Abstract
Elevated levels of cadmium (Cd) and lead (Pb) in the edible parts of rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown in agricultural soils may enter the human body through the food chain, posing significant health risks. In this study, rice and paired rhizosphere soil samples were collected from 194 locations in Jiangsu Province, China, with 60 samples selected for diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) extraction analysis. The findings indicate that total soil concentrations of Cd and Pb are inadequate for assessing cadmium bioavailability, implying that current soil quality standards may not accurately reflect the bioaccessible fractions of these metals. Both DGT and soil solution measurements effectively predicted crop Cd levels, with the effective concentration (CE) derived from the DGT-induced soil flux (DIFS) model showing the strongest correlation with rice Cd content. Pearson correlation analysis and a random forest (RF) model further identified critical factors influencing rice uptake of Cd and Pb, including soil iron (Fe) content, cation exchange capacity (CEC), pH, and the levels of zinc (Zn) and selenium (Se), which antagonize Cd uptake.
1. Introduction
Cadmium (Cd) has been identified as a major inorganic contaminant in China’s agricultural soils, with its widespread presence posing potential threats to the safety of agricultural products and human health [1]. The contamination of soil by cadmium primarily results from the complex interactions between natural weathering processes and human activities, including industrial development (such as industrial wastewater discharge), agricultural practices (such as fertilizer application), and waste disposal. While geological background and mineral resources, influenced by natural factors like rainfall, can contribute to elevated cadmium levels in certain regions, human activities, particularly industrial wastewater discharge and agricultural production, have significantly exacerbated cadmium pollution, especially in central China, the Yangtze River Delta, and the Pearl River Delta [2]. Compared to other heavy metals, staple crops such as rice are more prone to absorbing cadmium from the soil, with greater efficiency in transferring it to roots, stems, and grains. As a highly toxic and carcinogenic element, cadmium exposure can lead to kidney dysfunction and various other health issues, with prolonged exposure significantly increasing the risk of cancer [3]. Additionally, research suggests that adequate selenium (Se) supplementation may help mitigate the adverse health effects of cadmium exposure. Selenium activates specific enzymes in the body, enhancing the detoxification and excretion of heavy metals, including cadmium, which may serve as a potential strategy for reducing environmental risks in highly cadmium-polluted regions [4].
Lead (Pb) contamination in Chinese agricultural soils has emerged as a significant concern, paralleling the issues associated with Cd. Like Cd, Pb accumulation results from both natural processes and anthropogenic activities. Naturally, Pb is present in mineral deposits and can be released into soils through the weathering of Pb-bearing rocks [5]. However, human activities, including industrial emissions, the historical use of leaded gasoline, the application of lead containing agrochemicals, and waste disposal practices, have substantially elevated Pb levels in many regions [6]. These anthropogenic sources have created persistent contamination, as Pb exhibits strong soil adsorption yet can become bioavailable under conditions such as soil acidification [7,8]. The uptake of Pb by edible crops is influenced by several soil properties, including pH, organic matter content, and cation exchange capacity (CEC), which modulate its mobility and bioavailability [9]. Studies have demonstrated that crops grown on contaminated soils can accumulate Pb in their edible parts, thereby introducing the metal into the human food chain [10]. Chronic exposure to even low levels of Pb is particularly worrisome due to its well-documented adverse effects on human health. The impact on the body varies depending on the route of entry, including inhalation, ingestion, or dermal absorption. Epidemiological research links Pb exposure to neurological deficits—especially in children—as well as cardiovascular, renal, and reproductive disorders in adults [11]. Moreover, regions with high soil Pb levels have been correlated with increased blood Pb concentrations in local populations, underscoring the urgent need for effective risk assessment and management strategies [12].
In response to these concerns, recent remediation efforts have focused on reducing Cd and Pb bioavailability and minimizing its uptake by crops. Techniques such as phytoremediation, the incorporation of organic amendments, and the application of phosphate fertilizers have been investigated as potential means to immobilize Cd and Pb in soils [13]. Additionally, research into the interactions between Cd, Pb, and other soil elements, such as zinc (Zn), suggests that manipulating these interactions could further reduce Pb bioaccessibility to plants [14]. These approaches provide promising avenues for mitigating Cd, Pb-related risks and ensuring the safety of agricultural products.
Soil properties such as pH, iron content, and cation exchange capacity (CEC) significantly influence the bioavailability of Cd and Pb. In acidic soils, reduced binding of Cd2+ and Pb2+ to soil particles increases their mobility, thereby heightening their potential toxicity to plants. Moreover, acidic conditions facilitate the dissolution of minerals containing these metals, while adsorption on kaolinite diminishes markedly at low pH because Cd is primarily adsorbed as outer-sphere complexes. In contrast, iron-rich soils and those with higher CEC tend to retain these metals more effectively due to competitive adsorption and enhanced fixation, respectively [15,16]. Nevertheless, the precise mechanisms through which these factors modulate Cd bioavailability remain inadequately understood. To investigate the influence of soil physicochemical parameters on Cd and Pb accumulation in rice grains, we employed classification and regression tree (CART) analysis, a machine learning method well-suited to uncovering complex intrinsic relationships. Additionally, random forest (RF), an advanced version of CART, further enhances predictive accuracy [17,18,19].
