Abstract
Southwestern Guizhou, China, is famous for hosting clusters of Carlin-type Au, Sb, and Hg-Tl deposits. These deposits are thought to be the products of a low-temperature hydrothermal metallogenic event. Calcite and fluorite are common and widespread gangue minerals in Au and Sb deposits, respectively. Ore-related calcite commonly coexists with stibnite, realgar, and orpiment at the periphery of high-grade orebodies in Au deposits, while ore-related fluorite is generally intergrown with stibnite in Sb deposits. In this study, ore-related calcite and fluorite samples from representative Au (Zimudang) and Sb (Dachang) deposits, respectively, were separated, and the rare earth element (REE) concentrations, Sm/Nd isotope ratios, and Sm–Nd isochron ages were analyzed. This study aims to determine the formation ages of the calcite and fluorite and to constrain the age of low-temperature metallogenic event in Southwestern Guizhou. The calcite and fluorite samples contain relatively high total concentrations of REEs (8.21–22.5 μg/g for calcite, 21.7–36.6 μg/g for fluorite), exhibit variable Sm/Nd ratios (0.51–1.01 for calcite, 0.35–0.49 for fluorite), and yield Sm–Nd isochron ages of 148.4 ± 4.8 and 141 ± 20 Ma, respectively. These ages are consistent with the age range constrained by the low-temperature thermochronology of zircon (132–160 Ma), crosscutting relationships of stratigraphy or intrusions (96–160 Ma), and previous dating results (135–150 Ma) in Southwestern Guizhou. Collectively, the ages obtained in this study add new evidence to previous geochronology studies, such that the low-temperature hydrothermal mineralization in Southwestern Guizhou can be constrained to 135–150 Ma, corresponding to the Yanshanian orogeny, which was associated with a weak extensional tectonic environment.
1. Introduction
The Youjiang basin hosts clusters of Carlin-type Au, Sb, and Hg-Tl deposits (Figure 1) [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8], such that it is the second largest low-temperature Carlin-type Au mineralized area in the world, after Nevada, USA [9,10,11,12,13]. The Au and Sb deposits in the Youjiang Basin are primarily located within Southwestern Guizhou and account for more than 70% of the deposits and endowments.
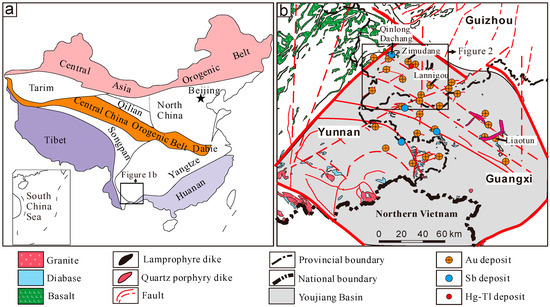
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic tectonic map of China showing the location of the Youjiang Basin. (b) Geologic map of the Youjiang Basin showing the locations of the Carlin-type Au, Sb, and Hg-Tl deposits.
Accurate geochronology is a crucial tool for understanding the genesis of ore deposits. Direct dating of Au and Sb deposits in Southwestern Guizhou has been problematic owing to a lack of suitable minerals for radiometric dating. Many studies have reported ages for Au and Sb deposits in Southwestern Guizhou, but the true ages remain controversial because the results span a large age interval, i.e., 235–195 [14,15], 135–150 [16,17,18,19,20], and 83–106 Ma [21,22]. This uncertainty hampers our understanding of the genesis of Au and Sb deposits and their relation to the geotectonic evolution of Southwestern Guizhou.
Sm and Nd have similar chemical properties, and the 143Nd daughter, which decays from the parent 147Sm, is easily preserved in a mineral lattice. Sm–Nd isotope systematics are liable to be kept closed and are partially capable of resisting weathering and/or alteration [23]. The Sm–Nd isochron method is an effective tool for dating hydrothermal Ca-bearing minerals and has been used in various hydrothermal deposits for geochronology studies (e.g., calcite [18,19,24,25,26], scheelite [27,28,29], fluorite [30,31,32], and tourmaline [27,28]).
Fluorite and calcite are widespread Ca-bearing minerals in Au and Sb deposits in Southwestern Guizhou, respectively. They usually have higher rare earth element (REE) concentrations and relatively variable Sm/Nd ratios, which are favorable for Sm–Nd isotope dating [18,19,20,33]. Ore-related calcite is generally intergrown with realgar and orpiment at Au deposits and is thought to be the product of decarbonatization (carbonate dissolution) of host rocks, providing Fe2+ to form Au-bearing pyrite [18,19,33]. Calcite deposited from decarbonatization reflects the age of Au mineralization [18,19]. Ore-related stibnite is symbiotic and coeval with fluorite crystallization, such that fluorite Sm–Nd dating can represent the age of Sb mineralization [20].
In this paper, we report the REE patterns, Sm/Nd isotope ratios, and Sm–Nd isochron ages of ore-related calcite and fluorite from representative Au (Zimudang) and Sb (Dangchang) deposits in Southwestern Guizhou, respectively. We aim to explore the temporal relationships of Au and Sb mineralization and constrain the age of low-temperature metallogenic events in Southwestern Guizhou.
