Abstract
The partitioning of precipitation into frozen and liquid components influences snow-derived water resources and flood hazards in mountain environments. We used a 915-MHz Doppler radar wind profiler upstream of the northern Sierra Nevada to estimate the hourly elevation where snow melts to rain, or the snow level, during winter (December–February) precipitation events spanning water years (WY) 2008–2017. During this ten-year period, a Mann-Kendall test indicated a significant (p < 0.001) positive trend in snow level with a Thiel-Sen slope of 72 m year−1. We estimated total precipitation falling as snow (snow fraction) between WY1951 and 2017 using nine daily mid-elevation (1200–2000 m) climate stations and two hourly stations spanning WY2008–2017. The climate-station-based snow fraction estimates agreed well with snow-level radar values (R2 = 0.95, p < 0.01), indicating that snow fractions represent a reasonable method to estimate changes in frozen precipitation. Snow fraction significantly (p < 0.001) declined during WY2008–2017 at a rate of 0.035 (3.5%) year−1. Single-point correlations between detrended snow fraction and sea-surface temperatures (SST) suggested that positive SST anomalies along the California coast favor liquid phase precipitation during winter. Reanalysis-derived integrated moisture transported upstream of the northern Sierra Nevada was negatively correlated with snow fraction (R2 = 0.90, p < 0.01), with atmospheric rivers representing the likely circulation mechanism producing low-snow-fraction storms.
Keywords:
atmospheric rivers; California; Nevada; precipitation; Sierra Nevada; snow; snow level; water resources 1. Introduction
As the climate warms, the partitioning of snowfall to rainfall in snow-dominated mountain watersheds is likely to change [1,2,3,4,5]. Changes in precipitation phase alter seasonal snowpack dynamics, ecological processes, peak streamflow timing, and winter flood hazards [5,6,7]. These changes present different challenges for water supply forecasting and reservoir operations [8], particularly in states that depend upon snow-derived water resources and are at risk for winter flooding [9,10]. Continued climate change, increased drought risk [11], and more intense extreme precipitation events [12] will necessitate adaptive water management strategies.
During the past seven water years (WY; 1 October–30 September), California and Nevada experienced the full range of hydroclimate extremes. Precipitation reductions during a multiyear drought from WY2012 to WY2015 were found to be consistent with average conditions that were estimated during the extreme and persistent Medieval droughts [13], with anomalous positive temperature anomalies enhancing drought severity [14]. Conversely, WY2017 was the wettest year in the past century and followed a near-average WY2016. These wide-ranging hydroclimatic conditions provide incentive to study the physical mechanisms that may be influencing hydrologic variability in the Sierra Nevada, as this knowledge can be used to inform and prioritize adaptation strategies for sustainable water management under a changing climate [15].
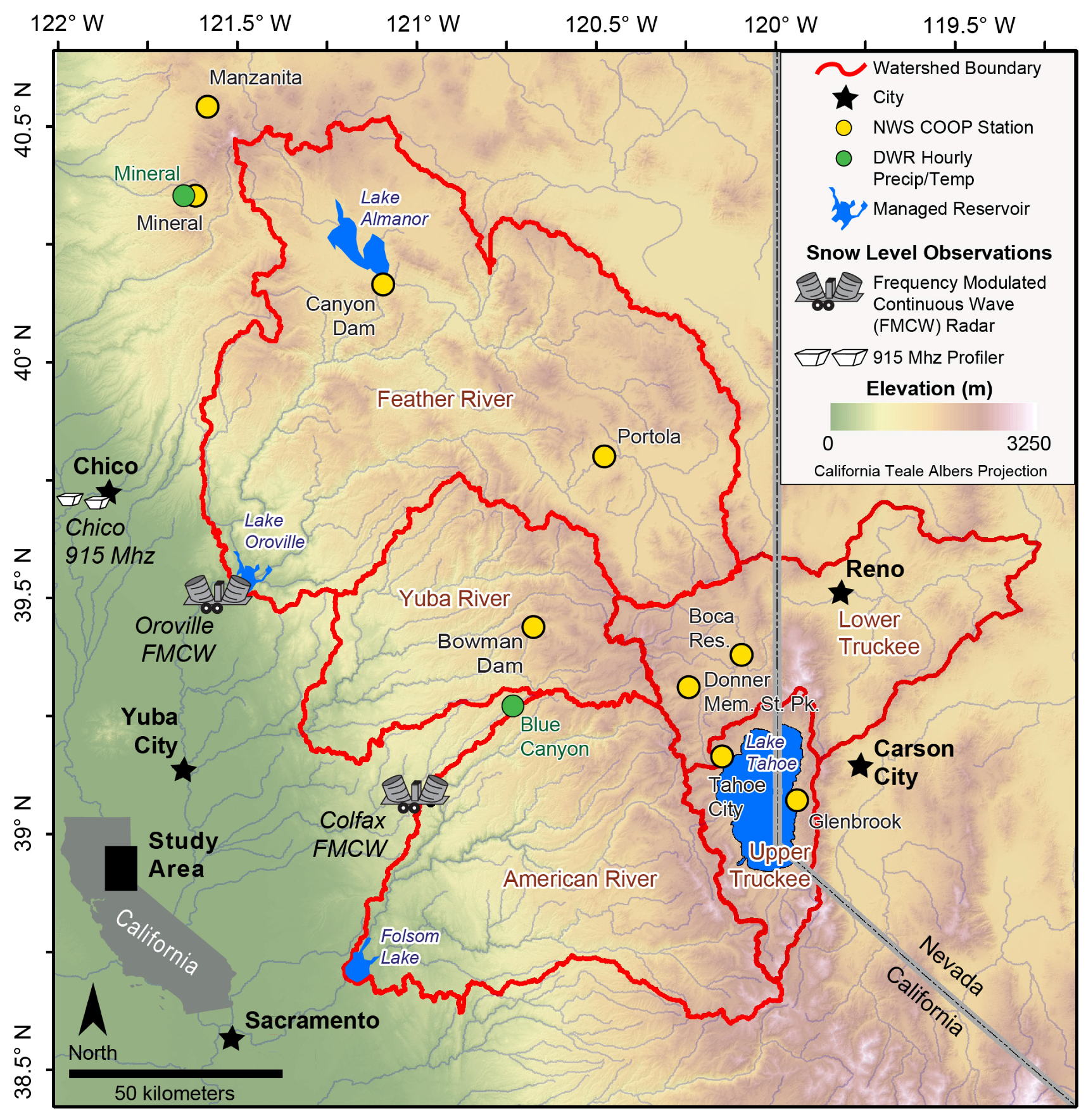
This study focuses on the northern Sierra Nevada, a 150 km wide north-south trending mountain range with crest elevations ranging from 2000 to 3000 m (Figure 1). Approximately 50% of annual precipitation occurs during the winter months (December–February; hereafter winter) [16]. The orientation of the northern Sierra Nevada orthogonal to prevailing westerly winds creates significant orographic precipitation effects that influence precipitation magnitude and spatial distribution (e.g., [17] and references therein). Water stored as snow that accumulates during the cool season (November–March) subsequently melts and runs off (typically during April–July) and provides the primary source of streamflow in the American, Yuba, Truckee, and Feather River basins (Figure 1). All of these basins are managed for multiple purposes, including flood control, and to meet ecological and human consumptive demands. The relatively low elevation of these basins makes them susceptible to changes in precipitation phase due to warming [18], which has significant implications for winter flooding [9,19] and warm season water availability [15]. Because of the importance of the northern Sierra Nevada for water resources and flood prevention in California and Nevada, a novel network of hydrometeorological measurements exist upstream of the Sierra Nevada [20] and offer a unique means to explore hydroclimatic change in this region.
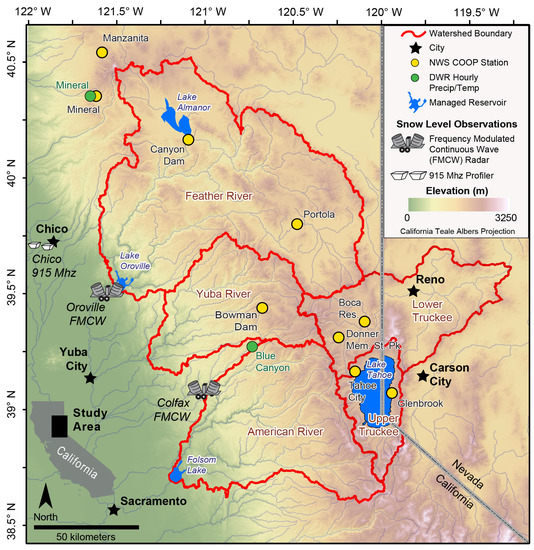
Figure 1.
