Abstract
Continental rifts represent one of the most important settings geologically and economically. The Suez Rift represents more than 74% of the Egyptian crude oil. It represents the northern end of the Red Sea, which understanding is vital to reconstructing the tectonics, dynamics, and time–temperature history of the whole region. An effective method to reveal rift-related history is by studying its flanks, which are represented here by the Arabian-Nubian Shield Neoproterozoic basement rocks. We applied an approach integrating new fission-track thermochronology data, new time–temperature modeling, stratigraphic information, and geological knowledge, which has proven its effectiveness in such geological settings. The collected samples from the Wadi Hebran area on the eastern flank of the Suez rift showed two differentiated cooling histories: The first has a Carboniferous zircon fission-track and a Cretaceous apatite fission-track age, and the second has a Triassic zircon fission-track and an Oligocene–Miocene apatite fission-track age. The time–temperature history modeling supported four distinct cooling events activated through the Neoproterozoic post-accretion erosional event, Variscan tectonic event, Gondwana disintegration, and the Suez Rift initiation. The rock uplift that accompanied the Suez Rift reaches up to 4 km, explaining the extraordinary elevations of the Catherina region, and supports an active rift component in the southern segment of the Suez Rift eastern flank.
1. Introduction
The Suez Rift was developed during the Oligocene–Miocene as the Red Sea’s northern extension. The Red Sea/Suez Rift system is flanked by the Arabian-Nubian Shield (ANS) basement rocks, which were developed between ca. 870 Ma and 540 Ma [1,2] as part of the East African Orogeny (EAO; ca. 900–650 Ma) [3]. Despite its geological significance and hydrocarbon potentiality, the accompanying rifting processes, flank exhumation, and the role of a mantle plume are still debatable [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. The ANS Neoproterozoic basement rocks of the Suez Rift flanks enclose the entire tectonic history since development till the rifting event. An approach integrating the low-temperature thermochronometry fission-track techniques, time-temperature modeling, and stratigraphic findings has proven to be effective in studying rifted regions [11,14,15,16].
Tectonically, the ANS (Figure 1) was affected by a major post-accretion erosional event (PAEE) directly after its construction, transforming this huge mountainous range into a peneplained surface before the Cambrian [9,15,17,18]. A consequent exhumation event was triggered due to an isostatic rebound to the PAEE [5,10,16]. During the tectonically stable Lower Paleozoic era, a thick Cambrian–Carboniferous sequence was deposited [19,20], which was mainly eroded due to the rock exhumations that accompanied the Variscan Carboniferous tectonism [21]. Tectonic stability dominated the whole region between the Carboniferous and the Cretaceous [22]. Gondwana breakup interrupted this tectonic stability through doming events of the Syrian arc system [23,24,25]. The effect of this Phanerozoic tectonism was earlier suggested to be limited to northern Egypt, identifying its unstable shelf [26,27]. Yet, recent research showed that it has been extended southward [10,12,26,27,28,29]. During the Oligocene–Miocene, the Suez rifting initiated, developing a rift axis with elevated flanks [13].
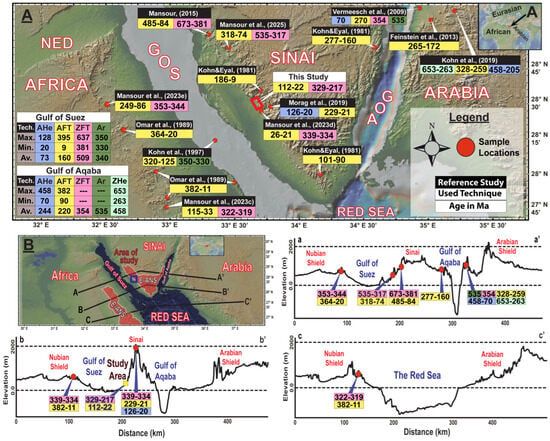
Figure 1.
(A) Simplified topographic map for the ANS in the Egyptian Eastern Desert and Sinai with the previous thermochronological studies [9]. The inset in the upper right corner outlines the area of study location between the African, Eurasian, and Arabian plates. Abbreviations used include Ar–Ar for argon–argon dating, ZFT for zircon fission-track, ZHe for zircon (U-Th)/He, AFT for apatite fission-track, and AHe for apatite (U-Th)/He methods [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,28,30,31,32]. (B) Elevation-based topographical map representing the Red Sea/Suez/Aqaba rift systems, which includes the Egyptian portion of the ANS (E-ANS), with various topographic cross-sections corresponding to thermochronological data points shown in part A. Profile aa′ traverses the Northern Eastern Desert (NED), center of the Suez Rift, north of the South Sinai, center of the Aqaba Rift, and north of the Arabian region; here the basement is located at approximately 3 km depth [33]. Profile bb′ extends through the NED, south of the Suez Rift, south of the South Sinai, south of the Aqaba Rift, and north of Arabia, showing basement depths reaching around 4 km [33]. Profile cc′ runs across the Central Eastern Desert (CED), north of the Red Sea, and the center of Arabia (modified after [9]).
Previous regional thermochronological studies concentrated mainly on the Suez Rift’s western flank and the Red Sea [5,7,10,12,13,16,20,31,32,34,35,36,37]. While fewer have studied the Suez Rift’s eastern flank [6,8,11,16,28] for accessibility issues. The reported cooling ages occupied a wide range, extending between 673 ± 76 Ma and 11 ± 2 Ma. Such contradictory data caused several doubts, including the rift type, the flanks’ exhumation patterns, the rift segmentation, and the localized signature of the regional pre-rift tectonism. An integration of fission-track techniques with the time–temperature (t–T) modelling was applied to nine representative samples that were collected from the less elevated outcrops that face the Suez Rift around the Wadi Hebran region (Figure 2). This approach could provide new insights into the aforementioned doubts, including the effects of the pre-rifting tectonism, the rifting processes, and the rifting segmentations.
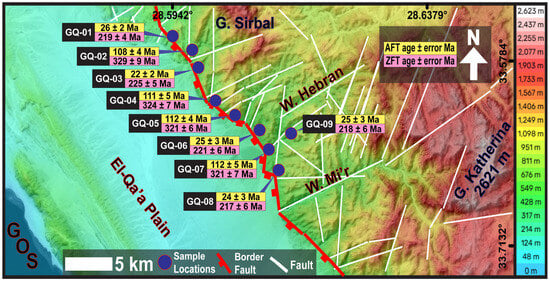
Figure 2.
Simplified topographic map outlining colored elevations above sea level and the main structural map elements for the Wadi Hebran area with sample locations, calculated cooling ages, and 1σ standard error.
2. Geological Setting
The Suez Rift extends across southern and central Sinai, which is a tectonically dynamic area where the effect of the interaction of East and West Gondwana and then the African, Eurasian, and Arabian plates is significant since the Neoproterozoic (Figure 1).
2.1. Basement Rocks
The Suez Rift’s flanks are constructed from the ANS Neoproterozoic basement rocks that represent the northern part of the EAO [2,3]. These flanks are composed of the island-arc metamorphic belts that are the earliest infrastructure rocks, formed in the region between 870 and 804 Ma [1,38,39]. The syn-orogeny granitoids represent a continuation of the compressional setting and were being formed from ca. 746 to 646 Ma [1,40,41]. The post-orogeny granitoids and dykes accompanied shifting the tectonic regime to an extensional setting during the last stage of the EAO between ca. 622 Ma and 543 Ma [1,41,42,43].
2.2. Phanerozoic Rocks
The lithostratigraphic sequence in the Suez Rift region stretches from the Cambrian to the Recent (Figure 3) and is categorized into:
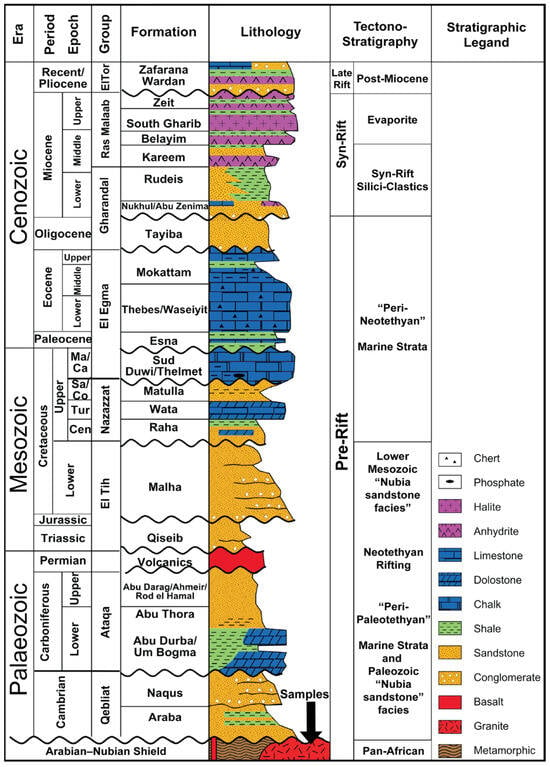
Figure 3.