Recent studies indicate that the uptake of Cd and Pb by crops depends not only on their total concentrations in the soil but also on their chemical forms and bioavailability. As crops absorb metal ions from the soil solution, a concentration gradient forms near the root zone, leading to the gradual replenishment of Cd and Pb ions from soil particles into the solution [20]. Consequently, over a certain period, the cumulative uptake of metal ions by crops corresponds to the dynamic replenishment of these metals from the solid phase to the soil solution. The diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) technique is widely used to assess the bioavailable concentrations of Cd and Pb in soil, as it simultaneously captures both the dissolved fraction in soil solution and the portion replenished from the solid phase, thereby simulating this biological process. Previous research has demonstrated the effectiveness of the DGT method in evaluating harmful metal elements in soil [21,22]. Furthermore, the DGT-induced fluxes in soils (DIFS) model quantifies the chemical exchange between the solid and solution phases under DGT perturbation, providing a dynamic analytical framework for the DGT system. This model can also calculate diffusion coefficients to correct DGT measurements [23,24].
Assessing the bioavailability of Cd and Pb in rice and identifying the key factors influencing their accumulation are central issues in this field of research. Therefore, the objectives of this study are: (1) to evaluate the predictive accuracy of multiple assessment methods—including total soil metal concentration, the DGT technique, soil solution analysis, and the DGT-DIFS model—for estimating Cd and Pb levels in rice grains; (2) to identify critical factors affecting Cd and Pb uptake in rice; and (3) to provide scientific recommendations for the safe utilization of Cd- and Pb-contaminated soils in typical agricultural regions of Jiangsu Province.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study area is in Jiangsu Province, located on the eastern coast of China, is an economically and agriculturally significant region. To support our research, we have established 194 sampling sites across all 13 cities in Jiangsu (45 in Suzhou, 35 in Wuxi, 33 in Lianyungang, 14 in Nanjing, 11 in Huai’an, 10 in Changzhou, 10 in Yangzhou, 9 in Xuzhou, 8 in Yancheng, 8 in Zhenjiang, 6 in Taizhou, 3 in Suqian, and 2 in Nantong). The annual average temperature ranges between 13 °C and 16 °C, with cold winters and hot, humid summers. The province receives an average annual precipitation of 800–1200 mm, with rainfall concentrated in the summer months due to the East Asian monsoon. The region is also influenced by typhoons and heavy rainfall events, particularly in the southeastern coastal areas.
Jiangsu Province is situated in the eastern part of the Yangtze River Delta, a region characterized by relatively young geological formations. The province’s geology is predominantly composed of Quaternary sediments, particularly along the coastal and alluvial plains. The northern part of Jiangsu consists of low-lying plains formed by the Yellow River’s historical sediment deposition, whereas the southern region, including areas around Nanjing and Zhenjiang, contains more diverse lithological compositions, including Mesozoic and Paleozoic rocks. Jiangsu Province has diverse soil types due to its varied geological and climatic conditions. The major soil types include: fluvo-aquic soils, which are predominantly found in the northern and central plains, formed from river alluvial deposits, and suitable for agriculture; yellow-brown soils, which are common in the southern hilly areas, particularly around Nanjing and Zhenjiang, and are derived from weathered sedimentary rocks; paddy soils, which are widely distributed across the province and developed due to long-term rice cultivation and irrigation practices; saline–alkali soils, which are found in coastal areas, particularly in regions such as Yancheng and Nantong, due to marine influences and poor drainage [25,26].
2.2. Sample Collection and Pretreatment
In this study, 194 rice grain samples were collected at the rice maturity stage, along with corresponding rhizosphere soil samples from a depth of 0–20 cm. All samples were sealed in airtight plastic bags following strict operational protocols and transported to the laboratory for preprocessing in a timely manner to ensure freshness and integrity. The soil samples were air-dried at room temperature, passed through a 10-mesh sieve to remove plant roots, debris, and large stones, and then ground into a fine, homogeneous powder. The dehulled rice grains were dried at 50 °C for three days until their weight remained stable. Subsequently, they were ground into a fine powder using a mortar and stored in sample bags for further analysis.
2.3. Chemical Analysis
Soil pH was determined using the ion-selective electrode (ISE) method [27]. Cation exchange capacity (CEC) was measured using the ammonium acetate exchange method [28]. The concentrations of major chemical elements in the soil (Si, Al, Fe, Mn, K, Ca, Na, and Mg) were analyzed via X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectrometry. The total concentrations of cadmium (Cd) and lead (Pb) in both soil and rice grains were assessed using 1 g of homogenized powdered samples. Soil samples were digested using a mixed acid solution of hydrofluoric acid, nitric acid, and perchloric acid, while rice grain samples were digested with a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and perchloric acid. The digested solutions were then analyzed using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) to quantify Cd, Pb, Zn, and Se. To ensure analytical accuracy and precision, strict quality assurance and quality control (QA/QC) measures were implemented in accordance with national and industry standards. These included blank samples, duplicate samples, and certified reference materials (GSS-9, GSS-18, GSS-23, and GSS-27) [29].
