Abstract
Originally conceived as a thought experiment, an apparatus consisting of two Stern–Gerlach apparatuses joined in an inverted manner touched on the fundamental question of the reversibility of evolution in quantum mechanics. Theoretical analysis showed that uniting the two partial beams requires an extreme level of experimental control, making the proposal in its original form unrealizable in practice. In this work, we revisit the above question in a numerical study concerning the possibility of partial-beam recombination in a spin-coherent manner. Using the Suzuki–Trotter numerical method of wave propagation and a configurable, approximation-free magnetic field, a simulation of a transversal Stern–Gerlach interferometer under ideal conditions is performed. The result confirms what has long been hinted at by theoretical analyses: the transversal Stern–Gerlach interferometer quantum dynamics is fundamentally irreversible even when perfect control of the associated magnetic fields and beams is assumed.
Keywords:
matter-wave interferometry; Stern–Gerlach interferometer; quantum evolution; reversibility; Humpty-Dumpty problem; split-operator approximation; Suzuki–Trotter factorization PACS:
02.60.Lj; 03.65.-w; 03.75.Dg; 07.60.Ly; 37.25.+k
1. Introduction
The experiment by Stern and Gerlach performed in 1921 (a centennial this year) [1,2] proved to be of fundamental importance for the development of quantum mechanics. Far from being a thing of the past, the original design of the Stern–Gerlach apparatus (SGA) has continued to inspire new questions [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12] and experimental techniques [13,14,15,16,17]. Professor David Bohm, in his well-known textbook on quantum theory, discusses a device consisting of two SGAs (([18] Section 22.11), see Figure 1) joined in an inverted manner so that
We note that in Bohm’s proposal the atom is deflected in regions of “uniform magnetic fields”—but there are no such Lorentz-type forces acting on electrically neutral atoms. All subsequent works, including ours, consider magnetic gradients to achieve the restoring deflection, with three more SGAs completing the interferometer sketched in Figure 1. There is also Wigner’s scheme, in which the inhomogeneous magnetic field from an electric current recombines the beams that emerge from the SGA [19]; it has not been used for a quantitative model.If the uniform magnetic fields (...) are set up in exactly the right way, and if the second inhomogeneous field is an exact duplicate of the first one, the two wave packets can be brought together into a single coherent packet. Although the precision required to achieve this result would be fantastic, it is, in principle, attainable.
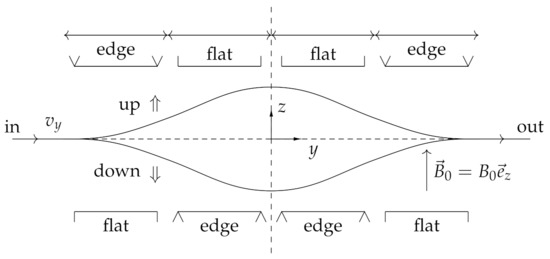
Figure 1.
A side view of a transversal Stern–Gerlach interferometer as envisioned by Bohm (with the modification noted in the text). Four Stern–Gerlach magnets are used to generate a magnetic field that first splits and then recombines the atomic beam of silver atoms, which move with velocity through the apparatus. The spin quantization axis is determined by the homogenous field oriented along the Z axis.
The analysis of Bohm’s proposal gave rise to what is known as the Humpty-Dumpty problem [20,21,22] of the coherent recombination of spatially separated partial atomic beams (i.e., the spin-up and spin-down components of the spinor wave function) from an SGA as well as to a plethora of experimental techniques within the domain of matter-wave interferometry, all of which use different approaches to work around the fantastic precision required to realize the original proposal by Bohm. Recent advances in atomic chip manufacturing allow the experimenters to realize a Stern–Gerlach-inspired interferometer [16,23,24,25,26], whereas the accuracy required for realizing a transversal Stern–Gerlach interferometer (SGI) as originally imagined remains fantastic.
In this work, we revisit the question of the time reversibility of a transversal SGI. Past theoretical work focused on the impossibility of perfect control of magnetic fields and beams, indicating a quick loss of spin coherence if such control could not be maintained [20,21]. However, what was also suggested by these analyses is that the very dynamics of a beam-splitting Stern–Gerlach apparatus might not be as reversible as imagined, even when perfect control over involved magnetic fields and beams is assumed [27]. To fill in the missing piece in the quantum Humpty-Dumpty riddle, we perform an accurate three-dimensional wave-propagation simulation of a transversal SGI in order to accurately capture all quantum mechanical effects that arise once a full, ideal magnetic field is accounted for. The results of our simulation confirm the intuition that the quantum dynamics of a Stern–Gerlach apparatus is not reversed by the application of inverse magnetic fields even if one has perfect control over the experimental apparatus.