2. Geological Setting
The Youjiang Basin is located at the southwestern margin of the Yangtze Craton (Figure 1a). This region is commonly referred to as the “Dian-Qian Gui” Golden Triangle Region (Figure 1b) [14]. The basin overlays a Lower Paleozoic basement, which evolved from a rift basin (Early Devonian to Late Devonian) to a passive continental margin (Early Carboniferous to Early Triassic) and then a foreland basin (Middle Triassic) [34]. The Youjiang Basin was then uplifted by the Indosinian orogeny at the end of the Late Triassic and, subsequently, folded by the Yanshanian orogeny after the Early Jurassic [35,36].
Southwestern Guizhou (Figure 2), situated north of the Youjiang Basin (Figure 1b), contains several super-large or large Au (e.g., Shuiyindong, Lannigou, Zimudang, and Getang) and Sb (e.g., Qinglong and Dachang) deposits. These deposits are thought to have formed during a low-temperature hydrothermal metallogenic event [1,5,17,37], where the Au and Sb orebodies were primarily controlled by short-axis anticlines (domes) and associated fracture zones (Figure 2). The majority of the exposed strata in this region are Devonian to Triassic, with the Triassic system being distributed most widely, which was followed by the Permian, while the Devonian and Carboniferous are sporadically exposed at some cores of anticlines or domes. The magmatic rocks mainly include the Emeishan flood basalts and alkaline ultrabasic pipes and dikes. An unconformity (SBT) between the Middle and Upper Permian, consisting of altered breccia [38], is thought to be the structural conduit that fed ore fluids into the cores of the anticlines (domes) [39]. The Au and Sb mineralization occurs primarily in the SBT and the Upper Permian to Lower Triassic systems.
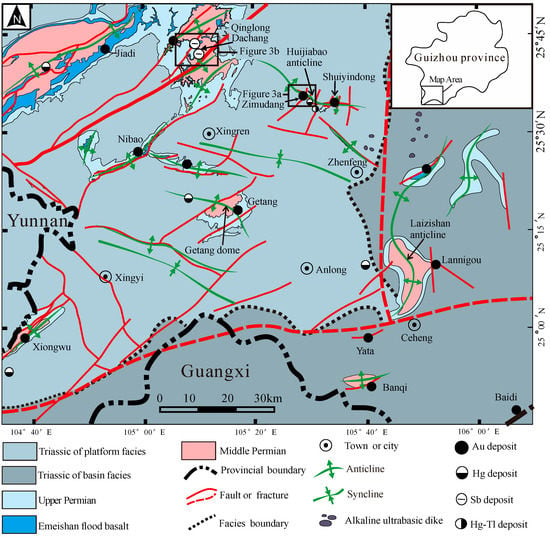
Figure 2.
Geological map of Southwestern Guizhou showing the distributions of major Carlin-type Au, Sb, Hg, and Hg-Tl deposits.
The Zimudang large Au deposit, with a total Au reserve of over 72 tons [17], is located west of the Huijiabao anticline. The Au orebodies tend to be found in silicified brecciated argillite and limestone of the SBT and in bioclastic limestone, siltstones, and claystone of the Upper Permian and Lower Triassic (Figure 3a,b). Hydrothermal alterations include silicification, decarbonatization, sulfidation, dolomitization, and argillization. Ore minerals consist primarily of arsenian pyrite and arsenopyrite, with small amounts of orpiment, realgar, stibnite, and cinnabar. Gangue minerals include calcite, quartz, and fluorite. The stibnite, realgar, and orpiment commonly coexist with the ore-related calcite vein (Figure 4a,b).
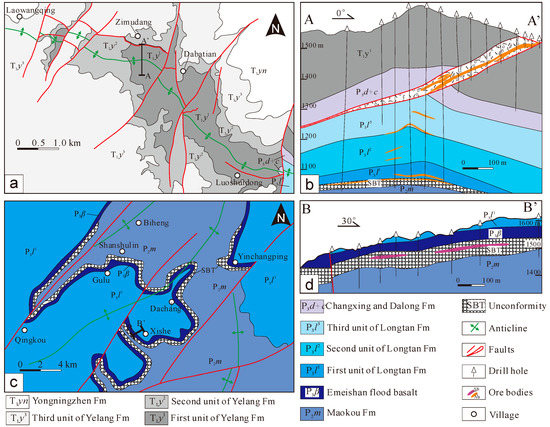
Figure 3.
Geologic plan and cross-section of the Zimudang Au deposit (a,b) and Dachang Sb deposit (c,d). Abbreviations: Fm = Formation.
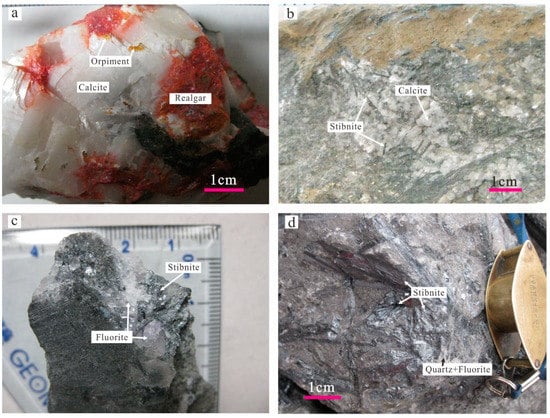

Figure 4.
Photographs of calcite (a,b) and fluorite (c,d) from the Zimudang Au deposit and Dachang Sb deposit, respectively.