2.4. Bioconcentration of Cd and Pb
The bioconcentration factor (BCF) is defined as the ratio of trace element concentrations, such as Cd and Pb, in plants to their concentrations in the topsoil where the crops are cultivated. It is a key indicator of a plant’s ability to enrich trace elements. The method for calibrating BCF is shown in Equation (1) [30]:
where BCF denotes the bioconcentration factor, Crice represents the concentration of the trace elements in rice grains, and Csoil indicates its corresponding concentration in surface soil. In the present research, BCF-Cd and BCF-Pb refer to the bioconcentration factors of Cd and Pb in rice, respectively.
2.5. DGT Measurements and the DIFS Model
In this study, Chelex-100 resin-based DGT devices (purchased from DGT® Research Ltd., Lancaster, UK) were used for the adsorption and extraction of Cd and Pb metal cations (Figure 1). All procedures adhered to standard guidelines and operational protocols for deploying and measuring DGT devices in soil [31]. A total of 60 rhizosphere soil samples with different Cd and Pb concentration gradients were selected from the 194 collected samples for DGT analysis. Before deployment, 40 g of air-dried soil was placed in a beaker and maintained at 60% of its maximum water-holding capacity (MWHC) for 48 h, then adjusted to 80% MWHC for an additional 24 h. The DGT devices were then deployed in the soil at a constant temperature of 25 °C for 24 h. After removal, the devices were thoroughly rinsed with deionized water and disassembled. The binding gels were eluted with 1 mL of 1 mol/L nitric acid and left to stand for 24 h before analysis. Finally, the eluate was diluted tenfold with nitric acid, and the concentrations of Cd and Pb in the diluted solution were determined using ICP-MS. A 100 ppb indium standard (used as an internal standard) was added to effectively correct signal drift, matrix effects, and instrument instability, thereby improving the measurement accuracy and repeatability of ICP-MS. The final DGT-based concentrations of Cd and Pb were then calculated.
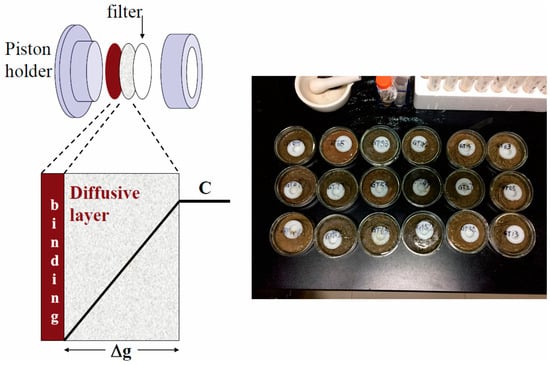
Figure 1.
DGT device sketch and deployment of DGT in soils.
The Cd or Pb concentration (CDGT) determined using the DGT method was calculated according to Equation (2), with a detailed explanation of the calculation provided in reference [21].
In this equation, M represents the mass of Cd or Pb (in ng) accumulated during deployment, ∆g is the thickness of the diffusive layer (in cm), D denotes the diffusion coefficient of Cd or Pb within the resin (in cm2·s−1), A is the area of the exposure window (in cm2), and t is the deployment time (in seconds).
After retrieval, the DGT devices were processed as follows: soil paste was collected, translocated into polyethylene tubes, and then centrifuged for 20 min to extract supernatant to obtain the soil solution. The supernatant was then filtered through a 0.45 μm filter, and the resulting filtrate was transferred into ICP-MS to quantify the cadmium or lead concentration in the soil solution (Css). The ratio (R) of CDGT/Css was calculated to evaluate the degree of Cd or Pb resupply from the solid phase to the liquid phase [32,33].
To further elucidate the kinetics of Cd or Pb release from the soil’s solid phase to the porewater or soil solution in the plant root zone and to determine the effective concentration (CE) of Cd or Pb, the DGT-induced fluxes in soils (DIFS) model was applied (Figure 2). Here, CE represents the theoretical diffusive concentration required to account for the measured accumulation of Cd or Pb on the DGT resin through diffusion [20]. Equation (3) is used to convert CDGT into CE:
Figure 2.
DIFS software interface corresponding to Cd and Pb.
Here, Rdiff represents the ratio of CDGT to Css when the metal accumulated by the DGT device occurs exclusively by diffusion. The DIFS model quantifies the relationship between Rdiff and both the rate and extent of Cd or Pb released from the solid phase to the liquid phase, accounting for the transition from soil to the interface as well as diffusion through the diffusive layer to the adsorption resin [22]. The 2D DIFS software (version 1.2.3, 2005, Lancaster, UK) [34] was used to calculate Rdiff values for Cd or Pb in the DGT-soil system.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
We conducted descriptive statistics and Pearson correlation analysis using IBM SPSS Statistics 27. To evaluate the factors influencing the bioavailability of Cd and Pb in agricultural soils, we utilized soil physicochemical parameters and elemental composition data from 194 samples. The random forest (RF) method was applied for this analysis, with the RF model implemented in R 4.4.2 using the random forest package [35]. Data visualization, including bubble plots of pH–Soil Cd/Pb–Rice Cd/Pb relationships, linear regression analyses of CE and Cd/Pb concentrations in rice grains, and factor importance plots for BCF-Cd/BCF-Pb, were performed using Origin 2021 (OriginLab, Northampton, MA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Descriptive Statistics of Physio-Chemical Parameters in Soils
The concentrations of Cd, Pb, and major elements in 194 soils from the surface layer (0–20 cm) of Jiangsu Province are shown in Table 1. The average concentration of Cd and Pb is 0.34 mg kg−1 and 43.04 mg kg−1 in the paddy soils of the study area, which are 2.25 and 1.60 times the local background values of surface soils (0.151 mg kg−1 for Cd and 26.8 mg kg−1 for Pb), respectively [36]. Statistical analysis reveals that Pb exhibits relatively low variability, with a coefficient of variation (CV) below 50%. This suggests low fluctuations in Pb concentrations across Jiangsu Province, limited variation among different geological formations, and a negligible influence of anthropogenic activities. In contrast, Cd, a highly toxic element with severe health risks upon excessive exposure, demonstrates significantly greater variability (CV = 149%). This substantial spatial variation in Cd concentrations is likely attributed to pronounced human impact.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics of Cd, Pb, major elements, CEC, and pH in soils (n = 194).