The northern Sierra Nevada study area.
Snow level, or the elevation where snow melts to rain, is a primary control on the sensitivity of mountain snowpack accumulation to climate warming during precipitation events [21]. The brightband elevation, or the altitude of maximum radar reflectivity in the melting layer, provides an adequate estimate of the snow-level height and thus the phase of precipitation for given elevations [22,23]. We employed measurements of brightband elevations using a network of snow-level sensing radars established for real-time hydrometeorological monitoring in California to evaluate observed snow-level changes during the past 10 winters in the northern Sierra Nevada (Figure 1) in order to address the following objectives: (1) Test the hypothesis that snow levels have been rising during the past decade; (2) See if consistency exists between the changes in inferred precipitation phase deduced from snow-level radar observations and those estimated by an empirical relationship at weather stations developed by Dai [24]; and, (3) Explore plausible physical mechanisms controlling precipitation phase using reanalysis products and observational data, with the hypothesis that atmospheric rivers will strongly control snow fraction and snow level.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Snow Level Radar
We estimated snow levels on the basis of brightband heights measured at hourly intervals from December 2007 through February 2017 from a 915-MHz Doppler radar wind profiler [25], located in Chico, California (Figure 1). These measurements were complemented by brightband elevations that were estimated by frequency-modulated, continuous-wave, snow-level radars [26] at Oroville and Colfax, California (Figure 1), spanning the meteorological winters from December 2010 (December 2011 for Oroville) to February 2017. The data for all three radars were obtained from the Earth Systems Research Laboratory [27]. The radar data and algorithm used to convert Doppler velocity and radar reflectivity into melting elevation are described in White et al. [28,29].
The brightband height data from the snow-level sensing radars as well as the precipitation and temperature observations from the weather stations (described in Section 2.2) were examined to identify possible outliers. These included snow levels above 4000 m and temperatures above 30 °C or below −15 °C, while hourly precipitation measurements greater than 50 mm were filtered to eliminate erroneous measurements. We applied a diurnal correction to account for over- and under-estimation to radar-derived snow levels [22]. We shifted snow-level values during daylight hours (9:00 A.M.–5:00 P.M. LST) upward 100 m for Chico and 20 m for Oroville and Colfax. We shifted snow-level values lower during nighttime hours (200 m for Chico and 150 m for Oroville and Colfax). We also applied a latitudinal correction [22] to Colfax consisting of a 20 m increase to facilitate comparisons with Oroville and Chico. Our trend analysis results did not change significantly with or without applying these corrections because these changes were systematically applied. The snow-level sensing radars are located upstream of the Sierra crest (Figure 1), therefore the brightband heights should be interpreted as the maximum values given potential mesoscale lowering of the snowline [21,30].
2.2. Station-Based Observations
We obtained hourly temperature and precipitation values from alter-shielded weighing gauges operated by the California Department of Water Resources [31] from two mid-elevation stations: Mineral, California (1511 m), and Blue Canyon (1609 m) (Figure 1). These data span the winters of 2008 through 2017 and were included to compare snow-fraction estimates made at high temporal resolution against snow-level radar observations. To examine the relationship between lower temporal resolution observations and snow-level radar observations as well as extend the snow fraction estimates back further in time, we also used daily minimum and maximum values of temperature and precipitation from nine National Weather Service Cooperative Observer (COOP) [32] stations with >85% complete records [33]. Data from these stations, that are in the northern Sierra Nevada snow belt (>1200 m; Figure 1), spanned December 1950 through February 2017. In order to develop a relationship between observed precipitable water and snow levels, hourly GPS-observed precipitable water data at Petaluma, California was acquired from SuomiNet [34]. We compared precipitable water data only during hours (n = 1249) when snow-level observations were present for six hours during a calendar day. The reported correlation of determination (R2 = 0.6) was maximized with a three-hour lag.
The fraction of precipitation falling as snow (hereafter, snow fraction) was estimated based upon the approach developed by [24] and employed by [35]. We summed hourly precipitation totals at 0.5 °C intervals from −15 °C through 25 °C with respective observations from Mineral and Blue Canyon. We calculated conditional frequencies of snow at each 0.5 °C interval using the hyperbolic tangent function developed by [24] but with parameters estimated for the Sierra Nevada ecoregion by [35]. The conditional probabilities can be interpreted as likelihoods of snow at given temperatures [22]. We multiplied the probability of snow by the total precipitation at each temperature interval. We then divided the sum of this value by the total precipitation to calculate the snow fraction for each water year. This calculation was repeated for the nine COOP stations at daily time steps for the WY1951–2017 period but with maximum temperatures [35]. We report the median snow fraction calculated as an average of median values from the nine stations.
2.3. Tests for Trend
To test the hypothesis that non-zero trends in snow level and snow fraction existed during the past decade (between WY2008–2017), we used the Mann-Kendall [36,37] test that was modified to account for serial correlation [38] and reported the Thiel-Sen slope [39] for this period.
2.4. Large-Scale Controls on Snow Level and Snow Fraction
We used 1° gridded monthly sea surface temperatures (SST) from the COBE-SST reanalysis [40] and 2.5° gridded output of daily precipitable water and 700 hPa geopotential heights from the National Center for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) reanalysis [41] from December 1950 through February 2017. We used integrated vapor (moisture) transport at a grid point that was located upstream of the northern Sierra Nevada from the NASA Modern Era Retrospective Analysis (MERRA) [42] and a catalog of atmospheric rivers developed using the atmospheric river detection method of Rutz et al. [43] for the winters spanning WY1981–2017.
To explore a plausible, large-scale, physical mechanism favoring precipitation-phase changes between snow and rain, we performed single-point correlations [16] to calculate Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r) between each SST grid point (averaged over winter) and the time series of the nine-station COOP median snow fractions from WY1951 to 2017. We removed linear trends from each time series prior to performing correlations [44]. We only noted grid points as statistically significant when the p-value of the correlations satisfied the false discovery rate test [45] at the alpha = 0.05 level.
To further investigate an atmospheric circulation mechanism driving observed high and low snow fraction events, we used the Tahoe City COOP (Figure 1) to identify precipitation days exceeding the 90th percentile of non-zero precipitation days. These days were subset into warm (>3 °C) and cold (<−2 °C) events. We selected Tahoe City because it is near many important river basins in our study area and because the observed snow-fraction variability from this station reasonably approximated the nine-station median (R2 = 0.67, p < 0.01). Under the two sets of temperatures, the snow-fraction calculation [24] implies that the cold days will be dominated by frozen precipitation, whereas warm days will result in the melting of the existing snowpack [22]. For the respective wet warm and cold combinations, we composited NCEP precipitable water and 700 hPa geopotential height fields over the eastern North Pacific domain. Next, to provide a continuous examination of the role of moisture transport on snow fraction, we correlated MERRA-derived integrated vapor transport with daily snow fraction bins from 0 to >0.95, with a bin size equal to 0.05 (or 5%). The number of atmospheric rivers identified by the method of [43] was counted for each bin.
