Assessing the Dynamics of Land Use/Land Cover Changes between 1974 and 2016: A Study Case of the Bustillos Basin Using Remote Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
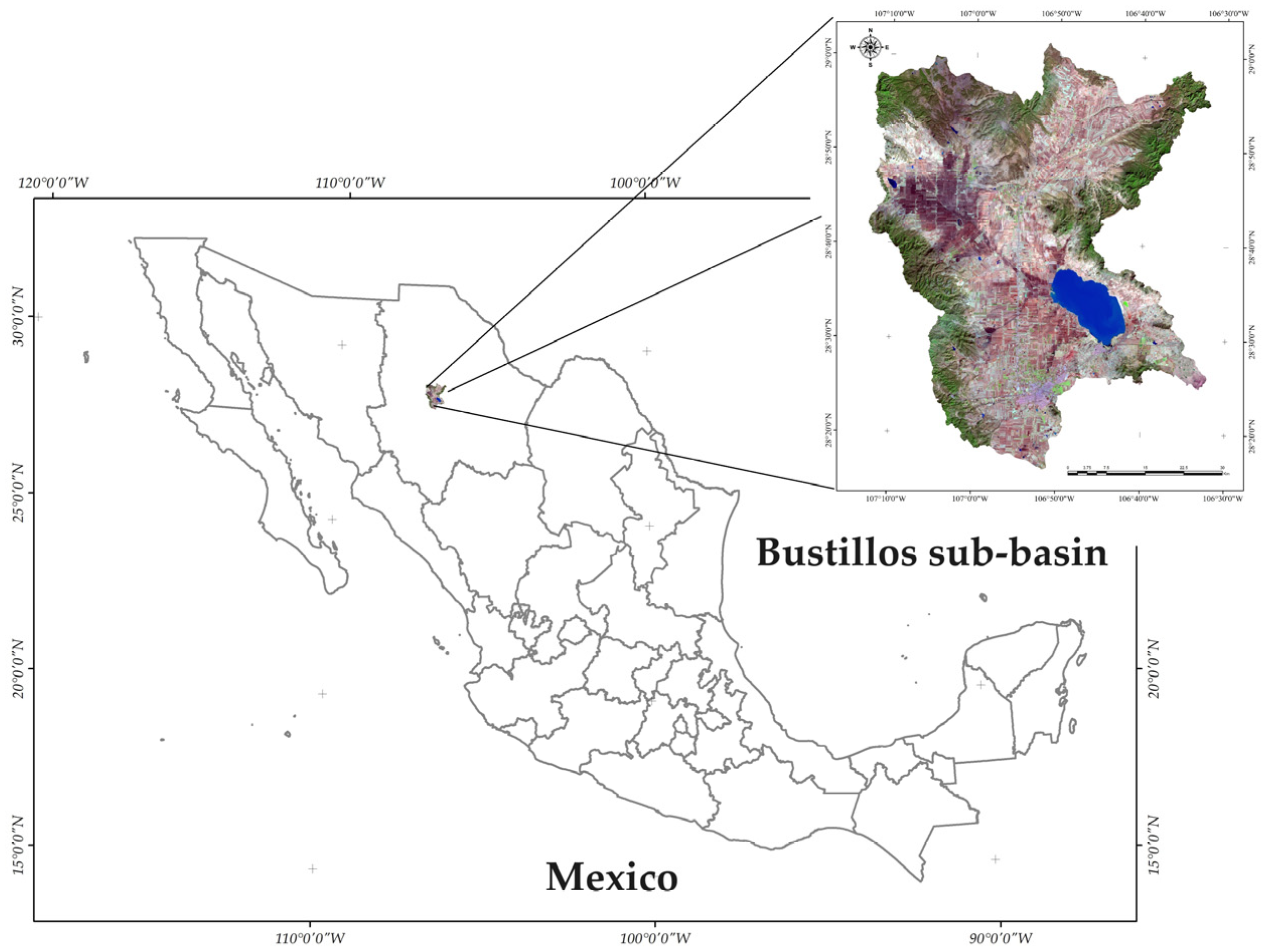
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
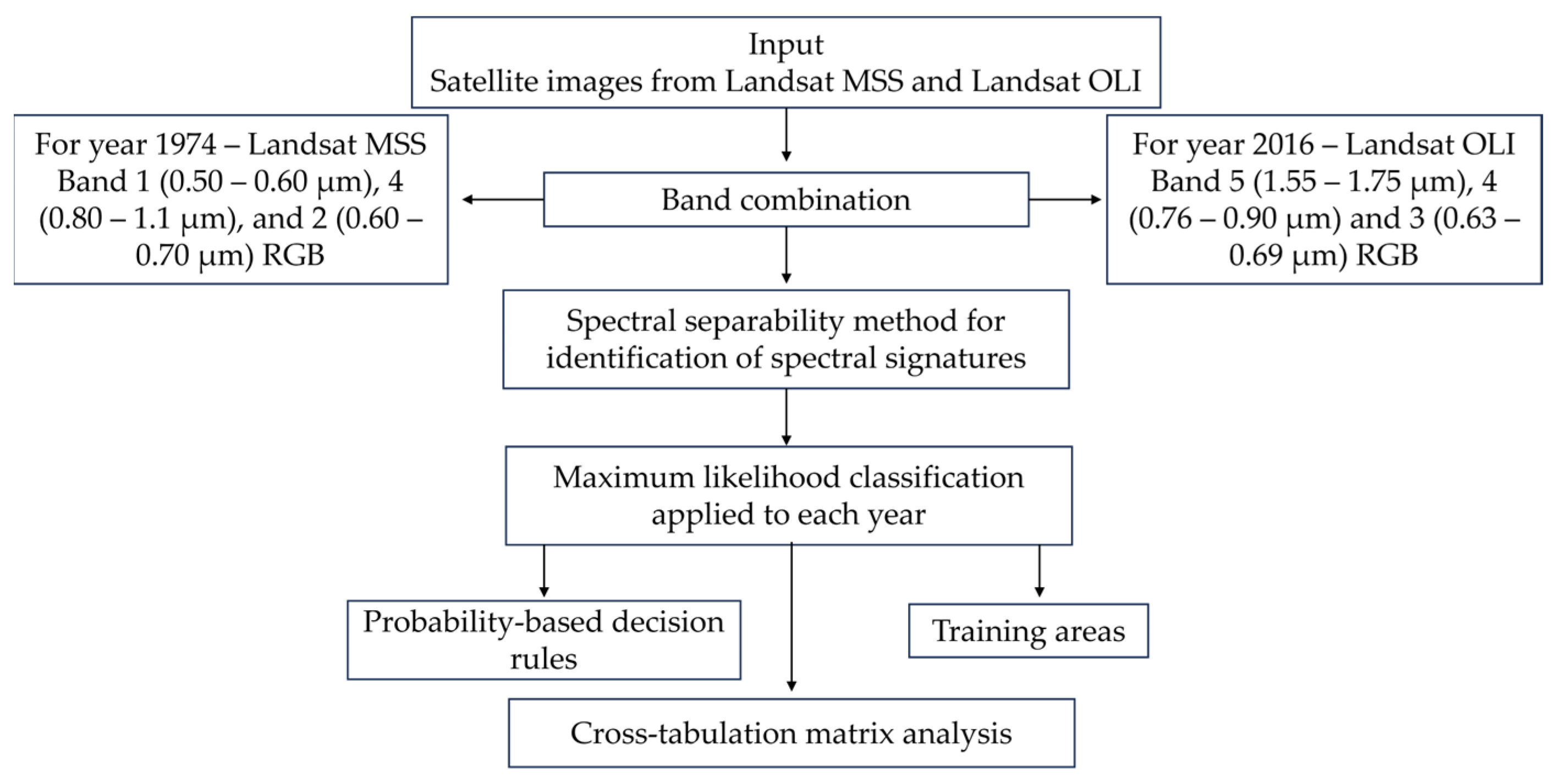
2.3. Image Processing
2.4. Classification Accuracy
2.5. Change Analysis
3. Results