3.2. Characteristics of Cd and Pb in Soil and Rice Grains
Figure 3 illustrates the relationships between soil pH, Cd and Pb concentrations in paddy soil and in rice grains within the study area. According to the national standard Risk Control Standards for Soil Environmental Quality of Agricultural Land (GB-15618-2018) issued by the Ministry of Ecology and Environment [37], the risk screening and risk intervention values are marked accordingly. The analysis reveals that among the 194 paddy soil samples collected, only 0.5% exceeded the Cd risk intervention value, while 7.2% surpassed the Cd risk screening value (Figure 3a). In contrast, no samples exceeded the risk intervention value of Pb, with 1.5% surpassing the Pb risk screening value (Figure 3b). However, there was no direct correspondence between the Cd and Pb concentrations in rice grains and their respective concentrations in soil.
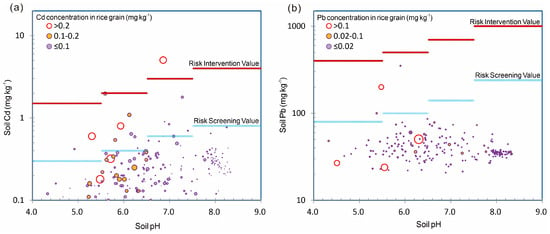
Figure 3.
Bubble diagram of soil (a) Cd, (b) Pb concentrations and pH values, in soil and rice grain samples.
The classification of soil environmental quality and the grading of land resources based solely on the Cd content in soil, as prescribed by this standard, neither effectively ensure the safe production of crops nor adequately protect human health. Moreover, such an approach may lead to unnecessary wastage of arable land resources. According to the national standard Maximum Levels of Contaminants in Food (GB-2762-2022) [38], the overall exceedance rate for Cd in the 194 rice grain samples from the study area was 3.6%, while the exceedance rate for Pb was 2.1%. Further statistical analysis of different soil pH ranges and their relationships with soil Cd and Pb concentrations, rice grain Cd and Pb concentrations, and exceedance rates indicated no clear correlation between the proportion of soil samples exceeding the Cd risk screening value and the variation trends of Cd concentrations and exceedance rates in rice grains (Figure 3).
The results also showed that Cd contents in soil increased with rising pH, whereas Cd contents and excessive rates in rice gradually decreased. Higher Cd contents in rice were predominantly observed in low-pH soils. For instance, when soil pH was below 5.5, the average Cd contents in soil was 0.188 mg kg−1, while the average Cd contents in rice was 0.100 mg kg−1. However, when soil pH surpassed 6.5, the average Cd concentration in soil increased to 0.353 mg kg−1, yet the average Cd contents in rice decreased to just 0.022 mg kg−1, only 22% of the Cd contents found in rice from soil with pH below 5.5.
In contrast, Pb concentrations in soil exhibited minimal variation with increasing pH. However, similar to Cd, higher Pb contents in rice were predominantly found in low-pH soils. When soil pH was below 5.5, the mean Pb contents in soil was 50.3 mg kg−1, with an average Pb contents of 0.048 mg kg−1 in rice. When soil pH exceeded 6.5, the average Pb concentration in soil decreased slightly to 39.5 mg kg−1, while the average Pb concentration in rice grains dropped significantly to 0.018 mg kg−1, which was considerably lower than the Pb concentration found in rice grains from soil with a pH below 5.5.
The translocation of trace elements like Cd and Pb from soil to rice is a critical pathway for human exposure to potentially toxic contaminants through the food chain. Understanding the enrichment characteristics of Cd and Pb is essential for assessing ecological risks and ensuring sustainable crop production.
Recent studies indicate that in certain Cd polluted areas of Jiangsu Province, the average BCF-Cd is about 0.155 [39]. Similarly, in the paddy lands of Henan, the average BCF-Cd is around 0.145, suggesting comparable levels of Cd uptake [40]. In the present study, the average BCF-Cd is higher (0.321), indicating greater Cd mobility in the contaminated areas of Jiangsu. However, based on national standards, the excessive rate of Cd in rice (3.6%) is much lower than that reported in a previous study in Jiangsu (30%). On the contrary, the average BCF-Pb (0.0005) is very low, indicating that Pb mobility in the study area is considerably low, leading to the low exceedance rate for Pb (2.1%) in rice grains.
