Abstract
The aim of this paper is to investigate generalized Ulam–Hyers stability and generalized Ulam–Hyers–Rassias stability for a system of partial differential equations of first order. More precisely, we consider a system of two nonlinear equations of first order with an unknown function of two independent variables, which satisfy the corresponding compatibility condition. The study method is that of differential inequalities of the Gronwall type.
Keywords:
system of partial differential equations; generalized Ulam–Hyers stability; generalized Ulam–Hyers–Rassias stability MSC:
34D20; 35L99; 45H99
1. Introduction
Ulam–Hyers stability is an important problem in functional equations theory, which was studied by many authors who can be found in the monograph [1].
The problem was posed by Ulam in 1940 (cf. [2,3]) in the following way. Let G be a group and H a metric group with metric d and For every such that, if verifies
then a homomorphism with
Firstly, Hyers [3] gaves an answer for additive Cauchy equation in Banach spaces, as follows.
Let be Banach spaces, and such that
There exists a unique additive mapping verifying
Ulam–Hyers stability of differential equations was firstly investigated by Alsina and Ger [4] in the following way. Let be an open interval and differentiable. If f satisfies
then differentiable such that and
The stability of differential linear equations of first order was studied in the papers [4,5]. Bernoulli equations were studied in [6] and Riccati equations in [7]. In [8], systems of first order linear differential equations were studied. Some results regarding linear differential equations of higher order were established in [9].
The first authors who studied Hyers-Ulam stability of partial differential equations were Prastaro and Rassias [10]. After that, a few results in this direction were given by other authors, regarding partial differential equations of first order [11,12], of order two [13], or of order three [14].
Recently, in a set of papers, Rus [13,15], has opened a new direction of study of the Ulam stability using Gronwall type inequalities and Picard operators technique. This will be used in this paper. Another direction of stability research is that in which results regarding fixed point theory are used [16].
In this paper, we will study the stability of a system of partial differential equations of order one, nonlinear. We mention that those are not studied yet in literature.
The general form of a system of n partial differential equations of first order for a function is
where
The normal form of this system is
If the functions admits continuous partial derivatives of order two, then These are the compatibility conditions and are not always identities.
We will consider the system in the case of functions of two variables, denoted by . Let
Example 1.
We consider the system
The compatibility condition is identically verified, The solution is
Example 2.
We consider the system
In this case, the compatibility condition is reduced to the equation Only two solutions are possible, namely and Verifying, we get that is the single solution.
Example 3.
We consider the system
The compatibility condition is not verified, hence the system has no solution.
From these examples, we see that Ulam stability for a system can be studied only for those which verify identical compatibility condition.
In the following lines, we will consider the system:
where and . Let . We consider endowed with Chebyshev norm that is Let .
From , the compatibility condition of the system is
2. Preliminaries
We will formulate the problem (2) + (3) as an integral equation, if condition (4) is satisfied. Since , the problem (2) + (3) is equivalent with the integral equation
Let and , nondecreasing in x and y. Let the inequalities
Definition 1.
Definition 2.
Remark 1.
A function v is a solution of (6) if and only if there exists a function such that
- (i)
- (ii)
Remark 2.
A function v is a solution of (7) if and only if there exists a function such that
- (i)
- (ii)
3. Generalized Ulam–Hyers Stability
The first result is the following.
Theorem 1.
If
- (i)
- , and such that on ;
- (ii)
- such that
- (iii)
- (iv)
- the compatibility condition (4) is satisfied;
then:
Proof.
(a) This is a consequence from the existence and uniqueness theorem (Rus [17], p. 210), since the conditions (i)–(iv) appear there.
(b) Let v be a solution to the inequality (6). Let u be the unique solution in to the problem (2) + (3). Using Remark 1, we obtain
Using Gronwall lemma ([18], p. 3) now, we get
hence where . Hence, Equation (5) is generalized Ulam–Hyers stable. □
Example 4.
Let , We consider the system
and the initial condition
The corresponding solution is The problem (8) + (9) is equivalent with the integral Equation (5), which became
We consider the inequality
Hence, on Thus, Equation (10) is generalized Ulam–Hyers stable.
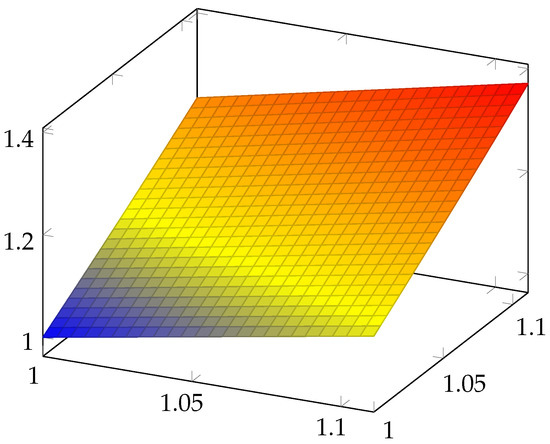
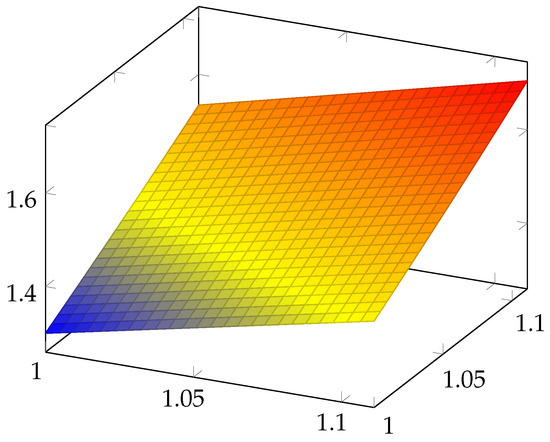
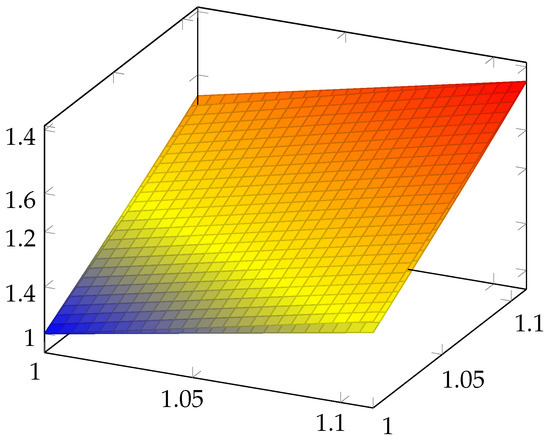
We remark that and represent two surfaces. We have drawn these surfaces in Figure 1 and Figure 2, respectively, and, in Figure 3, both of them are overlapping. We can see that these surfaces are close to one another.