2. Modeling the Transversal SGI
A beam of silver atoms is prepared in a pure spin state directed along the X axis, , with the initial wave function chosen to be a Gaussian wave packet of width ,
The atoms enter the apparatus from the left at time at , , and ; travel in the Y direction with velocity ; and exit at , with sufficiently far from the SGI center at to be outside the magnetic fringing fields. Inside the apparatus, the magnetic field is generated by two symmetrically placed linear “magnetic charge” distributions of opposite charge at the height a from the beam’s initial position, according to the arrangement depicted in Figure 2.
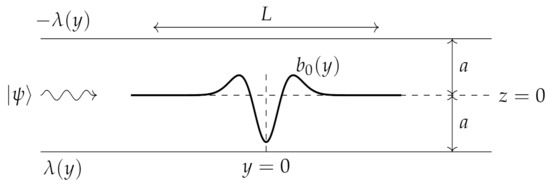
Figure 2.
Magnetic field model used in our simulation. In the Y,Z plane, we have a fictitious magnetic line charge at and the opposite charge at . For points on the Y axis, the resulting magnetic field is in the Z direction, . The model is defined by specifying ; see Section 2.2.
Here, we exploit the analogy between Maxwell’s equations for a static electric field and a static magnetic field and so model the magnetic field through a scalar potential as though generated by a charge distribution, with the details given in Section 2.2. It is, of course, also possible to model the magnetic field with adjustable electric currents (see, e.g., [28]) but the magnetic-line-charge model is simpler to implement. While a parameterization of the magnetic field by an arrangement of a few magnetic point charges shares this simplicity [29], it is less flexible.
The magnetic field associated with the magnetic line charges is symmetric across the XY plane and the nonlinear dependence on the z coordinate of the magnetic field due to a single charge line, which ordinarily would result in slightly different trajectories for the spin-up and spin-down components, no longer poses an obstacle for spatial beam recombination. Furthermore, to fix the spin quantization axis along the Z axis, a bias field in the Z direction (here, is the unit vector in the Z direction, and is the magnitude of the bias field) is applied throughout the apparatus. The magnitude of this field is chosen to be much greater than the magnitudes of the , components in the apparatus to suppress the effects of Larmor precession around axes other than Z.
The Larmor spin precession angle that the particle accumulates as it travels through the apparatus results in the final spin of the atom not necessarily pointing in the X direction despite our best efforts, even if the beams are recombined coherently. It is therefore inappropriate to check whether the final spin state is equal to the initial one. Instead, we measure the degree of preserved coherence, , by the purity of the statistical operator for the spin degree of freedom,
where is the vector of Pauli spin matrices. The spin coherence ranges between and , between a completely mixed spin state (coherence lost) and a pure spin state (coherence preserved), with intermediate values indicating some degree of coherence loss. After time T, when the particle has traversed the length of the apparatus L and reached the position , it emerges on the right and its spin coherence is measured. It is our goal that the final value of the spin coherence is as close to its maximal value as possible; in a perfect experiment, we have .
During the evolution, the peak separation between the partial beams reaches (henceforth denoted by ). One has to ensure that is large compared with the width of the atom wave packet to say that the partial beams have truly separated. If despite partial beam separation in the middle of the apparatus the spin coherence has been preserved, then the evolution in the left half of the apparatus has been reversed or, in the playful language of [20], Humpty-Dumpty (who is really an egg) has been put back again after his great fall. After this overview of the experiment, we move onto describing the methods used in the simulation.
2.1. Quantum Dynamics of the Apparatus
Following the usual quantum treatment of an SGA, we have the following Hamiltonian describing the spin-1/2 silver atom comprising the beam:
with the momentum operator , the position operator , the magnetic moment , the vector of Pauli spin matrices , and the position-dependent magnetic field in the apparatus. The numerical values for m and that are used in the simulation and other simulation parameters are included in Appendix A.
To solve the equations of motion with an accuracy high enough to model coherent beam recombination, we employ a fourth-order Suzuki–Trotter operator splitting method [30]. In this scheme, given any Hamiltonian with a potential-energy term , the time propagator , which advances the wave function by a time step t, is split into several exponential terms, each involving only the momentum operator or the potential operator with coefficients specially chosen, such that the whole formula is accurate to a certain order k,
where and correspond, respectively, to potential and momentum operator terms. While approximations for increasing N yield higher-order formulas and can achieve any desired level of accuracy, the computational cost goes up considerably with increasing N, as between each application of operators either in momentum or in position space, one has to perform a Fourier transformation on the wave function. For our purposes, we chose a fourth-order Suzuki–Trotter method of a special form that involves a gradient term of the potential and five operator terms in total, compared with 11 terms in the standard Suzuki–Trotter formula needed to achieve the same order [31,32,33]. The time propagator in this “ approximation” is
where the notation is a reminder that this is a limiting case of a gradient-free seven-factor approximation as in Equation (4); see [34] for the technical details.