3.3. Charaterizaion of Cd and Pb Bioavailability
In this study, the Cd concentration measured by DGT (CDGT) showed a significantly positive correlation with Cd contents in rice grains (r = 0.71), though its predictive capability was slightly lower than that for Pb (r = 0.76) (Table 2). Similarly, the concentrations of Cd and Pb in soil solution (Css) showed a strong positive correlation with their respective concentrations in crops, though the Pearson correlation coefficients were slightly lower than those between their DGT concentrations and rice grain contents.

Table 2.
Correlation coefficients (r) between Cd and Pb concentrations in rice and various measurements of Cd and Pb bioavailability in soils (n = 60).
In soil, the ability of the solid phase (soil particles) to resupply heavy metals to the soil solution could be calibrated using the R value (R = CDGT/Css, where 0 < R < 1). A higher R value (closer to 1) implied a stronger capacity of solid phase to replenish Cd and Pb in the soil solution [20]. When the release of Cd and Pb from the solid phase to the liquid phase is limited or nearly negligible (primarily diffusion-driven), the R value reaches its minimum (close to 0).
The average R value for soils with a pH above 6.5 was 0.41 and 0.43 for Cd and Pb, respectively, significantly lower than that of other soil types, suggesting a continuous resupply of Cd and Pb from the solid phase to the soil solution in mildly alkaline soils. However, in more acidic soils, particularly those with a pH of 4.5–5.5, the R value was higher (average 0.64 and 0.58 for Cd and Pb, respectively), indicating a relatively abundant supply of Cd and Pb from the solid phase to the soil solution under more acidic conditions. In these strongly acidic soils, as plants absorb Cd and Pb from the soil solution, the solid phase releases additional bioavailable Cd and Pb into the liquid phase, enhancing their mobility and uptake.
To investigate the concentrations of bioavailable heavy metals in both the solid phase and soil solution, the concept of effective concentration (CE) is commonly used in DGT-based soil environment studies. The calculation of CE follows Equation (2). The diffusion coefficient (Rdiff), derived from the DIFS model, is applied to correct CDGT, thereby determining the bioavailable concentration of analytes in soil. When the correlation between CDGT and Cd and Pb concentrations in rice grains is suboptimal, CE is often employed for predicting Cd accumulation in rice, yielding improved results [22].
In this study, CDGT alone did not provide fully satisfactory predictions of Cd accumulation in crops. Therefore, corrections using CDGT and Rdiff were applied to derive CE for more precise estimations. This approach significantly enhanced prediction accuracy, as evidenced by the stronger correlation between CE and Cd accumulation in rice (r = 0.89, Figure 4a), which exceeded the correlation between CDGT and Cd in rice (r = 0.71). Similarly, the effective concentration of Pb (CE) showed superior predictive performance for Pb accumulation in rice (r = 0.92, Figure 4b) compared to CDGT alone (r = 0.76). These findings highlight the enhanced capability of combining DGT technology with the DIFS model to simulate the dynamic migration of Cd and Pb within the soil–crop system more accurately.
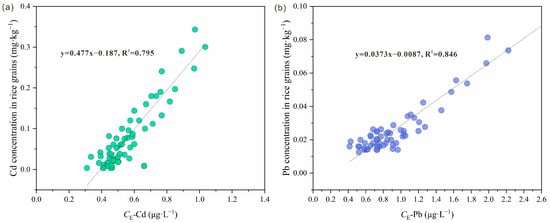
Figure 4.
Relationships between Cd and Pb concentrations in rice grains and effective concentration (derived from DGT and DIFS) of (a) Cd (CE-Cd) and (b) Pb (CE-Pb) in soils.
3.4. Factors Controlling Cd and Pb Uptake by Rice
To identify the key factors influencing the rice uptake of Cd and Pb from soil, we conducted a correlation analysis between BCF-Cd, BCF-Pb, and various soil physio-chemical parameters. Table 3 presents the Pearson correlation coefficients between the BCF values of rice samples and soil properties. Overall, significant correlations were observed between BCF-Cd, BCF-Pb, and soil properties such as iron (Fe) content, pH, CEC, zinc (Zn), and selenium (Se) content. In contrast, the effects of manganese (Mn), silicon (Si), and aluminum (Al) on BCF-Cd and BCF-Pb were minimal and could be disregarded.

Table 3.
Correlation coefficients (r) between BCF-Cd/BCF-Pb and soil parameters (n = 194).
Given the complexity of factors influencing Cd and Pb mobility and accumulation in the soil–rice system, we employed the random forest (RF) method as an advanced classification approach to further validate the determinants of Cd and Pb uptake in rice. The RF model, an extension of the classification and regression tree (CART) model, is comprehensively described by Breiman [17]. Compared with other models, RF offers advantages such as reduced sensitivity to noise and minimized bias in error estimation [18]. Notably, soil properties, including CEC, Fe content, pH, Se, and Zn content, contributed 22.4%, 20.6%, 19.6%, 13.4%, and 12.3%, respectively, to BCF-Cd variation (Figure 5a). Similarly, Fe content, Se and Zn content, CEC, and pH accounted for 24.6%, 21.8%, 17.4%, 15.4%, and 7.9%, respectively, of BCF-Pb variation (Figure 5b).
