Abstract
The Montado in Portugal and Dehesa in Spain is a unique agro-silvo-pastoral system designed to overcome food needs in a scarce resource’s environment. The system competitiveness is not clear and it is now under severe threats, caused by extensification or abandonment of less fertile areas and by intensification in more fertile ones. The aim of the undertaken research is to compare the cow-calf production within these systems in Portugal and Spain, identifying their strengths and weaknesses and the main drivers of their evolution, and to compare these systems with other European countries’ systems, ranking their competitiveness and efficiency among other systems in the EU. The research indicates that Montado/Dehesa farms systems are dependent on the type of farming system, its context and management, i.e., on the decision and its context; so, in a context of Mediterranean land system changes, the future of the Montado/Dehesa ecosystem depends on the ability of the cow-calf production systems to face the future and to perceive the modifications needed to overcome new challenges and take advantage of new opportunities.
1. Introduction
The agro-silvo-pastoral system known as Montado, in Portugal, and Dehesa, in Spain is a unique landscape occupying around 3.5–4 million ha in Spain and Portugal [1], most of which is still in production today [2]. It is a “man-made” system designed to overcome food needs in a scarce resources environment: the open Mediterranean oak woodlands allows pastures growth, animal production and forestry production, and has been refined over time [3].
Land use in the Montado/Dehesa is characterized by an extensive animal production system, mainly based on under cover pastures that provide income but also shrub control while allowing the production of forest products—of which cork is the main one but acorn, charcoal and wood can be referred to as well—and other uses, such as hunting, fishing and tourism.
This system’s leverage of resources is a source of teachings and inspiration about agriculture and forest sustainable multifunctional models that are currently being sought and defined at the European and world level [3] because it produces ecological and economic values; as a result, it has been considered by the European Union as a High Nature Value (HNV) system. Additionally, and according to Plieninger [4], the social value should not be neglected, as the Montado/Dehesa system is a fundamental component of regional identity.
Nevertheless, the system competitiveness is not clear and the system is now facing severe threats, on one hand caused by extensification or abandonment of less fertile areas and on the other hand caused by intensification in more fertile ones [5].
The objective of this paper is to compare the cow-calf production within these systems in Portugal and Spain, identifying their strengths and weaknesses and the main drivers of their evolution and to compare these systems with other European countries’ systems, ranking their competitiveness and efficiency among other systems in the EU.
The present paper is structured in five sections. Beside this introduction, the section System Description and Objectives provides a brief presentation of the Montado/Dehesa system and presents the main objectives of this study. The Material and Methods present the concepts underlying the agri benchmark network and provides a brief presentation of the cow-calf farms from Portugal and Spain. The results section presents the results of the applied methodology for the cow-calf farms considered and benchmarks these farms against other cow-calf farms in Europe. In the Discussion and Conclusions section the results obtained are discussed, considering the reasons behind them and the main conclusions of this study are provided.
2. Systems Description and Objectives
The Montado in Portugal occupies around 1.2 millon ha that is mainly used for extensive livestock grazing [6]. Depending on the type of Montado (terrain, soils and characteristics of the farms) its main use is for herds of sheep or goats and Iberian pigs or cattle, although some farms still breed a combination of livestock and there is an on-going movement towards cattle breeding [6].
Despite the difficulties posed by environmental and edapho-climatic conditions, their heterogeneity assured that these systems could prosper historically. According to Plieninger [4], Montado/Dehesa is one of the most prominent and best preserved low-intensity farming systems in Europe; the integration of traditional land-use and biodiversity conservation that is characteristic of this system is considered to be an exemplar for the wise management of the countryside as a whole.
Young [7] defines a sustainable land use system as one that “achieves production combined with the conservation of the resources on which that production depends, thereby permitting the maintenance of productivity”. Sassenrath et al. [8] define sustainable agricultural production as: “an approach to producing food and fiber which is profitable, uses on-farm resources efficiently to minimize adverse effects on environment and people, preserves the natural productivity and quality of the land and water, and sustains vibrant rural communities”. If the statement above [4] already pointed to an interesting system involving sustainability, then based on these definitions, we can infer that economic viability and efficiency (both production efficiency and resources´ use efficiency) are key issues for the future of Montado/Dehesa systems.
Cow calf is nowadays recognized as an important production industry; in European farms and in spite of the diversified origin of animals used and different ways of breeding, cow-calf production is recognized as an important branch for agricultural development [9]. According to this author, cow-calf’s increasing importance in the European Union (it increased by almost 5% in production during 2013–2016 and 4% in consumption) may indicate that the interest in this production will increase in the coming years as an alternative to the unstable dairy market.