To propagate the wave function, the five unitary operators of Equation (5) are applied in their respective space. For instance, the application of the first two terms from the right
on as part of the algorithm requires two Fourier transformations :
A single application of the propagator requires the execution of four Fourier transformations for a spinless wave function. The time propagation of a spin-1/2 particle requires eight Fourier transformations per time step, an operation that contributes heavily to the computational cost.
Once this split-operator machinery is in place, we can simulate the quantum evolution of any system described by a reasonable Hamiltonian with a position-dependent potential, including the quantum dynamics of an SGI. However, when attempting to do so according to the method presented above, one is quickly faced with rising computational space and time resources required to perform the computation to a sufficient degree of accuracy. The storage cost of a wave function across the region of the apparatus is prohibitive, as is the time required to perform repeated Fourier transformations in each time step.
To make the calculation feasible, we transform the Hamiltonian into the co-moving frame of the atomic beam traveling with velocity along the Y axis of the apparatus. This is performed at the cost of making the potential term in the Hamiltonian time-dependent,
and thus requires a re-evaluation of the split-operator method, which, presented in its most basic form, is applicable only to Hamiltonians not explicitly dependent on time. The extension of the split-operator method to time-dependent non-commuting Hamiltonians is treated in full generality in [35]. Here, we just note the elegant result: in the time-dependent split-operator method , the reference time has to be advanced cumulatively at each encountered term, , so that subsequently applied potential operator terms use the newly advanced time , until the next application of a position propagator, etc. The resulting formula for the time-dependent propagator is then guaranteed to be accurate to the same order as the original formula. Using this simple prescription, we readily obtain the time-dependent propagator , for the evolution from time T to time ,
In this way, one has to keep track only of the wave function in the region required to model the beam deflection in the Z axis, which is very small compared with the total extent of the apparatus, as the movement along the Y direction has been taken care of by transforming the Hamiltonian into the co-moving frame. The outstanding challenge is an efficient and accurate computation of the magnetic field , which in each time step has to be evaluated across the domain of the wave function, now in the co-moving frame of the beam.
2.2. Magnetic Field in the Apparatus
To our best knowledge, all previous quantum treatments of Stern–Gerlach-like experiments employed a magnetic field that either did not satisfy the Maxwell equations through neglect of the X and Y field components and linear approximations [20,21,36] or used a simple model of a magnetic field that neglects the fringing fields at the entrance and exit of the apparatus [37,38]. For the purposes of our work, it is crucial that the employed field model is free from both of these approximations, since it is clear that either of these simplifications results in an apparatus that seemingly has no problem with reuniting the partial beams in a coherent manner as long as the beams and fields are accurately controlled.
In the traditional design, at least four Stern–Gerlach magnets have to be employed. As the particle goes through the apparatus, the partial beams corresponding to the spin-up and spin-down components are first imparted a momentum, which leads to their spatial separations, as seen in the schematic trajectories in Figure 1. Subsequently, the evolution both in momentum and position has to be reversed. The second and third magnets first decelerate the particle and then impart momenta equal in magnitude to the momentum gained in the first stage, and finally, the last magnet decelerates the particle, whereupon, if the conditions were ideal, we should find the partial beams reunited and the particle in a pure spin state.
In our scheme, we exploit the correspondence between the Maxwell equations for the electric field and the static magnetic field,
and introduce a fictitious magnetic “charge” potential , which obeys the Laplace equation
and results in a physical magnetic field
in full analogy to a static electric field. In this manner, we obtain a configurable model of a magnetic field free from approximations. This is in contrast to other approaches to the Humpty-Dumpty problem, which tend to turn the problem of reversing the evolution into a technical difficulty depending solely upon the experimenter’s skill, thereby possibly concealing difficulties of a more fundamental nature, while our aim is precisely to uncover those difficulties that arise once all simplifications are put aside.
The scalar potential for the pair of magnetic line charges (see Figure 2) is
where
are the respective distances from the charged lines and is the zeroth-order modified Bessel function of the second kind. On the Y axis, we have
with and related to each other by
where is the first-order modified Bessel function of the second kind. Upon expressing in terms of ,
one confirms that satisfies the Laplace Equation (10) for by an exercise in differentiation, for which the relations [39]
are useful.
