Indication, Location of the Lesion, Diagnostic Yield, and Therapeutic Yield of Double-Balloon Enteroscopy: Seventeen Years of Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Endoscopy
2.3. Definitions
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients and Indications
3.2. Endoscopic Results
3.3. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Yields
3.4. The Location of Lesion and Final Diagnosis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- May, A. Double-Balloon Enteroscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 27, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akerman, P.A.; Agrawal, D.; Cantero, D.; Pangtay, J. Spiral enteroscopy with the new DSB overtube: A novel technique for deep peroral small-bowel intubation. Endoscopy 2008, 40, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baniya, R.; Upadhaya, S.; Subedi, S.C.; Khan, J.; Sharma, P.; Mohammed, T.S.; Bachuwa, G.; Jamil, L.H. Balloon enteroscopy versus spiral enteroscopy for small-bowel disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 86, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujikawa, T.; Saitoh, Y.; Andoh, A.; Imaeda, H.; Hata, K.; Minematsu, H.; Senoh, K.; Hayafuji, K.; Ogawa, A.; Nakahara, T.; et al. Novel single-balloon enteroscopy for diagnosis and treatment of the small intestine: Preliminary experiences. Endoscopy 2008, 40, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, P.; Domagk, D. Single-Balloon Enteroscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 27, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Sekine, Y.; Sato, Y.; Higashizawa, T.; Miyata, T.; Iino, S.; Ido, K.; Sugano, K. Total enteroscopy with a nonsurgical steerable double-balloon method. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2001, 53, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivano, F.H.; Villela, I.R.; Miranda, L.F.; Nakadomari, T.S. Analysis of double balloon enteroscopy: Indications, findings, therapeutic and complications. Arq. Bras. De Cir. Dig. ABCD = Braz. Arch. Dig. Surg. 2017, 30, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jang, H.J. Does Single Balloon Enteroscopy Have Similar Efficacy and Endoscopic Performance Compared with Double Balloon Enteroscopy? Gut Liver 2017, 11, 451–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Saygili, F.; Saygili, S.M.; Oztas, E. Examining the whole bowel, double balloon enteroscopy: Indications, diagnostic yield and complications. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 7, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.Y.; Lin, W.P.; Chiu, C.T. Experience of double balloon enteroscopy. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. JCMA 2018, 81, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messer, I.; May, A.; Manner, H.; Ell, C. Prospective, randomized, single-center trial comparing double-balloon enteroscopy and spiral enteroscopy in patients with suspected small-bowel disorders. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2013, 77, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, A.; Färber, M.; Aschmoneit, I.; Pohl, J.; Manner, H.; Lotterer, E.; Möschler, O.; Kunz, J.; Gossner, L.; Mönkemüller, K.; et al. Prospective multicenter trial comparing push-and-pull enteroscopy with the single- and double-balloon techniques in patients with small-bowel disorders. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Liao, Z.; Jiang, Y.P.; Li, Z.S. Indications, detectability, positive findings, total enteroscopy, and complications of diagnostic double-balloon endoscopy: A systematic review of data over the first decade of use. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 74, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.N.; Kim, E.R.; Ye, B.D.; Jang, H.J.; Jeon, S.R.; Park, S.J.; Im, J.P.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, C.H.; Choi, H.; et al. Indications, diagnostic yield, and complication rate of balloon-assisted enteroscopy (BAE) during the first decade of its use in Korea. Dig. Endosc. Off. J. Jpn. Gastroenterol. Endosc. Soc. 2016, 28, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Choi, K.Y.; Eun, C.S.; Jang, H.J.; Park, D.I.; Chang, D.K.; Kim, J.O.; Ko, B.M.; Lee, M.S.; Huh, K.C.; et al. Korean experience with double balloon endoscopy: Korean Association for the Study of Intestinal Diseases multi-center study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2007, 66, S22–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.R.; Kim, J.O.; Kim, H.G.; Lee, T.H.; Kim, W.J.; Ko, B.M.; Cho, J.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, M.S. Changes over time in indications, diagnostic yield, and clinical effects of double-balloon enteroscopy. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Correa, J.J.E.; Ramirez-Garcia, J.J.; Garcia-Contreras, L.F.; Fuentes-Orozco, C.; Irusteta-Jimenez, L.; Michel-Espinoza, L.R.; Carballo Uribe, A.S.; Torres Chavez, J.A.; Gonzalez-Ojeda, A. Double-balloon enteroscopy: Indications, approaches, diagnostic and therapeutic yield, and safety. Early experience at a single center. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2018, 83, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heine, G.D.; Hadithi, M.; Groenen, M.J.; Kuipers, E.J.; Jacobs, M.A.; Mulder, C.J. Double-balloon enteroscopy: Indications, diagnostic yield, and complications in a series of 275 patients with suspected small-bowel disease. Endoscopy 2006, 38, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baars, J.E.; Theyventhiran, R.; Aepli, P.; Saxena, P.; Kaffes, A.J. Double-balloon enteroscopy-assisted dilatation avoids surgery for small bowel strictures: A systematic review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 8073–8081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.X.; Zhang, J.; Cui, L.H.; Tian, J.J.; Wei, R. Efficacy of Therapeutic Endoscopy for Gastrointestinal Lesion (GI): A network meta-analysis. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 35, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baracat, F.; Moura, E.; Bernardo, W.; Pu, L.Z.; Mendonça, E.; Moura, D.; Baracat, R.; Ide, E. Endoscopic hemostasis for peptic ulcer bleeding: Systematic review and meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. Surg. Endosc. 2016, 30, 2155–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, A.Y.; Lee, B.J.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, S.H.; Joo, M.K.; Kim, H.J.; Park, J.J. Clinicopathological Features of Small Bowel Tumors Diagnosed by Video Capsule Endoscopy and Balloon-Assisted Enteroscopy: A Single Center Experience. Clin. Endosc. 