Abstract
In this paper, we introduce the notions of matching BiHom-Rota-Baxter algebras, matching BiHom-(tri)dendriform algebras, matching BiHom-Zinbiel algebras and matching BiHom-pre-Lie algebras. Moreover, we study the properties and relationships between categories of these matching BiHom-algebraic structures.
Keywords:
matching BiHom-Rota-Baxter algebras; matching BiHom-dendriform algebras; matching BiHom-pre-Lie algebras; matching BiHom-Zinbiel algebras; matching BiHom-Lie algebras MSC:
17A30; 17B38; 17B61
1. Introduction
The Hom-Lie algebra was introduced by Hartwig, Larsson and Silvestrov [1]. Further research on Hom-Lie algebras could be found in [2,3,4,5,6,7] and references cited therein. As a generalization of Hom- Lie algebra, Graziani etc. [8] also introduced BiHom-Lie algebras. More precisely, a BiHom-Lie algebra is a -module together with bilinear operation and two commuting linear transformations , for , satisfying
Identities (1) is called multiplicative, identity (2) is called BiHom-skew symmetry and identity (3) is called BiHom-Jacobi identity. Recently, BiHom-type algebras have been further developed in mathematics and mathematical physics, including BiHom-pre-Lie algebra [9], BiHom-(tri)dendriform algebra [10], BiHom-Zinbiel algebra [10] and BiHom-quadri-algebra [10].
Rota-Baxter operator was introduced by Baxter [11] in the study of the fluctuation problems in probability, and further developed by Rota [12] in combinatorics. It is widely used in many fields, such as mathematics and mathematical physics. The partial study of Rota-Baxter algebra can be seen in [9,10,13,14,15]. More precisely, a Rota-Baxter algebra of weights is an algebra A together with a linear operator P, and for all , it satisfies the following Rota-Baxter identity:
For more detailed introduction of Rota-Baxter algebra, please refer to Guo’s book [16]. Recently, as a generalization of Rota-Baxter algebras, the concept of matching Rota-Baxter algebra [17] came from the study of matching pre-Lie algebra [18], and from the pioneering work of Bruned, Hairer and Zambotti [19] on the algebraic renormalization of regularization structure. The research shows that the matching Rota-Baxter algebra is formed by associative Yang-Baxter equation [20] and linear structure of Rota-Baxter operators [17].
The notions of matching Hom-Rota-Baxter algebras, matching Hom-(tri)dendriform algebras and matching Hom-pre-Lie algebras are introduced by [21]. The main purpose of this paper is to extend these matching algebraic structures to the BiHom-algebras setting and study the connections between these categories of BiHom-algebras. Thus the purpose of this paper is to obtain the following categories and functor commutative graph.
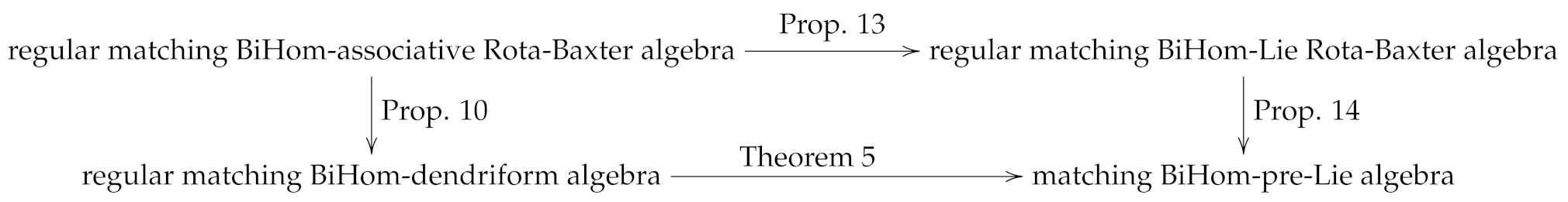

This paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we introduce the matching BiHom-associative, matching BiHom-pre-Lie and matching BiHom-Lie algebras. In Section 3, we explore the relationships between the matching Rota-Baxter algebras and BiHom-associative algebras. In Section 4, we give the relationships between the matching BiHom-dendriform algebras, BiHom-Zinbiel algebras and matching BiHom-tridendriform algebras. In Section 5, we study the properties and relationships between matching Rota-Baxter operators and BiHom-Lie algebras.