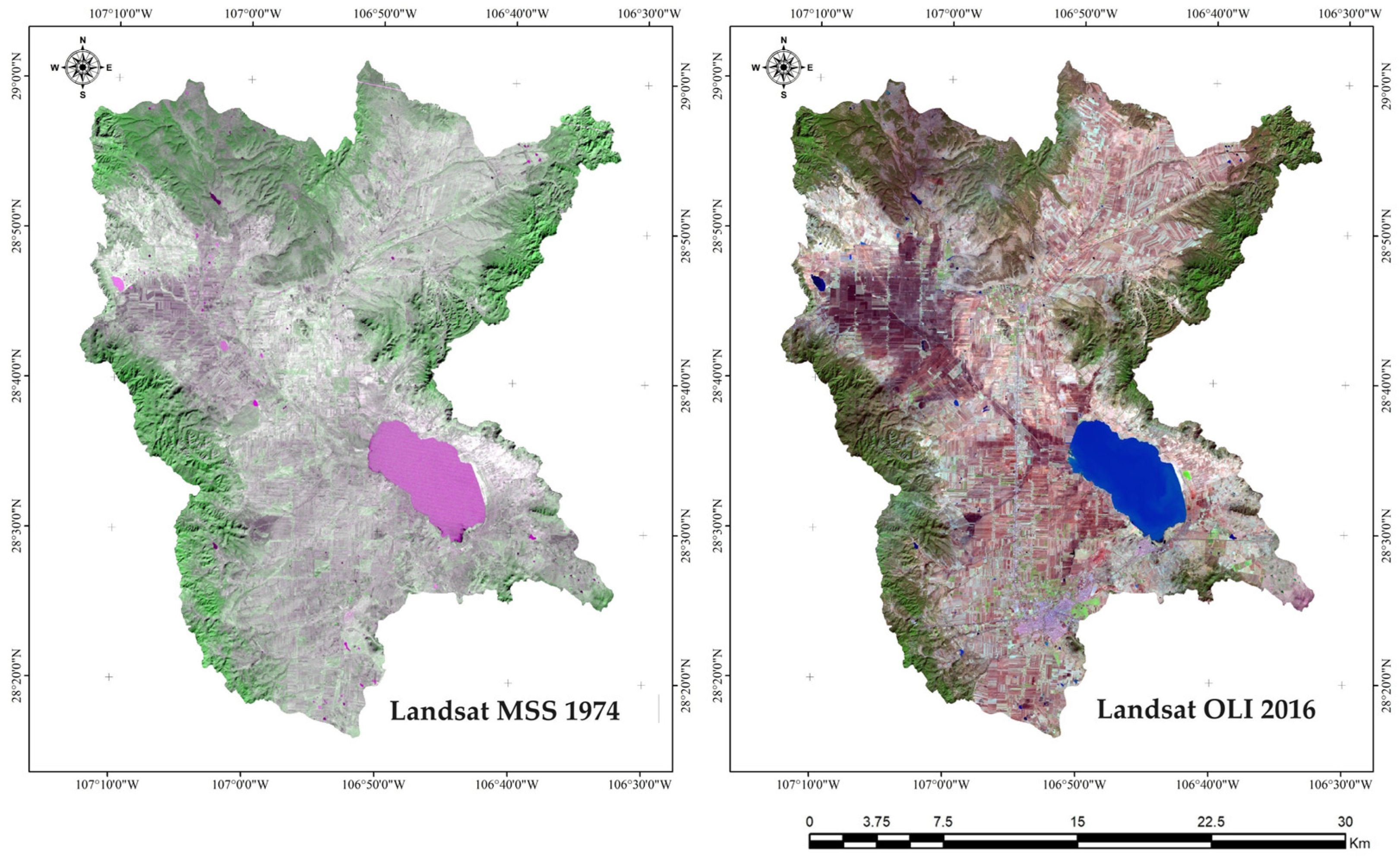
3.1. False-Color Images
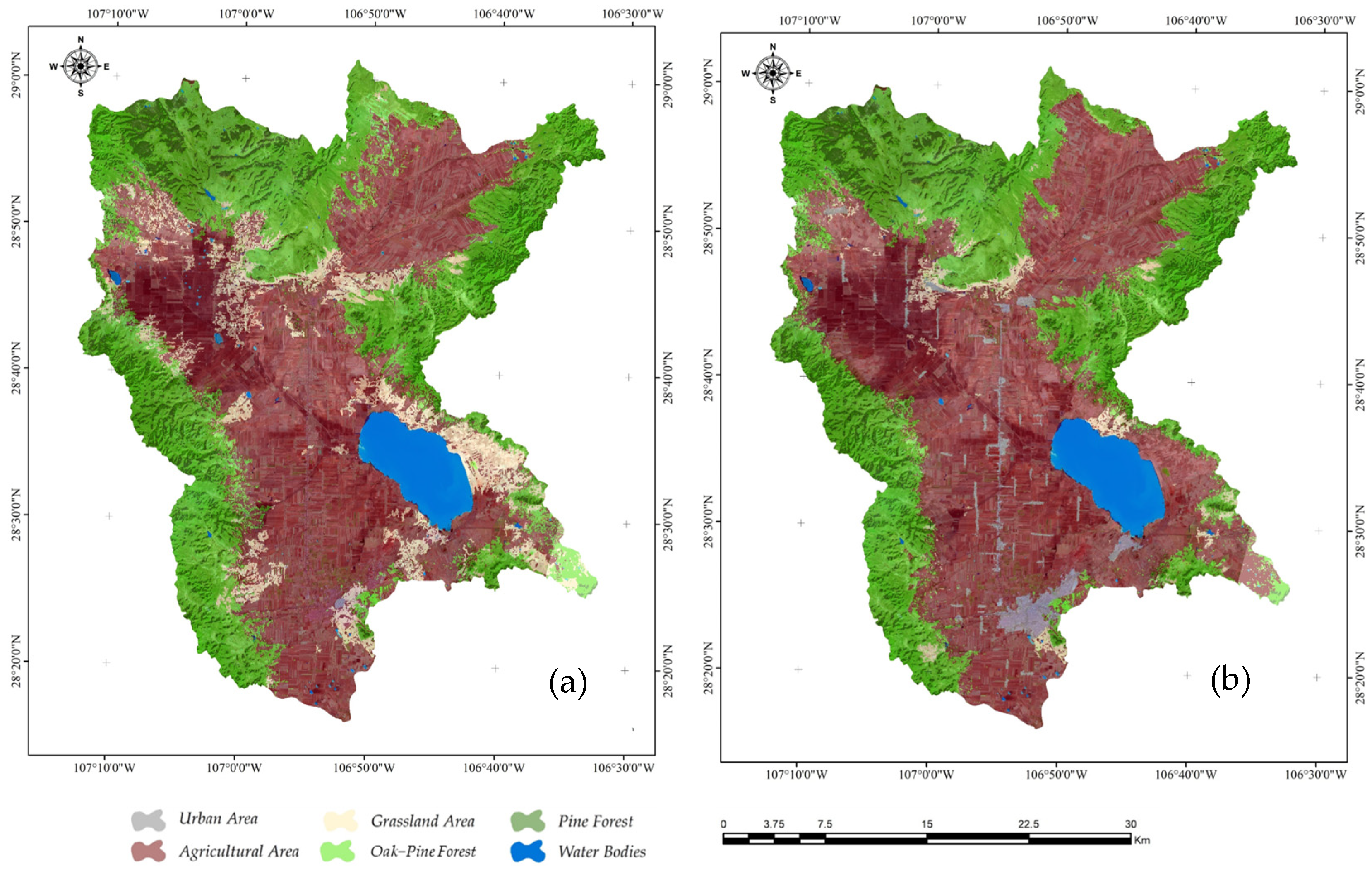
3.2. Land Use Classification
3.3. Land Use Changes
3.4. Gains, Losses, and Exchanges of the Categories
4. Discussion
4.1. False-Color Composites and Classes Delimitation
4.2. Land Use Changes and Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perring, M.P.; De Frenne, P.; Baeten, L.; Maes, S.L.; Depauw, L.; Blondeel, H.; Carón, M.M.; Verheyen, K. Global environmental change effects on ecosystems: The importance of land-use legacies. Glob. Change. Biol. 2016, 22, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fifth National Climate Assessment, Changes in Climate and Land Use Affect Land-System Resilience. Available online: https://nca2023.globalchange.gov/chapter/6/ (accessed on 17 June 2024).