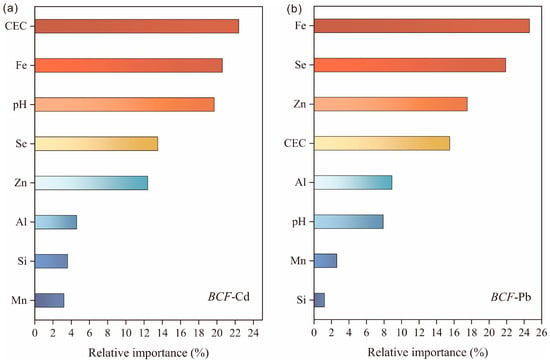
Figure 5.
Factor importance derived from the random forest (RF) model for bioconcentration of (a) Cd (BCF-Cd) and (b) Pb (BCF-Pb) in rice grains.
Soil pH has been identified as a key factor influencing cadmium (Cd) uptake in rice, exhibiting a significant negative correlation with BCF-Cd (Table 2). Soil pH affects the speciation of Cd, and as pH increases, the reduction in H⁺ concentration leads to an increase in negative charges on the soil surface. This, in turn, enhances Cd2+ adsorption by various soil minerals. Additionally, pH influences Cd reactivity, compound solubility, and the hydroxylation degree of Cd2+ on mineral surfaces. Conversely, soil acidification reduces the adsorption capacity and affinity of soil minerals for Cd2+, shifting Cd adsorption from specific adsorption to nonspecific ion exchange. As a result, the application of lime can decrease the bioavailability of Cd in soil, making it less accessible for uptake by crops such as rice. In comparison, soil pH has a relatively smaller effect on Pb bioavailability.
Soil cation exchange capacity (CEC) is significantly and negatively correlated with both BCF-Cd and BCF-Pb, particularly BCF-Cd (Table 2). This is primarily because an increase in CEC provides more negatively charged sites in the soil, which can adsorb and immobilize Cd2+ and Pb2+, thereby reducing their bioavailability. Additionally, high-CEC soils contain more exchangeable cations, such as calcium (Ca2+), magnesium (Mg2+), and potassium (K⁺), which compete with Cd2+ and Pb2+ for adsorption sites, further limiting their mobility and plant uptake. Lastly, organic matter and clay minerals in high-CEC soils readily form stable complexes with Cd and Pb, preventing their leaching and reducing their bioavailability to plants [41,42].
Soil Fe content exhibits a significant negative correlation with both BCF-Cd and BCF-Pb, particularly with BCF-Pb. This is primarily due to the presence of iron oxides, such as hematite (Fe2O3), goethite (FeOOH), and magnetite (Fe3O4), which have large specific surface areas and abundant surface hydroxyl (–OH) groups. These iron oxides can form stable surface complexes with Cd2+ and Pb2+, thereby immobilizing these metals and reducing their concentrations in soil solutions. Under anaerobic conditions, such as in paddy soils, Fe3+ is reduced to Fe2+ by microbial activity, leading to the release of Cd2+ and Pb2+ previously adsorbed onto iron oxides. However, when the soil is re-exposed to oxygen, Fe2+ undergoes oxidation and precipitates, re-adsorbing Cd2+ and Pb2+ and further reducing their bioavailability. This dynamic Fe redox cycle plays a crucial role in long-term Cd and Pb immobilization, thereby limiting their mobility and uptake by plants.
Furthermore, previous studies have shown an antagonistic interaction between Se and heavy metals such as Cd and Pb. An increase in soil Se content promotes the deposition of Cd and Pb in root cell walls or vacuoles, thereby reducing their translocation to other plant organs and ultimately lowering their bioavailability [43,44]. In this study, soil Se content ranked fourth and second among the factors influencing Cd and Pb uptake in rice, respectively (Figure 5). Because selenium-oxidizing bacteria can enhance Se bioavailability in soil [45], the application of these bacteria in Se-containing soils has been identified as an effective strategy for reducing Cd uptake in crops like rice and limiting its translocation to aboveground plant parts.
Soil Zn content is another key factor affecting Cd uptake in rice. The soil–crop system forms a complex network in which changes in the concentration of one element can influence the function of others, ultimately affecting the mobility of heavy metals such as Cd. Zn has an antagonistic relationship with divalent metals like Cd and Pb. Previous studies have found that applying low doses of ZnO in soil can mitigate the toxic effects of Cd on crop growth [46]. Due to structural similarities between Zn2+ and Cd2+, higher Zn concentrations in soil can alleviate the toxicity of Cd and Pb in crops, thereby promoting plant growth. As Zn bioavailability increases, the bioavailable concentrations of Cd and Pb in soil decrease significantly [47]. In this study, soil Zn content ranked fifth and third among the factors influencing Cd and Pb uptake in rice, respectively.
4. Conclusions
We analyzed the characteristics of Cd and Pb concentrations in soil and rice within the study area. The proportions of soil samples exceeding the screening values for Cd and Pb were 7.2% and 1.5%, respectively, while the proportions of rice samples exceeding Cd and Pb limits were 3.6% and 2.1%, respectively. However, the correlation between total heavy metal concentrations in soil and their levels in rice was weak. This indicates that existing soil environmental standards may not accurately assess Cd and Pb contamination in rice. The findings suggest that evaluating the bioavailability of heavy metals based solely on their total concentrations in soil is inaccurate. When the more advanced DGT method was used to assess Cd and Pb bioavailability, a strong positive correlation was observed between Cd and Pb concentrations in crops and those measured by single DGT and soil solution analysis. The most accurate predictions were obtained using the corrected CE values derived from Rdiff, calculated based on the dynamic DIFS model, which reflects the kinetic processes occurring in the soil environment.