The Dachang large Sb deposit contains a proven and inferred Sb resource of approximately 30 ten thousand tons [5]. The Sb orebodies are generally found within silicified brecciated basalt, basaltic volcanic tuff, and limestone of the SBT (Figure 3c,d). Hydrothermal alterations are similar to the Au deposits in the region, including silicification, decarbonatization, sulfidation, argillization, fluoritization, and minor baritization. Stibnite is the dominant ore mineral, and fluorite and quartz are the major gangue minerals. Quartz and fluorite are generally in assemblage with stibnite (Figure 4c,d).
3. Samples and Analytic Methods
A total of five calcite and five fluorite samples were collected from the Zimudang Au and Dachang Sb deposits, respectively. The calcite samples are intergrown with realgar and orpiment in high-grade Au ores (Figure 4a,b), and the fluorite samples coexist with stibnite and quartz (Figure 4c,d) in high-grade Sb ores. The paragenesis suggests that the calcite and fluorite are closely related to Au and Sb mineralization, respectively. The fluorite and calcite samples were crushed into 40 to 60 meshes and then hand-picked under a binocular microscope, yielding a mineral purity of more than 99%. Finally, the pure calcite and fluorite separates were finely crushed to 200 mesh in an agate mortar.
The REE contents for calcite and fluorite were analyzed using an ELAN 6000 inductively coupled plasma quadrupole mass spectrometer at the Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Guiyang, China). The detailed analytical methods are described by Qi et al. [40], and the analysis accuracy was better than ±5%. Sm and Nd concentrations and their isotope ratio measurements were performed using an IsoProbe Thermal Ionization Mass Spectrometer at the Tianjin Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (Tianjin, China). Detailed analytical procedures are available in Peng et al. [23], Su et al. [18], and Zhang et al. [41]. The reproducibility of the isotopic ratios was better than 0.005% (2σ). The precision for the Sm and Nd content was less than 0.5% of the quoted values (2σ). Sm–Nd isochron ages were calculated using the Excel add-in ISOPLOT 2.9 (U.S. Geological Survey, Washington, DC, USA) [42], and the decay constant used in the calculation was λ147Sm = 6.54 × 10−12/year.
4. Results
The REE concentrations and Sm–Nd isotopic compositions of calcite and fluorite are presented in Table 1 and Table 2, respectively. The ΣREE contents of calcite and fluorite range from 8.21–22.5 and 21.7–36.6 μg/g, showing variable Sm/Nd ratios of 0.51–1.01 and 0.35–0.49, respectively. C1 chondrite-normalized [43] REE patterns of calcite (Figure 5a) and fluorite (Figure 5b) exhibit apparent differences, although all samples show middle rare earth element (MREE) enrichment characteristics. The calcite samples from the Zimudang Au deposit are characterized by positive Eu anomalies (δEu = 1.24–1.38), whereas the fluorite samples from the Dachang Sb deposit are characterized by negative Ce anomalies (δCe = 0.67–0.72).

Table 1.
Rare earth element (REE) compositions (μg/g) of the calcite and fluorite samples.

Table 2.
Sm–Nd isotopic compositions of the calcite and fluorite samples.
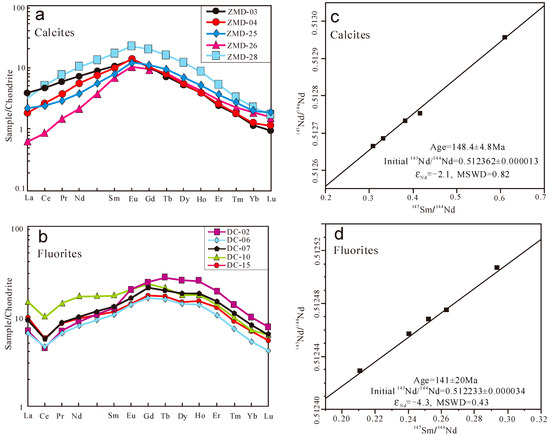
Figure 5.
C1 chondrite-normalized [43] rare earth element (REE) patterns (a,b) and corresponding Sm–Nd isochron ages (c,d) of the calcite and fluorite.
The calcite samples show 147Sm/144Nd and 143Nd/144Nd values ranging from 0.3093 to 0.6105 and 0.512612 to 0.512956, respectively. The fluorite samples have 147Sm/144Nd and 143Nd/144Nd values of 0.2109–0.2934 and 0.512429–0.512507, respectively. Calcite and fluorite all display good linear relationships in the 147Sm/144Nd-143Nd/144Nd diagram (Figure 5c,d). Calcite yields an Sm–Nd isochron age of 148.4 ± 4.8 Ma, with a low mean square of weighted deviates (MSWD) of 0.82 and an initial 143Nd/144Nd ratio of 0.512362 ± 0.000013 (initial = −2.1). Fluorite yields an Sm–Nd isochron age of 141 ± 20 Ma, with a low MSWD of 0.43 and an initial 143Nd/144Nd ratio of 0.512233 ± 0.000034 (initial = −4.3).
5. Interpretations and Discussion
5.1. REE Features in Calcite and Fluorite
MREE-enriched patterns of calcite and fluorite are currently not well understood. MREE-enriched calcite and fluorite also occur in other low-temperature hydrothermal deposits in Southwestern Guizhou, such as calcite in the Shuiyindong [18] and Banqi [44] Au deposits, and fluorite in the Qinlong [20] and Banpo [25] Sb deposits. MREE-enriched patterns were also observed in natural terrestrial waters and acidic leachates by Johannesson et al. [45,46]. Johannesson et al. [45] proposed solid-liquid exchange reactions, dissolution of MREE-enriched surface Fe-Mn coatings, particulates, secondary mineral phases, and sulfate complexation as possible mechanisms to develop these MREE-enriched patterns. The ore-forming fluids for the Au and Sb deposits in Southwestern Guizhou may be MREE-enriched, and the calcite and fluorite likely inherited the MREE-enriched pattern of the ore forming fluids from which the calcite and fluorite precipitated [33].
