Impact of Chronic Prostatitis on the PI-RADS Score 3: Proposal for the Addition of a Novel Binary Suffix
Abstract
1. Introduction
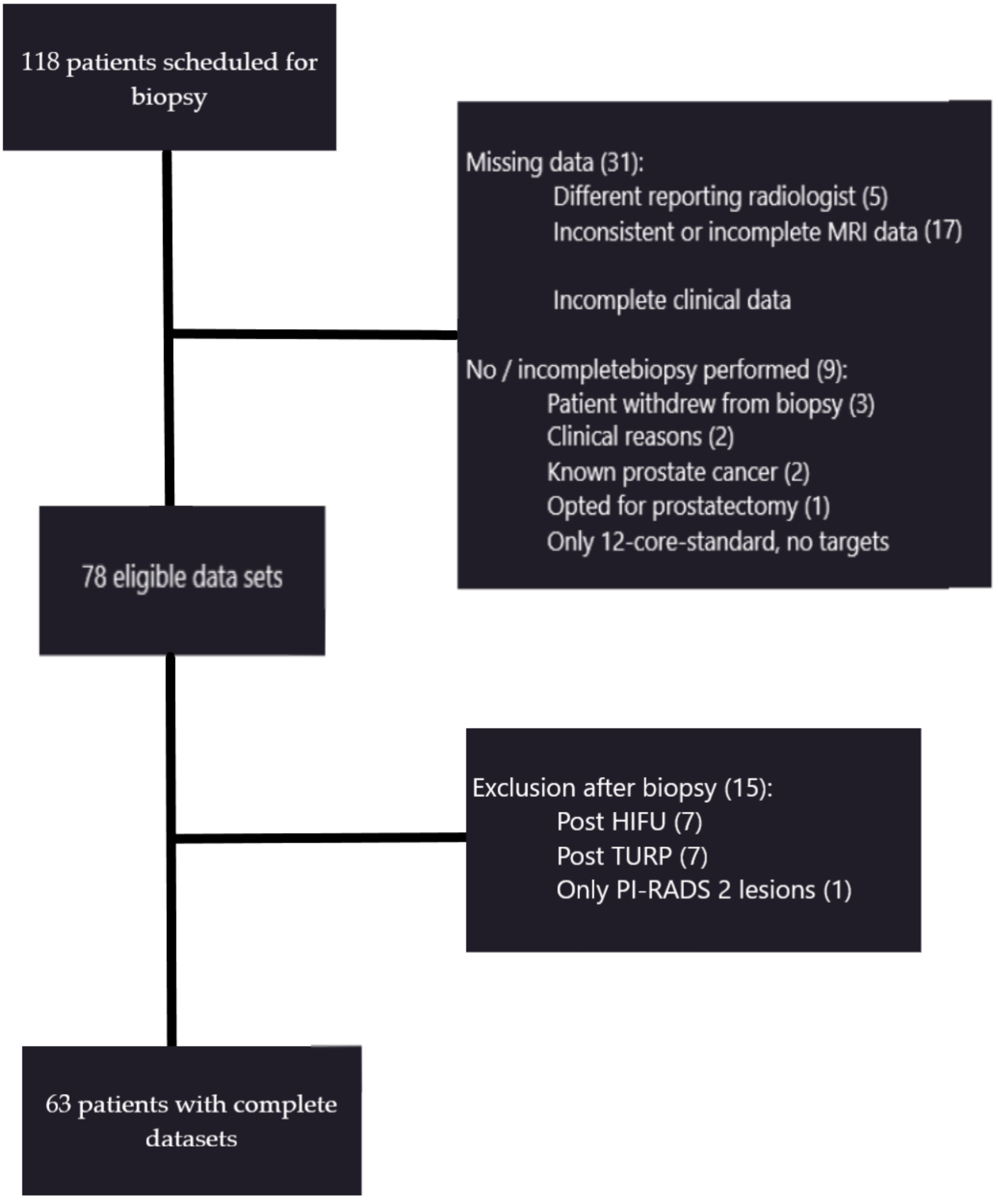
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Lesions
2.2. MRI
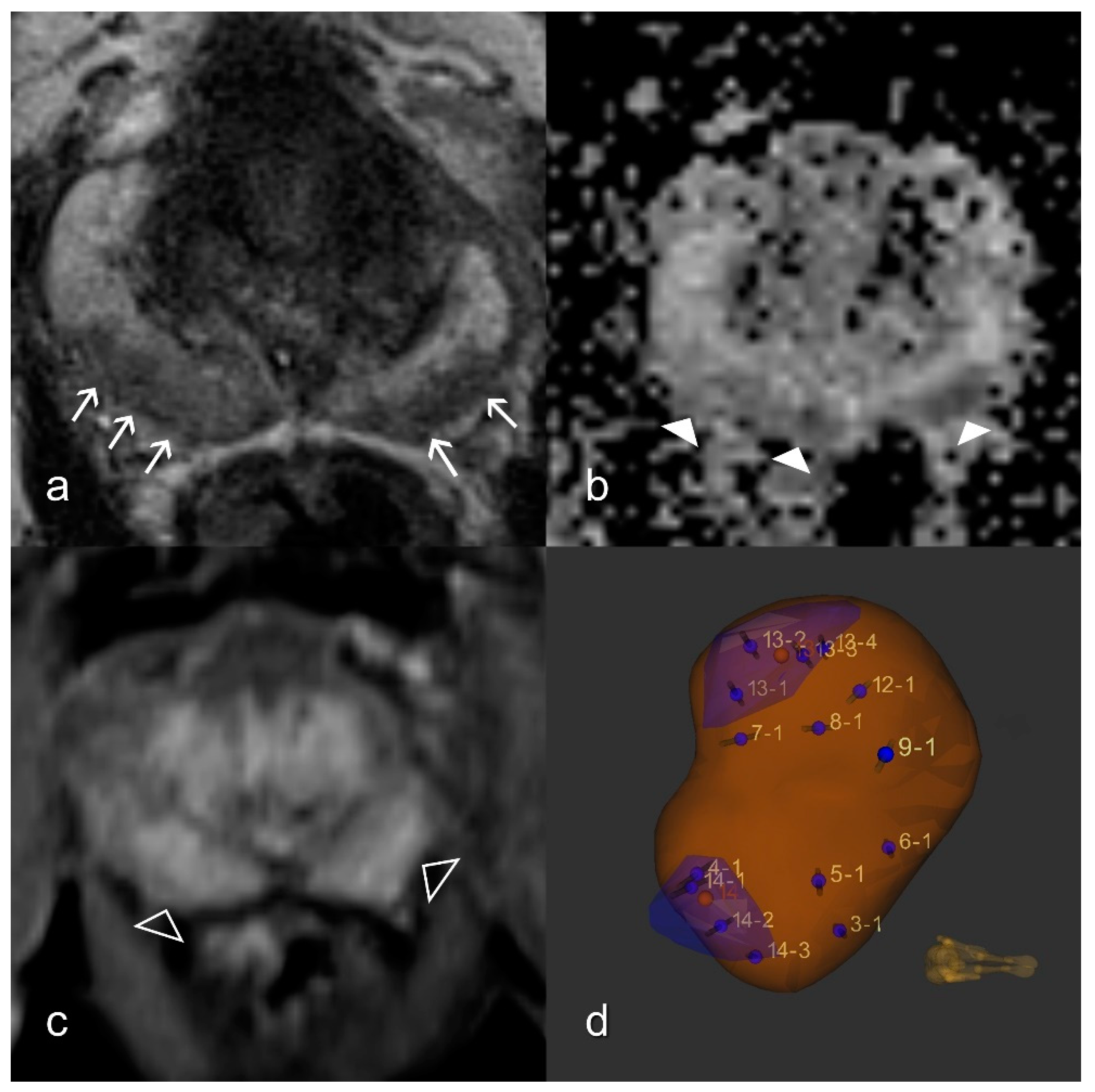
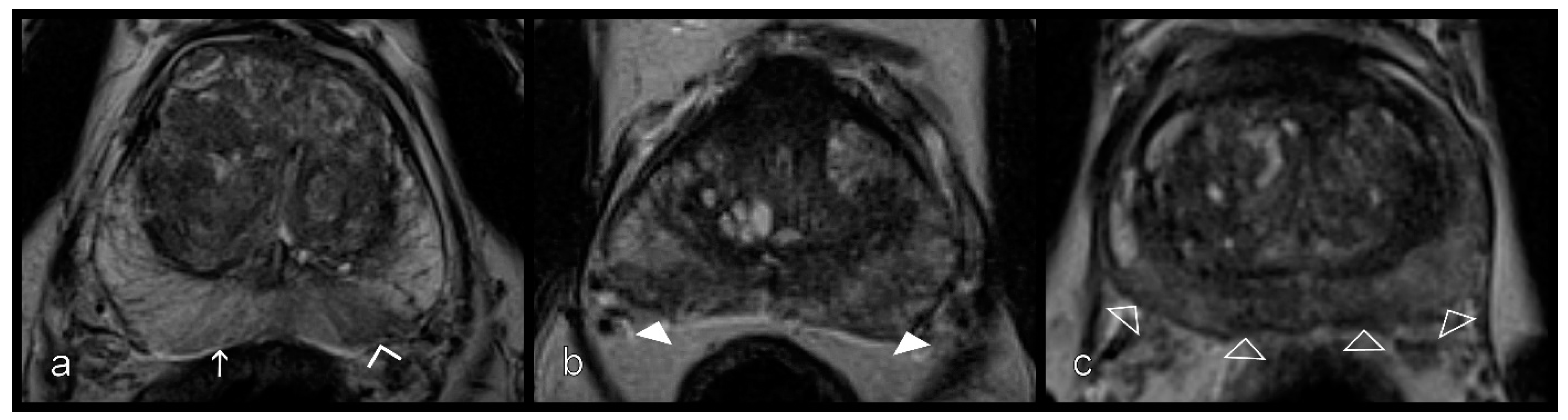
2.3. Prostatitis Assessment
2.4. DWI
2.5. DCE Analysis
2.6. MR/US Fusion-Guided Biopsy and Gold Standard
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Lesions and Histopathologic Findings
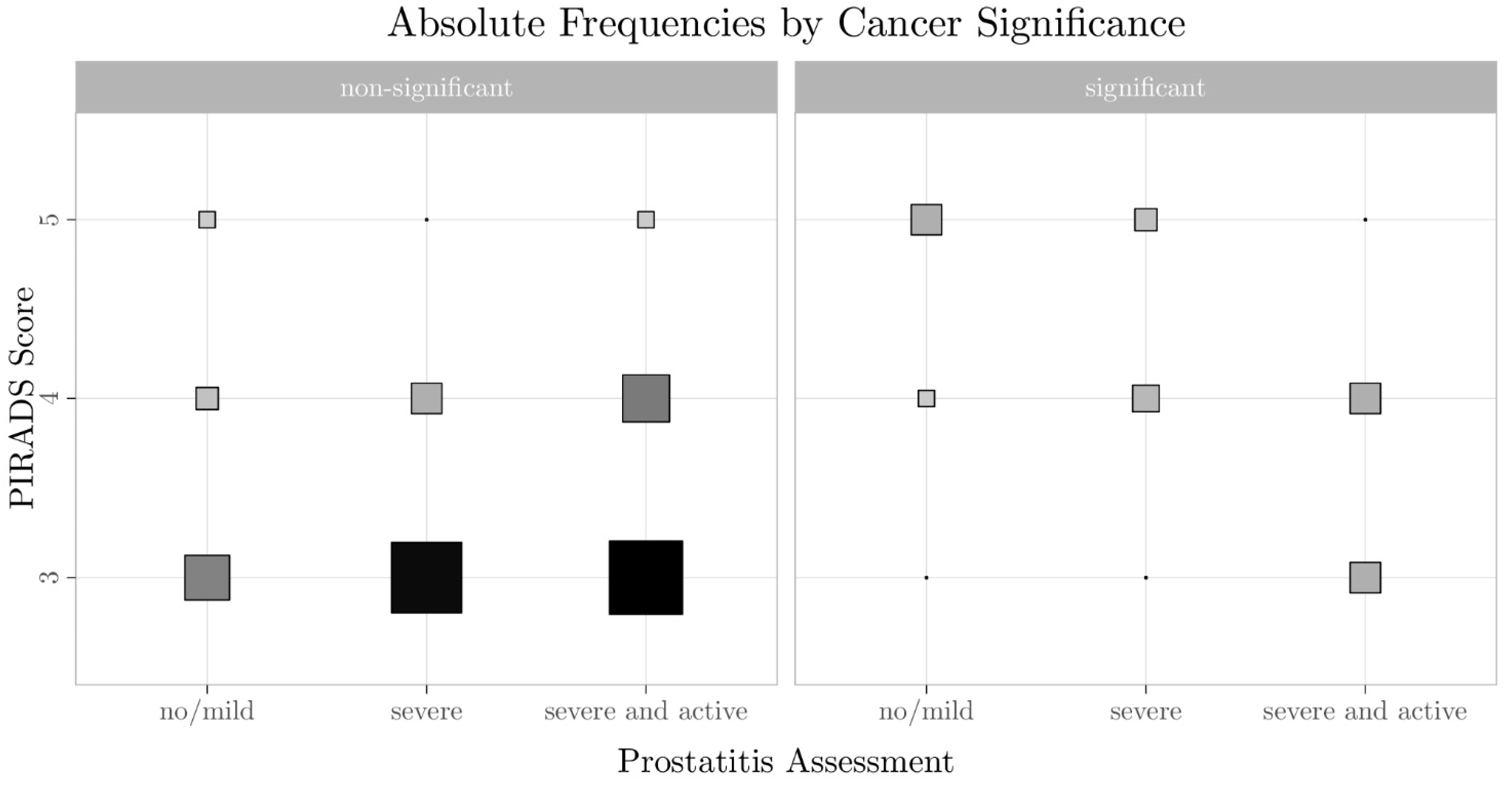
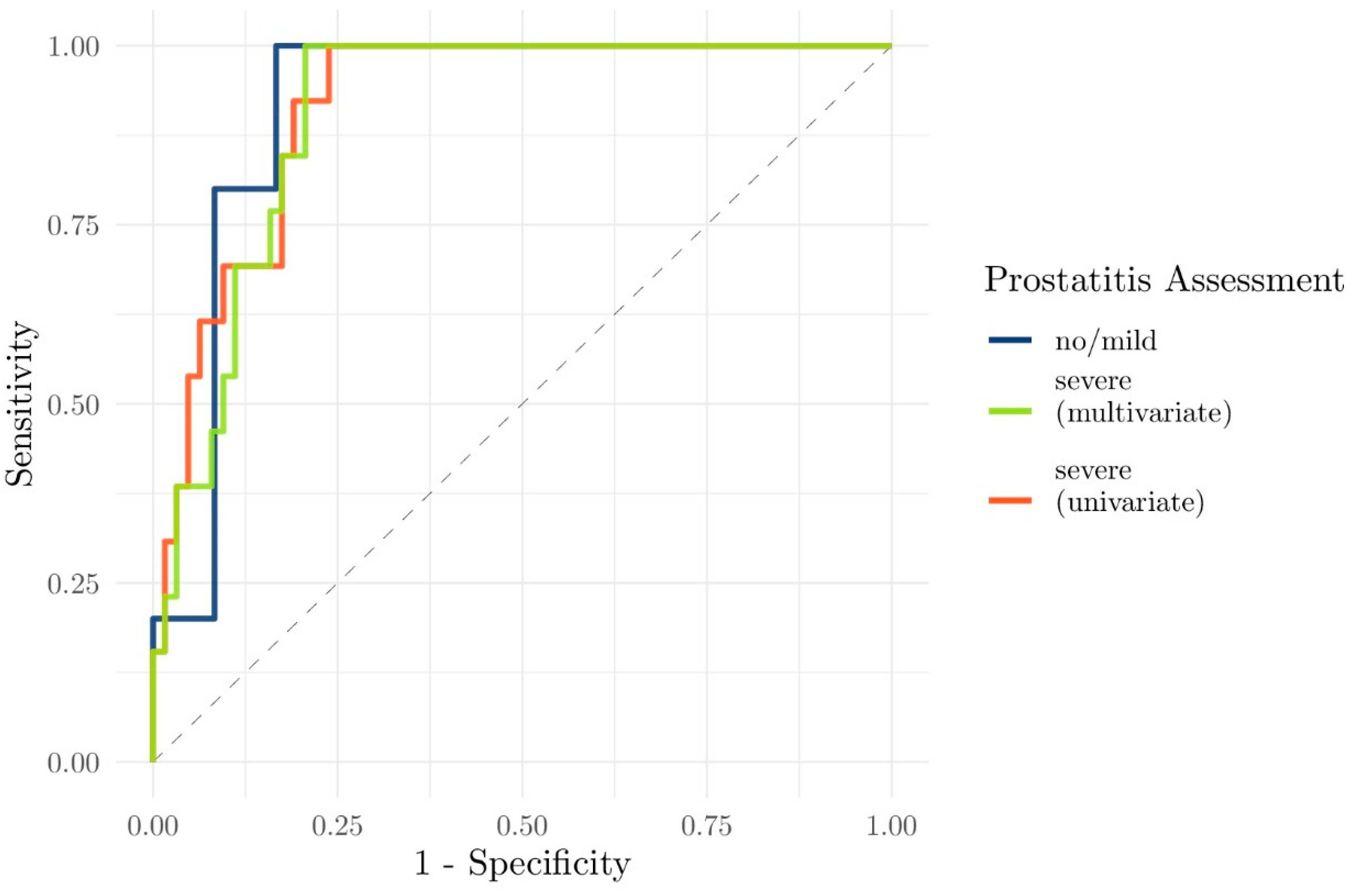
3.2. Relationship Between PI-RADS Score, csPCa, and Prostatitis
3.3. Evaluation of the Performance of Clinical and Functional Imaging Parameters to Predict csPCa
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonekamp, D.; Jacobs, M.A.; El-Khouli, R.; Stoianovici, D.; Macura, K.J. Advancements in MR imaging of the prostate: From diagnosis to interventions. RadioGraphics 2011, 31, 677–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donati, O.F.; Jung, S.I.; Vargas, H.A.; Gultekin, D.H.; Zheng, J.; Moskowitz, C.S.; Hricak, H.; Zelefsky, M.J.; Akin, O. Multiparametric prostate MR imaging with T2-weighted, diffusion-weighted, and dynamic contrast-enhanced sequences: Are all pulse sequences necessary to detect locally recurrent prostate cancer after radiation therapy? Radiology 2013, 268, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, H.U.; El-Shater Bosaily, A.; Brown, L.C.; Gabe, R.; Kaplan, R.; Parmar, M.K.; Collaco-Moraes, Y.; Ward, K.; Hindley, R.G.; Freeman, A.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of multi-parametric MRI and TRUS biopsy in prostate cancer (PROMIS): A paired validating confirmatory study. Lancet 2017, 389, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rooij, M.; Hamoen, E.H.J.; Fütterer, J.J.; Barentsz, J.O.; Rovers, M.M. Accuracy of multiparametric MRI for prostate cancer detection: A meta-analysis. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, L.; Ahmed, H.U.; Allen, C.; Barentsz, J.O.; Carey, B.; Futterer, J.J.L.; Heijmink, S.W.; Hoskin, P.J.; Kirkham, A.; Padhani, A.R.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging for the detection, localisation, and characterisation of prostate cancer: Recommendations from a European consensus meeting. Eur. Urol. 2011, 59, 477–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barentsz, J.O.; Richenberg, J.; Clements, R.; Choyke, P.; Verma, S.; Villeirs, G.; Rouviere, O.; Logager, V.; Fütterer, J.J. ESUR prostate MR guidelines 2012. Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, C.M.; Kasivisvanathan, V.; Eggener, S.; Emberton, M.; Fütterer, J.J.; Gill, I.S.; Grubb, R.L., III; Hadaschik, B.; Klotz, L.; Margolis, D.J.; et al. Standards of reporting for MRI-targeted biopsy studies (START) of the prostate: Recommendations from an international working group. Eur. Urol. 2013, 64, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Kim, S.; Lim, R.P.; Hindman, N.; Deng, F.-M.; Babb, J.S.; Taneja, S.S. Prostate cancer localization using multiparametric MR imaging: Comparison of prostate imaging reporting and data system (PI-RADS) and Likert scales. Radiology 2013, 269, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawa, S.M.; Benzon Larsen, S.; Helgstrand, J.T.; Iversen, P.; Brasso, K.; Røder, M.A. What is the risk of prostate cancer mortality following negative systematic TRUS- guided biopsies? A systematic review. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e040965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkbey, B.; Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Haider, M.A.; Padhani, A.R.; Villeirs, G.; Macura, K.J.; Tempany, C.M.; Choyke, P.L.; Cornud, F.; Margolis, D.J.; et al. Prostate imaging reporting and data system version 2.1: 2019 update of prostate imaging reporting and data system version 2. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, K.N.A.; Schouten, M.G.; Hambrock, T.; Litjens, G.J.S.; Hoeks, C.M.A.; Haken, B.T.; Barentsz, J.O.; Fütterer, J.J. Differentiation of prostatitis and prostate cancer by using diffusion-weighted MR imaging and MR-guided biopsy at 3 T. Radiology 2013, 267, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinreb, J.C.; Barentsz, J.O.; Choyke, P.L.; Cornud, F.; Haider, M.A.; Macura, K.J.; Margolis, D.; Schnall, M.D.; Shtern, F.; Tempany, C.M.; et al. PI-RADS prostate imaging—Reporting and data system: 2015, version 2. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 16–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, T.; Rajesh, A.; Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Choyke, P.L.; Turkbey, B. PI-RADS version 2.1: One small step for prostate MRI. Clin. Radiol. 2019, 74, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rourke, E.; Sunnapwar, A.; Mais, D.; Kukkar, V.; DiGiovanni, J.; Kaushik, D.; Liss, M.A. Inflammation appears as high prostate imaging—Reporting and data system scores on prostate magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) leading to false positive MRI fusion biopsy. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2019, 60, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liddell, H.; Jyoti, R.; Haxhimolla, H.Z. mp-MRI prostate characterised PIRADS 3 lesions are associated with a low risk of clinically significant prostate cancer—A retrospective review of 92 biopsied PIRADS 3 lesions. Curr. Urol. 2015, 8, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureka, B.; Elhence, P.; Khera, P.S.; Choudhary, G.R.; Pandey, H.; Garg, P.K.; Yadav, K.; Goel, A. Quantitative contrast-enhanced perfusion kinetics in multiparametric MRI in differentiating prostate cancer from chronic prostatitis: Results from a pilot study. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20190181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, A.; Karaosmanoğlu, A.D.; Karcaaltıncaba, M.; Akata, D.; Akdogan, B.; Baydar, D.E.; Ozmen, M.N. Prostatitis, the great mimicker of prostate cancer: Can we differentiate them quantitatively with multiparametric MRI? AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuenod, C.A.; Balvay, D. Perfusion and vascular permeability: Basic concepts and measurement in DCE-CT and DCE-MRI. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2013, 94, 1187–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, F.; Soliman, A.; El-Baz, A.; Abou El-Ghar, M.; El-Diasty, T.; Gimel’farb, G.; Ouseph, R.; Dwyer, A.C. Models and methods for analyzing DCE-MRI: A review. Med. Phys. 2014, 41, 124301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottet, N.; Cornford, P.; van den Bergh, R.C.N.; Briers, E. EAU Guidelines. In Proceedings of the EAU Annual Congress, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 17–21 July 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J.I.; Egevad, L.; Amin, M.B.; Delahunt, B.; Srigley, J.R.; Humphrey, P.A. The 2014 international society of urological pathology (ISUP) consensus conference on Gleason grading of prostatic carcinoma: Definition of grading patterns and proposal for a new grading system. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Hallac, R.R.; Yuan, Q.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, X.