After including the bias field and a strength parameter f, the magnetic field is
Rather than specifying the line-charge density , we define the model by the choice for , essentially along the level trajectory of the atom that traverses the SGI. This makes it easier to ensure that the magnetic field decreases rapidly outside the SGA. Indeed, as we show below, one can model a magnetic field suitable for coherent beam recombination by an appropriate choice for , the strength parameter f, and the separation between the two line charges.
2.3. Beam Recombination in the Calibrated Magnetic Field
The conventional treatment of an SGA assumes that the atom’s deflection is caused by a linear field, thus making the force position-independent, which greatly aids in subsequent beam recombination. However, a field such as this is unphysical, it does not satisfy the Maxwell equations, and thus conclusions regarding the reversibility of the SGA’s dynamics based on reasoning that neglects this issue are unconvincing as they risk missing quantum effects that might have an impact on the spin coherence. A physical field necessarily has a nonlinear dependence on the z coordinate and thus requires fine-tuning to make the partial beams come back to zero separation.
In our scheme, one can calibrate the field to result in a desired peak separation by adjusting the field strength parameter f and the distance between the top and bottom line charges. For , we choose a magnetic field profile composed of two Gaussians with an adjustable width parameterized by (as shown schematically in Figure 2),
The parameter determines the longitudinal stretch of the apparatus over which the particle is deflected, influencing the overall deflection as well as the range of the fringing fields—the wider the Gaussian peaks, the slower the decay of the magnetic field off the Y axis. As such, a judicious choice of is needed, first to avoid a Gaussian that is too narrow and expensive to resolve numerically and second to avoid a Gaussian too wide, which then makes it necessary to model an apparatus sufficiently wide to have the fringing fields negligible at both ends of the apparatus.
The force in the Z direction resulting from such a profile, as shown in Figure 3, effectively consists of four regions of unequal length symmetric accross the Z axis. These regions are indicated by the direction of the force in each sector: +, −, −, +. Such an arrangement allows us to mimic the effect of the four-magnet setup of Figure 1 in a simple way, without having to introduce a model of the magnetic field for each SG magnet separately. Note that this is even in y and, therefore, we can replace the exponential factors in Equation (16) by their real parts.
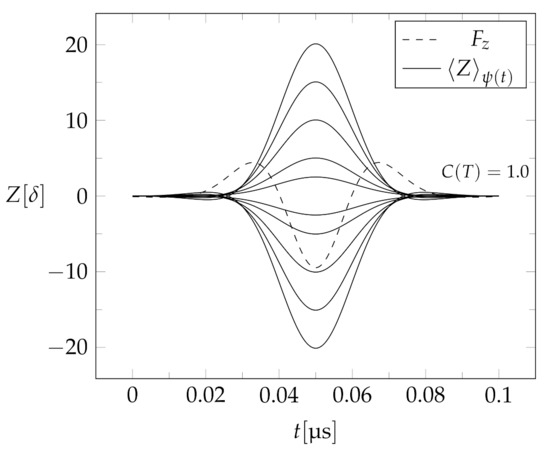
Figure 3.
Trajectories of the partial beams for beam separations according to the quantum dynamics of the simplified Hamiltonian. The spin-up and spin-down partial trajectories for each peak separation are symmetric. The final coherence is rounded to four decimal places and is regardless of the magnitude of peak separation. The slightly visible ribbon shape of the trajectories near the input and output of the apparatus for higher peak separations is a feature of the fringing fields of the employed magnetic field. The dashed line is the force , in units of , acting on the partial spin-up beam of the largest separation .
The field felt by the particle along its trajectory is approximately as long as the deflections are much smaller than the length scale of the field changes. Then, the vanishing of the integral
makes the Larmor precession around the Z axis approximately equal to 0, with the spin pointing in the X direction at the output. Beam recombination along the Y axis is facilitated by energy conservation—changes in potential energy coming chiefly from the changes in along the trajectory in the left half of the interferometer (Figure 1) are reversed by the opposite changes in the right half (since ). However, the choice for dictated by this reasoning is not a sufficient guarantee of coherent recombination. The real trajectory is not level and becomes minutely sensitive to the exact field, nonlinear in its z coordinate dependence, in the apparatus. With the two remaining parameters at hand, the line charge separation and the field strength f, we perform a bisection search for these parameters, constrained by the desired value of the peak separation and with the objective of vanishing final spatial separation of the beams,
This is performed in a semiclassical manner: the Z axis quantum and classical dynamics are in good agreement, with the classical simulation being much cheaper to perform than the quantum counterpart, thus making this optimization scheme feasible. We obtain a range of parameters a, f that result in spin-coherent recombination for different values of the peak separation, . With this set of optimized parameters at hand (their values can be found in Appendix B), each choice resulting in a suitable magnetic field and trajectories with peak separation , we can now proceed to simulating the quantum dynamics of the SGI.