The first objective of this study is to compare the economic indicators on a farm-to-farm basis (cow-calf and mix cow-calf/ewe) and to understand what are the reasons for any differences. Continuing on a farm-to-farm basis, production efficiency and resources use efficiency should also be compared. This will lead us to comparisons between the Montado/Dehesa system and other systems in Europe in order to learn about the strengths, weaknesses and the competitiveness and sustainability of these systems among European cow-calf production systems.
3. Material and Methods
The research was conducted using the agri benchmark database. Established in 2001 as part of the International Farm Comparison Network, agri benchmark is a global, non-profit network of agricultural economists, advisors, producers and specialists in key sectors of agricultural and horticultural value chains that use internationally standardized methods to analyze farms, production systems and their profitability. The farm-level knowledge provided by partners all around the world is combined with an analysis of international commodity markets and value chains, allowing the provision of scientifically consistent and soundly based answers on strategic issues to decision-makers in policy, agriculture and agribusiness (http://www.agribenchmark.org/agri%20benchmark/who-we-are.html).
This is an exploratory study because it compares the Montado and Dehesa cow-calf production systems and benchmarks these systems using other European cow-calf production systems. The study began with data collection from secondary sources, namely a literature review and statistical data, and then analyzed the data from the agri benchmark Beef and Sheep branch database to compare the Portuguese and Spanish systems and benchmark them against other systems in Europe.
The agri benchmark database contains farms from both Montado and Dehesa production systems. These are typical farms, defined as:
- being an existing farm or a data set describing a farm,
- being in a specific region which represents a major share of output for the product considered,
- running the prevailing production system for the product considered,
- reflecting the prevailing combination of enterprises as well as land and capital resources,
- reflecting the prevailing type of labor organization.
The typical farms are never averages of survey data because averages do not provide consistent production system data sets. They are the result of a panel meeting with 4–6 farmers and an advisor, where each figure is obtained in a consensus, or are based on individual farms which were ‘typified’ by replacing farm individual particularities with prevailing characteristics, figures, technologies and procedures. In the Beef and Sheep branch of agri benchmark, farms are mainly characterized by their beef and sheep production (cow-calf, beef fattening, dairy, ewe, lamb finishing or sheep milk) and their land and labor characteristics.
The Portuguese farms are:
- PT_625_0: A cow-calf farm, with 623 cows and 1650 ha of land. All the land is rented and the labor is totally hired;
- PT_250_0: A cow calf + ewe farm, with 250 cows and 650 ewes, and 756 ha of land, of which 700 of owned land and 56 ha rented, and the labor is totally hired.
The Spanish farms are:
- ES_180_0: A cow-calf farm, with 180 cows and 1700 ha of land. All the land is rented and the labor is all family labor;
- ES_80_0: A cow-calf farm, with 80 cows and 149 ha of owned land. They use family (30%) and hired (70%) labor;
The study compared these farms on a whole farm basis and on an enterprise basis, to understand what are the reasons for their differences and how their efficiency compares to that of other farms. As Montado/Dehesa systems are very particular systems, with a non-negligible environmental role, it was also important to compare them with the other systems in the EU (+UK) in order to rank their competitiveness among other systems in EU (+UK) and anticipate their future sustainability.
The economic situation of the farms was assessed using standard economic indicators both on the structure of the farm and on the economic viability of the productions.
The agri benchmark calculation model TIPI-CAL [10] was used for the calculations. TIPI-CAL is a production and accounting model, a pure simulation without algorithms or optimization, which covers the whole farm and enterprise levels. It is an Excel based model offered as shareware for agri benchmark partners. TIPI-CAL consists of a basic model and additional modules for cost analysis and data management.
Agri benchmark provides whole farm analysis, considering the main indicators of a whole farm that are important to analyze the system in place as each decision, at the farm level, impacts not only the production activity for which the decision was taken but also the entire farm—any agricultural system moves together as a consequence of every decision. The network also provides enterprise analysis for each of the network’s enterprises that compose the farm (cow-calf, beef fattening, dairy, ewe, lamb finishing or sheep milk), to allow a more in-depth analysis of these activities and their particularities.
3.1. Whole-Farm Analysis
- Return structure: this indicator weights the different farm activities on the farm returns.
- Profit margin whole farm: this indicator gives the % share of farm income in total returns.
- Percentage composition of whole farm returns: this indicator shows where, in a percentage basis, the whole farm returns come from.
- Whole farm costs: both in absolute and % values. This indicator details the enterprises’ cost structure.
- Whole farm profitability: this indicator identifies the various components of the farm profitability, comparing the costs with the market returns and the coupled and decoupled payments.
3.2. Enterprise Analysis
The enterprise indicators chosen access production efficiency, resources’ use efficiency and economic situations.