Generalized lithostratigraphic and tectonostratigraphic succession of the Suez Rift area (modified after [28]).
(A) The Paleozoic succession (Figure 4), which was divided into three units that separated from the basement rocks by a major unconformity [44,45,46]; (A1) The Qebliat Group, which was constructed from cycles of Cambrian near-shore marine to fluvial sediments with ca. 130 m thickness [45,46,47]. (A2) The marine Um Bogma Formation comprises Carboniferous sandy marl, dolomite, and interbedded sandstone and silt with a thickness of ca. 225 m. Um, Bogma is separated from the Qebliat Group with a major unconformity representing the in-between hiatus [48,49]. (A3) The fluvial/shallow marine Abu Thora Formation (Carboniferous age, ~214 m thick), which is constructed from varicolored intercalations of fluvial to near-shore sandstones, shale, siltstone, and localized coal layers. The Abu Thora Formation is transected at its top by numerous basaltic sills [48,50]. The whole region was uplifted before the Permian, as supported by the absence of any related marine deposits [51,52].
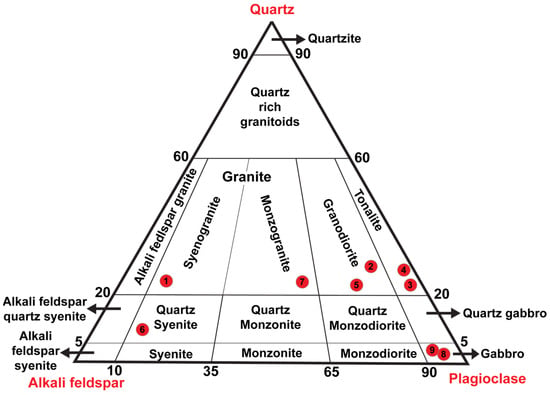
Figure 4.
Modal data plot on the IUGS quartz–alkali feldspar–plagioclase diagram of the collected samples of the study area.
(B) The Mesozoic stratigraphy of the Suez Rift region spans the Triassic to the Late Cretaceous (Figure 4) and is characterized by multiple unconformities. This succession is divided into (B1) the fluvial/paralic Qiseib Formation that comprises a Triassic erosional shale, sandstones, siltstones, and clastic carbonates at its top with a total thickness of ca. 327 m [50,53]. (B2) The fluvial Malha Formation (Lower Cretaceous age, ~149 m thick) comprises a lower Member of shale, clay, and sandstone with conglomerate, and an upper Member of tabular and cross-bedded sandstone [54,55,56]. (B3) The shallow-to-deep marine Raha and Sudr Formations (Upper Cretaceous age) represent shallow marine deposits of carbonate and clastic nature [25,57,58].
(C) The Cenozoic succession extends from the Paleocene to the Quaternary (Figure 3) and comprises (C1) the open marine Esna Formation of a Paleocene green shale with ca. 35 m thickness [51]. (C2) The shallow marine Lower Eocene Thebes and the lagoonal to subtidal Middle-Upper Eocene Mokattam Formations, which are constructed from chalky limestone interbedded by bands of flint [26,49,59]. (C3) The fluvial/shallow marine Oligocene Tayiba Formation that unconformably marks the transition from the pre-rift Eocene marine deposits to the Early Miocene rift transgression deposits with a total thickness of ca. 152 m [60]. (C4) The shallow marine Abu Zenima (Nukhul) Formation of the Lower Miocene alluvial deposits and volcanics of ca. 100 m thickness, representing the rift initiation stage that unconformably overlies the pre-rift deposits [61,62]. (C5) The deep marine Rudeis Formation of the Lower to Middle Miocene deep marine ca. 191 m deposits, resting conformably over the Abu Zenima Formation [63,64]. (C6) The deep marine to lagoonal formations of the Kareem, Belayim, South Gharib, and Zeit are characterized by their Middle to Late Miocene evaporitic sequence that is transected by shales and sandstones with a total thickness of ca. 1250 m, which conformably lie on the rocks of the Rudeis Formation [64,65,66]. (C7) The lagoonal/continental Zafarana Wardan Formation, which is represented by the Pliocene sandstone and clay streaks of ca. 120 m thickness [64,66].
2.3. Tectonic Setting
The ANS represents the northern part of the EAO that was constructed during the Neoproterozoic by collision between East and West Gondwana [3,67]. This collision developed a highly elevated mountainous range, which was entirely eroded by Cambrian time through the PAEE [15,16]. After the PAEE, the ANS was peneplained, and a Lower Paleozoic fluvial-marine succession of >2.5 km was deposited (Figure 3) [68,69].
The Variscan tectonic event occurred during the Carboniferous, when the African plate moved northward as part of the Gondwana and Laurasia collision [21,70]. Consequently, the northern African plate was influenced by enormous uplifts and erosions, which resulted in a major erosion of the Lower Paleozoic sediments [10,16,31,34,51,62,71]. Then, the initiation of Pangea rifting during the Late Triassic to Early Cretaceous caused global-scale uplifts and magmatic activities [72,73]. A consequent fragmentation of the Gondwana during the Cretaceous caused the African plate to move eastward, suturing the Eurasian plate, concluding the Tethys Paleo-Ocean [74]. This movement affected northern Africa by intense sinistral shearing, normal fault systems, restricted volcanism, intra-cratonic basin inversions, and the Syrian Arc domal structures [23,24,74,75]. Drifting of the Arabian plate from the African plate during the Oligocene–Miocene developed the Red Sea/Suez rift system by forming a diminished axis, elevated shoulders, basaltic dikes, and normal fault systems [13,76]. Lastly, the Dead Sea transform fault activated during the Miocene, developing the Aqaba Rift to act as the main regional boundary between the African and Arabian plates since the Middle Miocene [32,77].
Structurally, the Suez Rift region is described by Moustafa and Yousif [62] to be dominated by three fault sets: (1) The NNW–NW fault system that is associated with the Suez Rifting, (2) the NE fault system that pre-dates the rift (unknown age), and (3) the ENE Precambrian fault system (Figure 2).
2.4. The Reported Thermochronological Data and Problem
The published thermochronological results from the Suez Rift’s eastern flanks concentrated mainly on its northern segment, revealing non-uniform uplifts characterized by block movements across bounding faults and older cooling ages, with no rift-associated (Oligocene–Miocene) ages (Figure 1) [6,8,10,15,16,28]. While the reported data from the southern segment shows a less extended cooling history, younger cooling ages, and the Oligocene–Miocene rift-associated ages [6,7,11]. Collectively, the AFT ages revealed from the Suez Rift flanks extended from 486 ± 17 Ma to 11 ± 2 Ma [6,7,10,15,16,28,31,35,36], ZFT ages between 673 ± 76 Ma and 335 ± 10 Ma [8,9,10,15,16,28,36], and AHe ages from 125 ± 5 Ma to 19 ± 1 Ma [11].
These extended thermochronological ages of the Suez Rift flanks and the considerable controversy between data from its northern and southern segments raise questions about the rift flanks’ response to the pre-rift tectonic events and the syn-rifting processes. Taking into account the current topography of the ANS that surrounds the Suez Rift, it has modest altitudes (<1 km), except for the Katherina complex (Figure 2).
3. Materials and Methods
Fission-track (FT) thermochronology is a radiometric dating method that relies on detecting and analyzing microscopic damage trails formed in mineral crystals due to the spontaneous fission of uranium-238. These damage trails, known as fission tracks, are produced as a result of high-energy fragments emitted during the fission process and can be revealed through chemical etching [78]. By counting these tracks (which represent the decay products) and measuring the uranium content (the parent isotope), we can determine the time since the mineral cooled below a certain temperature threshold, known as the closure temperature. This temperature defines the upper boundary of the partial annealing zone (PAZ), a temperature range over which tracks are progressively shortened by a range of rates from ~0.5 to ~0.9 of the initial length with respect to time and temperature, depending on the mineral type [79,80]. We calculate the FT age based on the U concentration as the parent isotope and the count of tracks as the daughter products; therefore, as the number of tracks does not reduce in the PAZ, the upper limit of the PAZ is considered as the Tc when the FT age starts to clock. The lengths of tracks are affected by the time and temperature within the PAZ; therefore, these lengths are being used to reconstruct the time-temperature history [79,81]. For apatite, the PAZ lies between approximately 60 and 110 °C [82,83], while for zircon, it spans from 180 to 240 °C [84,85]. We apply this zircon PAZ despite the fact that a wider PAZ has also been concluded [86]. This is because we believe that the field-based estimates [84,85,87] are more reliable than the laboratory-based estimates [86], as our zircons were collected from the field under similar conditions, history, and variables. Additionally, Yamada et al. [86] also evaluated both parallel and fanning curvilinear models; however, they were unable to achieve convergence with the fanning model, while the parallel model was ultimately dismissed due to inconsistencies with geological evidence [79].