3. Quantum Dynamical Simulation of the SGI
Using the optimized magnetic fields and the methods discussed in the preceding sections, we can now perform the wave-propagation simulation of the SGI. In the first step, we performed a quantum simulation of the beam’s evolution in the optimized fields neglecting the microscopic quantum motions in the X and Y axes. The effective Hamiltonian for this case is a simplified one-dimensional version of the full Hamiltonian of Equation (7):
The simulated beam trajectories are presented in Figure 3.
Regardless of the magnitude of the peak separation , the beams are recombined coherently. Note that this happens only because the magnetic field, which depends on the z coordinate in a nonlinear fashion (making the force position-dependent), is finely calibrated for each separately. The standard recipe of taking the inverted fields to reverse the evolution of the beam that underwent the splitting by SG magnets therefore seems to work as long as the fields are calibrated in an “exactly right” way. But is this really true? The standard argument assumes that the neglected X and Y movements are miniscule compared with the large deflection in the Z axis and, therefore, should not influence the overall analysis. However, since coherent beam recombination is concerned precisely with the relative microscopic realignment of the partial spin-up, spin-down beams, it is necessary to simulate the full dynamics.
We calculated the quantum dynamics of the original Hamiltonian of Equation (7), again varying the peak separation and measuring the final spin coherence . The peak separation–spin coherence curve together with the final relative displacements of the partial beams in y and z coordinates are presented in Figure 4. Although for very small separations up to the partial beams are recombined coherently—note that this does not mean that the evolution was fully reversed: the spreading of the wave packet, though inconsequential, has not been undone—once the peak separation exceeds this value, the evolution rapidly becomes irreversible, with indicating complete spin decoherence by the time separation reaches . The cause of this loss of spin coherence is the growing microscopic separation in the Z and Y axes between the up- and down-spin components, as shown in Figure 4b, which, although barely exceeding in Z and negligible in Y, is enough to completely prevent coherent beam recombination.
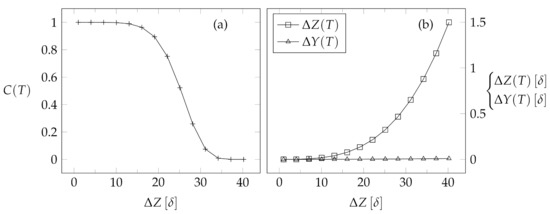
Figure 4.
The final spin coherence in panel (a) and relative partial beam displacements , in panel (b) as a function of increasing peak separation . The magnetic field that results in perfect beam recombination when the microscopic quantum movements in the X and Y axis are neglected is no longer sufficient to reverse the full quantum evolution when becomes appreciable.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
An SGA entangles the spin degree of freedom of a spin-1/2 atom with its orbital degrees of freedom, so that the outcome of a position measurement informs us about the spin of the atom (“up” or “down” in the traverse direction that is probed). The transition from the initial not-entangled state to the final entangled state is unitary; it is not an irreversible event that can be amplified and recorded. (In passing, we note that Haag emphasized the fundamental role of events [40] and their random realization [41]; see also [42].) Since unitary processes compose a group, they are invertible in a mathematical sense. Is the entangling action of an SGA also invertible as a physical process, that is, by another unitary transition? Processes that trap the atom and re-prepare it in the initial not-entangled state are not unitary and do not count.
“Yes,” answered Bohm [18] and later Wigner [19], and others parroted their wisdom. While Bohm acknowledged that the reversal would require a “fantastic” precision in controlling the apparatus and Wigner observed that such an experiment “would be difficult to perform,” both took the reversibility for granted and did not elaborate on the matter. It is, however, unclear whether elementary unitary quantum processes are reversible—in marked contrast to macroscopic processes, which are known to be irreversible, as witnessed by the folk wisdom of the medieval Humpty-Dumpty rhyme, the laws of thermodynamics, the lessons of deterministic chaos, the ubiquitous ageing of living organisms, and other familiar phenomena.