2021, 54, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, M.; Oka, S.; Tanaka, S.; Igawa, A.; Kunihara, S.; Ueno, Y.; Ito, M.; Chayama, K. Indications for Small-bowel Capsule Endoscopy in Patients with Chronic Abdominal Pain. Intern. Med. 2017, 56, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abutalib, H.; Yano, T.; Shinozaki, S.; Lefor, A.K.; Yamamoto, H. Roles of Capsule Endoscopy and Balloon-Assisted Enteroscopy in the Optimal Management of Small Bowel Bleeding. Clin. Endosc. 2020, 53, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Chen, X.; Shi, L.; Si, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, S. Small-bowel capsule endoscopy in patients with unexplained chronic abdominal pain: A systematic review. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 81, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | n = 267 |
|---|---|
| Age, years * | 46 (33–59) |
| Female sex, n (%) | 98 (36.7) |
| History of gastrointestinal surgery †, n (%) | 26 (9.7) |
| Comorbidity, n (%) | |
| History of cancer | 10 (3.7) |
| GI cancer/Other cancer | 6/4 |
| Diabetes | 28 (10.5) |
| Hypertension | 61 (22.8) |
| Dyslipidemia | 42 (15.7) |
| Chronic kidney disease | 10 (3.7) |
| Liver cirrhosis | 13 (4.9) |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease/Asthma | 1 (0.4)/0 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis/Ankylosing spondylitis | 1 (0.4)/0 |
| Heart disease | 14 (5.2) |
| Stroke | 7 (2.6) |
| Medication, n (%) | |
| Antiplatelet agent | 21 (7.9) |
| Anticoagulant | 9 (3.4) |
| NSAIDs | 20 (7.5) |
| Oral steroid | 3 (1.1) |
| Variables | n = 267 |
|---|---|
| Indication for the test, n (%) | |
| Obscure GI bleeding | 123 (46.1) |
| Unexplained chronic abdominal pain or diarrhea | 52 (19.5) |
| Abnormal findings on diagnostic imaging | 36 (13.5) |
| Histological confirmation of suspected disease | 12 (4.5) |
| Evaluation of underlying disease | 38 (14.2) |
| Foreign body removal | 6 (2.2) |
| Examination time, min * | 55 (38–69) |
| Insertion route, n (%) | |
| Anterograde approach | 96 (36.0) |
| Retrograde approach | 114 (42.7) |
| Both mouth and anus | 57 (21.3) |
| Diagnostic yield, n (%) | 210 (78.7) |
| Frequency of diagnostic findings, n (%) | |
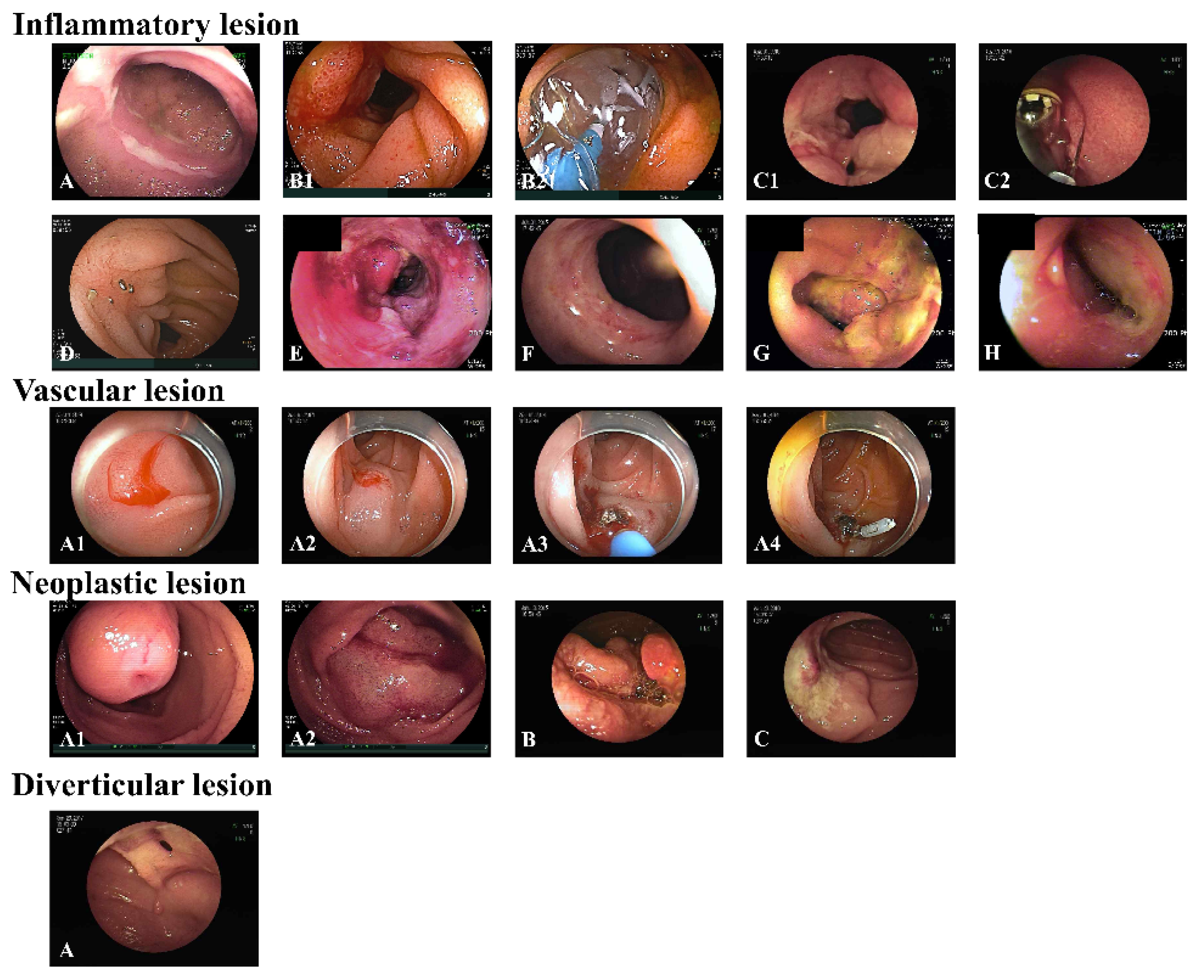
| Inflammatory lesion | 114 (42.7) |
| Vascular lesion | 19 (7.1) |
| Neoplastic lesion | 58 (21.7) |
| Diverticular lesion | 14 (5.2) |
| Foreign body | 5 (1.9) |
| Negative finding | 57 (21.3) |
| Biopsy | 113 (42.3) |
| Location of the lesion | |
| Duodenum | 12 (4.5) |
| Proximal jejunum | 43 (16.1) |
| Mid-jejunum | 27 (10.1) |
| Distal jejunum | 18 (6.7) |
| Proximal ileum | 20 (7.5) |
| Mid-ileum | 17 (6.4) |
| Distal ileum | 73 (27.3) |
| No lesion | 57 (21.3) |
| Therapeutic yield, n (%) | 66 (24.7) |
| Frequency of performed therapy, n (%) | |
| Polypectomy or endoscopic mucosal resection | 16 (6.0) |
| Argon plasma coagulation | 11 (4.1) |
| Hemoclipping | 20 (7.5) |
| Epinephrine injection | 10 (3.7) |
| Steroid injection | 1 (0.4) |
| Balloon dilatation | 6 (2.2) |
| Tattooing before surgery | 11 (4.1) |
| Foreign body removal | 6 (2.2) |
| Procedure-related complications, n (%) | 7 (2.6) |
| Bleeding/Bowel perforation/Pancreatitis | 5/1/1 |
| Procedure-related death | 0 |
| Surgery after enteroscopy, n (%) | 55 (20.6) |
| Reason for the surgery | |