The sensitivity of fission tracks to thermal conditions makes FT analysis a valuable tool for reconstructing time–temperature (t–T) histories using software such as HeFTy v.2.1.7 [88].
In this research, samples were systematically collected from across the Wadi Hebran region, situated along the Suez Rift’s eastern flank, parallel to its shoreline (Figure 2). An approach includes ZFT and AFT dating, and t–T modeling was applied on nine representative samples of the ANS Neoproterozoic basement rocks (Table 1). The collected samples represent the root of the ANS outcrops (the most recent exhumed part), which encompasses the effect of the last tectonic event (i.e., the Suez rifting) [15,28].

Table 1.
Summary of sample localities and age results.
The collected granitoids and metamorphosed granitic samples were plotted on the IUGS quartz (Q)-alkali feldspar (A)-plagioclase (P) diagram for plutonic rocks (Figure 4). Samples are plotted on the corresponding fields based on the apparent QAP percentage in hand specimens (Figure 4).
Apatite and zircon crystals were separated from rock samples through standard mineral separation procedures, including crushing, sieving, magnetic separation using a Frantz magnetic separator (S.G. Frantz Co., Inc., Tullytown, PA, USA), and the application of heavy liquids [81]. These steps were carried out in the mineral separation facility at Port Said University, Egypt. At Kanazawa University in Japan, approximately 100 individual grains of zircon and apatite were manually selected from each sample under a stereoscopic microscope (Nikon Solutions Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), aligning the grains with their crystallographic c-axes. Apatite grains were embedded in EpoFix resin within circular plastic holders of 2.5 cm diameter, while zircon grains were mounted in thermal-resistant Teflon. Both sets of mounts were polished to expose internal surfaces suitable for fission track analysis (4π geometry). For revealing spontaneous fission tracks, apatite was etched using 5.5 M nitric acid (HNO3) at a temperature of 21 ± 1 °C for 20 s [81]. Zircon etching involved immersion in a eutectic mixture of NaOH and KOH at 220 ± 5 °C [84] for durations ranging from 60 to 210 min.
Fission track (FT) counting and horizontal confined track (HCT) length measurements were performed using a Nikon Eclipse 80i microscope (Nikon Solutions Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) equipped with a high-resolution digital camera, image analysis software, and dry objectives. For each analyzed apatite grain, the etch pit (Dpar) value was also measured as an indicator of track annealing kinetics [81,90].
Uranium isotopic concentrations were determined via laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) at Kanazawa University. Using a MicroLas GeoLas Q plus 193 nm (Excimer ArF) laser ablation system (Microlas, Göttingen, Germany) attached to an Agilent 7500s ICP-MS instrument (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA). The laser spot was 20 μm in diameter, the repetition rate was 5 Hz, and the energy density was about 8 J/cm2. Operational details followed the methodology outlined by Tamura et al. [91]. Each analysis point was evaluated in real time to ensure data quality by avoiding inclusions, zonation, or significant fractionation. Background-corrected intensity values were used to calculate uranium concentrations. External standards, such as NIST glass, were employed for calibration to minimize instrument bias and laser-induced elemental fractionation. For apatite, U concentrations were referenced against the SRM 610 [92] silicate glass standard (U-238 = 456 ppm), using calcium-43 as an internal standard and previously published compositional data [93,94]. In the case of zircon, silicon-29 was used as the internal standard, with normalization based on established zircon geochemistry [85,95].
The obtained FT cooling ages are reported as central values with associated 1-σ uncertainty, calculated by the IsoplotR code (https://www.ucl.ac.uk/~ucfbpve/isoplotr/home/, accessed on 15 June 2025) [89].
Thermal history models were constructed using HeFTy version 2.1.7 [88], which uses a 20 °C surface temperature and 50 °C/km geothermal gradients for time-depth model reconstruction. This geothermal gradient is double the current gradient, which is expected during tectonically active periods [32,37,96]. Single-grain AFT ages, c-axes corrected HCTs, and Dpar measurements were used as input data along with the multi-kinetic model of tracks annealing of Ketcham et al. [97]. The t–T constraints that were used to guide the inverse modeling are a deep initial Neoproterozoic (formation age [1,41]) to start the history of these plutonic rocks from depth, followed by a near-surface, as indicated by erosion of the ANS before the Cambrian, ZFT age-based, and AFT age-based (Table 2). The FT community is divided into two groups about using AFT constraint during modeling. One group supports its removal because the AFT parameters are already used as input data. The other group, which we belong to, supports AFT constraint usage because our measured data are more trustworthy than the modelling, and if any differences between the measured ages and the models exist, the measured data are the most trustworthy every time. Therefore, we use the AFT constraints to guide the t–T paths, and if these paths do not follow the measured AFT ages, then the model is not correct. Before running the inverse modeling, an initial forward model with an excellent fit to the inputted thermochronological data were constructed to test the behavior of the inverse t–T paths with a high degree of freedom.

Table 2.
Specifications of the constraints used for T-t modeling.
4. Results
The analyzed samples represent the different rock units and structural blocks on the southern segment of the Suez Rift’s eastern shoulder (Figure 2). The collected samples belong to the basement rocks of the ANS with formation ages between the Tonian and the Ediacaran (Table 1). The Chi-square (χ2) statistical test for homogeneity within one-age population was passed by all samples with values between 4.8 and 47.4 (Table 3 and Table 4).

Table 3.
Zircon fission-track analyzed samples data, descriptions, and central ages.

Table 4.
Apatite fission-track analyzed samples data, descriptions, and central ages.
4.1. ZFT Results
The uranium-238 concentrations in the treated samples varied between 471 and 213 μg/g (Table 3). However, no consistent relationship was observed between ZFT single-grain ages and uranium content (Figure 5). The calculated ZFT central ages, along with their respective standard errors, spanned from 329 ± 9 Ma to 217 ± 6 Ma (Figure 2), grouping clearly into two distinct age clusters (Table 3).
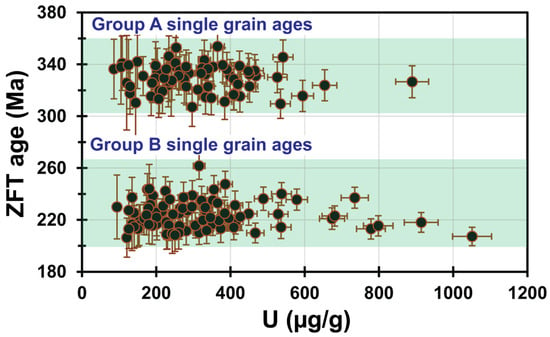
Figure 5.
A scatter plot comparing ZFT ages with corresponding uranium concentrations, where each dot denotes an individual grain, reveals no consistent pattern. This lack of correlation suggests that metamictization has not significantly influenced the ZFT results.
The older age cluster, designated as Group A, includes samples GQ-02, GQ-04, GQ-05, and GQ-07. These samples recorded ZFT cooling ages ranging between 329 ± 9 Ma and 321 ± 6 Ma. Despite covering a time interval of roughly eight million years, the ages in this group overlap within analytical uncertainties, yielding a mean ZFT age of 324 ± 7 Ma (Table 3; Figure 2).
The younger cluster, designated as Group B, includes samples GQ-01, GQ-03, GQ-06, GQ-08, and GQ-09. These samples show ZFT ages ranging from 225 ± 5 Ma to 217 ± 6 Ma (Table 3; Figure 2). This age span covers an interval of about eight million years, yet demonstrates overlap within the margin of error. The average cooling age for this younger group is calculated at 220 ± 5 Ma (Table 3).
