Spherical Particle Orbits around a Rotating Black Hole in Massive Gravity
Abstract
1. Introduction and Motivation
2. Massive Theory of Gravity and Its Static Black Hole Solution in the Cosmological Background
3. Spherical Particle Orbits
3.1. Radii of Planar Orbits
Non-Monotonic Behavior of the Solutions
4. Analytical Solutions for the Spherical Particle Orbits
4.1. The Latitudinal Motion
4.2. The Azimuth Motion
4.3. Explicit Examples of Non-Planar Orbits
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. The Roots of the Polynomial Equation Δ(r) = 0
References
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.; Abernathy, M.R.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; et al. Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 061102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, K.; Alberdi, A.; Alef, W.; Asada, K.; Azulay, R.; Baczko, A.K.; Ball, D.; Baloković, M.; Barrett, J.; Bintley, D.; et al. First M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. IV. Imaging the Central Supermassive Black Hole. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 875, L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, K.; Alberdi, A.; Alef, W.; Algaba, J.C.; Anantua, R.; Asada, K.; Azulay, R.; Bach, U.; Baczko, A.K.; Ball, D.; et al. First Sagittarius A* Event Horizon Telescope Results. I. The Shadow of the Supermassive Black Hole in the Center of the Milky Way. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2022, 930, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, P.; Mangalam, A. Astrophysically relevant bound trajectories around a Kerr black hole. Class. Quantum Gravity 2019, 36, 045009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapec, D.; Lupsasca, A. Particle motion near high-spin black holes. Class. Quantum Gravity 2020, 37, 015006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gralla, S.E.; Lupsasca, A. Null geodesics of the Kerr exterior. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 044032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, L.C.; Warburton, N. Location of the last stable orbit in Kerr spacetime. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 064007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compère, G.; Druart, A. Near-horizon geodesics of high spin black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 084042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, P.; Mangalam, A. A Geometric Origin for Quasi-periodic Oscillations in Black Hole X-ray Binaries. Astrophys. J. 2020, 903, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, B. Global Structure of the Kerr Family of Gravitational Fields. Phys. Rev. 1968, 174, 1559–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mino, Y. Perturbative approach to an orbital evolution around a supermassive black hole. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 67, 084027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, R.; Hikida, W. Analytical solutions of bound timelike geodesic orbits in Kerr spacetime. Class. Quantum Gravity 2009, 26, 135002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lämmerzahl, C.; Hackmann, E. Analytical Solutions for Geodesic Equation in Black Hole Spacetimes. In 1st Karl Schwarzschild Meeting on Gravitational Physics; Nicolini, P., Kaminski, M., Mureika, J., Bleicher, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 170, pp. 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, D.C. Bound Geodesics in the Kerr Metric. Phys. Rev. D 1972, 5, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, M.; Ruffini, R. Generalized Wilkins effect and selected orbits in a Kerr-Newman geometry. Phys. Rev. D 1974, 10, 2324–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoghianidis, E.; Tsoubelis, D. Polar orbits in the Kerr space-time. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 1987, 19, 1235–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.A. Evolution of circular, nonequatorial orbits of Kerr black holes due to gravitational-wave emission. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 61, 084004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.A. Evolution of circular, nonequatorial orbits of Kerr black holes due to gravitational-wave emission. II. Inspiral trajectories and gravitational waveforms. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 64, 064004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraniotis, G.V. Precise relativistic orbits in Kerr and Kerr–(anti) de Sitter spacetimes. Class. Quantum Gravity 2004, 21, 4743–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayos, F.; Teijón, C. Geometrical locus of massive test particle orbits in the space of physical parameters in Kerr space–time. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2008, 40, 2433–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hackmann, E.; Lämmerzahl, C.; Kagramanova, V.; Kunz, J. Analytical solution of the geodesic equation in Kerr-(anti-) de Sitter space-times. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 044020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, R.; Levin, J.; Perez-Giz, G. Harmonic structure of generic Kerr orbits. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 023012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hod, S. Marginally bound (critical) geodesics of rapidly rotating black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 087502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, E. Spherical orbits around a Kerr black hole. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2021, 53, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavlayan, A.; Tekin, B. Radii of spherical timelike orbits around Kerr black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 124059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, E.; Esposito, G. Geodesic motion in Euclidean Schwarzschild geometry. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, W.L.; Turner, M.S. Colloquium: Measuring and understanding the universe. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2003, 75, 1433–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriou, T.P.; Faraoni, V. f(R) theories of gravity. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2010, 82, 451–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Felice, A.; Tsujikawa, S. f(R) Theories. Living Rev. Relativ. 2010, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiros, I. Selected topics in scalar–tensor theories and beyond. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2019, 28, 1930012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Maeda, K.-i. The Scalar-Tensor Theory of Gravitation; Cambridge Monographs on Mathematical Physics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierz, M.; Pauli, W.E.; Dirac, P.A.M. On relativistic wave equations for particles of arbitrary spin in an electromagnetic field. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1939, 173, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rham, C.; Gabadadze, G. Generalization of the Fierz-Pauli action. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 82, 044020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rham, C.; Gabadadze, G.; Tolley, A.J. Resummation of Massive Gravity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 231101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rham, C. Massive Gravity. Living Rev. Relativ. 