Figure 1.
Representation of the surface on

Figure 2.
Representation of the surface on

Figure 3.
Representation of the surfaces , on together.
4. Generalized Ulam–Hyers–Rassias Stability
We study, now, generalized Ulam–Hyers–Rassias stability of system (2).
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we have studied generalized Ulam–Hyers and respectively Ulam–Hyers–Rassias stability of system (2), if condition (4) is satisfied, with initial condition (3). We have reduced this problem to Equation (5). We have used the method of differential inequalities, Gronwall types inequalities, and Picard operators technique. It is well known that these systems have many applications in the study of some partial differential equations of higher order, as in physics, chemistry, and other domains of science. Many problems from the domain Symmetry are modeled by differential equations and partial differential equations and those are approached in the stability point of view. The future study could be the stability of general system (1).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.M., S.A.C. and N.L.; methodology, D.M., S.A.C. and N.L.; writing–original draft preparation, D.M.; writing–review and editing, D.M., S.A.C. and N.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Brzdek, J.; Popa, D.; Rasa, I.; Xu, B. Ulam Stability of Operators; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ulam, S.M. A Collection of Mathematical Problems; Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Hyers, D.H. On the stability of the linear functional equation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1941, 27, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsina, C.; Ger, R. On some inequalities and stability results related to exponential function. J. Inequal. Appl. 1998, 2, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.-M. Hyers-Ulam stability of linear differential equations of first order. Appl. Math. Lett. 2004, 17, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.-M.; Rassias, T.M. Ulam’s problem for approximate homomorphisms in connection with Bernoulli’s differential equation. Appl. Math. Comput. 2007, 187, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.-M.; Rassias, T.M. Generalized Hyers-Ulam stability of Riccati differential equation. Math. Inequal. Appl. 2008, 11, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.-M. Hyers–Ulam stability of a system of first order linear differential equations with constant coefficients. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2006, 320, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimpean, D.S.; Popa, D. On the stability of the linear differential equation of higher order with constant coefficients. Appl. Math. Comput. 2010, 217, 4141–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prastaro, A.; Rassias, T.M. Ulam stability in geometry of PDE’s. Nonlinear Funct. Anal. Appl. 2003, 8, 259–278. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.-M. Hyers-Ulam stability of linear partial differential equations of first order. Appl. Math. Lett. 2009, 22, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungu, N.; Popa, D. Hyers-Ulam stability of a first order partial differential equation. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2012, 385, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungu, N.; Rus, I.A. Ulam stability of nonlinear hyperbolic partial differential equations. Carpatian J. Math. 2008, 24, 403–408. [Google Scholar]
- Lungu, N.; Ciplea, S.A. Ulam–Hyers–Rassias stability of pseudoparabolic partial differential equation. Carpatian J. Math. 2015, 31, 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Rus, I.A. Ulam stability of ordinary differential equations. Stud. Univ. Babes Bolyai Math. 2009, 54, 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Brzdek, J.; Cădariu, L.; Ciepliński, K. Fixed Point Theory and the Ulam Stability. J. Funct. Spaces 2014, 2014, 829419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rus, I.A. Principii si Aplicatii ale Teoriei Punctului Fix; Dacia: Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmikantham, V.; Leela, S.; Martynyuk, A.A. Stability Analysis of Nonlinear Systems; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1989; Volume 125. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).