| Malignancy potential | 18 |
| Small bowel stricture or obstruction | 14 |
| Persistent GI bleeding | 21 |
| Foreign body removal | 1 |
| Diagnostic evaluation | 1 |
| Referred to another hospital for surgery | 10 (3.7) |
| Variables | Positive DBE Finding (n = 210) | Negative DBE Finding (n = 57) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years * | 45 (33–59) | 50 (36–61) | 0.231 |
| ≥60 years | 48 (22.9) | 18 (31.6) | 0.225 |
| Female sex | 72 (34.3) | 26 (45.6) | 0.124 |
| Comorbidity | |||
| History of cancer | 7 (3.4) | 3 (5.3) | 0.379 |
| Diabetes | 21 (10.0) | 7 (12.3) | 0.628 |
| Hypertension | 49 (23.3) | 12 (21.1) | 0.859 |
| Dyslipidemia | 35 (16.7) | 7 (12.3) | 0.539 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 10 (4.8) | 0 | 0.126 |
| Liver cirrhosis | 8 (3.8) | 5 (8.8) | 0.159 |
| Heart disease | 13 (6.2) | 1 (1.8) | 0.314 |
| Medication | |||
| Antiplatelet agent | 15 (7.1) | 6 (10.5) | 0.409 |
| Anticoagulant | 5 (2.4) | 4 (7.0) | 0.101 |
| NSAIDs | 16 (7.6) | 4 (7.0) | 1.000 |
| Indication | |||
| Obscure GI bleeding | 84 (40.0) | 39 (68.4) | <0.001 |
| Unexplained chronic abdominal pain or diarrhea | 44 (21.0) | 8 (14.0) | 0.345 |
| Abnormal findings on diagnostic imaging | 29 (13.8) | 7 (12.3) | 1.000 |
| Histological confirmation of suspected disease | 11 (5.2) | 1 (1.8) | 0.471 |
| Evaluation of underlying disease | 37 (17.6) | 1 (1.8) | 0.001 |
| Foreign body removal | 5 (2.4) | 1 (1.8) | 1.000 |
| History of gastrointestinal surgery† | 21 (10.0) | 5 (8.8) | 1.000 |
| Procedure time, min * | 52 (36–68) | 60 (48.5–75.5) | 0.013 |
| ≥90 min | 22 (10.5) | 7 (12.3) | 0.640 |
| Endoscopic Findings and Final Diagnosis | Location of the Lesion | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duodenum, n (%) | Proximal Jejunum, n (%) | Mid-Jejunum, n (%) | Distal Jejunum, n (%) | Proximal Ileum, n (%) | Mid-Ileum, n (%) | Distal Ileum, n (%) | Total | |
| Inflammatory lesion | 2 (1.8) | 8 (7.0) | 10 (8.8) | 8 (7.0) | 14 (12.3) | 12 (10.5) | 60 (52.6) | 114 |
| Crohn’s disease | 1 (1.6) | 0 | 3 (4.8) | 4 (6.5) | 6 (9.7) | 6 (9.7) | 42 (67.7) | 62 |
| Intestinal tuberculosis | 0 | 0 | 1 (12.5) | 1 (12.5) | 2 (25) | 1 (12.5) | 3 (37.5) | 8 |
| NSAID enteropathy | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (33.3) | 2 (33.3) | 2 (33.3) | 6 |
| Behcet’s disease | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (100) | 1 |
| HS purpura | 0 | 1 (100) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Eosinophilic enteritis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (50) | 0 | 0 | 1 (50) | 2 |
| Ischemic enteritis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (33.3) | 0 | 2 (66.7) | 3 |
| CMUSE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (100) | 1 |
| Non-specific erosion or ulcer | 1 (5.9) | 4 (23.5) | 3 (17.6) | 1 (5.9) | 3 (17.6) | 1 (5.9) | 4 (23.5) | 17 |
| Stricture of unknown cause | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (100) | 2 |
| Non-specific inflammation | 0 | 3 (50) | 1 (16.7) | 1 (16.7) | 0 | 0 | 1 (16.7) | 6 |
| Anastomosis site ulcer or stricture | 0 | 0 | 2 (40) | 0 | 0 | 2 (40) | 1 (20) | 5 |
| Vascular lesion | 3 (15.8) | 5 (26.3) | 5 (26.3) | 3 (15.8) | 1 (5.3) | 1 (5.3) | 1 (5.3) | 19 |