3. Results
3.1. Snow Levels and Snow Fractions
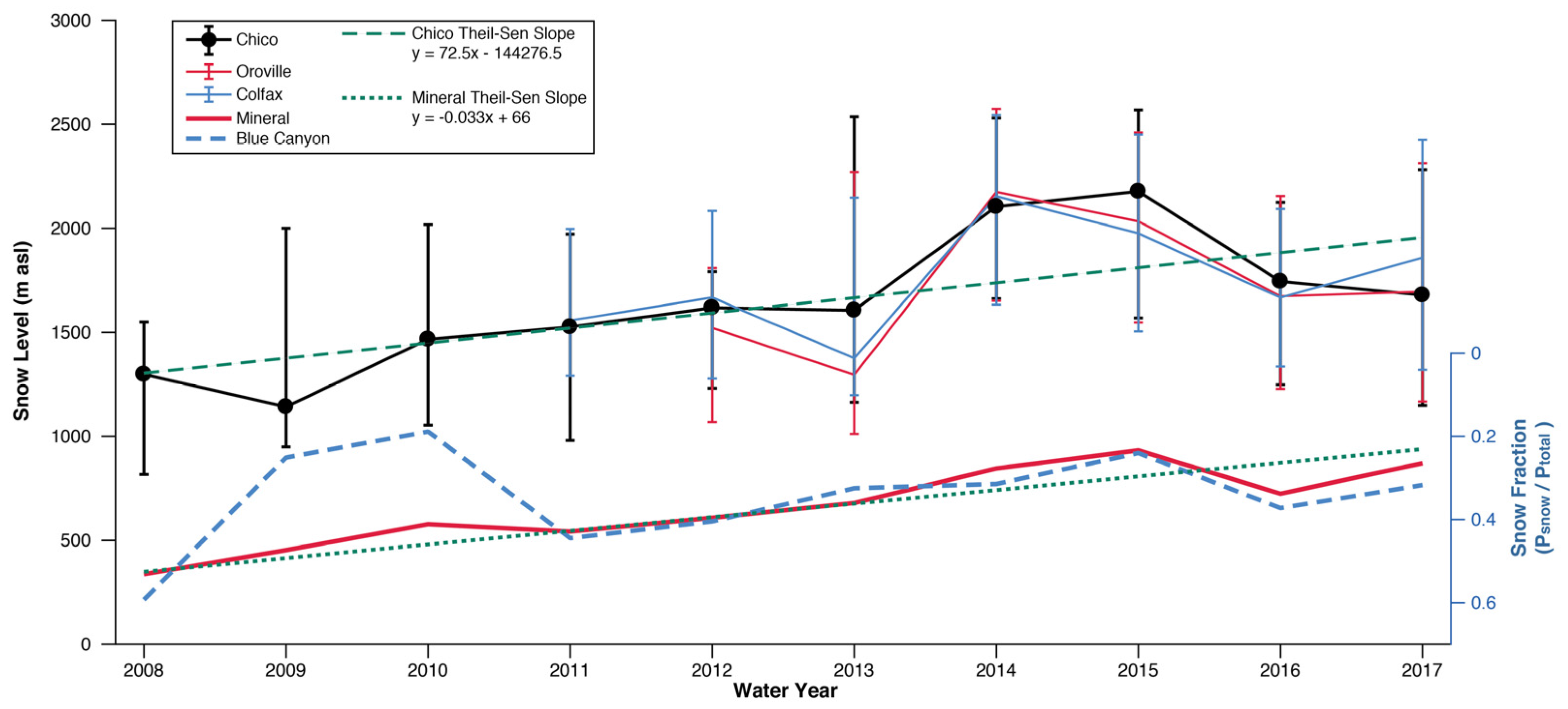
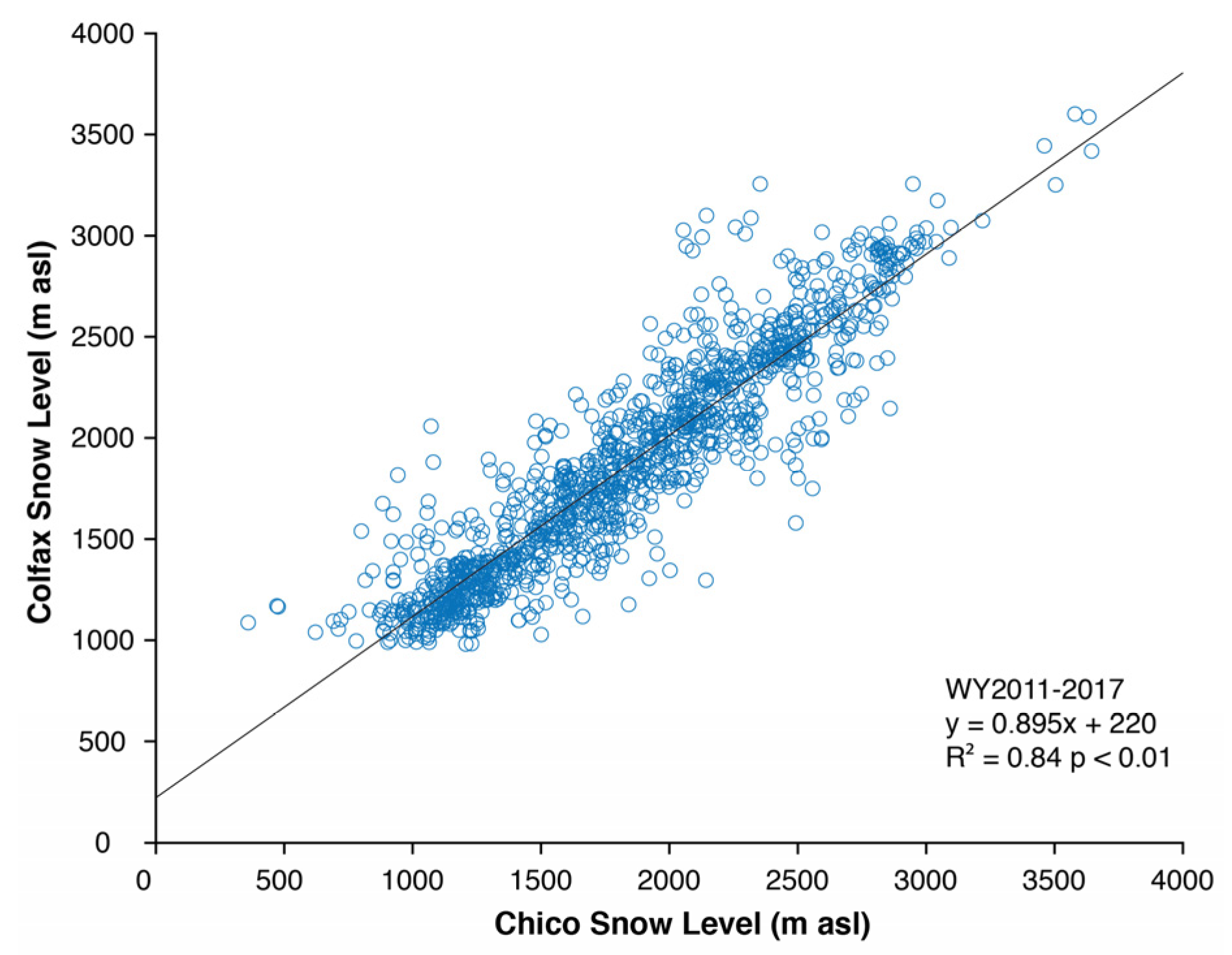
Snow levels at Chico were variable across years during the observed record (Figure 2). The lowest median value was observed during WY2009, and the highest values were observed during the peak drought years of WY2014–2015 (Figure 2). A significant non-zero trend (p < 0.001) during WY2008–2017 was identified with a Thiel-Sen slope of 72 m year−1 (Figure 2). This trend was broadly consistent with the WY2011–2017 slopes at Oroville and Colfax (approximately 50 m year−1). Observed snow levels at Chico and Colfax were positively correlated (R2 = 0.84, p < 0.01); Figure 3). Snow fractions at Blue Canyon and Mineral were moderately well correlated (R2 =0.57, p < 0.05) and varied from as high as 0.55 to as low as 0.19. The correlation between Chico snow level and Mineral snow fraction was −0.72 (p < 0.01). The average 2008–2017 median snow level at Chico was 1640 m. Separating the past decade into two, five-year halves, WY2008–2012 had an average median of 1410 m, while WY2013–2017 had an average median of 1860 m. A Wilcoxon rank sum test calculated using hourly values indicated that the WY2008–2012 and WY2013–2017 medians were significantly different (p < 0.0001).
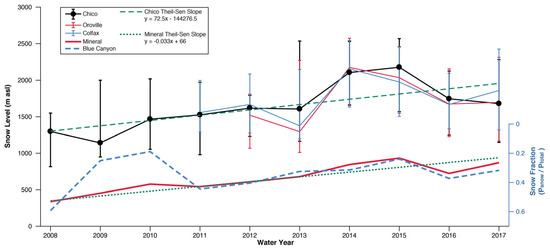
Figure 2.
Water year (WY) 2008–2017 snow levels observed by the Chico radar and snow levels observed by the Oroville (WY2012–2017) and Colfax radars (WY2011–2017). Capped bars designate upper and lower quartiles with black dots showing Chico median values. Right y-axis: Snow fractions at the Mineral and Blue Canyon hourly precipitation stations. Note the reversal of the right y-axis such that an upward slope indicates a decrease in snow fraction.
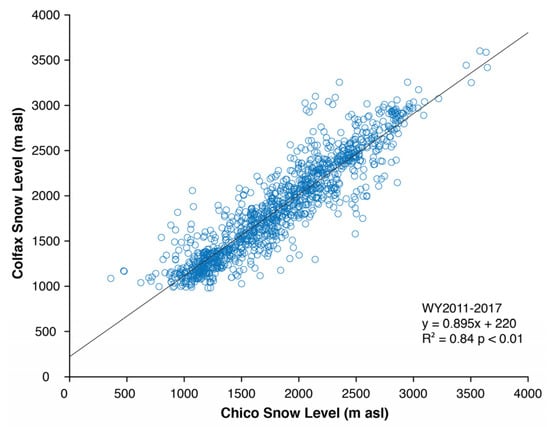
Figure 3.