The production efficiency and the resources’ use efficiency were assessed using the following standard indicators:
- Weaned calves per 100 cows and year: this indicator compares production efficiency regardless of mother’s weight or breed.
- Share of purchased feed: together with the previous one this indicator can be seen as a proxy to farm resources’ efficiency use.
The economic indicators can be expressed per animal, per ha and per 100 kg live weight sold, and are:
- Total cost by factor and non-factor costs.
- Total cost by cash costs, depreciation and opportunity costs.
Productivity figures are:
|  | These indicators measure the production system resources’ use efficiency. |
4. Results
4.1. Whole Farm Analysis
The return structure of the four farms analyzed (Figure 1) shows that those that have bigger areas (PT_625_0 and ES_180_0) mainly depend on cow-calf to assure their returns, while the other two have a more diverse return structure—in the case of ES_80_0, around 30% of the returns come from Iberian pigs, while for the other Portuguese farm, almost 30% of the returns also come from ewes and from the rental of land for pig fattening or other activities. This diversification is desirable and is in line with the targets of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals to be achieved by 2030 in terms of food security and the sustainability of farm systems and producers [11].
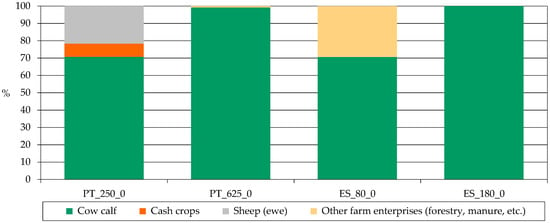
Figure 1.
Return Structure (% of different farm activities on total farm returns). Source: model results. PT_625_0: A cow-calf farm, with 623 cows and 1650 ha of land. All the land is rented and the labor is totally hired; PT_250_0: A cow calf + ewe farm, with 250 cows and 650 ewes, and 756 ha of land, of which 700 of owned land and 56 ha rented, and the labor is totally hired; ES_180_0: A cow-calf farm, with 180 cows and 1700 ha of land. All the land is rented and the labor is all family labor; ES_80_0: A cow-calf farm, with 80 cows and 149 ha of owned land. They use family (30%) and hired (70%) labor.
For the whole farm profit margin (Figure 2), it can be seen that in these systems, the share of farm income in total returns is low. The more diversified Portuguese farm (PT_250) has the biggest share, reaching its farm income at around 42% of the farm returns.
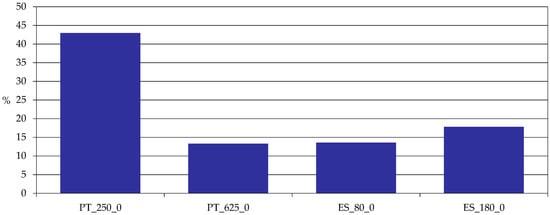
Figure 2.
Profit margin whole farm (% share of farm income in total returns). Source: model results.
In fact, we can observe the percentage composition of whole farm returns in Figure 3, which indicates that for these farms, an important share of farm returns comes from coupled and decoupled payments.
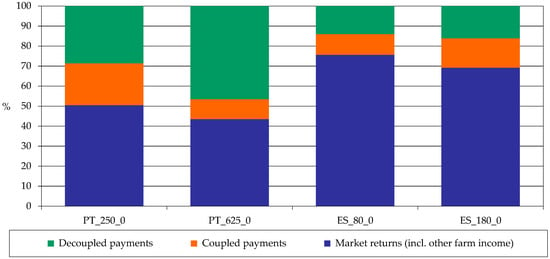
Figure 3.
Composition of whole farm returns (%). Source: model results.
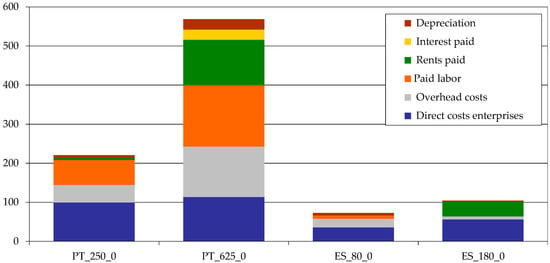
Figure 4.
Whole farm costs in absolute values (€/farm). Source: model results.
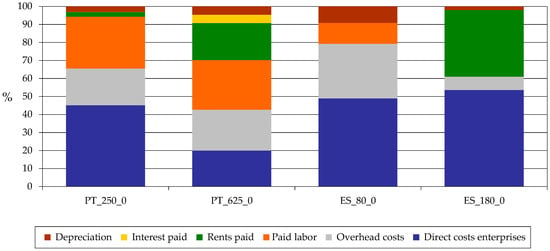
Figure 5.