Soils with higher alkalinity, iron content, and CEC are considered more suitable for growing rice with lower Cd and Pb concentrations. In addition to these three soil properties, Se and Zn levels also play crucial roles in regulating Cd and Pb uptake by rice. Although Se is known to antagonize Cd and Pb absorption in crops, the co-enrichment of Se with Cd and Pb in soil often results in their simultaneous accumulation in rice. This phenomenon may lead to Se-rich crops exceeding permissible Cd and Pb limits. Our findings suggest that the application of iron fertilizers or selenium-oxidizing bacteria could be a promising strategy to enhance Se bioavailability while potentially mitigating Cd/Pb accumulation in crops. However, further studies, including field trials, are necessary to confirm their effectiveness in ensuring safe cultivation and minimizing heavy metal contamination risks.
Author Contributions
S.C.: investigation, visualization, methodology, writing—original draft; J.L.: investigation, conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft; F.J.: methodology, investigation, writing—review and editing; Y.W.: conceptualization, methodology, funding acquisition, supervision, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 42207236), and the Fundamental Science Project of Nantong (no. JC12022075).
Data Availability Statement
The data is unavailable due to confidentiality agreement.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Kopittke, P.M.; Zhao, F.-J. Cadmium contamination in agricultural soils of China and the impact on food safety. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.-J.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Tang, Z.; McGrath, S.P. Soil Contamination in China: Current Status and Mitigation Strategies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mao, C.; Song, Y.; Chen, L.; Ji, J.; Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Yang, Z.; Ayoko, G.A.; Frost, R.L.; Theiss, F. Human health risks of heavy metals in paddy rice based on transfer characteristics of heavy metals from soil to rice. Catena 2018, 175, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natasha; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Khalid, S.; Murtaza, B.; Bibi, I.; Rashid, M.I. A critical review of selenium biogeochemical behavior in soil-plant system with an inference to human health. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 915–934. [Google Scholar]
- Bouida, L.; Rafatullah, M.; Kerrouche, A.; Qutob, M.; Alosaimi, A.M.; Alorfi, H.S.; Hussein, M.A. A review on cadmium and lead contamination: Sources, fate, mechanism, health effects and remediation methods. Water 2022, 14, 3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Yang, Y.; Li, C.; Shen, Z.; Li, J.; Mei, N.; Wang, D. Heavy metal pollution in agricultural soils from surrounding industries with low emissions: Assessing contamination levels and sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170610. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Shen, Z.; Dou, C.; Dou, Z.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Q. Effects of soil properties on heavy metal bioavailability and accumulation in crop grains under different farmland use patterns. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicińska, A.; Pomykała, R.; Izquierdo-Diaz, M. Changes in soil pH and mobility of heavy metals in contaminated soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 73, e13203. [Google Scholar]
- Businelli, D.; Onofri, A.; Massaccesi, L. Factors involved in uptake of lead by some edible crops grown in agricultural soils of Central Italy. Soil Sci. 2011, 176, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Prasad, S.; Yadav, K.K.; Shrivastava, M.; Gupta, N.; Nagar, S.; Malav, L.C. Hazardous heavy metals contamination of vegetables and food chain: Role of sustainable remediation approaches—A review. Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas-Acien, A.; Guallar, E.; Silbergeld, E.K.; Rothenberg, S.J. Lead exposure and cardiovascular disease—A systematic review. Environ. Health Perspect 2007, 115, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tan, H.; Zhou, S.; Dong, K.F.; Xiao, G. Regional characteristics of dietary lead intake in the Chinese population. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hettiarachchi, G.M.; Pierzynski, G.M. Soil lead bioavailability and in situ remediation of lead-contaminated soils: A review. Environ. Prog. 2004, 23, 78–93. [Google Scholar]
- Khaliq, M.A.; James, B.; Chen, Y.H.; Saqib, H.S.A.; Li, H.H.; Jayasuriya, P.; Guo, W. Uptake, translocation, and accumulation of Cd and its interaction with mineral nutrients (Fe, Zn, Ni, Ca, Mg) in upland rice. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 916–924. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Ji, J.; Yang, Z.; Chen, L.; Browne, P.; Yu, R. Effects of Soil Properties on the Transfer of Cadmium from Soil to Wheat in the Yangtze River Delta Region, China—A Typical Industry–Agriculture Transition Area. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2012, 148, 264–274. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, T.; Li, Z.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, D.; Hou, J.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Christie, P. Estimating cadmium availability to the hyperaccumulator Sedum plumbizincicola in a wide range of soil types using a piecewise function. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 637–638, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Yin, A.; Yang, X.; Wu, P.; Fan, M.; Wu, J.; Zhang, M.; Gao, C. Changes in surface soil organic/inorganic carbon concentrations and their driving forces in reclaimed coastal tidal flats. Geoderma 2019, 352, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ji, W.; Wei, N.; Liao, Q.; Huang, D.; Meng, X.; Song, Y. Influencing Factors of Elevated Levels of Potentially Toxic Elements in Agricultural Soils from Typical Karst Regions of China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, F.-J.; Davison, W. Distinguishing Diffusional and Plant Control of Cd and Ni Uptake by Hyperaccumulator and Nonhyperaccumulator Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6636–6641. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhuo, X.; Guan, D.