Scatterplot of hourly Chico versus Colfax observed winter snow levels between WY2011 and 2017. Outlier points exceeding 1000 m difference between stations were removed for a total of n = 1195 observations.
Consistent with the rise in snow level shown by snow-level radar, we observed a negative trend in snow fraction at both Blue Canyon and Mineral (Figure 2), but only the slope at Mineral was significant (p < 0.001). With the exception of WY2009–2010, snow fractions at Blue Canyon and Mineral were well correlated, and varied from as high as 0.55 to as low as 0.19. Snow fraction declined at a faster rate at Mineral (−0.033 year−1 or −3.3% year−1) than at Blue Canyon (−1.4% year−1). Assuming an average environmental lapse rate over all land of 5.1 °C per 1000 m [24] and on the basis of the modified equation for precipitation phase [24,35], the 450 m increase in average median snow levels between the five-year periods spanning WY2008–2012 and WY2013–2017 (Figure 2) equates to a warming of approximately 2.3 °C. At Mineral, 50% of precipitation fell on days below 1 °C. Therefore, an increase of 2.3 °C reduced the snow fraction by about 25%. This value falls between the linear estimate of snow-fraction change during the 10-year period (33%) and the difference in average snow fraction between these periods (15%). The observed mean annual winter temperature during hours when precipitation was recorded at Mineral rose by 1.6 °C between these periods. This is lower but broadly consistent with the estimated warming from median snow levels that were found using an average environmental lapse rate.
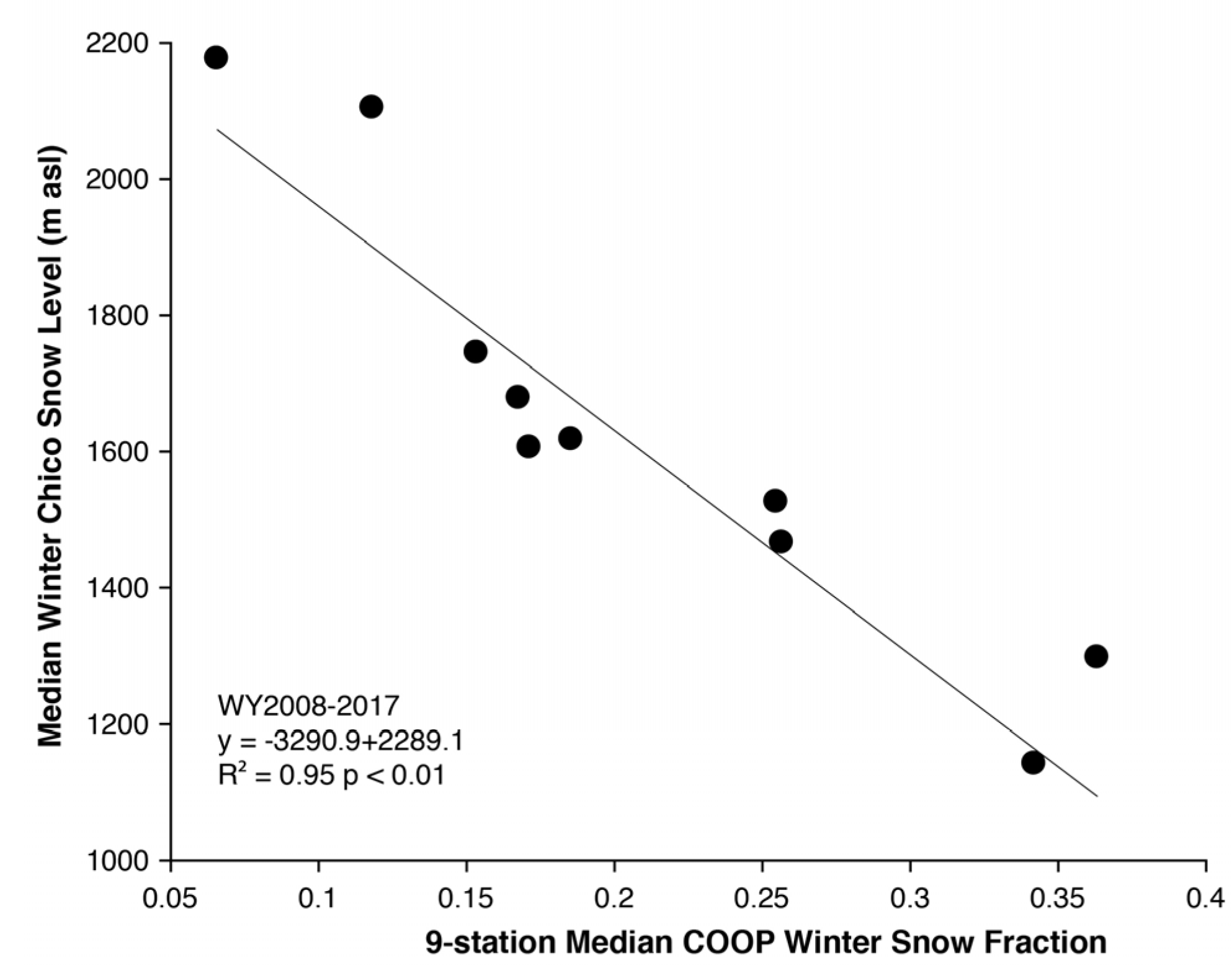
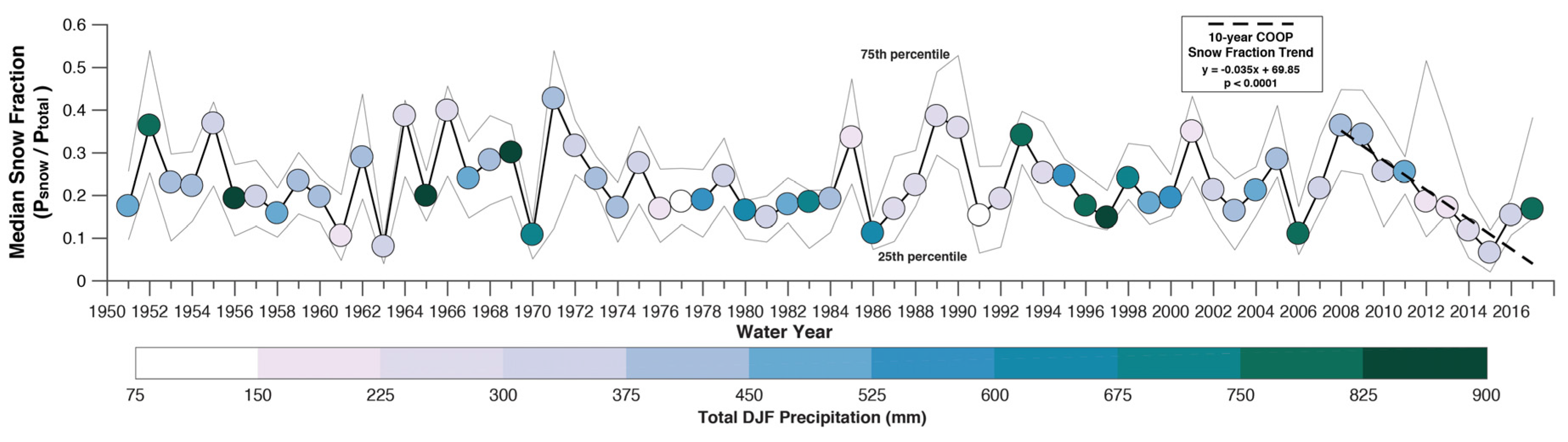
Between WY2008 and WY2017, the COOP snow fraction (Figure 4) and median Chico snow level were negatively correlated (R2 = 0.95, p < 0.001; calculated using Spearman’s rank correlation due to the shorter time period). The past ten years of COOP data demonstrated decreases in snow fractions (Figure 5) that are consistent with the increasing snow levels observed by snow-level radar and decreasing snow fractions at hourly stations (Figure 2). Of the 67 years analyzed, the median snow fraction varied substantially among years from more than 0.4 in WY1971 to less than 0.1 in WY2015 (Figure 5). Wet winters can have low (e.g., WY1956, WY1997, WY2017) or high (e.g., WY1969 and WY1993) snow fractions. Dry winters also can have either low (e.g., WY1991 and WY2015) or high (e.g., WY 1965 and WY1985) snow fractions. These results are consistent with [46], with no significant correlation between winter precipitation and snow fraction. The snow fraction slope of −3.5% year−1 (p < 0.0001; Figure 5) during WY2008-2017 was the steepest negative slope of any observed in the 10-year period from WY1951–2017, and its Thiel-Sen slope was consistent with the declines estimated for Mineral (−0.035 versus −0.033).