Throughout this paper, we work on a unitary commutative ring of characteristic different 2, which will be the base ring of all modules, algebras, tensor products, operations as well as linear maps, where tensor products will be denoted by . We always suppose that is a non-empty set. We denote , where is a set indexing the linear operators or bilinear operations.
2. Matching BiHom-Associative, Matching BiHom-Pre-Lie and Matching BiHom-Lie Algebras
In this section, we study the relationship among a kind of matching BiHom-type algebras, including matching BiHom-associative algebras, compatible BiHom-associative algebras, compatible BiHom-pre-Lie algebras and compatible BiHom-Lie algebras. The main results of this section are given as the following categories commutative graph.
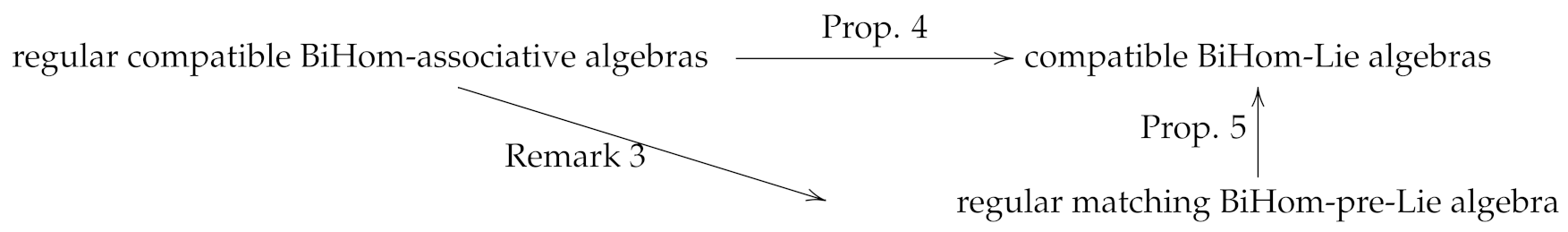

Definition 1.
A matching BiHom-associative algebra is a 4-tuple consisting of a -module A, a family of bilinear operations and two linear transformations , satisfying
for all and . In particular, if p and q are algebra automorphisms, we call it a regular matching BiHom-associative algebra.
A matching BiHom-associative algebra is called totally compatible if it satisfies
for all and .
Definition 2.
A compatible BiHom-associative algebra is a 4-tuple consisting of a -module A, a family of bilinear operations and two linear transformations , satisfying the following conditions,
for all and . In particular, if p and q are algebra automorphisms, we call it a regular compatible BiHom-associative algebra.
Remark 1.
- (i)
- Obviously, compatible BiHom-associative algebras include matching BiHom-associative algebras or totally compatible BiHom-associative algebras.
- (ii)
- Matching (Hom)-associative algebras, totally compatible (Hom)-associative algebras and compatible (Hom)-associative algebras given in [17,21] are special cases of above definitions, when .
- (iii)
- If Ω is a singleton, BiHom-associative algebras introduced in [8] are special cases of matching BiHom-associative algebras and compatible BiHom-associative algebras.
Definition 3.
A matching BiHom-Lie algebra is a 4-tuple consisting of a -module , a family of bilinear operations and two linear transformations satisfying the following conditions,
for all and . In particular, if p and q are algebra automorphisms, we call it a regular matching BiHom-Lie algebra.
Proposition 1.
Let be a regular matching BiHom-associative algebra. One can define the Lie bracket defined by
for and . Then is a matching BiHom-Lie algebra.
Proof.
Similar to [8]. □
Lemma 1.
Let be a matching BiHom-Lie algebra. Consider linear combinations
where for with finite supports. Then
for .
Proof.
For , by (8), we have
Similarly, we also have
Since is a matching BiHom-Lie algebra, then
Thus
as desired. □
Proposition 2.