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Panagos, P.; Lugato, E.; Yang, J.E.; Alewell, C.; Wuepper, D.; Montanarella, L.; Ballabio, C. Land use and climate change impacts on global soil erosion by water (2015–2070). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21994–22001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pool, D.B.; Panjabi, A.O.; Macias-Duarte, A.; Solhjem, D.M. Rapid expansion of croplands in Chihuahua, Mexico threatens declining North American grassland bird species. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 170, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavina, M.; Melchiorri, M.; Corbane, C.; Florczyk, A.J.; Freire, S.; Pesaresi, M.; Kemper, T. Multi-scale estimation of land use efficiency (SDG 11.3. 1) across 25 years using global open and free data. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz Caravantes, R.; Bravo Peña, L.C.; Alatorre Cejudo, L.C.; Sánchez Flores, E. Geospatial Analysis of the Interaction between Land and Water Use in the Peri-Urban Area of Cuauhtémoc, Chihuahua: A Socio-Environmental Study in Northern Mexico. Investig. Geogr. Boletín 2014, 83, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.S.; Zhen, L.; Miah, M.G.; Ahamed, T.; Samie, A. Impact of land use change on ecosystem services: A review. Environ. Dev. 2020, 34, 100527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; The Strategic Plan 2020–2023; United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs Habitat, U.N.: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations (UN)-Hábitat. La Dimensión Urbana de los Objetivos de Desarrollo Sostenible. Available online: https://onuhabitat.org.mx/ (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Maja, M.M.; Ayano, S.F. The impact of population growth on natural resources and farmers’ capacity to adapt to climate change in low-income countries. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 5, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; Defries, R.; Asner, G.P. Global Consequences of Land Use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarity and Leadership for Environmental Awareness and Research (CLEAR Center). Cattle and Land Use: The Differences between Arable Land and Marginal Land and How Cattle Use Each. Available online: https://clear.ucdavis.edu/explainers/cattle-and-land-use-differences-between-arable-land-and-marginal-land-and-how-cattle-use (accessed on 18 February 2024).
- Viana, C.M.; Freire, D.; Abrantes, P.; Rocha, J.; Pereira, P. Agricultural land systems importance for supporting food security and sustainable development goals: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.; Ramankutty, N.; Brauman, K.; Cassidy, E.S.; Gerber, J.S.; Johnston, M.; Mueller, N.D.; O’Connell, C.; Ray, D.K.; West, P.C.; et al. Solutions for a Cultivated Planet. Nature 2011, 478, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K.; Tagil, S.; Cushman, S.A. Surface metrics: An alternative to patch metrics for the quantification of landscape structure. Landsc. Ecol. 2009, 24, 433–450. [Google Scholar]
- Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (SEMARNAT). Información Adicional al Trámite SEMARNAT-02-001 Solicitud de Autorización de Cambio de Uso de Suelo en Terrenos Forestales. Gobierno de México. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/semarnat/documentos/tramite-semarnat-02-001 (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- López-Vazquez, V.H.; Balderas, P.M.; Chávez, M.C.; Perez, J.J.; Gutiérrez, C.G. Cambio de uso de suelo e implicaciones socioeconómicas en un área mazahua del altiplano mexicano. CIENCIA Ergo-Sum 2015, 22, 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- INEGI (Instituto Nacional de Estadística Geografía e Informática). Subsistema de Información Demográfica y Social. Censos y Conteos de Población y Vivienda. 2024. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/programas/ccpv/1970/#publicaciones (accessed on 20 July 2024).
- SADER (Secretaría de Agricultura y Desarrollo Rural). Servicio de Información Agroalimentaria y Pesquera (SIAP), Datos Abiertos. Chihuahua, México. 2024. Available online: http://infosiap.siap.gob.mx/gobmx/datosAbiertos.php (accessed on 20 July 2024).
- INEGI (Instituto Nacional de Estadística Geografía e Informática). V Censo Agrícola Ganadero y Ejidal 1970. Dirección General de Estadística. México. 1975. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/contenidos/productos/prod_serv/contenidos/espanol/bvinegi/productos/historicos/1329/702825111144/702825111144_1.pdf (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- INEGI (Instituto Nacional de Estadística Geografía e Informática). Dirección General de Difusión. In Cuaderno Estadístico Municipal Cuauhtémoc Chihuahua 2001; INEGI (Instituto Nacional de Estadística Geografía e Informática): Chihuahua, Mexico, 2002; 174p. [Google Scholar]
- Conociendo la Laguna de Bustillos. Available online: https://storymaps.arcgis.com/stories/45b00034bc9942bcbe5e9ee6c4bd6b3d (accessed on 17 June 2024).
- Comisión Nacional Para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad (CONABIO). 37 Lago Bustillos. Available online: http://www.conabio.gob.mx/conocimiento/regionalizacion/doctos/rhp_037.html (accessed on 18 July 2024).
