Abstract
Background: Anisakis allergy has been increasing, and the diagnosis of it is based on specific serum IgE detection. Recently, the IgE-crosslinking-induced luciferase expression (EXiLE) test has been proposed as convenient tool for detecting functionally specific IgE antibodies. Here, we investigated if the EXiLE test is a useful tool in the diagnosis of Anisakis allergy. Methods: HuRa-40 cells were sensitized using six serum types from three patients with Anisakis allergy at the time of the initial test and after 6–12 months. Thereafter, various concentrations of Anisakis worm protein (AWP) were reacted to measure the degree of EXiLE. The degree of EXiLE was compared with Anisakis-specific IgE antibody levels measured by the CAP-FEIA method, and the IgE-antibody-binding protein profile was examined using IgE immunoblotting. Results: The results showed a good correlation between the CAP-FEIA values and EXiLE obtained with 5 μg/mL of AWP (R = 0.91, p < 0.01), a strong response on IgE immunoblotting in the region containing proteins weighing ≥40,000 Da. In addition, after the onset of Anisakis allergy, the degree of serum EXiLE decreased in two patients whose Anisakis-specific IgE antibody levels decreased over time but increased in one patient whose specific IgE antibodies increased after repeated antigen sensitization. Conclusions: Based on these data, the AWP-induced EXiLE test seemed to be useful and convenient for the diagnosis of Anisakis allergy, supplementing specific IgE determinants. After allergy onset, the use of this method to observe changes in specific IgE levels over time may be important for predicting the risk of recurrence.
1. Introduction
Anisakis simplex is a pathogenic nematode belonging to the genus Anisakis, family Anisakidae, and order Ascaridida. Human anisakiasis is a gastrointestinal tract parasitic infection caused by third-stage larvae (L3) of A. simplex. The life cycle of Anisakis nematodes involves marine fish, squid, and crustaceans as intermediate or paratenic hosts and marine mammals as definitive hosts [1]. Humans are accidental hosts and are infected by consuming raw or inadequately cooked fish containing Anisakis L3 larvae. Therefore, infection has been directly linked to eating habits.
Symptoms of anisakiasis include severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting caused by damage to the human gastrointestinal tract, primarily the stomach and intestines, secondary to mucosal and submucosal penetration of Anisakis L3 larvae [2]. In addition to the pathogenic effects of tissue damage, allergic reactions in sensitized humans can be caused by Anisakis larvae. In 1990, the first allergic reaction to Anisakis-contaminated fish was reported in Japan by Kasuya et al., who pointed out the allergenic potency of Anisakis antigens in addition to active gastrointestinal tract larval penetration [3]. Shortly after that report, 28 patients allergic to Anisakis were reported in Spain in 1996 [4].
Anisakis allergy is an IgE-mediated allergic reaction primarily caused by consumption of raw seafood containing A. simplex, and its recurrence has been thought to be caused by eating raw or undercooked seafood [5,6,7,8,9]. Gastrointestinal allergy is also referred to as gastroallergic anisakiasis (GAA) [10,11], which requires long-term management to deal with the acute phase and prevent prolonged allergic symptoms. In addition, most patients develop Anisakis allergy by oral sensitization, although sensitization by inhalation has been reported in occupational allergy [12], in which sensitization is caused by Anisakis worm protein (AWP) and not by live Anisakis worms. Anisakis allergy has been mainly reported in Southeast Asia and Western Europe, with Japan having the highest prevalence (>90%) [13]. Furthermore, in Japan, 10% to 30% of adult allergies are thought to be caused by Anisakis [14].
The diagnosis of Anisakis allergy is mainly based on measurement of specific IgE level using the CAP-FEIA method, measurement of total IgE level, and skin prick test [14,15]. In addition, the BAT method for measuring specific IgE levels in blood cells has been reported to correlate well with symptoms [16]. Another possible tool is the IgE-crosslinking-induced luciferase expression (EXiLE) test [17,18,19], which is a convenient in vitro method of measuring the function of specific IgE antibodies using cultured cells without using patient blood cells for the diagnosis of Anisakis allergy. In this study, we aimed to examine the utility of the EXiLE method for the diagnosis and long-term management of Anisakis allergy by comparing it with the CAP-FEIA method and investigating fluctuations in specific IgE blood levels over time in patients detected to have allergic reactions by the EXiLE method.