-J.; Francis, F.; Roehrborn, C.G.; Sims, R.D.; Costa, D.N.; et al. Incorporating Oxygen-Enhanced MRI into Multi-Parametric Assessment of Human Prostate Cancer. Diagnostics 2017, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assinder, S.J.; Bhoopalan, V. A Promising Future for Prostate Cancer Diagnostics. Diagnostics 2017, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Schroers, M.; Kukuk, G.; Wolter, K.; Decker, G.; Fischer, S.; Marx, C.; Traeber, F.; Sprinkart, A.M.; Block, W.; Schild, H.H.; et al. Differentiation of prostatitis and prostate cancer using the prostate imaging-reporting and data system (PI-RADS). Eur. J. Radiol. 2016, 85, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.H.; Hu, C.H.; Chen, J.X. Differentiation of prostatitis and clinically significant prostate cancer in peripheral zone using the prostate imaging-reporting and data system. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2019, 99, 2455–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, E.J.; Fiske, C.; Zagoria, R.; Westphalen, A.C. PI-RADS v2 and ADC values: Is there room for improvement? Abdom. Radiol. 2018, 43, 3109–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermie, I.; van Besien, J.; de Visschere, P.; Lumen, N.; Decaestecker, K. Which clinical and radiological characteristics can predict clinically significant prostate cancer in PI-RADS 3 lesions? A retrospective study in a high-volume academic center. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 114, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, A.T.; Fan, R.E.; Sonn, G.A.; Vasanawala, S.S.; Ghanouni, P.; Loening, A.M. How often is the Dynamic Contrast Enhanced Score Needed in PI-RADS Version 2? Curr. Probl. Diagn. Radiol. 