Error in Figure
In the original publication [1], there was a mistake in the second image of Figure 1A: “Low HMGA1 Group; High HMGA1 Group” as published. The corrected image “Low FOXM1 Group; High FOXM1 Group” appears below. The authors state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
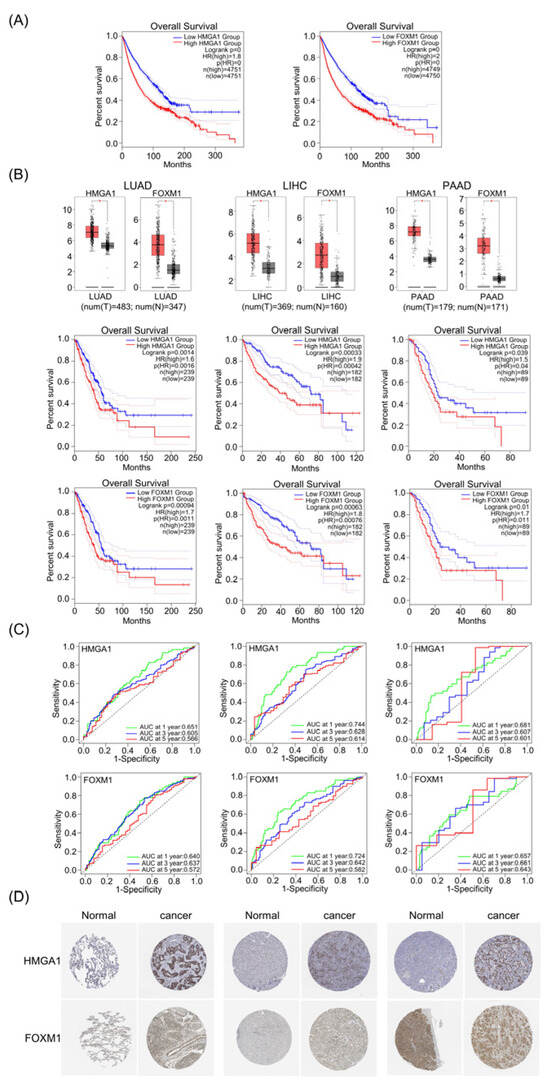
Figure 1.
HMGA1 and FOXM1 were overexpressed and negatively correlated with prognosis in LIHC, LUAD and PAAD. (A) Overall survival of HMGA1 and FOXM1 in various types of cancer by GEPIA web. (B) HMGA1 and FOXM1 expression and overall survival in LUAD, LIHC and PAAD. * indicates p < 0.05. (C) Time-dependent ROC curves of HMGA1 and FOXM1 predicted the 1-year, 3-year and 5-year survival rates of LUAD, LIHC and PAAD (significance discrimination of AUC: 0.5 < AUC < 0.6 = poor discrimination, 0.6 < AUC < 0.7 = moderate discrimination, 0.7 < AUC < 0.8 = acceptable discrimination, 0.8 < AUC < 1 = excellent discrimination). (D) The immunohistochemical images were obtained from The Human Pathology Atlas project (HPA), showing the trend of differential expression of LUAD and LIHC in normal tissues and cancer tissues.
Reference
- Zheng, Q.; Luo, Z.; Xu, M.; Ye, S.; Lei, Y.; Xi, Y. HMGA1 and FOXM1 Cooperate to Promote G2/M Cell Cycle Progression in Cancer Cells. Life 2023, 13, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).