In natural aqueous systems, the occurrence of Eu and Ce anomalies, which are due to redox reactions, may indicate reducing conditions for the former and oxidizing conditions for the latter [47]. Fluid inclusion studies of quartz in the Zimudang Au deposit [48] show that the ore-forming fluids were low temperature (approximately 200–230 °C), CO2 and CH4 rich, and reducing. Thermodynamic calculations suggest that, at an elevated temperature (>200 °C) and reducing conditions, Eu2+ should be dominant over Eu3+ [49] and may preferentially substitute for Ca2+ over trivalent REEs in calcite, leading to the positive Eu anomalies observed in this study. Negative Ce anomalies have been extensively investigated in sea and river waters [47]. The Ce anomaly occurs in response to the oxidation of Ce3+ to Ce4+ and the precipitation of Ce4+ from solution as CeO2 [50]. Fluid inclusion studies for fluorite in the Dachang Sb deposit [48] show that a large volume of meteoric water was involved in the ore-forming fluids at the Sb metallogenic stage, decreasing the fluid temperature (140–160 °C), which may have led to the negative Ce anomalies in fluorite.
The initial values can also be used to obtain evidence on the source of Nd. The relative higher initial value (−2.1) for calcite is similar to calcite from the Shuiyindong Au deposit (−2.0 to −1.1 at 145 Ma; [18,19]), and the lower initial value (−4.3) for fluorite resembles that from the Qinglong Sb deposit (−3.7 to −5.8 at 145 Ma) [20]. The host rocks of the Au and Sb mineralization in Southwestern Guizhou are primarily limestone and basaltic volcanic tuff from the Permian. The initial values of calcite and fluorite in this study are within the range of values for Permian limestone (−6.3) and basaltic volcanic tuff (+1.5) at 145 Ma [20,51]. Thus, the values of the calcite and fluorite may have been sourced from mixtures of basaltic volcanic tuff and bioclastic limestone in the Permian.
5.2. Au and Sb Metallogenic Age in Southwestern Guizhou
The linear relationships shown in Figure 5c,d represent isochrons or mixed lines with two end-members characterized by significantly different 143Nd/144Nd and 147Sm/144Nd ratios. In the former, the slopes of the straight lines determine the ages of the fluorite and calcite. In the latter, the slopes have no meaning. The calcite and fluorite did not yield linear relationships in the 1/Nd vs. 143Nd/144Nd diagram (Figure 6a) and show a consistent Y/Ho ratio in the Y/Ho vs. La/Ho diagram (Figure 6b), respectively. Therefore, the two lines have isochronal significance and can accurately reflect the ages of the calcite (148.4 ± 4.8 Ma) and fluorite (141 ± 20 Ma).
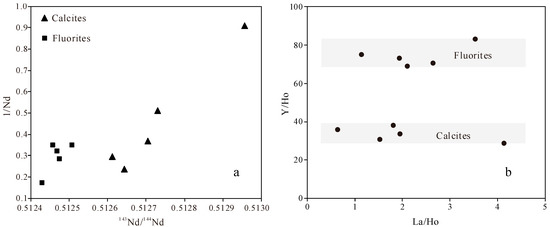
Figure 6.
Diagrams of 1/Nd vs. 143Nd/144Nd (a) and Y/Ho vs. La/Ho (b) for the calcite and fluorite.
Hydrothermal deposits are the product of a geological thermal event. Fission tracks and (U–Th)/He ratios are temperature-sensitive radiometric dating techniques. Huang et al. [35] reported fission track and (U–Th)/He ages of detrital zircons collected from the Shuiyindong, Taipingdong, Yata, and Getang Au deposits in Southwestern Guizhou. Two thermal events (i.e., 192–216 and 132–160 Ma) with temperatures higher than the Au ore-formation temperature (~210 °C [9]) were obtained. The Au and Sb metallogenic event in Southwestern Guizhou occurred at 192–216 and/or 132–160 Ma. Tan et al. [19] also reported two instances of hydrothermal fluorite (200.1 ± 8.6 Ma) and calcite (150.2 ± 2.2 Ma) minerals at the Shuiyindong Au deposit, corresponding to the Indosinian orogeny and Yanshanian orogeny, respectively.
The crosscutting relationship of stratigraphy or intrusions is the most reliable method for constraining the mineralization epoch. The Au and Sb mineralization in Southwestern Guizhou is primarily located in the Upper Permian to Triassic systems. Wang [52] described a remnant exposure of Jurassic strata near the Zimudang Au deposit that is unconformably parallel to and folded with Late Triassic strata (Figure 7b). We note that many fault-controlled orebodies in the Zimudang Au deposit crosscut the anticline. Therefore, the Au and Sb mineralization is synchronous with or younger than the folding, and the Jurassic is the maximum age limit of the Au and Sb mineralization. The parallel unconformity (ca. 200 Ma) between the Early Jurassic and Late Triassic strata may represent the weak remote response of the Indosinian orogeny that transformed the Youjiang Basin uplift into land. Huang et al. [35] reported that the oldest group of zircon fission tracks and (U–Th)/He ages (192–216 Ma) may record the cooling age of the pre-ore thermal event caused by the Indosinian orogeny. In addition, there is another exposure of Late Cretaceous sedimentary rocks (ca. 100 Ma) north of Guizhou, which is angularly unconformable to Middle Jurassic rocks (ca. 160 Ma) (Figure 7c) [36]. The angular unconformity resulted from the Yanshanian orogeny, which initiated the pervasive folding and faulting of Middle Jurassic and underlying strata and created the present structural appearance of Guizhou Province. Chen et al. [53] described a 96 Ma unaltered quartz porphyry dike that crosscuts the orebodies in the Liaotun Au deposit in Guangxi Province, which represents the minimum age limit of Au mineralization in the Youjiang Basin [4,9,54,55]. In summary, these field surveys indicate that the Au and Sb mineralization in Southwestern Guizhou formed between the Middle Jurassic (ca. 160 Ma) and Late Cretaceous periods (96 Ma).