Whole farm costs in % values. Source: model results.
The two larger farms (PT_625_0 and ES_180_0) have big differences in their absolute costs. While both farms have almost the same amount of land, the Portuguese farm has almost six times the costs of the Spanish farm, even though it has only 3.5 times more cows. Thus, the diversified scale and structure of production influenced the costs and, consequently the income received by individual farms. Nevertheless, the main differences are due to rents paid and paid labor: in fact the values for land rents are much higher in Portugal; for these two farms (which as mentioned before almost have the same area, i.e., no scaling differences), the Portuguese rent/ha is 3 times the Spanish one. For labor, the Spanish farm has no hired labor, which introduces a big difference in the cost structure of farms. When comparing the costs without considering the origin of land and labor (i.e., the differences among countries for these two groups of factors) and the overhead costs, the costs per cow are very similar.
For the % values, we can observe that the main differences are in three important aspects: the proportion of rents on total costs; the overhead cost, with the biggest Spanish farm managing to keep overhead costs very low compared with the other enterprise costs; and the direct costs, with the biggest Portuguese farm managing also to keep these costs as a low % of total costs. In both cases, this gives them some space to accommodate the other costs.
Whole farm profitability identifies the various components of a farm’s profitability, comparing the costs with the market returns and the coupled and decoupled payments. This gives us a detailed picture on the market competitiveness of these farms and on the importance of coupled and decoupled payments (Figure 6).
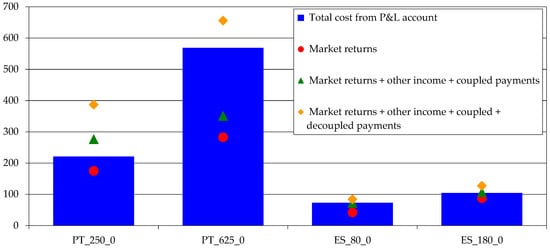
Figure 6.
Whole farm profitability (1000 €/farm). Source: model results.
This indicator shows that the biggest Portuguese farm relies entirely on decoupled payments to maintain its activity. The biggest Spanish farm and both the smaller Portuguese and Spanish farms need the coupled payments and the other incomes to cover total costs, which mean their competitiveness depends on coupled payments and other incomes.
4.2. Enterprise Analysis
The production efficiency and the resources’ use efficiency are important indicators used to analyze production systems. Even when systems are not competitive in the market, their efficient use of resources can be an important measure of their sustainability.
4.2.1. Production Efficiency
Despite the differences on cow’s weight or breed, the weaned calves per 100 cows and different years can be used to compare each system’s production efficiency. For the farms being analyzed, we can observe on Figure 7 that there are no remarkable differences between Portuguese and Spanish systems. Nevertheless, it can be observed that the least market competitive farm (PT_625_0) produces a higher number of calves per 100 cows and year.
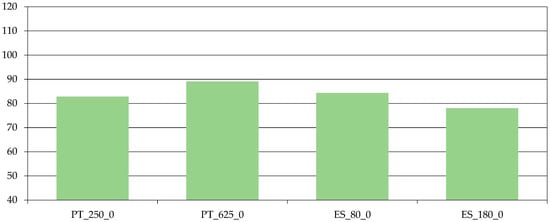
Figure 7.
Weaned calves per 100 cows and year (n°). Source: model results.
Finally, the share of purchased feed, combined with the previous indicator, highlights the farm resources’ efficiency use. We can observe in Figure 8 that both Portuguese farms have a very low input of purchased feed. In fact, the feeding of their animals is based on a pasture under cover, which is complemented by some home grown hay and/or silage. The Spanish approach is different. The bigger farm does not sow anything (which leads to less operational costs) and buys, beside the concentrate food, almost 50% of the roughage food the animals need. The smaller farm has only 149 ha of pasture and due to land limitations (beside the area, there is a strong seasonal pasture production, due to a long dry season and low soil quality) it is necessary to supplement the animals’ food with hay and concentrates.
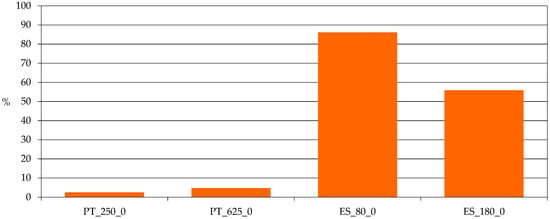
Figure 8.
Share of purchased feed. Source: model results.