Let be a matching BiHom-Lie algebra. Consider linear combinations
with a finite support. Then is a BiHom-Lie algebra.
Proof.
It follows from Lemma 1 by taking . □
More generally.
Definition 4.
A compatible BiHom-Lie algebra is a 4-tuple consisting of a -module , a family of bilinear operations and two linear transformations satisfying the following conditions:
for all and . In particular, if p and q are algebra automorphisms, we call it a regular compatible BiHom-Lie algebra.
Remark 2.
- (i)
- Matching BiHom-Lie algebras are special cases of compatible BiHom-Lie algebras.
- (ii)
- Given two BiHom-Lie algebras and . Define a new bracket as follows:for some . Easily to check that this new bracket is BiHom-skew symmetry. By a direct calculation, we can check that is a BiHom-Lie algebra. In fact, the BiHom-Jacobi identityis equivalent to identity (10).
Proposition 3.
Let be a matching BiHom-Lie algebra. Then for and we have
Proof.
Since (7) holds for any and , we get
By (7) and (11), we have
By the arbitrariness of , we have
Thus
□
Proposition 4.
Let be a regular compatible BiHom-associative algebra. Then is a compatible BiHom-Lie algebra, where
for and
Proof.
Obviously, p and q are multiplicative with respect to . Clearly, is BiHom-skew symmetry.
Now we prove that (10) holds. For and , we have
Similarly, we have
By (6), we get
Hence is a compatible BiHom-Lie algebra. □
Definition 5.
A matching BiHom-pre-Lie algebra is a 4-tuple consisting of a -module A, a family of bilinear operations and two linear transformations satisfying the following condition,
for all and . In particular, if p and q are algebra automorphisms, we call it regular matching BiHom-pre-Lie algebra.
Remark 3.
Obviously, every compatible BiHom-associative algebra is a matching BiHom-pre-Lie algebra.
In the following, we check that matching BiHom-pre-Lie algebras can induce compatible BiHom-Lie algebras.
Proposition 5.
Let be a regular matching BiHom-pre-Lie algebra. Then is a compatible BiHom-Lie algebra, where
for and
Proof.
Obviously, p and q are multiplicative with respect to . Clearly, is BiHom-skew symmetry.
Now we prove that (10) holds. For and , we have
Similarly, we have
By (13), we have
Hence is a compatible BiHom-Lie algebra. □
3. Matching BiHom-Associative Rota-Baxter Algebras
In this section, we introduce the notion of matching BiHom-associative Rota-Baxter algebras and discuss its properties.
Definition 6
([17]). Let be a set of scalars indexed by Ω. A matching associative Rota-Baxter algebra of weight is a 3-tuple consisting of an associative algebra , a family of linear operators satisfying the matching Rota-Baxter identity,
for all and .
Definition 7.
A matching BiHom-associative Rota-Baxter algebra is a 5-tuple consisting of a matching Rota-Baxter algebra , a BiHom-associative algebra satisfying , . In particular, if p and q are algebra automorphisms, we call it regular matching BiHom-associative Rota-Baxter algebra.
Theorem 1.
Let be a matching associative Rota-Baxter algebra and be two commuting algebra endomorphisms such that and for all . Then is a matching BiHom-associative Rota-Baxter algebra.
Proof.
For , we have
Similarly, .
Hence, is a BiHom-associative algebra. For ,
Hence is a matching BiHom-associative Rota-Baxter algebra. □
Conversely, we have.
Proposition 6.
Let be a regular matching BiHom-assoicative Rota-Baxter algebra. Then is a matching associative Rota-Baxter algebra.
Proof.
For , we have
Thus the associativity condition holds. For , we have
Hence is a matching associative Rota-Baxter algebra. □
Remark 4.
With the method of Proposition 6, we can give other types of regular BiHom-algebras, which can construct this type of non-Hom-algebras, for example, matching BiHom-pre-Lie Rota-Baxter algebras, matching BiHom-Leibniz Rota-Baxter algebras and so on.
Definition 8.
Let be a BiHom-associative algebra and . The n-th derived BiHom-associative algebra of A is defined by
Theorem 2.