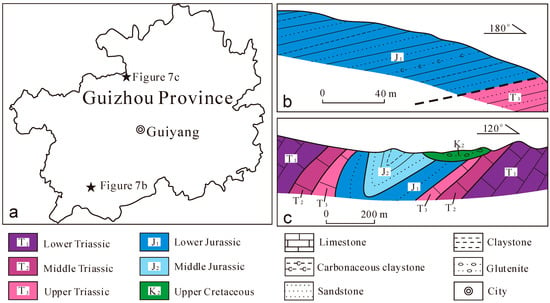
Figure 7.
Two cross-sections in Guizhou Province showing the contact relations from the Lower Triassic to the Upper Cretaceous systems. (a) Geographical map of Guizhou showing the locations of the geologic cross sections; (b) Geologic cross section near the Zimudang Au deposit showing Jurassic strata is unconformably parallel to and folded with Late Triassic strata; (c) Geologic cross section north of Guizhous showing Late Cretaceous strata is angularly unconformable to Middle Jurassic rocks.
Over the past few decades, some important progress has been made in dating hydrothermal minerals in Au and Sb deposits in Southwest Guizhou. Chen et al. [15] obtained an 40Ar–39Ar plateau age of 194.6 ± 2 Ma using sericite in quartz veins from the Lannigou Au deposit. Chen et al. [14] reported ages of 204 ± 19 Ma and 235 ± 33 Ma based on the Re–Os isotopes of arsenopyrite from the Lannigou and Shuiyindong deposits, respectively. Sm–Nd isochron ages of 134 ± 3 and 136 ± 3 Ma have been reported for calcite from the Shuiyindong Au deposit [18]. Tan et al. [19] reported another Sm–Nd isochron age of 150.2 ± 2.2 Ma of calcite from the Shuiyindong Au deposit. Peng et al. [20] obtained Sm–Nd isochron ages of 148 ± 8 and 142 ± 16 Ma from fluorite in the Qinglong Sb deposit. Chen et al. [16] obtained a weighted-mean secondary ion mass spectrometry Th–Pb age of 141 ± 3 Ma for apatite from the Nibao Au deposit. Zheng et al. [17] dated fluid inclusions in quartz from the Nibao Au deposit and obtained Rb–Sr isochron ages of 142 ± 3 and 141 ± 2 Ma.
The reported Re–Os isochron ages of the Lannigou and Shuiyindong Au deposits are likely significantly mixed and older than the Au mineralization. Ore-stage arsenopyrite is commonly intergrown with fine-grained diagenetic pyrite and is very difficult to separate [9,16,19,54]. Additionally, the reported Ar–Ar age spectrum of the sericite is highly irregular and has no plateau, indicating that this age is not reliable [9]. Excluding the unreliable ages of arsenopyrite and sericite, the age range obtained by calcite and fluorite Sm–Nd, quartz fluid inclusions Rb–Sr, and apatite Th–Pb methods is 135–150 Ma [9,16,17,19,20], which is consistent with the age interval constrained by low-temperature thermochronology (132–160 Ma) and the crosscutting relationships of stratigraphy or intrusions (96–160 Ma). The ages obtained in this study add new evidence to previous geochronology studies and reveal the regional Au and Sb mineralization age interval of 135–150 Ma corresponding to the Yanshanian orogeny.
Many studies have proposed magmatic origin models for the Au and Sb mineralization in Southwestern Guizhou based on δ34S (ore-related sulfide, approximately −5 to +5‰ [3,4,56,57,58], Δ199Hg (mineralized rocks, −0.1 to 0.1‰ [59]) and He isotope data (minerals of main ore stage, R/RA ratios ranging from 0.01 to 0.4 [2]). According to a synthesis of structural, petrological, geochronological, and geochemical studies, South China notably underwent a tectonic transition from contraction to large-scale extension and experienced extensive magmatic activity ca. 135–150 Ma as a result of the westward flat-slab subduction of the Pacific oceanic lithosphere beneath South China [60,61]. Although magmatic outcrops from 135–150 Ma are absent in Southwestern Guizhou, gravity and magnetic geophysical investigations indicate the presence of a pluton ~5 km below the surface of the Huijiabao anticline district [4]. Collectively, the low-temperature hydrothermal Au and Sb mineralization in Southwestern Guizhou is likely related to the Yanshanian magmatic activity associated with a weak, extensional, tectonic environment.