4.2. AFT Results
The AFT cooling ages from the analyzed samples span a broad range, from 112 ± 4 Ma to 22 ± 2 Ma. These ages can be clearly grouped into two distinct temporal populations (Table 4). Group A includes four samples, all of which yielded Early Cretaceous (Albian) cooling ages between 112 ± 4 Ma and 108 ± 4 Ma (Table 4; Figure 2), averaging approximately 111 ± 5 Ma. In contrast, Group B comprises the remaining five samples, which exhibit Oligocene–Miocene cooling ages ranging from 26 ± 2 Ma to 22 ± 2 Ma (Table 4; Figure 2), with a calculated mean age of 24 ± 3 Ma.
The horizontal confined track lengths (HCTL) across all samples varied between 13.5 ± 1.3 μm and 11.3 ± 2.0 μm, while the corresponding c-axis corrected track lengths (Lc) ranged from 14.4 ± 0.8 μm to 12.8 ± 1.0 μm (Table 5). A total of 2605 Dpar values were measured, falling within the range of 1.6 ± 0.1 μm and 1.4 ± 0.1 μm (Table 5). These Dpar values showed no consistent trend compared to the AFT ages (Figure 6), suggesting minimal influence of apatite chemistry on the age data.

Table 5.
Comprehensive measurements of the horizontal confined tracks in apatite and corresponding Dpar values.
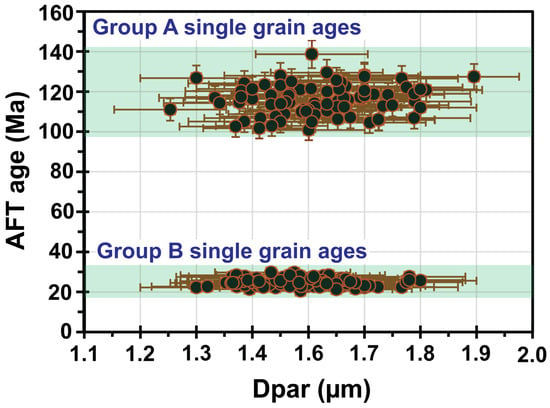
Figure 6.
The Dpar versus AFT age plot shows no notable variation in AFT ages relative to changes in Dpar values, suggesting that differences in apatite chemical composition did not significantly impact the resulting AFT ages.
4.3. Time–Temperature History Reconstruction
The time–temperature (t–T) modeling was performed using the HeFTy software v.2.1.7 [88], which relies on user-defined time–thermal constraint boxes to direct the Monte Carlo simulations. In this study, constraint boxes were formulated according to the measured ZFT and AFT cooling ages, in combination with the regionally recognized post-ANS erosional event (PAEE). The PAEE caused the near-complete denudation of the ANS high topography before the close of the Cambrian [15,27]. The temporal width of each constraint was adjusted in line with the observed cooling ages and their associated uncertainties. The quality and resolution of the t–T models strongly depend on the number of HCT length measurements (Table 5).
The t–T models for the older group reveal a broadly consistent thermal history (Figure 7). During the Neoproterozoic Era, all the tested samples underwent a fast initial cooling, suggesting initial uplift and exhumation of the plutonic rocks studied toward the Earth’s surface. This was followed by a potential reheating phase, likely due to burial beneath the Lower Paleozoic sediments, which persisted through the Devonian–Carboniferous (Figure 7). A subsequent rapid cooling event during the Jurassic–Cretaceous caused further exhumation, bringing the samples into the PAZ of the AFT technique. Following this phase, the region experienced a limited interval of slow cooling, followed by a rapid cooling event representing the final exhumation to present-day elevations during the Oligocene–Miocene.
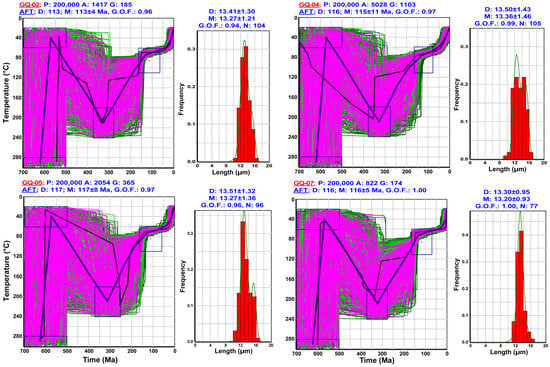
Figure 7.
The reconstructed thermal history for the older AFT age group reveals distinct cooling episodes through the Neoproterozoic–Cambrian, Devonian–Carboniferous, Cretaceous, and Oligocene–Miocene periods. These models were generated using the HeFTy software v.2.1.7 [83], based on inverse modeling approaches. The resulting t–T paths are categorized by fit quality: Green paths indicate acceptable fits, purple paths denote good fits, the black path represents the best-fit model, and the blue path shows the weighted mean path [83,98]. Model output details include P—the total number of inverse modeling iterations; A—the count of acceptable fit paths; G—the number of good fit paths; D—modeled AFT pooled ages and confined track lengths with 1σ uncertainties; M—measured AFT pooled ages and HCTLs; G.O.F.—the goodness-of-fit metric; and N—the number of single-grain ages and track length measurements used in the model.
The younger age group sample models suggest a similar cooling history with a limited response to the Jurassic–Cretaceous cooling event and, therefore, exhumation from temperatures higher than the PAZ of the AFT technique (Figure 8).
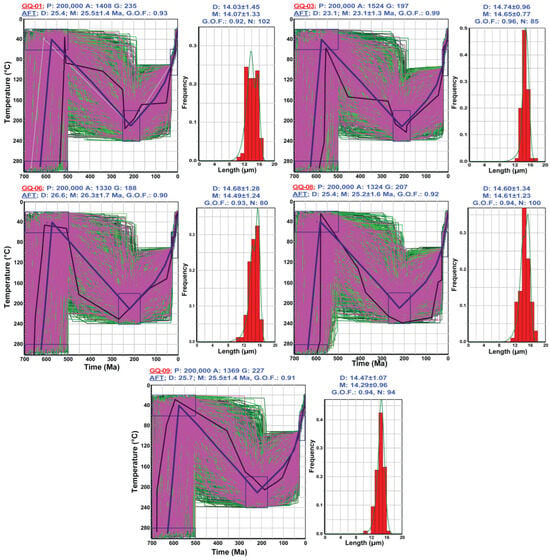
Figure 8.
The reconstructed thermal history for samples of the younger AFT age group. For more details, see Figure 7.
The pronounced PAEE led to the complete removal of the exposed ANS basement rocks by the end of the Cambrian [27,34]. However, whether the currently exposed rocks were exposed at the surface or remained buried at shallower depths during the Cambrian period remains unclear. We tested both possibilities by limiting the temperature zone of the PAEE constraint to the surface temperatures and extending it to other samples. The t–T models, unfortunately, could not provide conclusive evidence for either scenario (Figure 7 and Figure 8).
5. Discussion and Interpretation
The Chi-square (χ2) values that were calculated for all analyzed samples ranged between 4.8 and 47.4, confirming that each sample comprises a single statistically coherent age population (Table 3 and Table 4) with an absence of any overdispersion or underdispersion [80]. The thermal–tectonic evolution of the Wadi Hebran area reflects differential uplift during the Carboniferous and Cretaceous tectonism. This style of segmented uplift across fault-bounded blocks is consistent with deformation patterns observed in other parts of the Arabian-Nubian Shield [6,9,12,16,32,35,37,99]. Nonetheless, pinpointing the specific fault systems responsible for such localized exhumation remains challenging due to their subtle or obscured surface expressions. The possibility of the hydrothermal solutions’ differential effect is eliminated as an interpretation for the cooling age differentiation, as we collected our samples far enough from the fault zone or any contact surface that might alter our cooling ages.
The integration of fission-track data with t–T models indicate multiple episodes of rapid cooling, likely corresponding to distinct phases of exhumation during the Cambrian, Devonian–Carboniferous, Jurassic–Cretaceous, and Oligocene–Miocene. These thermal events align with frequently reported tectonic activities [16,37,71,100] and shifts observed in the region’s stratigraphic depositional history.
5.1. ZFT Data
The ZFT cooling ages from the analyzed samples fall into two distinct age clusters, centered around 324 ± 7 Ma and 220 ± 5 Ma, respectively (Table 3). The potential influence of metamictization was not found, as no significant relationship was observed between uranium-238 concentrations and ZFT cooling ages (Figure 5). This lack of relationship indicates that neither the chemical composition of the treated zircons nor the damage to the crystal lattice from radiation had a discernible impact on the resulting cooling ages [79,84,101].