Let be a matching BiHom-associative Rota-Baxter algebra. Then
is also a matching BiHom-associative Rota-Baxter algebra.
Proof.
Obviously, is a BiHom-associative algebra. Now we show the matching Rota-Baxter identity holds. For and , we have
Hence is a matching BiHom-associative Rota-Baxter algebra. □
Remark 5.
The conclusion of Proposition 6 and Theorem 2 is that existence is not unique. For example. Let be a matching BiHom-associative Rota-Baxter algebra.
- (i)
- Set . Then is a matching associative Rota-Baxter algebra.
- (ii)
- Then is also a matching BiHom-associative Rota-Baxter algebra.
4. Matching BiHom-Zinbiel Algebras and Matching BiHom-(Tri)Dendriform Algebras
In this section, we study the relationship among a kinds of matching BiHom-type algebras, which includes matching BiHom-dendriform algebras, matching BiHom-Zinbiel and matching BiHom-tridendriform algebras. The main results of this section are given as the following categories commutative graph.
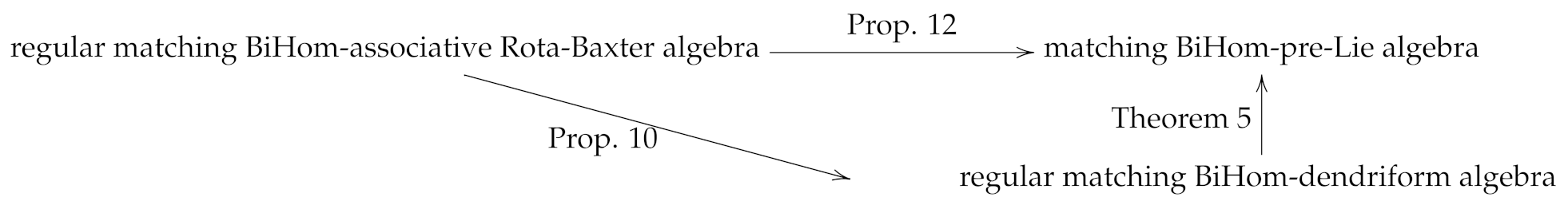

Definition 9.
A matching BiHom-dendriform algebra is a 5-tuple consisting of a k-module D, a family of bilinear operations , , and two linear transformations satisfying the following conditions,
for all and In particular, if , we call it a commutative matching BiHom-dendriform algebra. If p and q are algebra automorphisms, we call it a regular matching BiHom-dendriform algebra.
Definition 10
([14]). A (left) matching Zinbiel algebra is a pair consisting of a k-module Z and a family of bilinear operations satisfying
for all and .
Definition 11.
A matching BiHom-Zinbiel algebra is a 4-tuple consisting of a k-module Z, a family of bilinear operations and two linear transformations satisfying the following conditions,
for and . In particular, if p and q are bijective, we call it a regular matching BiHom-Zinbiel algebra.
Proposition 7.
Let be a matching Zinbiel algebra and be two commuting algebra endomorphisms. Define a new multiplication on Z by , for all and . Then is a matching BiHom-Zinbiel algebra.
Proof.
For we compute:
finishing the proof. □
As well as we know that a Zinbiel algebra is equivalent to a commutative dendriform algebra. Now we extend this result to the matching BiHom-algebra case.
Proposition 8.
- (i)
- Let be a commutative matching BiHom-dendriform algebra. Define the operation for all and . Then is a matching BiHom-Zinbiel algebra.
- (ii)
- Conversely, let be a regular matching BiHom-Zinbiel algebra. Define new operationsThen is a commutative matching BiHom-dendriform algebra.
Proof.
- (i)
- For and , we have
- (ii)
- Obviously, D is commutative since . Clearly, p and q are multiplicative with respect to and . Now we prove (16), (17) and (18). For and ,Also,Further,as required.
□
Definition 12.
A matching BiHom-tridendriform algebra is a 6-tuple consisting of a -module D, a family of bilinear operations , , , and two linear transformations satisfying the following conditions,
for all and
Definition 13.