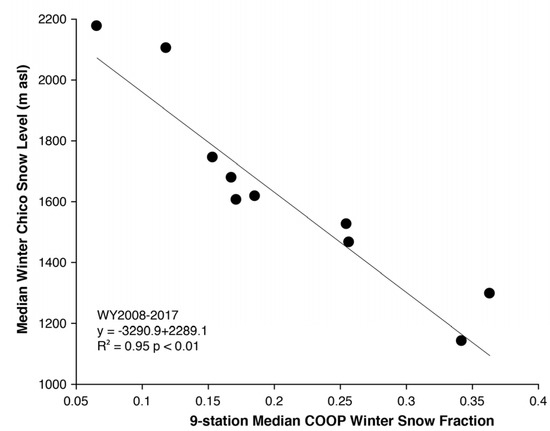
Figure 4.
Scatterplot of winter median Chico observed winter snow levels versus winter median National Weather Service Cooperative Observer (COOP) snow fractions between WY2008 and 2017.
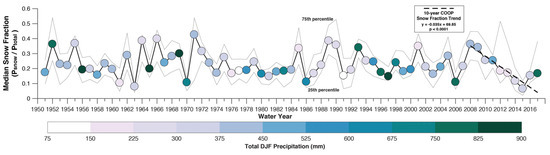
Figure 5.
Median winter snow fraction for nine COOP stations between WY1951 and 2017. Dots are colored by total winter precipitation. The grey lines indicate the upper and lower quartile values.
3.2. Seasonal and Event Relationships Between Large-Scale Circulations, Snow Level, and Snow Fraction
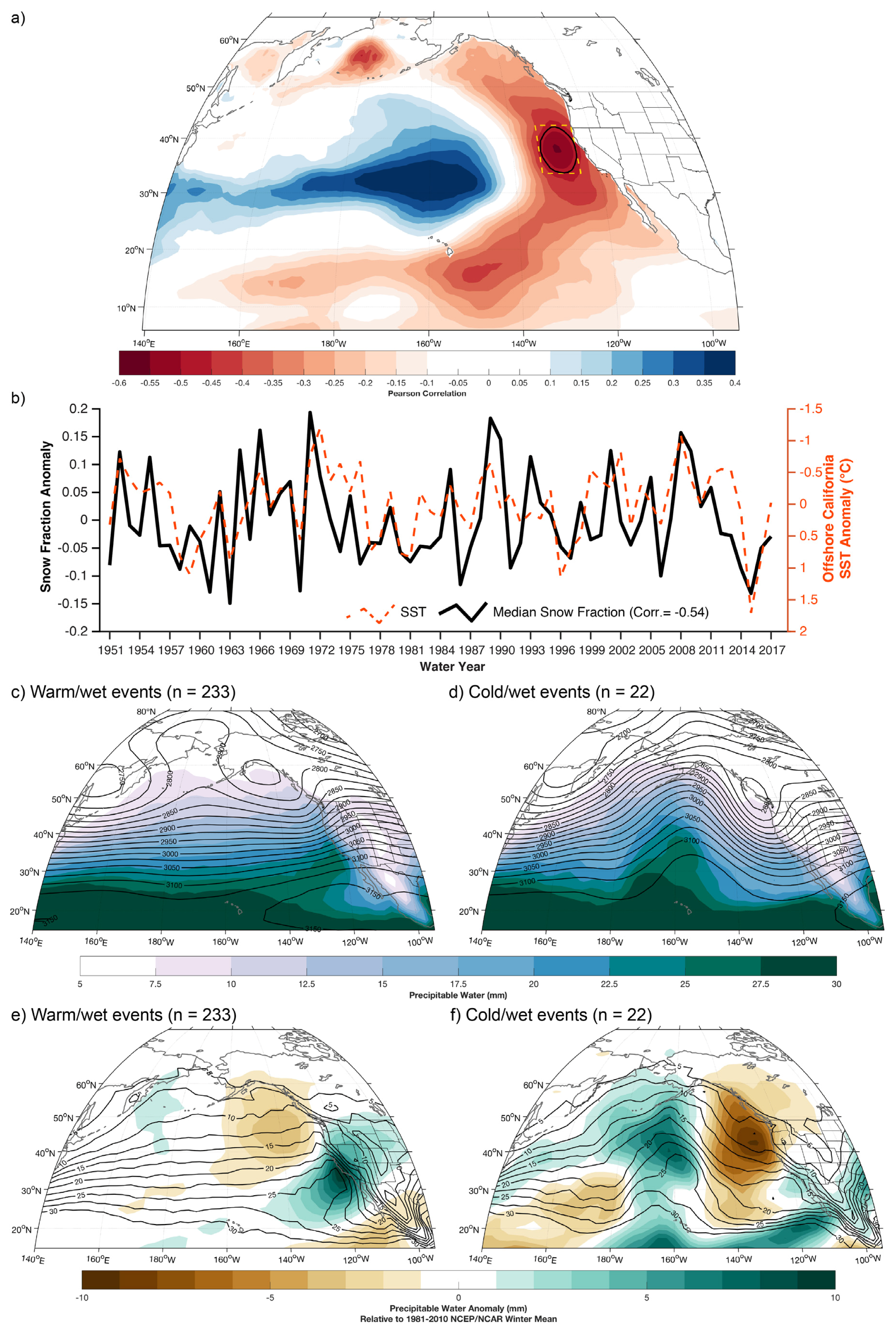
At the seasonal timescale, single-point correlations between the time series of COOP-derived snow fractions and SSTs broadly resembled an expression of the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO; Figure 6a) [47] and are negatively correlated (R2 = 0.13, p < 0.01) with the winter PDO index [48]. No correlation existed (R2 = 0.01, p = 0.354) between September-November multivariate El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) index [49] and subsequent winter snow fraction. The only significant negative correlations between snow fraction and SST anomalies (R2 > 0.25, p < 0.05) were found immediately offshore of California. Following [16], we produced a time series by averaging SST anomalies in this region for comparison against snow-fraction anomalies. The resulting time series illustrates the generally negative correlation between SSTs and snow fractions (Figure 6b; note reversal of right y-axis) with occasional exceptions (e.g., WYs 1973 and 2013). The correlations were the strongest when no lag was applied (i.e., using December–February SSTs instead of November–January SSTs). Positive SST anomalies offshore of California were associated with reductions in observed winter snow fractions.
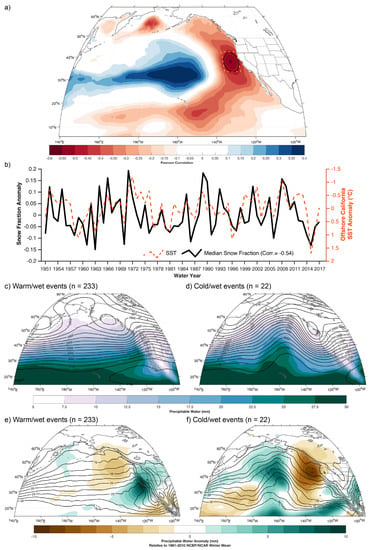
Figure 6.
(a) Single-point correlations between winter northern Sierra Nevada median snow fraction and sea surface temperatures (SSTs) during WY1951–2017. Black contours encircle grid points at which correlations were statistically significant (p < 0.05). (b) Time series of northern Sierra Nevada median snow fraction anomaly (right y-axis) and average SST anomalies (left y-axis) within the gold box shown in (a). Composites of National Center for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) precipitable water (filled contours) and 700 hPa geopotential heights for 90th percentile winter precipitation events at Tahoe City (Figure 1) on warm days (maximum temperatures > 3 °C) (c) and cold days (maximum temperatures < −2 °C). (d) Composite precipitable water (contours, interval 2.5 mm) and precipitable water anomalies (filled contours, in mm) calculated as differences between the (e) warm/wet composite days and (f) cold/wet composite days and the long-term mean 1981–2010 winter precipitable water output from the NCEP reanalysis.