In particular, we compared the results of the EXiLE method with the specific IgE levels detected by the CAP-FEIA method and evaluated fluctuations in specific IgE blood levels over time in patients detected to have allergic reactions by the EXiLE method.
To the best of our knowledge, this was the first study to demonstrate the application of the EXiLE test.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Anisakis Worm Proteins
Species plural identification as A. simplex nematodes was performed using a PCR-based method [20]. After being collected from the abdomen of a chub mackerel (Scomber japonicus) purchased at local markets in Ehime, Japan, A. simplex L3 larvae were washed in PBS and immediately frozen at −20 °C until use. For antigen preparation, according to Carballeda-Sangiao’s method [21], 10 larvae were suspended in 0.8 mL of PBS containing a protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma-Aldrich, Burlington, MA, USA); ground with biomarker (Nippi Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan); and sonicated for 30 s 10 times in an ultrasonic crushing device (BIORUPTORII, Sonic Bio Co., Ltd., Samukawa, Japan). After centrifugation at 12,000× g at 4 °C for 5 min, protein extract was obtained and it was used as the antigen sample (i.e., AWP) in the experiment. Protein concentrations were determined using Protein Assay CBB solution (# 29449-44, Nacalai tesque, Kyoto, Japan). The protein solutions were stored in aliquots at −80 °C until use.
2.2. Analysis of Serum Samples
This study was approved by the ethics committee of the National Hospital Organization, Sagamihara National Hospital, Okayama University of Sciences, Teikyo Heisei University. Six serum types were collected from three patients during consultation at the first visit and after 6–12 months. The total and Anisakis-specific IgE levels in each serum sample were measured using ImmunoCAP-FEIA (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) [15] at the date of serum collection. The results of the serum sample analyses are presented in Table 1. Pooled serum samples from healthy donors were purchased from Cosmo Bio (Tokyo, Japan) and used as negative controls.

Table 1.
Information on patient sera regarding Anisakis allergy.
2.3. IgE Immunoblotting
First, after adjusting the AWP concentration to 1 mg/mL using PBS, an equal volume of 2× Laemmli Sample Buffer (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) and a 1/10 volume of 1M dithiothreitol solution (Nacalai tesque, Kyoto, Japan) were added [22]. After boiling the prepared sample at 100 °C for 2 min, SDS-electrophoresis was performed using 80 μL of sample in a 3.5 cm well and 10 μL of rainbow marker (Cytiva, Uppsala, Sweden) added to a 12% mini protean TGX precast gel (IPG well) (#4861041, Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) at a constant current of 20 mA. After completion of electrophoresis, the precast gel removed from the fixation plate was applied to a transfer buffer containing 10% methanol (Tris/glycine transfer buffer) for equilibration. The activated 0.2 μm polyvinylidene difluoride membrane (PVDF, Bio-Rad, Herules, CA, USA) was then subjected to overnight electrical transfer at 3 W constant power. After the transfer, the PVDF membrane was immersed in PBS–0.05% Tween 20 (PBS-T), washed under shaking for 5 min, and then immersed in Blocking One (Nacalai tesque, Kyoto, Japan) for 1 h. The cleaned PVDF membrane was cut into 4 mm wide 7 strips. The washed PVDF strips were immersed in primary antibodies from the serum samples of each patient, 10-fold-diluted with 5% Blocking One–PBS-T, and shaken at 4 °C overnight. After incubation with the primary antibody, the strips were rinsed twice with PBS-T and washed three times under shaking for 10 min each. The strips were then immersed in a secondary antibody [goat anti-human IgE, HRP conjugate (Nordic-MUbio, Susteren, Netherlands)], 2000-fold-diluted with 5% Blocking One–PBS-T, and incubated under shaking at room temperature for 1 h. After incubation with the secondary antibody, the strips were rinsed twice with PBS-T and washed three times under shaking for 10 min, and 7 strips were gathered on a Saran wrap sheet and then incubated with Amersham ECL Prime Western Blotting Detection Reagent (Cytiva, Uppsala, Sweden) for approximately 1 min to detect chemiluminescence using an Amersham Imager 680 (Cytiva, Uppsala, Sweden). All experiments were performed at least twice to confirm reproducibility.