In the older ZFT age group (Table 3; group A), ages range from 329 ± 9 Ma to 321 ± 6 Ma, consistent with previously published ZFT and ZHe results obtained from different regions across the ANS [7,9,20,32,34]. These ages were interpreted as a consequence of tectonically induced uplift during the Devonian–Carboniferous period, associated with the broader Variscan orogenic activity [7,9,15,16,20,32,34]. This uplift is supported by a marked shift in the depositional environment, transitioning from Early Carboniferous marine settings to dominantly erosional conditions in the Late Carboniferous (Figure 3). It also aligns with stratigraphic records indicating that a substantial portion (>2.5 km) of the Lower Paleozoic sedimentary cover was once present in the region [20,68].
In the younger ZFT age group (Table 3; group B), ages range from 225 ± 5 Ma to 217 ± 6 Ma (Table 1). These ages are consistent with previously published ZFT and ZHe results obtained from different regions across the ANS [7,9,15,16,20,32,34] and are attributed to tectonically driven uplifts and volcanic activities, accompanied by the initiation of Pangea rifting during the Late Triassic to Early Cretaceous [34,72,73,102]. This phase of exhumation is also associated with regionally observed unconformities and the Permian basalt flow, both of which suggest the occurrence of a significant uplift and associated thermal event during that time (Figure 3).
5.2. AFT Data
The resulting AFT ages can be classified into two distinct age clusters spanning around 112 ± 4 Ma and 22 ± 2 Ma (Table 4; Figure 2). This division reflects contrasting tectonic and thermal evolution pathways across the sampled region, which is driven by local movements of blocks through their bounding faults [6,9,10,12,16,32,35,37]. The lack of a consistent correlation between Dpar values and AFT ages (Figure 6) implies that variations in apatite chemistry had no significant influence on the derived cooling ages [79,81,98,103].
The older AFT group (Table 4; group A), ages ranging between ca. 112 and 108 Ma, was synchronous with a transition in the depositional setting from the marine Wata Formation to the continental Matulla Formation (Figure 3). This synchronicity points to a likely regional uplift event. Comparable AFT cooling ages have also been documented in other sectors of the ANS [5,9,10,11,12,15,16,34,37]. These AFT thermochronological ages represent the effect of the closure of the Tethys on the studied region.
The younger AFT (Table 4; group B), ages ranging between ca. 26 and 22 Ma, dates the rifting event of the Red Sea/Suez rift and the accompanying rift flanks uplift. Similar cooling ages were reported in the Suez Rift region exclusively from the southern segment of the rift’s eastern flank [6,7,11], while the other parts of the rift shoulders show older ages [12,15,28,35,36,37]. These ages indicate rock exhumations from depths of higher temperatures than ca. 110 °C in response to the Suez Rifting processes.
The yielded Dpar values, which fall within the range of 1.6 ± 0.1 μm to 1.4 ± 0.1 μm (Table 5), are characteristic of fluorapatite-dominated compositions. The lack of any observable correlation between Dpar values and AFT ages suggests that the chemical characteristics of the apatite had no discernible impact on the resulting cooling ages (Figure 6).
5.3. Thermal-Tectonic History Reconstruction
The t–T modeling showed two possible scenarios: One for samples of each age group. All group A samples presented an identical t–T history characterized by four major cooling events (Figure 7). These cooling phases can be interpreted as episodes of rock exhumation, particularly when considered in conjunction with the obtained cooling ages, recognized geological processes, and sedimentological evidence. These cooling/uplifting pulses were developed as a response to four tectonic events: (1) A Neoproterozoic-Cambrian event supported by the well-documented PAEE and the fluvio-marine nature of the Cambrian sedimentological sequence. (2) A significant Devonian–Carboniferous tectonic event (Figure 8), substantiated by the older ZFT age group (Table 3). These ages align with the broader Variscan orogeny [21], which caused regional uplifts and a pronounced shift in depositional regimes, transitioning from marine sedimentation during the Early Carboniferous to predominantly erosional deposits in the Late Carboniferous (Figure 3). (3) The Cretaceous tectonic event (Figure 7), indicated by both the younger ZFT and older AFT age groups, is most likely linked to the rifting associated with the opening of the Mid-Atlantic Ocean. This tectonic process drove the eastward drift of the African plate, prompting localized uplift and exhumation, particularly along the northern margin of Africa and in the Gulf of Suez [10,16,25]. Additional geological evidence, such as widespread stratigraphic hiatuses, the dominance of erosional deposits (Figure 3), and the development of tectonically induced strike-slip faulting during this period, supports this interpretation [5,34]. (4) The Oligocene–Miocene rifting of the northern Red Sea and Suez region represents a later exhumation phase (Figure 7). This stage is associated with the uplift of rift shoulders from the PAZ of the AFT and is further supported by the lack of complete thermal resetting in the older AFT age group during this period.
All samples within Group B exhibited a consistent thermal evolution marked by three distinct episodes of accelerated cooling, indicating a shared tectono-thermal history across the group (Figure 8). These are similar to those of group A samples, with a limited effect of both the Carboniferous and Cretaceous tectonic events (Figure 7). This indicates blocks’ differential uplifts in response to these tectonic activities, as previously reported. Instead, group B samples were pronouncedly exhumed during the Suez Rift initiation from depths equivalent to temperatures of the AFT total annealing zone (>110 °C; Figure 8), as supported by the reset of the AFT of the younger age group to the Oligocene–Miocene time.
5.4. Geological Implications
The integration of the thermochronological data with the t–T models highlighted distinct phases of rapid cooling and exhumation that correspond well with recognized regional tectonic events and transitions in the stratigraphic record. These events include significant exhumation episodes during the Cambrian, Devonian/Carboniferous, Cretaceous, and Oligocene/Miocene periods. The uplifting value is calculated using HeFTy v.2.1.7 using 20 °C surface temperature and 50 °C/km geothermal gradients for time-depth models reconstruction. This geothermal gradient is double the current gradient, which is expected during tectonically active periods [32,37,96].
Together, the thermochronological ages, modeled temperature–time paths, and established geological context point to four principal cooling pulses, the earliest of which occurred during the Neoproterozoic/Cambrian transition, where the PAEE was initiated following significant continental crustal thickening and widespread plutonic intrusions associated with the EAO. The PAEE triggered isostatic uplift, leading to regional exhumation processes that brought the presently exposed rock units to shallower depths between ca. 0.8 and 2 km from the surface (Figure 9). Then, these rocks were overlain by a sedimentary sequence of Lower Paleozoic age of more than 2.5 km thickness to reach depths of ca. 3.2–5.5 km (Figure 9).
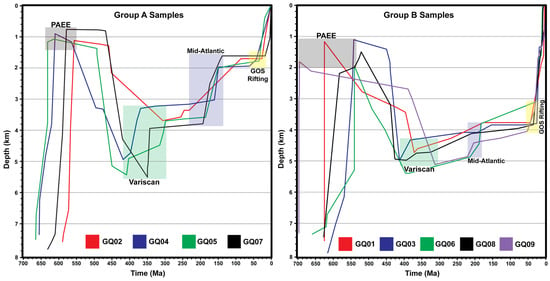
Figure 9.
Time-depth history reconstruction for the studied samples shows the exhumation history and responses to the different tectonic events.
During the Devonian–Carboniferous period, the region experienced significant rock exhumation associated with the Variscan orogenic event. This tectonic phase likely triggered uplifting of ca. 2–2.5 km for group A samples and much less for group B samples (Figure 9), and a later erosional process contributed to the removal of the Lower Paleozoic succession. During the Permian, the region witnessed limited volcanic activity, which was subsequently followed by the deposition of erosional deposits spanning the Triassic/Jurassic periods (Figure 3).
During the Cretaceous, the initiation of the Mid-Atlantic Ocean significantly influenced the area, leading to localized uplift events that mainly affected the blocks of group A samples, raising them to a depth of ca. 1.5–2 km. While blocks of group B samples experienced limited uplifts to reach a depth of ca. 3.8–4.8 km (Figure 9).
Throughout the Oligocene–Miocene, the evolution of the northern Red Sea and Suez rift system led to the formation of axial grabens accompanied by pronounced uplift along the rift shoulders, which were limited to less than 2 km in blocks of group A samples (Figure 9). These limited uplifts are similar to those previously reported from the northern segment of the Suez Rift flanks [10,15,16,34,36]. While the blocks of group B samples show uplifts between ca. 4 and 3.2 km (Figure 9). This amount of uplift explains the extraordinarily elevated area, which is restricted to this particular region (Catherina region) in South Sinai (Figure 2). Additionally, it supports the additional thermal component of an active rift type to be limited to the southern segment of the Suez Rift’s eastern flank.