- (i)
- Let and be two matching BiHom-dendriform algebras. A linear map is called a matching BiHom-dendriform algebra morphism if for all ,and
- (ii)
- Let and be two matching BiHom-teidendriform algebras. A linear map is called a matching BiHom-terdendriform algebra morphism if for all ,and
Theorem 3.
- (i)
- Let be a matching dendriform algebra and let be matching dendriform algebra endomorphisms such that . Then is a matching BiHom-dendriform algebra, where and .Moreover, suppose that is another matching dendriform algebra and let be matching dendriform algebra endomorphisms such that . If is a matching dendriform algebra morphism that satisfies , thenis a morphism of matching BiHom-dendriform algebras.
- (ii)
- Let be a matching tridendriform algebra and let be matching tridendriform algebra endomorphisms such that . Then , where and for each , is a matching BiHom-tridendriform algebra.Moreover, suppose that is another matching tridendriform algebra and let be matching tridendriform algebra endomorphisms such that . If is a matching tridendriform algebra morphism that satisfies , thenis a morphism of matching BiHom-tridendriform algebras.
Proof.
We just prove Item (ii) and Item (i) can be proved similarly. Clearly, p and q are multiplicative with respect to and . For any and , we have
Thereby
that is, (19) holds for . Similarly, (20)–(25) hold. Thus is a matching BiHom-tridendriform algebra. And
Thus is a morphism of matching BiHom-tridendriform algebras. □
Proposition 9.
Let I be an non-empty set. For each , let be a map with finite supports, identified with finite set .
- (i)
- Let be a matching BiHom-dendriform algebra. Define the following bilinear operations:Then is also a matching BiHom-dendriform algebra.
- (ii)
- Let be a matching BiHom-tridendriform algebra. Define the following bilinear operations:Then is also a matching BiHom-tridendriform algebra.
Proof.
We just prove Item (ii) and Item (i) can be proved similarly. Clearly, p and q are multiplicative with respect to and . For any and , we have
Hence, (19) holds. Similarly, (20)–(25) hold. Hence is a matching BiHom-tridendriform algebra. □
Theorem 4.
- (i)
- Let be a matching BiHom-dendriform algebra. Then is a compatible BiHom-associative algebra, where
- (ii)
- Let be a matching BiHom-tridendriform algebra. Then is a compatible BiHom-associative algebra, where
Proof.
We only prove Item (ii) and Item (i) can be proved similarly. Clearly, p and q are multiplicative with respect to . For and , we have
and
By (19)–(25), we get
Hence is a compatible BiHom-associative algebra. □
Theorem 5.
Let be a regular matching BiHom-dendriform algebra. Then is a matching BiHom-pre-Lie algebra, where
Proof.
Obvious, p and q are multiplicative with respect to For and , we have
and
By (16)–(18), we get
Hence is a matching BiHom-pre-Lie algebra. □
Proposition 10.
- (i)
- Let be a matching BiHom-associative Rota-Baxter algebra of weight 0. Define the operations and for byThen is a matching BiHom-dendriform algebra.
- (ii)
- Let be a matching BiHom-associative Rota-Baxter algebra. Define the operations and for byThen is a matching BiHom-dendriform algebra.
Proof.
Since Item (i) can be seen as a special case of Item (ii) by taking , we only prove Item (ii). Clearly, p and q are multiplicative with respect to and . For and , we have
Also,
and
Hence is a matching BiHom-dendriform algebra. □
Proposition 11.
Let be a matching BiHom-associative Rota-Baxter algebra. Define the operations , and for by
Then is a matching BiHom-tridendriform algebra.
Proof.
Clearly, p and q are multiplicative with respect to , and . For and , we have
as required. □
Proposition 12.
- (i)
- Let be a regular matching BiHom-associative Rota-Baxter algebra of weight 0. Then is a matching BiHom-pre-Lie algebra, where
- (ii)
- Let be a regular matching BiHom-associative Rota-Baxter algebra. Then is a matching BiHom-pre-Lie algebra, where
Proof.
- (i)
- It follows from Theorem 5 and Proposition 10 (i).