2020, 49, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausmann, D.; Kreul, D.; Klarhöfer, M.; Nickel, D.; Grimm, R.; Kiefer, B.; Riffel, P.; Attenberger, U.I.; Zöllner, F.G.; Kubik-Huch, R.A. Morphological and functional assessment of the uterus: “one-stop shop imaging” using a compressed-sensing accelerated, free-breathing T1-VIBE sequence. Acta Radiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanec, S.H.; Bickel, H.; Wengert, G.J.; Arnoldner, M.; Clauser, P.; Susani, M.; Shariat, S.F.; Pinker, K.; Helbich, T.H.; Baltzer, P.A.T. Can the addition of clinical information improve the accuracy of PI-RADS version 2 for the diagnosis of clinically significant prostate cancer in positive MRI? Clin. Radiol. 2020, 75, 157.e1–157.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Prostatitis Grading | Mild | Severe |
|---|---|---|
| T2W | Stripes/sharp wedges | Wedges with obscured margins Patchy Diffuse |
| No/mild | Severe | |
| DCE | No Mild | Severe and early |
| PI-RADS Score | No/Discrete Prostatitis | Severe Prostatitis | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| PI-RADS 5 | 5 | 3 | 8 |
| PI-RADS 4 | 3 | 21 | 24 |
| PI-RADS 3 | 9 | 52 | 61 |
| Total | 17 | 76 | 93 |
| PI-RADS Score | Non-Significant Cancer | Significant Cancer | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No/Discrete Prostatitis | Severe Prostatitis | Severe/Active Prostatitis | No/Discrete Prostatitis | Severe Prostatitis | Severe/Active Prostatitis | |
| PI-RADS 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 0 |
| PI-RADS 4 | 2 | 4 | 10 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| PI-RADS 3 | 3 | 23 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Variable | Mean (SD) | t-Statistic | p-Value | Adj. p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADCmin | 985.3 (354.7) | 6.639 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| ADCmean | 1272.1 (309.0) | 9.346 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| ADCmax | 1539.4 (3448) | 7.205 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Kep | 0.726 (0.388) | −2.309 | 0.031 | 0.249 |