4.2.2. Resources’ Use Efficiency
The enterprise costs can be calculated per animal, per ha and per 100 kg live weight. The relation between cost and production (translated, in this case, as cost/100 kg LW) is one of the most used measures of enterprise efficiency. Figure 9 shows the cost by factor and non-factor costs, expressed as €/100 kg LW. The PT_250_0 is, from this point of view, the most efficient enterprise. Nonetheless, we can observe that three of these farms have similar (below 200€) non-factor costs per 100 kg LW; for the other Spanish farm, the heavy non-factor costs have a direct linkage with the feed costs observed before. It is remarkable that although Spanish farms have a much lower price of land, the cost of land per 100 kg LW only reflects this fact on the smaller farm, which is certainly due to the very low stocking rate. Finally, it is also remarkable that all enterprises show a very low level of capital costs per 100 kg LW.
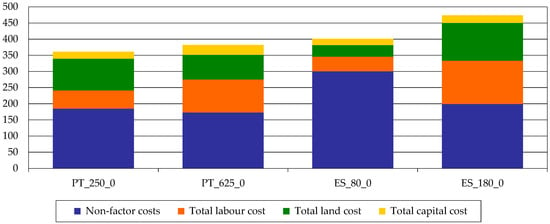
Figure 9.
Cost by factor and non-factor costs (€/100 kg LW). Source: model results.
The productivity of labor is also an important measure of efficiency. The question is, in this case, if the extensive systems of Montado/Dehesa also have an extensive use of labor or if the scale of production implies inefficiency on labor use. Figure 10 shows the economic labor productivity, measured in EUR returns/EUR labor costs.
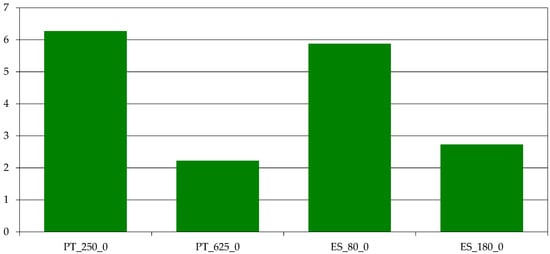
Figure 10.
Economic labor productivity (EUR returns/EUR labor costs). Source: model results.
It can be seen that economic labor productivity is lower on the biggest farms, but attention should now be paid to physical productivity of resources (labor, land and capital). Figure 11 shows an unclear pattern for labor (kg LW/h) with the biggest Portuguese farm having a better performance, which may be linked to a different management option—this is the only farm that has two different mobs, reflecting a particular management option (the production of pure limousine and cross breed calves).
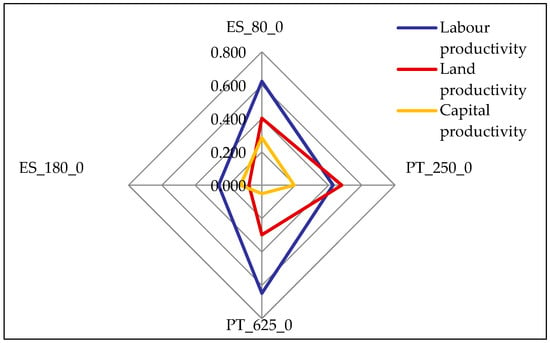
Figure 11.
Productivity: Labor (kg LW/h), Land (kg LW/ha) and Capital (kg LW/1000 €). Source: model results.
For land productivity, it should be highlighted that although we are considering extensive systems, which of course have low land productivity, it is interesting to observe that the best land productivity is achieved by the smaller Portuguese farm (which, in any case, is much bigger than the smaller Spanish farm). It is also interesting to see that the larger farms have very different land productivity. This is linked with the big difference on the animals they have, since cow-calf production is the only activity participated in by both farms. PT_625_0 runs a farm with 623 cows, while ES_180_0 has only 180 cows.
Finally, for capital productivity, we can see that the efficiency on capital use has a different pattern. In this case, the smaller farms are more efficient but, for the bigger ones, the Spanish farm is more capital efficient, which is probably linked to the smaller structural investment needed for this type of enterprise.
4.3. The Montado/Dehesa Farms in Europe
The Montado/Dehesa system is a very particular and less common system in Europe. In fact, in the other European countries, animals are not outside all year, being in barns at least during winter. If we compare the Montado/Dehesa system with other systems used in EU countries, which share the same EU policies, some of these figures show interesting results. The comparison is made with all typical cow-calf farms of the agri benchmark database in the EU for the countries: Austria, Czechia, Germany, France, the United Kingdom, Ireland and Poland. The UK is still in this comparison because until now the country has followed the Common Agricultural Policy rules.
The composition of whole farm returns (Figure 12) shows that the Portuguese Montado/Dehesa farms are among those where a bigger share of returns comes from coupled and decoupled payments.