2.4. Luciferase Assay
HuRa-40 cells were seeded at a density of 5 × 104 cells/50 µL/well in a clear-bottom 96-well plate (#165306, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and sensitized overnight using 100-fold-diluted serum samples from the three patients (six types). Subsequently, the cells were washed three times with sterile PBS and then added with different concentrations of AWP solution (0, 0.06, 0.22, 0.78, 2.72, 9.52, 33.3, 117, 408, 1429, and 5000 ng/mL) to make a volume of 50 μL/well. The cells were cultured/stimulated for 3 h at 37 °C in the incubator. We used goat anti-human IgE antibodies (100 ng/mL; Bethyl Laboratories, Montgomery, TX, USA) as positive controls.
After stimulation, a homogeneous luciferase substrate solution (ONE-GloTM EX, Promega, Madison, WI, USA) was added to a volume of 50 μL/well, and the plate was placed for 5 min at room temperature. The chemiluminescence (luciferase activity) in each well was measured using a GloMax® luminometer (GM3510, Promega, Madison, WI, USA). The EXiLE results were measured as the fold-change in luciferase activity; cell activity without antigen stimulation was set at 1. The cut-off value was established based on the highest value (+3 SD) obtained in the experiments using control serum samples.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analyses were performed using Microsoft Excel 2016 MSO (version 2412). Spearman’s rank correlation test was performed to compare the results between the EXiLE and CAP-FEIA methods, and the correlation coefficient (R) and p value were obtained.
3. Results
3.1. IgE Immunoblotting
The results of the IgE immunoblot analyses are presented in Figure 1, and those for the serum sample analyses are shown in Table 1. In patient C, who had high Anisakis-specific IgE antibody levels on CAP-FEIA, the serum IgE antibodies were confirmed to be bound to multiple AWPs (Figure 1, lane 5). In particular, according to the identified molecular weight (MW), the major binding proteins seemed to be Ani s 7 (135 kDa) [23], Ani s 7 dimer (>225 kDa), Ani s 2 (102 kDa) [24], and Ani s 3 (44 kDa) [25]. Moreover, the IgE-binding activity of AWP was stronger in serum C-1, which had a CAP-FEIA value of 2400 (Figure 1, lane 5), than in serum C-2, which had a CAP-FEIA value of 87.5 (Figure 1, lane 6). The IgE-binding activity of AWP was weaker in the serum of patient B than in the serum of patient C (Figure 1, lanes 3 and 4). Using serum B-2, which had a CAP-FEIA value of 48.1, a clear IgE immunoblotting pattern was obtained (Figure 1, lane 4), and the main binding proteins had MWs of 135, 102, and 44 kDa. The binding activity in lane 3 using serum B-1 with a CAP-FEIA value of 27.8 was almost the same but weaker than that in lane 4. IgE binding to AWP using the serum samples of patient A was slight (Figure 1, lanes 1 and 2); that in A-1 seemed to be slightly higher than that in A-2 (CAP-FEIA value: 8.06 vs. 6.49).
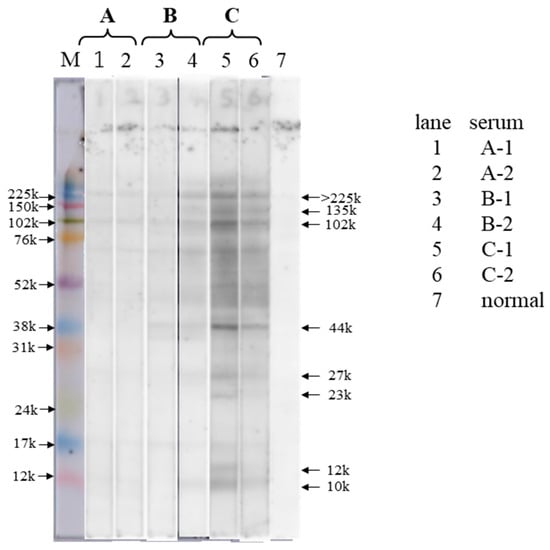
Figure 1.
IgE immunoblot analysis of serum samples from patients with Anisakis allergy and Anisakis worm proteins (AWPs). AWP (10 μg/lane) solution was subjected to 12% SDS-PAGE and IgE immunoblotting using serum samples from patients with Anisakis allergy. Lanes 1, 2: patient A’s serum samples after allergy onset (A-1: at 1 y and 6 mo and A-2: at 2 y and 6 mo). Lanes 3, 4: patient B’s serum samples (B-1: at 3 y and 6 mo after allergy onset and B-2: at 1 mo after the second recurrence, which occurred 4 y post-first allergy onset). Lanes 5, 6: patient C’s serum samples after allergy onset (C-1: at 4 mo and C-2: at 10 mo). Lane 7: normal serum samples from a healthy donor. AWP, Anisakis worm protein; M, molecular weight marker. Note: The unit “y” means year and “mo” means month.