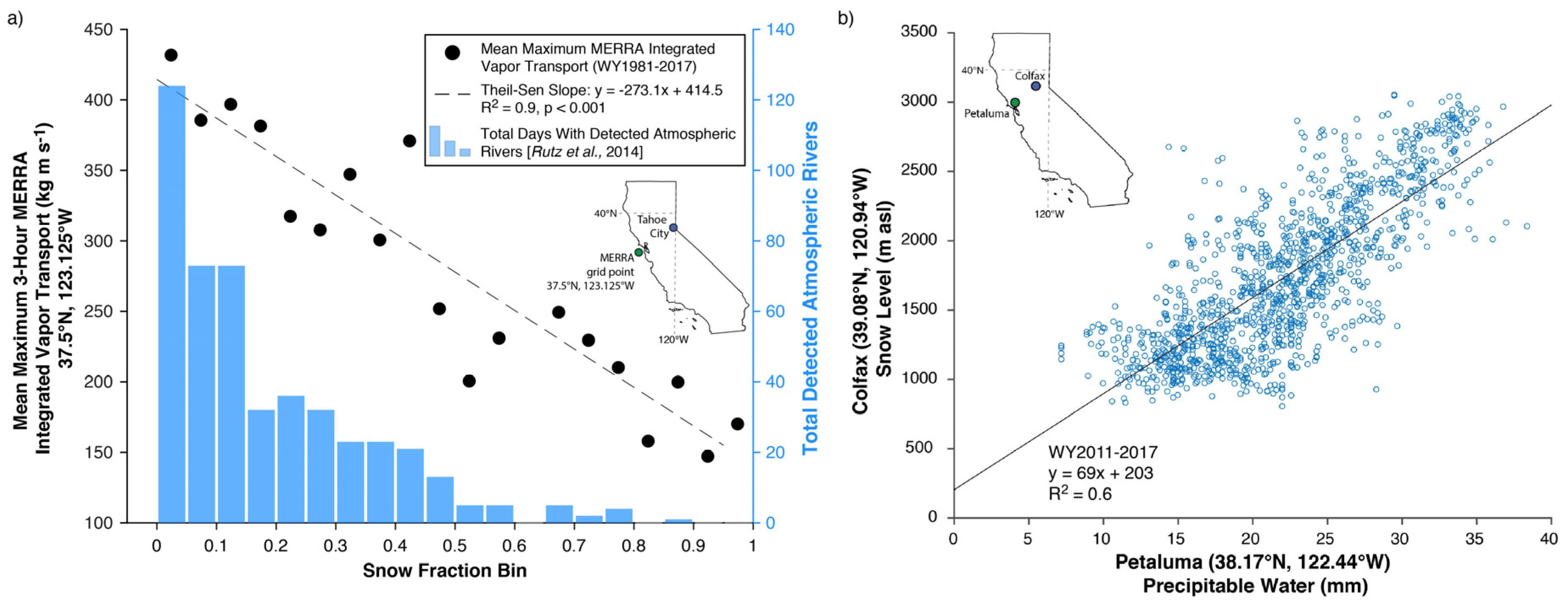
Composites of precipitable water and 700 hPa geopotential height for warm, wet days (Figure 6c) at Tahoe City demonstrated a coherent, southwest-northeast oriented precipitable water plume in the southeastern subtropical Pacific that exceeded 25 mm with positive precipitable water anomalies (calculated as differences between composited events and mean 1981–2010 winter precipitable water) exceeding 8 mm (Figure 6e). The shape and orientation of this composite moisture plume resembled an atmospheric river [50]. This agreed with the negative correlation between MERRA-derived integrated vapor transport (R2 = 0.90, p < 0.01; calculated using Spearman’s rank correlation) and the finding that the four lowest snow fraction bins (0–0.2) had nearly twice the number of identified atmospheric rivers as all the other bins combined (302 versus 170; Figure 7a). This was also consistent with the positive relationship between GPS-observed precipitable water at the coast and Chico snow level (R2 = 0.6, p < 0.01; Figure 7b). Warm and wet days corresponded with zonal flow, a negatively tilted trough in the northeastern Pacific, and an omega block over the Bering Sea (Figure 6c). These features are similar to composites of leeside flood-producing storms with high snow levels [9]. The cold and wet days had a weaker composite signal of subtropical moisture (<20 mm precipitable water) between Hawaii and California (Figure 6d). Precipitable water anomalies ranged from +2 mm offshore of southern California to −3 mm near 30 °N, 140 °W with a broad area of negative precipitable water anomalies (−4 to −8 mm) in the eastern Gulf of Alaska and northeastern Pacific (Figure 6f). These composite days demonstrated a meridional flow with a deeper negatively tilted northeastern Pacific trough and an amplified ridge centered near 160 °W (Figure 6d).
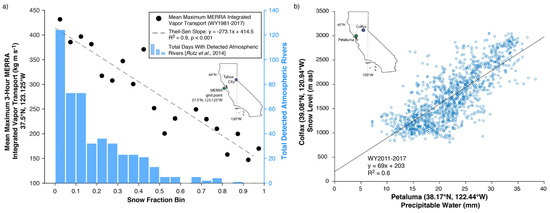
Figure 7.
(a) (Left y-axis): Scatterplot of mean maximum Modern Era Retrospective Analysis (MERRA) [42] integrated vapor transport (kg·m·s−1) at an upstream grid point from Tahoe City (note inset maps) for each 0.05 (5%) bin of snow fraction (e.g., 0–0.49, 0.5–0.99, …). (Right y-axis): Bar chart of total atmospheric rivers detected using the Rutz et al. [43] algorithm for each snow fraction bin. MERRA output used spans the period 1 January 1980 to 28 February 2017. (b) Scatterplot of observed precipitable water at Petaluma, California (near the California Coast) and snow level at Colfax, California between 2011 and 2017.
4. Discussion
We used snow-level radar to identify a trend in median snow levels between WY2008 and 2017 in the northern Sierra Nevada (Figure 2) with an estimated annual rate of 72 m year−1. This rise coincides with decreases in snow fractions derived from both hourly (Figure 2) and daily (Figure 5) weather station observations. The consistency between changes in inferred snow fraction at stations (Figure 2 and Figure 5) and those that were estimated by applying an average environmental lapse rate to snow-level changes (Figure 2) gives us confidence that the snow-level radars are accurately recording a robust change in precipitation phases, hence supporting our first objective. The significant positive correlation (R2 = 0.95, p < 0.01) between snow levels and snow fractions provides confidence that the snow-level radars are accurately recording precipitation phases. The correlation also affords confidence that the empirically-based estimate of snow fraction represents a reasonable means to estimate past or future changes in precipitation phase (e.g., [51]), thus supporting our second objective. These conclusions are despite uncertainties that are posed by storm-scale variability [22], potential bias in snow-fraction calculations because of precipitation gauge collection efficiency [52,53], and errors in snow-level observations. The ability to estimate changes in precipitation phase operates under the assumption that the empirical relationship to calculate snow fraction [15] remains stationary in time and is not sensitive to rain and snow transitions or spatiotemporal variability [46]. Further improvement in the snow-fraction calculations could be obtained by developing site-specific parameter values [46] and using additional observations [5].
Note that much of our study period corresponded with a period of notable hydroclimatic extremes. A severe drought during WY2012–2015 [12,13] was followed by subsequent average and record wet years during WY2016 and WY2017, respectively. The 67-year calculation of nine-station median snow fractions indicated that high or low snow fractions (Figure 5), and thus snow levels (Figure 2) could occur during either wet or dry winters, as consistent with [42]. We speculate that dry, low-snow-fraction years (e.g., WY2015) would have a more severe impact on hydrologic systems than a dry, high-snow-fraction year (e.g., WY1989). Continuing work seeks to more closely examine streamflow responses to winters with varying combinations of precipitation total and precipitation phase distributions. These years may provide analogs to possible future climate regimes that can inform water management strategies [14].
Our third objective was to evaluate the role of circulation (atmospheric rivers) and regional climate conditions (SSTs) in influencing snow fraction and snow levels. Our composite analysis indicating that low-snow-fraction storms have stronger (anomalous positive) moisture plumes (Figure 6c,e) is consistent with rain-on-snow climatologies [9,54]. Further evidence is provided by the negatively correlated (R2 = 0.90, p < 0.001) relationship between mean-maximum-upstream, MERRA-derived vapor transport and Tahoe City snow fraction (Figure 7a). The positive relationship (R2 = 0.6, p < 0.01) between observed precipitable water near the California coast and the three-hour lagged snow level at Colfax (Figure 7b) supports the notion that storms with greater precipitable water (Figure 6c) and moisture transport (Figure 7a) are associated with higher snow levels. This relationship is consistent with [55] although our correlation is weaker, perhaps because of the distance between Colfax and Petaluma. Overall, these results support the hypothesis that atmospheric rivers are important drivers of snow level and snow fraction variability at the event scale.
