual disability | Recurrent sinopulmonary infections Deafness | Umbilical or inguinal hernias | Milder forms of valve disease and Cardiomyopathy | - | + | Thickened and rough skin texture |
| MPS IV | - | Recurrent sinopulmonary infections Deafness | - | Milder forms of valve disease and Cardiomyopathy | Mild corneal opacities | + | Thickened and rough skin texture |
| MPS VI | Pachymeningitis cervicalis with normal intelligence | Recurrent sinopulmonary infections OSAS Pulmonary hypertension | - | Valve disease Cardiomyopathy Endocardial fibroelastosis Coronary heart disease | Corneal clouding | ++ | Thickened and rough skin texture |
| MPS VII | Hydrops fetalis Intellectual disability (mild or absent) | ++ | - | Milder forms of valve disease and Cardiomyopathy | Corneal clouding Retinopathy Optical nerve compression | + | Thickened and rough skin texture |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costi, S.; Caporali, R.F.; Marino, A. Mucopolysaccharidosis: What Pediatric Rheumatologists and Orthopedics Need to Know. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13010075
Costi S, Caporali RF, Marino A. Mucopolysaccharidosis: What Pediatric Rheumatologists and Orthopedics Need to Know. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(1):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13010075
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosti, Stefania, Roberto Felice Caporali, and Achille Marino. 2023. "Mucopolysaccharidosis: What Pediatric Rheumatologists and Orthopedics Need to Know" Diagnostics 13, no. 1: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13010075
APA StyleCosti, S., Caporali, R. F., & Marino, A. (2023). Mucopolysaccharidosis: What Pediatric Rheumatologists and Orthopedics Need to Know. Diagnostics, 13(1), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13010075