6. Conclusions
Calcite and fluorite samples, collected from the Zimudang Au deposit and the Dangchang Sb deposit, respectively, are symbiotic with sulfides of a metallogenic stage (e.g., realgar, orpiment, and stibnite), and they are thought to be coeval with Au and Sb mineralization. The ore-related calcite and fluorite yielded Sm–Nd isochron ages of 148.4 ± 4.8 and 141 ± 20 Ma, respectively. These results, combined with regional low-temperature thermochronology, crosscutting relationships of stratigraphy or intrusions, and previous dating results, indicate that the Au and Sb deposits in Southwestern Guizhou most likely formed at 135–150 Ma, corresponding to the Yanshanian orogeny associated with a weak, extensional, tectonic environment.
Author Contributions
Q.T. and Y.X. designed the study concept and revised the manuscript. Z.W. contributed to the analysis, data interpretation, and manuscript preparation. J.L. (Jianzhong Liu), C.Y., S.L., J.L. (Jumhai Li), F.C., X.W., Q.P., and D.W. collected the calcite and fluorite samples. Q.T. drew the geologic maps. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of Deep penetrating Geochemistry (2016YFC0600607, 2017YFC0601500, and 2020YFC1807700), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1812402; 41803046), and the Science & Technology Department of Guizhou Province ([2019]2833, [2019]1424).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful suggestions, which improved the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, J.; Hu, R.; Xiao, J.; Zhuo, Y.; Yan, J.; Oyebamiji, A. Genesis of gold and antimony deposits in the Youjiang metallogenic province, SW China: Evidence from in situ oxygen isotopic and trace element compositions of quartz. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 116, 103257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.-Y.; Hofstra, A.H.; Hunt, A.G.; Liu, J.-Z.; Yang, W.; Li, J.-W. Noble gases fingerprint the source and evolution of ore-forming fluids of Carlin-type gold deposits in the golden triangle, south China. Econ. Geol. 2020, 115, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Hu, R.Z.; Liu, S.; Lin, Y.T.; Zhang, J.C.; Fu, S.L. NanoSIMS element mapping and sulfur isotope analysis of Au-bearing pyrite from Lannigou Carlin-type Au deposit in SW China: New insights into the origin and evolution of Au-bearing fluids. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 92, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.J.; Xia, Y.; Cline, J.S.; Pribil, M.J.; Koenig, A.; Tan, Q.P.; Wei, D.T.; Wang, Z.P.; Yan, J. Magmatic origin for sediment-hosted Au deposits, Guizhou Province, China: In situ chemistry and sulfur isotope composition of pyrites, Shuiyindong and Jinfeng deposits. Econ. Geol. 2018, 113, 1627–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, R.-D.; Du, L.-J.; Zheng, L.-L.; Gao, J.-B.; Lai, C.-K.; Wei, H.-R.; Yuan, M.-G. Mineralogy, geochemistry and fluid inclusions of the Qinglong Sb-(Au) deposit, Youjiang basin (Guizhou, SW China). Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 92, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.-T.; Xia, Y.; Gregory, D.D.; Steadman, J.A.; Tan, Q.-P.; Xie, Z.-J.; Liu, X.-J. Multistage pyrites in the Nibao disseminated gold deposit, southwestern Guizhou Province, China: Insights into the origin of Au from textures, in situ trace elements, and sulfur isotope analyses. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 122, 103446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Xia, Y.; Steadman, J.; Xie, Z.; Liu, X.; Tan, Q.; Bai, L.A. Tennantite-Tetrahedrite-Series minerals and related pyrite in the Nibao Carlin-type gold deposit, Guizhou, SW China. Minerals 2020, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chang, J.; Li, C.; Han, Z.; Wang, T.; Han, H. Significance of calcite trace elements contents and C-O isotopic compositions for ore-Forming fluids and gold prospecting in the Zhesang Carlin-Like gold deposit of Southeastern Yunnan, China. Minerals 2020, 10, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.C.; Dong, W.D.; Zhang, X.C.; Shen, N.P.; Hu, R.Z.; Hofstra, A.H.; Cheng, L.Z.; Xia, Y.; Yang, K.Y. Carlin-Type gold deposits in the Dian-Qian-Gui “golden triangle” of Southwest China. In Diversity of Carlin-Style Gold Deposits, Reviews in Economic Geology; Muntean, J.L., Ed.; Society of Economic Geologists, Inc.: Littleton, CO, USA, 2018; Volume 20, pp. 157–185. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.Z.; Fu, S.L.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, M.F.; Fu, S.H.; Zhao, C.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Bi, X.W.; Xiao, J.F. The giant South China Mesozoic low-temperature metallogenic domain: Reviews and a new geodynamic model. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 137, 9–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntean, J.L.; Cline, J.S.; Simon, A.C.; Longo, A.A. Magmatic-Hydrothermal origin of Nevada’s Carlin-type gold deposits. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, J.S.; Hofstra, A.H.; Muntean, J.L.; Tosdal, R.M.; Hickey, K.A. Carlin-Type gold deposits in Nevada: Critical geologic characteristics and viable models. In Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume; Society of Economic Geologists, Inc.: Littleton, CO, USA, 2005; pp. 451–484. [Google Scholar]