| Angiodysplasia, AV malformation, or Dieulafoy’s lesion | 3 (17.6) | 4 (23.5) | 4 (23.5) | 3 (17.6) | 1 (5.9) | 1 (5.9) | 1 (5.9) | 17 |
| Hemangioma | 0 | 1 (50) | 1 (50) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Neoplastic lesion | 5 (8.6) | 26 (44.8) | 12 (20.7) | 5 (8.6) | 2 (3.4) | 2 (3.4) | 6 (10.3) | 58 |
| Malignant lymphoma | 0 | 1 (14.3) | 2 (28.6) | 2 (28.6) | 1 (14.3) | 0 | 1 (14.3) | 7 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 0 | 6 (85.7) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (14.3) | 7 |
| Adenomatous polyp | 0 | 1 (100) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Hyperplastic polyp | 0 | 1 (33.3) | 1 (33.3) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (33.3) | 3 |
| Hamartomatous polyp (Except PJS) | 0 | 1 (50) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (50) | 2 |
| PJS | 1 (7.7) | 8 (61.5) | 3 (23.1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (7.7) | 0 | 13 |
| GIST | 2 (28.6) | 2 (28.6) | 1 (14.3) | 1 (14.3) | 0 | 0 | 1 (14.3) | 7 |
| Leiomyoma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (100) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Lipoma | 0 | 2 (40) | 1 (20) | 0 | 1 (20) | 1 (20) | 0 | 5 |
| Ectopic pancreas | 1 (25) | 1 (25) | 1 (25) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (25) | 4 |
| Adenomyoma | 0 | 1 (100) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Brunneroma | 1 (100) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Lymphangioma or lymphangiectasia | 0 | 1 (50) | 1 (50) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Subepithelial lesion without histologic confirmation | 0 | 1 (33.3) | 2 (66.7) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Diverticular lesion | 1 (7.1) | 3 (21.4) | 0 | 0 | 2 (14.3) | 2 (14.3) | 6 (42.9) | 14 |
| Meckel’s diverticulum | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (12.5) | 2 (25) | 5 (62.5) | 8 |
| Other diverticulum | 1 (16.7) | 3 (50) | 0 | 0 | 1 (16.7) | 0 | 1 (16.7) | 6 |
| Foreign body | 1 (20) | 1 (20) | 0 | 2 (40) | 1 (20) | 0 | 0 | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.P.; Jang, H.J.; Kae, S.H.; Lee, J.G.; Kwon, J.H. Indication, Location of the Lesion, Diagnostic Yield, and Therapeutic Yield of Double-Balloon Enteroscopy: Seventeen Years of Experience. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2224. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12092224
Lee SP, Jang HJ, Kae SH, Lee JG, Kwon JH. Indication, Location of the Lesion, Diagnostic Yield, and Therapeutic Yield of Double-Balloon Enteroscopy: Seventeen Years of Experience. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(9):2224. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12092224
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sang Pyo, Hyun Joo Jang, Sea Hyub Kae, Jae Gon Lee, and Ji Hye Kwon. 2022. "Indication, Location of the Lesion, Diagnostic Yield, and Therapeutic Yield of Double-Balloon Enteroscopy: Seventeen Years of Experience" Diagnostics 12, no. 9: 2224. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12092224
APA StyleLee, S. P., Jang, H. J., Kae, S. H., Lee, J. G., & Kwon, J. H. (2022). Indication, Location of the Lesion, Diagnostic Yield, and Therapeutic Yield of Double-Balloon Enteroscopy: Seventeen Years of Experience. Diagnostics, 12(9), 2224. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12092224