6. Conclusions
The Wadi Hebran area, situated in the northern section of the ANS, originated during the Neoproterozoic as part of the EAO. By the close of the Cambrian, intense erosion had removed the exposed basement complexes. This erosional phase, associated with the PAEE, brought the currently exposed rocks within ca. 2 km of the Earth’s surface. Subsequently, the region experienced the formation of intracratonic basins, where the Lower Paleozoic strata accumulated, burying the basement rocks to depths between ca. 3.2 and 5.5 km. During the Devonian/Carboniferous, the Variscan tectonic event triggered differential rock uplifts along fault-bounded blocks and significant denudation of the previously deposited Lower Paleozoic sequence. In the following period, stable platform sedimentation dominated the region until the Cretaceous, when the convergence of the African and Eurasian plates likely caused localized uplifts. Later, the development of the Suez Rift uplifted the flanks to varying extents, with group A sample blocks rising less than 2 km and group B sample blocks reaching elevations between approximately 3.2 and 4 km. Over time, erosion and surface processes gradually modified the uplifted rift shoulders, shaping the modern-day topography.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M. and N.H.; methodology, S.M., A.T. and N.H.; validation, S.M., A.S.A., M.A.G., A.E. and N.H.; formal analysis, A.T., A.E., A.S.A. and S.M.; investigation, S.M., A.S.A., A.E., M.A.G. and N.H.; resources, N.H., A.E. and A.S.A.; data curation, S.M. and M.A.G.; writing—original draft preparation, S.M.; writing—review and editing, N.H., A.S.A., A.T., M.A.G. and A.E.; visualization, S.M., A.S.A., A.E. and M.A.G.; supervision, N.H.; project administration, S.M., A.T., A.S.A. and A.E.; funding acquisition, N.H., A.S.A. and A.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported and funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University (IMSIU) (grant number IMSIU-DDRSP2502).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors without undue reservation.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support and funding of the Deanship of Scientific Research at Imam Mohammad ibn Saud Islamic University (IMSIU) (grant number IMSIU-DDRSP2502).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the Funding section. This change dose not affect the scientific content of the article.
References
- Mansour, S.; Hasebe, N.; Meert, J.G.; Tamura, A.; Khalaf, F.I.; El-Shafei, M.K. Evolution of the Arabian-Nubian Shield in Gabal Samra Area, Sinai; Implications from Zircon U–Pb Geochronology. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2022, 192, 104538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, R.J. ARC Assembly and Continental Collision in the Neoproterozoic East African Orogen: Implications for the Consolidation of Gondwanaland. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1994, 22, 319–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meert, J.G. A Synopsis of Events Related to the Assembly of Eastern Gondwana. Tectonophysics 2003, 362, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, W.; Stockli, D.F.; Helgeson, D.E. Integrated Outcrop, 3D Seismic, and Geochronologic Interpretation of Red Sea Dike-Related Deformation in the Western Desert, Egypt—The Role of the 23Ma Cairo “Mini-Plume”. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 109, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinstein, S.; Eyal, M.; Kohn, B.P.; Steckler, M.S.; Ibrahim, K.M.; Moh’d, B.K.; Tian, Y. Uplift and Denudation History of the Eastern Dead Sea Rift Flank, SW Jordan: Evidence from Apatite Fission Track Thermochronometry: Uplift History of Dead Sea Rift Flank. Tectonics 2013, 32, 1513–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, B.P.; Eyal, M. History of Uplift of the Crystalline Basement of Sinai and Its Relation to Opening of the Red Sea as Revealed by Fission Track Dating of Apatites. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1981, 52, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S. Tectonic Development of Wadi Mi’ar Area, Sinai, Egypt: Implications of Low-Temperature Thermochronology Techniques. Alfarama J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2023, 4, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S. Long-Term Topographic Evolution of the African Plate, Causes and Consequences for Surrounding Lithospheric Plates. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, S.; Hasebe, N.; Khedr, M.Z.; Tamura, A.; Shehata, A.A. Tectonic-Thermal Evolution of the Wadi El-Dahal Area, North Eastern Desert, Egypt: Constraints on the Suez Rift Development. Minerals 2023, 13, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.; Hasebe, N.; Abdelrahman, K.; Fnais, M.S.; Tamura, A. Reconstructing the Tectonic History of the Arabian–Nubian Shield in Sinai: Low-Temperature Thermochronology Implications on Wadi Agar Area. Minerals 2023, 13, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morag, N.; Haviv, I.; Eyal, M.; Kohn, B.P.; Feinstein, S. Early Flank Uplift along the Suez Rift: Implications for the Role of Mantle Plumes and the Onset of the Dead Sea Transform. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2019, 516, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, G.I.; Steckler, M.S.; Buck, W.R.; Kohn, B.P. Fission-Track Analysis of Basement Apatites at the Western Margin of the Gulf of Suez Rift, Egypt: Evidence for Synchroneity of Uplift and Subsidence. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1989, 94, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, G.I.; Steckler, M.S. Fission Track Evidence on the Initial Rifting of the Red Sea: Two Pulses, No Propagation. Science 1995, 270, 1341–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarand, J.; Marques, F.O.; Hildenbrand, A.; Pinna-Jamme, R.; Nogueira, C.R. Thermal Evolution of Onshore West Iberia: A Better Understanding of the Ages of Breakup and Rift-to-Drift in the Iberia-Newfoundland Rift. Tectonophysics 2021, 813, 228926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.; Hasebe, N.; Glasmacher, U.A.; Tamura, A.; El-Shafei, M.K. New Insights into the Thermo-tectonic Development of the Suez Rift within the Framework of the Northern Arabian–Nubian Shield. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2025, 50, e6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.; Hasebe, N.; Abdelrahman, K.; Fnais, M.S.; Tamura, A. The Gulf of Suez Rifting: Implications from Low-Temperature Thermochronology. Int. Geol. Rev. 2024, 67, 694–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodner, K.; Avigad, D.; McWilliams, M.; Wooden, J.L.; Weissbrod, T.; Feinstein, S. Provenance of North Gondwana Cambrian–Ordovician Sandstone: U–Pb SHRIMP Dating of Detrital Zircons from Israel and Jordan. Geol. Mag. 2006, 143, 367–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schott, B.; Schmeling, H. Delamination and Detachment of a Lithospheric Root—ScienceDirect. Tectonophysics 1998, 296, 225–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, W.; McClay, K. Structural and Stratigraphic Evolution of the Neogene Gulf of Suez, Egypt: A Synthesis; Memoires du Museum National d’Histrorie Naturelle de Paris: Peritethys Programme (PTP) and International Geological Correlation Program (IGCP): Paris, Frace, 2001; Voluem 186. [Google Scholar]
- Kohn, B.P.; Eyal, M.; Feinstein, S. A Major Late Devonian-Early Carboniferous (Hercynian) Thermotectonic Event at the NW Margin of the Arabian-Nubian Shield: Evidence from Zircon Fission Track Dating. Tectonics 1992, 11, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stampfli, G.M.; von Raumer, J.F.; Borel, G.D. Paleozoic Evolution of Pre-Variscan Terranes: From Gondwana to the Variscan Collision. In Variscan-Appalachian Dynamics: The Building of the Late Paleozoic Basement; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-0-8137-2364-8. [Google Scholar]
- Alsharhan, A.S.; Nairn, A.E.M. Sedimentary Basins and Petroleum Geology of the Middle East; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; ISBN 978-0-444-82465-3. [Google Scholar]
- Meneisy, M.Y. Mesozoic Igneous Activity in Egypt. Qatar Univ. Sci. Bull. 1986, 6, 317–328. [Google Scholar]