- Cline, J.S. Nevada’s Carlin-type gold deposits: What we’ve learned during the past 10 to 15 years. In Diversity of Carlin-Style Gold Deposits, Reviews in Economic Geology; Muntean, J.L., Ed.; Society of Economic Geologists, Inc.: Littleton, CO, USA, 2018; Volume 20, pp. 7–37. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.H.; Mao, J.W.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Dang, Y. Re-Os isochron ages for arsenopyrite from Carlin-like gold deposits in the Yunnan–Guizhou–Guangxi “golden triangle”, southwestern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 64, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Huang, Q.W.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zhang, W. Genetic type of Phyllosilicate (Micas) and its Ar-Ar dating in Lannigou gold deposit, Guizhou Province, China. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2009, 29, 353–362, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.H.; Bagas, L.; Liao, X.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Li, Q.L. Hydrothermal apatite SIMS ThPb dating: Constraints on the timing of low-temperature hydrothermal Au deposits in Nibao, SW China. Lithos 2019, 324–325, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.L.; Yang, R.D.; Gao, J.B.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.Z.; Li, D.P. Quartz Rb-Sr isochron ages of two type orebodies from the Nibao Carlin-Type gold deposit, Guizhou, China. Minerals 2019, 9, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.C.; Hu, R.Z.; Xia, B.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Y.P. Calcite Sm-Nd isochron age of the Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit, Guizhou, China. Chem. Geol. 2009, 258, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Xia, Y.; Xie, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wei, D.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, J.; Li, S. Two hydrothermal events at the Shuiyindong Carlin-Type gold deposit in Southwestern China: Insight from Sm-Nd dating of fluorite and calcite. Minerals 2019, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.T.; Hu, R.Z.; Jiang, G.H. Samarium-Neodymium isotope system of fluorites from the Qinglong antimony deposit, Guizhou Province: Constrains on the mineralizing age and ore-forming materials’ sources. Acto Petrol. Sin. 2003, 19, 785–791, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Yang, K.Y. Mineralization time of fission track in disseminated gold deposits in Southwest Guizhou. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1992, 37, 1593–1595, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.C.; Yang, K.Y.; Hu, R.Z.; Chen, F. Fluid inclusion chronological study of the Carlin-type gold deposits in southwestern China: As exemplified by the Lannigou gold deposit, Guizhou province. Acta Mineral. Sin. 1998, 18, 359–362, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.T.; Hu, R.Z.; Burnard, P.G. Samarium-Neodymium isotope systematics of hydrothermal calcites from the Xikuangshan antimony deposit (Hunan, China): The potential of calcite as a geochronometer. Chem. Geol. 2003, 200, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.C.; Hu, R.Z.; Bi, X.W.; Wu, L.Y.; Feng, C.X.; Tang, Y.Y. Absolute and relative dating of Cu and Pb-Zn mineralization in the Baiyangping area, Yunnan Province, SW China: Sm-Nd geochronology of calcite. Geochem. J. 2015, 49, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, J.S.; Wen, H.J.; Fan, H.F.; Zhu, J.J. Sm-Nd geochronology, REE geochemistry and C and O isotope characteristics of calcites and stibnites from the Banian antimony deposit, Guizhou Province, China. Geochem. J. 2012, 46, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, I.T.; Zhao, J.X.; Golding, S.D.; Lawrence, M.G.; Glikson, M.; Collerson, K.D. Sm-Nd dating and rare-earth element tracing of calcite: Implications for fluid-flow events in the Bowen Basin, Australia. Chem. Geol. 2007, 238, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglin, C.D.; Jonasson, I.R.; Franklin, J.M. Sm-Nd dating of scheelite and tourmaline; Implications for the genesis of Archean gold deposits, Val d’Or, Canada. Econ. Geol. 1996, 91, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.; Palmer, M.R.; Waller, L. Sm-Nd and REE characteristics of tourmaline and scheelite from the Bjorkdal gold deposit, northern Sweden: Evidence of an intrusion-related gold deposit? Econ. Geol. 2006, 101, 1415–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, K.; Anglin, C.; Franklin, J. Sm-Nd and Rb-Sr isotope systematics of scheelites: Possible implications for the age and genesis of vein-hosted gold deposits. Geology 1989, 17, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesley, J.T.; Halliday, A.N.; Kyser, T.K.; Spry, P.G. Direct dating of Mississippi valley-type mineralization; use of Sm-Nd in fluorite. Econ. Geol. 1994, 89, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.; Premo, W.; Courjault-Rade, P. Sm-Nd dating of fluorite from the worldclass Montroc fluorite deposit, southern Massif Central, France. Miner. Depos. 2005, 39, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.G.; Fan, H.R.; Hu, F.F.; Santosh, M.; Yang, K.F.; Lan, T.G.; Wen, B.J. Geochronology of the Guilaizhuang gold deposit, Luxi Block, eastern North China Craton: Constraints from zircon U-Pb and fluorite-calcite Sm-Nd dating. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 65, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.P.; Xia, Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Xie, Z.J.; Wei, D.T. Carbon-Oxygen isotopes and rare earth elements as an exploration vector for Carlin-type gold deposits: A case study of the Shuiyindong gold deposit, Guizhou Province, SW China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 148, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Huang, H.; Yang, J.; Huang, H.; Tao, P.; Huang, Z.; Hu, L.; Xie, X. The basin translation from late Paleozoic to Triassic of the Youjiang basin and its tectonic signification. Geol. Rev. 2013, 59, 1–11, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Hu, R.Z.; Bi, X.W.; Fu, S.L.; Peng, K.Q.; Gao, W.; Oyebamiji, A.; Zhaanbaeva, A. Low-Temperature thermochronology of the Carlin-type gold deposits in southwestern Guizhou, China: Implications for mineralization age and geological thermal events. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 115, 103178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizhou Institute of Geological Survey. The Regional Geology of China, Guizhou Province; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2017; (In Chinese with English abstract).