-X.; Song, Y.; Guo, C.; Ji, J. Evaluation of various approaches to predict cadmium bioavailability to rice grown in soils with high geochemical background in the karst region, Southwestern China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 258, 113645. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.N.; Zhang, H.; Davison, W.; Zhao, S.; Lu, Y.; Dong, F.; Zhang, L.; Pan, Q. Evaluation of in Situ DGT Measurements for Predicting the Concentration of Cd in Chinese Field-Cultivated Rice: Impact of Soil Cd:Zn Ratios. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8009–8016. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Almås, R.; Lombnæs, P.; Sogn, T.A.; Mulder, J. Speciation of Cd and Zn in contaminated soils assessed by DGT-DIFS, and WHAM/Model VI in relation to uptake by spinach and ryegrass. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, D.-X.; Zheng, J.-L.; Luo, J.; Zhang, H.; Davison, W.; Ma, L.Q. A diffusive gradient in thin-films technique for the assessment of bisphenols desorption from soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 331, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- FAO. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, World reference base for soil resources. In International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Q.; Evans, L.J.; Gu, X.; Fan, D.; Jin, Y.; Wang, H. A regional geochemical survey of soils in Jiangsu Province, China: Preliminary assessment of soil fertility and soil contamination. Geoderma 2007, 142, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Callesen, I.; Keck, H.; Andersen, T.J. Particle size distribution in soils and marine sediments by laser diffraction using Malvern Mastersizer 2000—Method uncertainty including the effect of hydrogen peroxide pretreatment. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 2500–2510. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, X.; Luo, J.; Yu, H.; Zhang, H. Evaluation of Holistic Approaches to Predicting the Concentrations of Metals in Field-Cultivated Rice. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7649–7654. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, T.; Bu, W.; Yan, W.; Shi, C.; Yan, M. New Series of Soil Geochemical Reference Materials (GSS 10-16) from the Main Overburden Region in China. Geostandard. Newslett. 2003, 27, 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, A.K.; Pathak, C. Accumulation of heavy metals in the vegetables grown in wastewater irrigated areas of Dehradun, India with reference to human health risk. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 445. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Cheng, H.; Ren, J.; Davison, W.; Zhang, H. Mechanistic Insights from DGT and Soil Solution Measurements on the Uptake of Ni and Cd by Radish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7305–7313. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tao, C.; Ji, W.; Huang, S.; Zhou, M.; Meng, X. Bioavailability of Cd in Agricultural Soils Evaluated by DGT Measurements and the DIFS Model in Relation to Uptake by Rice and Tea Plants. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Xing, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, H.; Jia, M.; Hu, W.; Huang, B. Cadmium phytoavailability under greenhouse vegetable production system measured by diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) and its implications for the soil threshold. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 412–421. [Google Scholar]
- Sochaczewski, Ł.; Tych, W.; Davison, B.; Zhang, H. 2D DGT induced fluxes in sediments and soils (2D DIFS). Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013; ISBN 3-900051-07-0. Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wen, Y. Distributions and Influencing Factors of Heavy Metals in Soils from Zhenjiang and Yangzhou, China. Minerals 2025, 15, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB-15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China (MEE): Beijing, China, 2018.
- GB2762-2022; National Standards for Food Safety and Limits of Contaminants for Food. NHFPC and NMPA, National Health and Family Planning Commission and National Medical Products Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Li, H.; Luo, N.; Li, Y.W.; Cai, Q.Y.; Mo, C.H.; Wong, M.H. Cadmium in rice: Transport mechanisms, influencing factors, and minimizing measures. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 622–630. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.X.; Shen, L.F.; Liu, J.W.; Wang, Y.W.; Li, S.R. Uptake of toxic heavy metals by rice (Oryza sativa L.) cul-tivated in the agricultural soil near Zhengzhou City, People’s Republic of China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 79, 209–213. [Google Scholar]
- Loganathan, P.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Naidu, R. Cadmium Sorption and Desorption in Soils: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 489–533. [Google Scholar]
- Tahervand, S.; Jalali, M. Sorption, desorption, and speciation of Cd, Ni, and Fe by four calcareous soils as affected by pH. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 322. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Zhou, W.; Dai, H.; Cao, F.; Zhang, G.; Wu, F. Selenium reduces cadmium uptake and mitigates cadmium toxicity in rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 235–236, 343–351. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Chang, Q.; Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Ayoko, G.A.; Frost, R.L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Song, W. Cadmium transfer from contaminated soils to the human body through rice consumption in southern Jiangsu Province, China. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2017, 19, 843–850. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Niu, Y.; Fan, K.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Zheng, S. Selenium-oxidizing Agrobacterium sp. T3F4 steadily colonizes in soil promoting selenium uptake by pak choi (Brassica campestris). Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 791, 148294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Adams, C.A.; Shi, Z.; Sun, Y. Combined effects of ZnO NPs and Cd on sweet sorghum as influenced by an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, P.P.; Lv, X.Z.; Wang, G.Y. Effects of Se and Zn supplementation on the antagonism against Pb and Cd in veg-etables. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).