- (ii)
- It follows from Theorem 5 and Proposition 10 (ii).
□
Example 1.
We consider the following 2-dimensional regular matching BiHom-associative Rota-Baxter algebra of weight 0 , , where bilinear operation ·, and are defined, with respect to a basis ([8,10]), by
where are parameters in k with By Proposition 12, we have
Obviously, the operations obtained above satisfies the Definition of matching BiHom-pre-Lie algebra.
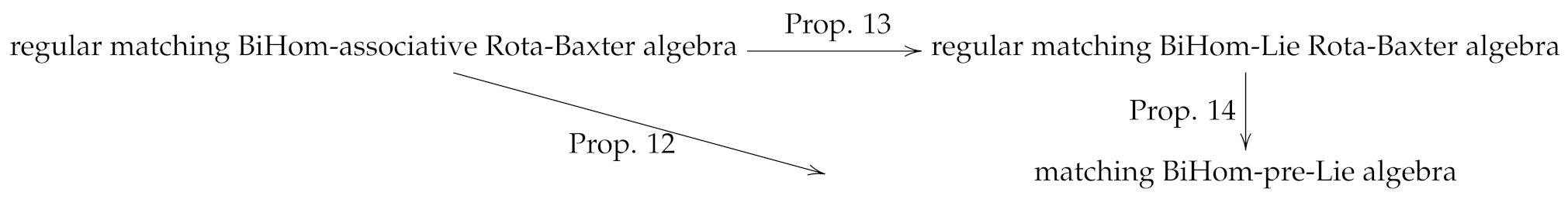
5. Matching BiHom-Lie Rota-Baxter Algebra
In this section, as a generalization of [9,17,20,22], we introduce the notion of matching BiHom-Lie Rota-Baxter algebras and discuss its properties. The main results of this section are given as the following categories commutative graph.

Definition 14.
Let be a family indexed by Ω. A matching BiHom-Lie Rota-Baxter algebra is a 5-tuple consisting of a BiHom-Lie algebra , a family of linear operators satisfying the following conditions:
for all and . In particular, if p and q are algebra automorphisms, we call it a regular matching BiHom-Lie Rota-Baxter algebra.
Theorem 6.
Let be a matching Lie Rota-Baxter algebra and be two commuting Lie algebra endomorphism such that for each . Then is a matching BiHom-Lie Rota-Baxter algebra, where .
Proof.
Clearly, p and q are multiplicative with respect to . In addition, for , we have
By the Jacobi identity and skew symmetry of , the BiHom-Jacobi identity and BiHom-skew symmetry of holds. Hence is a BiHom-Lie algebra.
For and , we have
as required. □
Theorem 7.
Let be a regular matching BiHom-Lie Rota-Baxter algebra. Then is a matching Lie Rota-Baxter algebra, where .
Proof.
Clearly, p and q are multiplicative with respect to . In addition, for , we have
By the BiHom-Jacobi identity and BiHom-skew symmetry of , the Jacobi identity and skew symmetry of holds. Hence is a Lie algebra.
For and , we have
as required. □
Definition 15.
Let be a BiHom-Lie algebra and . The n-th derived BiHom-algebra of is defined by
Theorem 8.
Let be a matching BiHom-Lie Rota-Baxter algebra. Then its n-th derived BiHom-algebra is a matching BiHom-Lie Rota-Baxter algebra.
Proof.
Clearly, p and q are multiplicative with respect to . In addition, for , we have
Hence is a BiHom-Lie algebra. For and , we have
as required. □
Proposition 13.
Let be a regular matching BiHom-associative Rota-Baxter algebra. Then is a matching BiHom-Lie Rota-Baxter algebra, where
Proof.
Following [8], is a BiHom-Lie algebra. For all , by (28), we have
By the matching Rota-Baxter identity (15), there are the following identity,
Hence is a matching BiHom-Lie Rota-Baxter algebra. □
Proposition 14.
Let be a regular matching BiHom-Lie Rota-Baxter algebra of weight zero. Then is a matching BiHom-pre-Lie algebra, where
Proof.