As found in field studies [56] and modeling experiments [57], anomalous positive SSTs offshore of continents modify air masses by contributing upward heat flux and decreasing static stability, leading to increases in downstream precipitation. At longer (seasonal) timescales, we observe that the negative correlations between snow fraction and SSTs offshore of California (Figure 6a,b) are located near the primary region of storm track activity that is correlated with winter California precipitation [16]. The warming effect of SSTs on the warm sector of the cyclone may enhance baroclinicity [58] and subsequently increase low-level winds and moisture fluxes (Figure 7a) that promote greater orographic precipitation [59]. Atmospheric rivers making landfall in California during warm coastal SST regimes are associated with stronger southerly winds and enhanced poleward moisture transport [60]. During warm (low snow fraction) storms, the large-scale zonal flow promotes the advection of warm, moist subtropical air into the southwestern U.S. (Figure 6c,e), with atmospheric rivers largely contributing to low-snow-fraction storms (Figure 7a).
Additional alternative hypotheses of the mechanisms producing snow level rise are the subject of ongoing study. Coupled ocean-atmosphere modeling approaches could help disentangle the relationship between wetter and warmer storms that result from increases in saturation vapor pressure due to temperature rise and those undergoing modifications from ocean heat fluxes (e.g., [61]) or poleward advection of subtropical airmasses [60]. Additional research is also necessary to better understand the relative roles of tropical-extratropical interactions (e.g., ENSO and the Madden-Julian Oscillation [62,63]) that influence winter snow level and snow fraction at timescales varying from seasonal to individual events.
Because of the short duration of analyzed data, we recommend further evaluation of observations to examine whether the apparent upward-snow-level trend continues. This represents a primary limitation of our study. We have provided evidence that the snow-level radar and snow- fraction estimates appear to offer reasonable metrics to observe and evaluate precipitation phase change in snow-dominated watersheds [1,5,28,29,30]. These changes will have marked effects on warm season streamflow [4], especially during drought years [13]—with negative implications for urban, ecological, and agricultural water demands [13,14,15,64]. If such a connection between SSTs, moisture plume strength, and snow fractions does exist, it suggests that snow accumulation may further decline with continued regional warming. This warming is expected to produce wetter, stronger atmospheric rivers [12], that in turn will contribute to shallower snowpacks and a greater potential for rain-on-snow events and flooding [9,10,54,55]. These changes also may limit drought recovery during occasional wetter years that occur during persistent droughts [65]. Warming background temperatures combined with changes from snow to rain leads to decreased water availability in spring and throughout the warm season [4,66,67,68]. Our findings thus suggest another mechanism that may act in tandem with background warming to amplify the loss of snow-derived water resources in the western U.S. [69,70]. This may be amplified if northeast Pacific SST variability and persistence increase, thus leading to longer duration episodes of anomalous warm SSTs [47] that support decreased snow fractions (Figure 6a,b).
5. Conclusions
We identified a statistically significant positive (negative) trend in winter snow levels (snow fractions) in the northern Sierra Nevada during the winters between WY2008 and 2017. We found consistency between increases in the elevation of winter snow levels measured by snow-level sensing radars and estimated snow fractions. Atmospheric rivers are predominantly associated with low- snow-fraction storms, and anomalously warm coastal SSTs appear to favor lower-snow-fraction winters—perhaps by enhancing the upward heat flux during atmospheric river landfalls and promoting zonal flow regimes that increase the advection of warm subtropical air into the northern Sierra Nevada, leading to storms with higher snow levels. This hypothesis will require modeling experiments to test its validity. If true, it suggests that continued increases in sea-surface temperatures and increased frequencies in atmospheric river landfalls may exacerbate future snowpack decline in the Sierra Nevada. Such changes will have negative implications for water availability. The hypothesis also emphasizes the importance of maintaining and expanding hydroclimatic monitoring in mountain environments [5,20,71].
Acknowledgments
The project described in this publication was supported by Grant Number G14AP00076 from the United States Geological Survey. Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the USGS. This manuscript is submitted for publication with the understanding that the United States Government is authorized to reproduce and distribute reprints for governmental purposes. We thank three anonymous reviewers for their constructive and insightful comments that improved this manuscript.
Author Contributions
B.J.H., B.D., and N.S.O. conceived and designed the analysis; B.J.H. performed the analysis; all authors analyzed and discussed the data and analysis. B.J.H. wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Mote, P.W.; Hamlet, A.F.; Clark, M.P.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Declining mountain snowpack in western North America. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 86, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, N.; Dettinger, M.D.; Cayan, D.R. Trends in snowfall versus rainfall in the western United States. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 4545–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, T.P.; Adam, J.C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Potential impacts of a warming climate on water availability in snow-dominated regions. Nature 2005, 438, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berghuijs, W.R.; Woods, R.A.; Hrachowitz, M. A precipitation shift from snow towards rain leads to a decrease in streamflow. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpold, A.A.; Kaplan, M.L.; Klos, P.Z.; Link, T.; McNamara, J.P.; Rajagopal, S.; Schumer, R.; Steele, C.M. Rain or snow: Hydrologic processes, observations, prediction, and research needs. Hydrol. Earth. Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.L.; Mitchell, M.J.; Groffman, P.M.; Christenson, L.M.; Hardy, J.P. Winter in northeastern North America, a critical period for ecological processes. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2005, 3, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, G.J.; Wolock, D.M. Warming may create substantial water supply shortages in the Colorado River basin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L22708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milly, P.C.D.; Betancourt, J.; Falkenmark, M.; Hirsch, R.M.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Stouffer, R.J. Stationarity is dead: Whither water management? Science 2008, 319, 573–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underwood, S.; Kaplan, M.L.; King, K.C. The role of upstream midtropospheric circulations in the Sierra Nevada enabling leeside (Spillover) precipitation. Part I: A synoptic-scale analysis of spillover precipitation and flooding in a leeside basin. J. Hydrometeorl. 2009, 10, 1309–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettinger, M.D.; Ralph, F.M.; Das, T.; Neiman, P.J.; Cayan, D.R. Atmospheric rivers, floods and the water resources of California. Water 2011, 3, 445–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.I.; Ault, T.R.; Smerdon, J.E. Unprecedented 21st century drought risk in the American Southwest and Central Plains. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1400082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavers, D.A.; Ralph, F.M.; Waliser, D.A.; Gershunov, A.; Dettinger, M.D. Climate change intensification of horizontal water vapor transport in CMIP5. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 5617–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatchett, B.J.; Boyle, D.P.; Putnam, A.E.; Bassett, S.D. Placing the 2012–2015 California-Nevada drought into a paleoclimatic context: Insights from Walker Lake, California-Nevada, USA. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 8632–8640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.P.; Seager, R.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Cook, B.I.; Smerdon, J.E.; Cook, E.R. Contribution of anthropogenic warming to California drought during 2012–2014. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 6819–6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterle, K.; Singletary, L. Adapting to variable water supply in the Truckee-Carson River system, Western USA. Water 2017, 9, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.K.M.; Zheng, C.; Lanigan, P.; Yau, A.M.W.; Neelin, J.D. Significant modulation of variability and projected change in California winter precipitation by extratropical cyclone activity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 5983–5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, J.D.; Minder, J.R.; Neiman, P.J.; Sukovich, E. Relationships between barrier jet heights, orographic precipitation gradients, and streamflow in the northern Sierra Nevada. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 1141–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterhuber, R. Precipitation intensity during rain-on-snow. In Proceedings of the 67th Annual Western Snow Conference, South Lake Tahoe, CA, USA, 19–22 April 1999; pp. 153–155. [Google Scholar]
- Das, T.; Dettinger, M.D.; Cayan, D.R.; Hidalgo, H.G. Potential increase in floods in California’s Sierra Nevada under future climate projections. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.B.; Anderson, M.L.; Dettinger, M.D.; Ralph, F.M.; Hinojosa, A.; Cayan, D.R.; Hartman, R.K.; Reynolds, D.W.; Johnson, L.E.; Schneider, T.L.; et al. A twenty-first-century California observing network for monitoring extreme weather events. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 1585–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minder, J.R. The sensitivity of mountain snowpack accumulation to climate warming. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 2634–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, J.D.; Neiman, P.J.; Martner, B.; White, A.B.; Gottas, D.J.; Ralph, F.M. Rain versus snow in the Sierra Nevada, California: Comparing Doppler profiling radar and surface observations of melting level. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 194–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.B.; Gottas, D.J.; Henkel, A.F.; Neiman, P.J.; Ralph, F.M.; Gutman, S.I. Developing a performance measure for snow-level forecasts. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A. Temperature and pressure dependence of the rain-snow phase transition over land and ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L12802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, D.A.; Gage, K.S.; Ecklund, W.L.; Angevine, W.M.; Johnston, P.E.; Riddle, A.C.; Wilson, J.; Williams, C.R. Developments in UHF lower tropospheric wind profiling at NOAA’s Aeronomy Laboratory. Radio Sci. 1995, 30, 977–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, P.E.; Jordan, J.R.; White, A.B.; Carter, D.A.; Costa, D.M.; Ayers, T.E. The NOAA FM-CW snow-level radar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2017, 34, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earth Systems Research Laboratory. Available online: ftp://ftp1.esrl.noaa.gov/psd2/data/realtime/ (accessed on 14 March 2017).