Based on the results, the main IgE-binding AWPs were considered to have relatively large MWs (>40 kDa), and IgE binding was observed in patients with Anisakis allergy and low serum Anisakis IgE levels on CAP-FEIA. The intensity of IgE binding seemed to be semiquantitative.
3.2. Luciferase Assay
The dose–response curves of the AWP concentration and luciferase activity (fold-change) (Figure 2) showed that the AWP concentration limit differed among the serum samples (0.22 ng/mL for C-1, 0.78 ng/mL for C-2, 9.52 ng/mL for B-2, 117 ng/mL for B-1, and 408 ng/mL for A-1). These results indicated that the detection limit decreased with the increase in the antigen-specific IgE value. Table 2 presents the EXiLE scores in the serum samples. The EXiLE scores in serum samples 1, 2, 3, and 4 corresponded to minimum concentrations of 1429, 117, 9.52, and 0.78 ng/mL, respectively, for the AWP response. We analyzed the correlation between the scores of the CAP-FEIA and EXiLE tests using Spearman’s rank test. There was a good correlation between the CAP-FEIA and EXiLE scores (R = 0.91, p < 0.01).
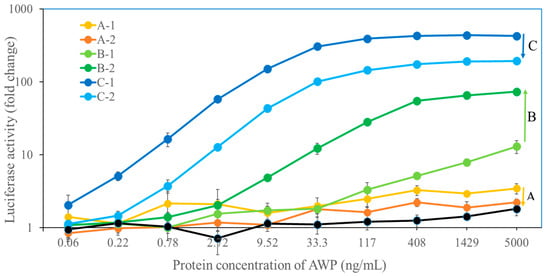
Figure 2.
EXiLE test of HuRa-40 cells using serum samples from patients with Anisakis allergy and various AWP concentrations. HuRa-40 cells were sensitized overnight with 1:100-diluted serum samples from patients with Anisakis allergy or healthy donors and then stimulated with various concentrations of AWP for 3 h. The horizontal axis represents the AWP concentration, and the vertical axis represents the degree of luciferase activity change. The degree of change was calculated as the ratio of the response in the presence of the antigen to the response in the absence of the antigen. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). The changes in luciferase activity over time at AWP concentration of 5000 mg/mL for individual patients were indicated by the arrow on the right side of the figure.

Table 2.
EXiLE in HuRa-40 cells sensitized with Anisakis-allergy-patient sera.
The obtained maximum luciferase activity (EXiLE level) in each serum sample using 5000 ng/mL of AWP demonstrated that as the antigen-specific IgE serum level (CAP-FEIA) increased, the maximum EXiLE level increased, and a good correlation between the two was observed (R = 0.91, p < 0.01) according to Spearman’s rank test. Figure 3 shows a scatter plot in Excel 2016 between the CAP–FEIA value and the maximum EXiLE level, and a good correlation was observed. Furthermore, the EXiLE level and CAP-FEIA value obtained with 1429, 408, 117, 33.3, and 9.52 ng/mL of AWP were found to have a good correlation (R > 0.92, p < 0.01).
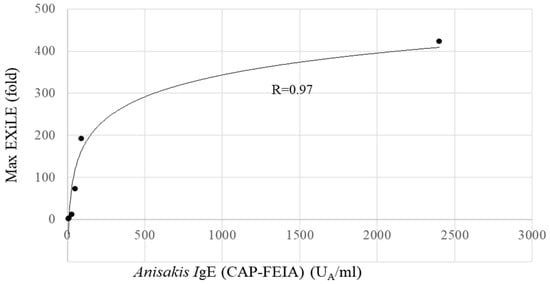
Figure 3.
Correlation between Anisakis IgE (CAP-FEIA) and EXiLE in HuRa-40 cells. This figure depicts the results in Table 2 in graphic form through an Excel scatter plot. Logarithmic approximation curve between the CAP-FEIA and EXiLE results obtained with 5 μg/mL of AWP is shown. The R-value was 0.97.