In the particular situation of an SGA, the atom’s spin and orbital degrees of freedom are coupled by the force resulting from the magnetic field gradient, and only this coupling is available for reversing the action of the SGA in a unitary fashion. We cannot undo the action of the unitary evolution operator , with H as in Equation (3), by applying its inverse because is not a physical Hamiltonian—so much for mathematical reversibility; more about this can be found in [27] and ([42] Section 5.2). Rather, we must carefully tailor the magnetic field to implement the disentangling reversal as well as we can.
We recall that Bohm’s “fantastic” accuracy amounts to controlling the macroscopic devices with submicroscopic precision [20], and if such control is granted, Maxwell’s equations prevent us from undoing the entanglement perfectly [21], even if we neglect the effects of fringing fields (as is the case in [21]). These theoretical works are supplemented here by a numerical study that fully accounts for the quantum dynamics with a magnetic field that obeys Maxwell’s equations throughout the volume probed by the atom.
Thereby, we assume that there are no uncontrolled imperfections. This is, of course, an over-idealization that lacks justification (as it ignores the lesson of [20]). Even with this stretch, we find that the action of the SGA cannot be undone if the SGA serves its purpose, namely separates the atoms into well distinguishable partial beams—, say.
In conclusion, the accurate wave-propagation results presented here quantitatively confirm that the microscopic quantum dynamical effects in a transversal SGI apparatus are enough to quickly destroy spin coherence beyond hope of recovery. The deceptively simple nature of the Stern–Gerlach beam-splitting apparatus and the seemingly obvious proposal to reverse its evolution by employing inverted fields might lead one to assume the fundamental reversibility of its quantum evolution as long as the apparatus is controlled sufficiently well. Such assumptions are, however, unwarranted.
Author Contributions
The project was conceived by B.-G.E.; both authors developed the formalism together; M.M.P. conducted the numerical computations; the manuscript was written and finalized by both authors jointly. Both authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding. The Centre for Quantum Technologies is a Research Centre of Excellence funded by the Ministry of Education and the National Research Foundation of Singapore.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The codes used for the numerical computations are available upon request.
Acknowledgments
We thank Jun Hao Hue for valuable discussions. The efforts by Tzyh Haur Yang and Ruiqi Ding, who conducted closely related undergraduate projects, are gratefully acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used:
| SG | Stern–Gerlach |
| SGA | Stern–Gerlach Apparatus |
| SGI | Stern–Gerlach Interferometer |
Appendix A. Particle Properties and Initial Wave Function
As in the original Stern–Gerlach experiment, we used a beam of silver atoms to simulate the splitting and recombination. The values of the various variables are given in Table A1. In the lapse of time T, the width of the wave function increases by a factor of
if there were force-free motion, and this amount of spreading is of no consequence.

Table A1.
Values used in the simulation: atom properties, apparatus geometry, and initial wave function.
Table A1.
Values used in the simulation: atom properties, apparatus geometry, and initial wave function.
| Variable | Value | First Occurrence | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| m | in Equation (1) | mass of a silver atom (: dalton) | |
| in Equation (3) | magnetic moment (: Bohr magneton) | ||
| L | after Equation (1) | length of the SGI | |
| T | after Equation (2) | time to traverse the SGI | |
| in Equation (1) | initial position | ||
| in Equation (1) | initial velocity | ||
| in Equation (1) | width of the initial wave function |
Appendix B. Magnetic Field
The parameter of the magnetic profile function of Equation (19), depicted in Figure 2, was chosen to be
The example parameters of the optimized fields, rounded to five decimal places, are displayed in Table A2. In Figure A1, the field lines of the component of the field calibrated for (the largest simulated peak separation) are shown. The overall magnitude of the component of the generated field is actually larger than the magnitude of . By adjusting , we make sure that the resulting field component is the largest magnetic field component in the apparatus. For the fields used in the simulations the suitable value of in units of , where a.u. denotes atomic units of magnetic field strength, is

Table A2.
Optimized magnetic field parameters: beam separation (cf. Figure 3), field-strength parameter f of Equation (18), and line-charge distance a (cf. Figure 2).
| f | ||
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0.00011 | 0.71919 |
| 10 | 0.00030 | 0.04353 |
| 20 | 0.00081 | 1.61404 |
| 30 | 0.00147 | 2.19168 |
| 40 | 0.00226 | 2.85283 |
The evaluation of the magnetic field integrals, the gradient of of Equation (16), across the wave function domain (the grid in the simulation for highest separation consists of 800 million points) was too time-consuming. Since the whole simulation was performed on a distributed computing cluster, we divided the domain into subdomains, with each subdomain being simulated on a separate processor. In each subdomain, then, the magnetic field was approximated by a second-order Taylor approximation, centered at the weighted position of the wave function chunk in a particular domain, and there was no loss of accuracy from this.