2014, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.G.; Tannukij, L.; Wongjun, P. A class of black holes in dRGT massive gravity and their thermodynamical properties. Eur. Phys. J. C 2016, 76, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panpanich, S.; Burikham, P. Fitting rotation curves of galaxies by de Rham-Gabadadze-Tolley massive gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 064008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtekar, A. Implications of a positive cosmological constant for general relativity. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2017, 80, 102901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonserm, P.; Ngampitipan, T.; Simpson, A.; Visser, M. Innermost and outermost stable circular orbits in the presence of a positive cosmological constant. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 024050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón, A.; Panotopoulos, G.; Lopes, I.; Cruz, N. ISCOs and OSCOs in the Presence of a Positive Cosmological Constant in Massive Gravity. Universe 2021, 7, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezhiani, L.; Chkareuli, G.; de Rham, C.; Gabadadze, G.; Tolley, A.J. On black holes in massive gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 044024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.F.; Easson, D.A.; Gao, C.; Saridakis, E.N. Charged black holes in nonlinear massive gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 064001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, E.T.; Janis, A.I. Note on the Kerr Spinning-Particle Metric. J. Math. Phys. 1965, 6, 915–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azreg-Aïnou, M. Generating rotating regular black hole solutions without complexification. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 064041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, J.M.; Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A. Rotating Black Holes: Locally Nonrotating Frames, Energy Extraction, and Scalar Synchrotron Radiation. Astrophys. J. 1972, 178, 347–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, J. Timelike and null geodesics in the Kerr metric. In Les Houches Summer School of Theoretical Physics: Black Holes; American Astronomical Society: Les Houches, France, 1973; pp. 215–240. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekhar, S. The Mathematical Theory of Black Holes; Oxford Classic Texts in the Physical Sciences; Oxford University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kraniotis, G.V. Gravitational redshift/blueshift of light emitted by geodesic test particles, frame-dragging and pericentre-shift effects, in the Kerr–Newman–de Sitter and Kerr–Newman black hole geometries. Eur. Phys. J. C 2021, 81, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokuchaev, V.I.; Nazarova, N.O. Visible Shapes of Black Holes M87* and SgrA*. Universe 2020, 6, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y. The evolutions of the innermost stable circular orbits in dynamical spacetimes. Eur. Phys. J. C 2021, 81, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Yang, H.Y.K. Curved accretion disks around rotating black holes without reflection symmetry. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospino, J.; Hernández-Pastora, J.L.; Núñez, L.A. All analytic solutions for geodesic motion in axially symmetric space-times. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Liu, W.; Wu, X. Integrability of Kerr-Newman spacetime with cloud strings, quintessence and electromagnetic field. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 105, 124039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogush, I.; Gal’tsov, D.; Gyulchev, G.; Kobialko, K.; Nedkova, P.; Vetsov, T. Photon surfaces, shadows, and accretion disks in gravity with minimally coupled scalar field. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 106, 024034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baines, J.; Berry, T.; Simpson, A.; Visser, M. Constant-r geodesics in the Painlevé–Gullstrand form of Lense–Thirring spacetime. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2022, 54, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dymnikova, I.; Dobosz, A. Orbits of Particles and Photons around Regular Rotating Black Holes and Solitons. Symmetry 2023, 15, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogush, I.; Kobialko, K.; Gal’tsov, D. Glued massive particles surfaces. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.12888. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi, M.; Olivares, M.; Villanueva, J.R. Spherical photon orbits around a rotating black hole with quintessence and cloud of strings. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2023, 138, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
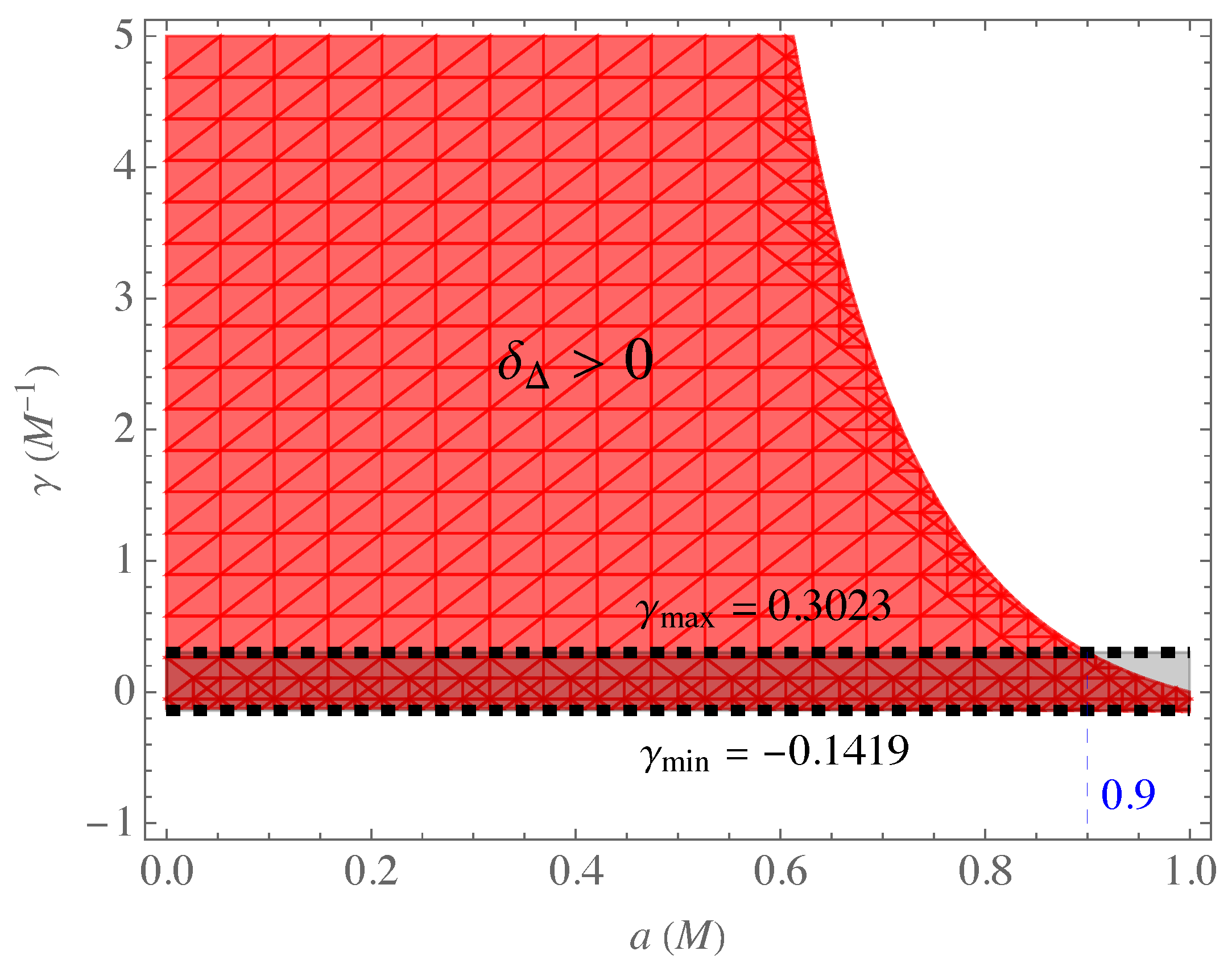
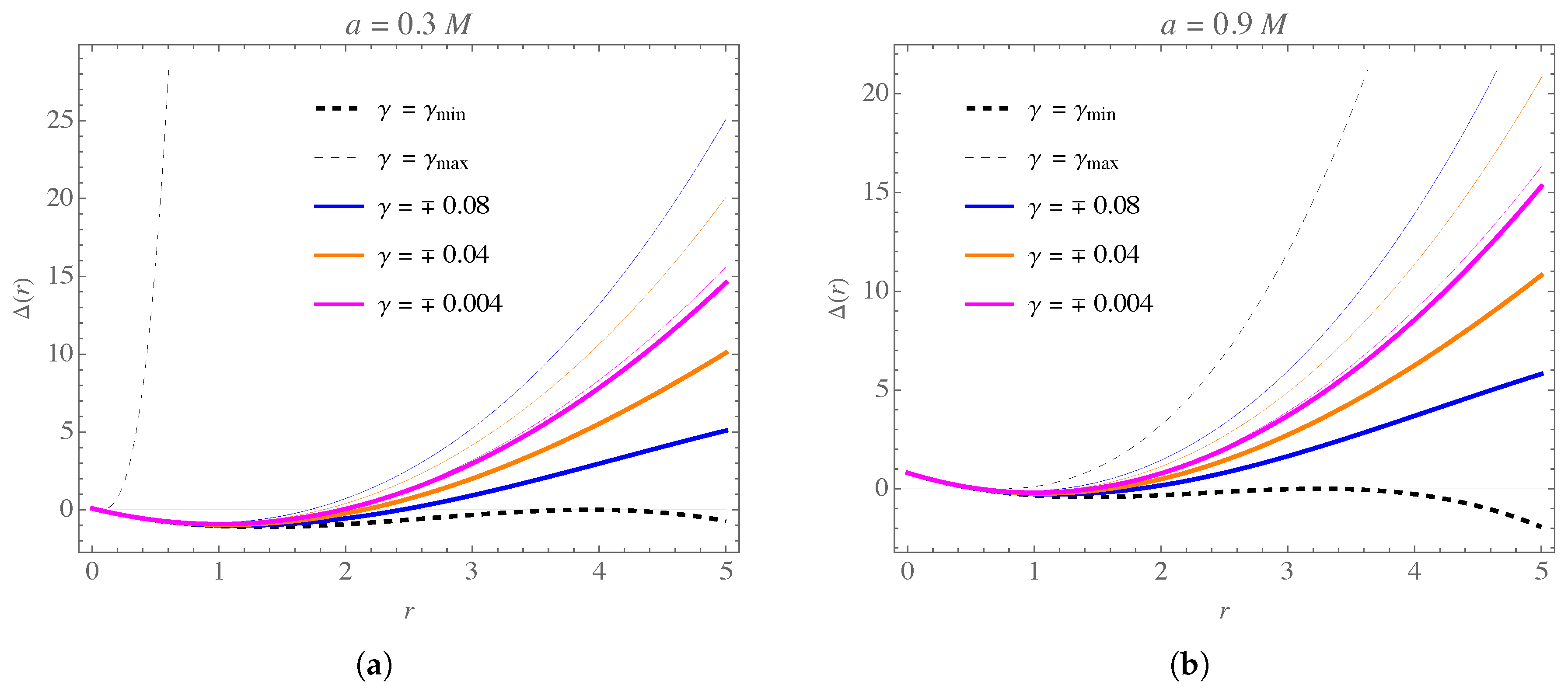
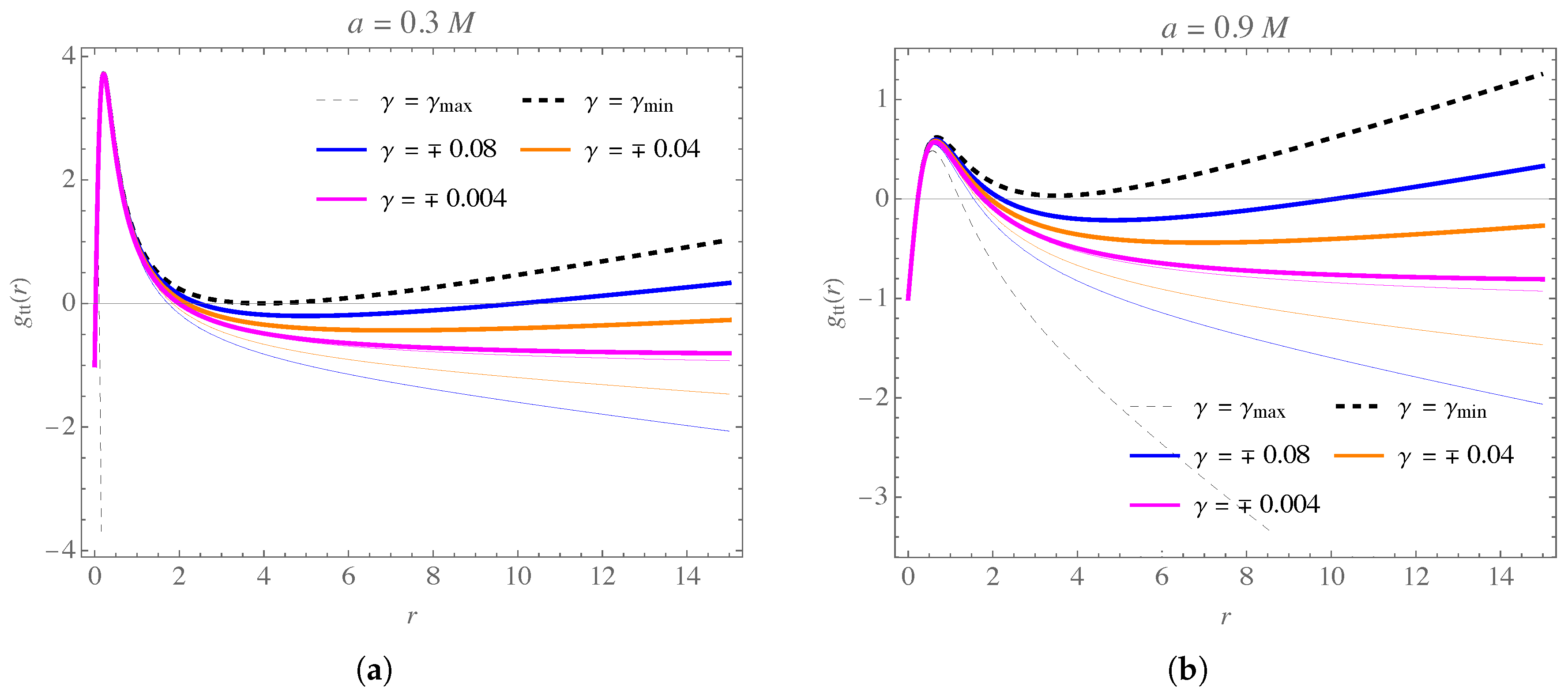
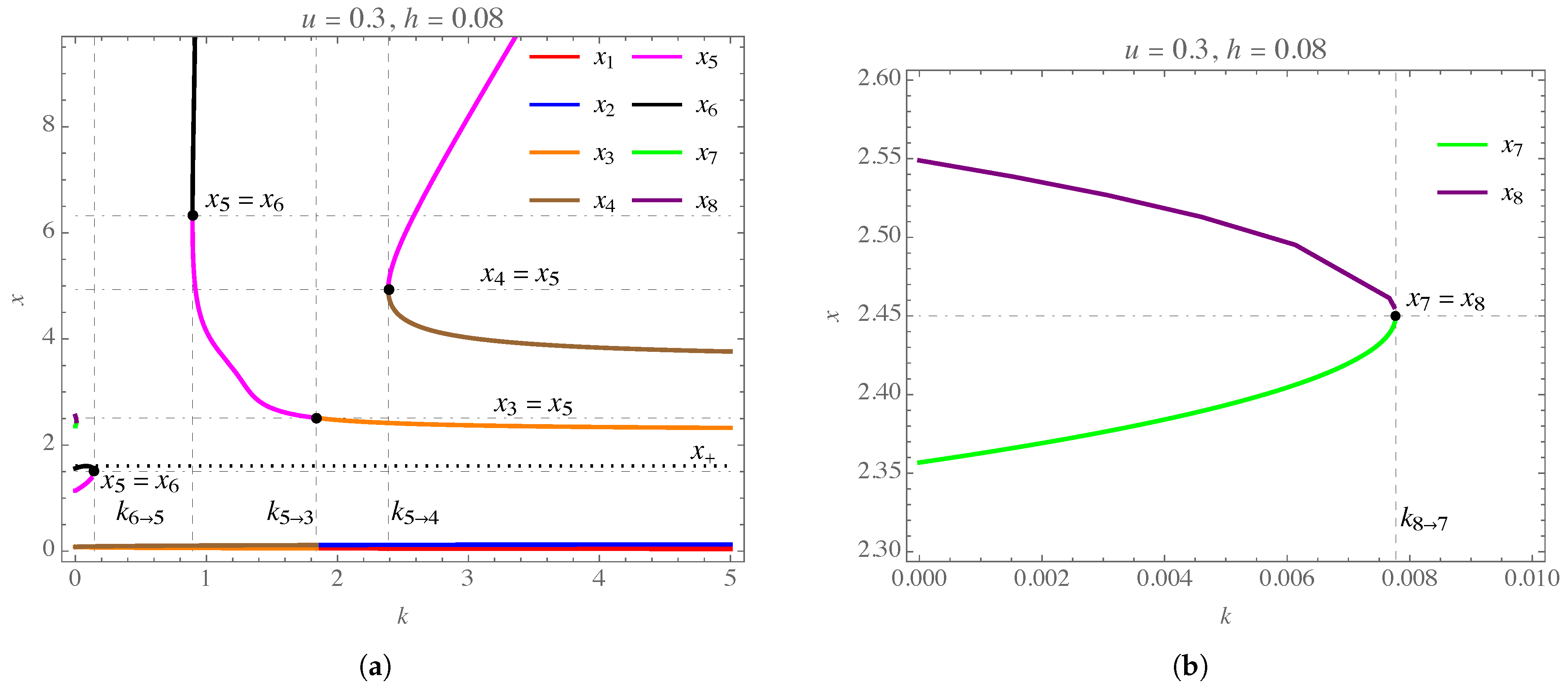
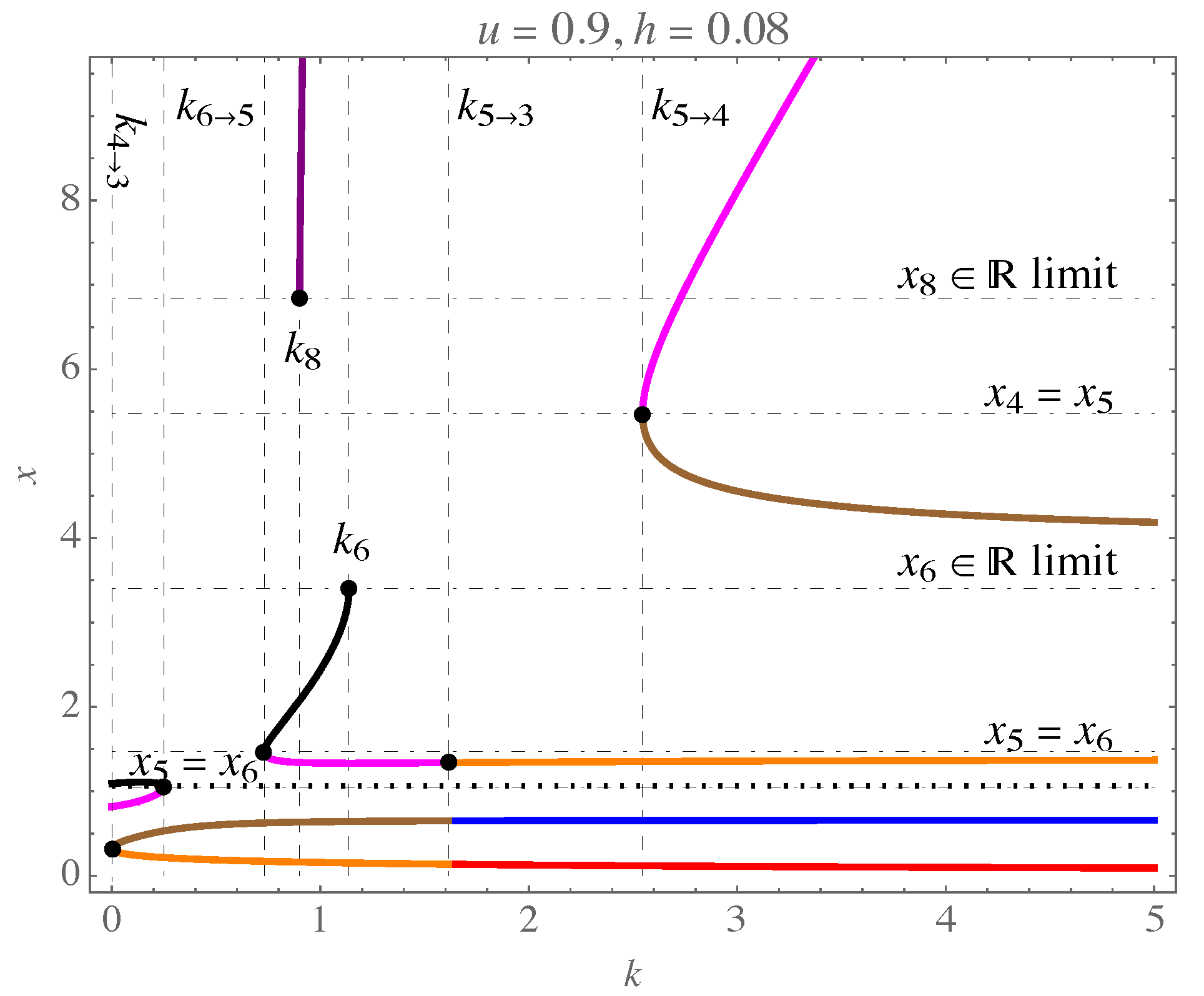

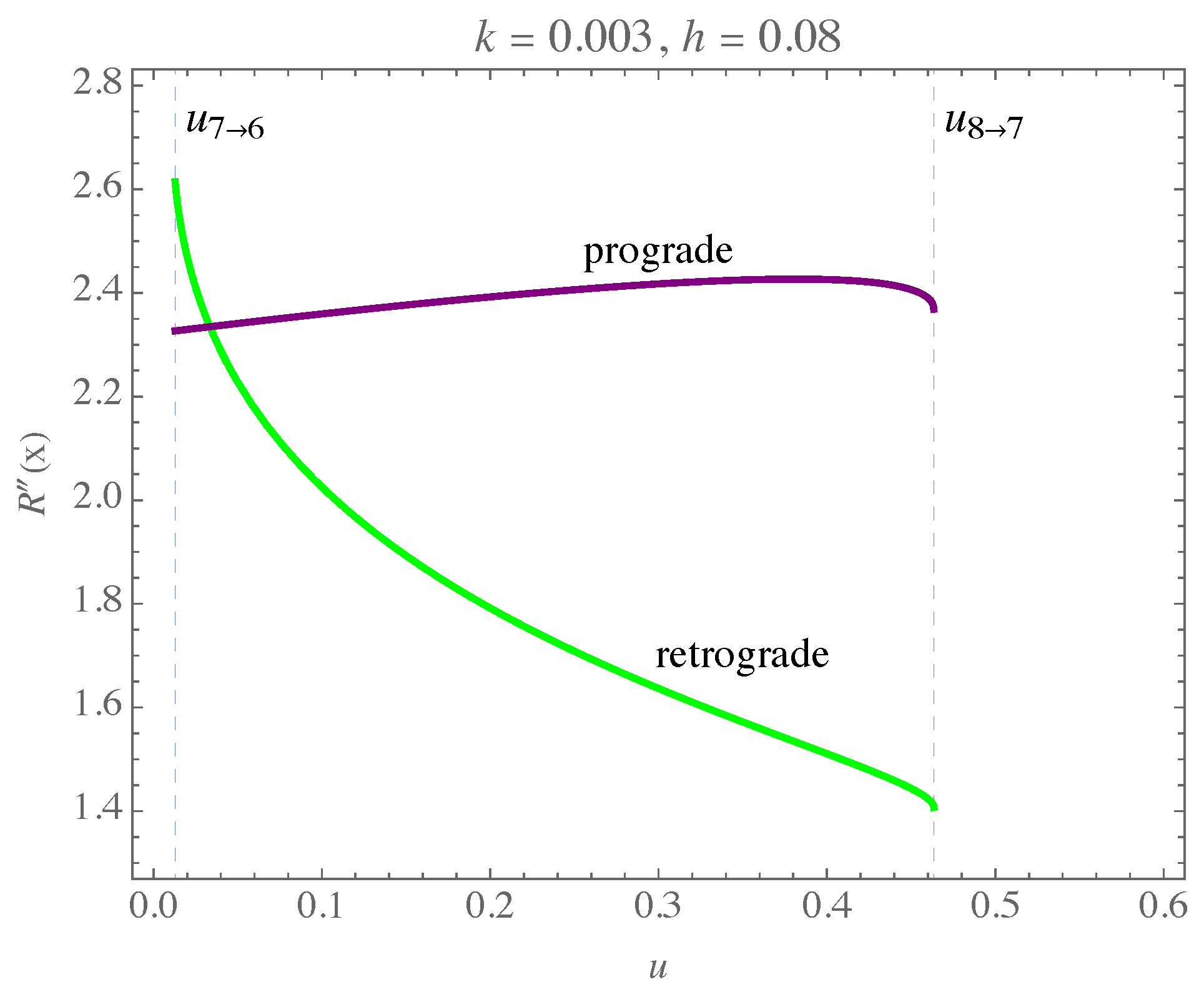

| k | u | k | u | k | u | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.1 | 1.762 | 2.213, 2.517 | 1 | 0.1 | – | 4.047 | 2 | 0.1 | 2.918 | – |
| 0 | 0.2 | 1.652 | 2.295, 2.533 | 1 | 0.2 | – | 4.096 | 2 | 0.2 | 2.677 | – |
| 0 | 0.3 | 1.562 | 2.357, 2.549 | 1 | 0.3 | – | 4.144 | 2 | 0.3 | 2.473 | – |
| 0 | 0.4 | 1.480 | 2.408, 2.564 | 1 | 0.4 | – | 4.193 | 2 | 0.4 | 2.289 | – |
| 0 | 0.5 | 1.403 | 2.452, 2.578 | 1 | 0.5 | – | 4.242 | 2 | 0.5 | 2.115 | – |
| 0 | 0.6 | 1.328 | 2.491, 2.593 | 1 | 0.6 | – | 4.290 | 2 | 0.6 | 1.944 | – |