- A la Torre, L.C.; García, A.K.; Rodríguez, A.J.; Erives, V.; González, E. Estimación de la erosión potencial de la cuenca laguna de Bustillos, Chihuahua, Mexico. Dialnet 2014, 249–258. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Suomalainen, J.; Liu, J.; Hyyppä, J.; Kaartinen, H.; Haggren, H. A review: Remote sensing sensors. Multi-Purp. Appl. Geospat. Data 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Quintero, G.; Solís-Moreno, R.; Pompa-García, M.; Villarreal-Guerrero, F.; Pinedo-Alvarez, C.; Pinedo-Alvarez, A. Detection and projection of forest changes by using the Markov Chain Model and Cellular Automata. Sustainability 2016, 8, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, S.E.; Yool, S.R. Sensitivity of change vector analysis to land cover change in an arid ecosystem. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 1069–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; Crossman, N.; Ellis, E.C. Land system science and sustainable development of the earth system: A global land project perspective. Anthropocene 2015, 3, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-sharif, A.A.; Pradhan, B. Monitoring and Predicting Land Use Change in Tripoli Metropolitan City Using an Integrated Markov Chain and Cellular Automata Models in GIS. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 4291–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, S.; Singha, P.; Mahato, S.; Pal, S.; Liou, Y.A.; Rahman, A. Land-use land-cover classification by machine learning classifiers for satellite observations—A review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.N.; Kuch, V.; Lehnert, L.W. Land cover classification using Google Earth Engine and random forest classifier—The role of image composition. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MohanRajan, S.N.; Loganathan, A.; Manoharan, P. Survey on Land Use/Land Cover (LU/LC) change analysis in remote sensing and GIS environment: Techniques and Challenges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2020, 27, 29900–29926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasa Earth Observatory. Available online: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/features/FalseColor (accessed on 16 June 2024).
- Pinedo, A.C.; Pinedo, A.A.; Martinez, Q.R.M. Análisis de áreas deforestadas en la región centro-norte de la Sierra Madre Occidental, Chihuahua, México. Tecnociencia Chihuah. 2007, 1, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, F.; Tricando, M.M. Evolución del paisaje y estado de conservación de la reserva forestal de Valdivia. Land 2003, 19, 197–209. [Google Scholar]
- Rimal, B.; Zhang, L.; Keshtkar, H.; Haack, B.; Rijal, S.; Zhang, P. Land use/land cover dynamics and modeling of urban land expansion by the integration of cellular automata and markov chain. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Base Referencial Mundial del Recurso Suelo. In Informes Sobre Recursos Mundiales del Suelo; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015; Volume 106. [Google Scholar]
- Comisión Nacional del Agua (CONAGUA). Registro Público de Derechos de Agua. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/conagua (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía (INEGI). Censo General de Población y Vivienda, Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Geografía e Informática, México. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Comisión Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad (CONABIO). La Biodiversidad en Chihuahua: Estudio de Estado. 2014. Available online: https://www.biodiversidad.gob.mx/region/EEB/estudios/ee_chihuahua (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Markham, B.L.; Arvidson, T.; Barsi, J.A.; Choate, M.; Kaita, E.; Levy, R.; Lubke, M.; Masek, J.G. Comprehensive Remote Sensing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 27–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, L.; Yamamoto, H. The wall: The Earth in true natural color from real-time geostationary satellite imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Eastman, J.R. Application of Fuzzy Measures in Multi-Criteria Evaluation in GIS. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2000, 14, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awotwi, A.; Anornu, G.K.; Quaye-Ballard, J.A.; Annor, T. Monitoring Land Use and Land Cover Changes Due to Extensive Gold Mining, Urban Expansion, and Agriculture in the Pra River Basin of Ghana, 1986–2025. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3331–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wu, G.; Ding, K.; Shi, T.; Li, Q.; Wang, J. Improving land use/land cover classification by integrating pixel unmixing and decision tree methods. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafy, A.A.; Shuvo, R.M.; Naim, M.N.H.; Sikdar, M.S.; Chowdhury, R.R.; Islam, M.A.; Sarker, H.S.; Khan, H.H.; Kona, M.A. Remote sensing approach to simulate the land use/land cover and seasonal land surface temperature change using machine learning algorithms in a fastest-growing megacity of Bangladesh. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 21, 100463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero Medina, J.A.; Alzate Atehortúa, B.E. Comparison of maximum likelihood, support vector machines, and random forest techniques in satellite images classification. Rev. Tecnura 2019, 23, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda-López, R.; Febvre, N.; Martínez, M. Importancia de proteger pequeñas áreas periurbanas por su riqueza avifaunística: El caso de Mompaní, Querétaro, México. Huitzil, Revista Mex. Ornitol. 2010, 11, 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- How Maximum Likelihood Classification Works. Esri. Available online: https://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/latest/tools/spatial-analyst-toolbox/how-maximum-likelihood-classification-works.htm (accessed on 26 May 2024).