The overall computational resources spent in the simulation of were as follows. The simulation was run on 40 cores in parallel, with a special parallelized FFT routine as the only step requiring inter-core communication. The computation time spent per core was 15 h, a total of 600 h. The breakdown of the average time spent in a single step of the time evolution loop: 30% spent on performing FFTs, 39% on potential propagators (costly because of field evaluations discussed in the preceding paragraph), 28% on observables calculations, and 3% on momentum propagators. The overall memory allocation per core was 3 GB, with a total of 120 GB.
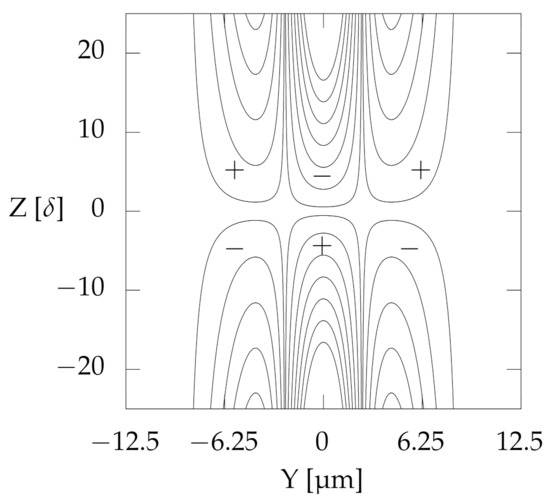
Figure A1.
Lines of constant of the magnetic field calibrated for shown in the YZ plane. The sign of the field in a particular region is indicated by a + () and − (). The nested contours increase in field strength as the field gets closer to the line charges located at a distance at the top and bottom, according to Table A2. Note that the width of the Gaussian wave packet is small on the length scale set by the overall changes of the field. In the middle of the apparatus ( line), the field vanishes exactly because the line charges of opposite sign are placed symmetrically across the XY plane.
References
- Stern, O. Ein Weg zur experimentellen Prüfung der Richtungsquantelung im Magnetfeld. Z. Phys. 1921, 7, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, W.; Stern, O. Der experimentelle Nachweis des magnetischen Moments des Silberatoms. Z. Phys. 1922, 8, 110–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, M.; Erdman, K. The transverse Stern–Gerlach experiment. Can. J. Phys. 1962, 40, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, H.M.; Marshall, T.W.; Santos, E.; Watson, E.J. Possible interference effect in the Stern–Gerlach phenomenon. Phys. Rev. A 1992, 46, 2265–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorceix, O.; Robert, J.; Nic Chormaic, S.; Miniatura, C.; Baudon, J. Dispersive and nondispersive phase shifts in atomic Stern–Gerlach interferometry. Phys. Rev. A 1994, 50, 5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, T.R.; Caldeira, A.O. Dissipative Stern–Gerlach recombination experiment. Phys. Rev. A 2006, 73, 042502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, S.; Bach, R.; Batelaan, H. Transverse quantum Stern–Gerlach magnets for electrons. New J. Phys. 2011, 13, 065018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatifi, M.; Durt, T. Revealing self-gravity in a Stern–Gerlach Humpty-Dumpty experiment. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.07420. [Google Scholar]
- Impens, F.; Guéry-Odelin, D. Shortcut to adiabaticity in a Stern–Gerlach apparatus. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 96, 043609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathevet, R.; Brodsky, K.; Perales, F.; Boustimi, M.; de Lesegno, B.V.; Reinhardt, J.; Robert, J.; Baudon, J. Some new effects in atom Stern–Gerlach interferometry. In Atomic and Molecular Beams; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Xiao-Ji, Z. Phase-dependent effects in Stern–Gerlach experiments. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2010, 27, 010309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, C.R.; Jalbert, G.; Impens, F.; Robert, J.; Medina, A.; Zappa, F.; de Castro Faria, N.V. Toward a test of angular-momentum coherence in a twin-atom interferometer. Europhys. Lett. (EPL) 2015, 110, 50001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Robert, J.; Gorceix, O.; Lawson-Daku, J.; Nic Chormaic, S.; Miniatura, C.; Baudon, J.; Perales, F.; Eminyan, M.; Rubin, K. Stern–Gerlach atomic interferometry with space- and time-dependent magnetic fields. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1995, 755, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, K.; Eminyan, M.; Perales, F.; Mathevet, R.; Brodsky, K.; Viaris de Lesegno, B.; Reinhardt, J.; Boustimi, M.; Baudon, J.; Karam, J.C. Atom interferometer using two Stern–Gerlach magnets. Laser Phys. Lett. 2004, 1, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perales, F.; Robert, J.; Baudon, J.; Ducloy, M. Ultra thin coherent atom beam by Stern–Gerlach interferometry. Europhys. Lett. (EPL) 2007, 78, 60003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amit, O.; Margalit, Y.; Dobkowski, O.; Zhou, Z.; Japha, Y.; Zimmermann, M.; Efremov, M.A.; Narducci, F.A.; Rasel, E.M.; Schleich, W.P. T3 Stern–Gerlach matter-wave interferometer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 083601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalit, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Dobkowski, O.; Japha, Y.; Rohrlich, D.; Moukouri, S.; Folman, R. Realization of a complete Stern–Gerlach interferometer. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.02708. [Google Scholar]