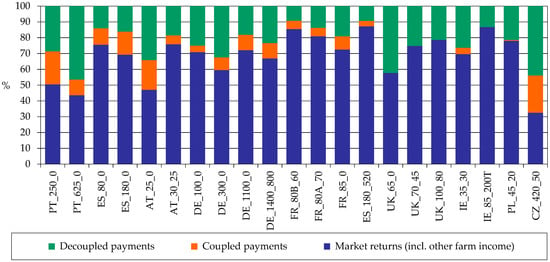
Figure 12.
Composition of whole farm returns (%). Source: model results.
When we look at the percentage composition of whole farm costs (Figure 13) it is clear that Montado/Dehesa farms belong to a smaller group of farms in which depreciation costs represent 10% or less of whole farm costs, which indicates a less capital intensive system.
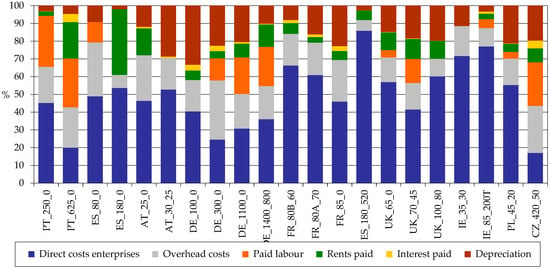
Figure 13.
Whole farm costs—% values. Source: model results.
The whole farm profitability shows that cow-calf systems, in the EU (+ UK), depend on policy support. For the Montado/Dehesa farms, most of the typical farms do not pay their costs only from market returns (Figure 14). In fact, only 46% of the farms in the database can pay their costs without decoupled payments and in only 25% of the sum of market returns do other incomes and decoupled payments exceed more than 5% the total costs.
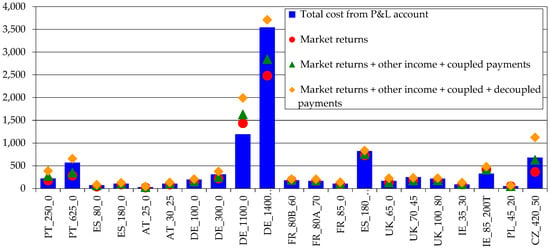
Figure 14.
Whole farm profitability (1000 €/farm). Source: model results.
For the enterprise analysis, 57% of the farms analyzed, including three of the Montado/Dehesa farms, wean between 80 and 90 calves per 100 cows a year. The least productive farm weans 78 calves per 100 cows a year and the most productive one weans 98.
The share of purchased feed does not have a clear pattern. A total of 25% of the farms purchase more than 50% of the feed available and 23% purchase less than 5% of the feed.
The economic productivity of labor shows also a diverse pattern. Nevertheless, the smaller Montado/Dehesa farms are among the best based on this indicator (Figure 15).
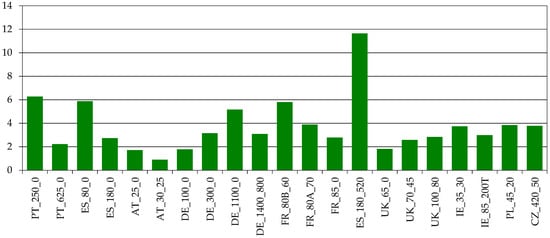
Figure 15.
Economic labor productivity (EUR returns/EUR labor costs). Source: model results.
Finally, we can observe on Figure 16, Figure 17 and Figure 18 the relative position of Montado/Dehesa farms within the group of EU + UK cow-calf farms for the productivity of labor, land and capital.
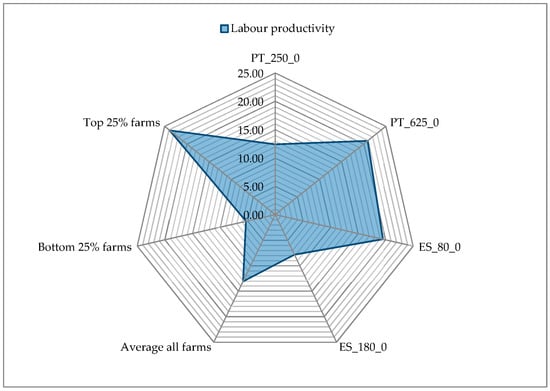
Figure 16.
Productivity of Labor (kg LW/h). Source: model results.
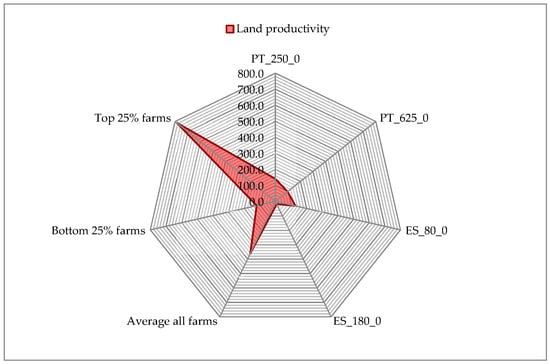
Figure 17.