On subsequent examination of the EXiLE level changes over time, the maximum EXiLE level in patients C and A decreased after the initial blood draw (C-1 to C-2 and A-1 to A-2); that in patient B increased (B-1 to B-2) (Figure 2), and this increase was consistent with the increase in the CAP-FEIA value (Table 1). In patient B, the reason for the increase in the maximum EXiLE level over time might be a result of resensitization due to consumption of raw tuna slices before the second blood draw.
4. Discussion
Anisakis allergy, which has been increasingly observed in recent years, has attracted attention as an IgE-dependent immediate allergy. A high blood titer of Anisakis-specific IgE antibody is the key finding for diagnosing Anisakis allergy, although results must be carefully interpretated, because some healthy people who have been sensitized do not develop Anisakis allergy [16]. In addition, Anisakis was reported to have 16 types of allergen components [26], but their clinical significance has not been established. Therefore, several issues in the diagnosis of Anisakis allergy remain to be addressed.
Table 3 summarizes the conventional immediate-type allergy diagnosis methods and their possible application to Anisakis allergy.

Table 3.
Conventional immediate-type allergy tests and possible application to Anisakis allergy.
The clinical diagnosis method of immediate allergy is broadly divided into three categories as follows: in vitro studies of Category 3 have the lowest invasiveness, followed by Category 2 ex vivo studies and Category 1 in vivo studies. The most common of these laboratory tests is Category 3 CAP-FEIA (ImmunoCAP) [28,29], which is a simple and highly sensitive method for measuring antigen-specific IgE. CAP-FEIA is also commercially available for Anisakis antigens, and although it can be performed normally, it only shows the binding of IgE antibodies to the antigen, and it is not possible to measure biological activity to see if it causes activation of target cells. In addition to CAP-FEIA, the Category 1 skin prick test (SPT) is often used as a screening test for the diagnosis of normal food allergies [28]. The SPT is a method of pricking a small amount of antigen into the skin and looking for redness, and it can be used to measure allergic reactions in the body compared with CAP-FEIA. It has already been used for the diagnosis of Anisakis allergy in many cases, but in the case of Anisakis, there are restrictions on its application because it is not possible to use commercially available antigens [14,15]. In addition, as a definitive diagnosis of food allergy, an OFC test [27] and a BAT test [28] may be performed to check the relationship with symptoms. Regarding OFC for patients with Anisakis allergy, from 1999 to 2004 [30,31,32,33], Spanish researchers reported some studies in which OFC was performed with dead worm proteins, and the challenges were all negative. Therefore, OFC does not seem to be effective for the diagnosis of Anisakis allergy. Regarding the BAT test for Anisakis allergy [16], one report has been published, and it seems to be a useful technique for diagnosing Anisakis allergy. However, as the BAT test requires fresh patient blood for basophil preparation, the test seems to be limited to special laboratories.
In this study, we examined the diagnostic utility of the EXiLE method a simple in vitro measurement of antigen-specific IgE antibodies that reflect clinical symptoms.
Our results showed a good correlation between the EXiLE level and the CAP-FEIA value and a sufficiently low detection limit of the antigen concentration (0.22 ng/mL). The lowest effective Anisakis antigen concentration of the EXiLE method was almost the same as the reported lowest effective concentration of peanuts or egg white solution [17,19]. These results strongly suggested that the increased luciferase expression in HuRa-40 cells reflects crosslinking of the antigen-specific IgE bound to FcεR1 on mast cells. Therefore, good EXiLE values were obtained using serum samples of patients with Anisakis allergy. Conversely, based on the detection limit of antigen-specific IgE, the sensitivity was slightly lower with the EXiLE method than with the CAP-FEIA method. For example, in serum sample A-2, the CAP-FEIA value was 6.49 UA/mL and was judged as positive, whereas the EXiLE value was less than the cut-off and was judged as negative. The reason for the negative ExiLE test result for A-2 was unclear; however, considering that this sample was obtained 2.5 years post-onset, the functional IgE level might have decreased over time. Nevertheless, the EXiLE method appeared to be useful for the diagnosis of Anisakis allergy and could supplement other tools, such as the skin prick test, for the determination of specific functional IgE.