- Smits, P.C.; Dellepiane, S.G.; Schowengerdt, R.A. Quality assessment of image classification algorithms for land-cover mapping: A review and a proposal for a cost-based approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 1461–1486. [Google Scholar]
- Congalton, R.G.; Oderwald, R.G.; Mead, R.A. Assessing Landsat classification accuracy using discrete multivariate analysis statistical techniques. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1983, 49, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar]
- Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Shusas, E.; McEachern, M. Detecting important categorical land changes while accounting for persistence. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 101, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Cheuk, M.L. A generalized cross-tabulation matrix to compare soft-classified maps at multiple resolutions. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2006, 20, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Bonilla, J.S.; Villarreal-Guerrero, F.; Prieto-Amparán, J.A.; Santellano-Estrada, E.; Pinedo-Alvarez, A. Characterizing the impact of Land-Use/Land-Cover changes on a Temperate Forest using the Markov model. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2021, 24, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Johnson, B.A. Land-use and land-cover classification in semi-arid areas from medium-resolution remote-sensing imagery: A deep learning approach. Sensors 2022, 22, 8750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasanta, T.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M. Complex land cover change processes in semiarid Mediterranean regions: An approach using Landsat images in northeast Spain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bretz, M.; Dewan, M.A.A.; Delavar, M.A. Machine learning in modelling land-use and land cover-change (LULCC): Current status, challenges and prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briceño-Hidalgo, Y.I. Análisis Espacio Temporal del Cambio de Uso de Suelo en Bosques Templados de la Sierra Tarahumara, Chihuahua. Bachelor’s Thesis, Autonomous University of Chihuahua (UACh), Chihuahua, Mexico, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hilker, T.M.; Wulder, N.; Coops, J.; Linke, G.; McDermid, J.; Masek, F.; Gaoy, J.C. A new data fusion model for high spatial- and temporal-resolution mapping of forest disturbance based on Landsat and MODIS. Remote Sens. Env. 2009, 113, 1613–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, S.P.; Cohen, W.B.; Zhiqiang, Y.; Krankina, O.N. Comparison of Tasseled Cap-based Landsat data structures for use in forest disturbance detection. Remote Sens. Env. 2005, 101, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemenkova, P. Robust vegetation detection using RGB colour composites and isoclust classification of the Landsat TM image. Geomat. Landmanag. Land. 2021, 147–167. [Google Scholar]
- Antillon, M.Y.; Corral, G.M.; A la Torre, L.C. Análisis de los Cambios de Cobertura y Uso de Suelo en los Márgenes de la Laguna de Bustillos Chihuahua: Efectos de la Expansión Agrícola. Available online: https://www.uacj.mx/CGTI/CDTE/JPM/Documents/SELPER/assets/m005.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Manjarrez-Domínguez, C.; Pinedo-Alvarez, A.; Pinedo-Alvarez, C.; Villarreal-Guerrero, F.; Cortes-Palacios, L. Cortes-Palacios, L. Vegetation Landscape Analysis due to Land Use Changes on Arid Lands. Pol. J. Ecol. 2015, 63, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Nieto, H.; García Daguer, R.R.; Moreno Sánchez, R.; González Ramos, A. Using Remote Sensors and GIS to Delimit Changes in Agricultural Land Use from 1970 to 1997 in the State of Guanajuato. Invest. Geog 2002, 47, 92–112. [Google Scholar]