Clearly, p and q are multiplicative with respect to . In addition, for and , we have
and
By the BiHom-Jacobi identity (3), it is not hard to check that
Hence is a matching BiHom-pre-Lie algebra. □
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we introduce the notions of matching BiHom-type algebras. Their construction methods are studied in detail. Further, we study the properties and relationships between categories of these matching BiHom-type algebraic structures. Here, in the future, we intend to try to further study the cohomology and deformation of these matching BiHom-type algebras.
Author Contributions
W.T.: writing—original draft preparation, T.Y.: supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors were supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11761017), the Guizhou province first-class construction discipline program funded project (C420001), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11461014), the Doctoral Starting Up Foundation of Guizhou Normal University (No.GZNUD[2019]13) and the Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Foundation (No. [2020]1Y005).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the referees for their valuable suggestions and improve the quality of this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hartwig, J.; Larsson, D.; Silvestrov, S. Deformations of Lie algebras using σ-derivations. J. Algebra 2006, 295, 314–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benayadi, S.; Makhlouf, A. Hom-Lie algebras with symmetric invariant nondegenerate bilinear form. J. Geom. Phys. 2014, 76, 38–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L. Quasitriangular Hom-Lie bialgebras. J. Lie Theory 2012, 22, 1075–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, L. Double Hom-Associative Algebra and Double Hom-Lie Bialgebra. Adv. Appl. Clifford Algebra 2020, 30, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zeng, H. (m, n)-Hom-Lie algebras. Publ. Math. Debrecen. 2018, 92, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y. Representations of Hom-Lie algebras. Algebr. Represent. Theory 2012, 15, 1081–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, B.; Ma, Y.; Chen, L. Biderivations and commuting linear maps on Hom-Lie algebras. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.11117. [Google Scholar]
- Graziani, G.; Makhlouf, A.; Menini, C.; Panaite, F. BiHom-associative algebras, BiHom-Lie algebras and BiHom-bialgebras. Symmetry Integr. Geom. Methods Appl. 2015, 11, 086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Makhlouf, A.; Menini, C.; Panaite, F. BiHom-pre-Lie algebras, BiHom-Leibniz algebras and Rota-Baxter operators on BiHom-Lie algebras. Georgian Math. J. 2021, 28, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Makhlouf, A.; Menini, C.; Panaite, F. Rota-Baxter operators on BiHom-associative algebras and related structures. Colloq. Math. 2020, 161, 263–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, G. An analytic problem whose solution follows from a simple algebraic identity. Pac. J. Math. 1960, 10, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rota, G.C. Baxter algebras and combinatorial identities, I, II. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 1969, 75, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebrahimi-Fard, K. Loday-type algebras and the Rota-Baxter relation. Lett. Math. Phys. 2002, 61, 130–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y. Commutative matching Rota-Baxter operators, shuffle products with decorations and matching Zinbiel algebras. J. Algebra 2021, 586, 402–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhlouf, A. Hom-Dendriform Algebras and Rota-Baxter Hom-Algebras. Operads Univers. Algebra 2012, 147–171. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L. An Introduction to Rota-Baxter Algebra; Surveys of Modern Mathematics, 4; International Press: Somerville, MA, USA; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Guo, L. Matching Rota-Baxter algebras, matching dendriform algebras and matching pre-Lie algebras. J. Algebra 2020, 552, 134–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foissy, L. Algebraic structures on typed decorated rooted trees. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.07572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruned, Y.; Hairer, M.; Zambotti, L. Algebraic renormalisation of regularity structures. Invent. Math. 2019, 215, 1039–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belavin, A.; Drinfeld, V. Solutions of the classical Yang-Baxter equation for simple Lie algebras. Funct. Anal. Appl. 1982, 16, 159–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Peng, X.; Zargeh, C.; Zhang, Y. Matching Hom-setting of rota-Baxter algebras, dendriform algebras, and pre-Lie algebras. Adv. Math. Phys. 2020, 2020, 9792726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov-Tian-Shansky, M.A. What is a classical r-matrix? Funct. Anal. Appl. 1983, 17, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).