- Sakran, S.; Shehata, A.A.; Osman, O.; El-Sherbiny, M. Superposed Tectonic Regimes in West Beni Suef Basin, Nile Valley, Egypt: Implications to Source Rock Maturation and Hydrocarbon Entrapment. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 154, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, A.A.; El Fawal, F.M.; Ito, M.; Aboulmagd, M.A.; Brooks, H.L. Senonian Platform-to-Slope Evolution in the Tectonically-Influenced Syrian Arc Sedimentary Belt: Beni Suef Basin, Egypt—ScienceDirect. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2020, 170, 103934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, R. The Geology of Egypt, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Said, R. The Geology of Egypt, 2nd ed.; A.A. Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, S.; Abdelfadil, K.M.; Hasebe, N.; Tamura, A.; Abdelrahman, K.; Gharib, M.A.; Fnais, M.S.; Shehata, A.A. Thermochronological Constraints on the Tectonic History of the Arabian–Nubian Shield’s Northern Tip, Sinai, Egypt. Minerals 2024, 14, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, A.R.; Saoudi, A.; Moubasher, A.; Ibrahim, I.M.; Molokhia, H.; Schwartz, B. Structural Setting and Tectonic Evolution of the Bahariya Depression, Western Desert, Egypt. GeoArabia 2003, 8, 91–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, B.; Weissbrod, T.; Chung, L.; Farley, K.; Bodorkos, S. Low-temperature Thermochronology of Francolite: Insights into Timing of Dead Sea Transform Motion. Terra Nova 2019, 31, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.; Gharib, M.A.; Hasebe, N.; Abdelrahman, K.; Fnais, M.S.; Tamura, A. Tectonic Evolution of the Gabal Loman Area, North Eastern Desert, Egypt: Implications from Low-Temperature Multithermochronometry on the Arabian-Nubian Shield. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeesch, P.; Avigad, D.; McWilliams, M.O. 500 m.y. of Thermal History Elucidated by Multi-Method Detrital Thermochronology of North Gondwana Cambrian Sandstone (Eilat Area, Israel). GSA Bull. 2009, 121, 1204–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabeh, T. Geotectonic Studies of Southern Sinai and Gulf of Suez Areas, Egypt. Ann. Geophys. 2003, 46, 1325–1337. [Google Scholar]
- Bojar, A.-V.; Fritz, H.; Kargl, S.; Unzog, W. Phanerozoic Tectonothermal History of the Arabian–Nubian Shield in the Eastern Desert of Egypt: Evidence from Fission Track and Paleostress Data. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2002, 34, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, B.P.; Feinstein, S.; Foster, D.A.; Steckler, M.S.; Eyal, M. Thermal History of the Eastern Gulf of Suez, II. Reconstruction from Apatite Fission Track and K-Feldspar Measurements. Tectonophysics 1997, 283, 219–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.; Hasebe, N.; Azab, E.; Elnaggar, A.Y.; Tamura, A. Combined Zircon/Apatite U-Pb and Fission-Track Dating by LA-ICP-MS and Its Geological Applications: An Example from the Egyptian Younger Granites. Minerals 2021, 11, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, G.I.; Kohn, B.P.; Lutz, T.M.; Faul, H. The Cooling History of Silurian to Cretaceous Alkaline Ring Complexes, South Eastern Desert, Egypt, as Revealed by Fission-Track Analysis. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1987, 83, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröner, A.; Kröger, J.; Rashwan, A.A.A. Age and Tectonic Setting of Granitoid Gneisses in the Eastern Desert of Egypt and South-West Sinai. Geol. Rundsch. 1994, 83, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.; Hasebe, N.; Tamura, A.; Abdelrahman, K.; Fnais, M.S.; Gharib, M.A.; Khedr, M.Z. Geochronological Assessment of the Arabian-Nubian Shield Plutonic Intrusions in the Arc Assemblages along the Qift-Quseir Transect, Central Eastern Desert of Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2024, 220, 105456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.; Hasebe, N.; Abdelrahman, K.; Fnais, M.S.; Gharib, M.A.; Habou, R.; Tamura, A. Development of the Arabian-Nubian Shield along the Marsa Alam-Idfu Transect, Central-Eastern Desert, Egypt: Geochemical Implementation of Zircon U-Pb Geochronology. Geochem. Trans. 2024, 25, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, R.J.; Hedge, C.E. Geochronologic and Isotopic Constraints on Late Precambrian Crustal Evolution in the Eastern Desert of Egypt. Am. J. Sci. 1985, 285, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.; Hasebe, N.; Tamura, A. Erosional Reservoir for the Northern Segment of the Arabian-Nubian Shield: Constrains from U-Pb Geochronology of the Lower Palaeozoic Succession, North Eastern Desert, Egypt. Precambrian Res. 2023, 388, 107017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, J.P.; England, P.C. Convective Removal of Lithosphere beneath Mountain Belts; Thermal and Mechanical Consequences. Am. J. Sci. 1994, 294, 307–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, T. The Topography and Geology of the Peninsula of Sinai (Western Portion); The Egyptian Geological Survey Department: Cairo, Egypt, 1907; Section III; pp. 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, A.A. A New Carboniferous Occurrencein Abu Durba, Sinai, Egypt. In Proceedings of the 6th Arab Petroleum Congress, Baghdad, Iraq, 6–13 March 1967; Volume 2, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Said, R. Explanatory Notes to Accompany the Geological Map of Egypt; Geological Survey of Egypt and Mining Authority: Cairo, Egypt, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Bosworth, W.; Huchon, P.; McClay, K. The Red Sea and Gulf of Aden Basins. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2005, 43, 334–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kora, M. The Paleozoic Outcrops of Um Bogma Area, Sinai. Ph.D. Thesis, Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- McClay, K.R.; Nichols, G.J.; Khalil, S.M.; Darwish, M.; Bosworth, W. Extensional Tectonics and Sedimentation, Eastern Gulf of Suez, Egypt. In Sedimentation and Tectonics in Rift Basins Red Sea: Gulf of Aden; Purser, B.H., Bosence, D.W.J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 223–238. ISBN 978-94-011-4930-3. [Google Scholar]
- Weissbrod, T. The Paleozoic of Israel and Adjacent Countries. Pt 1: The Subsurfacealeozoic Stratigraphy of Southern Israel. Isr. Geol. Surv. Bull. 1969, 47, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Klitzsch, E. Paleozoic. In The Geology of Egypt; Said, R., Ed.; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; Volume 24, pp. 451–486. [Google Scholar]
- Klitzsch, E.; Wycisk, P. Geology of the Sedimentary Basins of Northern Sudan and Bordering Areas. Berl. Geowiss. Abh. Reihe A Geol. Und Palaeontol. 1987, 75, 97–136. [Google Scholar]
- Abdallah, A.M.; El-Adindani, A. Stratigraphy of Upper Paleozoic Rocks of Western Side of Gulf of Suez PDF|PDF. Geol. Surv. Egypt 1963, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Zied, R. Palaeoenvironmental Significance of Early Cretaceous Foraminifera from Northern Sinai, Egypt. Cretac. Res. 2007, 28, 765–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, A.; Sharaf, L.; Baghdady, A.; Abd El-Naby, A. Cenomanian/Turonian Oceanic Anoxic Event 2 in October Oil Field, Central Gulf of Suez, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2020, 165, 103817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, I.Z. On the Presence of Middle Jurassic Miospores at Gebel El Iseila, West Central Sinai, Egypt. Bull. Fac. Sci. Alex. Univ. 1985, 25, 26–40. [Google Scholar]
- El Sharawy, M.S.; Nabawy, B.S. Geological and Petrophysical Characterization of the Lower Senonian Matulla Formation in Southern and Central Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2016, 41, 281–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A. Upper Cretaceous Foraminifera of Western Sinai. Fac. Eng. Bull. Cairo Univ. 1954, 26, 335–365. [Google Scholar]
- El-Azabi, M.H. Sedimentological Characteristics, Palaeoenvironments and Cyclostratigraphy of the Middle Eocene Sequences in Gabal El-Ramliya, Maadi-Sukhna Stretch, North Eastern Desert. In Proceedings of the Egyptian 8th International Conference on the Geology of Arab World, Cairo, Egypt, 13–16 February 2006; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Refaat, A.A.; Imam, M.M. The Tayiba Red Beds: Transitional Marine-Continental Deposits in the Precursor Suez Rift, Sinai, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 1999, 26, 467–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Anwar, E. Geochemical Studies of Carbonates of the Tayiba Formation (Upper Eocene), Abu Zenima Area, West Central Sinai. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, A.R.; Yousif, M.S.M. Structural Evolution of the Eastern Shoulder of the Suez Rift: Um Bogma Area. Neues Jahrb. Geol. Paläontologie—Monatshefte 1993, 1993, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Heiny, I.; Martini, E. Miocene Foraminiferal and Calcareous Nannoplankton Assemblages from the Gulf of Suez Region and Correlations. Geol. Mediterr. 1981, 8, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, E.S.; Afife, M.M.; Fares, M.; van Loon, A.J.; Ruban, D.A. Sedimentary Facies and Diagenesis of the Lower Miocene Rudeis Formation (Southwestern Offshore Margin of the Gulf of Suez, Egypt) and Implications for Its Reservoir Quality. Mar. Geol. 2019, 413, 48–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, M.; El Araby, A. Petrography and Diagenetic Aspects of Some Siliclastic Hydrocarbon Reservoirs in Relation to Rifting of the Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Geodynamics and Sedimentation of the Red Sea—Gulf of Aden Rift System. Egypt. J. Geol. 1994, 3, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Tewfik, N.; Harwood, C.; Deighton, I. The Miocene, Rudeis and Kareem Formations in the Gulf of Suez: Aspects of Sedimentology and Geochemistry. EGPC Explor. Semin. Cairo I 1992, 11, 84–113. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, W.Q. The Structural Differentiation of Africa in the Pan-African (±500 m.y.) Tectonic Episode. Leeds Univ. Res. Inst. Afr. Geol. Dep. Earth Sci. Annu. Rep. Sci. Results 1964, 8, 48–49. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, S.; Gharib, M.A. Tectonic Assessment of the Northwestern Nubian Shield at Southern Sinai, Egypt. Spectr. Sci. J. 2025, 2, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perron, P.; Le Pourhiet, L.; Guiraud, M.; Vennin, E.; Moretti, I.; Portier, É.; Konaté, M. Control of Inherited Accreted Lithospheric Heterogeneity on the Architecture and the Low, Long-Term Subsidence Rate of Intracratonic Basins. BSGF-Earth Sci. Bull. 2021, 192, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frizon de Lamotte, D.; Raulin, C.; Mouchot, N.; Wrobel-Daveau, J.; Blanpied, C.; Ringenbach, J. The Southernmost Margin of the Tethys Realm during the Mesozoic and Cenozoic: Initial Geometry and Timing of the Inversion Processes. Tectonics 2011, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klitzsch, E. Plate Tectonics and Cratonal Geology in Northeast Africa (Egypt, Sudan). Geol. Rundsch. 1986, 75, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullin, F.; Solari, L.; Solé, J.; Ortega-Obregón, C. Mesozoic Exhumation History of the Grenvillian Oaxacan Complex, Southern Mexico. Terra Nova 2021, 33, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, R.; Ortega-Gutiérrez, F.; Ortíz-Joya, G.A. Subduction of Proterozoic to Late Triassic Continental Basement in the Guatemala Suture Zone: A Petrological and Geochronological Study of High-Pressure Metagranitoids from the Chuacús Complex. Lithos 2018, 308–309, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girdler, R.W. Problems Concerning the Evolution of Oceanic Lithosphere in the Northern Red Sea. Tectonophysics 1985, 116, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, J.F.; Pitman, W.C.; Ryan, W.B.F.; Bonnin, J. Plate Tectonics and the Evolution of the Alpine System. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1973, 84, 3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, S.C.; Balestrieri, M.-L.; Kohn, B. Thermo-Tectonic Imaging of the Gulf of Aden-Red Sea Rift Systems and Afro-Arabian Hinterland. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 222, 103824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steckler, M.S.; Feinstein, S.; Kohn, B.P.; Lavier, L.L.; Eyal, M. Pattern of Mantle Thinning from Subsidence and Heat Flow Measurements in the Gulf of Suez: Evidence for the Rotation of Sinai and along-Strike Flow from the Red Sea. Tectonics 1998, 17, 903–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, G.A. Spaltspurenalter von Mineralen Und Natürlichen Gläsern: Eine Übersicht. Fortschritte Mineral. 1972, 114–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketcham, R.A. Fission-Track Annealing: From Geologic Observations to Thermal History Modeling. In Fission-Track Thermochronology and Its Application to Geology; Malusà, M.G., Fitzgerald, P.G., Eds.; Springer Textbooks in Earth Sciences, Geography and Environment; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 49–75. ISBN 978-3-319-89419-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kohn, B.P.; Ketcham, R.A.; Vermeesch, P.; Boone, S.C.; Hasebe, N.; Chew, D.; Bernet, M.; Chung, L.; Danišík, M.; Gleadow, A.J.W.; et al. Interpreting and Reporting Fission-Track Chronological Data. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2024, 136, 3891–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donelick, R.A.; O’Sullivan, P.B.; Ketcham, R.A. Apatite Fission-Track Analysis. In Low-Temperature Thermochronology; Reiners, P.W., Ehlers, T.A., Eds.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 49–94. ISBN 978-1-5015-0957-5. [Google Scholar]
- Gleadow, A.J.W.; Duddy, I.R. A Natural Long-Term Track Annealing Experiment for Apatite. Nuclear Tracks 1981, 5, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketcham, R.A.; Donelick, R.A.; Balestrieri, M.L.; Zattin, M. Reproducibility of Apatite Fission-Track Length Data and Thermal History Reconstruction. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 284, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garver, J.I. Etching Zircon Age Standards for Fission-Track Analysis. Radiat. Meas. 2003, 37, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, R.; Tagami, T.; Nishimura, S.; Ito, H. Annealing Kinetics of Fission Tracks in Zircon: An Experimental Study. Chem. Geol. 1995, 122, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, R.; Murakami, M.; Tagami, T. Statistical Modelling of Annealing Kinetics of Fission Tracks in Zircon; Reassessment of Laboratory Experiments. Chem. Geol. 2007, 236, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernet, M.; Brandon, M.; Garver, J.; Balestieri, M.L.; Ventura, B.; Zattin, M. Exhuming the Alps through Time: Clues from Detrital Zircon Fission-Track Thermochronology. Basin Res. 2009, 21, 781–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketcham, R.A. Forward and Inverse Modeling of Low-Temperature Thermochronometry Data. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2005, 58, 275–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeesch, P. IsoplotR: A Free and Open Toolbox for Geochronology. Geosci. Front. 2018, 9, 1479–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleadow, A.J.W.; Duddy, I.R.; Green, P.F.; Lovering, J.F. Confined Fission Track Lengths in Apatite: A Diagnostic Tool for Thermal History Analysis. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1986, 94, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, A.; Sagawa, T.; Okino, K.; Morishita, T. Determination of Whole-Rock Trace-Element Compositions of Siliceous Rocks Using MgO-Diluted Fused Glass and LA-ICP-MS. Geochem. J. 2022, 56, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, N.J.G.; Perkins, W.T.; Westgate, J.A.; Gorton, M.P.; Jackson, S.E.; Neal, C.R.; Chenery, S.P. A Compilation of New and Published Major and Trace Element Data for NIST SRM 610 and NIST SRM 612 Glass Reference Materials. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 1997, 21, 115–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walder, A.J.; Platzner, I.; Freedman, P.A. Isotope Ratio Measurement of Lead, Neodymium and Neodymium–Samarium Mixtures, Hafnium and Hafnium–Lutetium Mixtures with a Double Focusing Multiple Collector Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometer. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1993, 8, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnevin, D.; Daly, J.S.; Waight, T.E.; Morgan, D.; Poli, G. Pb Isotopic Zoning of K-Feldspar Megacrysts Determined by Laser Ablation Multi-Collector ICP-MS: Insights into Granite Petrogenesis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 1899–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, V.A. Arc Furnace Assisted Carbothermal Decomposition of Zircon. Refract. Ind. Ceram. 2005, 46, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.; Boulos, F.K.; Hennin, S.F.; El-Sherif, A.A.; El-Sayed, A.A.; Basta, N.Z.; Melek, Y.S. Heat Flow in Eastern Egypt: The Thermal Signature of a Continental Breakup. J. Geodyn. 1985, 4, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketcham, R.A.; Carter, A.; Donelick, R.A.; Barbarand, J.; Hurford, A.J. Improved Measurement of Fission-Track Annealing in Apatite Using c-Axis Projection. Am. Miner. 2007, 92, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketcham, R.A.; Donelick, R.A.; Carlson, W.D. Variability of Apatite Fission-Track Annealing Kinetics; III, Extrapolation to Geological Time Scales. Am. Mineral. 1999, 84, 1235–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinstein, S.; Kohn, B.P.; Steckler, M.S.; Eyal, M. Thermal History of the Eastern Margin of the Gulf of Suez, I. Reconstruction from Borehole Temperature and Organic Maturity Measurements. Tectonophysics 1996, 266, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshref, W. Tectonic Framework of Egypt. In Geology of Egypt; Said, R., Ed.; A.A. Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 113–156. [Google Scholar]
- Nasdala, L.; Reiners, P.W.; Garver, J.I.; Kennedy, A.K.; Stern, R.A.; Balan, E.; Wirth, R. Incomplete Retention of Radiation Damage in Zircon from Sri Lanka. Am. Mineral. 2004, 89, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frizon de Lamotte, D.; Fourdan, B.; Leleu, S.; Leparmentier, F.; de Clarens, P. Style of Rifting and the Stages of Pangea Breakup. Tectonics 2015, 34, 1009–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasebe, N.; Barbarand, J.; Jarvis, K.; Carter, A.; Hurford, A.J. Apatite Fission-Track Chronometry Using Laser Ablation ICP-MS. Chem. Geol. 2004, 207, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).