- Chen, J.; Huang, Z.-L.; Yang, R.-D.; Du, L.-J.; Liao, M.-Y. Gold and antimony metallogenic relations and ore-forming process of Qinglong Sb(Au) deposit in Youjiang basin, SW China: Sulfide trace elements and sulfur isotopes. Geosci. Front. 2020, 12, 605–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Xia, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, F.E.; You, B.; Fu, Z. SBT study and ideas in patform lithofaices area in the Southwest Guizhou. Guizhou Geol. 2010, 27, 178–184, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Q.P.; Xia, Y.; Xie, Z.J.; Yan, J. Migration paths and precipitation mechanisms of ore-forming fluids at the Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit, Guizhou, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 69, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Hu, J.; Gregoire, D.C. Determination of trace elements in granites by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Talanta 2000, 51, 507–513. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.R.; Wen, H.J.; Qiu, Y.Z.; Zhang, Y.X.; Li, C. Ages of sediment-hosted Himalayan Pb-Zn-Cu-Ag polymetallic deposits in the Lanping basin, China: Re-Os geochronology of molybdenite and Sm-Nd dating of calcite. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 73, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, R.K. ISOPLOT: A Plotting and Regression Program for Radiogenic Isotope Data (Version 2.9); U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; pp. 91–445. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Han, Z.; Li, C.; Gao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, G. REE, Fe and Mn contents of calcites and their prospecting significance for the Banqi Carlin-type gold deposit in Southwestern China. Geotecton. Metallog. 2018, 42, 494–504, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Lyons, W.B.; Yelken, M.A.; Gaudette, H.E.; Stetzenbach, K.J. Geochemistry of the rare-earth elements in hypersaline and dilute acidic natural terrestrial waters: Complexation behavior and middle rare-earth element enrichments. Chem. Geol. 1996, 133, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Lyons, W.B. Rare-Earth element geochemistry of Colour Lake, an acidic freshwater lake on Axel Heiherg Island, Northwest Territories, Canada. Chem. Geol. 1995, 119, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Möller, P. Rare earth element fractionation in metamorphogenic hydrothermal calcite, magnesite and siderite. Mineral. Petrol. 1992, 45, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.P.; Xia, Y.; Song, X.Y.; Liu, J.Z.; Yang, C.F.; Yan, B.W. Study on the evolution of ore-formation fluids for Au-Sb ore deposits and the mechanism of Au-Sb paragenesis and differentiation in the southwestern part of Guizhou Province, China. Chin. J. Geochem. 2013, 32, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sverjensky, D.A. Europium redox equilibria in aqueous solution. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1984, 67, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollinson, H.R. Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation; Longman Scientific and Technical: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.-L.; Jahn, B.-M. Plume-Lithosphere interaction in generation of the Emeishan flood basalts at the Permian-Triassic boundary. Geology 1995, 23, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Affirmation of the Jurassic in Longtoushan of Zhenfeng, Guizhou and its geological significance. Guizhou Geol. 1997, 13, 201–203, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.H.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Lu, G.; Liu, S. Determination of upper limit of metallogenic epoch of Liaotun gold deposit in western Guangxi and its implications for chronology of Carlin-type gold deposits in Yunnan-Guizhou-Gangxi golden triangle area. Miner. Depos. 2014, 33, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.J.; Xia, Y.; Cline, J.S.; Koenig, A.; Wei, D.T.; Tan, Q.P.; Wang, Z.P. Are there Carlin-type gold deposits in China? A comparison of the Guizhou, China, deposits with Nevada, USA, deposits. In Diversity of Carlin-Style Gold Deposits, Reviews in Economic Geology; Muntean, J.L., Ed.; Society of Economic Geologists, Inc.: Littleton, CO, USA, 2018; Volume 20, pp. 187–233. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.J.; Hu, R.Z.; Richards, J.P.; Bi, X.-W.; Stern, R.; Lu, G. No genetic link between Late Cretaceous felsic dikes and Carlin-type Au deposits in the Youjiang basin, Southwest China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 84, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liang, J.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Hao, J.; Sun, W.; Li, J.; Xie, J. Gold and sulfur sources of the Taipingdong Carlin-type gold deposit: Constraints from simultaneous determination of sulfur isotopes and trace elements in pyrite using nanoscale secondary ion mass spectroscopy. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 117, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Zhai, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Sun, W.; Song, M.; Li, J. Multiple element mapping and in-situ S isotopes of Au-carrying pyrite of Shuiyindong gold deposit, southwestern China using NanoSIMS: Constraints on Au sources, ore fluids, and mineralization processes. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 123, 103576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.P.; Xia, Y.; Xie, Z.J.; Yan, J.; Wei, D.T. S, C, O, H, and Pb isotopic studies for the Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit, Southwest Guizhou, China: Constraints for ore genesis. Chin. J. Geochem. 2015, 34, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Deng, C.; Lehmann, B.; Sun, G.; Lepak, R.F.; Hurley, J.P.; Zhao, C.; Xu, G.; Tan, Q.; Xie, Z.; et al. Magmatic-Hydrothermal origin of mercury in Carlin-style and epithermal gold deposits in China: Evidence from mercury stable isotopes. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2019, 3, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.Z.; Zhou, M.F. Multiple Mesozoic mineralization events in South China—An introduction to the thematic issue. Miner. Depos. 2012, 47, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Li, X.H. Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China: A flat-slab subduction model. Geology 2007, 35, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).