- Bohm, D. Quantum Theory; Prentice-Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Wigner, E.P. The Problem of Measurement. Am. J. Phys. 1963, 31, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englert, B.-G.; Schwinger, J.; Scully, M.O. Is spin coherence like Humpty-Dumpty? I. Simplified treatment. Found. Phys. 1988, 18, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwinger, J.; Scully, M.O.; Englert, B.-G. Is spin coherence like Humpty-Dumpty? II. General theory. Z. Phys. D Atoms. Mol. Clust. 1988, 10, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwinger, J.; Scully, M.O.; Englert, B.-G. Spin coherence and Humpty-Dumpty. III. The effects of observation. Phys. Rev. A Gen. Phys. 1989, 40, 1775–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miniatura, C.; Perales, F.; Vassilev, G.; Reinhardt, J.; Robert, J.; Baudon, J. A longitudinal Stern–Gerlach interferometer: The “beaded” atom. J. Phys. II 1991, 1, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miniatura, C.; Robert, J.; Le Boiteux, S.; Reinhardt, J.; Baudon, J. A longitudinal Stern–Gerlach atomic interferometer. Appl. Phys. B 1992, 54, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudon, J.; Mathevet, R.; Robert, J. Atomic interferometry. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 1999, 32, R173–R195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machluf, S.; Japha, Y.; Folman, R. Coherent Stern–Gerlach momentum splitting on an atom chip. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englert, B.-G. Time Reversal Symmetry and Humpty-Dumpty. Z. Naturforschung A 1997, 52, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R. Higher-Order Split-Operator Approximations. In UROPS Project; National University of Singapore: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.H. Stern–Gerlach Interferometer with Realistic Magnetic Field. In UROPS Project; National University of Singapore: Singapore, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, M. Generalized Trotter’s formula and systematic approximants of exponential operators and inner derivations with applications to many-body problems. Commun. Math. Phys. 1976, 51, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, N.; Suzuki, M. Finding exponential product formulas of higher orders. arXiv 2005, arXiv:0506007, doi:10.1007/11526216_2. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, S.A. Symplectic integrators from composite operator factorizations. Phys. Lett. A 1997, 226, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hue, J.H.; Eren, E.; Chiew, S.H.; Lau, J.W.Z.; Chang, L.; Chau, T.T.; Trappe, M.I.; Englert, B.-G. Fourth-order leapfrog algorithms for numerical time evolution of classical and quantum systems. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.05308. [Google Scholar]
- Chau, T.T.; Hue, J.H.; Trappe, M.-I.; Englert, B.-G. Systematic corrections to the Thomas–Fermi approximation without a gradient expansion. New J. Phys. 2018, 20, 073003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M. General decomposition theory of ordered exponentials. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 1993, 69, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japha, Y. A general wave-packet evolution method for studying coherence of matter-wave interferometers. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.07759. [Google Scholar]
- Manoukian, E.B.; Rotjanakusol, A. Quantum dynamics of the Stern–Gerlach (SG) effect. Eur. Phys. J. At. Mol. Opt. Plasma Phys. 2003, 25, 253–259. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, B.C.; Berrondo, M.; Van Huele, J.F.S. Stern–Gerlach dynamics with quantum propagators. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 83, 012109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambramowitz, M.; Stegun, A.I. Handbook of Mathematical Functions, Published by the National Bureau of Standards; Dover: New York, NY, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Haag, R. Fundamental irreversibility and the concept of events. Commun. Math. Phys. 1990, 132, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, R. On the sharpness of localization of individual events in space and time. Found. Phys. 2013, 43, 1295–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Englert, B.-G. On quantum theory. Eur. Phys. J. D 2013, 67, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).