| Ktrans | 0.145 (0.099) | −1.445 | 0.166 | 1 |
| PSAvelocity | 2.778 (6.282) | −0.302 | 0.766 | 1 |
| log(PSAdensity) | −2.159 (0.769) | −2.063 | 0.053 | 0.428 |
| log(PSAlatest) | 1.878 (0.669) | −1.736 | 0.096 | 0.768 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Merat, S.; Blümlein, T.; Klarhöfer, M.; Nickel, D.; Singer, G.; Zöllner, F.G.; Schoenberg, S.O.; Kubik-Huch, R.A.; Hausmann, D.; Hefermehl, L. Impact of Chronic Prostatitis on the PI-RADS Score 3: Proposal for the Addition of a Novel Binary Suffix. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11040623
Merat S, Blümlein T, Klarhöfer M, Nickel D, Singer G, Zöllner FG, Schoenberg SO, Kubik-Huch RA, Hausmann D, Hefermehl L. Impact of Chronic Prostatitis on the PI-RADS Score 3: Proposal for the Addition of a Novel Binary Suffix. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(4):623. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11040623
Chicago/Turabian StyleMerat, Sascha, Theresa Blümlein, Markus Klarhöfer, Dominik Nickel, Gad Singer, Frank G. Zöllner, Stefan O. Schoenberg, Rahel A. Kubik-Huch, Daniel Hausmann, and Lukas Hefermehl. 2021. "Impact of Chronic Prostatitis on the PI-RADS Score 3: Proposal for the Addition of a Novel Binary Suffix" Diagnostics 11, no. 4: 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11040623
APA StyleMerat, S., Blümlein, T., Klarhöfer, M., Nickel, D., Singer, G., Zöllner, F. G., Schoenberg, S. O., Kubik-Huch, R. A., Hausmann, D., & Hefermehl, L. (2021). Impact of Chronic Prostatitis on the PI-RADS Score 3: Proposal for the Addition of a Novel Binary Suffix. Diagnostics, 11(4), 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11040623