Land (kg LW/ha). Source: model results.
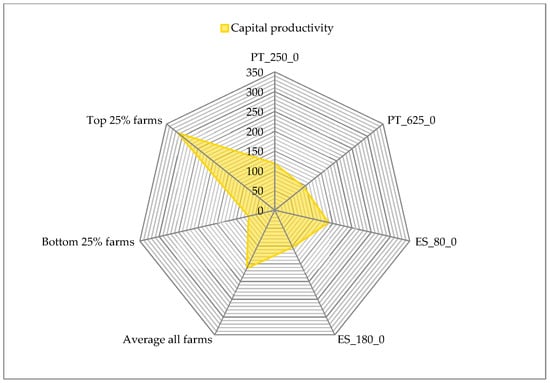
Figure 18.
Capital (kg LW/1000 €). Source: model results.
For labor, Montado/Dehesa farms have considerable differences, as was already seen on Figure 11. Except for the bigger Spanish farm, which has a labor productivity clearly below the average rate as a consequence of the assumption that the two family members have full time work on the farm, the others have a comfortable position that is close to average or clearly above it.
Figure 17 shows the productivity of land. For this indicator, as expected, the values for the Montado/Dehesa system are very low. In fact, being an extensive system, one of its characteristics is to have a very low productivity of land, which is confirmed by the figure.
Finally, the comparison of Montado/Dehesa farms with the others in regards to capital productivity is shown on Figure 18. For this figure, a farm from Ireland was discarded for having an outlier value that would have prevented a correct analysis.
As can be seen, capital productivity of the less extensive Montado/Dehesa farms is close to the average, though for the bigger and more extensive farms it is lower than the average, while clearly remaining above the lower 25% of farms.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Montado/Dehesa areas represent an important ecosystem for Portugal and Spain. The usually low capacity soils, the long dry season and the consequent strong seasonal pasture production are big threats to the future of these systems. For the traditional farms in the agri benchmark database, the main risk is abandonment.
The comparison of Portuguese and Spanish farms shows clearly that in these farms the main returns come from cow-calf activity. Farmers have different strategies to deal with costs—these are linked with different cost for factors or to differences in the enterprise type. Nonetheless, the Montado/Dehesa farms are, compared with other EU farms, clearly less capital intensive.
One of the main results of this study is the profitability comparison. As it is clear in Figure 14 data, most of the EU typical farms do not pay their costs only from market returns. The Montado/Dehesa farms belong to this category. Dupraz and Rainelli [12] and Arnaud and Dupraz [13] state that the maintenance of extensive cattle farming may have an important role in maintaining the ecological value of a rural area. It can be argued that coupled and decoupled payments are in fact paying an ecological service, the maintenance of which, in the case of Montado/Dehesa farms, relies on human occupation and management.
The efficiency on resources’ use is surely a concern for society as a whole. From this point of view and without considering the land productivity that is traditionally low in extensive systems such as the Montado/Dehesa system, the farms analyzed have intermediate positions on the EU ranking for economic labor, physical labor and capital productivity, which means they are competitive among EU cow-calf production. It can be argued that the combination of land use and capital’s extensiveness with this competitiveness gives these systems resilience to changes in the internal and external environment, which provides a good indicator on the future sustainability of these Montado/Dehesa systems among EU cow-calf production systems in general.
We can argue that these systems’ strengths are their less intensive capital needs and the unique Mediterranean landscape with protected trees and habitats.
Their weaknesses are related to a growing concern regarding the sustainability of these pasture-based ruminant systems, the lack of scale and some political and social demotivation.
As a conclusion, the main driver for the future of the Montado/Dehesa ecosystem depends on the ability of these systems to face the future and to perceive the modifications needed to overcome new challenges and take advantage of new opportunities. Both positive and negative aspects of Montado/Dehesa farm systems are dependent on the type of farming system, its context and management.
According to Olesen [14], active resource management and the utilization of renewable raw materials as substitutes for metal and oil-based products and fossil fuels will be the main challenge for future policies; this will need to considerate the provision of biomass for food, feed, bioenergy and biomaterials within the bioeconomy, the recycling of nutrients and resilient organic matter within agricultural systems, the maintenance of soil carbon stocks and the provision of other ecosystem goods and services, such as clean water and air and a diverse natural environment. Montado/Dehesa systems may be key actors for this strategy.