- White, A.B.; Gottas, D.J.; Ralph, F.M.; Neiman, P.J. Operational bright-band snow level detection using Doppler radar. U.S. Patent 6,615,140, 2 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- White, A.B.; Gottas, D.J.; Strem, E.T.; Ralph, F.M.; Neiman, P.J. An automated brightband height detection algorithm for use with Doppler radar spectral moments. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minder, J.R.; Kingsmill, D.E. Mesoscale variations of the atmospheric snow line over the Northern Sierra Nevada: Multiyear statistics, case study, and mechanisms. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 70, 916–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- California Department of Water Resources Data Exchange Center. Available online: http://cdec.water.ca.gov/queryTools.html (accessed on 15 April 2017).
- Southwest Climate and Environmental Information Collaborative. Available online: https://wrcc.dri.edu/csc/scenic/ (accessed on 30 March 2017).
- Perica, S.; Dietz, S.; Heim, S.; Hiner, L.; Maitaria, K.; Martin, D.; Pavlovic, S.; Roy, I.; Trypaluk, C.; Unruh, D.; et al. Precipitation Frequency Atlas of the United States; U.S. Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Weather Service: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2014; Volume 6, Version 2.3.
- COSMIC Suominet Real-time Integrated Atmospheric Water Vapor From GPS. Available online: http://suominet.ucar.edu/ (accessed on 20 April 2017).
- Rajagopal, S.; Harpold, A.A. Testing and improving temperature thresholds for snow and rain prediction in the Western United States. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2016, 52, 1142–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods, 5th ed.; Griffin: London, UK, 1975; ISBN 978-0195208375. [Google Scholar]
- Hamed, K.H.; Rao, R.A. A modified Mann Kendall test for autocorrelated data. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, R.O. Sen’s nonparametric estimator of slope. In Statistical Methods for Environmental Pollution Monitoring, 1st ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 217–219. ISBN 978-0-471-28878-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, M.; Shouji, A.; Sugimoto, S.; Matsumoto, T. Objective analyses of sea-surface temperature and marine meteorological variables for the 20th century using ICOADS and the Kobe collection. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 865–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienecker, M.M.; Suarez, M.J.; Gelaro, R.; Todling, R.; Bacmeister, J.; Liu, E.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Schubert, S.D.; Takacs, L.; Kim, G.-K.; et al. MERRA: NASA’s modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 3624–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutz, J.J.; Steenburgh, W.J.; Ralph, F.M. Climatological characteristics of atmospheric rivers and their inland penetration over the western United States. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 905–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benestad, R.E. Solar Activity and Earth’s Climate, 2nd ed.; Springer-Praxis: Chichester, UK, 2006; p. 202. ISBN 978-3-540-30620-7. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Safeeq, M.; Shukla, S.; Arismendi, I.; Grant, G.E.; Lewis, S.L.; Nolin, A. Influence of winter season climate variability on snow-precipitation ratio in the western United States. Int. J. Clim. 2015, 36, 3175–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, E.; Mantua, N. Multi-year persistence of the 2014/2015 North Pacific marine heatwave. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantua, N.J.; Hare, S.R.; Zhang, Y.; Wallace, J.M.; Francis, R.C. A Pacific interdecadal climate oscillation with impacts on salmon production. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolter, K.; Timlin, M.S. El Niño/Southern Oscillation behaviour since 1871 as diagnosed in an extended multivariate ENSO index (MEI.ext). Intl. J. Climatol. 2001, 31, 1074–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiman, P.J.; Ralph, F.M.; Wick, G.A.; Lundquist, J.D.; Dettinger, M.D. Meteorological characteristics and overland precipitation impacts of atmospheric rivers affecting the West Coast of North America based on eight years of SSM/I satellite observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 22–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klos, P.Z.; Link, T.E.; Abatzoglou, J.T. Extent of the rain-snow transition zone in the western U.S. under historic and projected climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 4560–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, R.; Baker, B.; Kochendorfer, J.; Meyers, T.; Landolt, S.; Fischer, A.P.; Black, J.; Thériault, J.M.; Kucera, P.; Gochis, D.; et al. How well are we measuring snow: The NOAA/FAA/NCAR winter precipitation test bed. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 811–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, G.; Lendvai, A.; Peretti, G.; Ranzi, R. Snow precipitation measured by gauges: Systematic error estimation and data series correction in the central Italian Alps. Water 2017, 9, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Waliser, D.E.; Ralph, F.M.; Fetzer, E.J.; Neiman, P.J. Hydrometeorological characteristics of rain-on-snow events associated with atmospheric rivers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 2964–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiman, P.J.; White, A.B.; Ralph, F.M.; Gottas, D.J.; Gutman, S.I. A water vapor flux tool for precipitation forecasting. Water Manag. 2009, 162, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, P.G.; Neiman, P.J.; Walter, B.B.; Bao, J.W.; Ralph, F.M. Contributions from California coastal-zone surface fluxes to heavy coastal precipitation: A CALJET case study during the strong El Niño of 1998. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 1175–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, D.; Rondanelli, R.; Garreaud, R.; Arriagada, A. Impact of warmer eastern tropical Pacific SST on the March 2015 Atacama floods. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 4441–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Chang, P.; Saravanan, R.; Montuoro, R.; Nakamura, H.; Wu, D.; Lin, X.; Wu, L. Importance of resolving Kuroshio front and eddy influence in simulating the North Pacific storm track. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 1861–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiman, P.J.; Ralph, F.M.; White, A.B.; Kingsmill, D.E.; Persson, P.G. The statistical relationship between upslope flow and rainfall in California’s coastal mountains: Observations during CALJET. Mon. Weather Rev. 2002, 130, 1468–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershunov, A.; Shulgina, T.M.; Ralph, F.M.; Lavers, D.; Rutz, J.J. Assessing climate-scale variability of atmospheric rivers affecting western North America. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putrasahan, D.A.; Miller, A.J.; Seo, H. Isolating mesoscale coupled ocean—atmosphere interactions in the Kuroshio Extension region. Dyn. Atmos. Oceans 2013, 63, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Waliser, D.E.; Molotch, N.P.; Fetzer, E.J.; Neiman, P.J. Does the Madden–Julian Oscillation influence wintertime atmospheric rivers and snowpack in the Sierra Nevada? Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundhenk, B.D.; Barnes, E.A.; Maloney, E.D. All-Season climatology and variability of atmospheric river frequencies over the North Pacific. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 4885–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatchett, B.J.; Koracin, D.K.; Mejia, J.F.; Boyle, D.P. Assimilating urban heat island effects into climate projections. J. Arid Environ. 2016, 128, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatchett, B.J.; Boyle, D.P.; Garner, C.B.; Kaplan, M.L.; Putnam, A.E.; Bassett, S.D. Magnitude and frequency of wet years under a megadrought climate in the western Great Basin, USA. Quatern. Sci. Rev. 2016, 152, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luce, C.H.; Holden, Z.A. Declining annual streamflow distributions in the Pacific Northwest United States, 1948–2006. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L16401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhart, T.B.; Molotch, N.P.; Livneh, B.; Harpold, A.A.; Knowles, J.F.; Schneider, D. Snowmelt rate dictates streamflow. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 8006–8016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musselman, K.N.; Clark, M.P.; Liu, C.; Ikeda, K.; Rasmussen, R. Slower snowmelt in a warmer world. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mote, P.W.; Rupp, D.E.; Li, S.; Sharp, D.J.; Otto, F.; Uhe, P.F.; Xiao, M.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Cullen, H.; Allen, M.R. Perspectives on the causes of exceptionally low 2015 snowpack in the western United States. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 10980–10988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, N.; Hall, A. Anthropogenic warming impacts on California snowpack during drought. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 44, 2511–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachan, S.; Kelsey, E.P.; Brown, R.F.; Dascalu, S.; Harris, F.; Kent, G.; Lyles, B.; McCurdy, G.; David Slater, D.; Smith, K. Filling the data gaps in mountain climate observatories through advanced technology, refined instrument siting, and a focus on gradients. Mount. Res. Devel. 2016, 36, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).