In addition, using the EXiLE method in addition to the CAP-FEIA method for long-term management, the reactivity of Anisakis-specific IgE was found to change over time after the onset of Anisakis allergy. In one patient, the reason for the increase in the maximum EXiLE level over time might be resensitization due to consumption of raw tuna slices before the second blood draw [15]. Long-term monitoring of antigen-specific IgE in serum is important for dietary guidance for patients with Anisakis allergy, especially in Japan, where consumption of raw fish is customary. In the future, collecting data from many monitored patients may help prevent the onset and recurrence of Anisakis allergy. Moreover, this novel in vitro EXiLE method for Anisakis allergy has potential applications for the following: (i) diagnostic supplementation for the determination of serum allergen-specific IgE following the CAP-FEIA test, (ii) screening of allergen components in Anisakis worm extract, and (iii) standardization of allergen extracts for clinical use.
Author Contributions
Investigation, H.A., M.N., C.K. and Y.H.; supervision, R.T.; writing—original draft, R.T.; writing—review and editing, H.A., Y.H. and Y.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This human serum study was approved by the ethics committee of National Hospital Organization, Sagamihara National Hospital (permission number: 2012-17-2, approved on the 4 July 2019), Okayama University of Sciences (permission number: I-4, approved on the 23 July 2019), and Teikyo Heisei University (permission number: 2024-067, approved on 2 September 2024).
Informed Concent Statement
Instead of formal informed consent, patient consent was obtained through an opt-out process by publicly disclosing the study details on the homepage of Sagamihara National Hospital according to the Japanese Act on the Protection of Personal Information (Article 27(2)).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflicts of interest are reported by the authors.
Abbreviations
| CAP-FEIA | CAP–fluorescence enzyme immunoassay |
| IgE | Immunoglobulin E |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| CBB | Coomassie Brilliant Blue |
| SD | Standard deviation |
References
- Nieuwenhuizen, N.E.; Lopata, A.L. Anisakis—A food-borne parasite that triggers allergic host defences. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Thiel, P.H. Anisakiasis. Parasitology 1962, 52, 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Kasuya, S.; Hamano, H.; Izumi, S. Mackerel-induced urticaria and anisakis. Lancet 1990, 335, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez de Corres, L.; Audicana, M.; Del Pozo, M.D.; Munoz, D.; Fernandez, E.; Navarro, J.A.; Garcia, M.; Diez, J.J. Anisakis simplex induces not only anisakiasis: Report on 28 cases of allergy caused by this nematode. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 1996, 6, 315–319. [Google Scholar]
- Hamada, Y.; Nakatani, E.; Watai, K.; Iwata, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Ryu, K.; Kamide, Y.; Sekiya, K.; Fukutomi, Y. Effects of raw seafood on the risk of hypersensitivity reaction recurrence in patients with an Anisakis allergy: A retrospective observational study in Japan. Allergol. Int. 2024, 73, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovic, J.; Baltic, M.Z.; Boskovic, M.; Kilibarda, N.; Dokmanovic, M.; Markovix, R.; Janjic, J.; Baltic, B. Anisakis allergy in human. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 59, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards. Scientific opinion of April 2010 on risk assessment of parasites in fishery products. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1543. [Google Scholar]
- Aibinu, I.E.; Smooker, P.M.; Lopata, A.L. Anisakis nematodes in fish and shellfish—From infection to allergies. IJP Parasites Wildl. 2019, 9, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, A.R.; Kiani, B.; Afshari, A.; Moghaddas, E.; Williams, M.; Shamsi, S. World-wide prevalence of Anisakis larvae in fish and its relationship to human allergic anisakiasis.: A systematic review. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 3585–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daschner, A.; Alonso-Gomez, A.; Cabanas, R.; Suarez-de-Parga, J.M.; Lopez-Serrano, M.C. Gastroallergic anisakiasis: Borderline between food allergy and parasitic disease—Clincal and allergologic evaluation of 20 patients with confirmed acute parasitism by Anisakis simplex. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 105, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daschner, A.; Cuellar, C. Progress in Anisakis allergy research: Milestones and reversals. Curr. Treat. Options Allergy 2020, 7, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuizen, N.; Lopata, A.L.; Jeebhay, M.F.; Herbert, D.R.; Robins, T.G.; Brombacher, F. Exposure to the fish parasite Anisakis causes allergic airway hyperreactivity and dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 117, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, F.J.; Gasser, R.B.; Jabbar, A.; Lopata, A.L. Foodborne anisakiasis and allergy. Mol. Cell. Probes 2014, 28, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishima, R.; Motojima, S.; Tsuneishi, D.; Kimura, T.; Nakashita, T.; Fudouji, J.; Ichikawa, S.; Ito, H.; Nishino, H. Anisakis is a major cause of anaphylaxis in seaside areas: An epidemiological study in Japan. Allergy 2020, 75, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, Y.; Sugano, S.; Kamide, Y.; Sekiya, K.; Fukutomi, Y. Anisakis allergy versus gastric anisakiasis: A case of repeated Anisakis-assosiated symptoms. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Glob. 2024, 3, 100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Munoz, M.; Luque, R.; Nauwelaers, F.; Moneo, I. Detection of Anisakis simplex-induced basophil activation by flow cytometry. Cytom. Part B 2005, 688, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Kurisaka, C.; Kumasaka, K.; Nakamura, R. Novel IgE crosslinking-induced luciferase expression method using human-rat chimeric IgE receptor-carrying mast cells. J. Immunol. Method 2024, 529, 113682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Kurisaka, C.; Muramatsu, D.; Takada, S.; Toyama, K.; Yoshioka, K.; Nakamura, R. Consideration of the EXiLE test for predicting anaphylaxis after diclofenac etalhyaluronate administration. J. Immunotox. 2024, 21, 2417758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, R.; Uchida, Y.; Higuchi, M.; Nakamura, R.; Tsuge, I.; Urisu, A.; Teshima, R. A convenient and sensitive allergy test: IgE crosslinking-induced luciferase expression in cultured mast cells. Allergy 2010, 65, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Z.; Yagi, K. Identification of anisakinae larvae by diasnostic PCR. Seikatsu Eisei 2005, 49, 168–171. [Google Scholar]
- Carballeda-Sangiao, N.; Rodriguez-Mahillo, A.I.; Careche, M.; Navas, A.; Moneo, I.; Gonzalez-Munoz, M. Changes over time in IgE sensitization to allergens of the fish parasite Anisakis spp. PLoS Neglect. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, E.; Anadon, A.M.; Garcia-Bodas, E.; Romaris, F.; Iglesias, R.; Garate, T.; Ubeira, F.M. Novel sequences and epitopes of diagnostic value derived from the Anisakis simplex Ani s 7 major allergen. Allergy 2008, 63, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Perez, J.; Fernandez-Caldas, E.; Maranon, F.; Sastre, J.; Bernal, M.L.; Rodriguez, J.; Bedate, C.A. Molecular cloning of paramyosin, a new allergen of Anisakis simplex. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2000, 123, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asturias, J.A.; Eraso, E.; Martinez, A. Cloning and high level expression in Escherichia coli of an Anisakis simplex tropomyosin isoform. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2000, 108, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, M.; Shimakura, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Azuma, N.; Matsui, K. Component analysis of three anisakiasis allergy cases in our department—Including comparison with 10 existing reports. J. Soc. Allergol. 2023, 72, 1154–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Upton, J.E.M.; Bird, J.A. Oral food challenges. Ann. Allergy Asthma Imunol. 2020, 124, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, H.A. Food Allergy. Part 2: Diagnosis and management. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 103, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ree, R.; Aalberse, R.C. Specific IgE without clinical allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 103, 1000–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Moreno-Ancillo, A.; Daschner, A.; Lopez-Serrano, M.C. Dietary assessment in five cases of allergic reactions due to gastroallergic anisakiasis. Allergy 1999, 54, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, F.; Blanco, J.G.; Garces, M.; Juste, S.; Fuentes, M.; Herrero, D. Freezing protects against allergy to Anisakis simplex. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2001, 11, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Gomez, A.; Morreno-Ancillo, A.; Lopez-Serrano, M.C.; Suarez-de-Parga, J.M.; Daschner, A.; Caballero, M.T.; Barranco, P.; Cabanas, R. Anisakis simplex only provokes allergic symptoms when the worm parasitises the gastrointestinal tract. Parasitol. Res. 2004, 93, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastre, J.; Lluch-Bernal, M.; Quirce, S.; Arrieta, I.; Lahoz, C.; Del Amo, A.; Fernandez-Caldas, E.; Maranon, F. A double-blind, placebo-controlled oral challenge study with lyophilized larvae and antigen on the fish parasite, Anisakis simplex. Allergy 2000, 55, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).