- A la Torre, L.C.; Granados, A.; Bravo, L.C.; Torres, M.E.; Wiebe, L.C.; Uc, M.I.; González, M.O.; Sánchez, E.; Rojas, H.L.; Salas, V. Ineficiencia de riego rodado agrícola en la cuenca de la laguna de Bustillos, Chihuahua, México: Características geométricas de las parcelas agrícolas y abatimiento del acuífero. Tecnol. Cienc. Agua 2019, 10, 241–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Amparán, J.A.; Pinedo-Alvarez, A.; Villarreal-Guerrero, F.; Pinedo-Alvarez, C.; Morales-Nieto, C.; Manjarrez-Domínguez, C. Past and future spatial growth dynamics of Chihuahua city, Mexico: Pressures for land use. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2016, 5, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado-Álvarez, J.P.; Pérez-Cutillas, P.; Ramirez-Valle, O.; Alarcón-Cabañero, J.J. Análisis de la calidad del agua en las lagunas de Bustillos y de los mexicanos (Chihuahua, México). Papeles De Geogr. 2016, 62, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, J.S.; Kumar, M. Monitoring Land Use/Cover Change Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques: A Case Study of Hawalbagh Block, District Almora, Uttarakhand, India. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2015, 18, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq Khan, M.; Ullah, S.; Sun, T.; Rehman, A.U.; Chen, L. Land-use/land-cover changes and its contribution to urban heat Island: A case study of Islamabad, Pakistan. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Sifuentes, A.R.; Villanueva-Díaz, J.; Estrada-Ávalos, J.; Vázquez-Vázquez, C.; Orona-Castillo, I. Soil loss and runoff modification caused by land use change in the Conchos River basin, Chihuahua. Nova Sci. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducks Unlimited of Mexico (DUMAC). The Current State of the Bustillos Lagoon behind the Ecological Disaster. Available online: https://dumac.org/2024/07/25/la-laguna-de-bustillos-detras-del-desastre-ecologico/ (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- De la Maza-Benignos, M.; Banda-Villanueva, I.; Mendoza-González, G.; Leal-Nares, O.A.; Rendón-Herrera, G. Reporte del estado de los pastizales del Desierto Chihuahuense. Pronatura Noreste-Am. Bird Conserv. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rafiei-Sardooi, E.; Azareh, A.; Shooshtari, S.J.; Parteli, E.J. Long-term assessment of land-use and climate change on water scarcity in an arid basin in Iran. Ecol. Model. 2022, 467, 109934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | 1970 | 1980 | 1990 | 2000 | 2003 | 2010 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population | 66,856.00 | 85,589.00 | 112,589.00 | 124,378.00 | NA | 154,639.00 | 180,638.00 |
| P.G.R. (%) | NA | 28.02 | 31.55 | 10.47 | NA | 24.33 | 16.81 |
| Total Land Crop | 113,366.00 | NA | 113,400.00 | 267,800.00 | NA | 272,390.00 | NA |
| Rainfed Agr. | 111,395.00 | NA | 77,432.00 | 67,767.00 | 67,005.00 | 64,156.77 | 73,517.00 |
| Irrigation Agr. | 1737.60 | NA | 33,186.00 | 40,192.00 | 45,879.45 | 46,393.91 | 49,789.30 |
| Planted area | 113,132.60 | NA | 110,618.00 | 107,959.00 | 112,844.45 | 110,550.00 | 123,306.30 |
| Data | Date | % Cloud | Data Source | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat MSS | November 1974 | 0 | Global Visualization Viewer (GloVis) from the USGS. https://glovis.usgs.gov | 30 m × 30 m |
| Landsat OLI | October 2016 | 0 | GloVis from the USGS. https://glovis.usgs.gov | 30 m × 30 m |
| Time 2 | Total Year 1 | Loss | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category 1 | Category 2 | Category 3 | Category 4 | |||
| Time 1 | ||||||
| Category 1 | P11 | P12 | P13 | P14 | P1+ | P1 ± P11 |
| Category 2 | P21 | P22 | P23 | P24 | P2+ | P2 ± P22 |
| Category 3 | P31 | P32 | P33 | P34 | P3+ | P3 ± P33 |
| Category 4 | P41 | P42 | P43 | P44 | P4+ | P4 ± P44 |
| Total year 2 | P + 1 | P + 2 | P + 3 | P + 4 | 1 | |
| Gain | P + 1 − P11 | P + 2 − P22 | P + 3 − P33 | P + 4 − P44 | ||
| Loss (L) | Gain (Gj) | Exchange (Exc) | Net Change (NC) | Total Change (TC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 ± L11 | L + 1−L11 | 2 × MIN (L,Gj) | TC − Exc | L + Gj or |
| L2 ± L22 | L + 2−L22 | Exc + NC |
| Year/Land Use | Classification Accuracy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Producer’s Accuracy (%) | User’s Accuracy (%) | Overall Accuracy (%) | Cohen’s Kappa | |
| 1974 | 92 | 0.90 | ||
| Urban Area | 89 | 88 | ||
| Agricultura Areas | 93 | 92 | ||
| Grassland | 92 | 91 | ||
| Oak–Pine Forest | 91 | 91 | ||
| Pine Forest | 92 | 91 | ||
| Water Body | 95 | 94 | ||
| 2016 | 94 | 0.92 | ||
| Urban Area | 90 | 90 | ||
| Agricultura Areas | 94 | 93 | ||
| Grassland | 93 | 93 | ||
| Oak–Pine Forest | 90 | 89 | ||
| Pine Forest | 91 | 90 | ||
| Water Body | 96 | 96 | ||
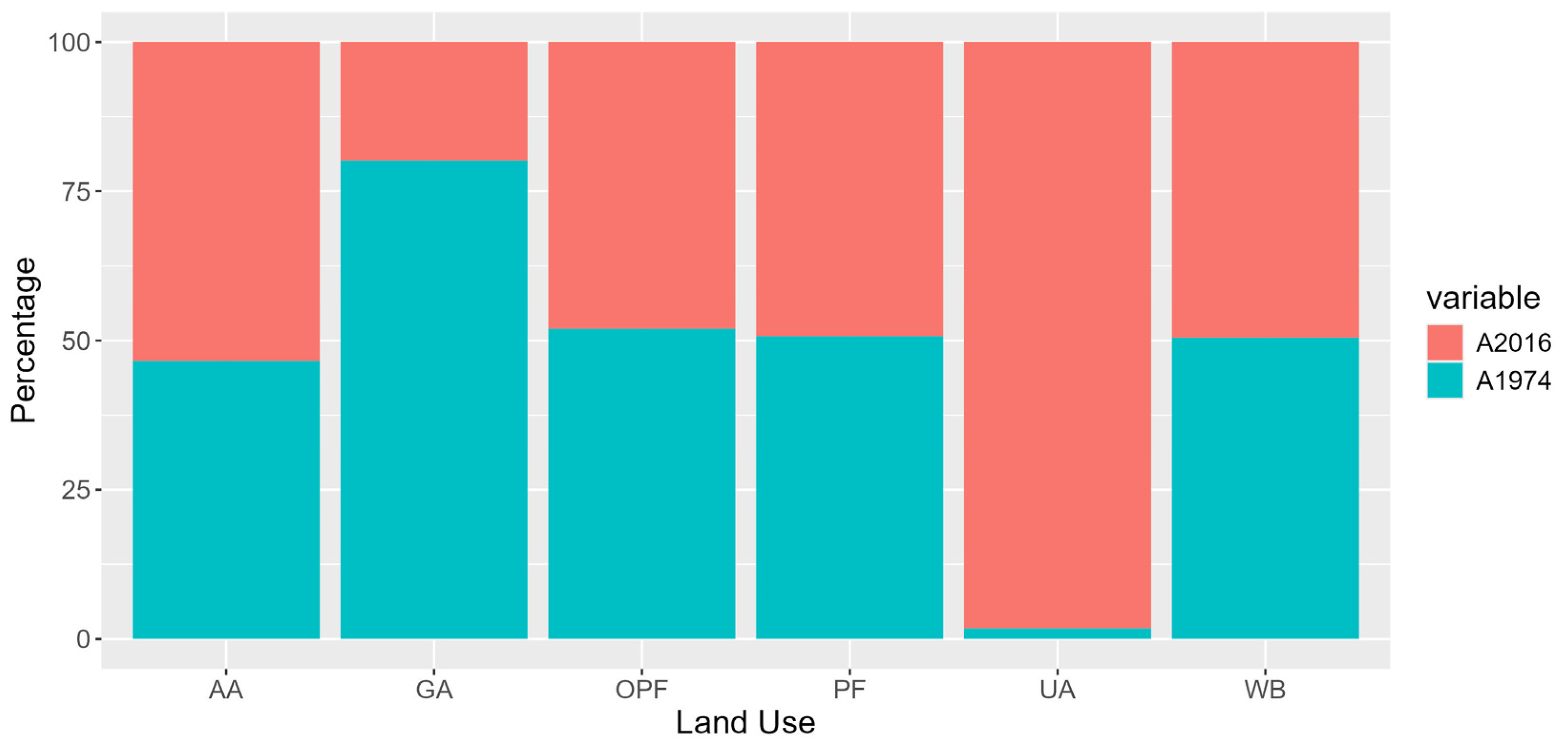
| Land Use | 1974 | 2016 | Difference 2016–1974 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Area | 141.86 | 7993.34 | 7851.48 |