| 0 | 0.7 | 1.252 | 2.526, 2.606 | 1 | 0.7 | – | 4.338 | 2 | 0.7 | 1.769 | – |
| 0 | 0.8 | 1.175 | 2.559, 2.619 | 1 | 0.8 | 1.730 | 2.269, 4.386 | 2 | 0.8 | 1.578 | – |
| 0 | 0.9 | 1.092 | 2.590, 2.632 | 1 | 0.9 | 1.335 | 2.437, 4.432 | 2 | 0.9 | 1.345 | – |
| 0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 2.618, 2.644 | 1 | 1.0 | – | 2.529, 4.478 | 2 | 1.0 | – | – |
| Name | u | h | k | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.08 | 0.003 | 2.342 | 7.093 |
| (b) | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.08 | 0.890 | 1.921 | 2.208 |
| (c) | 0.85 | 0.3 | 0.04 | 0.91 | 5.038 | 6.590 |
| (d) | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.004 | 1.1 | 2.533 | 3.938 |
| (e) | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.0004 | 0.93 | 5.803 | 7.916 |
| (f) | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.01 | 1.3 | 4.109 | 2.711 |
| (g) | 0.9 | 0.001 | 0.9 | 2.922 | 1.067 | |
| (h) | 0.85 | 1 (polar) | 0.0001 | 1 | 3.497 | 0.0045 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fathi, M.; Villanueva, J.R.; Cruz, N. Spherical Particle Orbits around a Rotating Black Hole in Massive Gravity. Symmetry 2023, 15, 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15081485
Fathi M, Villanueva JR, Cruz N. Spherical Particle Orbits around a Rotating Black Hole in Massive Gravity. Symmetry. 2023; 15(8):1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15081485
Chicago/Turabian StyleFathi, Mohsen, José R. Villanueva, and Norman Cruz. 2023. "Spherical Particle Orbits around a Rotating Black Hole in Massive Gravity" Symmetry 15, no. 8: 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15081485
APA StyleFathi, M., Villanueva, J. R., & Cruz, N. (2023). Spherical Particle Orbits around a Rotating Black Hole in Massive Gravity. Symmetry, 15(8), 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15081485