Rouquette and Aiken [15] state that natural resource principles should encourage animal production systems management to practice environmental stewardship with adaptive management; adopt practices to improve air quality and minimize net greenhouse gas emissions; protect grasslands, native ecosystems and valuable conservation areas from land conversion and degradation; implement land management practices that conserve and enhance ecosystem health; incorporate efficient management practices to maintain or improve soil health; enhance native plants and animal biological diversity; and implement management practices for sustainable-product feed sources. With this in mind, future EU support for farming should be used strategically to support these adaptations and the correct balance between environmental and agricultural resource base protection and high-production output of healthy and safe foods.
Author Contributions
All authors have read and agree to the published version of the manuscript. Formal analysis, M.d.B.C.F. and M.R.V.-L.; Methodology, L.I. and C.D.; Validation, M.d.B.C.F., M.R.V.-L. and L.I.; Writing—original draft, M.d.B.C.F. and M.R.V.-L.; Writing—review & editing, M.d.B.C.F., M.R.V.-L., L.I. and C.D.
Funding
This research was funded by National Funds through Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia, grant numbers UIDB/05183/2020 and UID/04007/2020.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the collaboration of Red Nacional de Granjas Típicas—RENGRATI (National Network of Typical Farms) | TRAGSATEC & Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación. Madrid, Spain https://www.mapa.gob.es/es/ganaderia/temas/produccion-y-mercados-ganaderos/sectores-ganaderos/red-de-granjas-tipicas/.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pinto-Correia, T.; Ribeiro, N.; Sá-Sousa, P. Introducing the montado, the cork and holm oak agroforestry system of Southern Portugal. Agrofor. Syst. 2011, 82, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olea, L.; San Miguel-Ayanz, A. The Spanish dehesa. A traditional Mediterranean silvopastoral system linking production and nature conservation. Grassl. Sci. Eur. 2006, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto-Correia, M.T.; Ribeiro, N.; Potes, J. Livro Verde dos Montados. ICAAM-Universidade de Évora. 2013. Available online: https://dspace.uevora.pt/rdpc/bitstream/10174/10116/1/Livro%20Verde%20dos%20Montados_Versao%20online%20%202013.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2020).
- Plieninger, T. (2007) Compatibility of livestock grazing with stand regeneration in Mediterranean holm oak parklands. J. Nat. Conserv. 2007, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz-de-Oliveira, M.I.; Azeda, C.; Pinto-Correia, T. Management of Montados and Dehesas for high nature value: An interdisciplinary pathway. Agrofor. Syst. 2016, 90, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Rojas, J.; Pinto-Correia, T.; Thorsoe, M.H.; Noe, E. The portuguese montado: A complex system under tension between different land use management paradigms. In Silvicultures-Management and Conservation; Álvarez, F.A., Gomez-Mediavilla, G., López-Estébanez, N., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A. Agroforestry for soil conservation. In International Council for Research in Agroforestry; CAB International: Wallingford, Oxon, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Sassenrath, G.F.; Hanson, J.D.; Hendrickson, J.R.; Archer, D.W.; Halloran, J.M.; Steiner, J.J.; Bohlen, P. Principles of Dynamic Integrated Agricultural Systems: Lessons Learned from an Examination of Southeast Production Systems; Agroecosystem Management for Ecological, Social, and Economic Sustainability, Advances in Agroecology Series; Taylor and Francis/CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 259–269. [Google Scholar]
- Wilczynski, A. Economic Comparison of Beef Production Systems in the EU. In Proceedings of the International Conference “Economic Science for Rural Development“, Jelgava, Latvia, 9–11 May 2018; pp. 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deblitz, C. Agri Benchmark: Benchmarking Beef Farming Systems Worldwide: Paper for AARES 54th Annual Conference. Available online: http://www.agribenchmark.org/fileadmin/Dateiablage/B-Beef-and-Sheep/Misc/CD-AARES-1002.pdf (accessed on 6 May 2020).
- United Nations. Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/ (accessed on 18 March 2020).
- Dupraz, P.; Rainelli, P. Institutional approaches to sustain rural landscapes in France. In Sustaining Agriculture and the Rural Economy; Brouwer, F., Ed.; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2004; pp. 162–182. [Google Scholar]
- Arnaud, S.; Dupraz, P. Farm Structure and Farm Characteristics Links to Non-commodity Outputsand Externalities. An Annotated BiblioFigurey of the French Academic Literature; INRA: Rennes, France, 2005; p. 26. [Google Scholar]
- Olesen, J.E. Socio Economic Impacts of Agricultural Systems. In North Sea Region Climate Change Assessment, Regional Climate Studies; Quante, M., Colijn, F., Eds.; SpringerOpen: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouquette, M., Jr.; Aiken, G.E. Introduction: Management strategies for sustainable cattle production in Southern Pastures. In Management Strategies for Sustainable Cattle Production in Southern Pastures; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).