| Agricultura Areas | 153,585.11 | 176,162.82 | 22,577.71 |
| Grassland | 27,883.86 | 6893.24 | −20,990.62 |
| Oak–Pine Forest | 112,216.05 | 103,607.49 | −8608.56 |
| Pine Forest | 20,488.44 | 19,901.74 | −586.7 |
| Water Body | 12,851.91 | 12,623.89 | −228.02 |
| Total | 327,167.23 | 327,182.52 |
| UA | AA | GA | OPF | PF | WB | TOTAL | LOSS | |
| UA | 141.86 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 141.86 | 0.00 |
| AA | 5756.41 | 147,827.34 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 153,583.75 | 5756.41 |
| GA | 1938.55 | 194,46.73 | 6498.42 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 27,883.70 | 21,385.28 |
| OPF | 156.52 | 8598.85 | 394.67 | 103,063.34 | 0 | 0 | 112,213.37 | 9150.03 |
| PF | 0 | 60.64 | 0 | 526.05 | 19,900.47 | 0 | 20,487.1624 | 586.69 |
| WB | 0 | 228.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12,623.85 | 12,851.87 | 228.02 |
| TOTAL | 7993.34 | 176,161.5691 | 6893.08752 | 103,589.386 | 19,900.4732 | 12,623.853 | ||
| GAIN | 7851.48 | 28,334.23 | 394.67 | 526.05 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Dynamics of Changes | Type of Change | Area |
|---|---|---|
| Persistence of urban areas | Anthropic persistence | 141.86 |
| Agricultural land to urban areas | Urbanization | 5756.41 |
| Grasslands to urban areas | Urbanization | 1938.55 |
| Oak–pine Forest to urban areas | Urbanization | 156.52 |
| Persistence of agricultural areas | Permanence | 147,827.34 |
| Grasslands to agricultural lands | Deforestation | 19,446.73 |
| Oak–pine Forest to agricultural lands | Deforestation | 8598.85 |
| Pine forest to agricultural lands | Deforestation | 60.64 |
| Water bodies to agricultural lands | Others | 228.02 |
| Grasslands persistence | Natural persistence | 6498.42 |
| Oak–pine Forest to grasslands | Degradation | 394.67 |
| Oak–pine Forest persistence | Natural persistence | 103,063.34 |
| Pine forest to oak–pine forest | Degradation | 526.05 |
| Pine forest persistence | Natural persistence | 19,900.47 |
| Water bodies | Natural persistence | 12,623.85 |
| Gains | Losses | Exchanges | Net Change | Total Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Areas | 7851.48 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 7851.48 | 7851.48 |
| Agricultural Areas | 28,334.23 | 5756.41 | 11,512.82 | 22,577.82 | 34,090.64 |
| Grasslands | 394.67 | 21,385.28 | 789.33 | 20,990.61 | 21,779.94 |
| Oak–pine Forest | 526.05 | 9150.03 | 1052.10 | 8623.98 | 9676.08 |
| Pine forest | 0.00 | 586.69 | 0.00 | 586.69 | 586.69 |
| Water bodies | 0.00 | 228.02 | 0.00 | 228.02 | 228.02 |
| Total | 37,106.42 | 37,106.42 | 13,354.24 | 60,858.60 | 74,212.85 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valencia-Gaspar, S.; Mejía-Leyva, F.; Valles-Aragón, M.C.; Martinez-Salvador, M.; Hernández-Quiroz, N.S.; Nevarez-Rodríguez, M.C.; López-Serrano, P.M.; Vázquez-Quintero, G. Assessing the Dynamics of Land Use/Land Cover Changes between 1974 and 2016: A Study Case of the Bustillos Basin Using Remote Sensing. Land 2024, 13, 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13081320
Valencia-Gaspar S, Mejía-Leyva F, Valles-Aragón MC, Martinez-Salvador M, Hernández-Quiroz NS, Nevarez-Rodríguez MC, López-Serrano PM, Vázquez-Quintero G. Assessing the Dynamics of Land Use/Land Cover Changes between 1974 and 2016: A Study Case of the Bustillos Basin Using Remote Sensing. Land. 2024; 13(8):1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13081320
Chicago/Turabian StyleValencia-Gaspar, Saúl, Fernanda Mejía-Leyva, María C. Valles-Aragón, Martin Martinez-Salvador, Nathalie S. Hernández-Quiroz, Myrna C. Nevarez-Rodríguez, Pablito M. López-Serrano, and Griselda Vázquez-Quintero. 2024. "Assessing the Dynamics of Land Use/Land Cover Changes between 1974 and 2016: A Study Case of the Bustillos Basin Using Remote Sensing" Land 13, no. 8: 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13081320
APA StyleValencia-Gaspar, S., Mejía-Leyva, F., Valles-Aragón, M. C., Martinez-Salvador, M., Hernández-Quiroz, N. S., Nevarez-Rodríguez, M. C., López-Serrano, P. M., & Vázquez-Quintero, G. (2024). Assessing the Dynamics of Land Use/Land Cover Changes between 1974 and 2016: A Study Case of the Bustillos Basin Using Remote Sensing. Land, 13(8), 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13081320








